Response of the Cyanobacteria Plankton Community to Anthropogenic Impact in Small Lakes of Urbanized Territory in the Permafrost Zone of Northeast Asia (Eastern Siberia, Yakutia)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Sampling
2.3. Water Chemistry Analysis
2.4. Algological Analysis
2.5. Bioindication and Statistics
2.6. Ecological Mapping and JASP
2.7. Species-Environments Relationships Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physico-Chemical Parameters
3.2. Composition of Cyanobacterial Community and Dominant Species
3.3. Bioindication
3.4. Comparative Statistics
3.5. Statistical Mapping
3.6. Biological and Environmental Variables Relationships
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Species | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anabaena bornetiana Collins | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
| Anabaena cylindrica Lemmermann | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
| Anabaenopsis elenkinii V.V.Miller | 3 | ||||||||||||||||
| Anabaenopsis tanganyikae (G.S.West) V.V.Miller | 2 | ||||||||||||||||
| Anagnostidinema amphibium (Gomont) Strunecký, Bohunická, J.R.Johansen & Komárek | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||||||
| Anagnostidinema tenue (Anisimova) Strunecky & al. | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||
| Anathece clathrata (West & G.S.West) Komárek, Kaštovský & Jezberová | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| Aphanizomenon flos-aquae Ralfs ex Bornet & Flahault | 6 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | ||||
| Aphanocapsa delicatissima West & G.S.West | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||||||
| Aphanocapsa holsatica (Lemmermann) G.Cronberg & Komárek | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| Arthrospira jenneri Stizenberger ex Gomont | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
| Chroococcus turgidus (Kützing) Nägeli | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||||||
| Coelosphaerium aerugineum Lemmermann | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
| Dolichospermum affine (Lemmermann) Wacklin, L.Hoffmann & Komárek | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||
| Dolichospermum circinale (Rabenhorst ex Bornet & Flahault) Wacklin, Hoffmann & Komárek | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
| Dolichospermum crassum (Lemmermann) P.Wacklin, L.Hoffmann & J.Komárek | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | |||||||||||||
| Dolichospermum flos-aquae (Bornet & Flahault) P.Wacklin, L.Hoffmann & Komárek | 3 | 2 | 3 | ||||||||||||||
| Dolichospermum lemmermannii (Richter) P.Wacklin, L.Hoffmann & J.Komárek | 2 | ||||||||||||||||
| Dolichospermum sigmoideum (Nygaard) Wacklin, L.Hoffmann & Komárek | 3 | 1 | 2 | ||||||||||||||
| Dolichospermum smithii (Komárek) Wacklin, L.Hoffmann & Komárek | 2 | 1 | 1 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||
| Dolichospermum spiroides (Klebahn) Wacklin, L.Hoffmann & Komárek | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| Dolichospermum viguieri (Denis & Frémy) Wacklin, L.Hoffmann & Komárek | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||
| Kamptonema chlorinum (Kützing ex Gomont) Strunecký, Komárek & J.Smarda | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
| Limnothrix planctonica (Wołoszyńska) Meffert | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
| Merismopedia glauca (Ehrenberg) Kützing | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||
| Merismopedia tranquilla (Ehrenberg) Trevisan | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||
| Microcrocis irregularis (Lagerheim) Geitler | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
| Microcystis aeruginosa (Kützing) Kützing | 2 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | ||||||||
| Microcystis flos-aquae (Wittrock) Kirchner | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 5 | 4 | 5 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 6 |
| Microcystis ichthyoblabe (G.Kunze) Kützing | 4 | 3 | |||||||||||||||
| Microcystis wesenbergii (Komárek) Komárek ex Komárek | 4 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 2 | |||
| Oscillatoria ornata Kützing ex Gomont | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
| Oscillatoria rupicola (Hansgirg) Hansgirg ex Forti | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||
| Oscillatoria tenuis C.Agardh ex Gomont | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||
| Phormidium breve (Kützing ex Gomont) Anagnostidis & Komárek | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
| Phormidium chalybeum (Mertens ex Gomont) Anagnostidis & Komárek | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
| Phormidium corium Gomont | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| Phormidium inundatum Kützing ex Gomont | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
| Planktolyngbya contorta (Lemmermann) Anagnostidis & Komárek | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
| Planktolyngbya limnetica (Lemmermann) Komárková-Legnerová & Cronberg | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
| Planktothrix agardhii (Gomont) Anagnostidis & Komárek | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | |||||||||||||
| Rhabdogloea smithii (Chodat & F.Chodat) Komárek | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||||||
| Snowella lacustris (Chodat) Komárek & Hindák | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| Woronichinia naegeliana (Unger) Elenkin | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||
| Total number of species | 7 | 8 | 4 | 14 | 11 | 5 | 6 | 11 | 11 | 12 | 9 | 14 | 14 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 11 |
Appendix B
| Species | Hab | OXY | HAL | pH | pH rank | TRO | Index S | SAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anabaena bornetiana Collins | ||||||||
| Anabaena cylindrica Lemmermann | P-B,S | aer | e | 1.7 | b-o | |||
| Anabaenopsis elenkinii V.V.Miller | P-B | st | me | 1.5 | o-b | |||
| Anabaenopsis tanganyikae (G.S.West) V.V.Miller | ||||||||
| Anagnostidinema amphibium (Gomont) Strunecký, Bohunická, J.R.Johansen & Komárek | P-B,S | st-str,H2S | hl | alf | 4.9–8.0 | m | 2.6 | a-o |
| Anagnostidinema tenue (Anisimova) Strunecky & al. | ||||||||
| Anathece clathrata (West & G.S.West) Komárek, Kaštovský & Jezberová | P-B | hl | me | 1.8 | o-a | |||
| Aphanizomenon flos-aquae Ralfs ex Bornet & Flahault | P-B | hl | alb | 7.0–8.2 | m | 1.95 | o-a | |
| Aphanocapsa delicatissima West & G.S.West | P-B | i | 7.6 | m | ||||
| Aphanocapsa holsatica (Lemmermann) G.Cronberg & Komárek | P-B | i | 6.8–8.0 | me | 1.4 | o-b | ||
| Arthrospira jenneri Stizenberger ex Gomont | P-B | st | 4.7–9.0 | m | 3.7 | b-p | ||
| Chroococcus turgidus (Kützing) Nägeli | P-B,S | aer | hl | alf | 8.1 | e | 0.8 | x-b |
| Coelosphaerium aerugineum Lemmermann | P | me | ||||||
| Dolichospermum affine (Lemmermann) Wacklin, L.Hoffmann & Komárek | P-B | 7.0–8.2 | om | 0.5 | x-o | |||
| Dolichospermum circinale (Rabenhorst ex Bornet & Flahault) Wacklin, Hoffmann & Komárek | P-B | i | om | |||||
| Dolichospermum crassum (Lemmermann) P.Wacklin, L.Hoffmann & J.Komárek | P | e | ||||||
| Dolichospermum flos-aquae (Bornet & Flahault) P.Wacklin, L.Hoffmann & Komárek | P-B | st | i | alb | e | |||
| Dolichospermum lemmermannii (Richter) P.Wacklin, L.Hoffmann & J.Komárek | P | i | e | |||||
| Dolichospermum sigmoideum (Nygaard) Wacklin, L.Hoffmann & Komárek | P | i | e | 1.7 | b-o | |||
| Dolichospermum smithii (Komárek) Wacklin, L.Hoffmann & Komárek | P | |||||||
| Dolichospermum spiroides (Klebahn) Wacklin, L.Hoffmann & Komárek | P-B | st-str | i | e | 1.3 | o | ||
| Dolichospermum viguieri (Denis & Frémy) Wacklin, L.Hoffmann & Komárek | P | e | 2.0 | b | ||||
| Kamptonema chlorinum (Kützing ex Gomont) Strunecký, Komárek & J.Smarda | P-B,S | st-str,H2S | 5.8–7.3 | 3.8 | b-p | |||
| Limnothrix planctonica (Wołoszyńska) Meffert | P | i | ot | 1.0 | o | |||
| Merismopedia glauca (Ehrenberg) Kützing | P-B | i | ind | 7.9–11 | e | |||
| Merismopedia tranquilla (Ehrenberg) Trevisan | P-B | i | ind | 8.1–8.9 | 2.3 | b | ||
| Microcrocis irregularis (Lagerheim) Geitler | P | i | 1.5 | o-b | ||||
| Microcystis aeruginosa (Kützing) Kützing | P-B | hl | acf | 6.0–7.8 | me | 2.2 | b | |
| Microcystis flos-aquae (Wittrock) Kirchner | P-B | i | 6.6–7.7 | e | 1.6 | b-o | ||
| Microcystis ichthyoblabe (G.Kunze) Kützing | P | i | e | |||||
| Microcystis wesenbergii (Komárek) Komárek ex Komárek | P-B | 2.3 | b | |||||
| Oscillatoria ornata Kützing ex Gomont | P-B,S | st-str | i | me | 1.5 | o-b | ||
| Oscillatoria rupicola (Hansgirg) Hansgirg ex Forti | P-B,S | aer | me | 2.7 | a-o | |||
| Oscillatoria tenuis C.Agardh ex Gomont | P-B,S | st-str | hl | |||||
| Phormidium breve (Kützing ex Gomont) Anagnostidis & Komárek | P-B,S | st,aer | alb | 8.2 | 3.1 | a | ||
| Phormidium chalybeum (Mertens ex Gomont) Anagnostidis & Komárek | P-B,S | st-str | 7.0 | e | 3.3 | a | ||
| Phormidium corium Gomont | B,S | st-str | m | 1.3 | o | |||
| Phormidium inundatum Kützing ex Gomont | B,S | aer | ot | 0.1 | x | |||
| Planktolyngbya contorta (Lemmermann) Anagnostidis & Komárek | P-B | alf | 7.6 | |||||
| Planktolyngbya limnetica (Lemmermann) Komárková-Legnerová & Cronberg | P-B,S | st-str | hl | alf | 7.9–8.1 | me | 1.8 | o-a |
| Planktothrix agardhii (Gomont) Anagnostidis & Komárek | P-B | st | hl | |||||
| Rhabdogloea smithii (Chodat & F.Chodat) Komárek | P | st | alf | 7.8–9.6 | 2.0 | b | ||
| Snowella lacustris (Chodat) Komárek & Hindák | P | i | alb | 8.1 | me | 1.6 | b-o | |
| Woronichinia naegeliana (Unger) Elenkin | P | st | e | 1.8 | o-a |
Appendix C
| Ecological Group | 1-Ma | 2-Un | 3-Un | 4-Yt | 5-Te | 6-Pr | 7-Kh | 8-Be | 9-So | 10-Us | 11-Oc | 12-Ba | 13-Ar | 14-Un | 15-Ma | 16-Dr | 17-Ch |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Habitat | |||||||||||||||||
| B | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| P-B | 13 | 12 | 5 | 16 | 14 | 8 | 13 | 15 | 16 | 15 | 13 | 14 | 14 | 12 | 15 | 13 | 14 |
| P | 3 | 2 | 6 | 6 | 10 | 4 | 0 | 4 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 7 | 5 | 3 | 0 | 4 | 3 |
| Oxygen | |||||||||||||||||
| aer | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| st-str | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| st | 3 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 7 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| Salinity | |||||||||||||||||
| i | 7 | 0 | 10 | 9 | 6 | 5 | 3 | 8 | 7 | 8 | 6 | 13 | 9 | 8 | 5 | 4 | 9 |
| hl | 6 | 0 | 1 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 9 | 7 | 7 | 8 | 6 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 7 | 3 |
| Water pH | |||||||||||||||||
| acf | 0 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 4 | 6 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 0 |
| ind | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| alf | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| alb | 10 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 0 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 9 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| Trophic state | |||||||||||||||||
| ot | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| om | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| m | 6 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 2 |
| me | 2 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 4 | 4 | 6 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 5 | 3 | 2 |
| e | 5 | 4 | 8 | 0 | 4 | 7 | 3 | 7 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 12 | 8 | 7 | 5 | 7 | 8 |
| Water Quality Class | |||||||||||||||||
| Class 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Class 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| Class 3 | 10 | 11 | 6 | 17 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 15 | 13 | 13 | 14 | 11 | 15 | 6 | 11 | 14 | 12 |
| Class 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
References
- Gaevaya, I.K.; Batozhergalova, I.I.; Konstantinova, V.A. (Eds.) Statistical Yearbook of the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia): Statistical Abstract; Local agency of the Federal State Statistics Service for the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia): Yakutsk, Russia, 2022; 542p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Makarov, V.N.; Chizhuk, A.L. The supply of phosphates to the lakes of Yakutsk. Nauka i Obrazovanie [Sci. Educ.] 2009, 4, 67–69. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Rufova, A.A.; Ksenofontova, M.I.; Yablovskaya, P.E. Monitoring of the state of the lakes of Yakutsk City by hydro-chemical indicators. Nauka i Obrazovanie [Sci. Educ.] 2012, 4, 52–55. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Rufova, A.A.; Ksenofontova, M.I.; Trofimova, L.N. The content of some trace elements in the water of Lake Saysary. Nauka i Obrazovanie [Sci. Educ.] 2013, 3, 139–141. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Ksenofontova, M.I.; Legostaeva, Y.B.; Yablovskaya, P.E.; Trofimova, L.N. Characteristics of the chemical composition of waters and bottom sediments of large reservoirs in Yakutsk City. Aktual’nye Problemy Gumanitarnykh i Estestvennykh Nauk [Actual Probl. Humanit. Nat. Sci.] 2013, 4, 493–500. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Rufova, A.A.; Ksenofontova, M.I. Hydrochemical composition as one of the indicators of modern conditions of lake formation (using the example of Yakutsk City). Nauka i Obrazovanie [Sci. Educ.] 2015, 2, 144–150. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Rufova, A.A.; Tatarinova, A.V. Anthropogenic influence on the hydrochemical and hydrobiological state of surface waters of northern cities (using the example of Yakutsk City). Sovremennye Problemy Nauki i Obrazovaniya [Mod. Probl. Sci. Educ.] 2015, 4, 503. Available online: https://sci-ence-education.ru/ru/article/view?id=20468 (accessed on 20 August 2024). (In Russian).
- Kaydalova, M.V.; Olesova, A.I. Lake “Saysary” Yakutsk. In Proceedings of the XI International Student Scientific Conference “Student Scientific Forum 2019”, Moscow, Russia, 23 May 2019; Available online: https://files.scienceforum.ru/pdf/2019/5c6bb00cee22f.pdf (accessed on 10 August 2024).
- Gabyshev, V.A.; Gabysheva, O.I. On study of influence of heavy metals onto the development of phytoplankton in the lakes of Yakutsk City and the surrounding area. Prirodnye Resursy Arktiki i Subarktiki [Arct. Subarct. Nat. Resour.] 2020, 25, 81–91. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaev, A.A.; Arkhipov, I.V. Ecological condition of the lakes in Yakutsk City for tourism and recreational use. Uspekhi Sovremennogo Estestvoznaniya [Adv. Curr. Nat. Sci.] 2021, 11, 106–113. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Popova, N.V.; Fedulova, S.I. The study of the water of Lake Saysary according to hydrochemical parameters. In Proceedings of the Chugunov Agronomic Readings. Collection of Scientific Articles Based on the Materials of the XIV All-Russian Scientific and Practical Conference of Agrotechnological Orientation Dedicated to the 100th Anniversary of the Formation of the Yakut Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic and the Year of Cultural Heritage of Peoples in Russia, Yakutsk, Russia, 20 May 2022. (In Russian). [Google Scholar]
- Legostaeva, Y.B.; Rufova, A.A. Analysis of the hydrochemical regime of the largest lakes in the Yakutsk City. Prirodnye Resursy Arktiki i Subarktiki [Arct. Subarct. Nat. Resour.] 2022, 27, 572–591. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rufova, A.A. Integral indicators of hydrochemical state of lacustrine waters in Yakutsk City. In Proceedings of the Actual Problems of Ecology and Nature Management. Collection of the XXIV International Scientific and Practical Conference. 2 volumes, Moscow, Russia, 20 April 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Chebykin, E.P.; Mal’nik, V.V.; Tomberg, I.V.; Kopyrina, L.I.; Suturin, A.N.; Zakharova, Y.R. Water quality and ecological state estimate of large lakes of Yakutsk City (Lake Saysary, Lake Sergelyakh) in the end of ice period in 2021. Limnol. Freshw. Biol. 2024, 4, 834–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilieva, I.I. Composition and Seasonal Dynamics of Phytoplankton in Lakes around the City of Yakutsk, Extended Abstract of Cand. Sci. (Biol.). Ph.D. Thesis, Central Siberian Botanic Garden, Novosibirsk, Russia, 1968. (In Russian). [Google Scholar]
- Kopyrina, L.I. Epiphytic algae are indicators of saprobity of some lakes in the vicinity of Yakutsk City. Nauka i Obrazovanie [Sci. Educ.] 2013, 4, 77–81. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Tatarinova, A.V.; Salova, T.A. Hydrobiological characteristics of urban and suburban lakes of Yakutsk City. Mezhdunarodnyy zhurnal Prikladnykh i Fundamental’nykh Issledovaniy [Int. J. Appl. Fundam. Res.] 2013, 8, 81–82. Available online: https://applied-re-search.ru/ru/article/view?id=3854 (accessed on 10 August 2024). (In Russian).
- Grigorieva, M.V.; Solovieva, M.I. The quality of the lakes of Yakutsk City according to the state of benthic communities. Problemy Regional’noy Ekologii [Reg. Environ. Issuses] 2020, 5, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherdonova, O.V.; Popova, N.V. The ecological state of Lake Saisary and the importance of plankton for the eco-system of the lake. In Proceedings of the All-Russian Conference “Strategy and Prospects for the Development of Agrotechnologies and the Forestry Complex of Yakutia until 2050”, Yakutsk, Russia, 17 November 2022; Available online: https://elibrary.ru/item.asp?edn=hgipve (accessed on 5 August 2024). (In Russian).
- Vasilyeva, I.I.; Ivanova, A.P.; Pshennikova, E.V. Species composition and seasonal dynamics of algae of lakes of Yakutsk and it’s environs (middle flow of Lena River). Algologia 1997, 7, 30–34. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Ivanova, A.P. Algae of Urban and Suburban Lakes of the Middle Lena Valley. Ph.D. Thesis, Moscow State University, Moscow, Russia, 2000. (In Russian). [Google Scholar]
- Kopyrina, L.I. Phytoplankton of the lake Dienkyudya. Nauka i Obrazovaniye [Sci. Educ.] 2007, 2, 13–18. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kopyrina, L.; Pshennikova, E.; Barinova, S. Diversity and ecological characteristic of algae and cyanobacteria of thermokarst lakes in Yakutia (northeastern Russia). Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2020, 49, 99–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izyumenko, S.A. (Ed.) Climate of the Yakut Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic (atlas); Gidrometeoizdat: Leningrad, Russia, 1968; 33p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Arzhakova, S.K.; Zhirkov, I.I.; Kusatov, K.I.; Androsov, I.M. Rivers and Lakes of Yakutia: A Brief Guide; Bichik: Yakutsk, Russia, 2007; 176p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Semenov, A.D. Guidance on the Chemical Analysis of Surface Waters of the Land; Gidrometeoizdat: Leningrad, Russia, 1977; 541p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Komárek, J.; Anagnostidis, K. Cyanoprokaryota. T. 1. Chroococcales; Gustav Fischer Verlag: Jena, Germany, 1998; 548p. [Google Scholar]
- Komárek, J.; Anagnostidis, K. Cyanoprokaryota. T. 2. Oscillatoriales. Elsevier: München, Germany, 2005; 759p. [Google Scholar]
- Komárek, J. Heterocytous Genera. Cyanoprokaryota. T. 3, P. 3; Springer Spektrum: Berlin, Germany, 2013; 1130p. [Google Scholar]
- Guiry, M.D.; Guiry, G.M. AlgaeBase. World-Wide Electronic Publication, University of Galway. 2024. Available online: https://www.algaebase.org (accessed on 20 July 2024).
- Barinova, S. How to Align and Unify the Cell Counting of Organisms for Bioindication. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Nat. Res. 2017, 2, 555585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barinova, S. Essential and practical bioindication methods and systems for the water quality assessment. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Nat. Resour. 2017, 2, 555588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barinova, S.S.; Bilous, O.P.; Tsarenko, P.M. Algal Indication of Water Bodies in Ukraine: Methods and Prospects; Publishing House of Haifa University: Haifa, Israel, 2019; 367p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- McAleece, N.; Gage, J.D.G.; Lambshead, P.J.D.; Paterson, G.L.J. BioDiversity Professional Statistics Analysis Software; Jointly Developed by the Scottish Association for Marine Science and the Natural History Museum London; Scottish Association for Marine Science: Oban, UK; Natural History Museum London: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Wessa, P. Person Correlation (v1.0.13) in Free Statistics Software (v1.2.1). Office for Research Development and Education. 2017. Available online: https://www.wessa.net/rwasp_correlation.wasp/ (accessed on 23 August 2024).
- Love, J.; Selker, R.; Marsman, M.; Jamil, T.; Dropmann, D.; Verhagen, J.A.; Ly, A.; Gronau, F.Q.; Smira, M.; Epskamp, S.; et al. JASP: Graphical statistical software for common statistical designs. J. Stat. Softw. 2019, 88, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ter Braak, C.J.F.; Šmilauer, P. CANOCO Reference Manual and CanoDraw for Windows User’s Guide: Software for Canonical Community Ordination, Version 4.5; Microcomputer Power Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2002; 500p. [Google Scholar]
- Hustedt, F. Die Diatomeenflora des Flußsystems der Weser im Gebiet der Hansestadt Bremen. Abhandlungen des Naturwissenschaftlichen Vereins zu Bremen 1957, 34, 181–440. [Google Scholar]
- Hustedt, F. Systematisch und Ökologische Untersuchungen über die Diatomeenflora von Java, Bali und Sumatra. Archiv für Hydrobiologie Suppl. 1938, 15, 131–790. [Google Scholar]
- Van Dam, H.; Mertens, A.; Sinkeldam, J. A coded checklist and ecological indicator values of freshwater diatoms from the Netherlands. Netherland J. Aquat. Ecol. 1994, 28, 117–133. [Google Scholar]
- Gabyshev, V.A.; Sidelev, S.I.; Chernova, E.N.; Vilnet, A.A.; Davydov, D.A.; Barinova, S.; Gabysheva, O.I.; Zhakovskaya, Z.A.; Voronov, I.V. Year-Round Presence of Microcystins and Toxin-Producing Microcystis in the Water Column and Ice Cover of a Eutrophic Lake Located in the Continuous Permafrost Zone (Yakutia, Russia). Toxins 2023, 15, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barinova, S. Environmental Preferences of Cyanobacteria in the Gradient of Macroclimatic Factors and Pollution. Theor. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 1, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabyshev, V.; Davydov, D.; Vilnet, A.; Sidelev, S.; Chernova, E.; Barinova, S.; Gabysheva, O.; Zhakovskaya, Z. Gloeotrichia cf. natans (Cyanobacteria) in the Continuous Permafrost Zone of Buotama River, Lena Pillars Nature Park, in Yakutia (Russia). Water 2023, 15, 2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Waal, D.B.; Verspagen, J.M.H.; Finke, J.F.; Vournazou, V.; Immers, A.K.; Kardinaal, W.E.A.; Tonk, L.; Becker, S.; Van Donk, E.; Visser, P.M.; et al. Reversal in competitive dominance of a toxic versus non-toxic cyanobacterium in response to rising CO2. ISME J. 2011, 5, 1438–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmen, S.; Aharonovich, D.; Grossowicz, M.; Blank, L.; Yacobi, Y.Z.; Sher, D.J. Distribution and Habitat Specificity of Potentially-Toxic Microcystis across Climate, Land, and Water Use Gradients. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paerl, H.W.; Paul, V.J. Climate change: Links to global expansion of harmful cyanobacteria. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1349–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibelings, B.W.; Vonk, M.; Los, H.F.J.; Van der Molen, D.T.; Mooij, W.M. Fuzzy modeling of cyanobacterial surface waterblooms: Validation with NOAA-AVHRR satellite images. Ecol. Appl. 2003, 13, 1456–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonk, L.; Bosch, K.; Visser, P.M.; Huisman, J. Salt Tolerance of the Harmful Cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2007, 46, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Otten, T.G. Duelling ‘CyanoHABs’: Unravelling the environmental drivers controlling dominance and succession among diazotrophic and non-N2-fixing harmful cyanobacteria. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabyshev, V.A.; Sidelev, S.I.; Chernova, E.N.; Gabysheva, O.I.; Voronov, I.V.; Zhakovskaya, Z.A. Limnological Characterization and First Data on the Occurrence of Toxigenic Cyanobacteria and Cyanotoxins in the Plankton of Some Lakes in the Permafrost Zone (Yakutia, Russia). Contemp. Probl. Ecol. 2023, 16, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dembowska, E.A. The Use of Phytoplankton in the Assessment of Water Quality in the Lower Section of Poland’s Largest River. Water 2021, 13, 3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salonen, K.; Vuorio, K.; Ketola, M.; Malin, I. Development of phytoplankton of Lake Vesijärvi during recovery from eutrophication. Hydrobiologia 2023, 850, 947–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, H.; Liu, J.; Guo, Y. Analysis of water quality and the response of phytoplankton in the low-temperature environment of Majiagou Urban River, China. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sládeček, V. Diatoms as indicators of organic pollution. Acta Hydrochim. Hydrobiol. 1986, 14, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
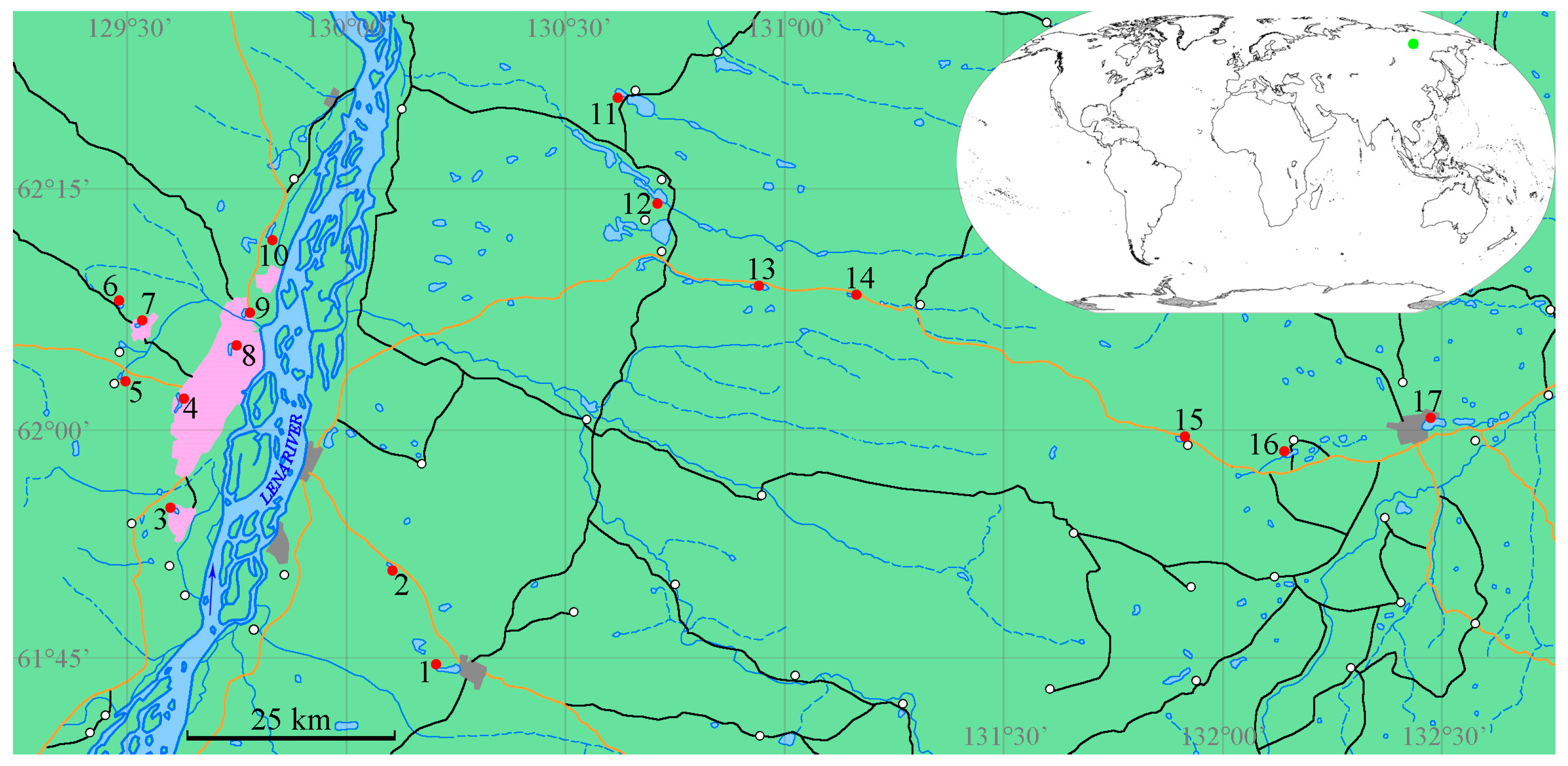

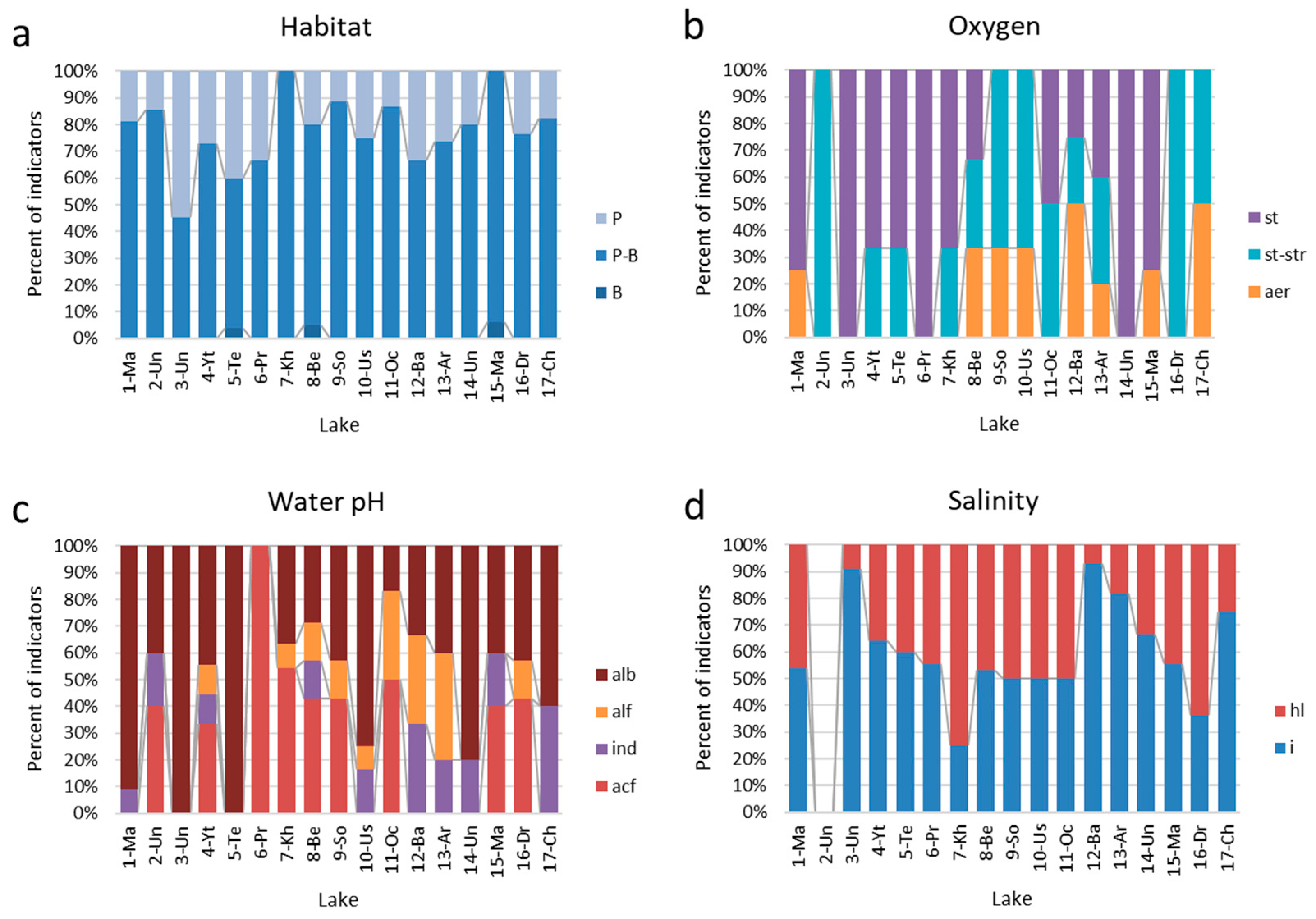



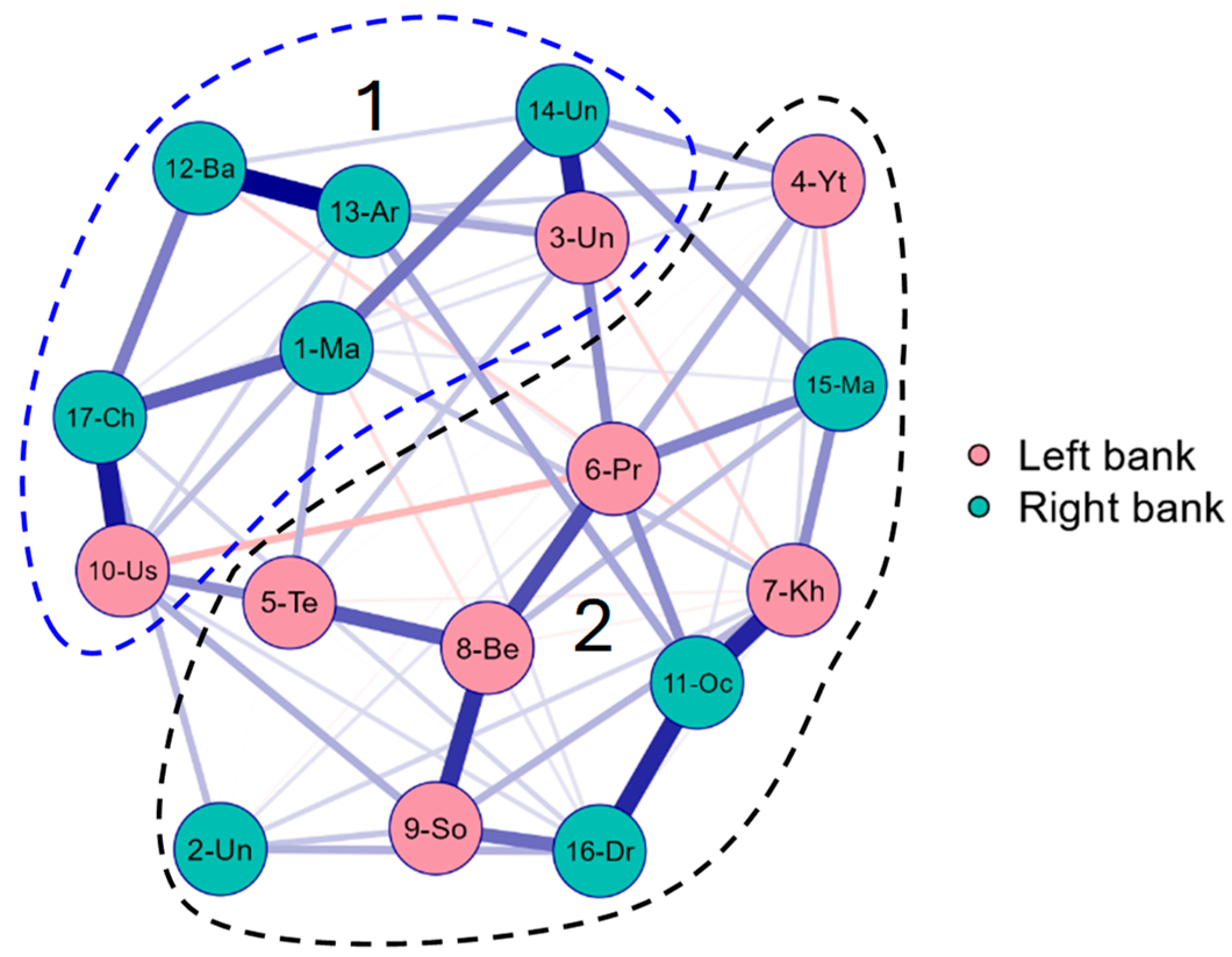
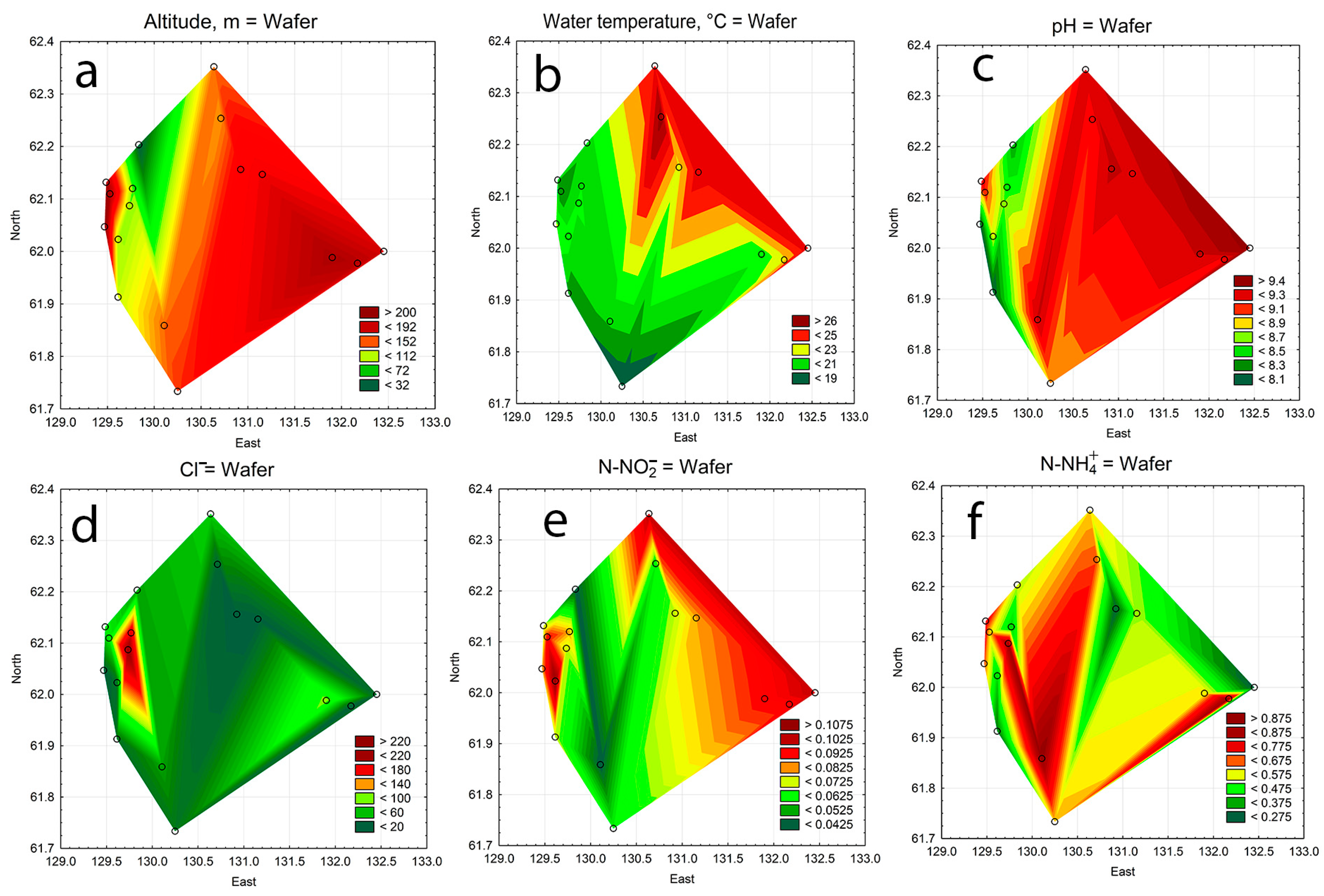


| No of Station | Code | Lake Name | Altitude Above Sea Level, m | Water Surface Area, km2 | Latitude, N | Longitude, E | Type of Origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1-Ma | Mayya | 155 | 1772.7 | 61°44′0.20″ | 130°14′56.78″ | C |
| 2 | 2-Un | Unnamed 1 | 148 | 72.6 | 61°51′31.26″ | 130°6′28.22″ | C |
| 3 | 3-Un | Unnamed 2 | 113 | 76.7 | 61°54′46.08″ | 129°36′50.26″ | C |
| 4 | 4-Yt | Ytyk-Kyuyol | 108 | 790.3 | 62°1′22.02″ | 129°36′59.0″ | R |
| 5 | 5-Te | Temiye | 219 | 483.1 | 62°2′48.93″ | 129°28′15.31″ | C |
| 6 | 6-Pr | Prokhladnoye | 204 | 61.5 | 62°7′53.82″ | 129°29′13.02″ | C |
| 7 | 7-Kh | Khomustakh | 204 | 90.7 | 62°6′34.55″ | 129°31′36.12″ | C |
| 8 | 8-Be | Beloye | 104 | 612.1 | 62°5′13.53″ | 129°44′12.88″ | R |
| 9 | 9-So | Solyonoe | 102 | 252.4 | 62°7′11.72″ | 129°46′11.85″ | R |
| 10 | 10-Us | Usun-Kyuyol | 31 | 126.7 | 62°12′11.55″ | 129°50′9.98″ | R |
| 11 | 11-Oc | Ochchuguy-Matta | 147 | 980.9 | 62°21′6.48″ | 130°38′17.43″ | C |
| 12 | 12-Ba | Balyktakh | 142 | 4349.5 | 62°15′12.89″ | 130°42′46.50″ | C |
| 13 | 13-Ar | Arylakh | 169 | 2845.9 | 62°9′21.34″ | 130°55′24.57″ | C |
| 14 | 14-Un | Unnamed 3 | 177 | 147.1 | 62°8′47.69″ | 131°9′17.29″ | C |
| 15 | 15-Ma | Maralayy | 203 | 357.5 | 61°59′17.36″ | 131°54′7.50″ | C |
| 16 | 16-Dr | Diring | 198 | 399 | 61°58′38.52″ | 132°10′17.26″ | C |
| 17 | 17-Ch | Churapcha | 185 | 3427.7 | 61°59′59.54″ | 132°27′9.39″ | C |
| Variables/Lake | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 8.91 | 9.32 | 8.08 | 8.74 | 8.08 | 9.23 | 9.07 | 8.61 | 8.55 | 8.33 | 9.27 | 9.12 | 9.33 | 9.27 | 9.31 | 9.18 | 9.54 |
| Water temperature, °C | 18.2 | 20.2 | 19.6 | 21.6 | 22.1 | 20.1 | 19.1 | 21.2 | 21.0 | 20.6 | 25.1 | 27.5 | 22.7 | 25.7 | 21.3 | 22.8 | 25.7 |
| TDS, mg L−1 | 408.5 | 802.1 | 209.4 | 448.6 | 214.4 | 798.4 | 844.9 | 872.5 | 784.4 | 328.4 | 1235.1 | 418.6 | 272.8 | 246.2 | 933.1 | 378.5 | 382.6 |
| Hardness, mg L−1 | 4.1 | 9.0 | 2.0 | 2.7 | 2.4 | 9.5 | 9.9 | 6.2 | 5.8 | 3.0 | 12.4 | 4.6 | 3.2 | 3.0 | 8.7 | 4.2 | 4.2 |
| Ca2+, mg L−1 | 26.7 | 23.9 | 26.5 | - | 31.5 | 29.3 | 36.5 | 43.7 | 32.1 | 34.5 | 18.2 | 25.5 | 25.5 | 29.5 | 23.9 | 33.7 | 27.1 |
| Mg2+, mg L−1 | 33.5 | 94.4 | 8.8 | - | 10.2 | 97.9 | 97.6 | 48.4 | 51.5 | 15.9 | 139.9 | 40.3 | 23.1 | 18.7 | 90.7 | 30.7 | 34.3 |
| Na+, mg L−1 | 30.4 | 47.4 | 19.4 | - | 9.1 | 32.0 | 23.2 | 150.8 | 123.6 | 35.2 | 94.2 | 19.1 | 10.6 | 5.6 | 104.8 | 17.3 | 25.3 |
| K+, mg L−1 | 13.5 | 5.2 | 2.0 | - | 4.0 | 33.2 | 53.0 | 30.4 | 17.2 | 4.3 | 23.8 | 8.9 | 6.0 | 4.9 | 13.2 | 7.7 | 5.3 |
| HCO3-, mg L−1 | 185.0 | 546.7 | 103.7 | - | 122.0 | 320.0 | 350.0 | 144.8 | 300.0 | 152.6 | 746.0 | 285.0 | 150.6 | 148.0 | 400.0 | 226.5 | 187.5 |
| Cl-, mg L−1 | 31.9 | 48.0 | 28.7 | - | 17.6 | 76.0 | 74.7 | 224.9 | 184.0 | 51.0 | 63.0 | 20.7 | 17.6 | 17.6 | 100.5 | 19.1 | 24.7 |
| SO42-, mg L−1 | 87.5 | 36.5 | 20.4 | - | 20.0 | 210.0 | 210.0 | 229.5 | 76.0 | 35.0 | 150.0 | 19.0 | 39.5 | 22.0 | 200.0 | 43.5 | 78.5 |
| N-NH4, mg L−1 | 0.61 | 0.90 | 0.31 | 0.41 | 0.67 | 0.75 | 0.61 | 0.87 | 0.40 | 0.53 | 0.60 | 0.67 | 0.27 | 0.52 | 0.58 | 0.89 | 0.26 |
| N-NO2, mg L−1 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0.11 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.10 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.10 |
| N-NO3, mg L−1 | 0.24 | 0.31 | 0.26 | 0.90 | 0.27 | 0.45 | 0.56 | 0.20 | 0.24 | 0.16 | 0.68 | 0.44 | 0.18 | 0.37 | 0.51 | 0.29 | 0.26 |
| P-PO4, mg L−1 | 0.31 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.15 | 0.01 | 0.26 | 0.30 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.07 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| P tot, mg L−1 | 0.60 | 0.20 | 0.07 | 0.46 | 0.20 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.21 | 0.18 | 0.11 | 0.70 | 0.16 | 0.18 | 0.70 | 0.36 | 0.43 | 0.36 |
| P org, mg L−1 | 0.29 | 0.19 | 0.06 | - | 0.19 | 0.14 | 0.10 | 0.20 | 0.17 | 0.11 | 0.68 | 0.15 | 0.17 | 0.64 | 0.34 | 0.41 | 0.34 |
| Fe tot, mg L−1 | 1.17 | 0.80 | 0.80 | 0.58 | 1.23 | 1.00 | 1.05 | 0.93 | 1.12 | 0.95 | 0.94 | 0.90 | 0.92 | 1.30 | 0.92 | 1.30 | 1.14 |
| Si-SiO2, mg L−1 | 1.41 | 1.09 | 0.68 | 1.31 | 1.34 | 2.16 | 1.93 | 0.80 | 1.25 | 0.78 | 1.37 | 0.80 | 0.81 | 2.45 | 1.16 | 1.94 | 1.63 |
| Color, Pt/Co grad. | 115 | 107 | 100 | 87.17 | 95 | 90 | 85 | 100 | 95 | 85 | 90 | 120 | 110 | 107 | 90 | 95 | 97 |
| COD, mg O L−1 | 83.3 | 83.0 | 82.7 | 47.2 | 81.8 | 80.9 | 79.2 | 82.8 | 81.6 | 64.2 | 78.7 | 83.8 | 83.2 | 83.0 | 79.5 | 81.8 | 82.0 |
| C org, mg L−1 | 31.2 | 31.1 | 31.0 | - | 30.7 | 30.3 | 29.7 | 31.1 | 30.6 | 24.1 | 29.5 | 31.4 | 31.2 | 31.1 | 29.8 | 30.7 | 30.8 |
| Diss. Org., mg L−1 | 62.5 | 62.3 | 62.0 | - | 61.4 | 60.7 | 59.4 | 62.1 | 61.2 | 48.2 | 59.0 | 62.9 | 62.4 | 62.3 | 59.6 | 61.4 | 61.5 |
| Variables/Lake | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of species | 7 | 8 | 4 | 14 | 11 | 5 | 6 | 11 | 11 | 12 | 9 | 14 | 14 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 11 |
| Sum of scores | 16 | 14 | 11 | 21 | 23 | 11 | 13 | 20 | 18 | 20 | 16 | 22 | 19 | 15 | 18 | 17 | 18 |
| Index S | 1.95 | 2.00 | 1.60 | 1.94 | 1.50 | 1.88 | 2.15 | 1.65 | 1.80 | 1.82 | 1.95 | 1.85 | 1.90 | 1.83 | 1.75 | 2.00 | 1.90 |
| Index WESI | 1.33 | 1.33 | 1.33 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.33 | 1.25 | 2.00 | 1.33 | 2.00 | 1.00 | 1.33 | 2.00 | 1.33 | 1.00 | 1.33 | 1.33 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barinova, S.; Gabyshev, V.A.; Gabysheva, O.I. Response of the Cyanobacteria Plankton Community to Anthropogenic Impact in Small Lakes of Urbanized Territory in the Permafrost Zone of Northeast Asia (Eastern Siberia, Yakutia). Water 2024, 16, 2834. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16192834
Barinova S, Gabyshev VA, Gabysheva OI. Response of the Cyanobacteria Plankton Community to Anthropogenic Impact in Small Lakes of Urbanized Territory in the Permafrost Zone of Northeast Asia (Eastern Siberia, Yakutia). Water. 2024; 16(19):2834. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16192834
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarinova, Sophia, Viktor A. Gabyshev, and Olga I. Gabysheva. 2024. "Response of the Cyanobacteria Plankton Community to Anthropogenic Impact in Small Lakes of Urbanized Territory in the Permafrost Zone of Northeast Asia (Eastern Siberia, Yakutia)" Water 16, no. 19: 2834. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16192834
APA StyleBarinova, S., Gabyshev, V. A., & Gabysheva, O. I. (2024). Response of the Cyanobacteria Plankton Community to Anthropogenic Impact in Small Lakes of Urbanized Territory in the Permafrost Zone of Northeast Asia (Eastern Siberia, Yakutia). Water, 16(19), 2834. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16192834







