Application Research of a High Turbulence Numerical Simulation Technique in a USBR Type III Stilling Basin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Structural Type and Numerical Simulation Principle
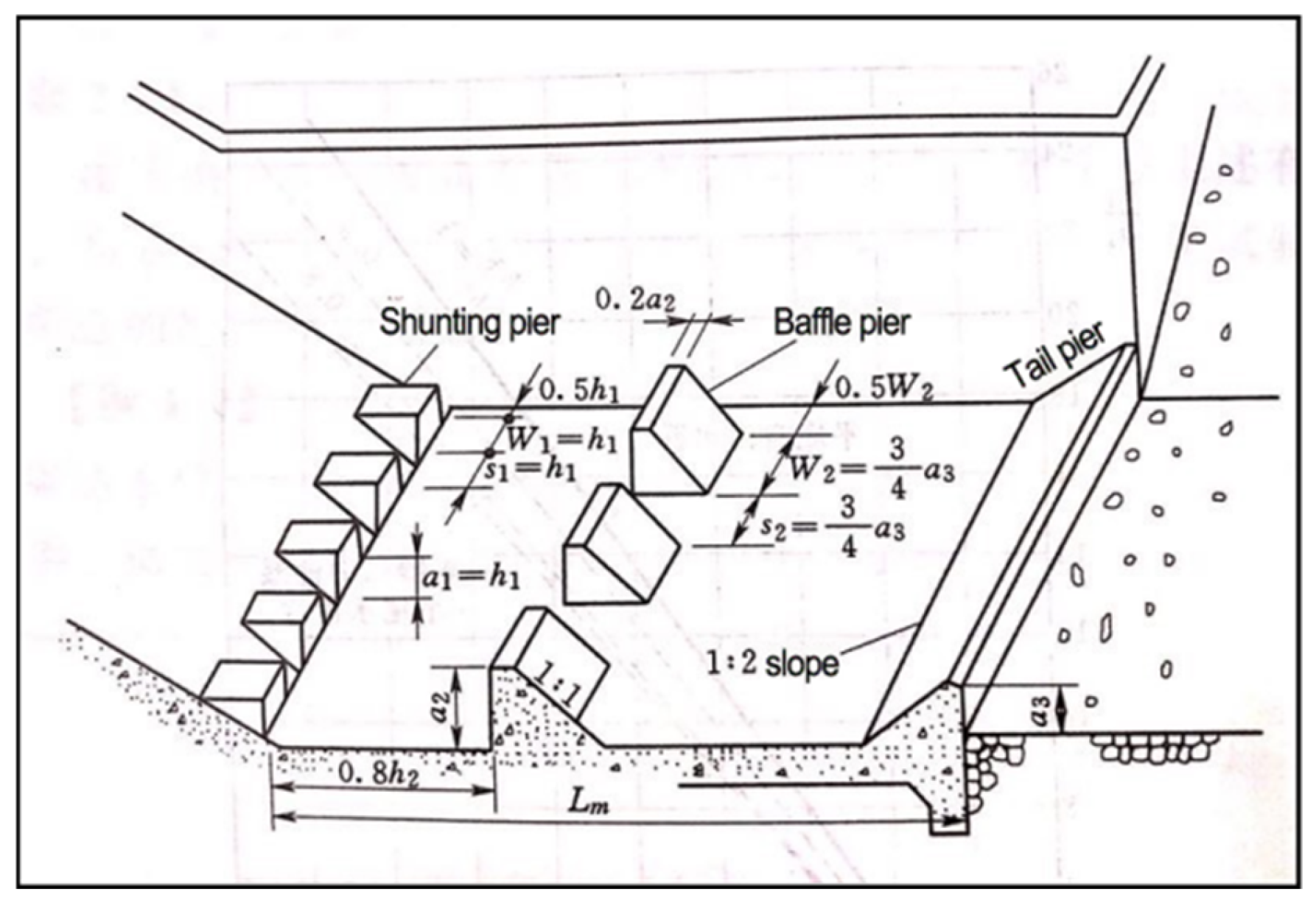
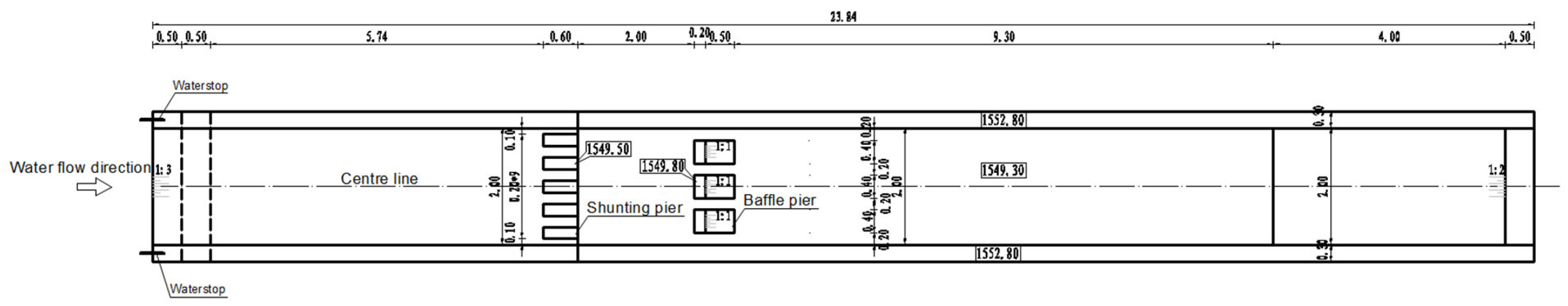
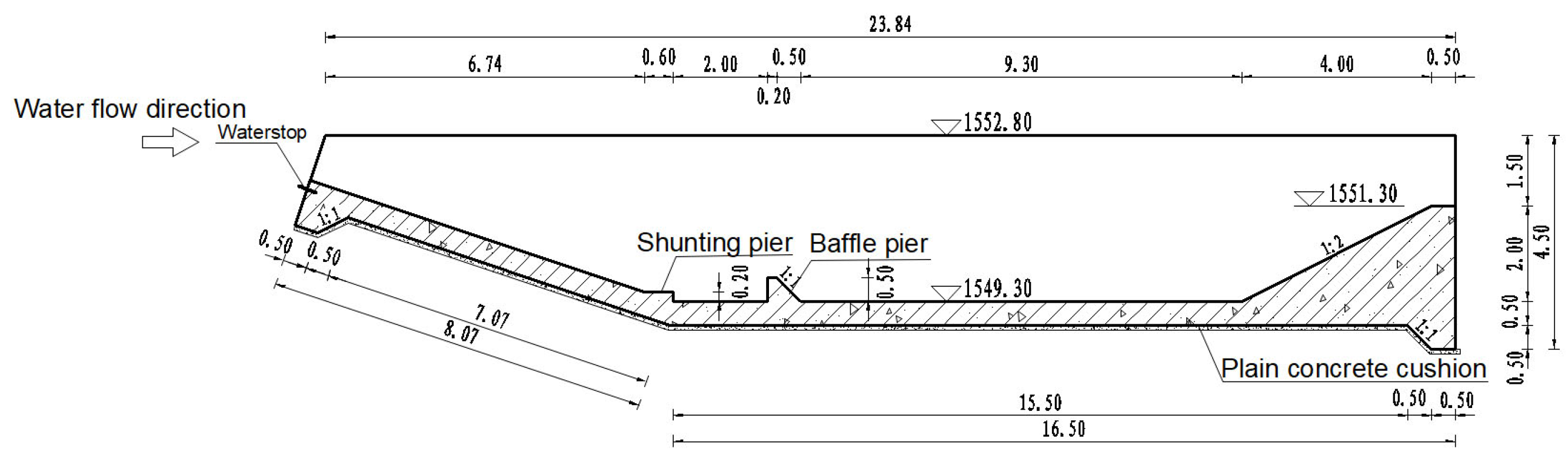
2.1. Structure of the Stilling Basin
2.2. Basic Principles of Numerical Simulation
- (1)
- Equation of Mass Conservation
- (2)
- Momentum Conservation Equation
2.3. The Significance of Numerical Simulation Technology
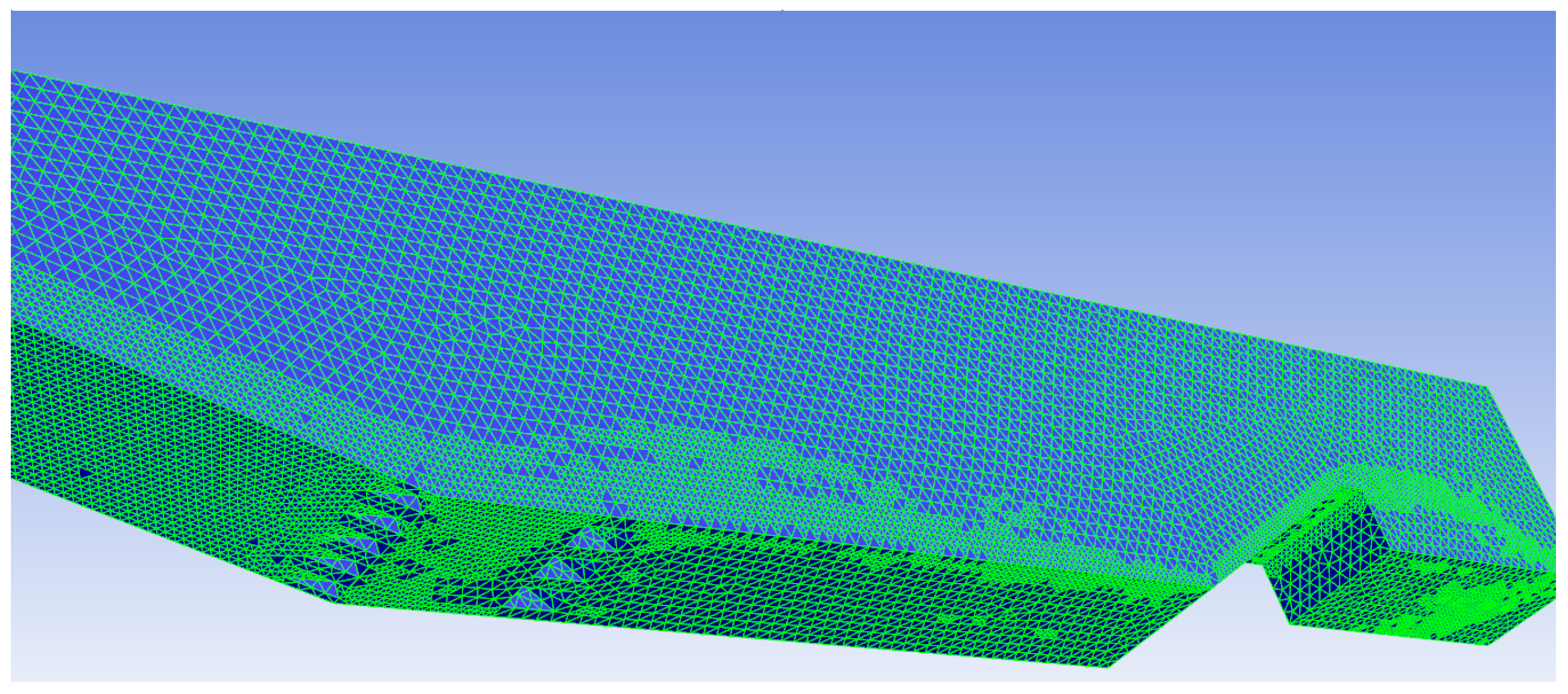
3. Model Construction and Parameter Determination
3.1. Model Construction
3.2. Boundary Parameters
- (1)
- Inlet boundary
- (2)
- Pressure boundary
- (3)
- Outlet boundary
- (4)
- Wall boundary
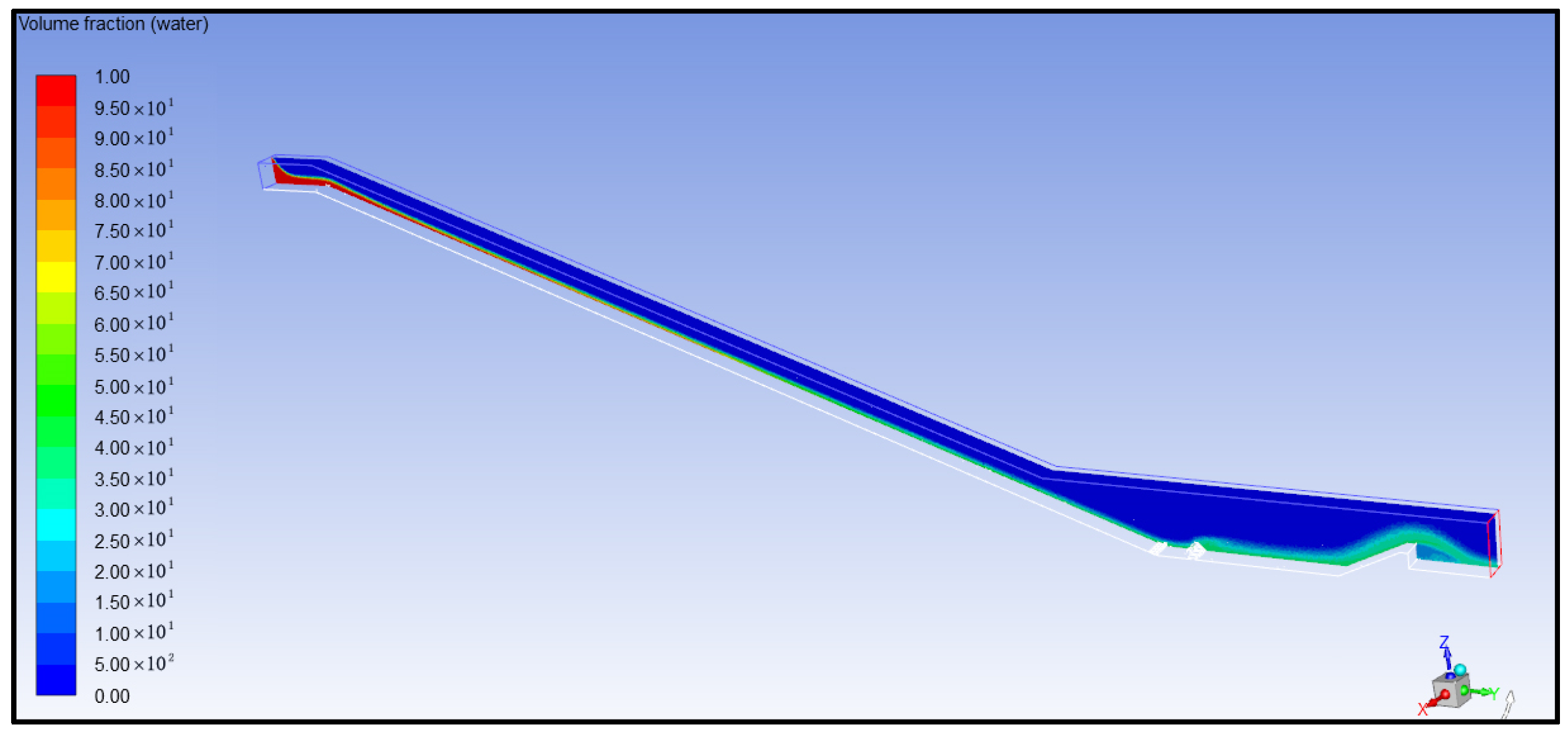
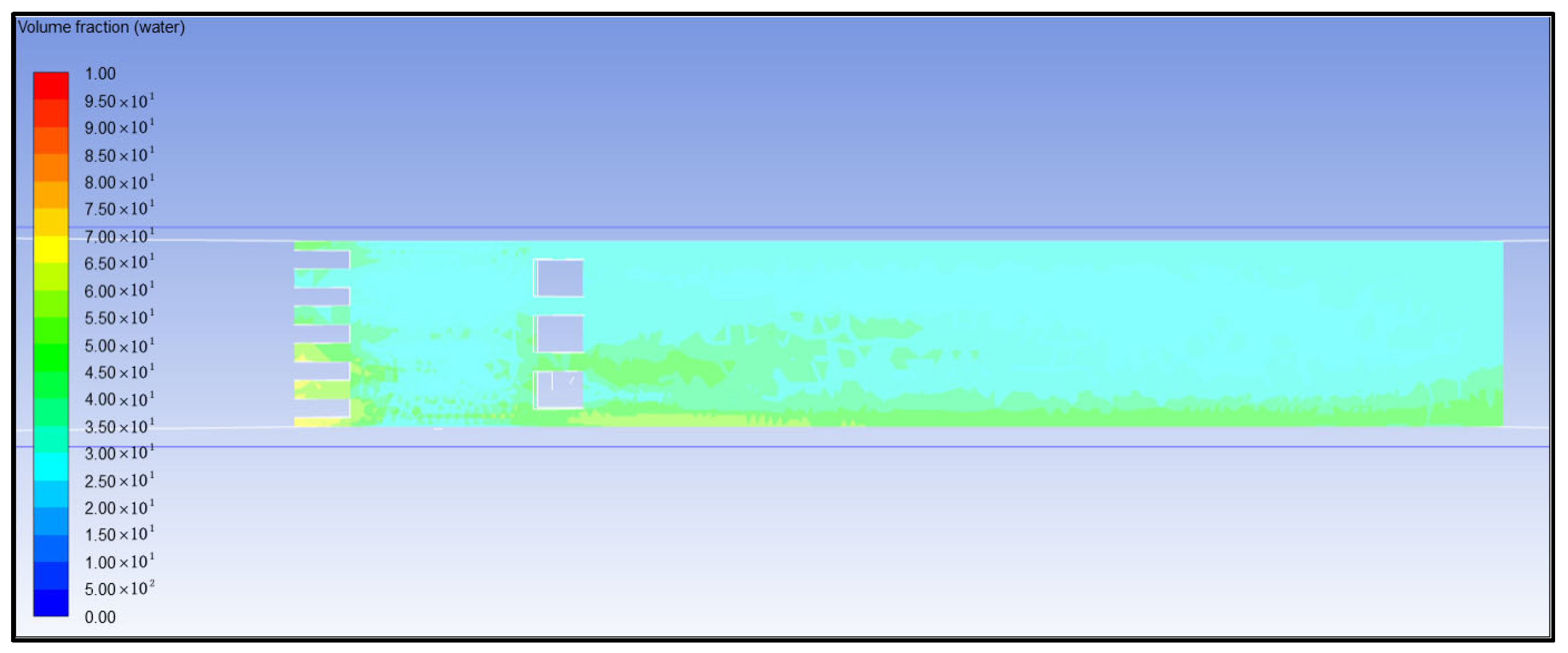
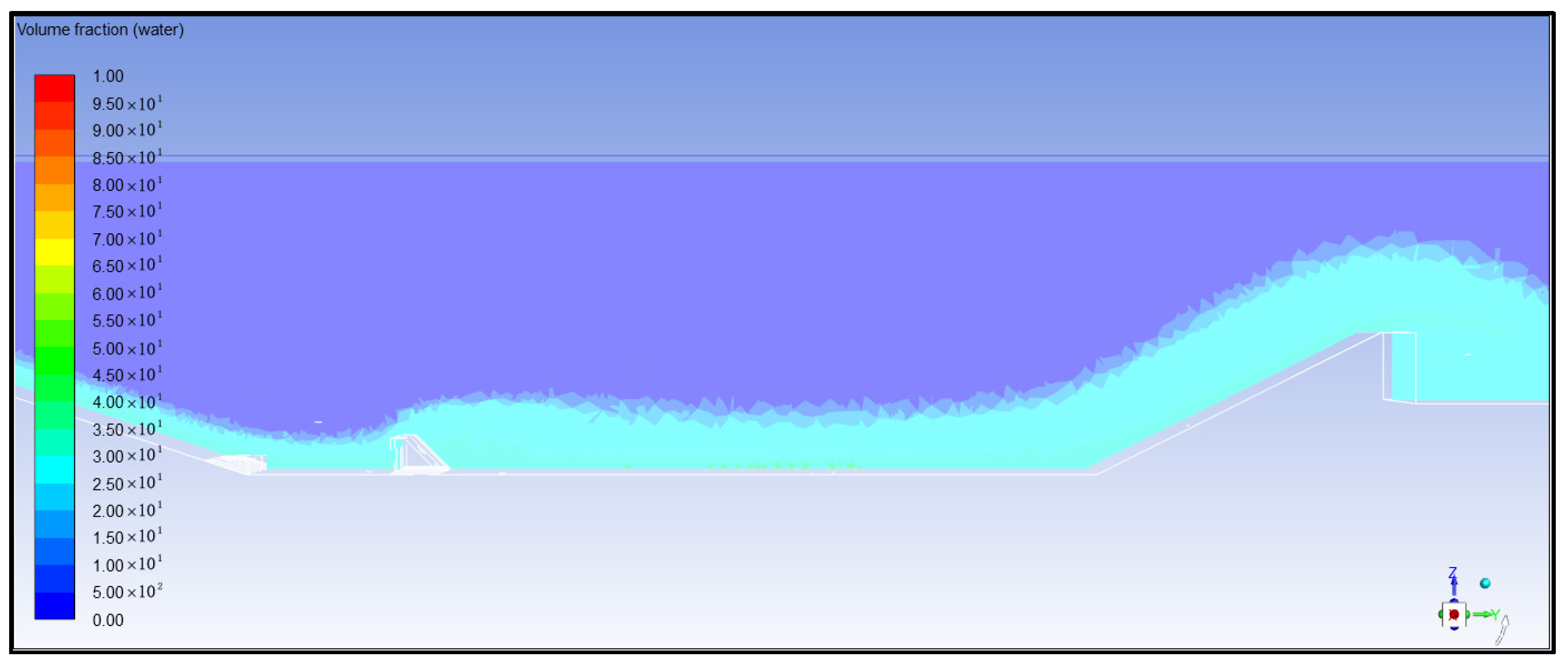
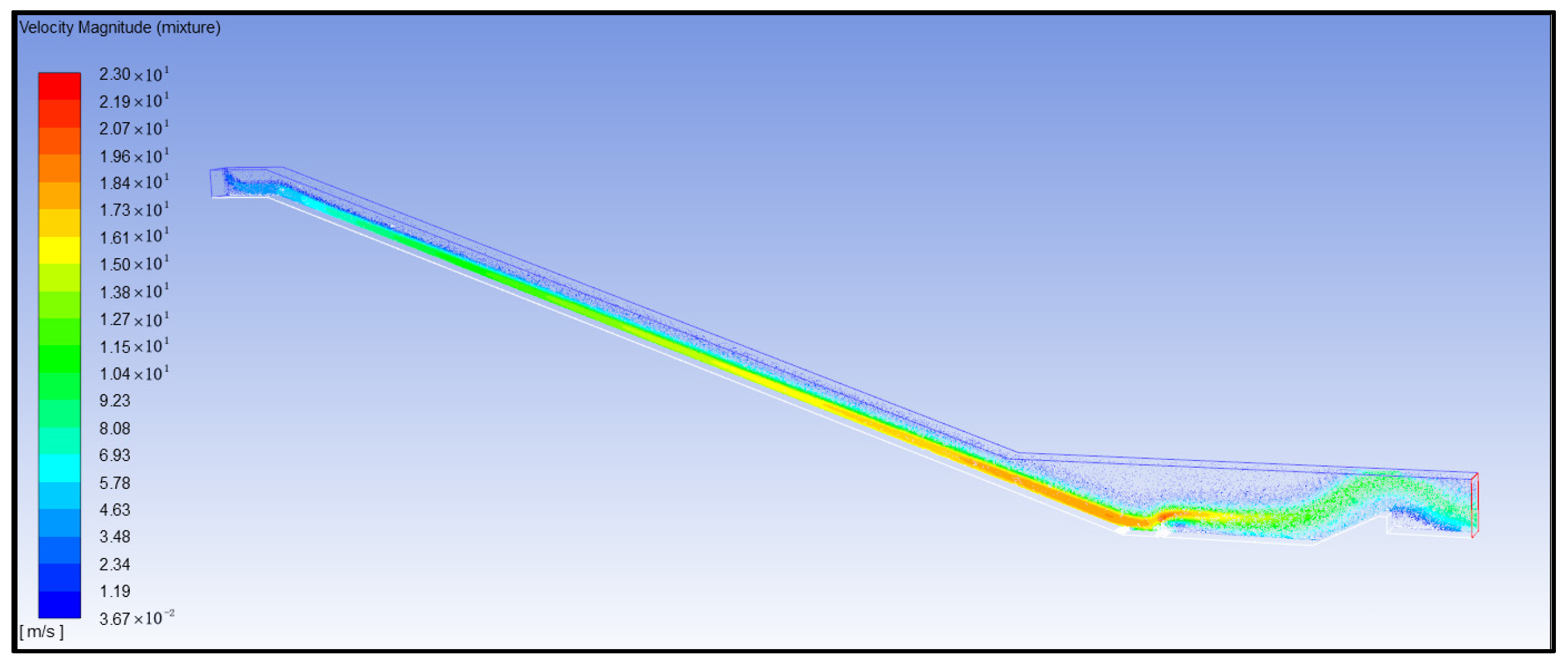
4. Simulation Calculation Results and Analysis
- (1)
- Analysis of Air Concentration
- (2)
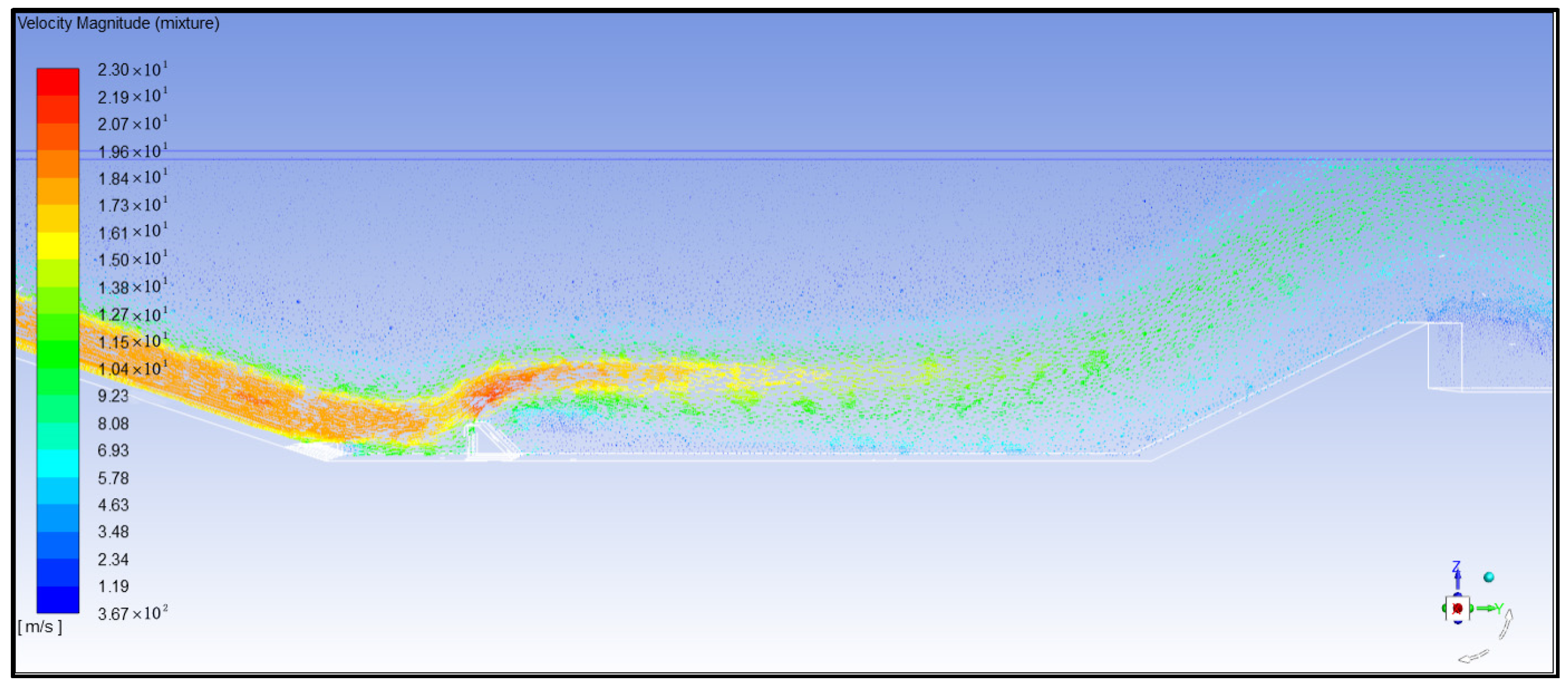
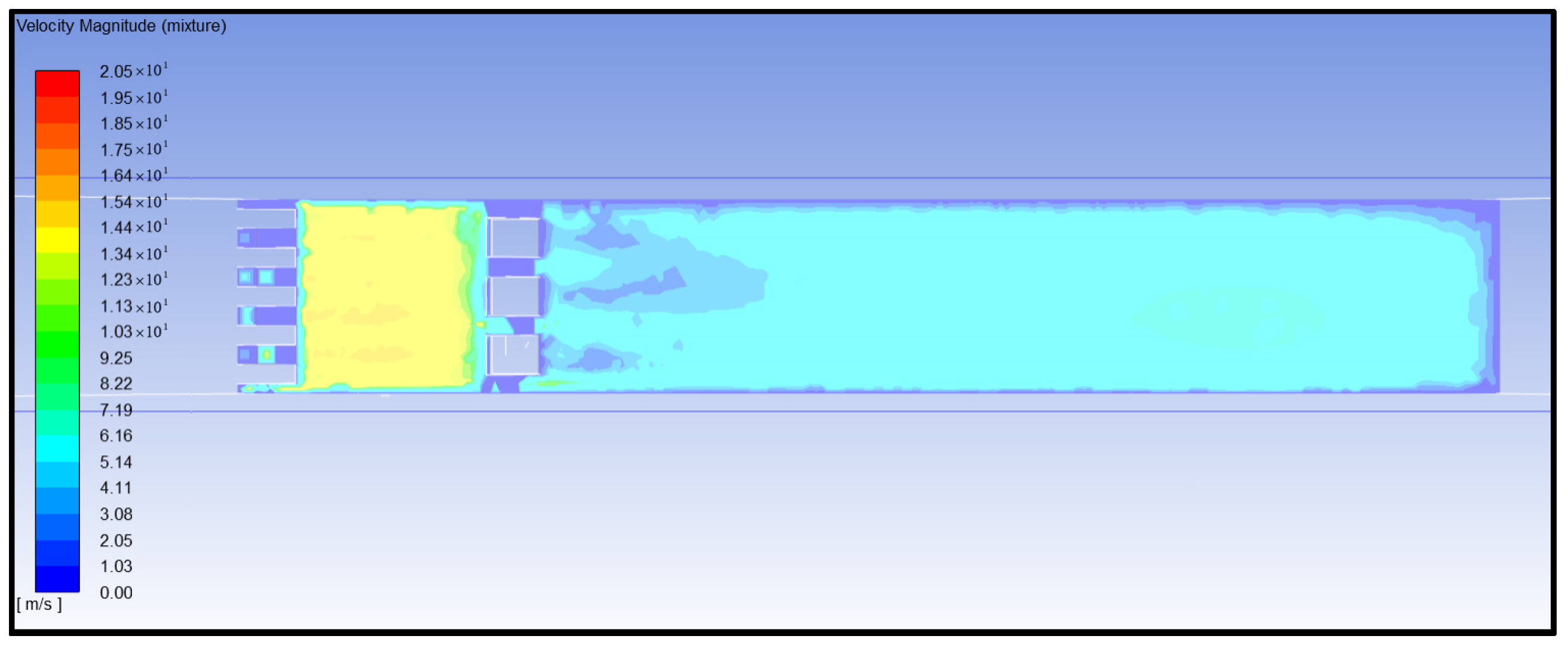
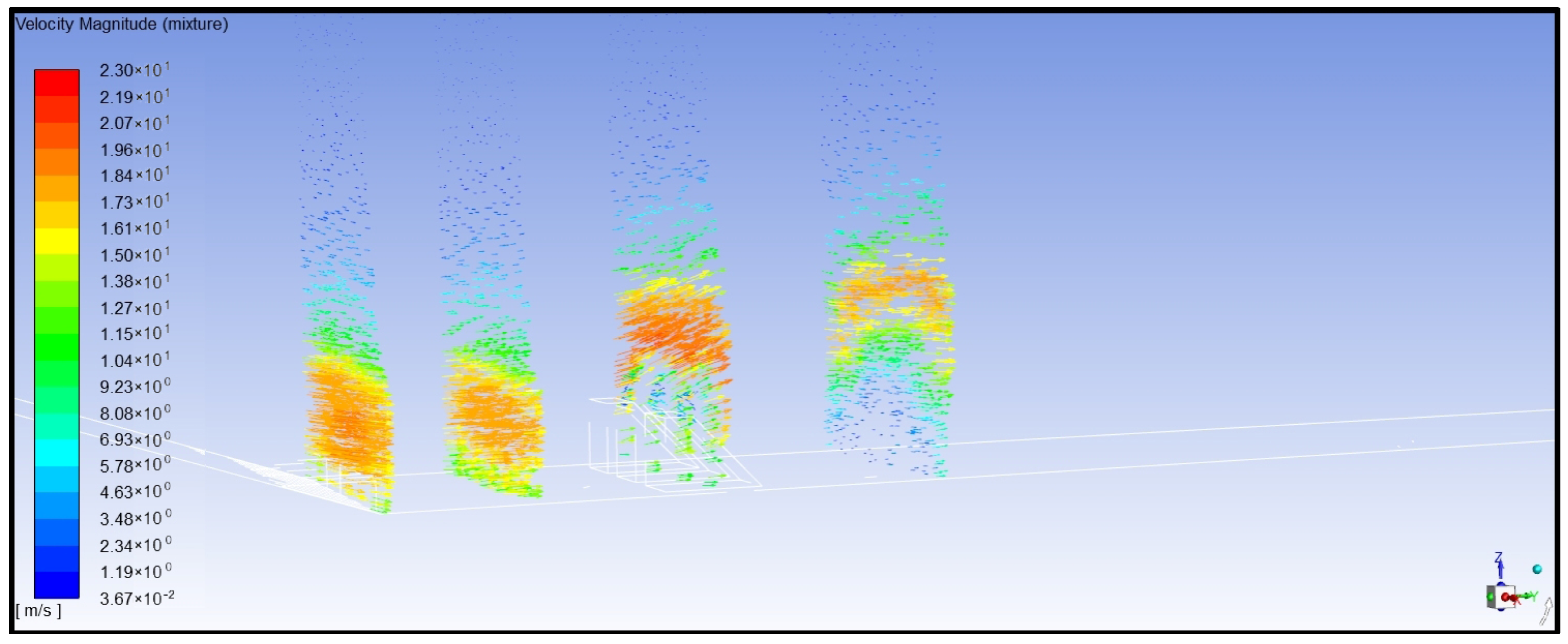
- Analysis of water flow velocity
- (3)
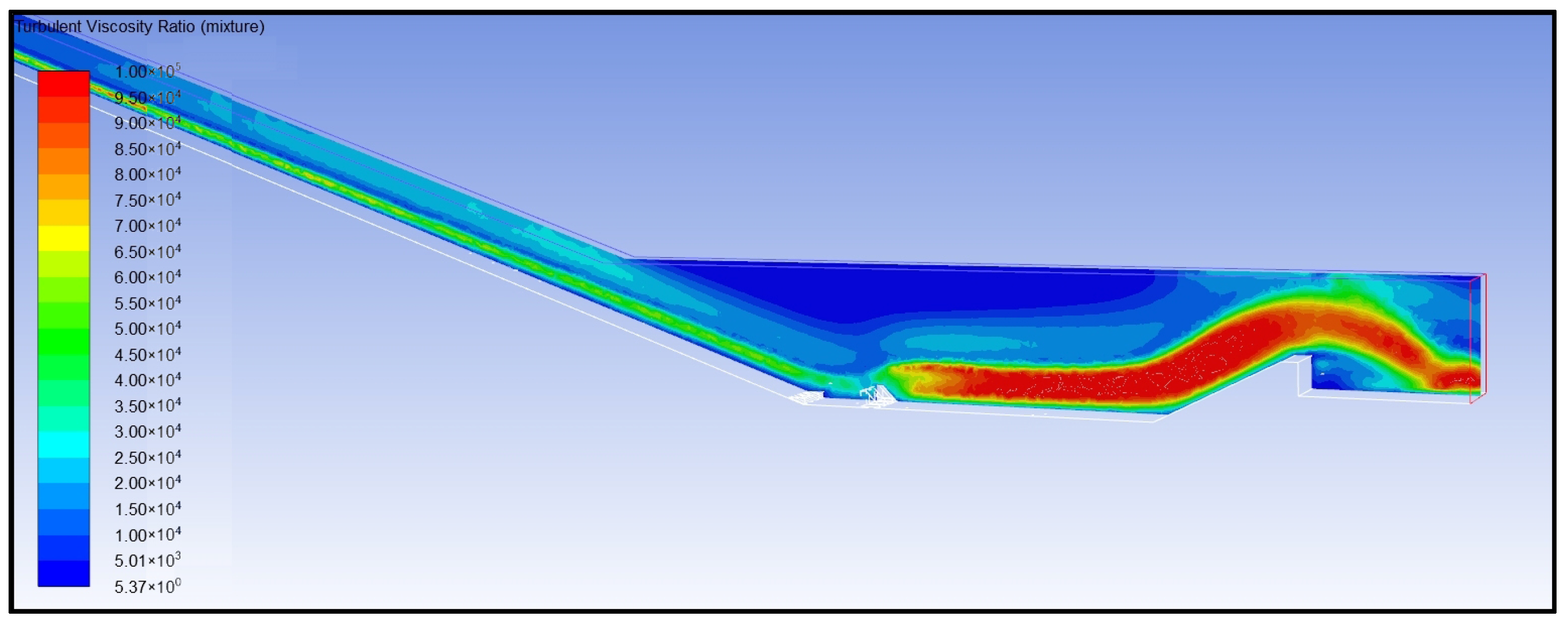
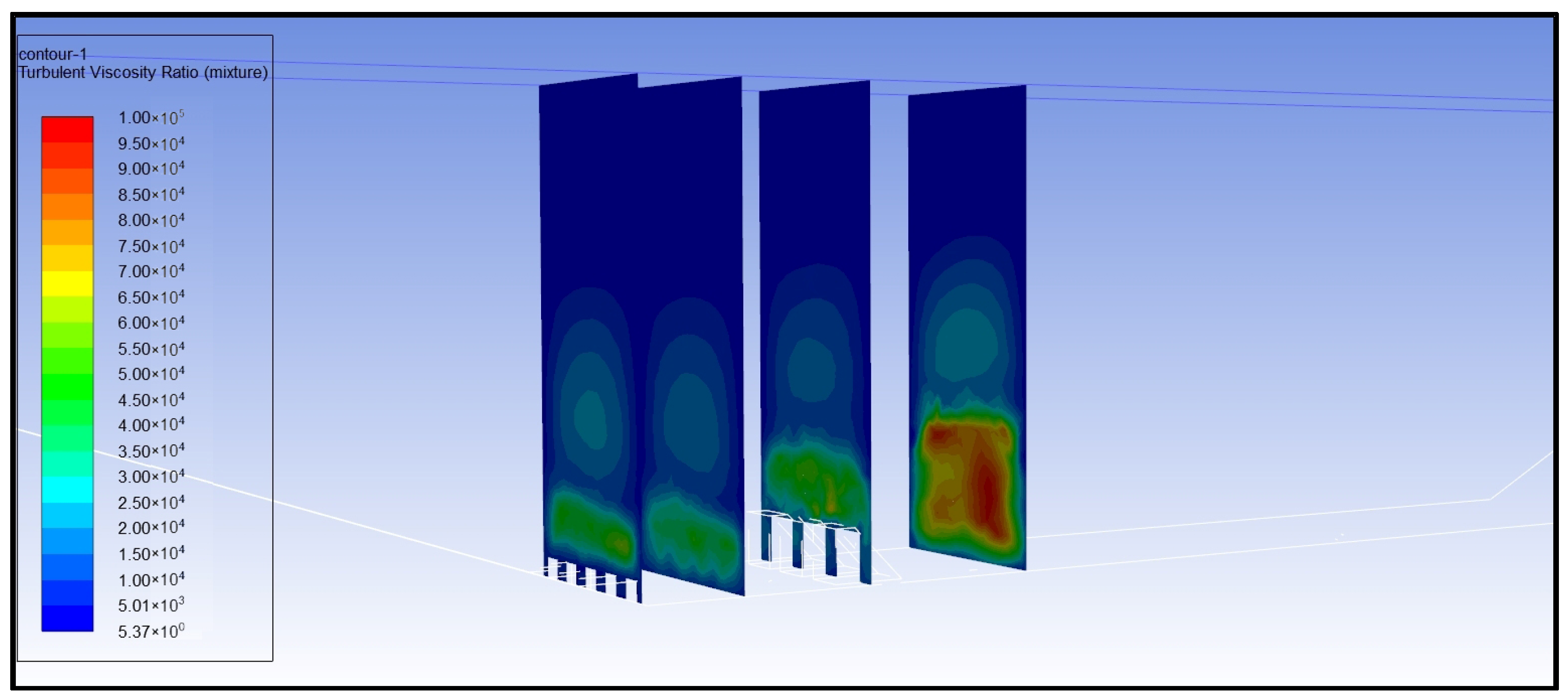
- Analysis of Turbulent Dissipation Rate
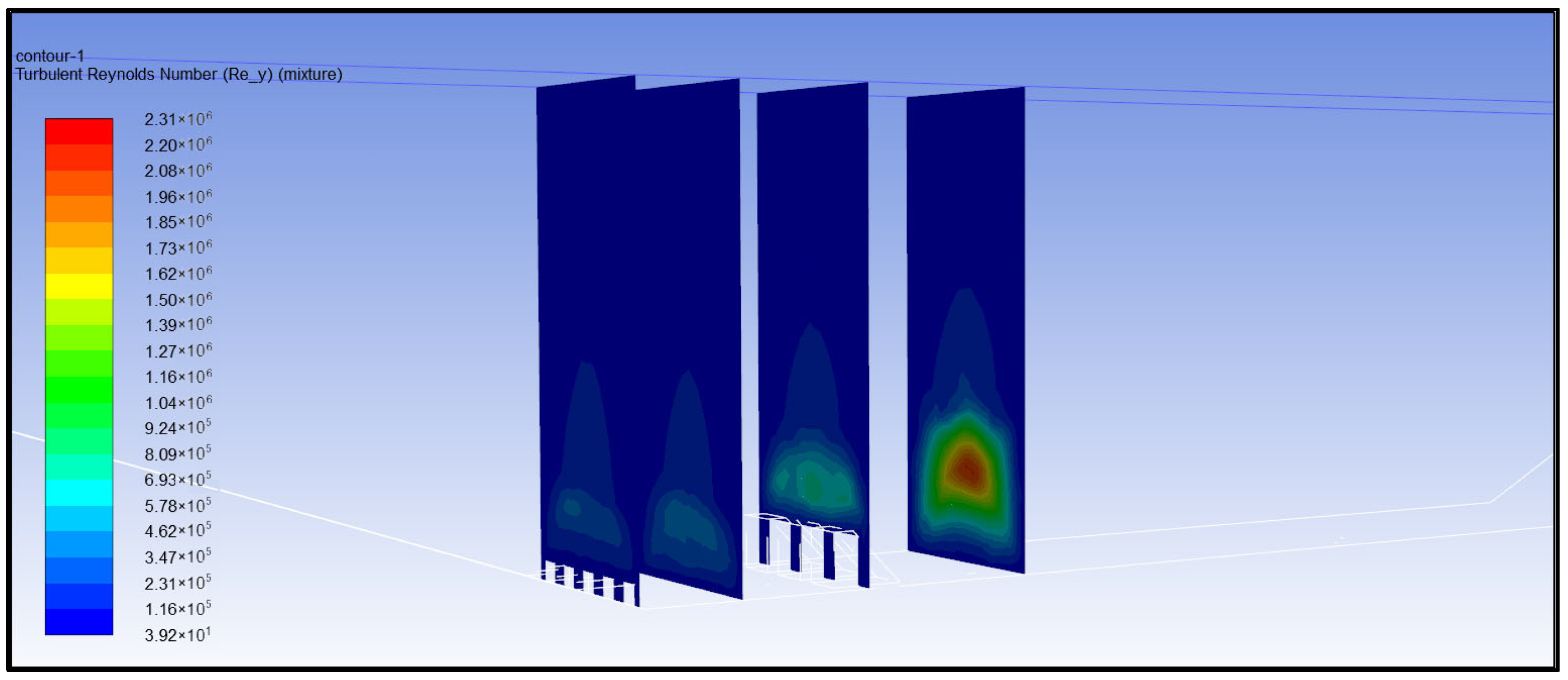
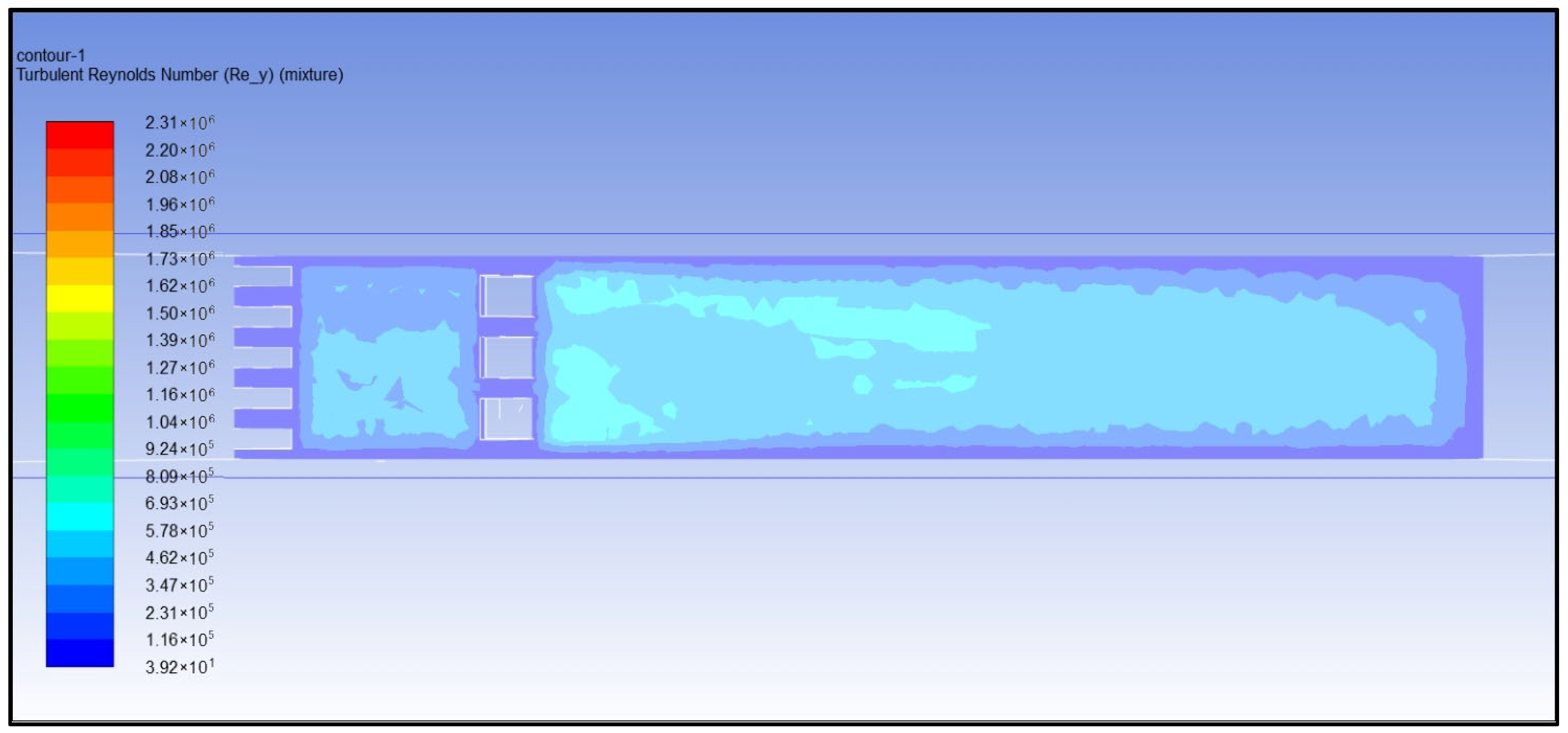
- (4)
- Reynolds number analysis of turbulent water flow
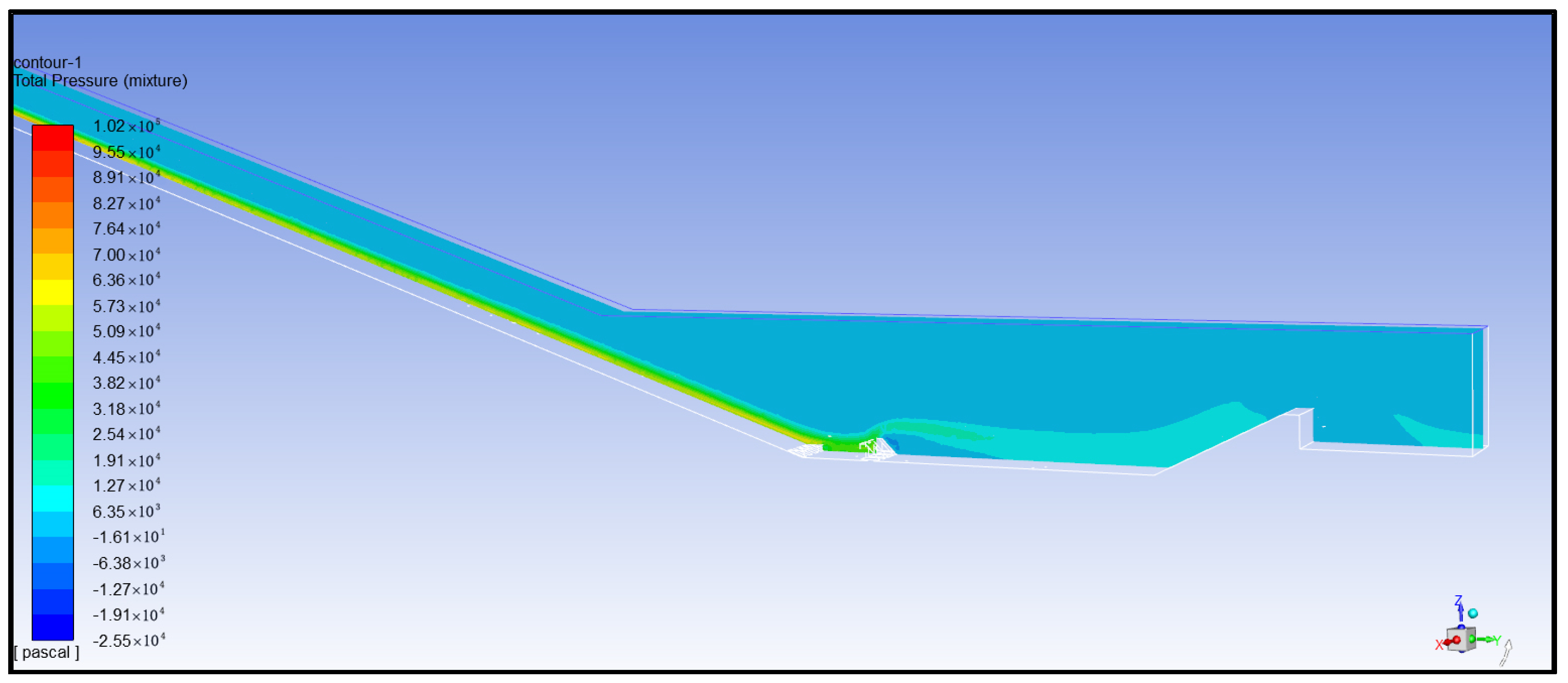
- (5)
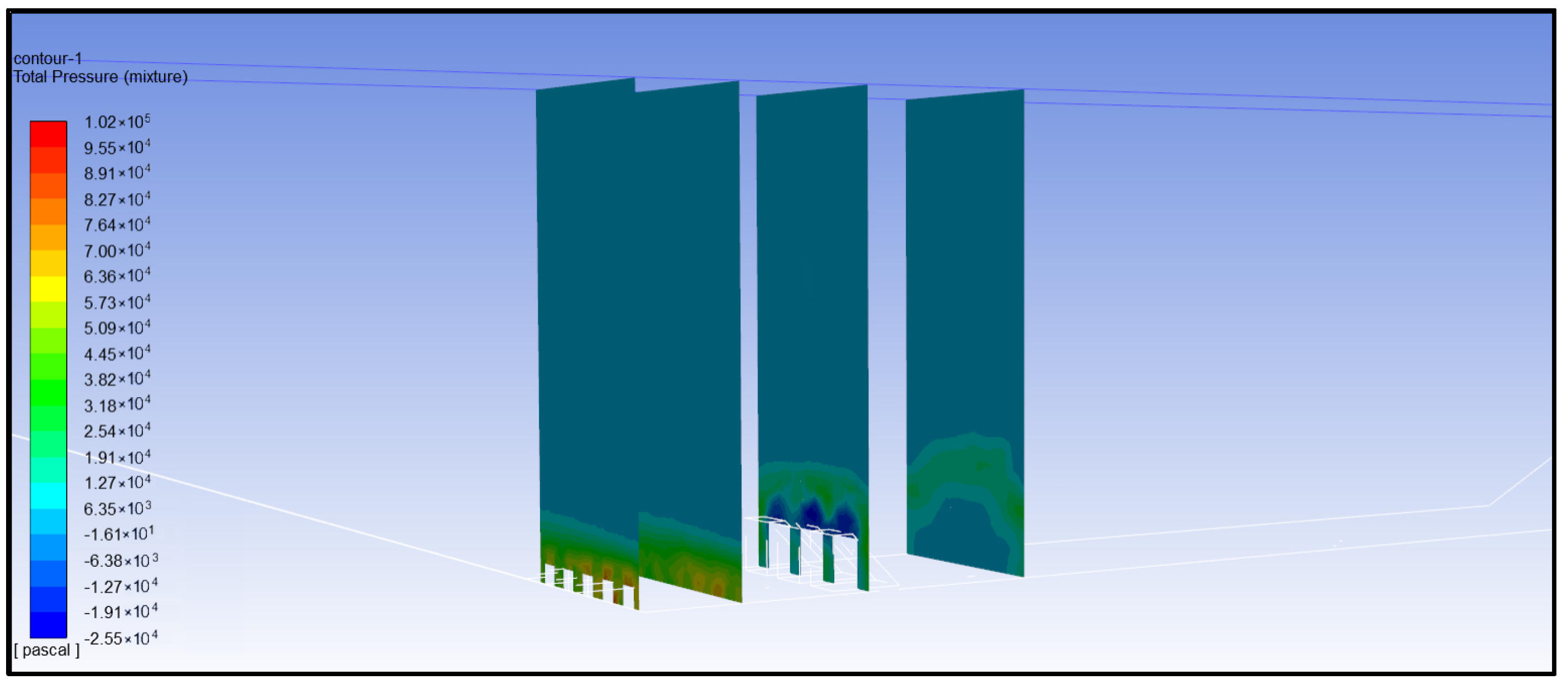
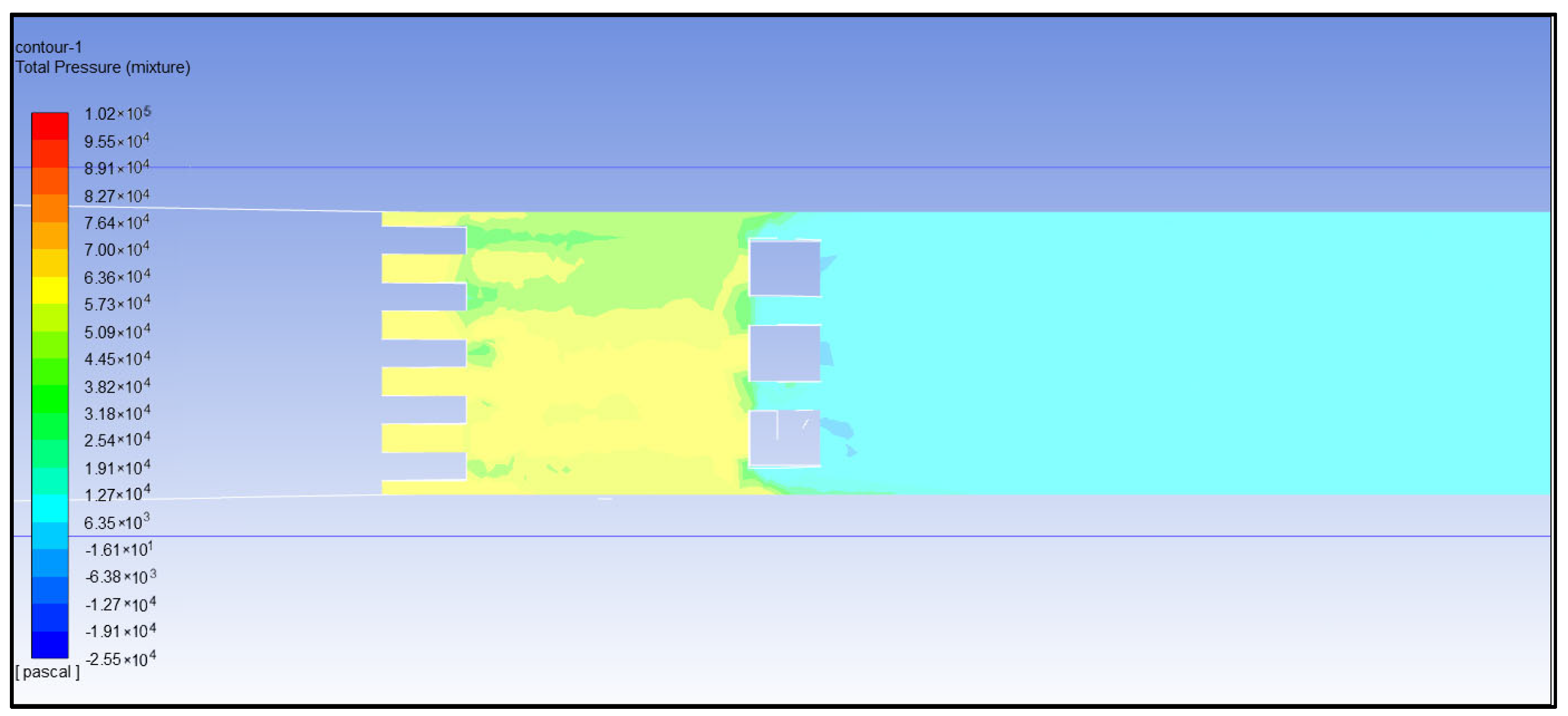
- Analysis of total pressure of water flow
- (6)
- Comprehensive analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yurdagul, S.K.; Kamil, I. Experimental and Numerical Modeling of Various Energy Dissipater Designs in Chute Channels. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 2–15. [Google Scholar]
- Viti, N.; Valero, D.; Gualtieri, C. Numerical Simulation of Hydraulic Jumps. Part 2: Recent Results and Future Outlook. Water 2018, 11, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valero, D.; Felder, S.; Kramer, M.; Wang, H.; Carrillo, M.J.; Pfister, M.; Bung, B.D. Air-water Flows. J. Hydraul. Res. 2024, 62, 319–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaffar, M.W.; Haasan, I.; Ghumman, A.R. Performance Evaluation of Different Stilling Basins Downstream of Barrage Using FLOW-3D Scour Models. Hydrology 2023, 10, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idfi, G.; Lasminto, U.; Kartika, A.A. Modification of USBR Type III Stilling Basin Using a Stepp Stair Model to Improve Hydraulic Performance and Energy Dissipation Effectiveness. J. Propuls. Technol. 2024, 45, 5403–5407. [Google Scholar]
- Badas, G.M.; Rossi, R.; Garau, M. May a Standard VOF Numerical Simulation Adequately Complete Spillway Laboratory Measurements in an Operational Context? The Case of Sa Stria Dam. Water 2020, 12, 1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadka, P.; Rai, S. Numerical Model Scenario Analysis of Stilling Basin: A Case Study of Tanahu Hydropower Project (140 MW). Int. J. Eng. Technol. 2023, 1, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaffar, M.W.; Hassan, I.; Latif, U.; Jahan, S.; Ullah, Z. Numerical Investigation of Scour Downstream of Diversion Barrage for Different Stilling Basins at Flood Discharge. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, J.M.; José, F.V.; Rafael, G. Assessment of the Performance of a Modified USBR Type II Stilling Basin by a Validated CFD Model. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2021, 147, 04021052. [Google Scholar]
- Su, X.Y.; Li, S.P.; Wang, M.M.; Cui, H.; Pan, K.; Yuan, J.; He, S. Numerical Simulation on Hydraulic Performance for Spillway Bends in Goushuipo Reservoir. Water Resour. Dev. Res. 2023, 23, 67–74. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.Y. Analysis of River Ecological Management Solution of Jinyuan District. Water Resour. Dev. Res. 2024, 24, 54–58. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.D. Analysis of the Impact of the Floating Bridge Project in Changtu County on the Flow Field of the Liaohe River. Water Resour. Dev. Res. 2016, 16, 55–57. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, L.W.; Hu, K.; Niu, G.L. Digital Twin Xiaolangdi: Construction and application of dam safety monitoring and management platformr. Water Resour. Dev. Res. 2024, 6, 2–8. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Jia, X.; Peng, Y.; Gao, Z.; Yu, H. Transient Sand Scour Dynamics Induced by Pulsed Submerged Water Jets: Simulation Analysis. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totu, A.-G.; Olariu, C.-T.; Trifu, A.-T.; Totu, A.-C.; Cican, G. Development and Assessment of a Miniaturized Test Rig for Evaluating Noise Reduction in Serrated Blades Under Turbulent Flow Conditions. Acoustics 2024, 6, 978–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Liu, H.; Hua, L.; Ji, Z.; Lu, T. Drops and Steep Slopes; China Water & Power Press: Beijing, China, 2009; p. 167. [Google Scholar]
- Kambe, T. New Perspectives on Mass conservation Law and Waves in Fluid Mechanics. Fluid Dyn. Res. 2020, 52, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cercos-Pita, J.L.; Dalrymple, R.A.; Herault, A. Diffusive Terms for the Conservation of Mass Equation in SPH. Appl. Math. Model. 2016, 40, 8722–8736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, J.; Kim, K.D.; Kim, B.J. Improvement of One-Dimensional Two-Fluid Momentum Conservation Equations for Vertically Stratified Flow. Nucl. Technol. 2018, 204, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.P.; He, X.; Deng, X.G. An Improved Second-Order Finite-Volume Algorithm for Detached-Eddy Simulation Based on Hybrid Grids. Commun. Comput. Phys. 2016, 20, 459–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheed, R.; Mohammadian, A.; Gildeh, H.K. A Comparison of Standard k–ε and Realizable k–ε Turbulence Models in Curved and Confluent Channels. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2019, 19, 543–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrman, D.R.; Li, Y.Z. Instability of the Realizable k–ε Turbulence Model Beneath Surface Waves. Phys. Fluids 2020, 32, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaki, T.; Su, T.L.; Kim, M.; Van Horn, M.L. An Evaluation of the Bootstrap for Model Validation in Mixture Models. Commun. Stat.-Simul. Comput. 2018, 47, 1028–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubke, G.H.; Luningham, J. Fitting Latent Variable Mixture Models. Behav. Res. Ther. 2017, 98, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venier, C.M.; Pairetti, C.I.; Damian, S.M.; Nigro, N.M. On the Stability Analysis of the PISO Algorithm on Collocated Grids. Comput. Fluids 2017, 147, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, D.D.; Sheng, C.H. A New Method towards High-order Weno Schemes on Structured and Unstructured Grids. Comput. Fluids 2020, 200, 104453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandowski, M.T.; Pluszka, P.; Pozorski, J. Influence of Inlet Boundary Conditions in Computations of Turbulent Jet Flames. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 2018, 28, 1433–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiran, I.N.; Beratlis, N.; Capuano, F.; Loke, Y.H.; Squires, K.; Balaras, E. Pressure Boundary Conditions for Immersed-boundary Methods. J. Comput. Phys. 2024, 510, 113057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.Y.; Wang, Z.D.; Tamai, T.; Koshizuka, S. Consistent Inlet and Outlet Boundary Conditions for Particle Methods. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 2019, 92, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado-Rodríguez, C.E.; Klapp, J.; Sigalotti, L.D.; Dominguez, J.M.; Sánchez, E.D.C. Non-reflecting Outlet Boundary Conditions for Incompressible Flows Using SPH. Comput. Fluids 2017, 159, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksin, V.A.; Utyuzhnikov, S.V. Implementation of Near-wall Boundary Conditions for Modeling Boundary Layers with Free-stream Turbulence. Appl. Math. Model. 2014, 38, 3591–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.M.; Aly, A.M.; Lee, S.W. Improved Wall Boundary Conditions in the Incompressible Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics Method. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 2018, 28, 704–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, R.D.; Zhang, F.X.; Liu, S.J.; Wang, W. Air Concentration and Bubble Characteristics Downstream of a Chute Aerator. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2016, 87, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.C.; Yang, F.; Wu, K.; Ma, Y.F.; Peng, C.; Liu, T.S.; Wang, L.P. Estimation of the Dissipation Rate of Turbulent Kinetic Energy: A Review. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2020, 29, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Sharma, A. Reynolds Number Effect on the Parameters of Turbulent Flows over Open Channels. Aqua-Water Infrastruct. Ecosyst. Soc. 2024, 73, 1030–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, L.R.; Lucchese, L.V.; Schettini, E.B.C. Comparison between Hydrostatic and Total Pressure Simulations of Dam-break Flows. J. Hydraul. Res. 2019, 58, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Bao, Z.J.; Wang, B. Three-dimensional Numerical Simulation of Flow in Stilling Basin Based on Flow-3D. Eng. J. Wuhan Univ. 2012, 45, 454–457. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.L.; Liao, H.S.; Yang, Y.Q.; Wu, C.G. Numerical Simulation of 3-D Turbulent Flows of Plunge Pool and Energy Dissipation Analysis. J. Hydrodyn. 1996, 11, 561–569. [Google Scholar]




| Peject | Length | Air Concentration | Water Flow Velocity (m/s) | Turbulent Dissipation Rate | Reynolds Number | Total Pressure of Water Flow (kpa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before optimization | 16.5 | 0.2~0.4 | 2.25~3.92 | (4.6~8.8) × 104 | (5.2~8.6) × 105 | 10.5~17.3 |
| After optimization | 14.6 | 0.1~0.3 | 2.05~4.11 | (5.0~8.5) × 104 | (5.8~9.2) × 105 | 12.7~19.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, B.; Wu, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, H.; Hu, Y.; Benson, D. Application Research of a High Turbulence Numerical Simulation Technique in a USBR Type III Stilling Basin. Water 2024, 16, 3568. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16243568
Meng X, Zhang C, Zhang B, Wu X, Wang W, Wang H, Hu Y, Benson D. Application Research of a High Turbulence Numerical Simulation Technique in a USBR Type III Stilling Basin. Water. 2024; 16(24):3568. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16243568
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Xiao, Chao Zhang, Bin Zhang, Xiao Wu, Wei Wang, Haoyu Wang, Yawei Hu, and David Benson. 2024. "Application Research of a High Turbulence Numerical Simulation Technique in a USBR Type III Stilling Basin" Water 16, no. 24: 3568. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16243568
APA StyleMeng, X., Zhang, C., Zhang, B., Wu, X., Wang, W., Wang, H., Hu, Y., & Benson, D. (2024). Application Research of a High Turbulence Numerical Simulation Technique in a USBR Type III Stilling Basin. Water, 16(24), 3568. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16243568







