Development Characteristics and Controlling Factors of Karst Aquifer Media in a Typical Peak Forest Plain: A Case Study of Zengpiyan National Archaeological Site Park, South China
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- To delineate the developmental characteristics and principal controlling factors of the karst water system media within the Zengpiyan area.
- (2)
- To elucidate how the heterogeneity and anisotropy of the karst aquifer media influence the movement and distribution of karst water.
- (3)
- To provide a quantitative depiction of the medium structure and developmental traits of the karst water system in the Zengpiyan area.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Area
2.2. Data Collection and Analysis
2.2.1. Fracture Sampling Area and Method
2.2.2. Calculation of Permeability Tensor
2.2.3. Underground Geophysical Analysis
3. Results
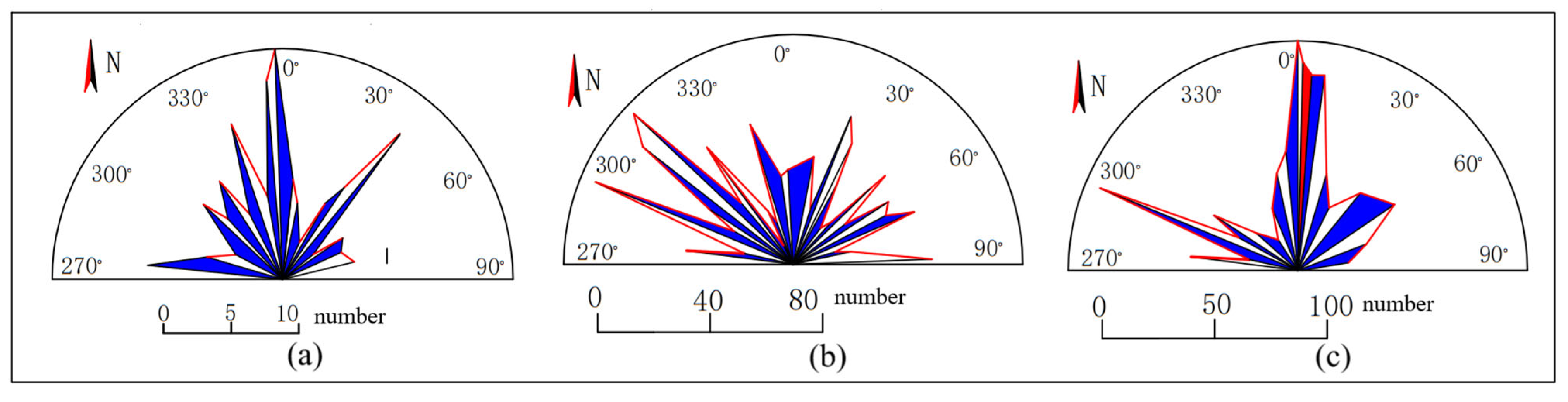
3.1. Development Characteristics of Surface Fissures
3.2. Anisotropy of Fractured Media
3.3. Uneven and Zonal Development of Underground Karst
4. Discussion
4.1. Development of Karst Surface Fissures and Analysis of Medium Anisotropy
4.2. Characteristics and Genesis Analysis of Underground Karst Development
4.3. Limitations and Prospects
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hartmann, A.; Goldscheider, N.; Wagener, T.; Lange, J.; Weiler, M. Karst Water Resources in a Changing World: Review of Hydrological Modeling Approaches. Rev. Geophys. 2014, 52, 218–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Auler, A.S.; Bakalowicz, M.; Drew, D.; Griger, F.; Hartmann, J.; Jiang, G.; Moosdorf, N.; Richts, A.; Stevanovic, Z.; et al. The World Karst Aquifer Mapping Project: Concept, Mapping Procedure and Map of Europe. Hydrogeol. J. 2017, 25, 771–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, W.B. Karst Hydrology: Recent Developments and Open Questions. Eng. Geol. 2002, 65, 85–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Qi, J.; Xu, M.; Li, X.; Qu, C.; Yi, L.; Wang, D. Change Analysis of Karst Landforms, Hydrogeological Conditions and Effects of Tunnel Excavation on Groundwater Environment in Three Topography Grades in China. Water 2023, 15, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Wang, S.; Bai, X.; Luo, G.; Li, Q.; Wu, L.; Yang, Y.; Tian, S.; Li, C.; Deng, Y. Changes in Ecosystem Service Values in Karst Areas of China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 301, 107026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L. Assessment of Water Resource Security in Karst Area of Guizhou Province, China. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-L.; Liu, C.-Q.; Chen, J.-A.; Wang, S.-J. Karst Ecosystem and Environment: Characteristics, Evolution Processes, and Sustainable Development. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 306, 107173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravbar, N.; Goldscheider, N. Comparative Application of Four Methods of Groundwater Vulnerability Mapping in a Slovene Karst Catchment. Hydrogeol. J. 2009, 17, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrič, M.; Ravbar, N.; Gostinčar, P.; Krsnik, P.; Gacin, M. GIS Database of Groundwater Flow Characteristics in Carbonate Aquifers: Tracer Test Inventory from Slovenian Karst. Appl. Geogr. 2020, 118, 102191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Shu, L.; Zhu, J.; Yu, Z.; Jiang, P. Storage and Drainage Characteristics of a Highly Heterogeneous Karst Aquifer in Houzhai Basin. Ground Water 2016, 54, 878–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frumkin, A.; Barzilai, O.; Hershkovitz, I.; Ullman, M.; Marder, O. Karst Terrain in the Western Upper Galilee, Israel: Speleogenesis, Hydrogeology and Human Preference of Manot Cave. J. Hum. Evol. 2021, 160, 102618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frumkin, A.; Langford, B.; Lisker, S. Hypogenic Karst at the Arabian Platform Margins: Implications for Far-Field Groundwater Systems. KIP Artic. 2017, 129, 11–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abotalib, A.Z.; Sultan, M.; Elkadiri, R. Groundwater Processes in Saharan Africa: Implications for Landscape Evolution in Arid Environments. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2016, 156, 108–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Wang, X.; Lü, Q.; Sun, H.; Guo, J. A New Determination Method for the Permeability Tensor of Fractured Rock Masses. J. Hydrol. 2020, 585, 124811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zheng, J.; Sun, H.; Lü, Q.; Ge, Q.; Tan, S. A Semi-Theoretical Method for Determining the Permeability Tensor of Fractured Rock Masses in Three-Dimensional Space. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 026613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso de Salis, H.H.; Monteiro da Costa, A.; Moreira Vianna, J.H.; Azeneth Schuler, M.; Künne, A.; Sanches Fernandes, L.F.; Leal Pacheco, F.A. Hydrologic Modeling for Sustainable Water Resources Management in Urbanized Karst Areas. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhou, H.; Qi, L.; Wang, J.; Yan, Z. Method for Characterizing Structure and Hydrological Response in Karst Water Systems: A Case Study in Y-M System in Three Gorges Area. Earth Sci. 2020, 45, 4512–4523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bresinsky, L.; Kordilla, J.; Engelhardt, I.; Livshitz, Y.; Sauter, M. Variably Saturated Dual-Permeability Flow Modeling to Assess Distributed Infiltration and Vadose Storage Dynamics of a Karst Aquifer—The Western Mountain Aquifer in Israel and the West Bank. J. Hydrol. X 2023, 18, 100143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.Y.; Liu, L.B.; Guo, C.Z.; Zhang, Z.H.; Hu, G.; Ni, J. Low carbon storage of woody debris in a karst forest in southwestern China. Acta Geochim. 2019, 38, 576–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Luo, D.H.; Xia, J.; Zhang, Z.H.; Hu, G. Vegetation in Karst Terrain of Southwestern China Allocates More Biomass to Roots. Solid Earth Discuss. 2015, 7, 1209–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Yang, H. The development and utilization technology of water resources in karst areas abroad and its enlightenment to China. J. Guangxi Acad. Sci. 2022, 38, 352–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.M.; Chang, W.; Guo, X.L.; Deng, Z.R.; Huang, K. Identification of the karst water flow system and its application in the tunnel line selection of water diversion projects. Bull. Geol. Sci. Technol. 2022, 41, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, J.; Lian, J.; Fu, Z.; Luo, Z.; Nie, Y.; Chen, H. Spatial Variability of Epikarst Thickness and Its Controlling Factors in a Dolomite Catchment. Geoderma 2022, 428, 116213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Fu, Z.; Nie, Y.; Lian, J.; Luo, Z.; Wang, F.; Chen, H. Microclimate Stability on the Critical Zone of a Karst Hillslope in Southwest China: Insights from Continuous Temperature Observations at the Air–Soil–Epikarst Interface. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 336, 117656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olarinoye, T.; Gleeson, T.; Marx, V.; Seeger, S.; Adinehvand, R.; Allocca, V.; Andreo, B.; Apaéstegui, J.; Apolit, C.; Arfib, B.; et al. Global Karst Springs Hydrograph Dataset for Research and Management of the World’s Fastest-Flowing Groundwater. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benteng, B.I.; Lixin, Z.; Chen, Y.; Yaqiong, Y.; Wenqiang, S.H.I. Karst Landforms and Development Vitality in Southwest China. CHINA Min. Mag. 2022, 31 (Suppl. S1), 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Tang, H.; Qu, S.; Zhao, L.; Li, Q. Drought Propagation in Karst and Non-Karst Regions in Southwest China Compared on a Daily Scale. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2024, 51, 101628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; He, Z.; Gu, X.; Xu, M.; Chen, L.; Yang, S.; Tan, H. Agricultural Drought-Driven Mechanism of Coupled Climate and Human Activities in the Karst Basin of Southern China. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 12072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.-J.; Liu, Q.-M.; Zhang, D.-F. Karst Rocky Desertification in Southwestern China: Geomorphology, Landuse, Impact and Rehabilitation. Land Degrad. Dev. 2004, 15, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghezelayagh, P.; Javadi, S.; Kavousi, A. COP*KAT: A Modified COP Vulnerability Mapping Method for Karst Terrains Using KARSTLOP Factors and Fuzzy Logic. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietruszczak, S.; Jameei, A.A. Assessment of Stress-Induced Evolution of Permeability Tensor in Rock Mass Containing Discrete Fracture Network. Comput. Geotech. 2024, 174, 106580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, H.; Jakada, H.; Zhang, L.; Han, Z.; Shi, T. Identifying Structure and Function of Karst Aquifer System Using Multiple Field Methods in Karst Trough Valley Area, South China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Xue, K.; Zhu, X.; Zhou, C.; Chen, J.; Han, K.; Luo, Q.; Yi, G. Application of the Opposing-Coils Transient Electromagnetic Method Combined with Ground-Penetrating Radar for the Identification of Shallow Geohazards: A Case Study in Xiacun Town, Xinyu City, China. Hydrogeol. J. 2024, 32, 1925–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Lin, J.; Huang, Q.; Liang, R. An Emerging Method Using Electromagnetic Wave Computed Tomography for the Detection of Karst Caves. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2020, 38, 2713–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza de Araújo, O.; Chemas Hindi, E.; Rigoti, A.; Rigoti, F.H. Improved Imaging of a Karst Aquifer Using Focused Source Electromagnetic and Differentially Normalized Method: A Qualitative Analysis. Geophys. Prospect. 2019, 67, 1965–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Chang, Y.; Wu, J.; Peng, F. Laboratory Investigation and Simulation of Breakthrough Curves in Karst Conduits with Pools. Hydrogeol. J. 2017, 25, 2235–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Zhang, X.; Chu, X.; Wu, Q. Simulation of Groundwater Dynamic Response to Hydrological Factors in Karst Aquifer System. J. Hydrol. 2020, 587, 124995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, Z.; Raeisi, E.; Zare, M. A Dye-Tracing Test as an Aid to Studying Karst Development at an Artesian Limestone Sub-Aquifer: Zagros Zone, Iran. Environ. Geol. 2007, 52, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doummar, J.; Margane, A.; Geyer, T.; Sauter, M. Assessment of Key Transport Parameters in a Karst System under Different Dynamic Conditions Based on Tracer Experiments: The Jeita Karst System, Lebanon. Hydrogeol. J. 2018, 26, 2283–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roded, R.; Aharonov, E.; Frumkin, A.; Weber, N.; Lazar, B.; Szymczak, P. Cooling of Hydrothermal Fluids Rich in Carbon Dioxide Can Create Large Karst Cave Systems in Carbonate Rocks. Commun. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assunção, P.; Galvão, P.; Lucon, T.; Doi, B.; Marshall Fleming, P.; Marques, T.; Costa, F. Hydrodynamic and Hydrodispersive Behavior of a Highly Karstified Neoproterozoic Hydrosystem Indicated by Tracer Tests and Modeling Approach. J. Hydrol. 2023, 619, 129300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiu, B.; Huang, W.; Mu, N.; He, M. Effect of Hydrothermal Fluids on the Ultra-Deep Ordovician Carbonate Rocks in Tarim Basin, China. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2020, 194, 107445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Yan, Y.; Dai, Q.; Yi, X.; Hu, Z.; Cen, L. Spatial and Temporal Dynamics of Rainfall Erosivity in the Karst Region of Southwest China: Interannual and Seasonal Changes. CATENA 2023, 221, 106763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Shu, L.; Wang, Y.; Tong, F.; Han, J.; Shu, W.; Li, D.; Wen, J. The Controlling Factors of the Karst Water Hydrochemistry in a Karst Basin of Southwestern China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabelo, J.G.; Maia, R.P.; Bezerra, F.H.R.; Silva, C.C.N. Karstification and Fluid Flow in Carbonate Units Controlled by Propagation and Linkage of Mesoscale Fractures, Jandaíra Formation, Brazil. Geomorphology 2020, 357, 107090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langston, G.; Hayashi, M.; Roy, J.W. Quantifying Groundwater-Surface Water Interactions in a Proglacial Moraine Using Heat and Solute Tracers. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 5411–5426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, L.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Hao, F.; Xu, R.; Zhou, L.; Liu, Z. Early Dolomitization and Subsequent Hydrothermal Modification of the Middle Permian Qixia Formation Carbonate in the Northwest Sichuan Basin. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2023, 221, 211384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Bruna, V.; Bezerra, F.H.R.; Souza, V.H.P.; Maia, R.P.; Auler, A.S.; Araujo, R.E.B.; Cazarin, C.L.; Rodrigues, M.A.F.; Vieira, L.C.; Sousa, M.O.L. High-Permeability Zones in Folded and Faulted Silicified Carbonate Rocks—Implications for Karstified Carbonate Reservoirs. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2021, 128, 105046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Lv, M.; Luo, P.; Yang, X.; Chen, M.; Weng, D.; Qu, Z.; Liu, Y. Assessment and Optimization of Fracture-Karst Cave Connectivity in Horizontal Well Hydraulic Fracturing of Carbonate Reservoirs. Rock Mech. Bull. 2024, 3, 100112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Su, Z.; Wei, L.; Wei, X.; Zhang, C.; Fu, S.; Han, Y.; Ren, J.; Chen, H. Residual Carbonate Karst Reservoir Reconstructed by Karst Planation: A Case Study of Ordovician Paleokarst Reservoir Characterization in Ordos Basin, North China. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2024, 233, 212508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Yao, J.; Couples, G.D.; Ma, J.; Iliev, O. 3-D Modelling and Experimental Comparison of Reactive Flow in Carbonates under Radial Flow Conditions. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, W.; Li, Z.; Shen, L.; Liu, W.; Guo, Y.; Xu, H.; Yong, R. Study on the Process of Mass Transfer and Deterioration of Limestone under Dynamic Dissolution of CO2 Solution. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, L.; Dimuccio, L.A.; Cunha, L. Assessing Endokarst Potential in the Northern Sector of Santo António Plateau (Estremadura Limestone Massif, Central Portugal). Sustainability 2023, 15, 15599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hashim, M.H.; Al-Aidaros, A.; Zaidi, F.K. Geological and Hydrochemical Processes Driving Karst Development in Southeastern Riyadh, Central Saudi Arabia. Water 2024, 16, 1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mount, J.F. Mixing of Siliciclastic and Carbonate Sediments in Shallow Shelf Environments. Geology 1984, 12, 432–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reik, G.A.; Currie, J.B. A Study of Relations between Rock Fabric and Joints in Sandstone. Can. J. Earth Sci. 1974, 11, 1253–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abusaada, M.; Sauter, M. Studying the Flow Dynamics of a Karst Aquifer System with an Equivalent Porous Medium Model. Groundwater 2013, 51, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; Feng, M.; Wang, X.; Zhang, B.; Xu, L.; Liu, X. Alteration Effects of Karstification and Hydrothermalism on Middle Permian Qixia Formation at the Wulong Section, South China. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 13128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Shang, J.; Shen, A.; Wen, L.; Wang, X.; Xu, L.; Liang, F.; Liu, X. Episodic Hydrothermal Alteration on Middle Permian Carbonate Reservoirs and Its Geological Significance in Southwestern Sichuan Basin, SW China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2024, 51, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, G.; Liu, M.; Wang, M. Formation Environments and Mechanisms of Multistage Paleokarst of Ordovician Carbonates in Southern North China Basin. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Liang, X.; Luo, M.; Zhou, H. Characterizing the Hierarchical Groundwater Flow Systems in Karstic Xiangxi River Basin, West Hubei, Central China. Appl. Geochem. 2022, 143, 105371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Parameters | Fissures | Stratum | Advantageous Occurrence dip∠Dipangle/(°) | Fracture Rate of Linear (/m) | Rock Fracture Width /(m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sampling Area | |||||
| 1 | 248 | D3r | 143∠76 | 0.99 | 0.001~0.12 |
| 2 | 1255 | D3r | 162∠60 | 5.02 | 0.001~0.23 |
| 3 | 1969 | D3r | 114∠64 | 4.92 | 0.001~0.45 |
| Total | 3472 | D3r | 125∠62 | 3.64 | 0.001~0.45 |
| Fissure Group | Recharge Area | Discharge Area | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sampling Zone 1 | Sampling Zone 3 | Sampling Zone 2 | |||||
| i = 1 | i = 2 | i = 3 | i = 4 | i = 5 | i = 6 | ||
| K1 | Value (m/d) | 0.44 | 0.78 | 2.75 | 6.69 | 7.37 | 9.22 |
| Strike α (°) | 167.14 | 2.55 | 3.52 | 21.70 | 60.81 | 23.50 | |
| Dip angle β (°) | 56.21 | 64.61 | 71.77 | 43.19 | 74.09 | 32.54 | |
| K2 | value (m/d) | 0.51 | 1.23 | 7.75 | 9.00 | 13.46 | 18.89 |
| Strike α (°) | 67.17 | 71.45 | 165.45 | 123.30 | 134.11 | 150.90 | |
| Dip angle β (°) | 18.42 | 37.22 | 42.33 | 10.62 | 31.21 | 61.06 | |
| K3 | value (m/d) | 0.74 | 3.37 | 16.28 | 16.18 | 21.04 | 23.98 |
| Strike α (°) | 1.35 | 135.20 | 8.78 | 112.32 | 155.12 | 143.25 | |
| Dip angle β (°) | 60.04 | 26.67 | 47.75 | 21.44 | 19.66 | 65.33 | |
| value (m/d) | 0.55 | 1.48 | 5.72 | 7.01 | 12.78 | 16.10 | |
| Borehole Elevation/(m) | Layer Number | Cave Elevation/(m) | Altitude/(m) | Stratigraphic | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZK1 | 155.5 | 150.3~149.2 | 1.1 | D3r | |
| ZK2 | 162.5 | 158.7~157.4 | 1.3 | D3r | |
| ZK3 | 154.9 | 1 | 152.0~151.2 | 0.8 | D3r |
| 2 | 150.6~150.3 | 0.3 | D3r | ||
| ZK6 | 155.3 | 148.0~147.3 | 0.7 | D3r | |
| ZK7 | 153.9 | 125.6~124.2 | 1.4 | D3r | |
| ZK9 | 155.4 | 114.5~113.9 | 0.6 | D3r | |
| ZK10 | 153.3 | 128.2~117.7 | 10.5 | D3r | |
| ZK11 | 153.5 | 143.2~142.8 | 0.4 | D3r | |
| ZK14 | 157.6 | 145.3~143.2 | 2.1 | D3r | |
| ZK16 | 164.5 | 1 | 142.0~141.2 | 0.8 | D3r |
| 2 | 135.0~124.5 | 10.5 | D3r | ||
| ZK19 | 152.8 | 145.8~137.0 | 8.8 | D3r | |
| YK1 | 155.7 | 154.5~153.0 | 1.5 | D3r | |
| YK3 | 155.3 | 154.1~152.8 | 1.3 | D3r |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, P.; Wu, Y.; Li, S.; Jiang, G.; Yuan, D.; Yang, J.; Guo, C.; Yue, F.; Yuan, P.; Wu, H.; et al. Development Characteristics and Controlling Factors of Karst Aquifer Media in a Typical Peak Forest Plain: A Case Study of Zengpiyan National Archaeological Site Park, South China. Water 2024, 16, 3486. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16233486
Wang P, Wu Y, Li S, Jiang G, Yuan D, Yang J, Guo C, Yue F, Yuan P, Wu H, et al. Development Characteristics and Controlling Factors of Karst Aquifer Media in a Typical Peak Forest Plain: A Case Study of Zengpiyan National Archaeological Site Park, South China. Water. 2024; 16(23):3486. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16233486
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Penghui, Yangyang Wu, Siliang Li, Guanghui Jiang, Daoxian Yuan, Jinli Yang, Chunzi Guo, Fujun Yue, Panli Yuan, Haobiao Wu, and et al. 2024. "Development Characteristics and Controlling Factors of Karst Aquifer Media in a Typical Peak Forest Plain: A Case Study of Zengpiyan National Archaeological Site Park, South China" Water 16, no. 23: 3486. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16233486
APA StyleWang, P., Wu, Y., Li, S., Jiang, G., Yuan, D., Yang, J., Guo, C., Yue, F., Yuan, P., Wu, H., Luo, X., & Luo, G. (2024). Development Characteristics and Controlling Factors of Karst Aquifer Media in a Typical Peak Forest Plain: A Case Study of Zengpiyan National Archaeological Site Park, South China. Water, 16(23), 3486. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16233486









