The Israeli Water Policy and Its Challenges During Times of Emergency
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Conservation and Protection of Natural Water Sources: This includes lakes, rivers, and groundwater sources and is aimed at ensuring these resources remain available for future generations.
- Development and Implementation of Efficient Water Use Practices: This involves promoting the use of water-efficient technologies, utilizing recycled water, and implementing water reuse systems to optimize water usage.
- Protection of Water Quality: Innovative technologies are adopted to enhance drinking water cleanliness, improve groundwater quality, and similar measures to safeguard water quality.
1.1. Water Management Policy in Israel
1.1.1. Israel’s Water Crisis in the Early 2000s
1.1.2. Seawater Desalination Policy as a Solution for the Crisis in Israel’s Water Sector
1.2. Political Aspects Related to Managing Israel’s Water Sector
1.3. The Water Sector in Times of Emergency as Reflected in the Research Literature
2. Methodology
3. Findings
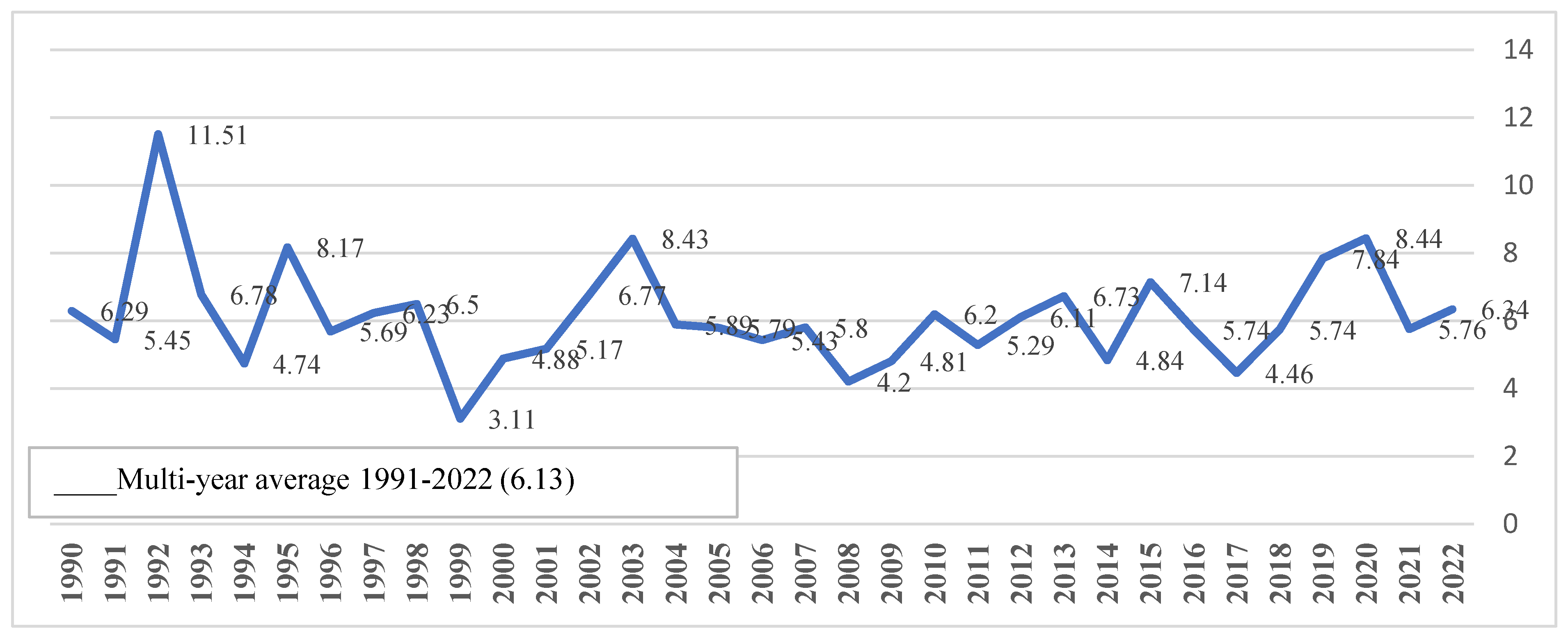
3.1. Production and Consumption of Water in the Israeli Economy
3.2. Natural Sources of Water Production in Israel
3.2.1. The Coastal Aquifer (Groundwater)
3.2.2. The Sea of Galilee
3.2.3. Artificial Sources of Water Production in Israel
3.2.4. The Amount of Desalinated Water of All Drinking Water Produced in Israel in the Last Decade
3.3. Israel’s Public Policy on Managing the Water Sector in an Emergency
3.4. Neglect of Natural Sources for Producing Water
4. Conclusions
Seawater Desalination Plants as an Asset in Times of Routine and a Burden in Emergencies
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- O’sullivan, J.N. Demographic Delusions: World Population Growth Is Exceeding Most Projections and Jeopardising Scenarios for Sustainable Futures. World 2023, 4, 545–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.B.; Kim, S.H.; Bae, D.H. The impacts of global warming on arid climate and drought features. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2023, 152, 693–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripple, W.J.; Wolf, C.; Gregg, J.W.; Levin, K.; Rockström, J.; Newsome, T.M.; Betts, M.G.; Huq, S.; Law, B.E.; Kemp, L.; et al. World Scientists’ Warning of a Climate Emergency 2022. BioScience 2022, 72, 1149–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Peña-Angulo, D.; Beguería, S.; Domínguez-Castro, F.; Tomás-Burguera, M.; Noguera, I.; Gimeno-Sotelo, L.; El Kenawy, A. Global drought trends and future projections. Philos. Trans. R Soc. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2022, 380, 20210285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iglesias, A.; Garrote, L.; Flores, F.; Moneo, M. Challenges to Manage the Risk of Water Scarcity and Climate Change in the Mediterranean. Water Resour. Manag. 2007, 21, 775–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feitelson, E.; Rosenthal, G. Desalination, space and power: The ramifications of Israel’s changing water geography. Geoforum. 2012, 43, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenne, A.; Hoffman, D.; Levi, E. Quantifying the actual benefits of large-scale seawater desalination in Israel. Desalination Water Treat. 2013, 51, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoeberl, M.R.; Dessler, A.E. Dehydration of the stratosphere. Atmospheric Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 8433–8446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochman, A.; Kunin, P.; Alpert, P.; Harpaz, T.; Saaroni, H.; Rostkier-Edelstein, D. Weather regimes and analogues downscaling of seasonal precipitation for the 21st century: A case study over Israel. Int. J. Climatol. 2020, 40, 2062–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwolatzky, T.; Brodsky, J.; Azaiza, F.; Clarfield, A.M.; Jacobs, J.M.; Litwin, H. Coming of age: Health-care challenges of an ageing population in Israel. Lancet 2017, 389, 2542–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, I.; Tsairi, Y.; Roth, M.B.; Tal, A.; Mau, Y. Effects of population growth on Israel’s demand for desalinated water. NPJ Clean Water. 2022, 5, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinreb, A. Demographic Trends in Israel: An Overview; State of the Nation Report: Society, Economy and Policy: Jerusalem, Israel, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Weinreb, A.; Shraberman, K. Demographic Trends in Israel: An Overview; State of the Nation Report: Society, Economy and Policy: Jerusalem, Israel, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Meir, M.B. Water Management Policy in Israel: A Comprehensive Approach. In Studies in Environmental Science [Internet]; Isaac, J., Shuval, H., Eds.; Water and Peace in the Middle East; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1994; Volume 58, pp. 33–39. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0166111608713980 (accessed on 26 November 2023).
- Kartin, A. Water scarcity problems in Israel. GeoJournal 2001, 53, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feitelson, E. Political Economy of Groundwater Exploitation: The Israeli Case. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2005, 21, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vengosh, A.; Rosenthal, E. Saline groundwater in Israel: Its bearing on the water crisis in the country. J. Hydrol. 1994, 156, 389–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feitelson, E.; Gazit, T.; Fischhendler, I. The Role of “Red Lines” in Safeguarding the Sea of Galilee (Lake Kinneret); Charles H. Revson Foundation: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wine, M.L.; Rimmer, A.; Laronne, J.B. Agriculture, diversions, and drought shrinking Galilee Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiritos, E.; Lipchin, C. Desalination in Israel. In Water Policy in Israel: Context, Issues and Options [Internet]; Becker, N., Ed.; Global Issues in Water Policy; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 101–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, N.; Lavee, D.; Katz, D. Desalination and Alternative Water-Shortage Mitigation Options in Israel: A Comparative Cost Analysis. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2010, 2, 1042–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garb, Y. Desalination in Israel: Status, Prospects, and Contexts. In Water Wisdom [Internet]; Tal, A., Rabbo, A.A., Eds.; Rutgers University Press: New Brunswick, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 238–245. Available online: https://www.degruyter.com/document/doi/10.36019/9780813549774-034/html (accessed on 28 November 2023).
- Teschner, N.; Garb, Y.; Paavola, J. The Role of Technology in Policy Dynamics: The Case of Desalination in Israel. Environ. Policy Gov. 2013, 23, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kew, S.F.; Philip, S.Y.; Jan Van Oldenborgh, G.; Van Der Schrier, G.; Otto, F.E.L.; Vautard, R. The Exceptional Summer Heat Wave in Southern Europe 2017. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2019, 100, S49–S53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lhotka, O.; Kyselý, J. The 2021 European Heat Wave in the Context of Past Major Heat Waves. Earth Space Sci. 2022, 9, e2022EA002567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Herrera, R.; Díaz, J.; Trigo, R.M.; Luterbacher, J.; Fischer, E.M. A Review of the European Summer Heat Wave of 2003. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 40, 267–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassardo, C.; Mercalli, L.; Berro, D. Characteristics of the Summer 2003 Heat Wave in Piedmont, Italy, and its Effects on Water Resources. J. Korean Meteorol. Soc. 2007, 43, 195–221. [Google Scholar]
- Pollastrini, M.; Bussotti, F.; Iacopetti, G.; Puletti, N.; Mattioli, W.; Selvi, F. Forest Tree Defoliation and Mortality in Tuscany (Central Italy) Connected to Extreme Drought and Heat Wave in the 2017 Summer: A Preliminary Report; EGU: Vienna, Austria, 2018; p. 9958. [Google Scholar]
- Poumadère, M.; Mays, C.; Le Mer, S.; Blong, R. The 2003 Heat Wave in France: Dangerous Climate Change Here and Now. Risk Anal. 2005, 25, 1483–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daghara, A.; Al-Khatib, I.A.; Al-Jabari, M. Quality of Drinking Water from Springs in Palestine: West Bank as a Case Study. J. Environ. Public Health 2019, 2019, e8631732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, F.M.; Arlosoroff, S.; Eckstein, Z.; Haddadin, M.; Hamati, S.G.; Huber-Lee, A.; Jarrar, A.; Jayyousi, A.; Shamir, U.; Wesseling, H. Optimal water management and conflict resolution: The Middle East Water Project. Water Resour. Res. 2002, 38, 25-1–25-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gvirtzman, H. The Israeli-Palestinian Water Conflict: An Israeli Perspective; Begin-Sadat Center for Strategic Studies: Ramat Gan, Israel, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Selby, J. Cooperation, Domination and Colonisation: The Israeli-Palestinian Joint Water Committee. Water Altern. 2013, 6, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Weinthal, E. Water as a Basic Human Right within the Israeli-Palestinian Conflict; American Diplomacy Publishers: Chapel Hill, NC, USA, 2016; Available online: https://go.gale.com/ps/i.do?p=AONE&sw=w&issn=10948120&v=2.1&it=r&id=GALE%7CA577909951&sid=googleScholar&linkaccess=abs (accessed on 3 December 2023).
- Elmusa, S.S. The Jordan-Israel Water Agreement: A Model or an Exception? J. Palest. Stud. 1995, 24, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, N.; Ward, F.A. Adaptive water management in Israel: Structure and policy options. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2015, 31, 540–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohner, A.K.; Rhoades, C.C.; Wilkerson, P.; Rosario-Ortiz, F.L. Wildfires Alter Forest Watersheds and Threaten Drinking Water Quality. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 1234–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landsman, M.R.; Rowles, L.S.; Brodfuehrer, S.H.; Maestre, J.P.; A Kinney, K.; Kirisits, M.J.; Lawler, D.F.; E Katz, L. Impacts of Hurricane Harvey on drinking water quality in two Texas cities. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 124046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, T.; Ward, N.; Julian, P.; Reddy, K.R.; Osborne, T.Z. Impacts of Hurricane Disturbance on Water Quality across the Aquatic Continuum of a Blackwater River to Estuary Complex. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njogu, H.W. Effects of floods on infrastructure users in Kenya. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2021, 14, e12746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antwi, S.H.; Getty, D.; Linnane, S.; Rolston, A. COVID-19 water sector responses in Europe: A scoping review of preliminary governmental interventions. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 762, 143068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowen, C.L. Emergency Drinking Water Supply Challenges for Public Health; ASCE: Reston, VA, USA, 2012; pp. 3811–3816. [Google Scholar]
- Barnaby, W. Do nations go to war over water? Nature 2009, 458, 282–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gleick, P.H. Water, War & Peace in the Middle East. Environ. Sci. Policy Sustain. Dev. 1994, 36, 6–42. [Google Scholar]
- Shultz, J. Bolivia: The Water War Widens. NACLA Rep. Am. 2003, 36, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starr, J.R. Water Wars. Foreign Policy 1991, 82, 17–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schillinger, J.; Özerol, G.; Güven-Griemert, Ş.; Heldeweg, M. Water in war: Understanding the impacts of armed conflict on water resources and their management. WIREs Water 2020, 7, e1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeitoun, M.; Eid-Sabbagh, K.; Loveless, J. The analytical framework of water and armed conflict: A focus on the 2006 Summer War between Israel and Lebanon. Disasters 2014, 38, 22–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auerbach, O.; Karassin, A.O. Management of Water Resources in Israel. In Pathways to Sustainability; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Kislev, Y. The Water Economy of Israel. 2001. Available online: https://ageconsearch.umn.edu/record/14995/files/dp0111.pdf (accessed on 30 November 2023).
- Plaut, S. Water Policy in Israel. Policy Studies 2000, 47, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Mizrahi, S. The Political Economy of Water Policy in Israel: Theory and Practice. J. Comp. Policy Anal. Res. Pract. 2004, 6, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, R.P.; Hall, R. Mixing Methods in Social Research: Qualitative, Quantitative and Combined Methods; SAGE: Newcastle upon Tyne, UK, 2020; 273p. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, E. The Nature of Israel’s Public Policy Aimed at Curbing the Rise in Property Prices from 2008–2015, as a Derivative of the Country’s Governance Structure. Econ. Sociol. 2016, 9, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, E. Traffic congestion on Israeli roads: Faulty public policy or preordained? Isr. Aff. 2019, 25, 350–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, E. Israel’s public policy for long-term care services. Isr. Aff. 2020, 26, 889–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelik, S.; Çorbacıoğlu, S. Multiple Approaches in Public Policy Analysis: A Critique of Positivist Approach. Sos. Bilim. Dergisi J. Soc. Sci. 2008, 32, 17. Available online: https://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&profile=ehost&scope=site&authtype=crawler&jrnl=13055143&AN=33767830&h=z5zoAII%2FnbRXaI%2FOexF5QalKxEeu93mStLTQGdJ%2BwIBE8e0QxODHDt9XHUtOuo0rqyalS5fDDy10qrb7nlKI0Q%3D%3D&crl=c (accessed on 21 December 2023).
- Cohen, E. Political instability in Israel over the last decades—Causes and consequences. Cogent. Soc. Sci. 2024, 10, 2293316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cohen, E. The Israeli Water Policy and Its Challenges During Times of Emergency. Water 2024, 16, 2995. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16202995
Cohen E. The Israeli Water Policy and Its Challenges During Times of Emergency. Water. 2024; 16(20):2995. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16202995
Chicago/Turabian StyleCohen, Erez. 2024. "The Israeli Water Policy and Its Challenges During Times of Emergency" Water 16, no. 20: 2995. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16202995
APA StyleCohen, E. (2024). The Israeli Water Policy and Its Challenges During Times of Emergency. Water, 16(20), 2995. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16202995





