Monitoring and Studying the Behavior of Metals in an Industrial Wastewater Treatment Plant in Italy
Abstract
1. Introduction
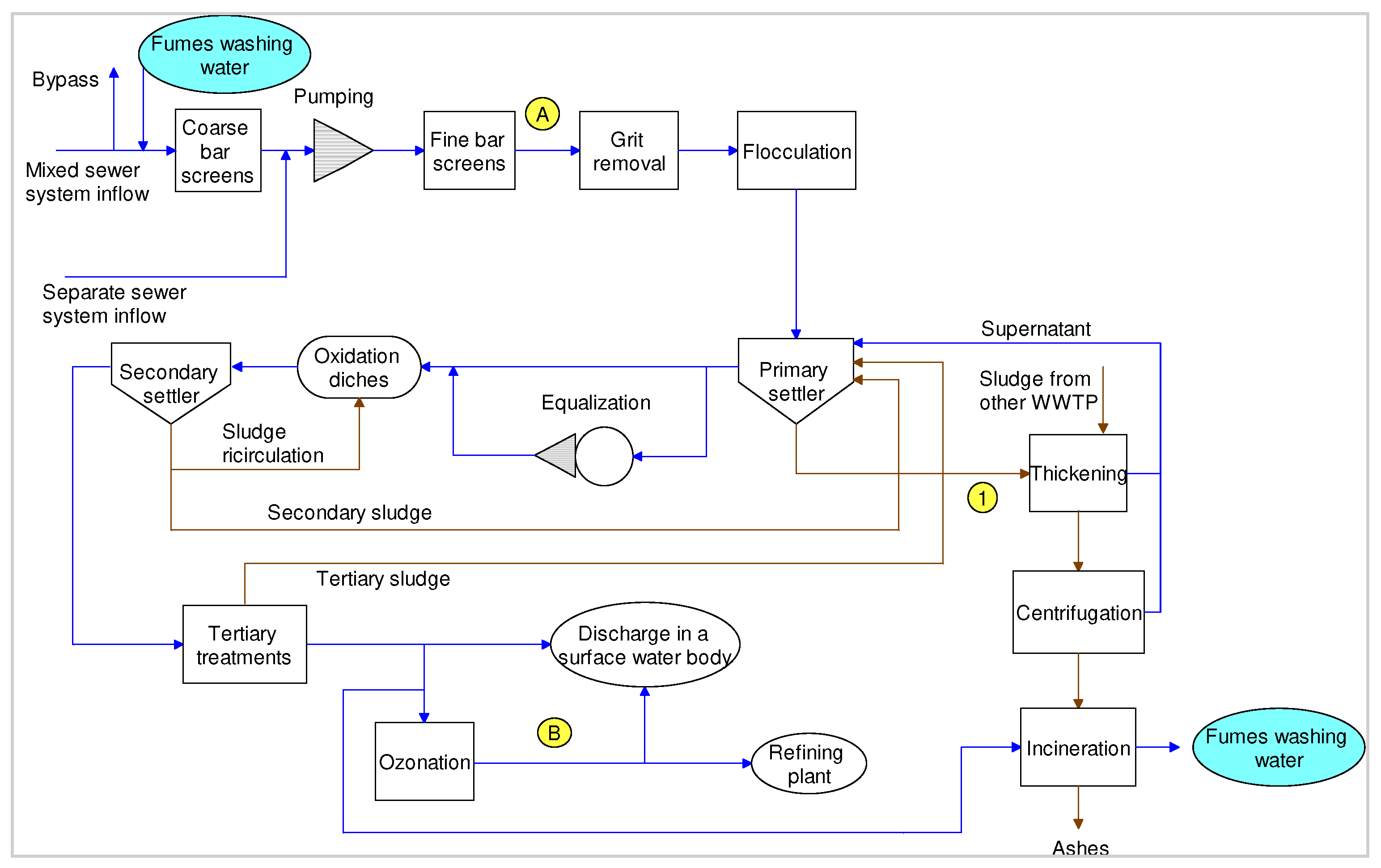
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Sample Analysis
2.3. Material Flow Analysis
- Ci = mean concentration of metal in the influent, [mg/L]
- Ce = mean concentration of metal in the effluent, [mg/L]
- Qi = influent flow rate, [m3/d]
- Qe = effluent flow rate, [m3/d]
- Mi = metal load in the influent, [g/d]
- Me = metal load in the effluent, [g/d]
- Qsludge I = mixed sludge flow rate, [m3/d]
- Csludge I = mixed sludge metal concentration, [mg/L]
2.4. Statistical Analysis of Quality Data
3. Results
3.1. Extensive Monitoring Campaign
3.2. Intensive Monitoring Campaign
3.3. Speciation of Metals
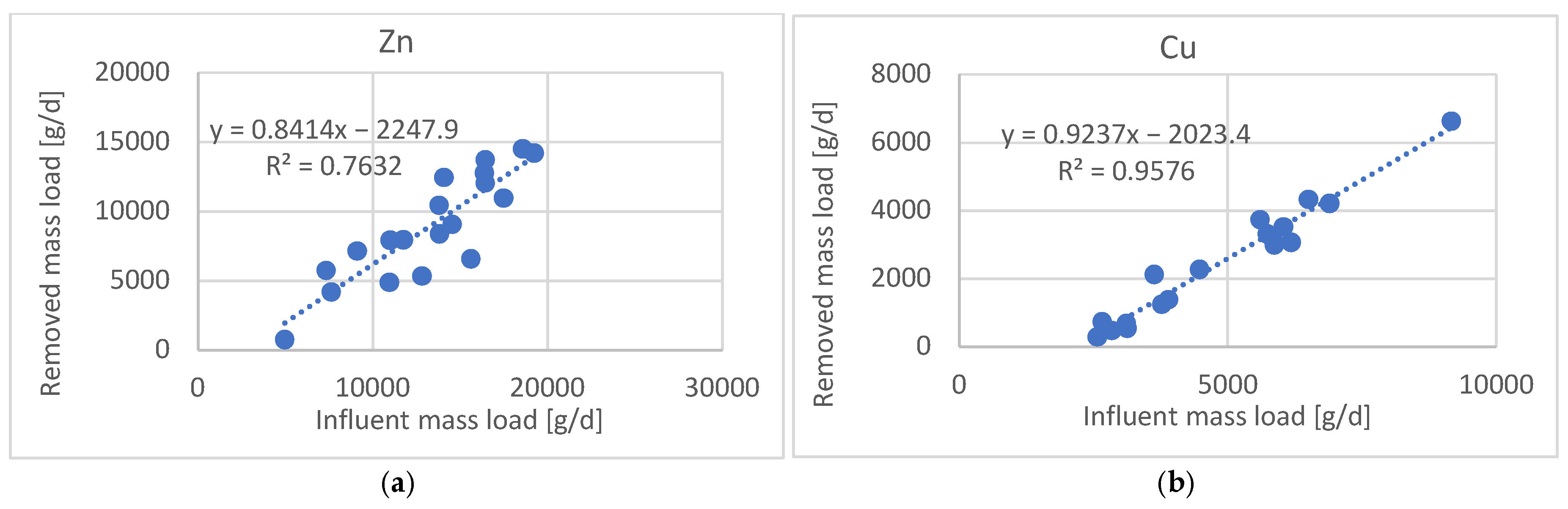
3.4. Removal Mechanisms and Correlation Analysis
3.5. Statistical Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Extensive Monitoring Campaign
4.2. Intensive Monitoring Campaign
4.3. Speciation of Metals
4.4. Removal Mechanisms and Correlation Analysis
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roth, J.; Zerger, B.; De Geeter, D.; Gómez Benavides, J.; Roudier, S. Best Available Techniques (BAT) Reference Document for the Textiles Industry; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; López-Grimau, V.; Vilaseca, M.; Crespi, M.; Ribera-Pi, J.; Calderer, M.; Martínez-Lladó, X. Reuse of textile wastewater treated by moving bed biofilm reactor coupled with membrane bioreactor. Color. Technol. 2021, 137, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, W.-J.; Ismail, A.F. Polymeric nanofiltration membranes for textile dye wastewater treatment: Preparation, performance evaluation, transport modelling, and fouling control—A review. Desalination 2009, 245, 321–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaseen, D.A.; Scholz, M. Textile dye wastewater characteristics and constituents of synthetic effluents: A critical review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 1193–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, N.; Tahmid, M.; Shoronika, A.Z.; Fariha, A.; Roy, H.; Pervez, M.d.N.; Cai, Y.; Naddeo, V.; Islam, M.S. A Comprehensive Review on the Sustainable Treatment of Textile Wastewater: Zero Liquid Discharge and Resource Recovery Perspectives. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turksoy, R.; Terzioglu, G.; Yalcin, İ.E.; Turksoy, Ö.; Demir, G. Removal of heavy metals from textile industry wastewater. Front. Life Sci. Relat. Technol. 2021, 2, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halimoon, N.; Yin, R.G.S. Removal of Heavy Metals from Textile Wastewater using Zeolite. Environ. Asia 2010, 3, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velusamy, S.; Roy, A.; Sundaram, S.; Kumar Mallick, T. A Review on Heavy Metal Ions and Containing Dyes Removal Through Graphene Oxide-Based Adsorption Strategies for Textile Wastewater Treatment. Chem. Rec. 2021, 21, 1570–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yu, X.; Wang, X.; He, Y.; Zhang, C.; Xue, G.; Liu, Z.; Lao, H.; Song, H.; Chen, W.; et al. Dyeing and finishing wastewater treatment in China: State of the art and perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 326, 129353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokmen, N.; Buyukakinci, B.Y. The usage of boron/boron compounds in the textile industry and its situation in Turkey. CBU Int. Conf. Proc. 2018, 6, 1158–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsacchi, L.; Barberis, V.; Pinelli, P. Circular economy and industrial symbiosis: The role of the municipality of Prato within the EU Urban Agenda partnership. In Proceedings of the 24th International Sustainable Development Research Society Conference (ISDRS 2018), Messina, Italy, 13–15 June 2018; pp. 716–722. [Google Scholar]
- Karvelas, M.; Katsoyiannis, A.; Samara, C. Occurrence and fate of heavy metals in the wastewater treatment process. Chemosphere 2003, 53, 1201–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chipasa, K.B. Accumulation and fate of selected heavy metals in a biological wastewater treatment system. Waste Manag. 2003, 23, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busetti, F.; Badoer, S.; Cuomo, M.; Rubino, B.; Traverse, P. Occurrence and removal of potentially toxic metals and heavy metals in the wastewater treatment plant of Fusina (Venice, Italy). Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 9264–9272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanpiwat, P.; Sthiannopkao, S.; Kim, K.W. Metal content variation in wastewater and biosludge from Bangkok’s central wastewater treatment plants. Microchem. J. 2010, 95, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantinho, P.; Matos, M.; Trancoso, M.A.; Correia dos Santos, M.M. Behaviour and fate of metals in urban wastewater treatment plants: A review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 13, 359–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hammoudani, Y.; Dimane, F.; El Ouarghi, H. Removal efficiency of heavy metals by a biological wastewater treatment plant and their potential risks to human health. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2021, 20, 995–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, H.; Christensen, T.H.; Guildal, T.; Scheutz, C. A comprehensive substance flow analysis of a municipal wastewater and sludge treatment plant. Chemosphere 2015, 138, 874–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo Sanz, M.; Gabet, V.M.; Gonzalez, J.L. Inputs of total and labile dissolved metals from six facilities continuously discharging treated wastewaters to the marine environment of Gran Canaria Island (Canary Islands, Spain). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health. 2021, 18, 1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carletti, G.; Fatone, F.; Bolzonella, D.; Cecchi, F. Occurrence and fate of heavy metals in large wastewater treatment plants treating municipal and industrial wastewaters. Water Sci. Technol. 2008, 57, 1329–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylwan, I.; Thorin, E. Removal of heavy metals during primary treatment of municipal wastewater and possibilities of enhanced removal: A review. Water 2021, 13, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.; Zhang, L.; Ma, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Mao, K.; Wang, N.; Li, Y.; He, J.; Zhang, X.; et al. Occurrence and fate of heavy metals in municipal wastewater in Heilongjiang province, China: A monthly reconnaissance from 2015 to 2017. Water 2020, 12, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuci, F.; Antal, A.; Doumett, S.; Fibbi, D.; Camisa, R.; Bettazzi, E.; Coppini, E.; Daddi, D.; Gori, R. Monitoring and study of specified metals’ behaviour in a large Italian wastewater treatment plant. In Proceedings of the ecoSTP2023-Conference Proceedings, Girona, Spain, 26–29 June 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Muoio, R.; Palli, L.; Ducci, I.; Coppini, E.; Bettazzi, E.; Daddi, D.; Fibbi, D.; Gori, R. Optimization of a large industrial wastewater treatment plant using a modeling approach: A case study. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 249, 109436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- APAT IRSA-CNR: 3000-Metalli e Specie Metalliche. In Metodi Analitici per le Acque; I.G.E.R. SRL: Rome, Italy, 2003; pp. 187–490.
- Zhou, Y.; Lei, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Lu, Y.; Wu, X.; Fang, H. Determining discharge characteristics and limits of heavy metals and metalloids for wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) in China based on statistical methods. Water 2018, 10, 1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agoro, M.A.; Adeniji, A.O.; Adefisoye, M.A.; Okoh, O.O. Heavy metals in wastewater and sewage sludge from selected municipal treatment plants in eastern Cape Province, South Africa. Water 2020, 12, 2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, F.; Stensel, H.D.; Tchobanoglous, G.; Metcalf & Eddy Inc. Statistical analysis of flowrates, constituent concentrations, and mass loadings. In Wastewater Engineering-Treatment and Reuse, 4th ed.; McGraw-Hill: Boston, MA, USA, 2003; pp. 170–178. [Google Scholar]
- Codice dell’Ambiente, Decreto Legislativo No. 152 of 3 April 2006; Gazzetta Ufficiale No. 88 of 14 April 2006, Supplemento ordinario No. 96.
- Oliveira, A.D.S.; Bodo, A.; Beltramini Trevilato, T.M.; Magosso Takayanagui, A.M.; Domingo, J.L.; Segura-Muñoz, S.I. Heavy metals in untreated/treated urban effluent and sludge from a biological wastewater treatment plant. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2007, 14, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulyás, G.; Pitás, V.; Fazekas, B.; Kárpáti, Á. Heavy Metal Balance in a Communal Wastewater treatment Plant. Hungarian J. Ind. Chem. 2015, 43, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbar, B.; Alem, A.; Marcotte, S.; Pantet, A.; Ahfir, N.D.; Bizet, L.; Duriatti, D. Experimental investigation on removal of heavy metals (Cu2+, Pb2+, and Zn2+) from aqueous solution by flax fibres. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2017, 109, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaimee, M.Z.A.; Sarjadi, M.S.; Rahman, M.L. Heavy metals removal from water by efficient adsorbents. Water 2021, 13, 2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Chemical Species | Limit of Detection |
|---|---|
| Antimony (Sb) | 0.02 |
| Total Chromium (Crtot) | 0.01 |
| Copper (Cu) | 0.05 |
| Nickel (Ni) | 0.05 |
| Zinc (Zn) | 0.01 |
| Arsenic (As) | 0.02 |
| Barium (Ba) | 0.1 |
| Boron (B) | 0.01 |
| Cadmium (Cd) | 0.01 |
| Manganese (Mn) | 0.05 |
| Lead (Pb) | 0.05 |
| Selenium (Se) | 0.002 |
| Tin (Sn) | 0.02 |
| Parameter | Value | U.M. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± STD | Maximum | Minimum | ||
| pH | 7.96 ± 0.16 | 8.49 | 7.26 | - |
| TSS | 126 ± 73 | 532 | 10 | [mg/L] |
| COD | 301 ± 134 | 994 | 40 | [mg/L] |
| BOD | 124 ± 42 | 280 | 43 | [mg/L] |
| TN | 36 ± 11 | 69 | 13 | [mg/L] |
| N-NO2− | 0.51 ± 0.38 | 2.17 | 0.05 | [mg/L] |
| N-NO3− | 2.35 ± 1.15 | 7.43 | 0.11 | [mg/L] |
| N-NH4+ | 24 ± 8 | 47 | 5 | [mg/L] |
| TP | 3 ± 0.84 | 6 | 1 | [mg/L] |
| Extensive Monitoring Campaign | Intensive Monitoring Campaign | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D. Lgs. 152/2006 [29] | Cin | Cout | RE | Cin | Cout | RE | |
| [mg/L] | [mg/L] | [mg/L] | [%] | [mg/L] | [mg/L] | [%] | |
| Zn | 0.5 | 0.15 ± 0.03 | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 66 ± 11 | 0.13 ± 0.03 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 76 ± 12 |
| Cu | 0.1 | 0.05 ± 0.02 | <0.05 | 37 ± 20 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | <0.05 | 57 ± 8 |
| Mn | 2.0 | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 31 ± 33 | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 0.06 ± 0.05 | 6 ± 11 |
| Se | 0.03 | 0.007 ± 0.007 | 0.003 ± 0.001 | 52 ± 32 | 0.003 ± 0.003 | 0.002 ± 0.001 | 31 ± 40 |
| Ba | 20 | 0.12 ± 0.01 | <0.1 | 58 ± 3 | 0.14 ± 0.01 | <0.1 | 63 ± 3 |
| B | 2.0 | 0.16 ± 0.08 | 0.14 ± 0.05 | 14 ± 12 | 0.17 ± 0.01 | 0.15 ± 0.01 | 13 ± 6 |
| Crtot | 2.0 | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.01 ± 0.003 | 79 ± 6 | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.01 ± 0.005 | 78 ± 11 |
| Sb | - | 0.35 ± 0.39 | 0.08 ± 0.03 | 68 ± 15 | 0.26 ± 0.09 | 0.10 ± 0.01 | 58 ± 21 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tuci, F.; Antal, A.; Doumett, S.; Fibbi, D.; Camisa, R.; Bettazzi, E.; Coppini, E.; Daddi, D.; Gori, R. Monitoring and Studying the Behavior of Metals in an Industrial Wastewater Treatment Plant in Italy. Water 2024, 16, 3164. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16223164
Tuci F, Antal A, Doumett S, Fibbi D, Camisa R, Bettazzi E, Coppini E, Daddi D, Gori R. Monitoring and Studying the Behavior of Metals in an Industrial Wastewater Treatment Plant in Italy. Water. 2024; 16(22):3164. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16223164
Chicago/Turabian StyleTuci, Francesca, Alexandra Antal, Saer Doumett, Donatella Fibbi, Roberto Camisa, Elena Bettazzi, Ester Coppini, Daniele Daddi, and Riccardo Gori. 2024. "Monitoring and Studying the Behavior of Metals in an Industrial Wastewater Treatment Plant in Italy" Water 16, no. 22: 3164. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16223164
APA StyleTuci, F., Antal, A., Doumett, S., Fibbi, D., Camisa, R., Bettazzi, E., Coppini, E., Daddi, D., & Gori, R. (2024). Monitoring and Studying the Behavior of Metals in an Industrial Wastewater Treatment Plant in Italy. Water, 16(22), 3164. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16223164









