Exploring Similarities and Differences in Water Level Response to Earthquakes in Two Neighboring Wells Using Numerical Simulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background and Observations
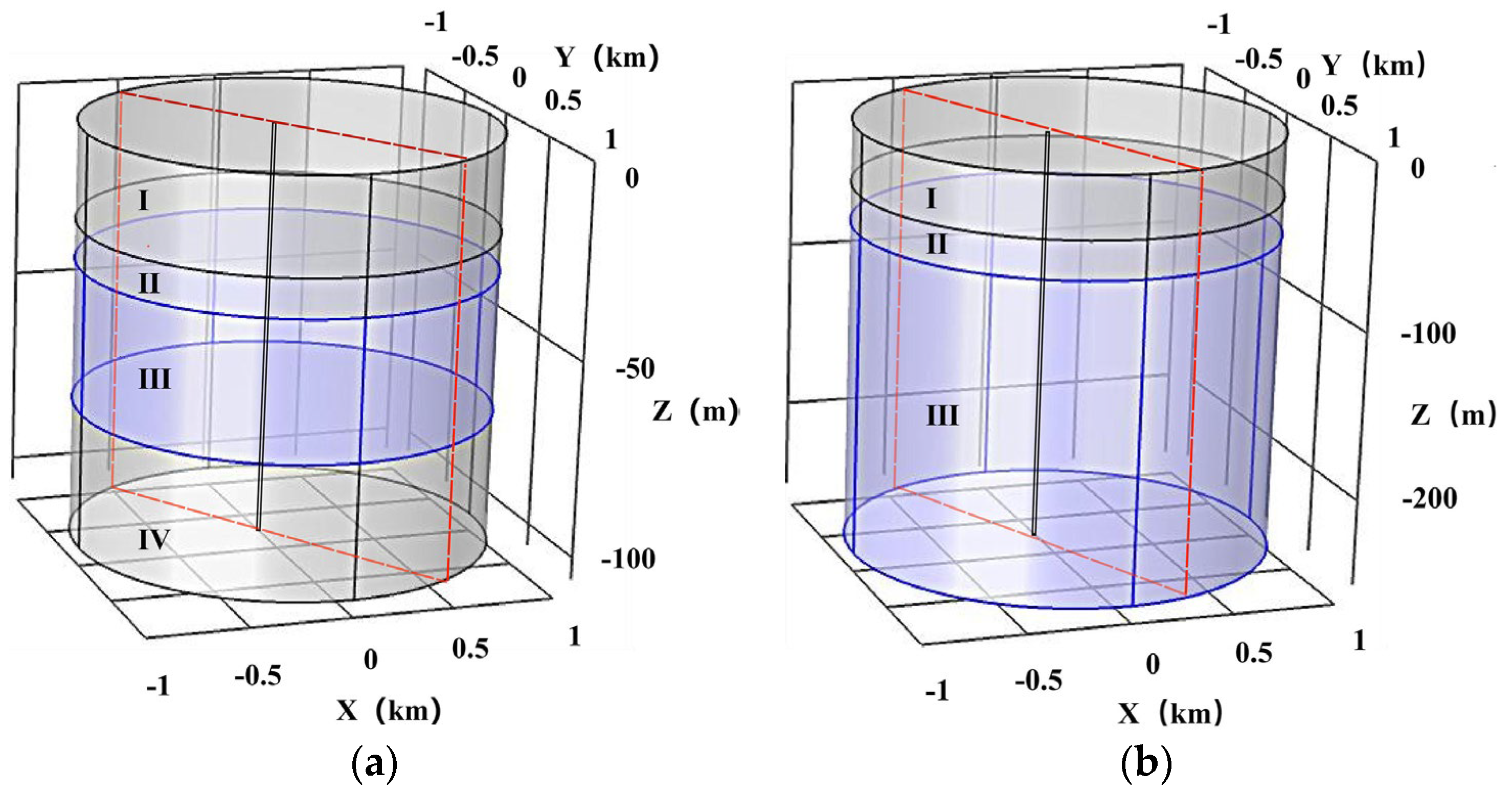
2.1. Information of Observation Wells
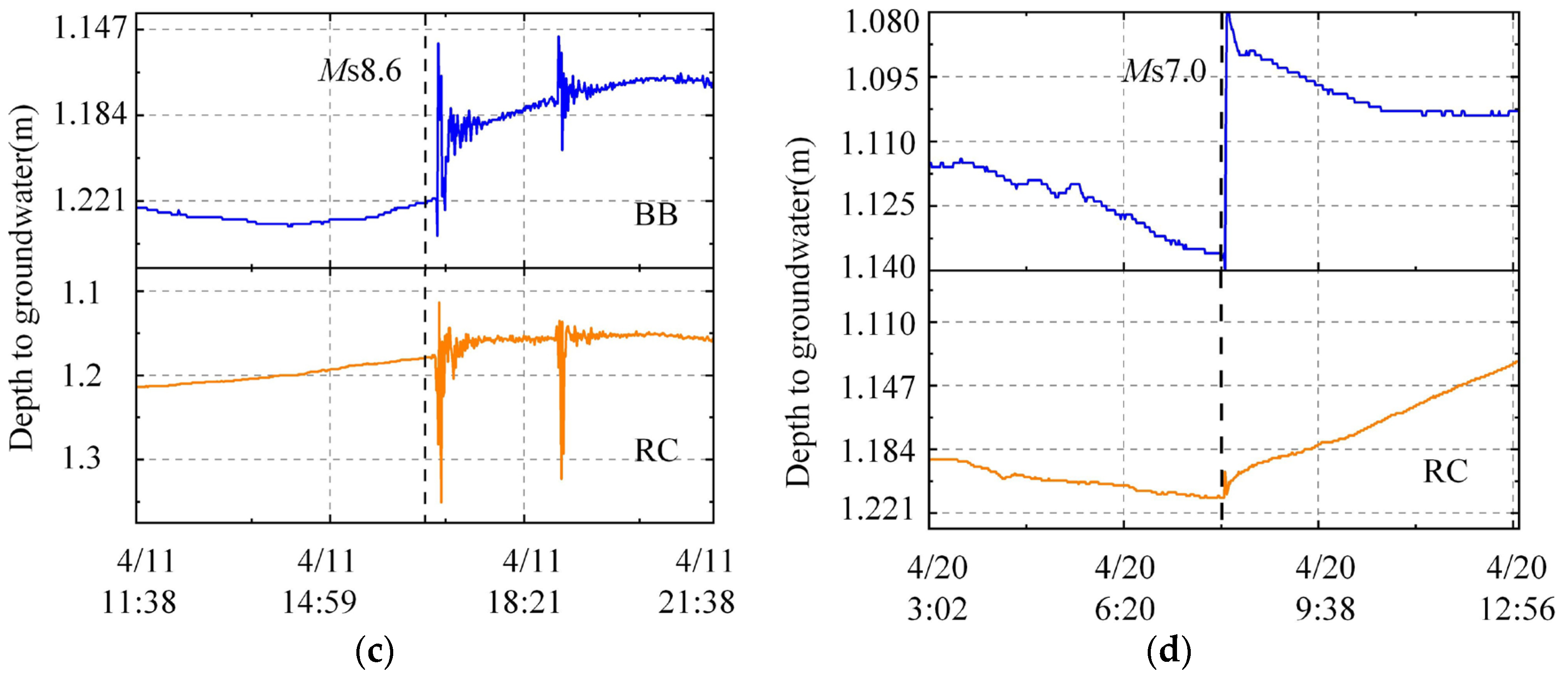
2.2. Response of Well Water Level to Multiple Earthquakes
3. Methods
3.1. Fault Rupture Model
3.2. Numerical Modeling of Pore Pressure Response
4. Results
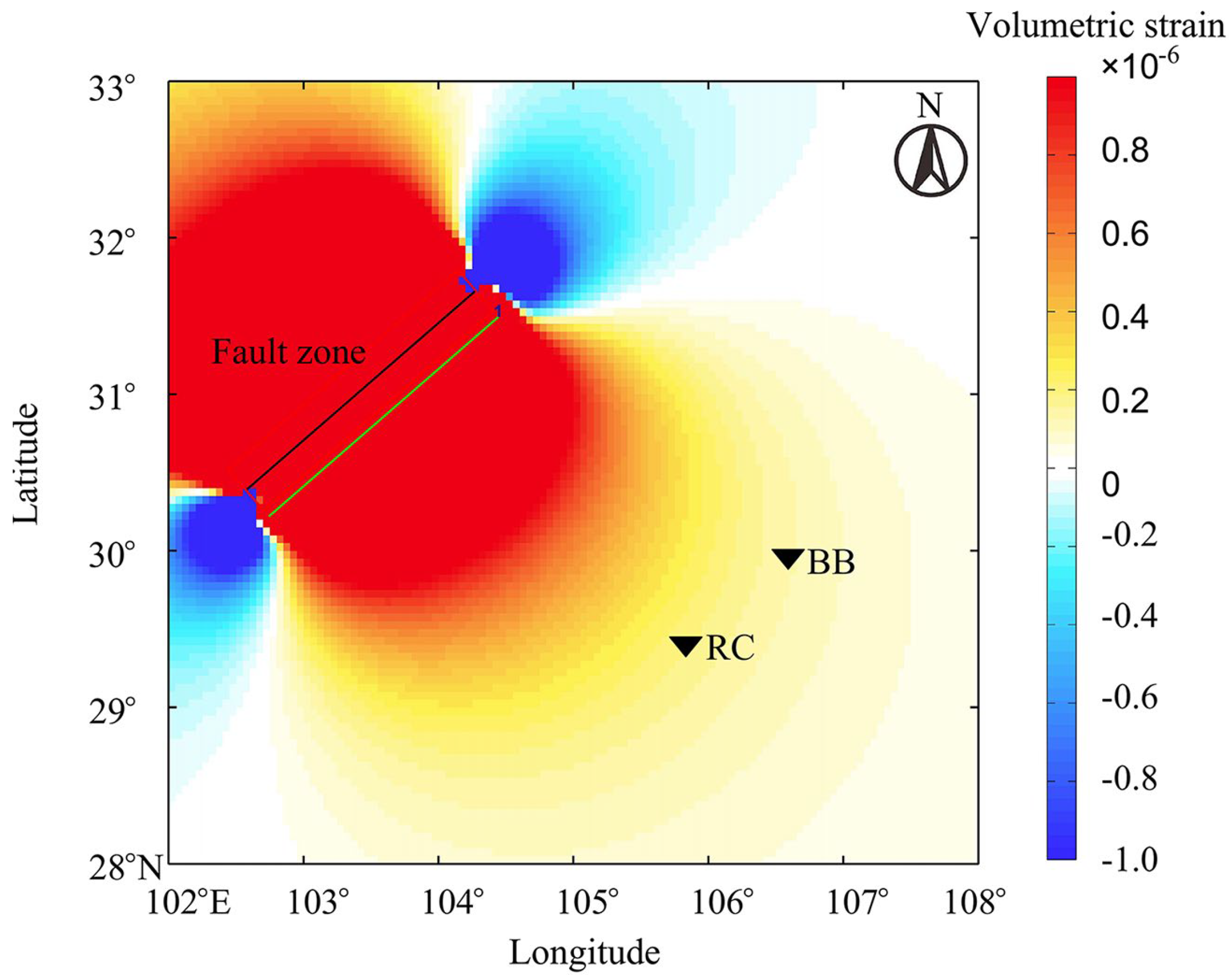
4.1. Seismic Stress–Strain Field
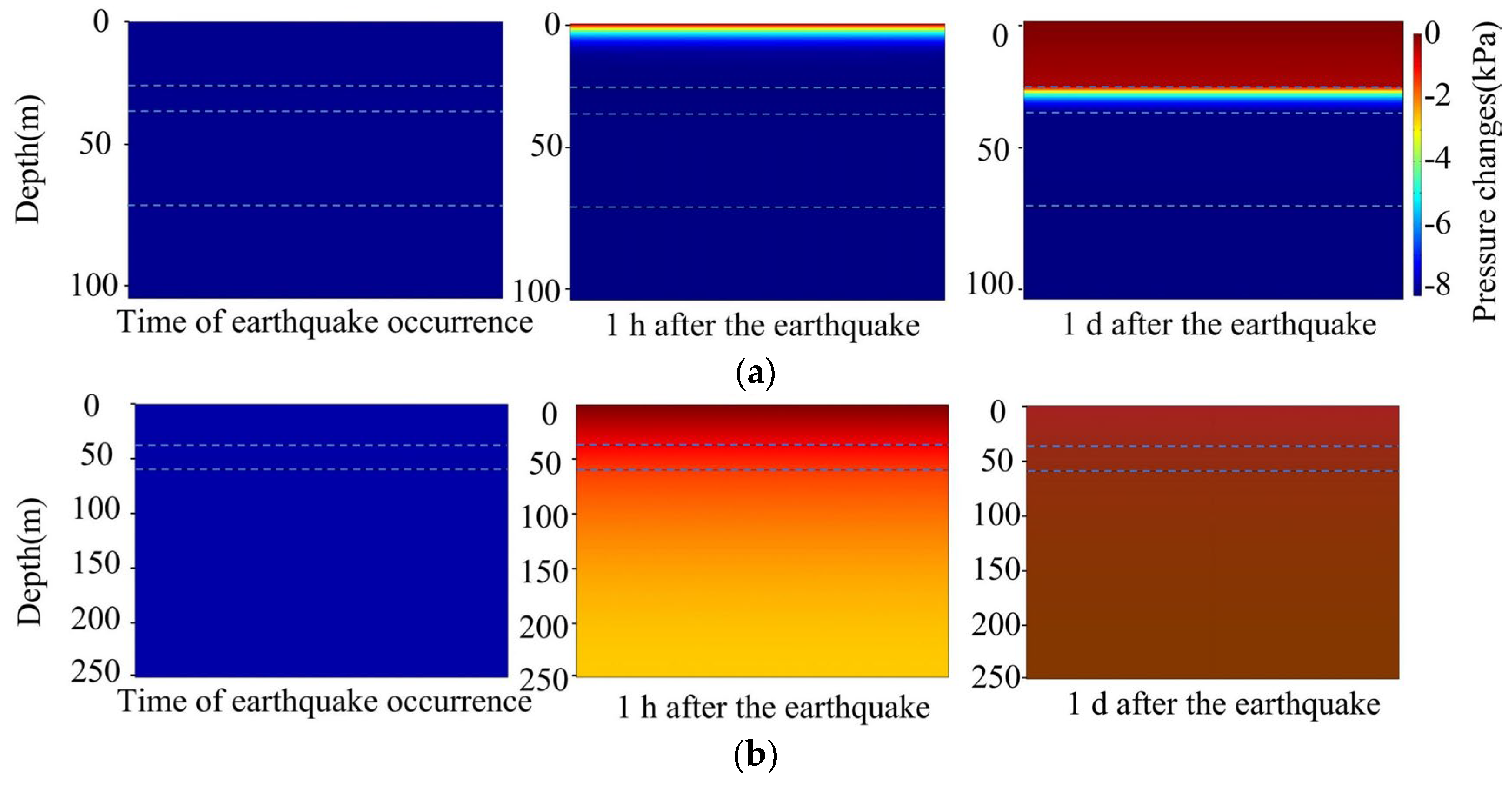
4.2. Results of Numerical Simulation
5. Discussion
5.1. Comparison Between the Simulated and Measured Values
5.2. Determination of Aquifer Confinement
5.3. The Impact of Confinement on the Continuous Change in Well Water Level
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bower, D.R.; Heaton, K.C. Response of an Aquifer near Ottawa to Tidal Forcing and the Alaskan Earthquake of 1964. Can. J. Earth Sci. 1978, 15, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Gaudio, E.; Stevenazzi, S.; Onorati, G.; Ducci, D. Changes in Geochemical and Isotopic Contents in Groundwater before Seismic Events in Ischia Island (Italy). Chemosphere 2024, 349, 140935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, S.; Chi, B.; Jiang, J. Comparison of Groundwater-Level Response to Near Earthquake and Distant Earthquake:Taking Wenchuan Earthquake and Sumatra Earthquake for Example. J. Jilin Univ. (Earth Sci. Ed.) 2011, 41, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Manga, M. Hydrologic Responses to Earthquakes and a General Metric. Geofluids 2010, 10, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Wang, C.-H.; Kuo, C.-H. Temporal Change in Groundwater Level Following the 1999 (M w = 7.5) Chi-Chi Earthquake, Taiwan. Geofluids 2004, 4, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Liao, X.; Li, G.; Chen, M. Dynamic characteristics of water level tides of four wells in the Huayingshan area. Technol. Earthq. Disaster Prev. 2016, 11, 600–610. [Google Scholar]
- Brace, W.F.; Paulding, B.W.; Scholz, C. Dilatancy in the Fracture of Crystalline Rocks. J. Geophys. Res. 1966, 71, 3939–3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakita, H. Water Wells as Possible Indicators of Tectonic Strain. Science 1975, 189, 553–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jónsson, S.; Segall, P.; Pedersen, R.; Björnsson, G. Post-Earthquake Ground Movements Correlated to Pore-Pressure Transients. Nature 2003, 424, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodsky, E.E.; Prejean, S.G. New Constraints on Mechanisms of Remotely Triggered Seismicity at Long Valley Caldera. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, 2004JB003211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkhoury, J.E.; Niemeijer, A.; Brodsky, E.E.; Marone, C. Laboratory Observations of Permeability Enhancement by Fluid Pressure Oscillation of in Situ Fractured Rock. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, B02311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Xiang, Y.; Shi, Z.; Wang, B. Preseismic Changes of Water Temperature in the Yushu Well, Western China. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2018, 175, 2445–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chia, Y. Mechanism of Water Level Changes during Earthquakes: Near Field versus Intermediate Field. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, 2008GL034227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Wang, C.; Liu, C. Disruption of Groundwater Systems by Earthquakes. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 9758–9763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturtevant, B.; Kanamori, H.; Brodsky, E.E. Seismic Triggering by Rectified Diffusion in Geothermal Systems. J. Geophys. Res. 1996, 101, 25269–25282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Shi, Z.; Wang, G.; Sun, X.; Yan, R.; Liu, C. Large Earthquake Reshapes the Groundwater Flow System: Insight from the Water-Level Response to Earth Tides and Atmospheric Pressure in a Deep Well. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 4207–4219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Manga, M. New Streams and Springs after the 2014 Mw6.0 South Napa Earthquake. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faoro, I.; Elsworth, D.; Marone, C. Permeability Evolution during Dynamic Stressing of Dual Permeability Media. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, 2011JB008635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Woith, H.; Wang, R. Groundwater Level Changes Induced by the 2011 Tohoku Earthquake in China Mainland. Geophys. J. Int. 2014, 199, 533–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itaba, S.; Koizumi, N.; Toyoshima, T.; Kaneko, M.; Sekiya, K.; Ozawa, K. Groundwater Changes Associated with the 2004 Niigata-Chuetsu and 2007 Chuetsu-Oki Earthquakes. Earth Planets Space 2008, 60, 1161–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Wang, G.; Liu, C. Co-Seismic Groundwater Level Changes Induced by the May 12, 2008 Wenchuan Earthquake in the Near Field. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2013, 170, 1773–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, Y. Changes of Groundwater Level Due to the 1999 Chi-Chi Earthquake in the Choshui River Alluvial Fan in Taiwan. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2004, 91, 1062–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nespoli, M.; Todesco, M.; Serpelloni, E.; Belardinelli, M.E.; Bonafede, M.; Marcaccio, M.; Rinaldi, A.P.; Anderlini, L.; Gualandi, A. Modeling Earthquake Effects on Groundwater Levels: Evidences from the 2012 Emilia Earthquake (Italy). Geofluids 2016, 16, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojstaczer, S. Determination of Fluid Flow Properties from the Response of Water Levels in Wells to Atmospheric Loading. Water Resour. Res. 1988, 24, 1927–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-Y. Liquefaction beyond the Near Field. Seismol. Res. Lett. 2007, 78, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, K.C.; Cox, S.C.; Townend, J.; Rutter, H.; Hamling, I.J.; Holden, C. Seismological and Hydrogeological Controls on New Zealand-Wide Groundwater Level Changes Induced by the 2016 M w 7.8 Kaikōura Earthquake. Geofluids 2019, 2019, 9809458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, D.R.; Manga, M. Streamflow and Water Well Responses to Earthquakes. Science 2003, 300, 2047–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.-Y.; Chia, Y.; Chuang, P.-Y.; Chiu, Y.-C.; Tseng, T.-L. Impacts of Hydrogeological Characteristics on Groundwater-Level Changes Induced by Earthquakes. Hydrogeol. J. 2018, 26, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, K.C.; Arnold, R.; Holden, C.; Townend, J.; Cox, S.C. A Probabilistic Model of Aquifer Susceptibility to Earthquake-Induced Groundwater-Level Changes. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2020, 110, 1046–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Wang, G.; Ma, Y.; Shi, Z.; Song, J. Local Groundwater and Tidal Changes Induced by Large Earthquakes in the Taiyuan Basin, North China from Well Monitoring. J. Hydrol. 2020, 582, 124479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Wang, G.; Shi, Z. Sustained Changes in Well Water Levels Following a Large Earthquake: Possible Evidence of Permeability Decreases in a Shallow Groundwater System. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2020GL090232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Gil, A.; Jimenez, J.; Gasco Cavero, S.; Marazuela, M.Á.; Baquedano, C.; Martínez-León, J.; Cruz-Pérez, N.; Laspidou, C.; Santamarta, J.C. Effects of the 2021 La Palma Volcanic Eruption on Groundwater Resources (Part II): Hydrochemical Impacts. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2023, 23, 100992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, G.B. Numerical Models of Fluid-Pressure Changes Resulting from the 1999 Chi-Chi Earthquake, Taiwan. Hydrogeology 2005, 543–551. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Gu, H.; Liu, Q.; Wei, H.; Xu, Y.; Sauter, M. Seismically-Induced Groundwater Flow into Confining Clays: An Experimental and Numerical Study. J. Hydrol. 2024, 640, 131716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeloffs, E.A. Hydrologic Precursors to Earthquakes: A Review. Pure Appl. Geophys. 1988, 126, 177–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhao, L.; Li, J.; Yao, Z. Rupture process of the Ms8.0 Wenchuan earthquake of Sichuan. Chin. J. Geophys. 2008, 51, 1403–1410. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Deng, Z.; Yang, X.; Tao, J. Comparison and Analysis of Well Water-Level Variations Caused by Lusan Ms7.0 Earthquake In 2013 and Wenchuan Ms8.0 Earthquake in 2008. Seismol. Geol. 2014, 36, 380–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Li, G.; Li, C.; He, M.; Gao, J. Research on hydrogeological and hydrochemical environmental characteristics of Rongchang well. Seismol. Geomagn. Obs. Res. 2021, 42, 212–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, K.K.; Gupta, H.V.; Wagener, T. A Process-based Diagnostic Approach to Model Evaluation: Application to the NWS Distributed Hydrologic Model. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, 2007WR006716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alakbar, T.; Burgan, H.I. Regional Power Duration Curve Model for Ungauged Intermittent River Basins. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2024, 15, 4596–4612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Gitau, M.W.; Pai, N.; Daggupati, P. Hydrologic and Water Quality Models: Performance Measures and Evaluation Criteria. Trans. ASABE 2015, 58, 1763–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Shi, Z.; Wang, G.; Yan, X.; Liu, C.; Sun, X.; Ma, Y.; Wen, D. Different Sensitivities of Earthquake-Induced Water Level and Hydrogeological Property Variations in Two Aquifer Systems. Water Resour. Res. 2021, 57, e2020WR028217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnadge, C.; Crosbie, R.; Barron, O. Comparing Methods of Barometric Efficiency Characterization for Specific Storage Estimation. Groundwater 2019, 57, 844–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahi, K.A.; Halihan, T. Identifying Aquifer Type in Fractured Rock Aquifers Using Harmonic Analysis. Groundwater 2013, 51, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bredehoeft, J.D. Response of Well-Aquifer Systems to Earth Tides. J. Geophys. Res. 1967, 72, 3075–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weeks, E.P. Barometric Fluctuations in Wells Tapping Deep Unconfined Aquifers. Water Resour. Res. 1979, 15, 1167–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Gao, X.; Yang, X.; Liang, H.; Xiang, Y.; Li, G. Precursory anomaly characteristics research of water radon based on M ≥ 5.0 earthquake case in China. Inland Earthq. 2016, 30, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Earthquake | Date | Time | Latitude (°N) | Longitude (°E) | Depth (km) | Magnitude (Ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wenchuan | 12 May 2008 | 14:28 | 103.4 | 30.9 | 33 | 8.0 |
| Lushan | 13 April 2013 | 08:02 | 103.0 | 30.3 | 13 | 7.0 |
| Tohoku | 11 March 2011 | 13:46 | 42.6 | 38.1 | 20 | 9.0 |
| Sumatra | 11 April 2012 | 16:38 | 93.1 | 2.3 | 20 | 8.6 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Longitude range (°E) | 102–108 |
| Latitude range (°N) | 28.0–33.0 |
| Warp and weft mesh division accuracy (°) | 0.05 |
| Surface wave magnitude | 8.0 |
| Fault zone length (km) | 216 |
| Fault zone width (km) | 45 |
| Fault zone depth (km) | 15.4 |
| Move towards (°) | 229 |
| Dip angle (°) | 32 |
| Mean slip angle (°) | 100 |
| Poisson’s ratio | 0.25 |
| BB | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Layer | Lithology | Depth (m) | Density (kg/m3) | Hydraulic Conductivity (m/s) | Porosity | Poisson’s Ratio | Young’s Modulus (Pa) |
| I | Mud | 0–30 | 1700 | 1.0 × 10−6 | 0.35 | 0.35 | 5 × 106 |
| II | Crystal filling | 30–40 | 2200 | 3.0 × 10−7 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 5 × 108 |
| III | Sand | 40–71 | 2000 | 3.0 × 10−6 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 5 × 107 |
| IV | sandy mudstone | 70–105.6 | 1850 | 2.0 × 10−6 | 0.32 | 0.30 | 3 × 107 |
| RC | |||||||
| Layer | Lithology | Depth (m) | Density (kg/m3) | Hydraulic conductivity (m/s) | Porosity | Poisson’s ratio | Young’s modulus (Pa) |
| I | Shale | 0–37 | 1800 | 1.0 × 10−6 | 0.35 | 0.35 | 6 × 106 |
| II | Sand | 37–60 | 2000 | 2.5 × 10−6 | 0.32 | 0.3 | 3 × 107 |
| III | Sand | 60–251 | 2000 | 3.0 × 10−6 | 0.30 | 0.3 | 5 × 107 |
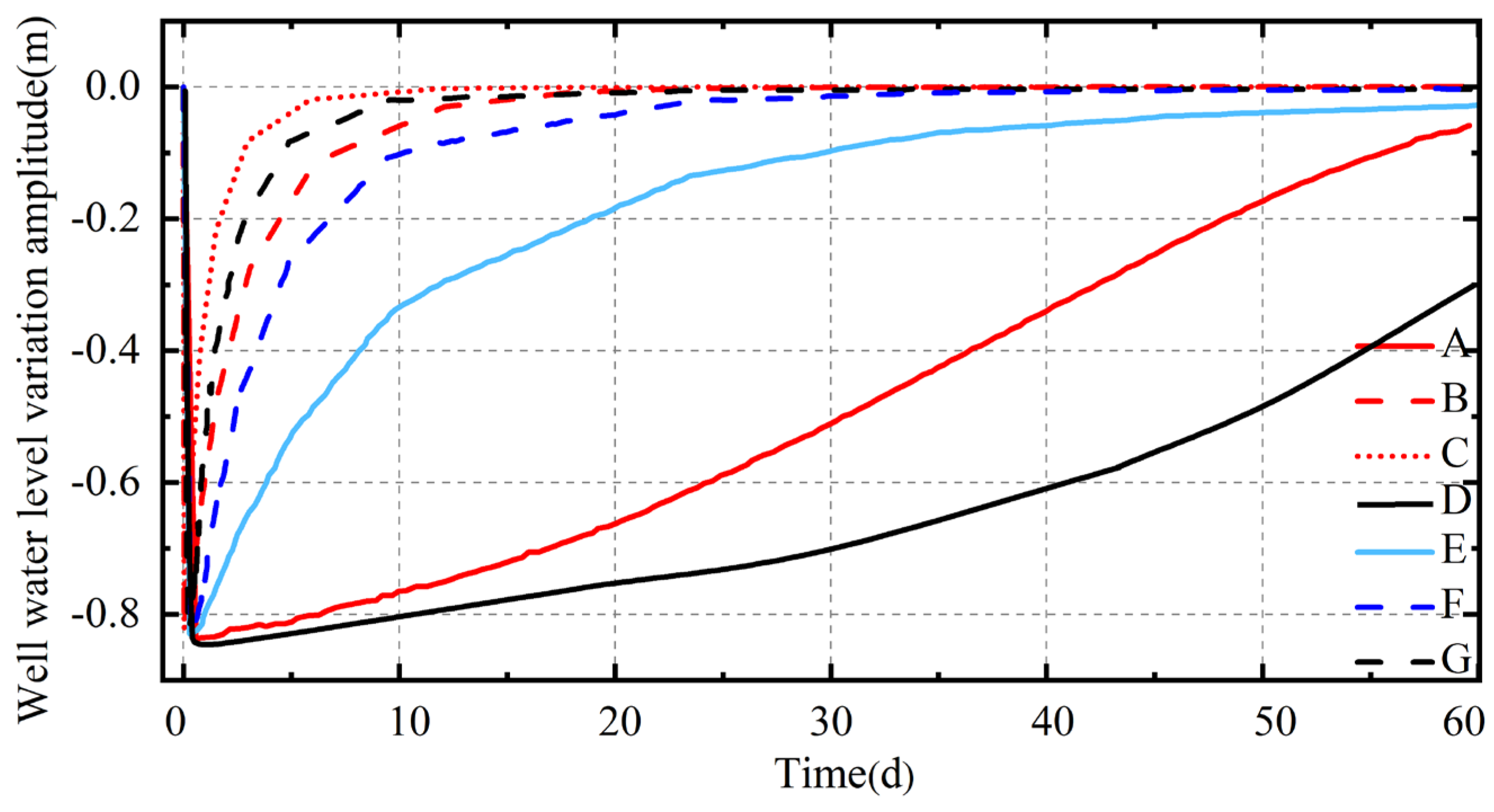
| Scenario | Hydraulic Conductivity (m/s) | Thickness (m) |
|---|---|---|
| Case A | 3.0 × 10−7 | 10 |
| Case B | 3.0 × 10−6 | 10 |
| Case C | 3.0 × 10−5 | 10 |
| Case D | 3.0 × 10−7 | 20 |
| Case E | 3.0 × 10−7 | 5 |
| Case F | 3.0 × 10−6 | 20 |
| Case G | 3.0 × 10−6 | 5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lan, S.; Mao, Z.; Chen, D.; Gu, H. Exploring Similarities and Differences in Water Level Response to Earthquakes in Two Neighboring Wells Using Numerical Simulation. Water 2024, 16, 3484. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16233484
Lan S, Mao Z, Chen D, Gu H. Exploring Similarities and Differences in Water Level Response to Earthquakes in Two Neighboring Wells Using Numerical Simulation. Water. 2024; 16(23):3484. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16233484
Chicago/Turabian StyleLan, Shuangshuang, Zhengtan Mao, Daian Chen, and Hongbiao Gu. 2024. "Exploring Similarities and Differences in Water Level Response to Earthquakes in Two Neighboring Wells Using Numerical Simulation" Water 16, no. 23: 3484. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16233484
APA StyleLan, S., Mao, Z., Chen, D., & Gu, H. (2024). Exploring Similarities and Differences in Water Level Response to Earthquakes in Two Neighboring Wells Using Numerical Simulation. Water, 16(23), 3484. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16233484






