Machine Learning Based Inversion of Water Quality Parameters in Typical Reach of Rural Wetland by Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Images
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
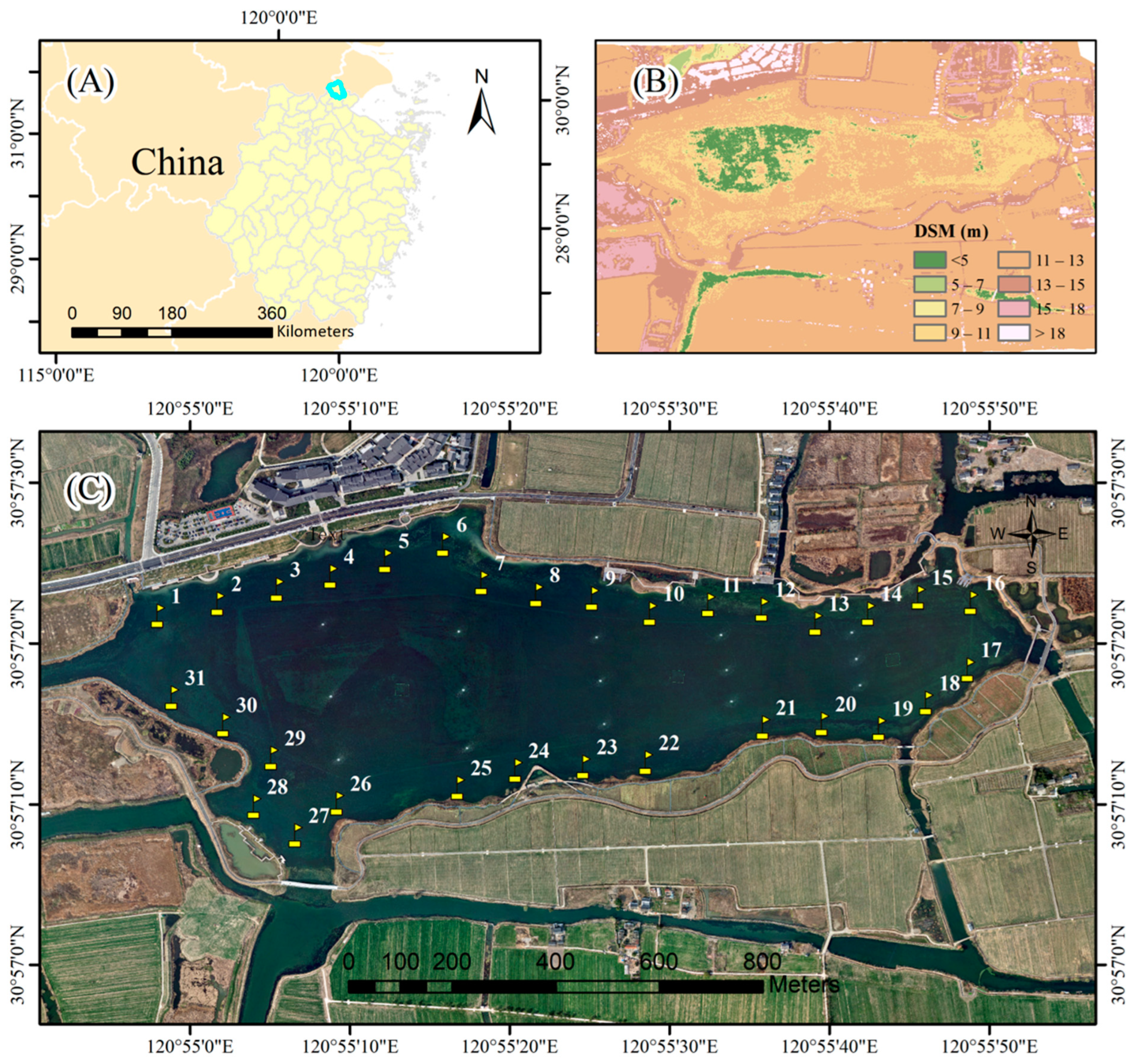
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
2.2.1. In Situ Water Quality Parameters Data Collection
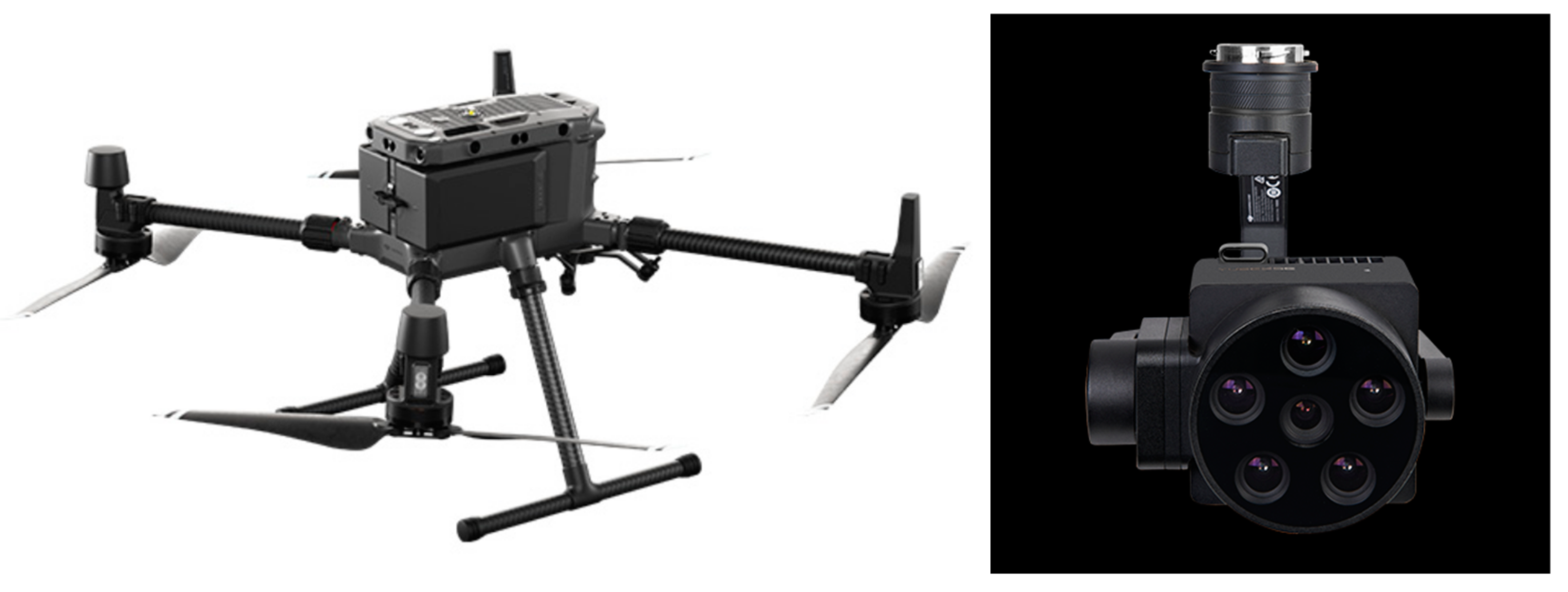
2.2.2. Drone Aerial Imagery Data Collection
2.3. Water Quality Parameters Estimation
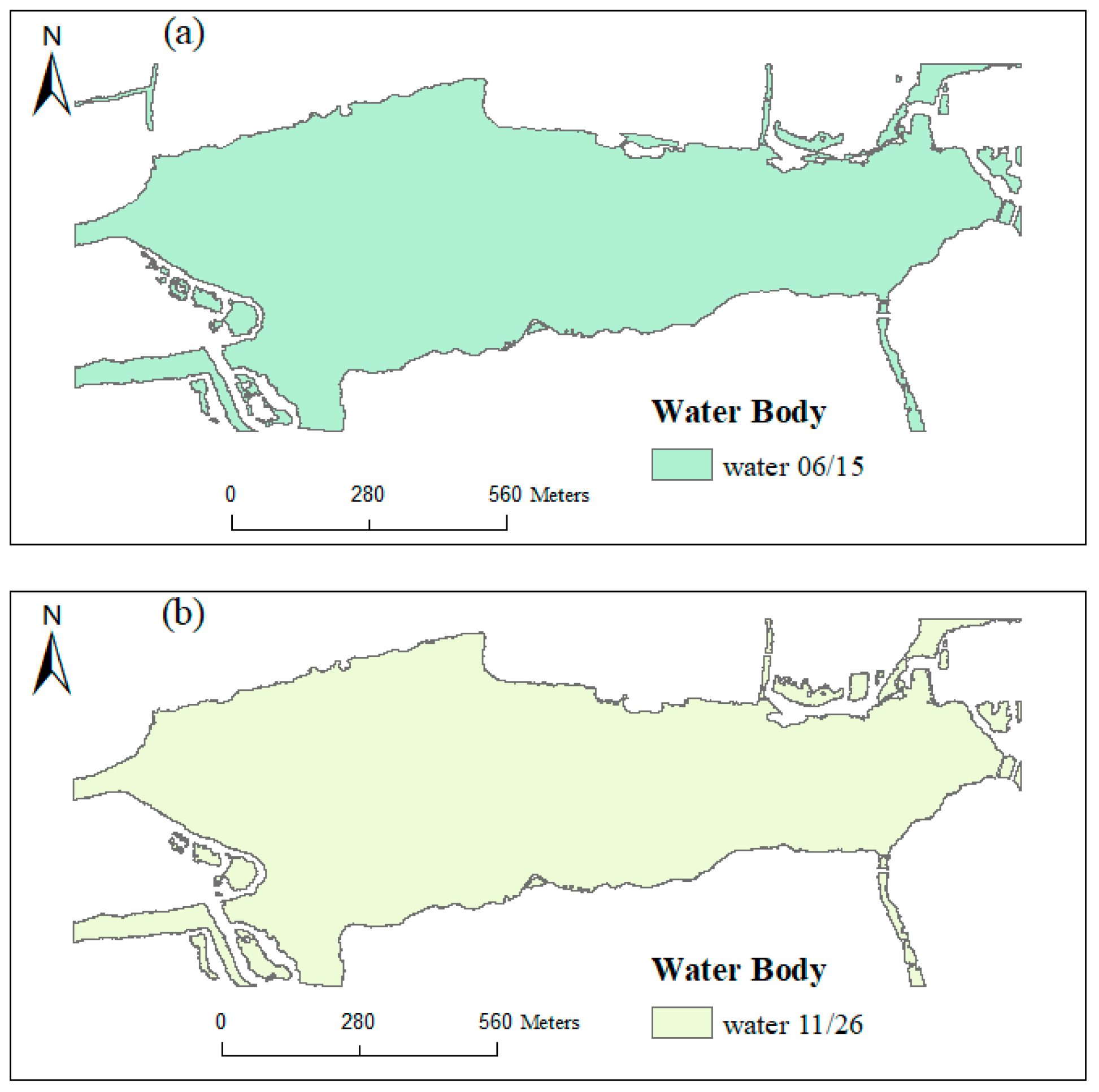
2.3.1. Extracted Water Body Area
2.3.2. Feature Variable Dataset Construction and Feature Selection
2.3.3. Machine Learning Methods
2.3.4. Accuracy Evaluation
2.3.5. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Water Quality in Xiangfudang
3. Results
3.1. Data Overview
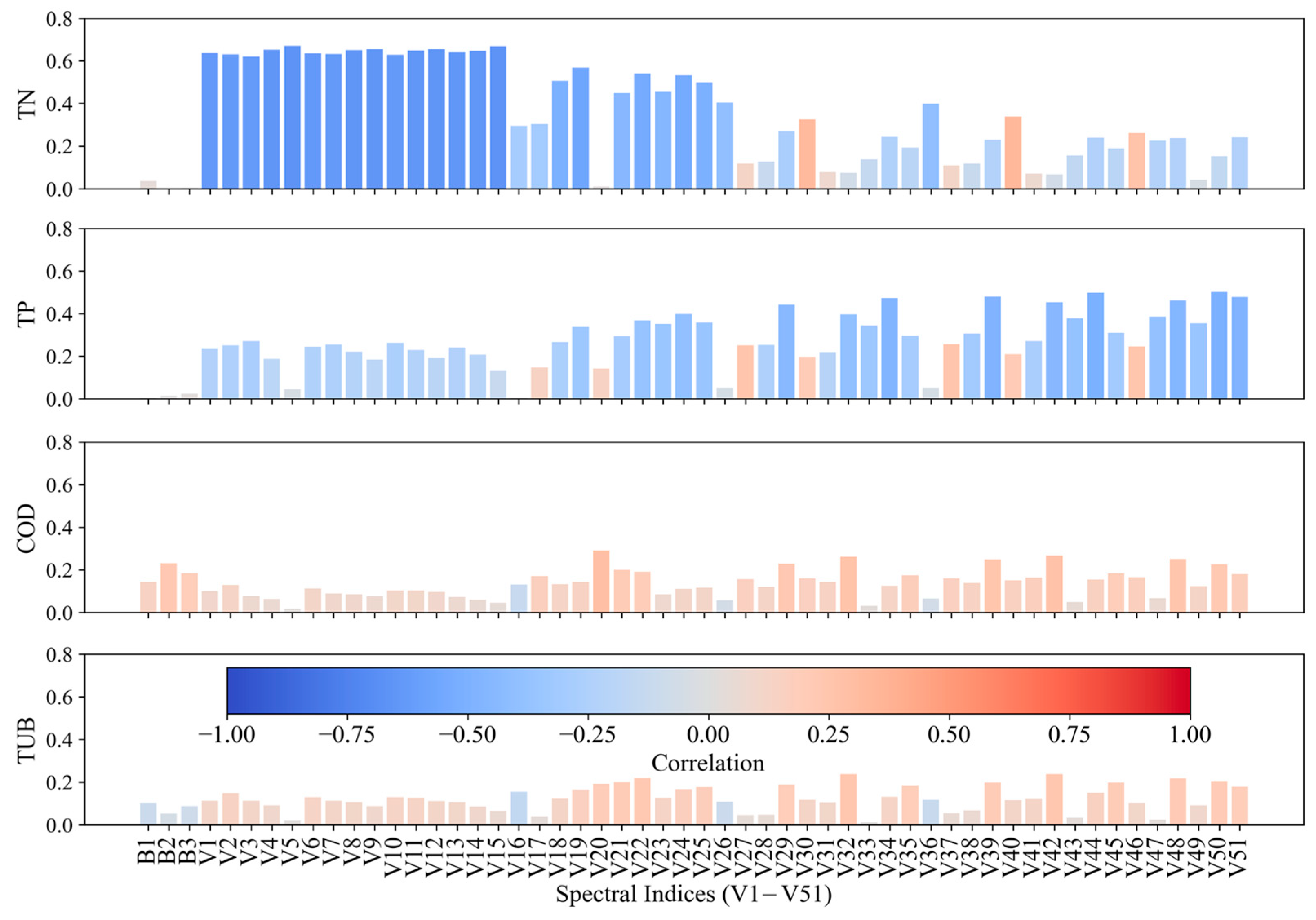
3.2. Spectral Index and Water Quality Parameters’ Correlation Analysis
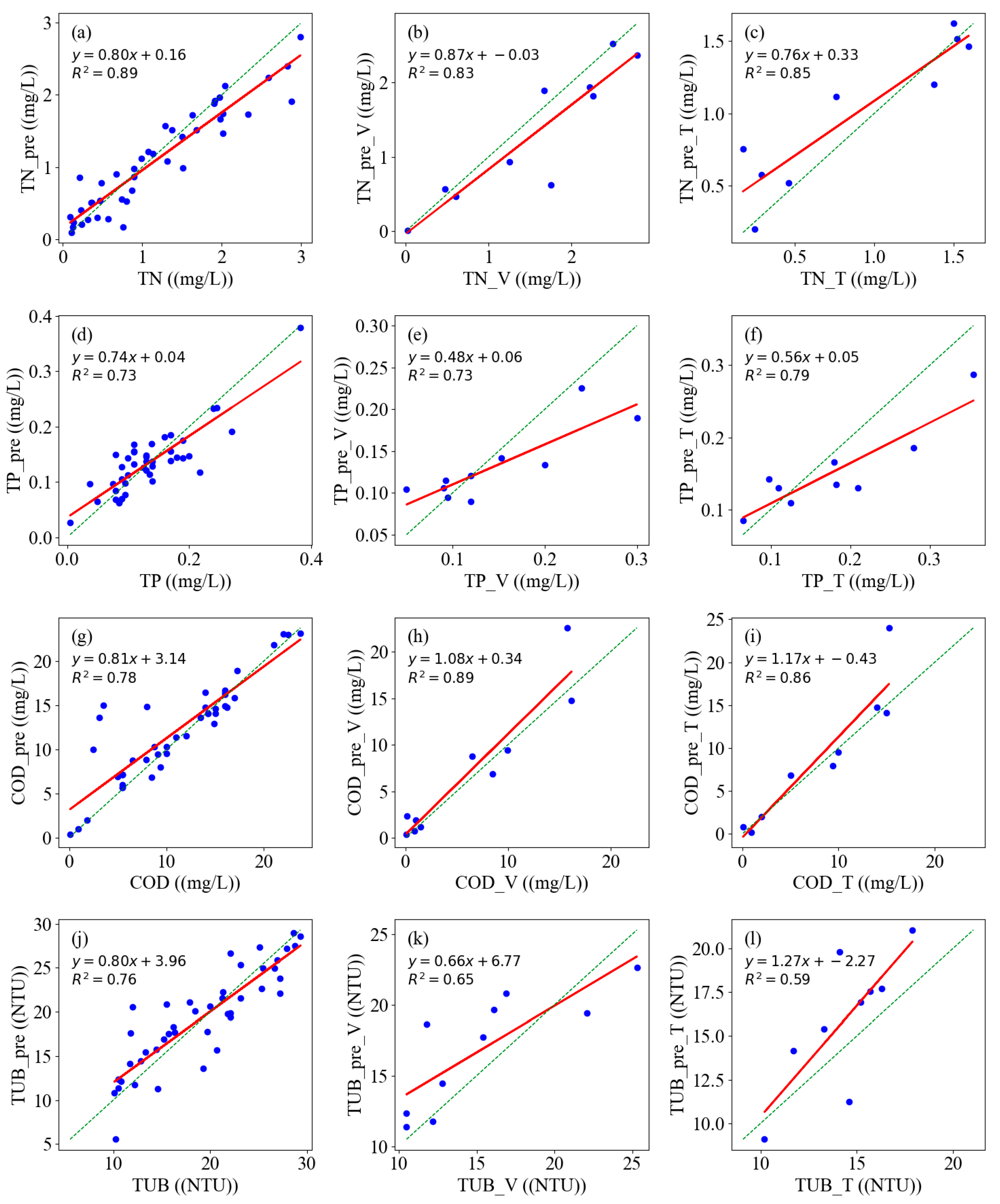
3.3. The Performance of Estimation Models
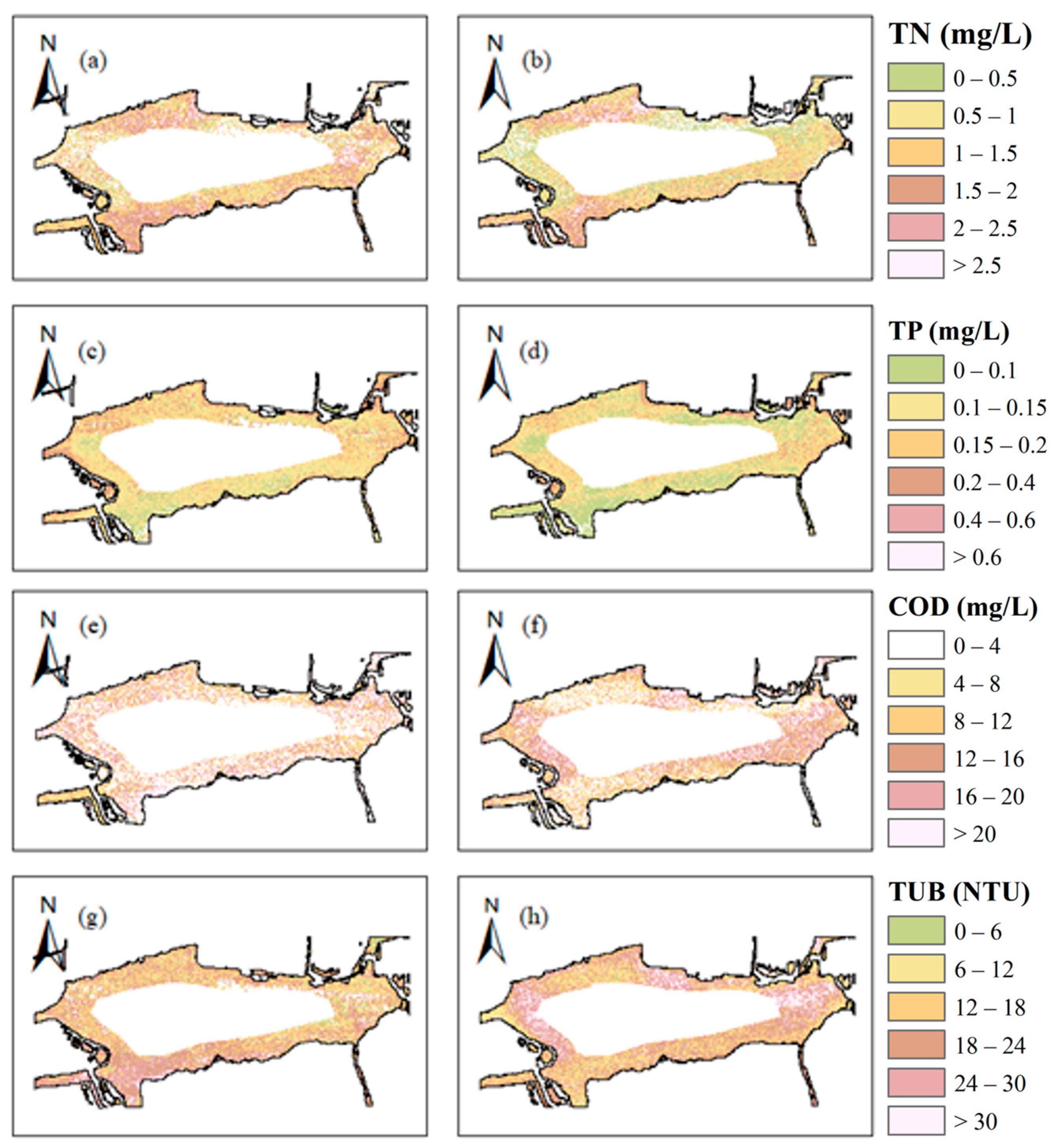
3.4. Water Quality Parameters’ Inversion by UAV Images
4. Discussion
4.1. Water Quality Monitoring Based on UAV Images
4.2. Water Quality Monitoring in Xiangfudang Wetland Park
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharma, S.; Singh, P. Wetlands Conservation: Current Challenges and Future Strategies; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, C.X.; Zhao, J.; Gong, P.; Ma, G.R.; Bao, D.M.; Tian, K.; Tian, R.; Niu, Z.G.; Zhang, H.; Xu, M.; et al. Wetland changes and droughts in southwestern China. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2012, 3, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, F.; Zhang, C. Analysis of change trend of water environment and cause in the Dongting Lake wetland. Ecol. Environ. 2011, 20, 1295. [Google Scholar]
- Bhateria, R.; Jain, D. Water quality assessment of lake water: A review. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 2, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.G.; Nash, S.; Rahman, A.; Olbert, A.I. A comprehensive method for improvement of water quality index (WQI) models for coastal water quality assessment. Water Res. 2022, 219, 118532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, N.; Syakir Ishak, M.I.; Bhawani, S.A.; Umar, K. Various Natural and Anthropogenic Factors Responsible for Water Quality Degradation: A Review. Water 2021, 13, 2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.K.; Singh, T.N. Prediction of water quality from simple field parameters. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 69, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whigham, D.F.; Chitterling, C.; Palmer, B. Impacts of freshwater wetlands on water quality: A landscape perspective. Environ. Manag. 1988, 12, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimparkar, A.M.; Patil, S.N.; Patil, B.D.; Kadam, A.K. Comparative assessment of wetland water quality from rural and urban area of Aurangabad District, Maharashtra, India using water quality index. HydroResearch 2023, 6, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachepsky, Y.; Kierzewski, R.; Stocker, M.; Sellner, K.; Mulbry, W.; Lee, H.; Kim, M. Temporal Stability of Escherichia coli Concentrations in Waters of Two Irrigation Ponds in Maryland. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e01876-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Xu, J.; Hu, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Xu, C.; Zhou, X.; Yang, J.; Nong, X.; Song, B.; et al. Off-Axis Four-Reflection Optical Structure for Lightweight Single-Band Bathymetric LiDAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 1000917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liu, W.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, E.; Zhu, Q.; Bai, Y. Shadow Detection on High-Resolution Digital Orthophoto Map Using Semantic Matching. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 4504420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- State Environmental Protection Administration of China. GB 3838-2002. Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water; Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2002.
- Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Qiao, X.; Qian, W. Water Chlorophyll a Estimation Using UAV-Based Multispectral Data and Machine Learning. Drones 2023, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Guo, Y.; Yin, G.; Zhang, X.; Shi, Y.; Hao, F.; Fu, Y. UAV Multispectral Image-Based Urban River Water Quality Monitoring Using Stacked Ensemble Machine Learning Algorithms—A Case Study of the Zhanghe River, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Luo, G.; He, L.; Xu, J.; Lyu, J. Analytical Approaches for Determining Chemical Oxygen Demand in Water Bodies: A Review. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2018, 48, 47–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anh, N.T.; Can, L.D.; Nhan, N.T.; Schmalz, B.; Luu, T.L. Influences of key factors on river water quality in urban and rural areas: A review. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2023, 8, 100424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behmel, S.; Damour, M.; Ludwig, R.; Rodriguez, M.J. Water quality monitoring strategies—A review and future perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 571, 1312–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chebud, Y.; Naja, G.M.; Rivero, R.G.; Melesse, A.M. Water Quality Monitoring Using Remote Sensing and an Artificial Neural Network. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2012, 223, 4875–4887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Kong, J.; Hu, H.; Du, Y.; Gao, M.; Chen, F. A Review of Remote Sensing for Water Quality Retrieval: Progress and Challenges. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, K.; Zhang, Y.; Li, N.; Wang, W.; Huang, X.; Qin, B. Monitoring water quality using proximal remote sensing technology. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 803, 149805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Kong, J.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, D. The optimal method for water quality parameters retrieval of urban river based on machine learning algorithms using remote sensing images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2023, 45, 7297–7317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, N.; He, H.; Ren, X.; Zhang, L.; Zeng, Y.; Fan, J.; Li, Y.; Niu, Z.; Zhu, X.; Chang, Q. The utility of fusing multi-sensor data spatio-temporally in estimating grassland aboveground biomass in the three-river headwaters region of China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 41, 7068–7089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagan, V.; Peterson, K.T.; Maimaitijiang, M.; Sidike, P.; Sloan, J.; Greeling, B.A.; Maalouf, S.; Adams, C. Monitoring inland water quality using remote sensing: Potential and limitations of spectral indices, bio-optical simulations, machine learning, and cloud computing. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2020, 205, 103187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Zhou, W.; Yao, Y.; Wang, W. Individual tree segmentation and tree species classification in subtropical broadleaf forests using UAV-based LiDAR, hyperspectral, and ultrahigh-resolution RGB data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 280, 113143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Mu, X.; Chen, P.; Wang, B.; Choi, J.; Park, H.; Xu, S.; Wu, Y.; Yang, H. Machine learning-based inversion of water quality parameters in typical reach of the urban river by UAV multispectral data. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 133, 108434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Si, W.; Wei, L.; Li, Z.; Xia, Z.; Ye, S.; Xia, Y. Retrieval of Water Quality from UAV-Borne Hyperspectral Imagery: A Comparative Study of Machine Learning Algorithms. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo-Mora, J.P.; Kalacska, M.; Løke, T.; Schläpfer, D.; Coops, N.C.; Lucanus, O.; Leblanc, G. Assessing the impact of illumination on UAV pushbroom hyperspectral imagery collected under various cloud cover conditions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 258, 112396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, H.; Xia, K.; Huang, X.; Feng, H.; Yang, Y.; Du, X.; Huang, L. Evaluation of water quality based on UAV images and the IMP-MPP algorithm. Ecol. Inform. 2021, 61, 101239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kageyama, Y.; Takahashi, J.; Nishida, M.; Kobori, B.; Nagamoto, D. Analysis of water quality in Miharu dam reservoir, Japan, using UAV data. IEEJ Trans. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2016, 11, S183–S185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.-C. A study of a matching pixel by pixel (MPP) algorithm to establish an empirical model of water quality mapping, as based on unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) images. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 58, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Richardson, M.; King, D.J. The impacts of environmental variables on water reflectance measured using a lightweight unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV)-based spectrometer system. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 130, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; She, Z.; Wang, B. Water Quality Sampling and Multi-Parameter Monitoring System Based on Multi-Rotor UAV Implementation. Water 2023, 15, 2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Zhang, A.; Lv, R.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, J.; Li, T. Machine learning algorithm inversion experiment and pollution analysis of water quality parameters in urban small and medium-sized rivers based on UAV multispectral data. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 78913–78932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Xia, K.; Feng, H.; Fang, Y. Inversion of water quality elements in small and micro-size water region using multispectral image by UAV. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2019, 39, 1241–1249. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, Y.; Fu, L.; Lu, T.; Huang, H.; Kong, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, C. Medium-Sized Lake Water Quality Parameters Retrieval Using Multispectral UAV Image and Machine Learning Algorithms: A Case Study of the Yuandang Lake, China. Drones 2023, 7, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.S.; Pyo, J.; Kwon, Y.-H.; Duan, H.; Cho, K.H.; Park, Y. Drone-based hyperspectral remote sensing of cyanobacteria using vertical cumulative pigment concentration in a deep reservoir. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 236, 111517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altenburger, R.; Ait-Aissa, S.; Antczak, P.; Backhaus, T.; Barceló, D.; Seiler, T.-B.; Brion, F.; Busch, W.; Chipman, K.; de Alda, M.L.; et al. Future water quality monitoring—Adapting tools to deal with mixtures of pollutants in water resource management. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 512–513, 540–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irie, M.; Manabe, Y.; Yamashita, M. Estimation Method of Chlorophyll Concentration Distribution Based on UAV Aerial Images Considering Turbid Water Distribution in a Reservoir. Drones 2024, 8, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, N.; Ren, X.; He, H.; Zhang, L.; Li, P.; Niu, Z. Estimating the grassland aboveground biomass in the Three-River Headwater Region of China using machine learning and Bayesian model averaging. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 114020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, N.; Ren, X.; He, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, D.; Ge, R.; Li, P.; Niu, Z. Estimating grassland aboveground biomass on the Tibetan Plateau using a random forest algorithm. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 102, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ren, H.; Wu, B.; Ye, L. A review of the application of machine learning in water quality evaluation. Eco-Environ. Health 2022, 1, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z. Research of Low-Carbon Urban Area Planning for Carbon Peaking and Carbon Neutrality Goals—A Case Study of XiangFu Dang District in Jianshan. Master’s Thesis, Beijing University of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Beijing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Environmental Protection of China. GB 11894-89. Water Quality-Determination of Total Nitrogen-Alkaline Potassium Persulfate Digestion-UV Spectrophotometric Method; China Standard Press: Beijing, China, 1989.
- Ministry of Environmental Protection of China. GB 11893-89. Water Quality-Determination of Total Phosphorus-Ammonium Molybdate Spectrophotometric Method; China Standard Press: Beijing, China, 1989.
- Ministry of Environmental Protection of China. GB 11914-89. Water Quality-Determination of Chemical Oxygen Demand-Dichromate Method; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 1989.
- Ministry of Environmental Protection of China. GB/T 13200. Water Quality-Determination of Turbidity-Nephelometric Method; China Standard Press: Beijing, China, 1994.
- Guo, Y.; Wang, H.; Wu, Z.; Wang, S.; Sun, H.; Senthilnath, J.; Wang, J.; Robin Bryant, C.; Fu, Y. Modified Red Blue Vegetation Index for Chlorophyll Estimation and Yield Prediction of Maize from Visible Images Captured by UAV. Sensors 2020, 20, 5055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achanta, R.; Shaji, A.; Smith, K.; Lucchi, A.; Fua, P.; Süsstrunk, S. SLIC Superpixels Compared to State-of-the-Art Superpixel Methods. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 34, 2274–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yue, X.; Wang, H.; Ling, K.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Hong, J.; Pen, W.; Song, H. Dynamic Inversion of Inland Aquaculture Water Quality Based on UAVs-WSN Spectral Analysis. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, M.; Fraihat, S. Recursive Feature Elimination with Cross-Validation with Decision Tree: Feature Selection Method for Machine Learning-Based Intrusion Detection Systems. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2023, 12, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, M.S.; Wang, J. Evaluation of Machine Learning Regression Techniques for Estimating Winter Wheat Biomass Using Biophysical, Biochemical, and UAV Multispectral Data. Drones 2024, 8, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghiabi, A.H.; Nasrolahi, A.H.; Parsaie, A. Water quality prediction using machine learning methods. Water Qual. Res. J. 2018, 53, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, H.-C.; Bae, D.; Jo, Y.-H. Data Reconstruction for Remotely Sensed Chlorophyll-a Concentration in the Ross Sea Using Ensemble-Based Machine Learning. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, X.; Wu, F. Twin support vector machine: Theory, algorithm and applications. Neural Comput. Appl. 2017, 28, 3119–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Ning, Z.; Chen, M.; Wu, D.; Hao, C.; Zhang, D.; Bai, R.; Liu, H.; Chen, X.; Li, W.; et al. Satellite and Machine Learning Monitoring of Optically Inactive Water Quality Variability in a Tropical River. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cockburn, J.; Holroyd, C.B. Feedback information and the reward positivity. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2018, 132, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elith, J.; Leathwick, J.R.; Hastie, T. A working guide to boosted regression trees. J. Anim. Ecol. 2008, 77, 802–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokhorenkova, L.; Gusev, G.; Vorobev, A.; Dorogush, A.V.; Gulin, A. Catboost: Unbiased Boosting with Categorical Features. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montréal, QC, Canada, 3–8 December 2018; pp. 6639–6649. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Water Resources of China. SL 368-2006. Water Quality Standard for Sewage Recycling; China Water & Power Press: Beijing, China, 2006.
- Horowitz, A.J. A Review of Selected Inorganic Surface Water Quality-Monitoring Practices: Are We Really Measuring What We Think, and If So, Are We Doing It Right? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 2471–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, M.J.; Chamberlain, M.J.; Buehler, D.A.; Sutton, W.B. Wetland Wildlife Monitoring and Assessment. In Wetland Techniques: Volume 2: Organisms; Anderson, J.T., Davis, C.A., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 265–318. [Google Scholar]
- Adeli, S.; Salehi, B.; Mahdianpari, M.; Quackenbush, L.J.; Brisco, B.; Tamiminia, H.; Shaw, S. Wetland Monitoring Using SAR Data: A Meta-Analysis and Comprehensive Review. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davranche, A.; Lefebvre, G.; Poulin, B. Wetland monitoring using classification trees and SPOT-5 seasonal time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 552–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, K.; Shirai, H.; Kageyama, Y.; Yokoyama, H. Improving the resolution of UAV-based remote sensing data of water quality of Lake Hachiroko, Japan by neural networks. Ecol. Inform. 2021, 62, 101276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jing, W.; Deng, Y.; Zhou, W.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Cai, Y.; Hu, Y.; Peng, X.; Lan, W.; et al. Water quality parameters retrieval of coastal mariculture ponds based on UAV multispectral remote sensing. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1079397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román, A.; Tovar-Sánchez, A.; Gauci, A.; Deidun, A.; Caballero, I.; Colica, E.; D’Amico, S.; Navarro, G. Water-Quality Monitoring with a UAV-Mounted Multispectral Camera in Coastal Waters. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmer, B.; Reshitnyk, L.Y.; Hessing-Lewis, M.; Juanes, F.; Costa, M. Comparing the Use of Red-Edge and Near-Infrared Wavelength Ranges for Detecting Submerged Kelp Canopy. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Dash, J.; Huang, W.; Peng, D.; Qin, Q.; Mortimer, H.; Casa, R.; Pignatti, S.; Laneve, G.; Pascucci, S.; et al. Vegetation Indices Combining the Red and Red-Edge Spectral Information for Leaf Area Index Retrieval. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 1482–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Shanmugam, P.; He, X.; Schroeder, T. UV-NIR approach with non-zero water-leaving radiance approximation for atmospheric correction of satellite imagery in inland and coastal zones. Opt. Express 2019, 27, A1118–A1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y. Mapping Mangrove Using a Red-Edge Mangrove Index (REMI) Based on Sentinel-2 Multispectral Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 4409511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Zhao, J.; Hou, R.; Duan, X.; Cai, S.; Wang, X. Clustered remote sensing target distribution detection aided by density-based spatial analysis. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2024, 132, 104019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Lu, X.; Wu, Y.; Miao, P.; Zhou, J. Retrieval and model construction of water quality parameters for UAV hyperspectral remote sensing. Sci. Surv. Mapp. 2020, 45, 60–64. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.; Zhu, J.; Xu, W.; Lv, X. Analysis on the safety of rural drinking water quality in Yangtze River Delta region. Sci. Technol. Innov. Appl. 2015, 26, 172. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G.; Li, P.; Lu, K.; Tantai, Z.; Zhang, J.; Ren, Z.; Wang, X.; Yu, K.; Shi, P.; Cheng, Y. Seasonal changes in water quality and its main influencing factors in the Dan River basin. CATENA 2019, 173, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.; Botta, S.; Kallam, R.; Angadala, R.; Andugala, J. Seasonal variation in water quality parameters of Gudlavalleru Engineering College pond. Curr. Res. Green Sustain. Chem. 2021, 4, 100058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, F.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.Q. Application of constructed wetland for urban lake water purification: Trial of Xing-qing Lake in Xi’an city, China. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2011, 46, 795–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Li, Y.; Yu, Z.; Yang, T.; Xu, J.; Chao, L.; Ni, J.; Wang, L.; Gao, Y.; Hu, Y.; et al. Xin’anjiang Nested Experimental Watershed (XAJ-NEW) for Understanding Multiscale Water Cycle: Scientific Objectives and Experimental Design. Engineering 2022, 18, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Band | Wavelength Range (nm) |
|---|---|
| Blue | 450 ± 35 |
| Green | 555 ± 27 |
| Red | 660 ± 22 |
| Edge_red | 720 ± 10 |
| NIR | 840 ± 30 |
| Index | Formula | Index | Formula | Index | Formula |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B1 | RGB−R | V16 | V1 − V2 | V34 | V3/V5 |
| B2 | RGB−G | V17 | V1 − V3 | V35 | V4/V5 |
| B3 | RGB−B | V18 | V1 − V4 | V36 | V16/V6 |
| V1 | blue | V19 | V1 − V5 | V37 | V17/V7 |
| V2 | green | V20 | V2 − V3 | V38 | V18/V8 |
| V3 | red | V21 | V2 − V4 | V39 | V19/V9 |
| V4 | Edge_red | V22 | V2 − V5 | V40 | V20/V10 |
| V5 | NIR | V23 | V3 − V4 | V41 | V21/V11 |
| V6 | V1 + V2 | V24 | V3 − V5 | V42 | V22/V12 |
| V7 | V1 + V3 | V25 | V4 − V5 | V43 | V23/V13 |
| V8 | V1 + V4 | V26 | V1/V2 | V44 | V24/V14 |
| V9 | V1 + V5 | V27 | V1/V3 | V45 | V25/V15 |
| V10 | V2 + V3 | V28 | V1/V4 | V46 | (V1 + V2 − V3)/(V1 + V2 + V3) |
| V11 | V2 + V4 | V29 | V1/V5 | V47 | (V1 + V3 − V4)/(V1 + V2 + V3) |
| V12 | V2 + V5 | V30 | V2/V3 | V48 | (V1 + V4 − V5)/(V1 + V4 + V5) |
| V13 | V3 + V4 | V31 | V2/V4 | V49 | (V2 + V3 − V4)/(V2 + V3 + V4) |
| V14 | V3 + V5 | V32 | V2/V5 | V50 | (V2 + V3 − V5)/(V2 + V3 + V5) |
| V15 | V4 + V5 | V33 | V3/V4 | V51 | (V3 + V4 − V5)/(V3 + V4 + V5) |
| No. | Indicator | Acceptable Range |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | TP | 0.4 mg/L |
| 2 | TN | 2.0 mg/L |
| 3 | COD | 40 |
| 2 | TUB | 30 |
| TN (gm/L) | TP (mg/L) | COD (gm/L) | TUB (NTU) | V1 (Blue) | V2 (Green) | V3 (Red) | V4 (Edge_Red) | V5 (NIR) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| count | 62 | 62 | 62 | 62 | 62 | 62 | 62 | 62 | 62 |
| mean | 1.19 | 0.14 | 9.10 | 17.76 | 0.38 | 0.39 | 0.35 | 0.26 | 0.19 |
| std | 0.83 | 0.07 | 6.98 | 5.83 | 0.19 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.12 | 0.079 |
| min | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.08 | 9.4 | 0.14 | 0.16 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.08 |
| 25% | 0.46 | 0.09 | 2.65 | 12.42 | 0.24 | 0.26 | 0.20 | 0.17 | 0.14 |
| 50% | 1.10 | 0.13 | 8.37 | 16.4 | 0.33 | 0.36 | 0.34 | 0.22 | 0.16 |
| 75% | 1.86 | 0.18 | 15 | 22.1 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 0.45 | 0.34 | 0.23 |
| max | 2.99 | 0.38 | 24.25 | 29.3 | 0.82 | 0.83 | 0.78 | 0.61 | 0.38 |
| Output Variable | Model | Input Variable | Training | Validation | Testing | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSE | R2 | RMSE | R2 | RMSE | |||
| TN | RF | V4, V5, V11, V15, V48 | 0.88 | 0.30 | 0.75 | 0.42 | 0.69 | 0.49 |
| CatBoost | 0.86 | 0.32 | 0.80 | 0.40 | 0.82 | 0.38 | ||
| ANN | 0.89 | 0.24 | 0.83 | 0.34 | 0.85 | 0.19 | ||
| SVR | 0.82 | 0.36 | 0.65 | 0.49 | 0.72 | 0.45 | ||
| TP | RF | V29, V32, V44, V50, V51 | 0.71 | 0.04 | 0.69 | 0.07 | 0.69 | 0.06 |
| CatBoost | 0.73 | 0.03 | 0.73 | 0.02 | 0.79 | 0.03 | ||
| ANN | 0.72 | 0.04 | 0.69 | 0.07 | 0.65 | 0.06 | ||
| SVR | 0.65 | 0.07 | 0.59 | 0.11 | 0.64 | 0.08 | ||
| COD | RF | B2, V20, V32, V39, V42 | 0.74 | 3.00 | 0.69 | 2.90 | 0.71 | 2.96 |
| CatBoost | 0.73 | 2.97 | 0.70 | 3.20 | 0.66 | 3.32 | ||
| ANN | 0.78 | 2.58 | 0.89 | 2.31 | 0.86 | 2.74 | ||
| SVR | 0.66 | 3.42 | 0.59 | 3.62 | 0.62 | 3.50 | ||
| TUB | RF | V2, V6, V28, V32, V42 | 0.73 | 3.76 | 0.57 | 3.80 | 0.55 | 3.83 |
| CatBoost | 0.76 | 3.52 | 0.55 | 3.82 | 0.56 | 3.72 | ||
| ANN | 0.76 | 2.71 | 0.65 | 2.29 | 0.59 | 2.34 | ||
| SVR | 0.62 | 3.97 | 0.50 | 4.03 | 0.47 | 4.22 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, N.; Ma, L.; Zheng, H.; Zhao, Y.; He, Z.; Deng, S.; Wang, Y. Machine Learning Based Inversion of Water Quality Parameters in Typical Reach of Rural Wetland by Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Images. Water 2024, 16, 3163. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16223163
Zeng N, Ma L, Zheng H, Zhao Y, He Z, Deng S, Wang Y. Machine Learning Based Inversion of Water Quality Parameters in Typical Reach of Rural Wetland by Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Images. Water. 2024; 16(22):3163. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16223163
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Na, Libang Ma, Hao Zheng, Yihui Zhao, Zhicheng He, Susu Deng, and Yixiang Wang. 2024. "Machine Learning Based Inversion of Water Quality Parameters in Typical Reach of Rural Wetland by Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Images" Water 16, no. 22: 3163. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16223163
APA StyleZeng, N., Ma, L., Zheng, H., Zhao, Y., He, Z., Deng, S., & Wang, Y. (2024). Machine Learning Based Inversion of Water Quality Parameters in Typical Reach of Rural Wetland by Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Images. Water, 16(22), 3163. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16223163





