Benthic Microbes on the Shore of Southern Lake Taihu Exhibit Ecological Significance and Toxin-Producing Potential Through Comparison with Planktonic Microbes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
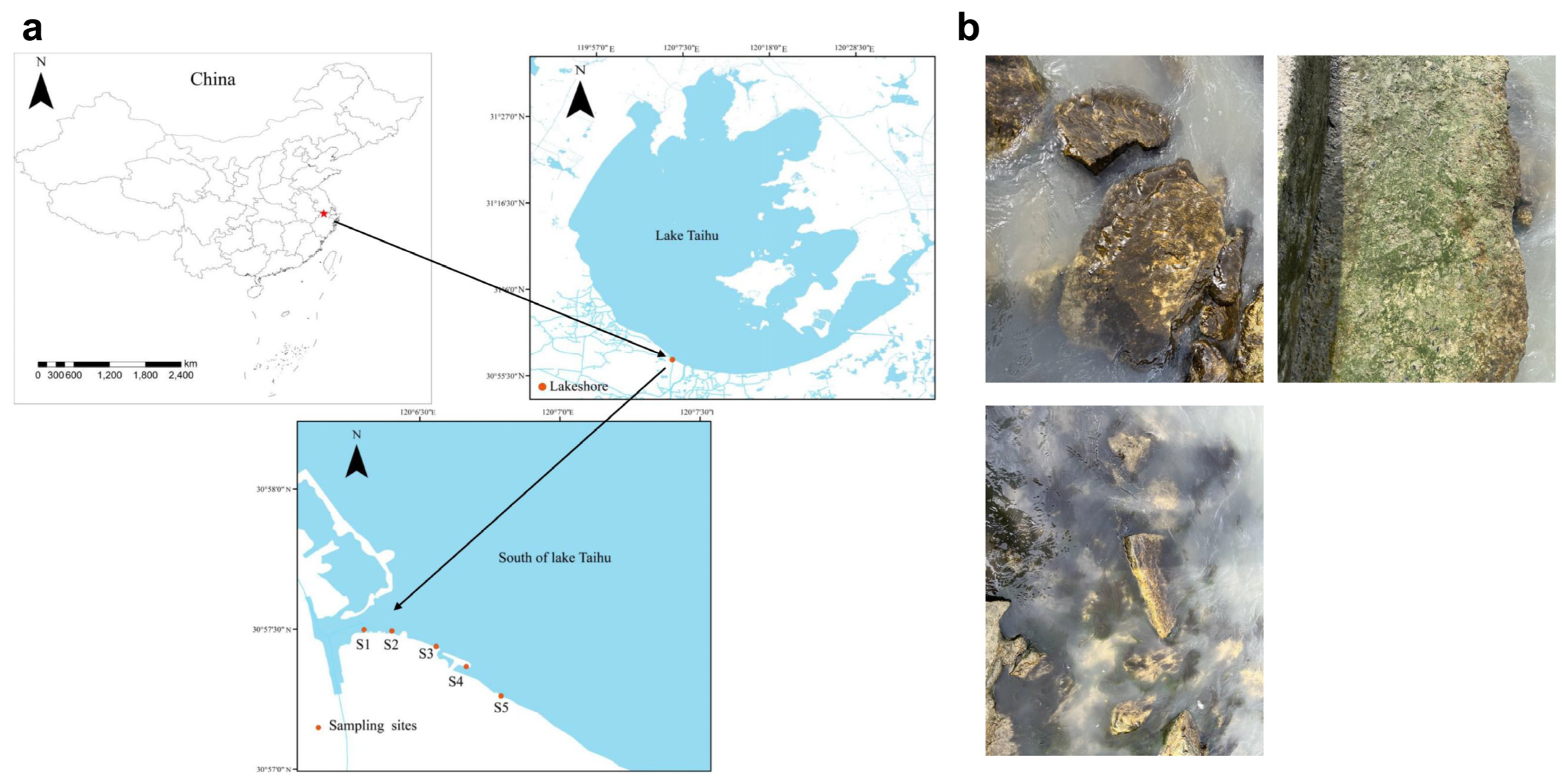
2.1. Study Area and Sampling Site
2.2. Field Investigation and Physicochemical Indexes
2.3. DNA Extraction, PCR, and Sequencing
2.4. Bioinformatic Processing
2.5. Community Assembly Analysis
2.6. Co-Occurrence Networks
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Result
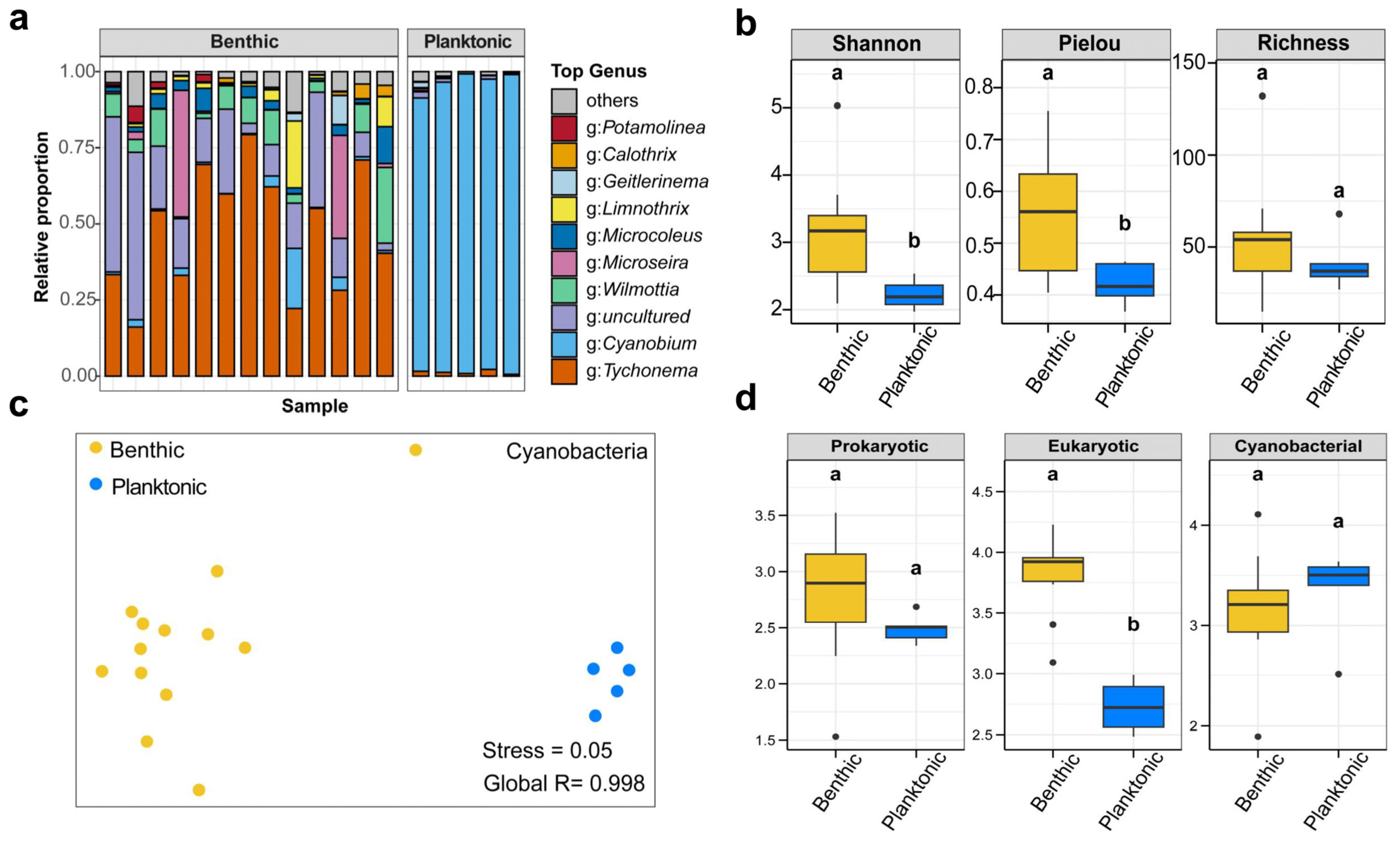
3.1. Structure, α-Diversity, and Niche Breadth of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Microbial Communities
3.2. Structure, α-Diversity, and Niche Breadth of Cyanobacterial Communities
3.3. β-Diversity of Prokaryotes, Eukaryotes, and Cyanobacteria
3.4. Community Assembly Governing Microbial Community Patterns Across Different Habitats
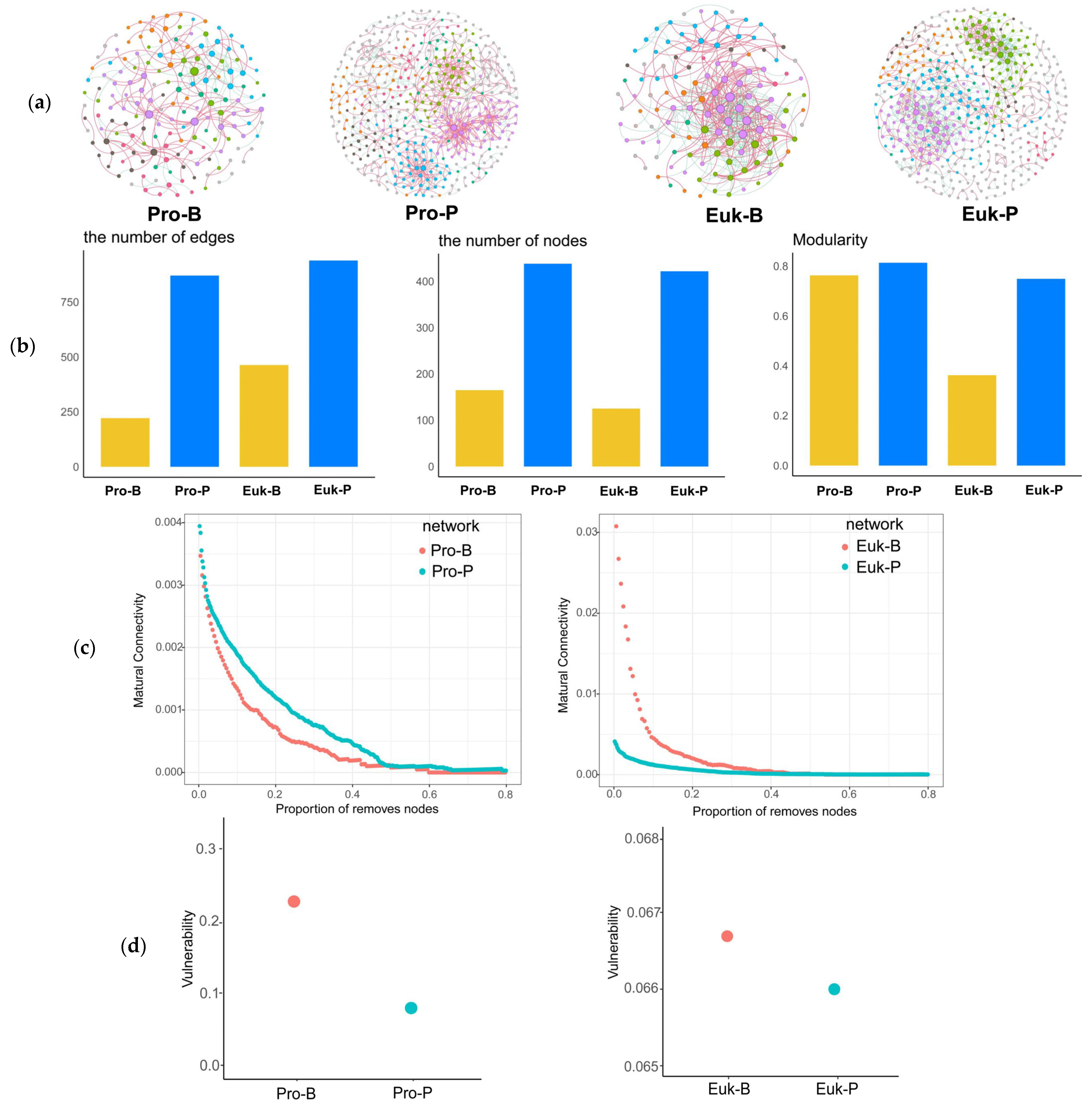
3.5. Network Pattern of Microbial Community Across Different Habitats
4. Discussion
4.1. Diversity and Structure of Benthic and Planktonic Microbial Communities
4.2. Ecological Processes of Benthic and Planktonic Microbial Communities
4.3. Co-Occurrence Patterns of Benthic and Planktonic Microbial Communities
4.4. Implications for Environmental Management
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Urbani, G.; Petkovska, V.; Pavlin, M. The relationship between littoral benthic invertebrates and lakeshore modification pressure in two alpine lakes. Fundam. Appl. Limnol. 2012, 180, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Shentu, H.; Yu, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Ma, J.; Zheng, H.; Huang, S.; Dong, L.; Wei, J. Impact of urbanization and land use on wetland water quality: A case study in Mengxi town. Urban Climate 2024, 55, 101855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, A.; Liu, J.; Xing, C.; Huang, S.; Huo, Y.; Yang, Z.; Huang, J.; Liu, W. Turnover of phytoplankton and zooplankton communities driven by human-induced disturbances and climate changes in a small urban coastal wetland. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 157, 111271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goździejewska, A.M.; Cymes, I.; Glińska-Lewczuk, K. Zooplankton functional diversity as a bioindicator of freshwater ecosystem health across land use gradient. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 18456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, X.; Xie, Y.; Song, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, H.; Burton, G.A. Zooplankton community profiling in a eutrophic freshwater ecosystem-lake tai basin by DNA metabarcoding. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Pan, B.; Zhao, X.; Liu, X.; Liu, X.; Zhao, G. Hydrological disturbances enhance stochastic assembly processes and decrease network stability of algae communities in a highland floodplain system. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 903, 166207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donghao, W.; Fangfei, C.; Jiaxin, H.; Guanning, J.; YaDong, S.; Aichun, S. The declining cyanobacterial blooms in Lake Taihu (China) in 2021: The interplay of nutrients and meteorological determinants. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 145, 109590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Pan, B.; Liu, X.; Han, X.; Zhu, P.; Li, G.; Li, D. Trophic level plays an enhanced role in shaping microbiota structure and assembly in lakes with decreased salinity on the Qinghai-Tibet and Inner Mongolia Plateaus. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 923, 171316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Zhang, P.; Li, X.; Yang, S.; Chao, X.; Liu, H.; Ba, S. Distribution patterns and community assembly processes of eukaryotic microorganisms along an altitudinal gradient in the middle reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo River. Water Res. 2023, 239, 120047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Xu, S.; Yan, R.; Wang, R.; Gao, Y.; Kong, M.; Yi, Q.; Zhang, Y. Similar geographic patterns but distinct assembly processes of abundant and rare bacterioplankton communities in river networks of the Taihu Basin. Water Res. 2022, 211, 118057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, G.; Székely, A.J.; Jeppesen, E. Eutrophication alters bacterial co-occurrence networks and increases the importance of chromophoric dissolved organic matter composition. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2021, 66, 2319–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, J.; Xiao, P.; Heino, J.; Tan, F.; Soininen, J.; Chen, H.; Yang, J. Eutrophication increases the similarity of cyanobacterial community features in lakes and reservoirs. Water Res. 2024, 250, 120977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Yan, D.; Xa, P.; Cao, H.; Lin, T.; Yi, Y. Community structure and assembly of denitrifying bacteria in epiphytic biofilms in a freshwater lake ecosystem. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2022, 40, 1039–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Liu, Y.; Sun, R.; Wu, Y.; Dolfing, J. Geographic imprint and ecological functions of the abiotic component of periphytic biofilms. Imeta 2022, 1, e60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, N.; Wang, T.; Kuzyakov, Y. Rhizosphere bacteriome structure and functions. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, P.; Aslam, M.; Du, H.; Liang, H.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Chen, W. Environmental factors shape the epiphytic bacterial communities of Gracilariopsis lemaneiformis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, P.; Metz, S.; Unrein, F.; Mayora, G.; Sarmento, H.; Devercelli, M. Environmental heterogeneity determines the ecological processes that govern bacterial metacommunity assembly in a floodplain river system. ISME J. 2020, 14, 2951–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logares, R.; Lindström, E.S.; Langenheder, S.; Logue, J.B.; Paterson, H.; Laybourn-Parry, J.; Rengefors, K.; Tranvik, L.; Bertilsson, S. Biogeography of bacterial communities exposed to progressive long-term environmental change. ISME J. 2013, 7, 937–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemergut, D.R.; Schmidt, S.K.; Fukami, T.; O’Neill, S.P.; Bilinski, T.M.; Stanish, L.F.; Knelman, J.E.; Darcy, J.L.; Lynch, R.C.; Wickey, P.; et al. Patterns and processes of microbial community assembly. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2013, 77, 342–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Ren, K.; Isabwe, A.; Chen, H.; Liu, M.; Yang, J. Stochastic processes shape microeukaryotic community assembly in a subtropical river across wet and dry seasons. Microbiome 2019, 7, 138. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, D.; Deng, Y.; Tiedje, J.M.; Zhou, J. A general framework for quantitatively assessing ecological stochasticity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 16892–16898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fargione, J.; Brown, C.S.; Tilman, D. Community assembly and invasion: An experimental test of neutral versus niche processes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 8916–8920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Ge, Z.; Ma, Z.; Huang, D.; Zhang, J. Seasonal changes driving shifts of aquatic rhizosphere microbial community structure and the functional properties. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 322, 116124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Wen, D. Archaeal and bacterial communities assembly and co-occurrence networks in subtropical mangrove sediments under Spartina alterniflora invasion. Environ. Microbiome 2021, 16, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Xie, G.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, B.; Shao, K.; Gao, G.; Tang, X. Similar assembly mechanisms but distinct co-occurrence patterns of planktonic vs. particle-attached bacterial communities across different habitats and seasons in shallow, eutrophic Lake Taihu. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 314, 120305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Li, S.; Al, M.A.; Mo, Y.; Zuo, J.; Grossart, H.P.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.; Jeppesen, E.; Yang, J. Community stability of planktonic and particle-attached bacteria in a subtropical reservoir with salinity fluctuations over 3 years. Water Res. 2024, 254, 121344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, J.; Liu, L.; Xiao, P.; Xu, Z.; Wilkinson, D.M.; Grossart, H.P.; Chen, H.; Yang, J. Patterns of bacterial generalists and specialists in lakes and reservoirs along a latitudinal gradient. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2023, 32, 2017–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fath, B.D.; Patten, B.C. Network synergism: Emergence of positive relations in ecological systems. Ecol. Modell. 1998, 107, 127–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Nuccio, E.E.; Shi, Z.J.; He, Z.; Zhou, J.; Firestone, M.K. The interconnected rhizosphere: High network complexity dominates rhizosphere assemblages. Ecol. Lett. 2016, 19, 926–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, F.; Zhang, H.; Xie, W.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, D. Co-occurrence patterns and assembly processes of microeukaryotic communities in an early-spring diatom bloom. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 711, 134624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Dong, P.; Zhao, T.; Deng, Y.; Li, J.; Song, L.; Wang, J.; Zhou, L.; Shi, J.; Wu, Z. Strategies for regulating the intensity of different cyanobacterial blooms: Insights from the dynamics and stability of bacterioplankton communities. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 918, 170707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, M.M.; Guo, X.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Y.A.; Xiao, N.; Ning, D.; Shi, Z.; Zhou, X.; Wu, L.; Yang, Y.; et al. Climate warming enhances microbial network complexity and stability. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2021, 11, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Y.; Peng, F.; Gao, X.; Xiao, P.; Logares, R.; Jeppesen, E.; Ren, K.; Xue, Y.; Yang, J. Low shifts in salinity determined assembly processes and network stability of microeukaryotic plankton communities in a subtropical urban reservoir. Microbiome 2021, 9, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, R.; Hu, S.; Li, Q.; Zhao, D.; Wu, Q.L.; Zeng, J. Greater transmission capacities and small-world characteristics of bacterial communities in the above-than those in the below-ground niches of a typical submerged macrophyte, Vallisneria natans. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 903, 166229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facey, J.A.; Michie, L.E.; King, J.J.; Hitchcock, J.N.; Apte, S.C.; Mitrovic, S.M. Severe cyanobacterial blooms in an Australian lake; causes and factors controlling succession patterns. Harmful Algae 2022, 117, 102284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J.; et al. Introducing mothur: Open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Dada, S.H. High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillou, L.; Bachar, D.; Audic, S.; Bass, D.; Berney, C.; Bittner, L.; Boutte, C.; Burgaud, G.; Vargas, V.D.; Decelle, J.; et al. The Protist Ribosomal Reference database (PR2): A catalog of unicellular eukaryote small sub-unit rRNA sequences with curated taxonomy. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D597–D604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloan, W.T.; Lunn, M.; Woodcock, S.; Head, I.M.; Nee, S.; Curtis, T.P. Quantifying the roles of immigration and chance in shaping prokaryote community structure. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegen, J.C.; Lin, X.; Fredrickson, J.K.; Chen, X.; Kennedy, D.W.; Murray, C.J.; Rockhold, M.L.; Konopka, A. Quantifying community assembly processes and identifying features that impose them. ISME J. 2013, 7, 2069–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, D.; Yuan, M.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhou, X.; Yang, Y.; Arkin, A.; Firestone, M.; Zhou, J. A quantitative framework reveals ecological drivers of grassland microbial community assembly in response to warming. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osburn, E.D.; Aylward, F.O.; Barrett, J.E. Historical land use has long-term effects on microbial community assembly processes in forest soils. ISME J. 2021, 1, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Jiang, Y.H.; Yang, Y.; He, Z.; Luo, F.; Zhou, J. Molecular ecological network analyses. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, N.; Zhou, A.; Kempher, M.L.; Zhou, B.Y.; Shi, Z.J.; Yuan, M.; Guo, X.; Wu, L.; Ning, D.; Nostrand, J.; et al. Disentangling direct from indirect relationships in association networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2109995119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Deng, Y.; Luo, F.; He, Z.; Tu, Q.; Zhi, X. Functional molecular ecological networks. mBio 2010, 1, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montesinos-Navarro, A.; Hiraldo, F.; Tella, J.L.; Blanco, G. Network structure embracing mutualism–antagonism continuums increases community robustness. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 1, 1661–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Shi, P.; Wei, G. Biogeography and ecological processes affecting root-associated bacterial communities in soybean fields across China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, S.E.; Gromiec, M.J. (Eds.) Developments in Environmental Modelling; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, C.; Gunina, A.; Luo, Y.; Wang, J.; He, J.Z.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Hemp, H.; Classen, A.; Ge, Y. Contrasting patterns and drivers of soil bacterial and fungal diversity across a mountain gradient. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 3287–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levins, R. Evolution in Changing Environments: Some Theoretical Explorations; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.Y. linkET: Everything Is Linkable. R Package Version 0.0.7.1. 2021. Available online: https://rdrr.io/github/Hy4m/linkET/ (accessed on 3 October 2024).
- Balan, B.; Dhaulaniya, A.S.; Varma, D.A.; Sodhi, K.K.; Kumar, M.; Tiwari, M.; Singh, D.K. Microbial biofilm ecology, in silico study of quorum sensing receptor-ligand interactions and biofilm mediated bioremediation. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 203, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonawane, J.M.; Rai, A.K.; Sharma, M.; Tripathi, M.; Prasad, R. Microbial biofilms: Recent advances and progress in environmental bioremediation. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 824, 153843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Tran, P.Q.; Kieft, K.; Anantharaman, K. Genome diversification in globally distributed novel marine Proteobacteria is linked to environmental adaptation. ISME J. 2020, 14, 2060–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, T.; Wen, D.; Bates, C.T.; Wu, L.; Guo, X.; Liu, S.; Su, Y.; Lei, J.; Zhou, J.; Yang, Y. Nutrient supply controls the linkage between species abundance and ecological interactions in marine bacterial communities. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, H.; Niu, L.; Habibul, N. Benthic biofilm bacterial communities and their linkage with water-soluble organic matter in effluent receivers. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adão, H. Metazoan Meiofauna: Benthic assemblages for sustainable marine and estuarine ecosystems. In Life Below Water; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Derelle, R.; López-García, P.; Timpano, H.; Moreira, D. A phylogenomic framework to study the diversity and evolution of stramenopiles (= heterokonts). Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 2890–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Zhu, M.; Yu, G.; Li, R. Occurrence of planktonic cyanobacterium Tychonema bouurrellyi in Erhai lake and its taxonomic studies. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2012, 36, 1171–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado-De-Lima, N.M.; Martins, M.D.; Branco, L.H. Description of a tropical new species of Wilmottia (Oscillatoriales, Cyanobacteria) and considerations about the monophyly of W.murrayi. Phytotaxa 2017, 307, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, R.; He, Z.; Gao, K.; Xiao, P.; Zhang, H.; Chen, S.; Li, H.; Yu, G.; Li, R. Neomicrocoleus gen. nov. (Microcoleaceae, Oscillatoriales), a novel cyanobacterial genus from benthic mats in a water channel. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2024, 42, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foysal, M.J.; Timms, V.; Neilan, B.A. Dynamics of the benthic and planktic microbiomes in a Planktothrix-dominated toxic cyanobacterial bloom in Australia. Water Res. 2024, 249, 120980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Cao, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, Q. Developing cyanobacterial bloom predictive models using influential factor discrimination approach for eutrophic shallow lakes. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 144, 109458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spicer, M.E.; Woods, C.L. A case for studying biotic interactions in epiphyte ecology and evolution. Perspect. Plant Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2022, 54, 125658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manirakiza, B.; Zhang, S.; Addo, F.G.; Isabwe, A.; Nsabimana, A. Exploring microbial diversity and ecological function of epiphytic and surface sediment biofilm communities in a shallow tropical lake. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 808, 151821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochieng, B.; Wu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Meng, F.; Xu, J.; Zhang, L.; Kimirei, I.; Wang, J. Beta diversity patterns and driving mechanisms of stream bacteria and fungi on Mt. Kilimanjaro. Ecol. Informatics. 2024, 82, 102747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penesyan, A.; Paulsen, I.T.; Kjelleberg, S.; Gillings, M.R. Three faces of biofilms: A microbial lifestyle, a nascent multicellular organism, and an incubator for diversity. npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2021, 7, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, X.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, C.; Ren, P.; Zeng, D.; Wu, L.; Ding, P. Beta-diversity partitioning: Methods, applications and perspectives. Biodivers. Sci. 2017, 25, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.B.; Lü, X.T.; Yao, J.; Wang, Z.W.; Deng, Y.; Cheng, W.X.; Zhou, J.; Han, X.G. Habitat-specific patterns and drivers of bacterial β-diversity in China’s drylands. ISME J. 2017, 11, 1345–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dini-Andreote, F.; Stegen, J.C.; Van Elsas, J.D.; Salles, J.F. Disentangling mechanisms that mediate the balance between stochastic and deterministic processes in microbial succession. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E1326–E1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, T.; Gong, X. Characterization of the physical properties of biofilms. Chin. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 33, 1390–1398. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Jin, L.; Zhang, C.; Li, S.; Zhou, T.; Hua, Z.; Wang, L.; Ji, S.; Wang, Y.; Gan, Y.; et al. Destabilized microbial networks with distinct performances of abundant and rare biospheres in maintaining networks under increasing salinity stress. iMeta 2023, 2, e79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Sun, X.; Adams, J.M.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; Chu, H. More robust co-occurrence patterns and stronger dispersal limitations of bacterial communities in wet than dry seasons of riparian wetlands. Msystems 2023, 8, e01187-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Fan, T.; Wang, S.; Yu, X.; Lu, A.; Wang, X.; Zhou, W.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, L. Seasonal changes driving shifts in microbial community assembly and species coexistence in an urban river. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Ning, D. Stochastic community assembly: Does it matter in microbial ecology? Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2017, 81, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shade, A.; Jones, S.E.; Caporaso, J.G.; Handelsman, J.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N.; Gilbert, J.A. Conditionally rare taxa disproportionately contribute to temporal changes in microbial diversity. MBio 2014, 5, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adrian, R.; O’Reilly, C.M.; Zagarese, H.; Baines, S.B.; Hessen, D.O.; Keller, W.; Livingstone, D.; Sommaruga, R.; Straile, D.; Donk, E.; et al. Lakes as sentinels of climate change. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54, 2283–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, C.; Li, G.; Xia, R.; Li, C.; Zhu, Q.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Zhao, C.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, L. New insights into cyanobacterial blooms and the response of associated microbial communities in freshwater ecosystems. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 309, 119781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.C.; Michalak, A.M.; Pahlevan, N. Widespread global increase in intense lake phytoplankton blooms since the 1980s. Nature 2019, 574, 667–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmikandan, M.; Li, M.; Pan, B. Cyanobacterial blooms in environmental water: Causes and solutions. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2024, 10, 606–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Qin, B.; Paerl, H.W.; Peng, K.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, Y. Environmental controls of harmful cyanobacterial blooms in Chinese inland waters. Harmful Algae 2021, 110, 102127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coloma, S.E.; Dienstbier, A.; Bamford, D.H.; Sivonen, K.; Roine, E.; Hiltunen, T. Newly isolated Nodularia phage influences cyanobacterial community dynamics. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Gardner, W.S.; Havens, K.E.; Joyner, A.R.; McCarthy, M.J.; Newell, S.E.; Qin, B.; Scott, J.T. Mitigating cyanobacterial harmful algal blooms in aquatic ecosystems impacted by climate change and anthropogenic nutrients. Harmful Algae 2016, 54, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Jia, Y.; Qin, B.; Li, R.; Carmichael, W.W.; Gan, N.; Xu, H.; Shan, K.; Sukenik, A. Harmful cyanobacterial blooms: Biological traits, mechanisms, risks, and control strategies. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2023, 48, 123–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, P.M.; Ibelings, B.W.; Bormans, M.; Huisman, J. Artificial mixing to control cyanobacterial blooms: A review. Aquat. Ecol. 2016, 50, 423–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, F.; Stix, M.; Bartha-Dima, B.; Geist, J.; Raeder, U. Spatio-temporal monitoring of benthic anatoxin-a-producing Tychonema sp. in the River Lech, Germany. Toxins 2022, 14, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shams, S.; Capelli, C.; Cerasino, L.; Ballot, A.; Dietrich, D.R.; Sivonen, K.; Salmaso, N. Anatoxin-a producing Tychonema (Cyanobacteria) in European waterbodies. Water Res. 2015, 69, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usman, A.S.; Merican, F.; Zaki, S.; Broady, P.; Convey, P.; Muangmai, N. Microcystin production by oscillatorialean cyanobacteria isolated from cryopreserved Antarctic mats. Harmful Algae 2022, 120, 102336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valadez-Cano, C.; Reyes-Prieto, A.; Lawrence, J. Novel virulent and temperate cyanophages predicted to infect Microcoleus associated with anatoxin-producing benthic mats. Environ. Microbiol. 2023, 25, 3319–3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, A.R.J.; Siqueira, A.S.; Vasconcelos, J.M.D.; Pereira, J.S.; Azevedo, J.S.N.D.; Moraes, P.H.G.; Aguiar, E.C.; Lima, C.P.S.; Vianez-Júnior, J.L.S.G.; Nunes, M.R.T.; et al. Insights into Limnothrix sp. metabolism based on comparative genomics. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson-Mungerson, M.; Williams, P.G.; Gurr, J.R.; Incrocci, R.; Subramaniam, V.; Radowska, K.; Hall, M.; Mayer, A.M. Biochemical and functional analysis of cyanobacterium Geitlerinema sp. LPS on human monocytes. Toxicol. Sci. 2019, 171, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaas, H.E.; Paerl, H.W. Toxic cyanobacteria: A growing threat to water and air quality. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 44–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, L.H.; Huang, Y.; Bermarija, T.D.; Rafuse, C.; Zamlynny, L.; Bruce, M.R.; Graham, C.; Comeau, A.M.; Valader-Cano, C.; Lawrence, J.E.; et al. Proliferation and anatoxin production of benthic cyanobacteria associated with canine mortalities along a stream-lake continuum. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 917, 170476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Q.; Wu, B.; Zuo, J.; Xiao, P.; Zhang, H.; Dong, Y.; Shang, S.; Ji, G.; Geng, R.; Li, R. Benthic Microbes on the Shore of Southern Lake Taihu Exhibit Ecological Significance and Toxin-Producing Potential Through Comparison with Planktonic Microbes. Water 2024, 16, 3155. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16213155
Zhao Q, Wu B, Zuo J, Xiao P, Zhang H, Dong Y, Shang S, Ji G, Geng R, Li R. Benthic Microbes on the Shore of Southern Lake Taihu Exhibit Ecological Significance and Toxin-Producing Potential Through Comparison with Planktonic Microbes. Water. 2024; 16(21):3155. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16213155
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Qihang, Bin Wu, Jun Zuo, Peng Xiao, He Zhang, Yaping Dong, Shuai Shang, Guanning Ji, Ruozhen Geng, and Renhui Li. 2024. "Benthic Microbes on the Shore of Southern Lake Taihu Exhibit Ecological Significance and Toxin-Producing Potential Through Comparison with Planktonic Microbes" Water 16, no. 21: 3155. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16213155
APA StyleZhao, Q., Wu, B., Zuo, J., Xiao, P., Zhang, H., Dong, Y., Shang, S., Ji, G., Geng, R., & Li, R. (2024). Benthic Microbes on the Shore of Southern Lake Taihu Exhibit Ecological Significance and Toxin-Producing Potential Through Comparison with Planktonic Microbes. Water, 16(21), 3155. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16213155







