Groundwater Depletion and Degradation in the North China Plain: Challenges and Mitigation Options
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Overview of North China Plain (NCP)
3. Environmental Challenges
3.1. Groundwater Depletion
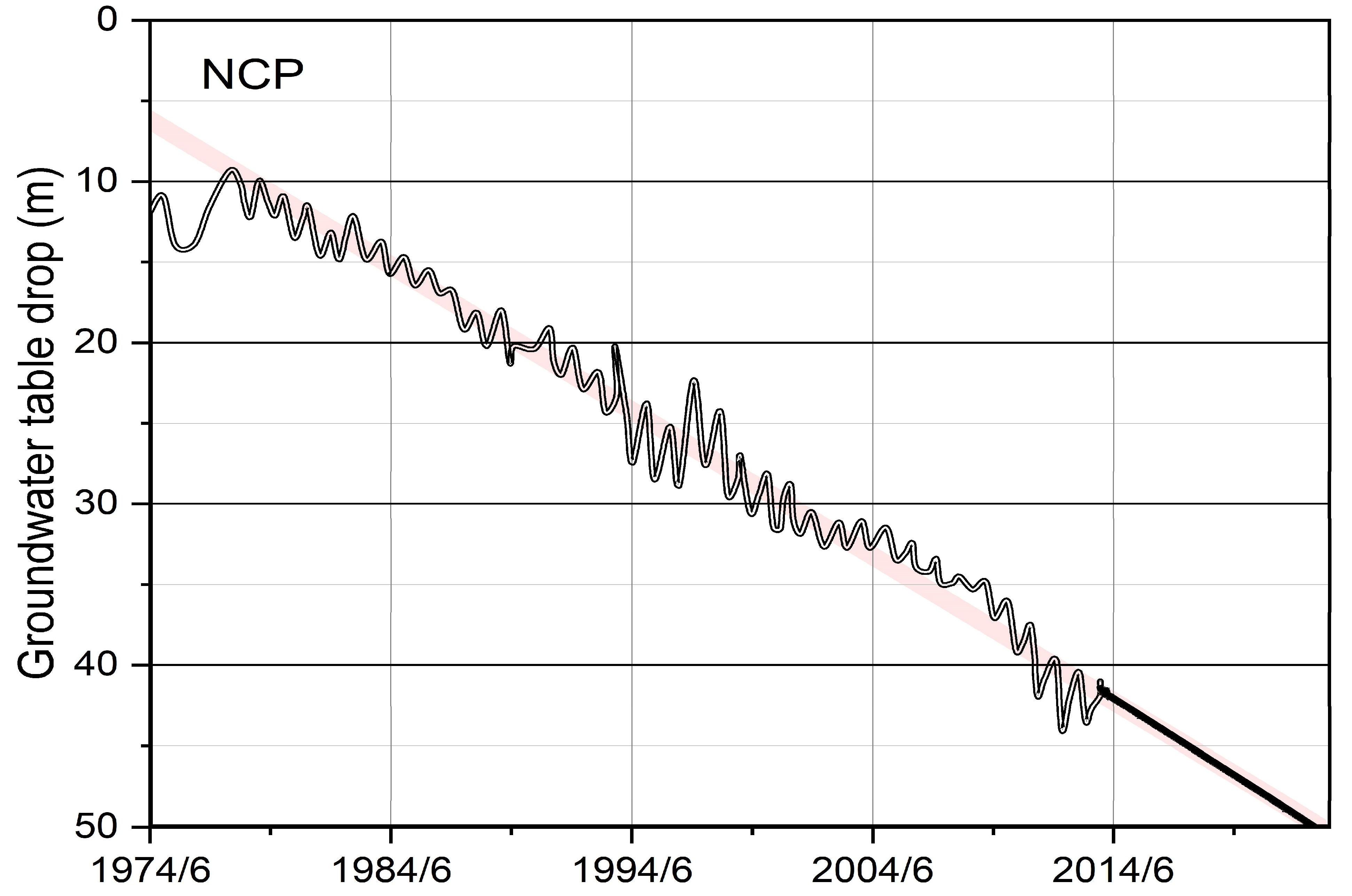
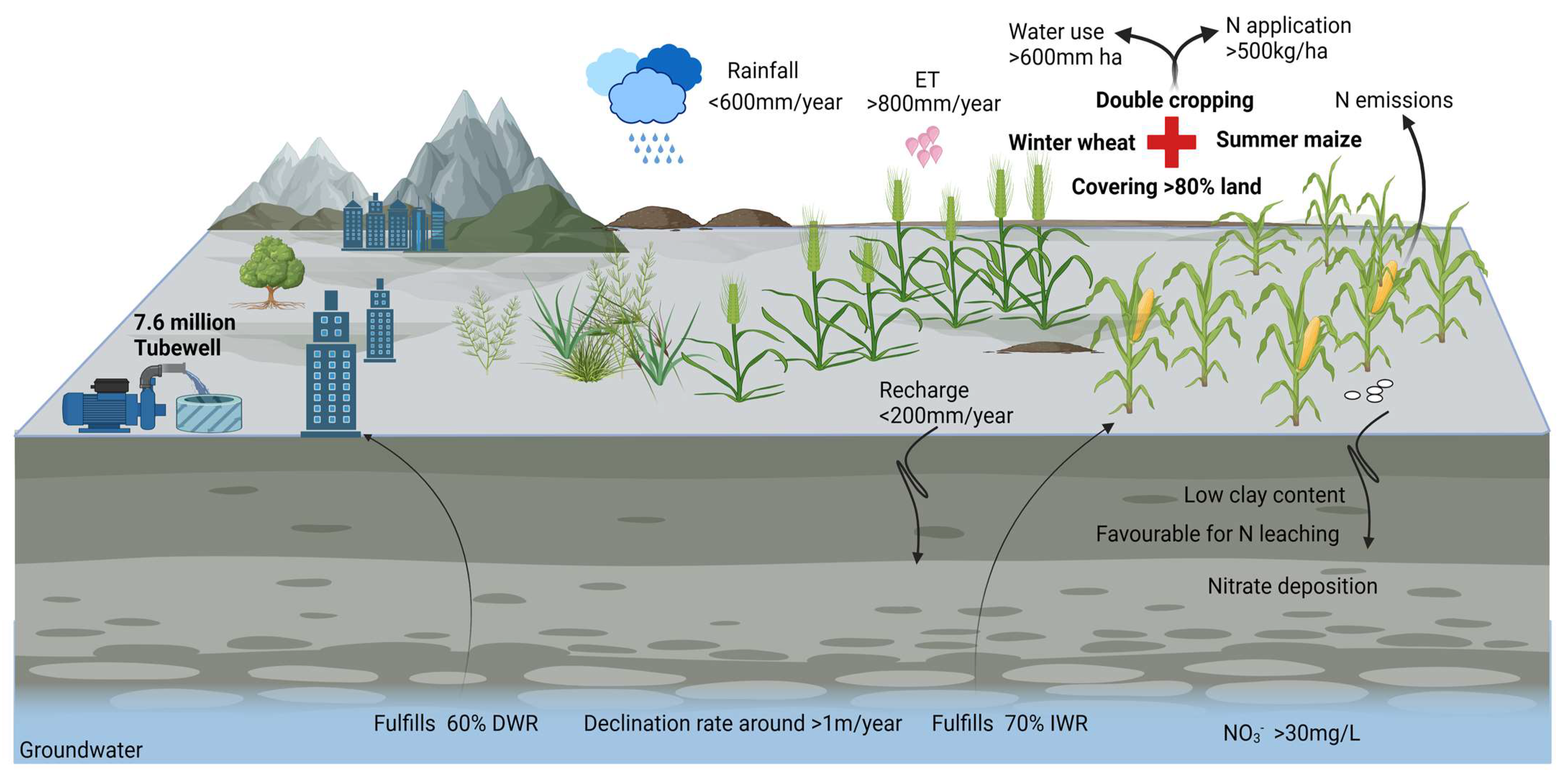
3.2. Groundwater Degradation
| GW Depletion | Location | NO3− Level | Location | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.10 m yr−1 | Hebei to Tianjin | 2.18 mg L−1 | Eastern Taihang Mountains | [67,68] |
| 3.83 m yr−1 | Zhangjiakou | 178.7 mg L−1 | Hutuo River Valley Plain | [69,70] |
| 1.30 m yr−1 | Luancheng | 10.34 mg L−1 | Baiyangdian Lake Area | [71,72] |
| 0.33 m yr−1 | Hebei | 1.840 mg L−1 | Beijing Urban Sides | [38,73] |
| 1.70 m yr−1 | Shijiazhuang | 70.40 mg L−1 | Rural Beijing | [74,75] |
| 0.59 m yr−1 | Beijing and Tianjin | 124.4 mg L−1 | Hutuo River Plain | [37,76] |
| 1.00 m yr−1 | WR | 6.230 mg L−1 | Pinggu District | [77,78] |
| 1.60 m yr−1 | Hebei | 50.00 mg L−1 | WR | [28,79] |
| 1.10 m yr−1 | Luancheng | 184.6 mg L−1 | Shandong | [66,80] |
| 1.14 m yr−1 | Taihang Mountain | 47.70 mg L−1 | Catchment Areas of Hutuo | [81,82] |
| 1.15 m yr−1 | Hufu Plain | 134.8 mg L−1 | Baiyang Lake Area | [83,84] |
| 1.25 m yr−1 | WR | 31.60 mg L−1 | Beiyishui Watershed | [30,85] |
| 1.50 m yr−1 | Luancheng | 10.00 mg L−1 | Luoyang Basin Area | [86,87] |
| 1.00 m yr−1 | WR | 29.60 mg L−1 | Yellow River Sides | [87,88] |
| 1.07 m yr−1 | Taihang Mountains | 13.40 mg L−1 | WR | [89,90] |
| 0.71 m yr−1 | Piedmont Plain | 56.80 mg L−1 | Tangshan | [91,92] |
| 0.80 m yr−1 | Xian | 9.370 mg L−1 | Hebei | [93,94] |
| 1.21 m yr−1 | Hebei | 13.80 mg L−1 | Beijing | [95,96] |
| 1.00 m yr−1 | WR | 10.00 mg L−1 | Huantai | [97,98] |
| 0.45 m yr−1 | Hebei | 20.00 mg L−1 | Quzhou | [99,100] |
| 0.87 m yr−1 | Ningjin | 20.00 mg L−1 | Shijiazhuang | [101,102] |
| 1.10 m yr−1 | Shijiazhuang | 45.00 mg L−1 | Beijing and Surroundings | [103,104] |
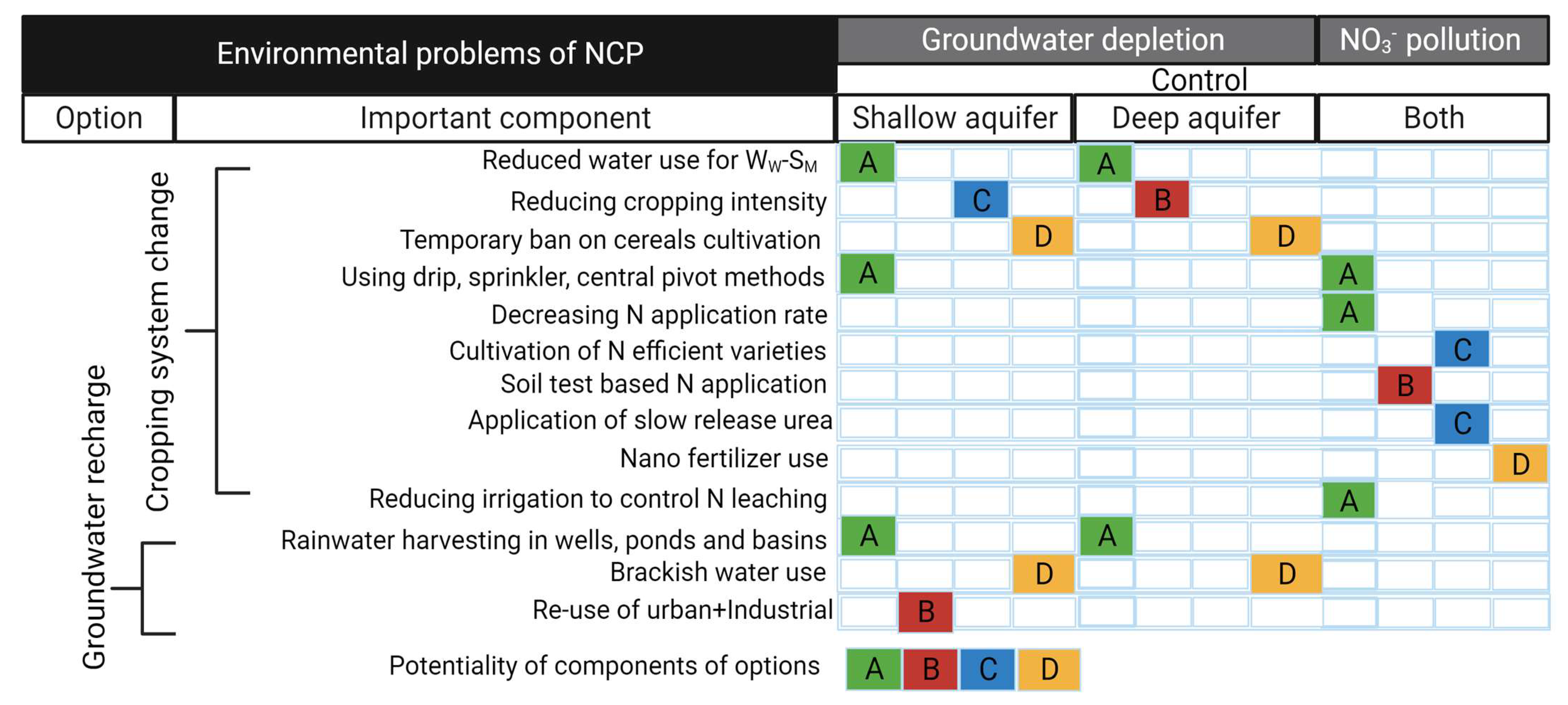
4. Mitigation Options
4.1. Cropping System Change Option
4.1.1. Groundwater Neutral Cropping Pattern
4.1.2. Groundwater-Friendly Farming Practices
4.2. Groundwater Recharge Option
| Recharge | Area | Reference | Recharge | Area | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 102.0 mm yr−1 | WR | [65] | 177.0 mm yr−1 | Lacustrine plain sites | [152] |
| 65.00 mm yr−1 | WR | [99] | 90.00 mm yr−1 | WR | [144] |
| 120.0 mm yr−1 | Central plain | [140] | 108.0 mm yr−1 | Liaocheng city | [153] |
| 200.0 mm yr−1 | WR | [141] | 85.80 mm yr−1 | Luancheng | [154] |
| 92.80 mm yr−1 | Central plain | [142] | 168.0 mm yr−1 | Weishan district | [155] |
| 130.0 mm yr−1 | WR | [156] | 126.8 mm yr−1 | Shijiazhuang | [157] |
| 188.0 mm yr−1 | Cangzhou | [158] | 63.80 mm yr−1 | Tongzhou | [159] |
| 180.0 mm yr−1 | Piedmont plain | [160] | 138.7 mm yr−1 | Hebei | [161] |
| 150.0 mm yr−1 | Taihang mountains | [133] | 124.3 mm yr−1 | Hengshui | [162] |
| 134.0 mm yr−1 | Luancheng | [163] | 175.0 mm yr−1 | Hebei | [164] |
5. Conclusions and Future Perspective
- ▪
- The government should take some steps to control excessive groundwater pumping and the application of nitrogen fertilizers.
- ▪
- Farmers would be facilitated with highly efficient irrigation and nitrogen application systems.
- ▪
- Control measures for NO3− leaching in the field should be well studied via large-scale research.
- ▪
- The groundwater recharge rate should be determined with the response to rainfall intensity throughout the region.
- ▪
- Artificial recharge options should be explored in every part of the region, the actual amount of water should be quantified, and safe utilization should be ensured via modern technology to minimize the risk of NO3− transport in the groundwater.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ravindiran, G.; Rajamanickam, S.; Sivarethinamohan, S.; Karupaiya Sathaiah, B.; Ravindran, G.; Muniasamy, S.K.; Hayder, G. A Review of the Status, Effects, Prevention, and Remediation of Groundwater Contamination for Sustainable Environment. Water 2023, 15, 3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Shady, A.; Siddique, M.S.; Yu, W. A Critical Review of Innovations and Perspectives for Providing Adequate Water for Sustainable Irrigation. Water 2023, 15, 3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinecke, R.; Gnann, S.; Stein, L.; Bierkens, M.; de Graaf, I. Global Accessibility of Groundwater Remains Highly Uncertain. 2023. Available online: https://eartharxiv.org/repository/view/5003/ (accessed on 1 January 2024).
- Rodrigues do Nascimento, F. Global Environmental Change, Climate Crisis and Desertification. In Global Environmental Changes, Desertification and Sustainability; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R. Fresh Water Availability and Its Global Challenge. Br. J. Multidiscip. Adv. Stud. 2023, 4, 1–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alijanzadeh Maliji, B.; Babayeemehr, A.; Rohani, K.; Mehrabani, S.; Aghajanpour, F. Role of the World Health Organization in Management of Gastrointestinal Diseases Caused by Contaminated Water in Children in the Middle East: A Review Article. J. Pediatr. Rev. 2023, 11, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmel, R.D.; Chaubey, I.; Ale, S.; Nejadhashemi, A.P.; Irmak, S.; Dejonge, K.C.; Evett, S.R.; Barnes, E.M.; Catley-Carlson, M.; Hunt, S.; et al. Perspectives on Global Water Security. Trans. ASABE 2023, 63, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagar, R.; Chandrappa, U. Environmental Law and Sustainable Development: A Comparative Analysis. 2023. Available online: www.ssrn.com (accessed on 1 January 2024).
- Gaaloul, N. Groundwater Quality in Arid Environments. In Clean Water and Sanitation; Gaaloul, N., Eslamian, S., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Yang, T.; Wang, G.; Liu, X.; Xu, N.; Stouthamer, E.; Yin, Y.; Wang, H.; Yan, X.; Huang, X. Control and Prevent Land Subsidence Caused by Foundation Pit Dewatering in a Coastal Lowland Megacity: Indicator Definition, Numerical Simulation, and Regression Analysis. Environ. Earth Sci. 2023, 82, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wu, M.; Duan, Z.; Zha, Y.; Wang, S.; Yang, L.; Zou, L.; Zheng, M.; Chen, P.; Cao, W.; et al. Forecasting the Human and Climate Impacts on Groundwater Resources in the Irrigated Agricultural Region of North China Plain. Hydrol. Process 2023, 37, e14853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, P.; He, J.; Liu, D.; Wang, M.; Wang, M.; Xia, S. Hydrochemical Characteristics, Water Quality, and Evolution of Groundwater in Northeast China. Water 2023, 15, 2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuhong, F.; Yaci, L.; Yasong, L.; Xilin, B.; Pengwei, Z.; Yuhong, F.; Yaci, L.; Yasong, L.; Xilin, B.; Pengwei, Z. Prospect of Groundwater Pollution Remediation Methods and Technologies in China. Geol. China 2022, 49, 420–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statista. Statista Account Overview. Available online: https://www.statista.com/accounts/pa (accessed on 11 January 2024).
- Huang, D.; Chen, Y.; Liu, T.; Liu, M. A GIS-Based Typological Interpretation of Cultivated Land Loss: A Spatiotemporal Analysis of Tai’an Prefecture in the North China Plain. Land 2023, 12, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Zhang, X.; Lal, R.; Zhang, F.; Chen, X.; Niu, Z.; Han, L.; Song, W. Groundwater Depletion by Agricultural Intensification in China’s HHH Plains, Since 1980s. In Advances in Agronomy; Academic Press Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; Volume 135, pp. 59–106. ISBN 9780128046937. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, Z.; Li, Z.; Yu, G.; Chen, Z.; Shi, P.; Qiao, Y.; Du, K.; Tian, C.; Zhao, F.H.; Leng, P.; et al. Climate Controls over Phenology and Amplitude of Net Ecosystem Productivity in a Wheat-Maize Rotation System in the North China Plain. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2023, 333, 109411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Data Access Viewer. NASAClimate POWER. Available online: https://power.larc.nasa.gov/data-access-viewer/ (accessed on 24 December 2023).
- Mao, R.; Fitzpatrick, R.W.; Liu, X.; Davies, P.J. Chemical Properties of Selecte Soils from the North China Plain. ACIAR Monogr. Ser. 2015, 84, 173–186. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, T.; Ju, X.; Yang, H. Nitrate Leaching in a Winter Wheat-Summer Maize Rotation on a Calcareous Soil as Affected by Nitrogen and Straw Management. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. Available online: http://www.stats.gov.cn/english/ (accessed on 11 May 2021).
- Meng, Q.; Sun, Q.; Chen, X.; Cui, Z.; Yue, S.; Zhang, F.; Römheld, V. Alternative Cropping Systems for Sustainable Water and Nitrogen Use in the North China Plain. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 146, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Qiao, Y.; Li, X.; Xue, Y.; Wang, N.; Yan, W.; Xue, Y.; Cui, Z.; van der Werf, W. Moderation of Nitrogen Input and Integration of Legumes via Intercropping Enable Sustainable Intensification of Wheat-Maize Double Cropping in the North China Plain: A Four-Year Rotation Study. Agric. Syst. 2023, 204, 103540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Yu, Q.; Wang, E.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, G.; Wang, J.; Li, L. Soil Nitrate Accumulation, Leaching and Crop Nitrogen Use as Influenced by Fertilization and Irrigation in an Intensive Wheat-Maize Double Cropping System in the North China Plain. Plant Soil. 2006, 284, 335–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Lu, F.; Pan, J.; Cui, Z.; Zou, C.; Chen, X.; He, M.; Wang, Z. The Effects of Cultivar and Nitrogen Management on Wheat Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency in the North China Plain. Field Crops Res. 2015, 171, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Liao, T.; Fang, G.; Ren, K.; Zhang, S. Exploring Optimal Joint Operating Rules for Large-Scale Inter-Basin Water Transfer Projects with Multiple Water Sources, Diversion Routes, and Water Demand Areas. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2023, 49, 101504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Wang, S.; Tian, L.; Sun, H.; Liu, X. Response of Soil Nitrate Accumulation and Leaching to Layered Soil Profiles in the Lowland Area of the North China Plain. J. Soil. Sci. Plant Nutr. 2023, 23, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zheng, W.; Currell, M.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Lv, M. Relationship between Land-Use and Sources and Fate of Nitrate in Groundwater in a Typical Recharge Area of the North China Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, M.H.; Jones, R.R.; Brender, J.D.; de Kok, T.M.; Weyer, P.J.; Nolan, B.T.; Villanueva, C.M.; van Breda, S.G. Drinking Water Nitrate and Human Health: An Updated Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2018, 15, 1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, X.; Xin, L.; Tan, M.; Li, S.; Wang, R. Ecological Compensation for Winter Wheat Abandonment in Groundwater Over-Exploited Areas in the North China Plain. J. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 1463–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hou, D.; O’Connor, D.; Shen, Z.; Shi, P.; Ok, Y.S.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Wen, Y.; Luo, M. Lead Contamination in Chinese Surface Soils: Source Identification, Spatial-Temporal Distribution and Associated Health Risks. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 1386–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, G.; Chen, Y.; Sui, P.; Pacenka, S.; Steenhuis, T.S.; Siddique, K.H.M. Reduced Groundwater Use and Increased Grain Production by Optimized Irrigation Scheduling in Winter Wheat–Summer Maize Double Cropping System—A 16-Year Field Study in North China Plain. Field Crops Res. 2022, 275, 108364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalczyk, A.; Kersebaum, K.C.; Dauck, H.P.; Roelcke, M.; Yue, S.C.; Chen, X.P.; Zhang, F.S. Quantifying Nitrogen Loss and Water Use via Regionalization and Multiple-Year Scenario Simulations in the North China Plain. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2020, 183, 718–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, M. Review of Soil Dissolved Organic Nitrogen Cycling: Implication for Groundwater Nitrogen Contamination. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 5, 132713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinzelbach, W.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, N. Groundwater Overexploitation in the North China Plain: A Path to Sustainability; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, D.; Tao, F. Contributions of Cultivars, Management and Climate Change to Winter Wheat Yield in the North China Plain in the Past Three Decades. Eur. J. Agron. 2014, 52, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Shen, Y.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, D. Evaluating Water Conservation Effects Due to Cropping System Optimization on the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Plain, China. Agric. Syst. 2018, 159, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Qin, W.; Hu, K.; Tao, H.; Li, B. Modelling Groundwater Level Dynamics under Different Cropping Systems and Developing Groundwater Neutral Systems in the North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 213, 732–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.L.; Chen, Y.Q.; Steenhuis, T.S.; Pacenka, S.; Gao, W.S.; Ma, L.; Zhang, M.; Sui, P. Mitigating Groundwater Depletion in North China Plain with Cropping System That Alternate Deep and Shallow Rooted Crops. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Shen, Y. Estimation of Agricultural Water Consumption from Meteorological and Yield Data: A Case Study of Hebei, North China. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.A.; Shen, Y.; Stricevic, R.; Pei, H.; Sun, H.; Amiri, E.; Penas, A.; del Rio, S. Evaluation of the FAO AquaCrop Model for Winter Wheat on the North China Plain under Deficit Irrigation from Field Experiment to Regional Yield Simulation. Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 135, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Jiang, S.; Ren, L.; Tan, H.; Ta, W.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, L.; Duan, Z. Spatiotemporal Changes of Terrestrial Water Storage and Possible Causes in the Closed Qaidam Basin, China Using GRACE and GRACE Follow-On Data. J. Hydrol. 2021, 598, 126274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X. Satellite-Based Estimates of Groundwater Depletion in the Badain Jaran Desert, China. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, W.; Zhong, M.; Lemoine, J.M.; Biancale, R.; Hsu, H.T.; Xia, J. Evaluation of Groundwater Depletion in North China Using the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) Data and Ground-Based Measurements. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 2110–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; Hu, L.; Jiao, J.J. Evaluation of Groundwater Storage Variations in Northern China Using GRACE Data. Geofluids 2017, 2017, 8254824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Jha, S.; Ramatshaba, T.S.; Wang, G.; Liang, Y.; Liu, H.; Gao, Y.; Duan, A. Response of Growth, Yield and Water Use Efficiency of Winter Wheat to Different Irrigation Methods and Scheduling in North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 217, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Biswas, A.; Bennett, E.M. Identifying Hotspots and Representative Monitoring Area of Groundwater Changes with Time Stability Analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 667, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chen, Y.; Pacenka, S.; Gao, W.; Zhang, M.; Sui, P.; Steenhuis, T.S. Recharge and Groundwater Use in the North China Plain for Six Irrigated Crops for an Eleven Year Period. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0115269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts Chinese Farms Cause More Pollution than Factories, Says Official Survey|Farming|The Guardian. Available online: https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2010/feb/09/china-farms-pollution (accessed on 11 May 2021).
- Wang, L.; Leghari, S.J.; Wu, J.; Wang, N.; Pang, M.; Jin, L. Interactive Effects of Biochar and Chemical Fertilizer on Water and Nitrogen Dynamics, Soil Properties and Maize Yield under Different Irrigation Methods. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1230023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Xu, C.C.; Wu, Y.; Wang, M.; Chen, F. Water Degradation Footprint of Crop Production in Hebei Province. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2018, 37, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Bai, Y.; Gao, J.; Li, J. Driving Factors on Accumulation of Cadmium, Lead, Copper, Zinc in Agricultural Soil and Products of the North China Plain. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 7429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leghari, S.J.; Wahocho, N.A.; Laghari, G.M.; HafeezLaghari, A.; MustafaBhabhan, G.; HussainTalpur, K.; Bhutto, T.A.; Wahocho, S.A.; Lashari, A.A. Role of Nitrogen for Plant Growth and Development: A Review. Adv. Environ. Biol. 2016, 10, 209–219. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.N.; Mobin, M.; Abbas, Z.K.; Alamri, S.A. Fertilizers and Their Contaminants in Soils, Surface and Groundwater; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 1–5, ISBN 9780128096659. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, X.T.; Xing, G.X.; Chen, X.P.; Zhang, S.L.; Zhang, L.J.; Liu, X.J.; Cui, Z.L.; Yin, B.; Christie, P.; Zhu, Z.L.; et al. Reducing Environmental Risk by Improving N Management in Intensive Chinese Agricultural Systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 3041–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, B.; Fa-Yun, H.; Xu, Q.M.; Bin, Y.; Cai, G.X. Denitrification Losses and N2O Emissions from Nitrogen Fertilizer Applied to a Vegetable Field. Pedosphere 2006, 16, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zheng, L.; Gu, S.; Shi, Y.; Liang, L.; Meng, F.; Guo, Y.; Ju, X.; Wu, W. Soil Nitrate Accumulation and Leaching in Conventional, Optimized and Organic Cropping Systems. Plant Soil. Environ. 2018, 64, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Yan, G.; Zheng, X.; Wang, R.; Liu, C.; Butterbach-Bahl, K. Straw Return Reduces Yield-Scaled N2O plus NO Emissions from Annual Winter Wheat-Based Cropping Systems in the North China Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 590–591, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Hu, K.; Li, B.; He, M.; Zhang, J. Evaluation of Water and Nitrogen Use Efficiencies in a Double Cropping System under Different Integrated Management Practices Based on a Model Approach. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 159, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ren, L.; Wan, L. Assessing the Trade-off between Shallow Groundwater Conservation and Crop Production under Limited Exploitation in a Well-Irrigated Plain of the Haihe River Basin Using the SWAT Model. J. Hydrol. 2018, 567, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ju, X.; Zhang, Y.; He, C.; Kopsch, J.; Fusuo, Z. Nitrogen Deposition in Agroecosystems in the Beijing Area. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2006, 113, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroder, J.L.; Zhang, H.; Girma, K.; Raun, W.R.; Penn, C.J.; Payton, M.E. Soil Acidification from Long-Term Use of Nitrogen Fertilizers on Winter Wheat. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2011, 75, 957–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.C.; Wu, J.W.; Cai, S.Y.; Yang, J.Z. Characteristics of Groundwater Recharge on the North China Plain. Groundwater 2014, 52, 798–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Chen, Y.; Pacenka, S.; Gao, W.; Ma, L.; Wang, G.; Yan, P.; Sui, P.; Steenhuis, T.S. Effect of Diversified Crop Rotations on Groundwater Levels and Crop Water Productivity in the North China Plain. J. Hydrol. 2015, 522, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Pan, Y.; Zheng, L.; Li, X.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, C.; Huang, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhou, C. Long-Term Groundwater Storage Changes and Land Subsidence Development in the North China Plain (1971–2015). Hydrogeol. J. 2018, 26, 1417–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, S.; Wang, Z. Optimizing Single Irrigation Scheme to Improve Water Use Efficiency by Manipulating Winter Wheat Sink-Source Relationships in Northern China Plain. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, H.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Wei, J.; Zhao, B. Geodesy and Geodynamics Terrestrial Water Storage Variation in Hebei Plain Area of China, Based on Ground Surface Gravimetry. Geod. Geodyn. 2021, 12, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, P.; Chen, M.; Dong, Z.; Lu, C. Groundwater Quality for Potable and Irrigation Uses and Associated Health Risk in Southern Part of Gu’an County, North China Plain. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 813–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Wang, H.; Liu, C. Long-Term Assessment of Groundwater Resources Carrying Capacity Using GRACE Data and Budyko Model. J. Hydrol. 2020, 588, 125042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, H. Assessment of Sources and Transformation of Nitrate in the Alluvial-Pluvial Fan Region of North China Using a Multi-Isotope Approach. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 89, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.L.; Chen, Y.Q.; Pacenka, S.; Steenhuis, T.S.; Sui, P. Managing Food and Bioenergy Crops with Declining Groundwater Levels in the North China Plain. Field Crops Res. 2019, 234, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Jin, X.; Tang, W.; Meng, X.; Shan, B. Comprehensive Analysis of Nitrogen Distributions and Ammonia Nitrogen Release Fluxes in the Sediments of Baiyangdian Lake, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 76, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, S.; Chen, W.; Wen, X.; Chang, A.C. Integration of HYDRUS-1D and MODFLOW for Evaluating the Dynamics of Salts and Nitrogen in Groundwater under Long-Term Reclaimed Water Irrigation. Irrig. Sci. 2019, 37, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Liu, X.; Shao, L.; Chen, S.; Wang, J.; Dong, X. Impact of Different Cropping Systems and Irrigation Schedules on Evapotranspiration, Grain Yield and Groundwater Level in the North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 211, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, M.; Guo, Q.; Strauss, H.; Wei, R.; Li, S.; Yue, F. Contamination Patterns in River Water from Rural Beijing: A Hydrochemical and Multiple Stable Isotope Study. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 654, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.; Wang, L. Tracing Nitrate Pollution Sources and Transformations in the Over-Exploited Groundwater Region of North China Using Stable Isotopes. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2018, 218, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, G.Y.; Zhang, X.; Yu, X.; Zou, Z. The Increasing Effects in Energy and GHG Emission Caused by Groundwater Level Declines in North China’s Main Food Production Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 203, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhang, C.; Zhong, H.; Zhao, T. The Nitrate Nitrogen in Groundwater of Intensive Agricultural Region in Pinggu District by Sampling and Monitoring for 12 Years. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 452, 022164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Oort, P.A.J.; Wang, G.; Vos, J.; Meinke, H.; Li, B.G.; Huang, J.K.; van der Werf, W. Towards Groundwater Neutral Cropping Systems in the Alluvial Fans of the North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 165, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Jiang, L.H.; Zhang, C.J.; Li, P.; Zhao, T.K. Nitrate-Nitrogen Contamination in Groundwater: Spatiotemporal Variation and Driving Factors under Cropland in Shandong Province, China. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Qingdao, China, 26–29 June 2017; Volume 82, p. 12059. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, E.; Chen, S.; Shao, L. Quantifying the Impact of Irrigation on Groundwater Reserve and Crop Production—A Case Study in the North China Plain. Eur. J. Agron. 2015, 70, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Sun, J.; Wang, J. Natural Background Levels of Chemical Components in Groundwater of Hutuo River Catchment Area, North China Plain. Environ. Forensics 2017, 18, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Fei, Y.; Liu, C.; Feng, H.; Yan, M.; Wang, J. Relationship between Decline of Shallow Groundwater Levels and Irrigated Agriculture on Hufu Plain of North China. Adv. Water Sci. 2013, 24, 228–234. [Google Scholar]
- Brauns, B.; Bjerg, P.L.; Song, X.; Jakobsen, R. Field Scale Interaction and Nutrient Exchange between Surface Water and Shallow Groundwater in the Baiyang Lake Region, North China Plain. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 45, 60–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.; Pang, Z. Groundwater Recharge and Dynamics in Northern China: Implications for Sustainable Utilization of Groundwater. Procedia Earth Planet. Sci. 2013, 7, 369–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chen, C.; Wang, E.; Yu, Q. Modelling the Effects of Climate Variability and Water Management on Crop Water Productivity and Water Balance in the North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 1175–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Liu, B.; Liu, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, L. Impacts of Groundwater Recharge from Rubber Dams on the Hydrogeological Environment in Luoyang Basin, China. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 183457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, F.; Zhang, Q.; Li, J.; Liu, Q. Tracing Nitrate Pollution Sources and Transformation in Surface- and Ground-Waters Using Environmental Isotopes. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 490, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Q.; Hayashi, S. Optimizing Irrigation Management for Wheat to Reduce Groundwater Depletion in the Piedmont Region of the Taihang Mountains in the North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 82, 25–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.; Ge, Y.; Chang, S.X.; Luo, W.; Chang, J. Nitrate in Groundwater of China: Sources and Driving Forces. Glob. Environ. Change 2013, 23, 1112–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Mo, X.; Cai, Y.; Li, X. Analysis on Groundwater Table Drawdown by Land Use and the Quest for Sustainable Water Use in the Hebei Plain in China. Agric. Water Manag. 2005, 75, 38–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Pang, Z.; Yuan, L. Nitrate in Groundwater and the Unsaturated Zone in (Semi)Arid Northern China: Baseline and Factors Controlling Its Transport and Fate. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 70, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Delgado, J.A.; Zhang, X.; Ma, L. Assessment of Groundwater Use by Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) in the Luancheng Xian Region and Potential Implications for Water Conservation in the Northwestern North China Plain. J. Soil. Water Conserv. 2005, 60, 80–88. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, N.; Zhang, G.Y.; Ru, S.H.; Sun, S.Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, G.J. Study on the Content and Influencing Factors of Groundwater Nitrate Nitrogen in Hebei Province. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Biotechnology, iCBEB 2012, Macau, Macao, 28–30 May 2012; pp. 1745–1749. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.Q.; Cai, Y.L. GIS-Based Analysis on Spatio-Temporal Change of Groundwater Level in the Hebei Plain. Acta Scicentiarum Nat. Univ. Pekinesis 2005, 41, 265–272. [Google Scholar]
- Du, L.F.; Zhao, T.K.; Zhang, C.J.; An, Z.Z.; Qiong , W.U.; Liu, B.C.; Peng, L.I. Investigations on Nitrate Pollution of Soil, Groundwater and Vegetable from Three Typical Farmlands in Beijing Region, China. Agric. Sci. China 2011, 10, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Pei, D.; Hu, C. Conserving Groundwater for Irrigation in the North China Plain. Irrig. Sci. 2003, 21, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.X.; Liu, G.D.; Wu, W.L.; Bao, Y.H.; Liu, W.N. Prediction of Agriculture Derived Groundwater Nitrate Distribution in North China Plain with GIS-Based BPNN. Environ. Geol. 2006, 50, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin-sheng, J.; Jing-jie, Y.; Chang-ming, L. Groundwater Regime and Calculation of Yield Response in North China Plain: A Case Study of Luancheng County in Hebei Province. J. Geogr. Sci. 2002, 12, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Huang, Y.; Li, H.; Li, B.; Chen, D.; White, R.E. Spatial Variability of Shallow Groundwater Level, Electrical Conductivity and Nitrate Concentration, and Risk Assessment of Nitrate Contamination in North China Plain. Environ. Int. 2005, 31, 896–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhen, L.; Routray, J.K. Groundwater Resource Use Practices and Implications for Sustainable Agricultural Development in the North China Plain: A Case Study in Ningjin County of Shandong Province, PR China. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2002, 18, 581–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Li-Wu, L. Training Effects of Different Approaching Steps on Overarm Throwing Performance for Boys Aged 7–12 Years. Sports Exerc. Res. 2010, 12, 191–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changming, L.; Jingjie, Y.; Kendy, E. Groundwater Exploitation and Its Impact on the Environment in the North China Plain. Water Int. 2001, 26, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Tang, C.; Sakura, Y.; Yu, J.; Fukushima, Y. Nitrate Pollution from Agriculture in Different Hydrogeological Zones of the Regional Groundwater Flow System in the North China Plain. Hydrogeol. J. 2005, 13, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Wang, S.; Kong, X.; Liu, X.; Sun, H. Modeling and Assessing Feasibility of Long-Term Brackish Water Irrigation in Vertically Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Cultivated Lowland in the North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 211, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, S.; Garduno, H.; Evans, R.; Olson, D.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, W.; Han, Z. Quaternary Aquifer of the North China Plain—Assessing and Achieving Groundwater Resource Sustainability. Hydrogeol. J. 2004, 12, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Zhao, Z.; Liang, L.; Meng, F.; Wu, W.; Guo, Y. Improving Nitrogen and Water Use Efficiency in a Wheat-Maize Rotation System in the North China Plain Using Optimized Farming Practices. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 212, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Ju, X.; Meng, Q.; Cui, Z.; Christie, P.; Chen, X.; Zhang, F. The Impact of Alternative Cropping Systems on Global Warming Potential, Grain Yield and Groundwater Use. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 203, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Sun, L.; Fischer, G.; Tian, Z.; Liang, Z. Optimizing Regional Cropping Systems with a Dynamic Adaptation Strategy for Water Sustainable Agriculture in the Hebei Plain. Agric. Syst. 2019, 173, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Q.; Pu, C.; Zhao, X.; Xue, J.F.; Zhang, R.; Nie, Z.J.; Chen, F.; Lal, R.; Zhang, H.L. Tillage Effects on Carbon Footprint and Ecosystem Services of Climate Regulation in a Winter Wheat-Summer Maize Cropping System of the North China Plain. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 67, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holst, J.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Q.; Doluschitz, R. Crop Evapotranspiration, Arable Cropping Systems and Water Sustainability in Southern Hebei, P.R. China. Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 141, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xiao, D.; Qi, Y.; Bai, H. Crop Yield and Water Consumption of Different Cropping Patterns under Different Precipitation Years in North China Plain. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2018, 34, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Shen, Y.; Qi, Y.; Moiwo, J.P.; Min, L.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Pei, H. Impact of Alternative Cropping Systems on Groundwater Use and Grain Yields in the North China Plain Region. Agric. Syst. 2017, 153, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Liu, D.L.; Feng, P.; Wang, B.; Waters, C.; Shen, Y.; Qi, Y.; Bai, H.; Tang, J. Future Climate Change Impacts on Grain Yield and Groundwater Use under Different Cropping Systems in the North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 246, 106685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Zang, H.; Yan, P.; Meki, M.N.; Doro, L.; Sui, P.; Jeong, J.; Zeng, Z. Alternative Cropping Systems for Groundwater Irrigation Sustainability in the North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 250, 106867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Hu, K.; Zhang, L.; Ji, Y.; Qin, W. Exploring Optimal Catch Crops for Reducing Nitrate Leaching in Vegetable Greenhouse in North China. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 212, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.T.; Jian, L.I.U.; Wang, H.Y.; Lei, Q.L.; Liu, H.B.; Zhai, L.M.; Zhang, J.Z. Suitability of the DNDC Model to Simulate Yield Production and Nitrogen Uptake for Maize and Soybean Intercropping in the North China Plain. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 2790–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.C.; Yang, X.L.; Xie, G.H. Establishing Sustainable Sweet Sorghum-Based Cropping Systems for Forage and Bioenergy Feedstock in North China Plain. Field Crops Res. 2018, 227, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Wang, H.; Yan, P.; Pan, J.; Lu, D.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, F.; Chen, X. Designing a New Cropping System for High Productivity and Sustainable Water Usage under Climate Change. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Sun, L.; Fischer, G.; Tian, Z.; van Velthuizen, H.; Liang, Z. Mission Impossible? Maintaining Regional Grain Production Level and Recovering Local Groundwater Table by Cropping System Adaptation across the North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 193, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Liu, Q.; Heerink, N.; Stomph, T.; Li, B.; Liu, R.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, C.; et al. Economic Performance and Sustainability of a Novel Intercropping System on the North China Plain. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Kröbel, R.; Müller, T.; Römheld, V.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, F.; Chen, X. Optimization of Yield and Water-Use of Different Cropping Systems for Sustainable Groundwater Use in North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2011, 98, 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beavis, S.G.; Wong, V.N.L.; Mosley, L.M.; Baldwin, D.S.; Latimer, J.O.; Lane, P.; Lal, A. Water Quality Risks in the Murray-Darling Basin. Australas. J. Water Resour. 2023, 27, 85–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, J.; Wan, J. Agriculture and Crop Science in China: Innovation and Sustainability. Crop J. 2017, 5, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Sun, C.; Wu, W.; Sun, C. Water Leakage and Nitrate Leaching Characteristics in the Winter Wheat-Summer Maize Rotation System in the North China Plain under Different Irrigation and Fertilization Management Practices. Water 2017, 9, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Pan, J.; Zhang, W.; Shi, J.; Chen, X.; Cui, Z. A High Plant Density Reduces the Ability of Maize to Use Soil Nitrogen. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Xu, X.; Lin, G.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Micro-Irrigation Improves Grain Yield and Resource Use Efficiency by Co-Locating the Roots and N-Fertilizer Distribution of Winter Wheat in the North China Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Ning, T.; Li, Z.; Han, H.; Zhang, Z.; Qin, S.; Zheng, Y. Coupling Effects of Urea Types and Subsoiling on Nitrogen-Water Use and Yield of Different Varieties of Maize in Northern China. Field Crops Res. 2013, 142, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, B.; Hu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Pan, Z.; Zhen, W. Effects of Optimized Subsoiling Tillage on Field Water Conservation and Summer Maize (Zea mays L.) Yield in the North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 247, 106732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Wang, S.; Jin, X.; Li, M.; Lv, M.; Feng, W. Using an Etwatch (Rs)-Uzf-Modflow Coupled Model to Optimize Joint Use of Transferred Water and Local Water Sources in a Saline Water Area of the North China Plain. Water 2020, 12, 3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Xu, Y.; Ma, X.; Ahmad, I.; Manzoor; Jia, Q.; Akmal, M.; Hussain, Z.; Arif, M.; Cai, T.; et al. Deficit Irrigation Strategies to Improve Winter Wheat Productivity and Regulating Root Growth under Different Planting Patterns. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 219, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Ren, L. Evaluating the Effects of Limited Irrigation on Crop Water Productivity and Reducing Deep Groundwater Exploitation in the North China Plain Using an Agro-Hydrological Model: I. Parameter Sensitivity Analysis, Calibration and Model Validation. J. Hydrol. 2019, 574, 497–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Lei, Q.; Luo, J.; Lindsey, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhai, L.; Wu, S.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; et al. Optimizing the Nitrogen Application Rate for Maize and Wheat Based on Yield and Environment on the Northern China Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 618, 1173–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Wang, S.; Sprenger, M.; Liu, B.; Cao, J. Response of Soil Water Movement and Groundwater Recharge to Extreme Precipitation in a Headwater Catchment in the North China Plain. J. Hydrol. 2019, 576, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Gong, S.; Xu, D.; Sui, J. Nitrogen Fertigation Effect on Photosynthesis, Grain Yield and Water Use Efficiency of Winter Wheat. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 179, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Liang, T.; Wang, L.; Zhou, C. No-Tillage and Fertilization Management on Crop Yields and Nitrate Leaching in North China Plain. Ecol. Evol. 2015, 5, 1143–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Qingjie, W.; Hongwen, L.; Lijin, L.; Huanwen, G. Effect of Alternative Tillage and Residue Cover on Yield and Water Use Efficiency in Annual Double Cropping System in North China Plain. Soil. Tillage Res. 2009, 104, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhang, X.; Chen, S.; Pei, D.; Liu, C. Effects of Harvest and Sowing Time on the Performance of the Rotation of Winter Wheat-Summer Maize in the North China Plain. Ind. Crops Prod. 2007, 25, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, S.; Liu, M.; Pei, D.; Sun, H. Improved Water Use Efficiency Associated with Cultivars and Agronomic Management in the North China Plain. Agron. J. 2005, 97, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Scanlon, B.R.; Han, D.; Zheng, C. Impacts of Thickening Unsaturated Zone on Groundwater Recharge in the North China Plain. J. Hydrol. 2016, 537, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, L.; Shen, Y.; Pei, H. Estimating Groundwater Recharge Using Deep Vadose Zone Data under Typical Irrigated Cropland in the Piedmont Region of the North China Plain. J. Hydrol. 2015, 527, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, L.; Qi, Y.; Shen, Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, S.; Liu, M. Groundwater Recharge under Irrigated Agro-Ecosystems in the North China Plain: From a Critical Zone Perspective. J. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 29, 877–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, Z.Y.; Zhang, Z.J.; Fei, Y.; Zhang, F.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z. Estimation of Natural Groundwater Recharge in the Hutuo River Alluvial-Proluvial Fan Using Environmental Tracers. Geol. Sci. Technol. Inf. 2009, 28, 114–118. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Zhao, J.; Duan, L. Simulation of Irrigation-Induced Groundwater Recharge in an Arid Area of China. Hydrol. J. 2021, 29, 525–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F. Groundwater Resources in the North China Plain. Environ. Geol. Water Sci. 1988, 12, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, L.S. Groundwater Resource Sustainable Utilization Planning in Beijing. In Proceedings of the Presentation by Liao Pingan, Director of International Relations, Beijing Water Authority, at Groundwater Roundtable, Royal Danish Embassy, Beijing, China, 29 March 2012; pp. 3–20. [Google Scholar]
- Noori, A.R.; Singh, S.K. Rainfall Assessment and Water Harvesting Potential in an Urban Area for Artificial Groundwater Recharge with Land Use and Land Cover Approach. Water Resour. Manag. 2023, 37, 5215–5234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaddadi, N.; Vansarochana, C. Investigation on Aquifer Recharge Potential of Rainwater Harvesting Using Geoinformatics Approach: Case Study of Pune City. Doctoral Dissertation, Naresuan University, Pune, India, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, K.; Kumar, R.; Pandit, B.A. Conservation and Management by Artificial Recharge of Aquifer. Adv. Water Manag. Under Clim. Change 2023, 319, 312–339. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, G.B.; Hwang, C.I.; Choi, M.R. Assessment of the Need and Potential for Groundwater Artificial Recharge Based on the Water Supply, Water Demand, and Aquifer Properties in a Water Shortage Region of South Korea. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Lyu, H.; Xu, G.; Chi, G.; Su, X. Hydrogeochemical Changes during Artificial Groundwater Well Recharge. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 900, 165778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, D.; Jin, M.; Brusseau, M.L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, D. Using Tracer Tests to Estimate Vertical Recharge and Evaluate Influencing Factors for Irrigated Agricultural Systems. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, W.; Qu, S.; Zheng, Y.; Li, W. Specific Types and Adaptability Evaluation of Managed Aquifer Recharge for Irrigation in the North China Plain. Water 2020, 12, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Sakura, Y.; Changyuan, T.; Hayashi, S. Groundwater-Table and Recharge Changes in the Piedmont Region of Taihang Mountain in Gaocheng City and Its Relation to Agricultural Water Use. Water SA 2002, 28, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, X.; Xu, Z.; Wang, T. Research on Characteristics of Groundwater Recharge in the Weishan Irrigated District Based on a Bromide Tracer. Water 2018, 10, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Han, D.; Song, X. Evaluating Actual Evapotranspiration and Impacts of Groundwater Storage Change in the North China Plain. Hydrol. Process 2014, 28, 1797–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Jin, M.; Liang, X.; Zhan, H. Estimation de La Recharge Des Eaux Souterraines Sous Des Champs Irrigués En Utilisant Les Traceurs Environnementaux Fluorure, Chlorure et Sulfate. Hydrogeol. J. 2013, 21, 1469–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Jin, M.; Liang, X. Using EARTH Model to Estimate Groundwater Recharge at Five Representative Zones in the Hebei Plain, China. J. Earth Sci. 2015, 26, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Feng, S.; Song, X. Evaluation of Optimal Irrigation Scheduling and Groundwater Recharge at Representative Sites in the North China Plain with SWAP Model and Field Experiments. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2015, 116, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, L.; Shen, Y.; Pei, H.; Wang, P. Water Movement and Solute Transport in Deep Vadose Zone under Four Irrigated Agricultural Land-Use Types in the North China Plain. J. Hydrol. 2018, 559, 510–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Jin, M.; Nimmo, J.R.; Yang, L.; Wang, W. Estimating Groundwater Recharge in Hebei Plain, China under Varying Land Use Practices Using Tritium and Bromide Tracers. J. Hydrol. 2008, 356, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Wang, G.; Zhang, W.; Cui, H.; Zhang, W. Estimation of Groundwater Recharge Using Tracers and Numerical Modeling in the North China Plain. Water 2016, 8, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, S.; Jin, M.; Liang, X.; Lin, D. Changes of Vertical Groundwater Recharge with Increase in Thickness of Vadose Zone Simulated by One-Dimensional Variably Saturated Flow Model. J. Earth Sci. 2014, 25, 1043–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Jin, M.; Van Genuchten, M.T.; Wang, B. Groundwater Recharge at Five Representative Sites in the Hebei Plain, China. Ground Water 2011, 49, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Recommendations | Supporting Comments for Recommendations | References |
|---|---|---|
| WW-SM-SPM | Water conserved up to 284 mm | [22] |
| WW-SM-SPM | Lowered groundwater decline by 0.33 m yr−1 | [38] |
| SP-C-SP-WW-SM | The system showed less groundwater decline by 0.4 m yr−1 | [66] |
| WW-SM-SPM-SPM | N fertilizer can be reduced up to 30–50% in the system | [112] |
| WW-EM-EM-F | Increased water saving of 2322 × 106 m3 | [113] |
| SM-monoculture | Showed 30% low water overdraft | [111] |
| 2Y3MS1 | Balanced groundwater overdraft | [114] |
| Ww-SMOpt | Saves 62% of groundwater use (minimum irrigated) | [115] |
| Catch crops | Decreased 23.6% drainage and 32.8% NO3− leaching | [116] |
| Mixing switchgrass | Lowered water table drop by 0.4 m yr−1 | [75] |
| SPM × SOY | Increased land utilization rate by >40% | [117] |
| Alfalfa-WW | Reduced water consumption by 70.5% and NO3− leaching by 35% | [57] |
| WW-SM-SPM-SPM | Resulted in less groundwater drop of 0.07 m yr−1 | [37] |
| SS-WW | Mitigate groundwater decline through fewer evaporations | [118] |
| Early maize only | It had 190 mm less groundwater overdraft | [112] |
| WW-SM-F-SPM | Revealed low water overdraft by 150 mm yr−1 only | [113] |
| SPM-monoculture | Showed 31% high grain yield via minimum water use | [119] |
| PN-WW-SM | The system had 19% low evapotranspiration | [39] |
| CT-WF-ESM | Exhibited 33.7% higher water utilization | [120] |
| WWOpt-no-till | Reduced risk of groundwater drop | [110] |
| WW-watermelon | Consumed low water and N fertilizer | [121] |
| SPM-monoculture | Showed lowest, 139 mm yr−1, water consumption | [122] |
| Recommendations | Supporting Comments for Recommendations | References |
|---|---|---|
| <200 kg N ha−1 | Because >200 kg N ha−1 caused N leaching from WWSM | [24] |
| Larger spike wheat | Larger spike wheat showed N efficiency > 10% | [25] |
| Straw incorporation | Significant inhibited annual N loss of about 31% | [58] |
| 75 mm watering | From jointing to booting stages in WW showed excellent result | [69] |
| 394 mm water yr−1 | Showed as optimum for WW-SM rotations | [75] |
| 330 kg N ha−1 yr−1 | Reduced N losses by 34% from WW-SM field | [39] |
| Soil test-based N | 85.2% NO3− leaching can be reduced from the wheat field | [125] |
| 7.5 plants m−2 | Showed higher NUE of maize than plant density, 9.0 m−2 | [126] |
| Subsoiling tillage (ST) | Water storage capacity increased in 2 m soil layer | [129] |
| ETWatch-UZF-MODFLOW | Improved the groundwater balance for shallow aquifers | [130] |
| Drip irrigation | Proven as efficient irrigation method in water-scarce area | [46] |
| BI→RI | RI showed 64.8% WUE compared to conventional BI | [131] |
| FP → OPT | Significantly decreased N loss by 28.6% in WW-SM | [132] |
| 43 kg N ha−1 | Concluded as the optimum ecological dose for maize | [133] |
| Sprinkler irrigation | Lowered water consumption and improved WUE (17.7%) | [134] |
| N via fertigation | Reduced risk of NO3− contamination in groundwater | [135] |
| Wide planting | Enhanced WUE and NUE compared to traditional method | [59] |
| CTS → NTS | NTS significantly decreased NO3− leaching losses | [136] |
| Use of coated urea | Slow-release coated urea increased maximum N recovery | [128] |
| Conservatory tillage | 30.1% WUE was improved compared to conventional tillage | [137] |
| 5-day-delay sowing | ET was decreased by 3.5 mm day−1 for wheat | [138] |
| Mulching in maize | Reduced soil evaporation loss by 40–50 mm yr−1 | [139] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, J.; Laghari, Y.; Wei, Y.-C.; Wu, L.; He, A.-L.; Liu, G.-Y.; Yang, H.-H.; Guo, Z.-Y.; Leghari, S.J. Groundwater Depletion and Degradation in the North China Plain: Challenges and Mitigation Options. Water 2024, 16, 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16020354
Du J, Laghari Y, Wei Y-C, Wu L, He A-L, Liu G-Y, Yang H-H, Guo Z-Y, Leghari SJ. Groundwater Depletion and Degradation in the North China Plain: Challenges and Mitigation Options. Water. 2024; 16(2):354. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16020354
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Jun, Yaseen Laghari, Yi-Chang Wei, Linyi Wu, Ai-Ling He, Gao-Yuan Liu, Huan-Huan Yang, Zhong-Yi Guo, and Shah Jahan Leghari. 2024. "Groundwater Depletion and Degradation in the North China Plain: Challenges and Mitigation Options" Water 16, no. 2: 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16020354
APA StyleDu, J., Laghari, Y., Wei, Y.-C., Wu, L., He, A.-L., Liu, G.-Y., Yang, H.-H., Guo, Z.-Y., & Leghari, S. J. (2024). Groundwater Depletion and Degradation in the North China Plain: Challenges and Mitigation Options. Water, 16(2), 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16020354







