Identification of the Driving Factors to Algal Biomass in Lake Dianchi: Implications for Eutrophication Control
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Source
2.3. Study Methodology
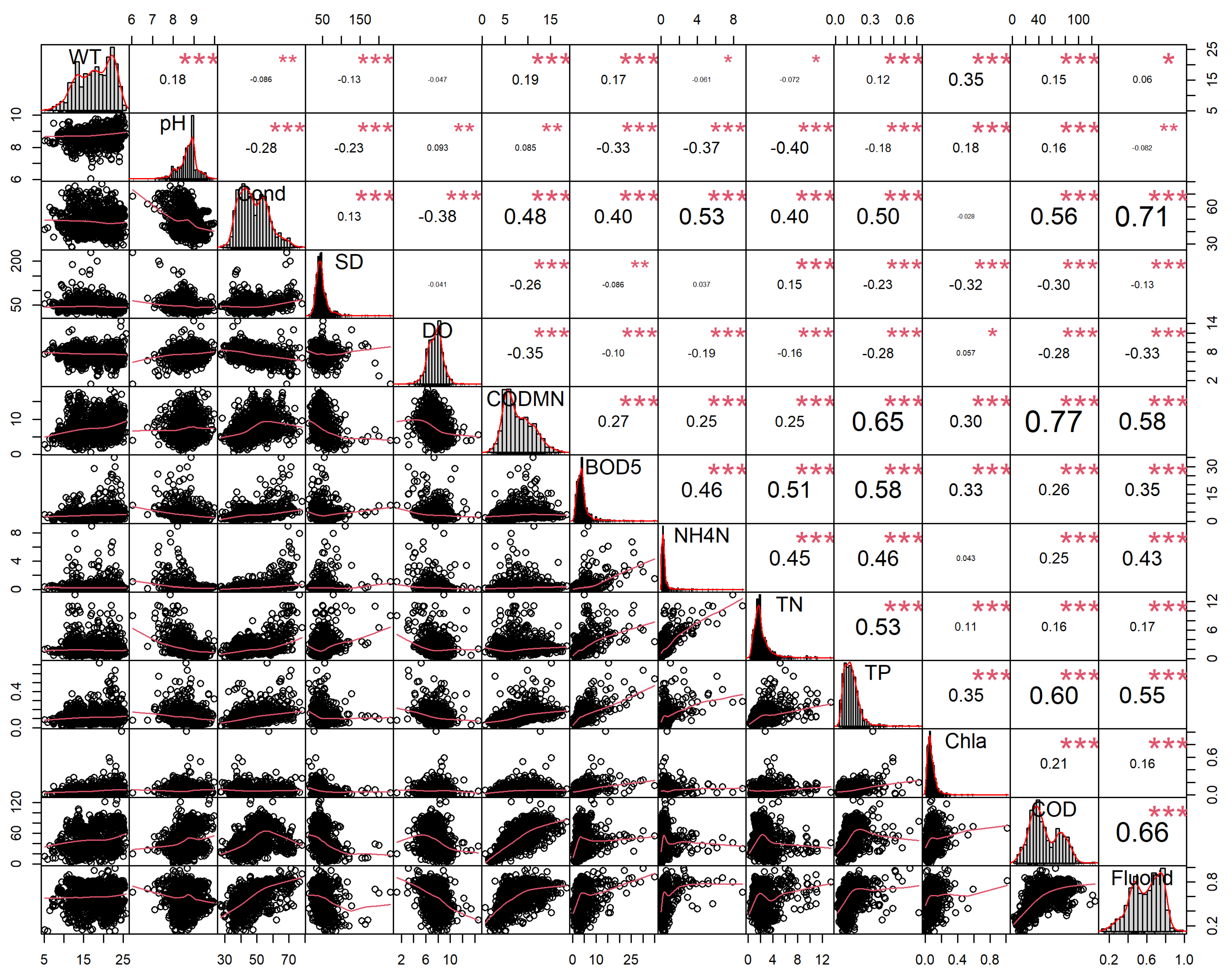
2.3.1. Correlation Analysis
2.3.2. Random Forest Analysis
2.3.3. Generalized Additive Model Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of Lake-Wide Scale
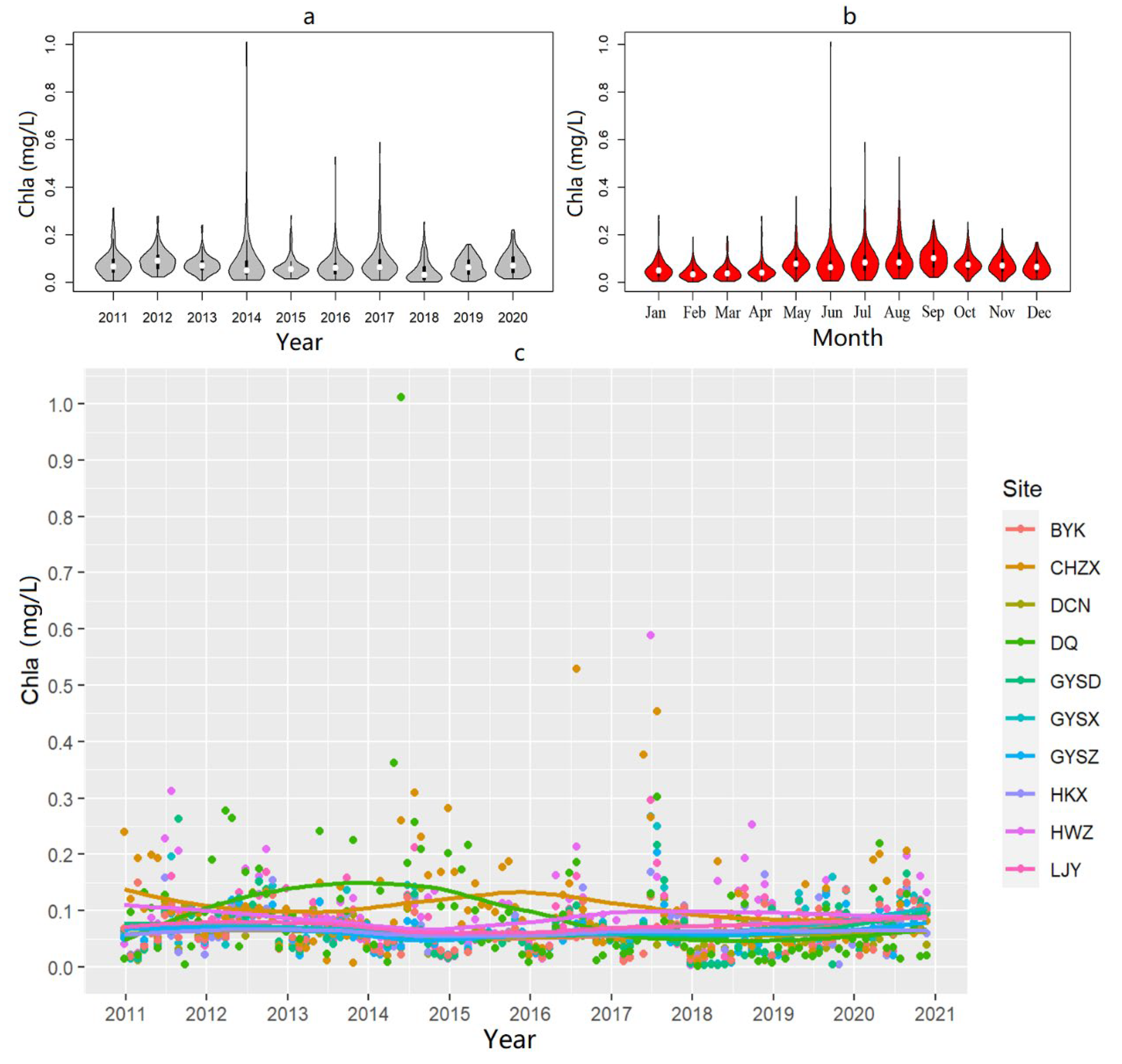
3.1.1. Descriptive Summary
3.1.2. Random Forest Analysis
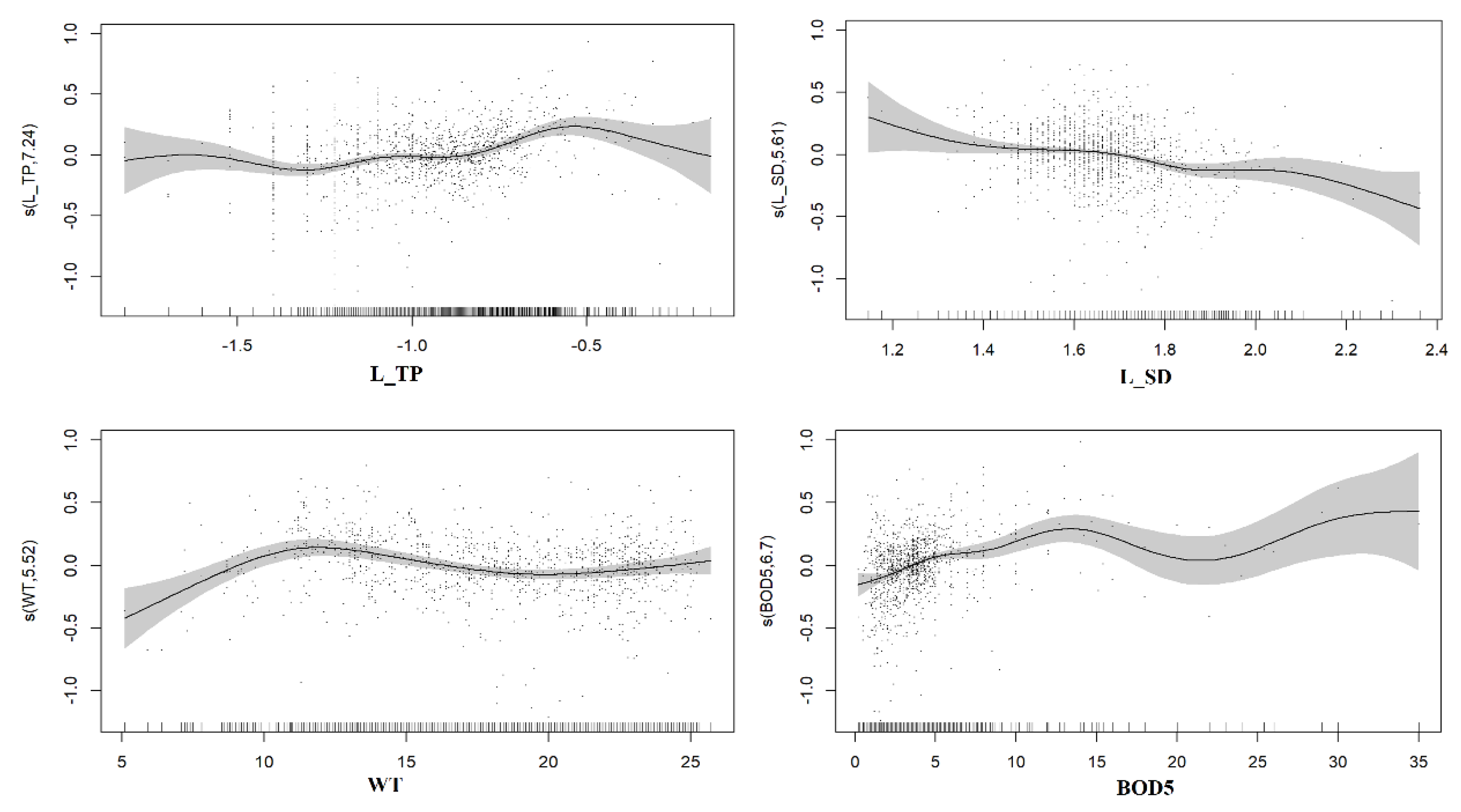
3.1.3. Generalized Additive Model Analysis
3.2. Evaluation of Local Scale
3.2.1. Descriptive Summary
3.2.2. Random Forest Analysis
3.2.3. Generalized Additive Model Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatiotemporal Variation in Algal Biomass in Dianchi Lake
4.2. Key Factors That May Influence the Algal Biomass
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brookes, J.D.; Carey, C.C. Ecology: Resilience to Blooms. Science 2011, 334, 46–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallin, M.A.; Johnson, V.L.; Ensign, S.H.; MacPherson, T.A. Factors Contributing to Hypoxia in Rivers, Lakes, and Streams. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2006, 51, 690–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glibert, P.M. Eutrophication, Harmful Algae and Biodiversity—Challenging Paradigms in a World of Complex Nutrient Changes. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 124, 591–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodds, W.K.; Bouska, W.W.; Eitzmann, J.L.; Pilger, T.J.; Pitts, K.L.; Riley, A.J.; Schloesser, J.T.; Thornbrugh, D.J. Eutrophication of U. S. Freshwaters: Analysis of Potential Economic Damages. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhi, M.; Zhang, Y. Combined Generalized Additive Model and Random Forest to Evaluate the Influence of Environmental Factors on Phytoplankton Biomass in a Large Eutrophic Lake. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 130, 108082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Missaghi, S.; Hondzo, M.; Melching, C. Three-Dimensional Lake Water Quality Modeling: Sensitivity and Uncertainty Analyses. J. Environ. Qual. 2013, 42, 1684–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, Z.; Li, G.; Liu, Y. Regime Shift in Lake Dianchi (China) during the Last 50 Years. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2018, 36, 1075–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zeng, W.H.; Wang, S.R.; Ni, Z.K. Temporal and Spatial Changes of Water Quality and Management Strategies of Dianchi Lake in Southwest China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 1493–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.; Xu, Z.; Wu, X.; Zhao, L.; Zhu, A.; Duan, C.; Chadwick, D.R.; Jones, D.L. Land Use Effects on Soil Phosphorus Behavior Characteristics in the Eutrophic Aquatic-Terrestrial Ecotone of Dianchi Lake, China. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 205, 104793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Yu, Z.; Luo, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, X. Spatial and Temporal Variations in the Relationship between Lake Water Surface Temperatures and Water Quality—A Case Study of Dianchi Lake. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 624, 859–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, W.; Zhang, K.; Xu, P.; Lu, Y. Phosphorus Release from Cyanobacterial Blooms during Their Decline Period in Eutrophic Dianchi Lake, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 13579–13588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Q.; Huang, S.; Wang, Z.; Li, D. Cyanobacterial Organic Matter (COM) Positive Feedback Aggravates Lake Eutrophication by Changing the Phosphorus Release Characteristics of Sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 892, 164540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment. The Planning for Water Pollution Prevention and Control in Key River Basins (2011–2015); Ministry of Ecology and Environment: Beijing, China, 2012; p. 478. [Google Scholar]
- Zuur, A.; Ieno, E.N.; Walker, N.; Saveliev, A.A.; Smith, G.M. Mixed Effects Models and Extensions in Ecology with R; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2009; ISBN 0387874585. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X. Using “Random Forest”for Classification and Regression. Chinese J. Appl. Entomol. 2013, 50, 1190–1197. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X. Preliminary Study on the Historical Geography of Dianchi Lake. Yunan Geogr. Environ. Res. 1999, 11, 7–15. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, B.G.; Carl, P.; Boudt, K.; Bennett, R.; Ulrich, J.; Zivot, E.; Cornilly, D.; Hung, E.; Lestel, M.; Balkissoon, K. Package ‘Performanceanalytics’. R Team Coop. 2018, 3, 13–14. [Google Scholar]
- Biau, G.; Scornet, E. A Random Forest Guided Tour. Test 2016, 25, 197–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Sun, M.; Li, X. Comparison of Models for Predicting the Changes in Phytoplankton Community Composition in the Receiving Water System of an Inter-Basin Water Transfer Project. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaw, A.; Wiener, M. Classification and Regression by RandomForest. R J. 2002, 2, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, S.N. Generalized Additive Models: An Introduction with R; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017; ISBN 1498728340. [Google Scholar]
- Zuur, A.F.; Ieno, E.N.; Elphick, C.S. A Protocol for Data Exploration to Avoid Common Statistical Problems. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2010, 1, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, Z. Extended Bayesian Information Criteria for Model Selection with Large Model Spaces. Biometrika 2008, 95, 759–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X. The Identification of Nutrient Limitations on Eutrophication in Dianchi Lake, China. Water Environ. J. 2017, 31, 592–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Duan, C.; Shen, X.; Yang, L. Environmental Degradation and Loss of Species Diversity in Dianchi Lake. Mar. Fish. 2006, 28, 71–78. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Shi, L.Q.; Mi, J.; Pan, X.J. Distribution and Fractions of Phosphorus and Nitrogen in Surface Sediments from Dianchi Lake, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2012, 6, 195–208. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Paerl, H.W.; Qin, B.; Zhu, G.; Hall, N.S.; Wu, Y. Determining Critical Nutrient Thresholds Needed to Control Harmful Cyanobacterial Blooms in Eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 1051–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, B.; Meng, D.; Zhou, H.; Lu, L.; Deng, W.; Shao, Z.; Qin, Y. Management of Water Quality Targets Based on River-Lake Water Quality Response Relationships for Lake Basins—A Case Study of Dianchi Lake. Environ. Res. 2020, 186, 109479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, Y.; Deng, X.; Shi, Z.; Yang, C. Characteristics of Spatial and Temporal Variation of Water Quality and Nutritional Status in Dianchi Lake. Yangtze River 2022, 53, 61–67. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Jian, Y.; Zhou, F. Decline in Nitrogen Concentrations of Eutrophic Lake Dianchi Associated with Policy Interventions during 2002–2018. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 288, 117826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmikandan, M.; Li, M.; Pan, B. Cyanobacterial Blooms in Environmental Water: Causes and Solutions. Curr. Pollut. Reports 2024, 10, 606–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, N.; Song, L.; Wang, R.; Liu, J. The Spatio-Temperal Distribution of Algal Biomass in Dianchi Lake and Its Impact Factors. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2008, 32, 188. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.H.; Li, C.; Xu, Y.P.; Li, S.Y.; Du, J.S.; Han, Y.P.; Hu, H.Y. Identifying Major Contributors to Algal Blooms in Lake Dianchi by Analyzing River-Lake Water Quality Correlations in the Watershed. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 315, 128144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X. Analysis of Eutrophication State and Trend for Lakes in China. J. Limnol. 2003, 62, 60–66. [Google Scholar]
- Havens, K.E.; Jin, K.R.; Iricanin, N.; James, R.T. Phosphorus Dynamics at Multiple Time Scales in the Pelagic Zone of a Large Shallow Lake in Florida, USA. Hydrobiologia 2007, 581, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, G.; Song, L.; Liu, J.; Xiao, B.; Liu, Y. Modeling of Cyanobacterial Blooms in Hypereutrophic Lake Dianchi, China. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2004, 19, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, M.; Chu, Q.; Ma, R. MODIS-Satellite-Based Analysis of Long-Term Temporal-Spatial Dynamics and Drivers of Algal. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, J.A. Fluoride Toxicity to Aquatic Organisms: A Review. Chemosphere 2003, 50, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieves, V.; Willis, J.K.; Patzert, W.C. Recent Hiatus Caused by Decadal Shift in Indo-Pacific Heating. Science 2015, 349, 532–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, J.C. Physiological Processes, Nutrient Availability, and the Concept of Relative Growth Rate in Marine Phytoplankton Ecology. In Primary Productivity in the Sea; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1980; pp. 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Wang, S.; Ni, Z.; Guo, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, G.; Li, H. No-Linear Dynamics of Lake Ecosystem in Responding to Changes of Nutrient Regimes and Climate Factors: Case Study on Dianchi and Erhai Lakes, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 781, 146761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeder, B.C. Primary Productivity Limitations in Relatively Low Alkalinity, High Phosphorus, Oligotrophic Kentucky Reservoirs. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 108, 477–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Chekroun, K.; Sánchez, E.; Baghour, M. The Role of Algae in Bioremediation of Organic Pollutants. Int. Res. J. Public Environ. Health 2014, 1, 19–32. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, W.; Yang, F.; Li, Y.; Wang, S. New Insights into the Source of Decadal Increase in Chemical Oxygen Demand Associated with Dissolved Organic Carbon in Dianchi Lake. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 603–604, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wang, X.; Yang, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Xu, L. Satellite Data Regarding the Eutrophication Response to Human Activities in the Plateau Lake Dianchi in China from 1974 to 2009. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 485–486, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; Yang, Y.; Xu, X.; Zheng, B.; Deng, W.; Shao, Z.; Lu, L.; Wang, L.; et al. A Study on the Relationship between Metabolism of Cyanobacteria and Chemical Oxygen Demand in Dianchi Lake, China. Water Environ. Res. 2019, 91, 1650–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Variables | Min | Median | Mean | Max | sd |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chla (mg/L) | 0.002 | 0.061 | 0.074 | 1.012 | 0.061 |
| WT (℃) | 5.1 | 18.5 | 18.1 | 25.7 | 4.4 |
| pH | 6.04 | 8.78 | 8.71 | 9.98 | 0.45 |
| Cond (ms/m) | 27.30 | 46.70 | 47.96 | 78.3 | 9.24 |
| SD (cm) | 14.0 | 45.0 | 47.9 | 230.0 | 17.5 |
| DO (mg/L) | 1.26 | 7.64 | 7.56 | 14.60 | 1.27 |
| CODMn (mg/L) | 0.60 | 7.00 | 7.73 | 18.50 | 3.23 |
| BOD5 (mg/L) | 0.20 | 3.45 | 3.99 | 35.00 | 3.15 |
| NH3N (mg/L) | 0.015 | 0.24 | 0.39 | 8.99 | 0.67 |
| TN (mg/L) | 0.20 | 1.82 | 2.22 | 13.40 | 1.54 |
| TP (mg/L) | 0.015 | 0.113 | 0.125 | 0.718 | 0.073 |
| COD (mg/L) | 2.00 | 42.00 | 47.83 | 125.00 | 22.37 |
| Fluoride (mg/L) | 0.12 | 0.61 | 0.59 | 0.99 | 0.16 |
| Explained Variables | Explanatory Variables | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (X) | edf | Deviance Explained | R2 (adj) | |
| L_ChlaT | L_TP | 7.24 *** | 51.60% | 0.49 |
| L_SD | 5.61 *** | |||
| WT | 5.52 *** | |||
| BOD5 | 6.70 *** | |||
| ChlaDCN | TP | 1.55 *** | 50.10% | 0.39 |
| ChlaHKX | Cond | 1.00 * | 70.60% | 0.58 |
| L_SD | 1.00 * | |||
| L_DO | 2.86 ** | |||
| L_NH3N | 8.08 *** | |||
| TN | 1.00 ** | |||
| L_TP | 2.77 ** | |||
| ChlaBYK | L_TN | 3.08 . | 53.70% | 0.42 |
| TP | 1.00 ** | |||
| ChlaGYSX | Cond | 1.00 ** | 78.60% | 0.72 |
| SD | 1.00 * | |||
| L_NH3N | 3.65 *** | |||
| L_Fluoride | 2.23 ** | |||
| L_ChlaGYSZ | L_TP | 5.64 * | 69.40% | 0.61 |
| L_ChlaGYSD | L_BOD5 | 7.54 * | 71.60% | 0.63 |
| L_ChlaLJY | L_TP | 2.38 *** | 58.10% | 0.48 |
| L_ChlaHWZ | L_TP | 2.65 *** | 65.20% | 0.54 |
| Fluoride | 5.47 ** | |||
| L_ChlaCHZX | L_WT | 3.52 * | 72.50% | 0.61 |
| L_SD | 2.10 ** | |||
| L_TN | 2.16 . | |||
| L_TP | 1.00 * | |||
| L_COD | 6.04 . | |||
| L_ChlaDQ | L_WT | 4.02 *** | 73.10% | 0.64 |
| L_pH | 1.07 * | |||
| L_SD | 2.10 *** | |||
| L_CODMn | 1.00 * | |||
| L_BOD5 | 2.15 ** | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, N.; Hu, S.; Duan, Y. Identification of the Driving Factors to Algal Biomass in Lake Dianchi: Implications for Eutrophication Control. Water 2024, 16, 3485. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16233485
Huang J, Zhang J, Wang N, Hu S, Duan Y. Identification of the Driving Factors to Algal Biomass in Lake Dianchi: Implications for Eutrophication Control. Water. 2024; 16(23):3485. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16233485
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Jie, Jing Zhang, Nenghan Wang, Sheng Hu, and Youai Duan. 2024. "Identification of the Driving Factors to Algal Biomass in Lake Dianchi: Implications for Eutrophication Control" Water 16, no. 23: 3485. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16233485
APA StyleHuang, J., Zhang, J., Wang, N., Hu, S., & Duan, Y. (2024). Identification of the Driving Factors to Algal Biomass in Lake Dianchi: Implications for Eutrophication Control. Water, 16(23), 3485. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16233485






