Abstract
This study highlights the geochemistry of water and sediments of the karstic springs of the transboundary aquifer (TBA) Žumberak–Samoborsko Gorje Mt. (NW Croatia). After calculating pollution indices, the analysis showed that the sediments are unpolluted. The geo-accumulation index (Igeo) showed only the elements Ba and Rb, indicating moderate levels of pollution, with the highest values in springs Vapnik and Bistrac. Statistical analysis confirmed their natural origin. The water of these springs is under possible anthropogenic influence as indicated by elevated concentrations of total nitrogen (TN) and total phosphorus (TP). According to a principal component analysis (PCA) for elements in sediments, PC1 described a combined lithogenic and oxidative–reductive influence, PC2 described a combined geological background including total organic carbon (TOC) content and oxidative–reductive influence, while TOC had the greatest influence on PC3. Depending on element composition, the factor scores related to PC1 and PC2 resulted in two different groups of sites, while the factor scores concerning PC1 and PC3 did not show separation in two groups. The hierarchical cluster analysis showed three clusters in relation to the content of the elements. The correlation coefficient between the sediment and related water samples showed that the springs placed in a low-permeability formation (dolomite) had a strong positive coefficient of correlation.
1. Introduction
For sustainable and good water management and protection of transboundary aquifers, monitoring of water and sediments is required [1]. It is important to understand the geochemical processes in the covered karst aquatic environment, especially in water and sediments [2,3,4,5,6]. The most important substances in the aquatic environment that are widely considered to be persistent are chemical elements. Atmosphere influences, flooding, and fires with no control cause the natural entering of elements into the aquatic environment and cause ecosystem damage. The second and third ways are from the leaching of the surrounding rocks and the various anthropogenic activities (discharge of effluents from household and agricultural areas, roads, industry, illegal landfills, etc.) [7]. The origin of elements in water and sediment can be either natural (geochemical) or anthropogenic. They vary in concentration and geographical distribution in aquifers and catchments depending on the interactions of natural conditions and anthropogenic influences [8,9,10,11,12,13]. Naturally occurring elements are most commonly found in less accessible or completely inaccessible forms, while elements from anthropogenic sources are most often found in relatively bioavailable forms [14]. Considering the needs of living organisms and ecosystems, elements are classified into essential, biologically important, and ecotoxic. Ecotoxic elements are not needed for life and are toxic even at low concentrations [15]. The mobility of individual elements in the environment varies depending on their nature and chemical properties. According to [16], depending on mobility, elements are classified into four main groups: (1) high-mobility elements (Cd, B, Se, As, Sb, Mo, and Sr), (2) medium-mobility elements (U, Si, Li, Mn, Ba, Cu, Co, Ni, and Rb), low-mobility elements (Zn, Cr, V, Pb, Be, Fe, and Cs), and very-low-mobility elements (Ti, Al, and Zr). Sediments are an important component in the geomorphological circle connected to erosion and play a major role in circulating substances in the aquatic environment [17]. They are a possible source of inorganic matter and nutrients, but also a pollution tank [18,19]. Therefore, it is very important to determine the concentration of elements both in water and sediments, especially the ones from springs that could be used by stakeholders [20,21] such as tourists and local/domestic settlements for drinking water consumption and also for agricultural irrigation. Sediments in aquatic environments, especially in karst areas, play a crucial role in the assessment and understanding of environmental pollution, as they act as sinks for a wide range of contaminants and are known as pollutant traps [22,23,24,25]. The elements deposited in sediments represent the current status of an aquatic environment and give information and an overview of the pollution history of the karst aquifer. The accumulation of elements, organic compounds, and all other types of pollutants in sediments is a significant concern, as these can bioaccumulate and biomagnify through the food chain, posing a threat to aquatic ecosystems and human health. They can occur due to various anthropogenic activities, such as industrial effluents, mining operations, and agricultural runoff [26]. These pollutants could become incorporated into the sedimentary matrix, where they can persist for extended periods, potentially creating long-term environmental issues [27]. The distribution and concentration of elements and all other types of pollutants in sediments can provide valuable insights into the extent and sources of pollution within a specific water body [28]. By analyzing the spatial and temporal patterns of element pollution in sediments, it is possible to assess the impact of human activities on aquatic ecosystems and identify potential remediation strategies [29]. The chemical and geochemical properties of sediments, such as pH, organic matter content, and redox conditions, could influence the speciation and mobility of elements, trace elements, heavy metals, etc., affecting their bioavailability and potential for remobilization. The elements in sediments under reductive and acidic conditions could be mobilized back into the water column by dissolution [27,28].
To interpret the data, a multivariate statistical approach and assessment of pollution in sediments of karst springs are used. Both approaches give an answer to the origin of the enrichment or pollution of the elements, whether natural or anthropogenic. Different pollution indices such as EF, CF, PI, PLI, mCd, and Igeo are widely used to evaluate the contamination level of elements in the sediment [30,31,32]. The Igeo indices are a helpful in estimating the pollution level in water sediment [33,34,35]. Similar to Igeo, the complex PLI indices provide data on the general toxicity of elements in a given location and a comparison of pollution levels between different sites [36].
Dependency on a shared groundwater aquifer between the Republic of Slovenia and the Republic of Croatia has increased the interest and political motivation to cooperate on the TBA Žumberak–Samoborsko Gorje Mt. This is demonstrated by reporting on the Sustainable Development Goal (SDG 6) indicator related to transboundary cooperation, SDG indicator 6.5.2 and SDG 6.3.2 related to the protection of groundwater and surface water quality, and is consistent with SDGs (2, 3, 7, 12, 13, and 15) [37,38]. With the establishment of a Joint Agreement on cooperation between Croatia and Slovenia, they have rights and obligations under the Water Convention and the Water Framework Directive. According to the methodology or hydro-political system archetype (HSA) concept proposed in [39], the Žumberak–Samoborsko Gorje Mt. TBA belongs to the archetype “Covert Measures and Overt Effects”, where two riparian states (Slovenia and Croatia) rely on a shared aquifer. Recognizing the importance of TBA as a source of water and the lack of knowledge about this environment, the current TBA Žumberak–Samoborsko Gorje Mt. is under the initiative of Internationally Shared Aquifer Resources Management (ISARM), e.g., scientific, socioeconomic, legal, institutional, and environmental aspects. Therefore, this study supports the knowledge related to the geochemistry of water and sediments and could supply the scientific work of the Joint Commission with data available for groundwater and BA in particular. Because of unique hydrogeological and hydrogeochemical characteristics, karst aquifers are particularly vulnerable to pollution and are difficult to manage. Additionally, this study establishes the first current geochemical status of the water and sediment quality on a selected spring that is not included in the public water supply system but is used for domestic use and irrigation by stakeholders and random passers in the scattered, sparsely populated rural area surrounded by semi-agricultural fields and local roads of a larger part of the transboundary zone between Slovenia and Croatia. This study also hosted information that could help in the future identify the types of measures (including long-term monitoring and installation of treatment plants or secure septic tanks, etc.) in this TBA that could be implemented to reduce the effects of human activities on the groundwater quality and then their effects on sediment quality in the Žumberak–Samoborsko Gorje Mt. aquifer. The production of a standardized set of data, collection and proposed assessment methodologies, which are now being applied, could be a good start to the scientific investigation of water and sediment geochemistry and quality, the origin of possible natural or anthropogenic pollution, and all other parameters which could be important for a selected TBA. Additionally, this study hosted a dataset of the TBA geochemistry baseline that could be used in long-term biomonitoring activities and environmental health-related issues. All monitored karst springs are located in the territory of the Republic of Croatia, and the springs represent a discharge area. The recharge area is situated on both sides close to the Croatian and Slovenian state border which is regulated and defined by geomorphological and geographical features [40]. This TBA has a strategic significance and is richer in surface water compared to most other karst areas in Europe. A lot of pressure on all aquatic ecosystems in the karst area makes them extremely sensitive to pollution [41]. Therefore, if neighboring countries want to restore and preserve water resources and dependent ecosystems following UN Sustainable Development Goal 6, they need to take actions related to the ecological, hydrological, and hydrogeological domains and the societal and policy context. According to the Water Framework Directive (WFD, 2000/60/EC) [42], which offers an overarching framework regarding international cooperation to secure water for future generations, it is necessary to use the joint TBA approach and knowledge domain from different sectors. The overall aim of this proposed research is to further understand the link between pollution levels and the chemical composition of water and sediment of the TBA Žumberak–Samoborsko Gorje Mt. The TBA requires a scientific approach that includes sustainable management of water and sediment quality. A combination of multi-complementary analyses was used for the purpose of the data discussion.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The transboundary area of Žumberak–Samoborsko Gorje Mt. is a poorly populated and predominantly rural low mountain area with a big share of forest landscapes [43,44], protected as a Nature Park since 1999. In border zones towards the east, southeast, and south (especially in the area of the town of Samobor), there are more intense anthropogenic pressures due to the denser network of settlements, roads, agriculture, and quarries (Figure 1). The area is predominantly karst and fluviokarst with a smaller ratio of fluvial relief [45,46]. This wider area is also interesting for transboundary aquifers and sub-aquifers, numerous speleological features [47], as well as the wealth of spring water, so the protection in the category of Nature Park is very important from an environmental viewpoint. Groundwater and surface water are hydraulically connected through a mostly well-developed karst drainage network that is unique and extremely sensitive to possible threats from anthropogenic activities.

Figure 1.
Topographic map of research area with relief, settlements, and road network. Legend for springs: S1—Vugrinov spring, S2—Migalić, S3—Vrtlišće, S4—Vapnik, S5—Bistrac, S6—Zdenac, S7—Slapnica, S8—Drobovnik, S9—Jaža, S10—Močile, S11—Obrv, S12—Rogovac, S13—Špilja pod Pećinom, S14—Vrulje.
The synthesis of the geological and hydrogeological research in the area of Žumberak–Samoborsko Gorje Mt. was done in [48]. Previous research in this area on the geochemical comparison of the stream and overbank sediments was done in [49,50,51], where the geochemical and mineralogical characteristics of overbank sediments were researched. The most data about springs, their distribution, and basic physicochemical properties were analyzed in [47]. According to discharge, springs with a capacity between 0.01 and 0.1 L/s dominate (35%), followed by springs with a capacity between 0.1 and 1 L/s. There is well-developed karst circulation with a lack of data about abyss-springs interconnections and karst aquifers characteristics. The authors in [52] researched basic hydrochemical characteristics (total calcium and magnesium water hardness) from four caves, one karst spring, and one sinking creek of the Žumberak–Samoborsko Gorje Mt. area, and they used the results to estimate the catchment areas. The authors in [53] researched the Bistrac spring in Samoborsko Gorje Mt., and with a simple dye tracing method proved its underground connection with the newly formed collapsed doline in Otruševec valley. The Jaža and Obrv springs in Žumberak Mt. were also researched by [47,54]. Although they are only 200 m apart, at similar elevations (240 m a.s.l.), located in a similar geological setting (contact between Upper Cretaceous breccia and Upper Triassic dolomite), and have similar capacity and dynamics, they are fed by two different aquifers or sub-aquifers. The Jaža spring is fed by an allogenic drainage basin formed in Cretaceous flysch through two abysses formed at the contact with carbonates, and the Obrv spring is fed by an antigenic aquifer formed in the same carbonate deposits where the spring is located. In both cases, karst water flows through well-permeable karst conduits [54]. Since such a hydrogeological situation is characteristic of large parts of Žumberak Mt., according to observations on the karst surface and in caves, it can apply to the rest of the area with similar geological conditions. Karst spring sediments and water with so many elements and other parameters have never been investigated in this area. An estimation of pollution indices and hazard evaluation from element concentrations in sediments of karst springs of the transboundary aquifer Žumberak–Samoborsko Gorje Mt. were performed for the first time for this study, which is notable novelty compared to previous research.
2.2. Landscape Structure and Climate Control of the Hydrology of the Investigated Area
Catchment characteristics determined by geology, geomorphology, climate, vegetation, and soil patterns are first-order controls of the hydrological characteristics of the area [55]. The Žumberak–Samoborsko Gorje Mt. massif is situated at the crossing between the SE Alps, the NW Dinarides, and the Pannonian basin [56] in the border zone between Croatia and Slovenia (Figure 2). Structurally, this is a boundary between the Inner Dinarides [30,31,32] and the Zagorje–Midtransdanubian shear zone, overthrusting on the External Dinarides [57]. Different tectonic and lithological settings represent a heterogeneous massif. The lowest parts have an altitude of generally 200–300 m a.s.l, and the highest peak is Sv. Gera, 1178 m. a. s. l. The largest part of Žumberak Mt., which occupies the larger western part of the research area, is dominantly characterized by karst and fluviokarst relief forms with more than 3200 sinkholes, 193 caves and shafts, and 847 springs recorded [45,47,48,58,59]. The area is part of the autochthonous Žumberak Tectonic Unit, built of sedimentary Middle-Upper Permian beds, covered with Upper Triassic (mostly dolomites), Upper Cretaceous (flysch and limestone) rocks, and Quarternary sediments ([60]; Figure 2). Its western part is dominated by Triassic dolomites and Jurassic limestone over pelagic siliciclastic rocks of the Upper Cretaceous age [61,62,63]. In contrast, Samoborsko Gorje Mt., located in the eastern part of the research area, is tectonically dissected, lithologically diverse, and built of Permian rocks (predominantly sandstones) in the core of the autochthonous block covered with younger Triassic and Miocene clastic and carbonate beds (sandstones and highly karstified Miocene limestone). The beds were fragmented by neotectonic faults [64]. Sedimentary rocks of the Triassic, Jurassic, and Cretaceous ages were thrust over the older substructure during the Alpine orogenesis. The present appearance of the horizontally dislocated mass resulted mostly from the subsequent partitioning of individual minor blocks, which reduced its original proportions. In contrast, the southern borders of the area went through different tectonic and morphological changes, which resulted in a tectonic subsidence and formation of the Karlovac Depression [65]. Both of these units suffered intense fragmentation during the neotectonic phase, which influenced the karstification and development of the karst hydrological network.
The distribution of springs and hydrological characteristics were also determined by climate conditions. The research area is, according to the Köppen–Geiger climate classification, characterized by a Cfb climate type—warm temperate humid climate with hot summers [66]. The mean annual air temperatures vary from 9–10 °C in the lower parts (200–300 m a.s.l.) to 4–5 °C in the highest parts (900–1178 m. a. s. l.) [67]. The mean air temperature in January is 0 °C, and in July it is 18 °C [68]. The annual average amount of precipitation is about 1300 mm, while the precipitation peaks (June) are more than 1700 mm [69].
The most common soil types in the research area are rendzina, brown soils, eutric brown soil, and luvisol. Rendzina is developed on the loose carbonate substrate (Cretaceous limestone, flysch, marl). The brown soil is developed on limestone or dolomite. It is related to forest habitats and grassland. Eutric brown soil (eutric cambisol) is developed on loess. It comes in mild and undulating relief, up to 500 m a.s.l. Luvisol develops on loose sedimentary rocks, loess, lake sediments of lighter texture, and older colluvial deposits. The relief is flat to undulating, reaching between 150 and 700 m a.s.l. [70,71].

Figure 2.
Geological map of the study area (springs map and data [72,73]). Legend for springs: S1—Vugrinov spring, S2—Migalić, S3—Vrtlišće, S4—Vapnik, S5—Bistrac, S6—Zdenac, S7—Slapnica, S8—Drobovnik, S9—Jaža, S10—Močile, S11—Obrv, S12—Rogovac, S13—Špilja pod Pećinom, S14—Vrulje.
The vegetation of the Žumberak–Samoborsko Gorje Mt. is dominated by forests. They cover 78.7% of the mountain and low hills area where researched springs are located (Figure 3). In the lower hilly area, the most widespread forest is sessile oak and common hornbeam. On steeper warm slopes, the forests of pubescent oak and black hornbeam prevail. In the highest areas, the most common are beech forests [71]. In recent times, forests have been subjected to overexploitation in some parts, which has already been reflected locally in destructive slope geomorphological processes (slope washing and erosion). Due to the long historical population in the studied area, there is a significant proportion of cultural landscapes marked by grasslands that are mainly in the phase of intensive secondary succession due to modern depopulation and abandonment of agricultural activities and farms. Arable land occupies 3.7% of the area, while areas of secondary succession on former arable land cover 4.9%. Grasslands account for almost 10% of the area. Due to its rural character, small villages predominate in the core of the area, occupying only 2.5% of the surveyed region. The strongest impact of anthropogenic activities on spring water quality is expected in areas with settlements, higher road density, arable land, and other economic activities. These include the northwestern zones (springs S5 and S6) and the southwestern zones of Samobor (springs S1–S4) in the Samoborsko Gorje mountain range (Figure 1 and Figure 3).

Figure 3.
Habitat and landcover map of research area (after Habitat map of Croatia, 2016; Bioportal, www.bioportal.hr, accessed on 15 September 2024) with location of researched springs. The legend for springs is available on Figure 1 and Figure 2.
2.3. Sampling and Sample Preparation
The sampling of water and sediments was performed on 14 springs in the area of the Žumberak–Samoborsko Gorje Mt. aquifer during four seasons in 2015 and 2016 (on 12 April 2015, 6 June 2015, 19 September 2015, 20 September 2015, 20 February 2016, and 21 February 2016) (Table 1). Analyses were performed in the Josip Juraj Strossmayer Water Institute, Main Water Laboratory (MWL), Zagreb, Croatia. Figure 2 shows the geographical positions of all 14 locations of sampling karst springs on the geological map of the study area. Figure S1 shows the situation of the selected springs (6 of 14) included in the study.

Table 1.
Sampling locations with hydrogeological characteristics.
Physicochemical parameters (pH, EC, turbidity) were measured using a SevenMulti instrument (Mettler Toledo, Greifensee, Switzerland) and a HACH 2100 N turbidimeter (HACH, Loveland, CO, USA). Previously, a pH electrode was calibrated with standard pH 4 and 7 buffer solutions. The standard for pH was [74]. For electrolytic conductivity (EC), the standard was [75], and for turbidity, the standard method was [76]. Dissolved anions and cations were determined by ion chromatography on a Dionex ICS 3000 device (Dionex, Sunnyvale, CA, USA), anions according to standard [77] and cations with standard [78]. Total nitrogen (TN) in water was determined using a Shimadzu analyzer TOC-VCPH with a TNM-1 unit (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) according to [79]. Dissolved organic carbon (DOC) was determined following the standard [80]. Before the measurement, the samples were filtered through a 0.45 µm filter paper and acidified with HCl, which removed inorganic carbon that was removed from the sample by blowing using synthetic air. Concentrations of thirty-two (32) dissolved elements (Al, As, B, Ba, Be, Ca, Cd, Co, Cr, Cs, Cu, Fe, K, Li, Mg, Mn, Mo, Na, Ni, TP, Pb, Rb, Sb, Si, Sn, Sr, Ti, Tl, U, V, Zn, and Zr) and total phosphorus (TP), were measured using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS, Elan 9000, PerkinElmer, Shelton, CT, USA), with a solution of 20 µgL−1 Rh, Ge, Re, Ce, and In as the internal standard according to standard [81]. The ICP-MS method quality control was performed by the analysis of the certified reference material TM-RAIN04 from the Council Canada and Complex Nutrients—Whole volume QS from Sigma-Aldrich (for phosphorus). A generally good agreement within 10% was observed between our data and the certified values. Sediments were sieved with a <63 µm sieve model RetschAS200, because this fraction is recommended in Guidance Document No: 25 under the Water Framework Directive, and then dried in a thermostat at a temperature of 40 °C. Sediment samples were degenerated with 7.5 mL of Suprapur nitric acid and 2.5 mL of puriss. hydrochloric acid in an Anton Paar Multiwave 3000 Oven (Anton Paar, Graz, Austria) according to [82]. Elements in sediment were detected by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry at ICP-MS Elan 9000, PerkinElmer. The ICP-MS method quality control was performed by the analysis of the elements of interest in a standard reference material (RTC, trace elements on water and sediment). Total phosphorus and total nitrogen in sediments were determined using a spectrophotometric method with a Perkin Elmer Lambda 25 UV/VIS spectrophotometer (Perkin Elmer, Shelton, CT, USA), total phosphorus according to [83] and total nitrogen according to [84]. Before determination, the samples were digested with concentrated reagents (H2SO4, K2SO4, and SeO2). After that, the samples were treated with hydrogen peroxide, releasing organic N as ammonium and organic P as phosphate.
The hydrochemical relationships of the eight important main ions Ca2+, Mg2+, Na+, K+, HCO3 −, CO3 2−, SO4 2−, and Cl− in the water samples are shown in the trilinear Piper diagram. The Piper diagram was used to define hydrochemical facies using the free USGS software GW Chart v.1.30.0 [85].
2.4. Assessment of Pollution Indices for Sediments
According to [23], five parameters acting as the indicators of the pollution level in the environment are enrichment factor (EF), contamination factor (CF), pollution index (PI) with pollution load index (PLI), modified degree of contamination (mCd), and geo-accumulation index (Igeo). The pollution indices are used for the assessment of the degree of contamination in the environment due to chemical element accumulation in a study area and are compared with health-related values suggested or mandated by international standards. The above pollution indices are widely recognized as valuable and useful tools for the comprehensive evaluation of the degree of contamination of sediments. Those pollution indices are important in the assessment of soil quality and the prediction of future ecosystem sustainability, especially in the case of farmlands. In this study, the above criteria were applied to the sediment samples from 14 karst springs and were used as indicators for evaluating the pollution risk caused by heavy metals.
According to [86], enrichment factor (EF) is used for the estimation of the degree of contamination due to trace elements in the soil or sediment samples. As the reference element, Fe is taken for normalization and estimation of the presence and intensity of anthropogenic contaminant deposition.
According to [87], sediment sample contamination is indicated using the contamination factor (CF), which presents the ratio of metal concentration in the sediment sample to the reference value of that metal.
According to [88], the geo-accumulation index (Igeo) is a quantitative measure of the degree of pollution in aquatic sediments and presents the concentration of metal accumulation in a sediment above the baseline concentration.
For the assessment of overall sediment toxicity, the pollution load index (PLI) presents the determination of the entire pollution level of a specific area.
For a better assessment value and the assessment of overall heavy metal contamination in sediment samples, the modified degree of contamination (mCd) and cumulative index are calculated by the sum of individual contamination factors (Cd).
2.5. Statistical Analysis
Multivariate and basic statistical analyses were applied to determine the relationship between elements. The statistical analysis included 14 samples of sediment and 56 samples of water. A descriptive statistical analysis was performed and included minimum value, maximum value, median, average, variance, standard deviation, and variance coefficient. Additionally, multivariate statistical analyses included principal component analyses (PCA), correlation analysis, factor analysis (FA), and cluster analyses (CA), which were performed using the statistical software package STATISTICA 10.0 program.
3. Results and Discussion
The measured values of physicochemical parameters, nutrient concentrations (ammonium, nitrates, nitrites, and orthophosphates), dissolved anions, alkalinity and total hardness, turbidity, and dissolved organic carbon (DOC) are presented through descriptive statistics and compared with the maximum allowed concentration and values (MAC) prescribed by The Regulation ([89]; Table S1). Descriptive statistics include the number of measurements, mean and median values, minimum, maximum, variance, standard deviation, and coefficient of variation. All the values of the measured indicators were below the MAC, except for turbidity, for which the mean value was 3.22 NTU but with the highest measured value at S4 (20.1 NTU), which exceeds the MAC, as did S5 (5.10 and 9.60 NTU), S7 (5.10 NTU), S8 4.70 NTU), S9 (5.60 and 7.10 NTU), S11 (17.4 NTU), S12 (4.70 NTU), S13 (5.30 NTU), and S14 (13.1 NTU). Although turbidity in spring waters usually increases during high water and most of the samples with higher values than prescribed were taken in that period during February 2016, the highest value of turbidity was measured in the low water period during July 2016.
The mean value of pH was 7.61, weakly alkaline, almost the same as the mean annual pH values reported by Vujnović [47] from previous investigations on springs from the same area or for karst springs from Biokovo Mt. reported by Matić et al. [10]. Sampling site S4 had the highest measured EC value of 789 µS cm−1, which was measured in the high water period during April 2015. However, the mean value of EC was 527 µS cm−1, which was a little higher than the values in the mentioned report by Vujnović [47] and from investigations of the Gacka River karst springs reported by Matić et al. [79] probably due to more soluble limestone rocks. The lowest measured concentration of dissolved organic carbon (DOC) was 0.420 mg L−1 while the highest concentration was 2.21 mg L−1 (S13). It is slightly higher than values from the karst springs of Biokovo Mt. and the Gacka River karstic springs reported by Matić et al. [10,90]. Namely, the research area is covered by forest, far more than the research area studied by Matić et al. [10,90], so this difference in DOC can be explained by the leaching of the organic component from the surrounding vegetation. The mean measured values of ammonium and orthophosphate were following the investigation of the Gacka River karst springs by Matić et al. [90] with maximum values for ammonium at S13 (0.028 mgL−1) and for orthophosphates at S5 (0.058 mgL−1), while the mean concentration of nitrates was eight times higher with the maximum at S4 (23.9 mgL−1). Considering that the concentrations of ammonium, nitrites, nitrates, orthophosphates, and DOC for all the studied karst springs were several times lower than the MAC values prescribed by The Regulation, it could be concluded that anthropogenic activity does not influence the investigated karst springs’ water quality. However, springs S4 and S5 had the highest measured concentrations of nitrates and orthophosphates throughout the sampling time, whereby S4 was most likely affected by nearby settlements (Figure 1 and Figure 3). During the fieldwork in the catchment area of spring S5 (Bistrac), in Otruševec Valley, there was recorded pollution by sewage discharges from households directly to streams connected by underground circulation with Bistrac [53].
A Piper diagram was used (Figure 4; [85]) to define the hydrochemical facies with USGS free software GW_Chart. Dissolved anions and cations in spring waters from the obtained data showed that groundwater belongs to the calcium type (Ca—HCO3), which is a slight difference from the research reported by Brkić et al. [48], in which the researched springs from a broader area belonged to the CaMg—HCO3 type. Mg content was somewhat higher in the Vugrinov spring (S1), Vrtlišće spring (S3), Vapnik spring (S4), Zdenac spring (S6), Slapnica spring (S7), and Obrv spring (S11), indicating that the geological composition is predominantly made of limestone with the presence of dolomite.

Figure 4.
Piper diagram for the investigated springs.
3.1. Elemental Composition of Water and Sediments
The concentrations of 32 elements, total nitrogen, and total phosphorus are presented through descriptive statistics in Table S2. In all investigated samples, only the maximum concentration of Fe at S12 (467 µgL−1) exceeded the maximum allowed concentration (MAC) laid down by The Regulation. It is interesting that in the same sample, which was taken during the high water period in April 2015, maximum concentrations of Al (149 µL−1) and Mn (41.6 µL−1) were also measured but with their values below the maximum allowed concentration. The increased concentrations of these elements probably occurred because of geological conditions during heavy rains and the washout of the surrounding area. The maximum TN and TP concentrations were measured at S4 (5.42 mgL−1 and 0.092 mgL−1). As previously stated in the case of nitrates and orthophosphates, elevated concentrations of TN and TP at S4 during the entire investigated period could lead to less anthropogenic influence. Increased Ti concentrations measured at S5 (4.18 µL−1) and S9 (6.99 µL−1), with a maximum at S4 (9.77 µL−1), were from geogenic origin due to highly anomalous points in northern Croatia related to Tertiary clastic rocks [91]. Additionally, the measured maximum concentrations of the elements Sn (2.33 µL−1), Cu (16 µL−1), Ni (4.19 µL−1), and Sb (1.13 µL−1) at S13 are most likely of geogenic origin due to Tertiary clastic rocks located at greater depths, whereby the water reaches the surface by an ascending way, where it forms spring in the cave. Compared to other similar areas in Croatia, the concentrations of dissolved elements are similar to or slightly above the values reported in [92] for the Kupa and Rječina karst springs and karst springs from Biokovo Mt. reported in [10].
The concentrations of 32 elements and TOC in the fraction <63 µm of the spring sediments are presented in Table S3 and discussed according to available sediment quality criteria from Ontario legislative, Canada (OL), Great Lakes, St. Lawrence River (Canada) and Guidelines for the pollution classification of Harbor sediments, summarized in [93]. The concentrations of As, Cr, and Ni at all investigated springs were higher than the concentrations that can cause a minimal toxic effect, as were those of Cd except at S1 and TN except at S12. On the other hand, the concentration of Ba at all springs and Mn at S3, S4, S5, S7, S8, S10, S11, S12, S13, and S14 exceeded the values that can cause a maximum toxic effect. In the nearby area of the Kupa River drainage basin, which is also a TBA, [92] reported Ba anomalies in stream sediments, of anthropogenic origin in the western part of the basin due to barite mining and of natural origin in the eastern part due to ore mineralization. In this case, it can be concluded that the elevated Ba concentrations were of natural origin, as is the elevated concentration of Mn. Namely, according to the Geochemical Atlas of Europe [91], it is possible that these concentrations of Mn near the Slovenian and Croatian border are of natural origin due to variable lithology and mineralization. Concentrations of TOC at S1, S2, S4, S5, S8, S9, S10, S13, and S14 exceeded the values that can cause a minimal toxic effect, while at S6, it exceeded the value that can cause a maximum toxic effect. Considering that the investigated springs are located in a predominantly forest area, it can be concluded that the increased concentrations of TOC were the result of the influence of the local vegetation and leaching of the surrounding soil rich in organic matter, except at S6 [94,95]. Additionally, it can be concluded that the increased concentrations of TN were of natural origin, from the surrounding vegetation and leaching soil. After plant material falls on the ground, it decomposes, and nitrogen is released back into the soil, from which it can then be leached away into the sediment [96,97]. On the other hand, the very high concentration of TOC captured at S6 (16.6%) was due to an unquestionable anthropogenic influence. Namely, near S6, there is a lake from which the sediment was sampled, where cattle are watered and houses are located nearby. Additionally, the mean concentrations of elements in the sediment of this study were in good agreement with research at similar locations in Croatia, the spring of the Rječina River reported by [98], the spring of the Kupa River reported by [99], and the springs of the Gacka River reported by [90].
3.2. Principal Component Analyses (PCA) and Cluster Analyses (CA) of Sediment Samples
Figure 5 shows the dependence diagram of components PC1 and PC2, while Figure 6 shows components PC1 and PC3 for sediments from researched karstic springs. The first three components explained 71.6% of the total variability of 22 variables. The first component described 35.8% of the data variance, the second 26.1%, and the third described 9.58% of the variance. High positive values of PC1 were characteristic of Fe, Ba, Cr, Al, Tl, Mo, Cd, As, Mn, Ni, and Co. Furthermore, the first component described TN, but not with high values. It can be concluded that the first component represented a combined lithogenic influence described primarily by the content of Fe and Al, an oxidative–reductive influence described by the content of Mo and Cd, as well as a biogenic influence described by the content of TN, considering that it comes from the surrounding vegetation. High positive PC2 values were characteristic of Ca, Mg, Si, V, U, Pb, and Zn. Additionally, the second component described TOC, but not with high values. It can be concluded that the second component reflected the combined influence of the geological background of the surrounding area, including TOC content, and an oxidative–reductive influence described by the content of U. TOC had high positive values and the greatest influence on PC3, while Si and V had negative but not high values.
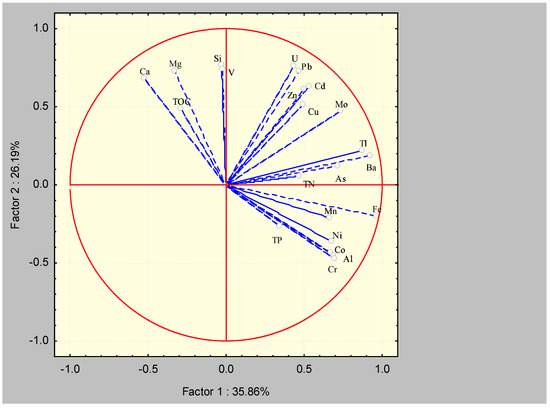
Figure 5.
Diagram of dependence of PC1 and PC2 for sediments from karstic springs of TBA Žumberak–Samoborsko Gorje Mt.
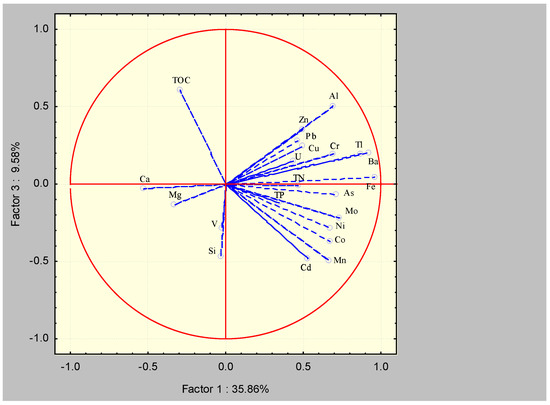
Figure 6.
Diagram of dependence of PC1 and PC3 for sediments from karstic springs of TBA Žumberak–Samoborsko Gorje Mt.
The distribution based on factor scores concerning components PC1 and PC2 according to Figure 7 showed two different groups of locations that were grouped according to their elemental composition, while the other springs remained relatively dispersed. The first group consisted of springs S8 and S14, which were grouped according to Ca content, while the second group consisted of springs S10, S12, and S13, which were grouped according to Mn and Si content. Spring S6 stood out from the others for its Ca, Mg, and especially TOC content, which were the highest of all sources. On the other hand, springs S4 and S5 stood out due to oxidative–reductive influence, which was the most pronounced in these springs considering the content of Mo and U, while S5 also stood out for its Fe content. Springs S1, S3, S9, and S11 did not form a group and stood out from the others concerning the first component, according to the content of Ba and Cr. The distribution based on the factor scores concerning components PC1 and PC3 (Figure 8) did not show the separation of springs into groups, but the springs remained quite dispersed. The separation of spring S7 according to the content of Si could certainly be seen.
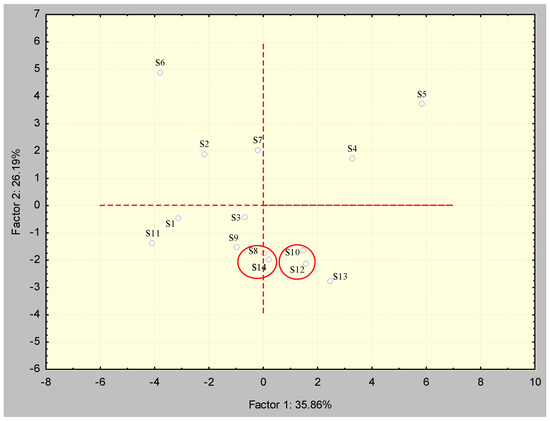
Figure 7.
Dependency diagram of factor scores for PC1 and PC2.
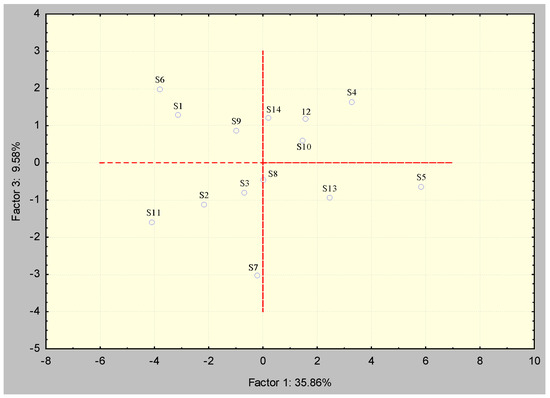
Figure 8.
Dependency diagram of factor scores concerning PC1 and PC2.
From the dendrogram of the hierarchical cluster analysis according to the concentration of an individual element and TOC (Figure 9), three clusters were visible: the first cluster consisting only of TOC (C1), the second consisting only of Ca (C2), and the third consisting of Al and all other elements (C3). Calcium is a lithogenic element that forms carbonate deposits at springs, while TOC is responsible for organic carbon-enriched deposits. Cluster 3 separates Al from all other elements that can be further divided into sub-clusters, the first of which consists of lithogenic elements Fe, K, Si, and Mg and all other elements.
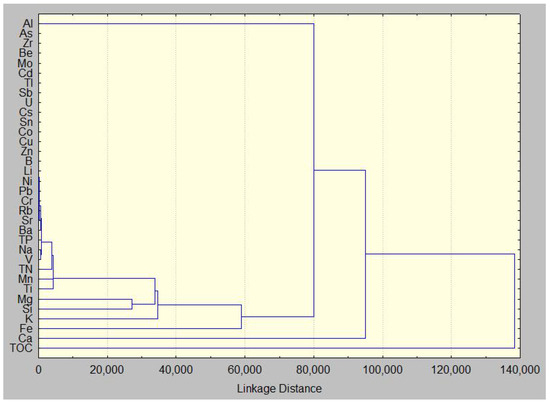
Figure 9.
Dendrogram of hierarchical cluster analysis concerning element content and TOC.
3.3. Correlation Coefficient between the Sediment and Related Water Samples
The strongest positive correlations were between sediment and water samples at S1 with an average correlation coefficient of 0.73, S6 with an average correlation coefficient of 0.64, and S7 with an average correlation coefficient of 0.56 (Table S4). These three springs are developed in the Middle to Upper Triassic sediments. Negative correlations were detected at locations S10 and S13, with an average correlation coefficient for both locations of −0.01. Both springs are placed at the Turonian sediments (K22). Other samples had a positive correlation, ranging from 0.01 to 0.47, and stratigraphically are placed in a wide range, from the Lower Triassic (T1) to the Upper Miocene (1M31).
According to the geological map [73], springs S8, S9, S10, S11, S13, and S14 are placed in the Upper Cretaceous, high permeability limestone (K22) and had slightly positive to negative correlations ranging from −0.01 to 0.35. The only exception was spring S11, where a strong positive correlation of 0.70 was registered in Sample 3. According to the geological map [73], spring S7, developed in the Middle/Upper Triassic, low permeability dolomite (T2,3), showed a strong positive correlation that ranged between 0.57 to 0.81. Spring S4 (T1) is developed in Lower Triassic high permeability limestone and had a slightly positive correlation ranging from 0.16 up to 0.30. Spring S5, developed in karstified Miocene limestone, had a slightly positive correlation as well, ranging from 0.09 up to 0.23. Spring S6, placed in Upper Triassic, low permeability dolomite (T3), showed a strong positive correlation that ranged from 0.57 up to 0.81. Springs S2 and S3 are placed in Lower Sarmatian (Upper Miocene) which consists of sandstone, marly limestone, and lime marls, with medium to low permeability. They had slightly strong positive correlations ranging from 0.37 up to 0.61. As a result of statistical analysis, it can be concluded that water from the springs placed in limestones of higher permeability had a slightly negative to slightly positive coefficient of correlation related to the sediment. The springs placed in medium to low-permeable formations (marls, sandstones, marly limestone) had a slight to strong positive coefficient of correlation related to the sediment. The springs placed in low-permeability formations (dolomite) had a strong positive coefficient of correlation related to the sediment. It is a consequence of the retention time of water in the underground; in high permeability formations with developed karst conduits, groundwater retention time is low and possibilities of interaction between water and sediments are lower than in low-permeability formations with a higher retention time.
3.4. Pollution Indices
Five parameters as indicators of pollution level or the degree of pollution in the environment were used: enrichment factor (EF), contamination factor (CF), geo-accumulation index (Igeo), pollution load index (PLI), and modified degree of contamination (mCd). After a comprehensive evaluation of the degree of contamination of the sediments, the above criteria were applied to the sediment samples from 14 karst springs and were used as indicators for evaluating the pollution risk caused by elements. These are dimensionless pollution parameters.
According to calculations of pollution indices, which are used as indicators to identify and quantify the degree of elemental pollution and to assess the intensity of natural and anthropogenic contaminants accumulated in spring sediments, it was indicated that there was no or low pollution. The calculated dimensionless pollution values were: pollution index (PLI) of 0.71, indicating a low pollution level or the degree of pollution, enrichment factor (EF) of 0.041, indicating a low pollution level, contamination factor (CF) of 0.71, indicating a low pollution level or the degree of pollution, pollution load index (PLI) value of 0.133, which means no pollution, modified degree of contamination (mCd) of 0.71, representing no or a very low degree of pollution, and geo-accumulation index (Igeo) of 1.911 for Ba and 1.167 for Rb, indicating moderate pollution for elements Ba and Rb and no pollution for other elements. Thus, all pollution indices of PI, EF, CF, PLI, and mCd similarly determined the quality of the sediment in the investigated area. It was the first indices analysis of sediment quality for the comprehensive valuation of the degree of sediment pollution in the TBA in Croatia. The individual and complex solution indices did not indicate pollution of the sediments.
The geo-accumulation index was used to determine the environmental quality of the sediments in terms of element accumulation. Only concentrations of elements Ba and Rb had moderate levels of pollution, and all other elements showed unpolluted levels. The sediment samples were suffering from moderate pollution with elements Ba and Rb mostly on the springs Vapnik and Bistrac, but not all other spring sediments with the studied elements according to Igeo values. Shortly, the whole aquatic and terrestrial environment may be polluted with the elements Ba and Rb. The richness of these elements may present potential health risks for the human populations residing in the vicinity of the studied area.
In the area of the Kupa River non-mountain drainage basin also a TBA, next to the current mountain study area, ref. [92] reported Ba anomalies that were found in stream sediments of the Kupa River. There were significant concentrations on two sites, one was of anthropogenic origin in the western part of the basin, whereas that in the eastern part of the basin was of natural origin. Enrichment of spring sediment in the study area with elements Ca, Mg, Al, Cu, Li, and Fe suggests that this was a significant natural enrichment originating from the geological background, karst Dinaric platform. Additonally, it can be concluded that significantly higher concentrations, primary of Ba and secondary of Rb, are of natural origin. A group of authors [13] reported higher concentrations of Ca, Mg, Al, and Fe of natural origin derived from the geological background (Dinaric platform). Furthermore, in this area, there is a known closed mining site from the history of the settlement of Rude, where there were Fe and Cu ores.
Significant values of correlation coefficients of elements Ba and Rb with lithogenic elements, such as Ba–Li (0.7), Ba–Fe (0.85), Rb–Al (0.88), Rb–Fe (0.73), and Rb–Li (0.71), were recorded. It suggests that the enrichment of Ba and Rb were of natural origin. Therefore, the sediments of the springs Vapnik and Bistrac, and all other springs with higher pollution indices, are under natural pollution or enrichment. However, all other pollution indices indicate that there is no or low risk for the human population and the whole ecosystem.
The results obtained by complementary methods will be useful for the general public, the scientific and professional community, and transboundary water management decision makers. Important facts from water and sediment quality analyses are these: the results showed that the quality of water and sediment is in line with the sixth goal of sustainable development (SDG 6.5.2 and SDG 6.3.2) and related SDGs that will help not only the Joint Commission dealing with the TBA between Croatia and Slovenia as a strategic source of drinking water, but also global reporting and finally the achievement of a common global goal and the 2030 Agenda. According to the law, the “polluter pays” principle is also incorporated, and the objective is maintaining or reaching a good ecological status for all water resources through the control of pollution by using threshold levels and standards. It also introduces innovative approaches concerning the protection of water quality and the transnational cooperation for the protection of the TBA. The obtained results are not limited only to environmental topics; they are also beneficial to geomedicine/medical geology/geochemistry and health investigations, where the results could be applied to biomonitoring, ecosystem management, human health protection, environmental health studies, etc. [100,101].
4. Conclusions
The study area was the transboundary (TBA) Žumberak–Samoborsko Gorje Mt., which belongs to a sensitive karst area between Croatia and Slovenia. Water and sediment samples were collected at 14 sampling sites, all of which are located in Croatian territory. The springs have capacities under 150 L s−1. Karst water and sediment quality (physicochemical parameters, nutrient concentrations, dissolved ions, alkalinity and total hardness, turbidity, DOC, and dissolved elements in water), including pollution indices, was investigated. It was found that the mean values of all measured parameters of the TBA in the period from 2015 to 2016 during four seasons were within the allowable limit values prescribed in The Regulation on compliance parameters, methods of analysis and monitoring of water intended for human consumption (OG 64/2023), except for turbidity, which exceeded the allowable limit values. This means that the water of the TBA has a good ambient status and is suitable and safe for the ecosystem. The hydrogeochemical type of water in all springs belongs to the Ca-HCO3 type due to its lithology. Additionally, the presence of DOC can be explained by the leaching of the organic component from the surrounding vegetation. Springs S4 and S5 had the highest measured concentrations of nitrates and orthophosphates throughout the sampling time, whereby S4 was most likely affected by nearby settlements. The elements in sediments were also analyzed with complementary analyses, which showed that higher concentrations of Ba in all spring sediments exceeded the values that can cause a maximum toxic effect. Although it is of lithogenic origin, awareness needs to be developed of increased concentrations of Ba in the environment due to ecosystem health. Enrichment of Ba was found in earlier investigations in the wider area of the Kupa River in the Karlovac depression. Enrichment of TOC in all springs except S6 could be under the influence of the local vegetation, leaching of the surrounding soil rich with organic matter, and TOC in the sediment of S6 indicates that the spring is under anthropogenic influence, e.g., cattle are watered and houses are located nearby. The strongest positive correlation was between sediment and related water samples at S1, S6, and S7, and these three springs are developed in the low permeability formation (Middle to Upper Triassic dolomites). The individual and complex solution indices did not indicate pollution of the sediments. According to pollution indices PI, EF, CF, PLI, and mCd, there is no pollution or there is a low level of pollution in the studied spring sediments. Igeo shows the presence of Ba and Rb in higher values of the spring’s sediments e.g., Vapnik and Bistrac indicating moderate pollution. This pollution is of natural origin. According to Igeo, there is no pollution for all other elements. Additionally, statistical analyses showed significant values of correlation coefficients of elements Ba and Rb with lithogenic elements, such as Ba–Li (0.7), Ba–Fe (0.85), Rb–Al (0.88), Rb–Fe (0.73), Rb–Li (0.71). It suggests that the enrichment of Ba and Rb could be from natural origin. According to the PCA for elements in sediments, PC1 showed combined lithogenic and oxidative–reductive influence, PC2 combined the geological background, including the influence of TOC content and oxidative–reductive reactions, while TOC had the greatest influence on PC3. Depending on element composition, the factor scores related to PC1 and PC2 resulted in two different groups of sites, while the factor scores concerning PC1 and PC3 did not show separation in the two groups. The hierarchical cluster analysis showed three clusters concerning the content of the elements. This study is in line with achieving the requirements of SDG 6.5.2. and 6.3.2. Water and sediment databases such as this which require knowledge about long-term pollution and various anthropogenic and geogenic pressures in the environment support the water management of the study TBA. Furthermore, it could provide baseline reference values for the study of all other aquifers in karst areas. Given the spatial heterogeneity of the aquifer, the geodiversity of the surface, more difficult accessibility to representative sampling sites, the complexity of the covered karst, as well as the different physical processes and chemical reactions that occur in the aquifer, a combination of field and laboratory methods was used. The laboratory instruments are highly sensitive, sophisticated, and expensive, but were able to detect and transform the relationships between surrounding rocks and water and sediments into numbers that are further used for statistical interpretation and calculation of pollution indices. The challenge was noticed when the results gave elevated values of unexpected elements in an environment such as TBA Žumberak–Samoborsko Gorje Mt., and it was an experience to explore the very scarce literature on this issue.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/w16192718/s1; Figure S1: The situation of selected springs included in the research: A—Bistrac (S5), B—Špilja pod Pećinom (S13), C—Drobovnik (S8), D—Rogovac (S12), E—Vapnik (S4) and F—Vugrinov spring (S1). All photos by N. Buzjak; Table S1: Descriptive statistics of physicochemical parameters; Table S2: Descriptive statistics of elements in Žumberak–Samoborsko Gorje Mt. spring water obtained by ICP-MS method; Table S3: Descriptive statistics of elements and TOC in spring sediments fraction <63 µm; Table S4: Calculated Pearson correlation coefficient between sediment, water samples, and average water sample; Table: Concentrations of physicochemical parameters of TBA Žumberak–Samoborsko Gorje Mt.; Table: Concentrations of elements in water of TBA Žumberak–Samoborsko Gorje Mt.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.B., N.M. and K.M.; methodology, K.M. and V.J.; software, K.M. and V.J.; analysis, K.M., N.B. and N.M.; investigation, N.M., K.M. and N.B.; collection data in the field, N.B. and K.M.; writing—original draft preparation, N.B., N.M. and K.M.; writing—review and editing, supervised the work, N.B. and V.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data will be made available on request.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the support provided by the Josip Juraj Strossmayer Water Institute, Main Water Laboratory (MWL), where laboratory work was performed; we thank Stipaničev, D. and Milović, S. We are thankful to Tomas, D. for field support and Vasiljević, R. for the useful tips. We are thankful to the University of Zagreb, Faculty of Science, and Croatian Waters for their permission to take minor data from the National monitoring database. English was edited by Jauk, T., and we thank her a lot for her kind help. We also appreciate the journal’s reviewers for taking their precious time to review the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Goldscheider, N.; Drew, D. Methods in Karst Hydrogeology: IAH: International Contributions to Hydrogeology, 26; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Quinlan, J.F. Types of Karst, with Emphasis on Cover Beds in Their Classification and Development. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Texas Austin, Austin, TX, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- White, W.B. Geomorphology and Hydrology of Karst Terrains; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1988; p. 464. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, P.W. Arête and Pinnacle Karst of Mount Kaijende. In Karst Rock Features: Karren Sculpturing; Ginés, Á., Knez, M., Slabe, T., Dreybrodt, W., Eds.; ZRC Publishing: Postojna, Slovenia, 2009; Volume 9, pp. 433–437. [Google Scholar]
- Veress, M. Covered Karsts; Springer Geology; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2016; ISBN 978-94-017-7518-2. [Google Scholar]
- Veress, M. Karst Types and Their Karstification. J. Earth Sci. 2020, 31, 621–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drew, D.; Hötzl, H. Karst Hydrogeology and Human Activities: Impacts, Consequences, and Implications: IAH International Contributions to Hydrogeology 20; Taylor and Francis: London, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- De Vivo, B.; Ander, E.L.; Bidovec, M.; Lima, A.; Pirc, S.; Reeder, S.; Siewers, U.; Smith, B. Distribution of elements in stream water. In Geochemical Atlas of Europe; De Vos, W., Tarvainen, T., Eds.; Part 2; Geological Survey of Finland: Espoo, Finland, 2005; pp. 33–35. [Google Scholar]
- De Vos, W.; Batista, M.J.; Pirc, S.; O’Connor, P.J.; Demetriades, A.; Tarvainen, T.; Salminen, R.; Reeder, S.; Salpeteur, I.; Gregorauskiene, V. Distribution of elements in stream sediment. In Geochemical Atlas of Europe; De Vos, W., Tarvainen, T., Eds.; Part 2; Geological Survey of Finland: Espoo, Finland, 2005; pp. 37–39. [Google Scholar]
- Matić, N.; Miklavčić, I.; Maldini, K.; Tomas, D.; Cuculić, V.; Cardellini, C.; Frančišković-Bilinski, S. Geochemical and isotopic characteristics of karstic springs in coastal mountains (Southern Croatia). J. Geochem. Explor. 2013, 132, 90–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meybeck, M. Heavy Metal Contamination in Rivers across the Globe: An Indicator of Complex Interactions between Societies and Catchments. In Understanding Freshwater Quality Problems in a Changing World, Proceedings of the H04, IAHS-IAPSO-IASPEI Assembly, Gothenburg, Sweden, 22–26 July 2013; IAHS Publisher: Wallingford, UK, 2013; Volume 61, pp. 3–16. [Google Scholar]
- Razak, I.S.; Tan, Z.Z.; Nor, Z.M.; Wahid, N.B.A.; Mushrifah, I.; Latif, M.T. Correlation between surfactants and heavy metals in a Natural Lake. Environ. Forensics 2012, 14, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldini, K.; Cukrov, N.; Pikelj, K.; Matić, N.; Mlakar, M. Geochemistry of Metals and Organic Matter in Water and Sediments of the Karst River Cetina, Croatia. Water 2023, 15, 1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massas, I.; Ehaliotis, C.; Gerontidis, S.; Sarris, E. Elevated heavy metal concentrations in top soils of an Aegean island town (Greece): Total and available forms, origin and distribution. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 151, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavreva-Veselinovska, S.; Živanović, J.; Đokić, M. The toxic influence of excessive concentrations of some heavy metals upon anthoccians, flavonoids, and phenols in pepper (Capsicum annum) as a vegetable. Nat. Montenegrina 2008, 7, 527–534. [Google Scholar]
- Gaillardet, J.; Viers, J.; Dupré, B. Trace elements in river waters. Treatise Geochem. 2003, 5, 605. [Google Scholar]
- Charlton, R. Fundamentals of Fluvial Geomorphology; Routledge: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Besser, J.M.; Leib, K.J. Toxicity of Metals in Water and Sediment to Aquatic Biota. In Integrated Investigations of Environmental Effects of Historical Mining in the Animas River Watershed, San Juan County, Colorado; Church, S.E., Ed.; U.S. Department of the Interior U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2007; Chapter E19; Volume 2, pp. 837–851. [Google Scholar]
- Dinelli, E.; Cortecci, G.; Lucchini, F.; Zantedeschi, E. Sources of major and trace elements in the stream sediments of the Arno river catchment (northern Tuscany, Italy). Geochem. J. 2005, 39, 531–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, D.; Williams, P. Karst Hydrogeology and Geomorphology; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann, A.; Goldscheider, N.; Wagener, T.; Lange, J.; Weiler, M. Karst water resources in a changing world: Review of hydrological modeling approaches. Rev. Geophys. 2014, 52, 218–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Luo, G.; Chen, X.; Yang, X. Integrated assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediments from a coastal industrial basin, NE China. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafie, N.A.; Aris, A.Z.; Zakaria, M.P.; Haris, H.; Lim, W.Y.; Isa, N.M. Application of geo-accumulation index and enrichment factors on the assessment of heavy metal pollution in the sediments. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2013, 48, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.B.; Shantaa, T.B.; Ahmeda, A.S.S.; Hossainb, M.K.; Semme, S.A. Baseline study of heavy metal contamination in the Sangu River estuary, Chattogram, Bangladesh. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 140, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Walker Davis, E.; Ma, G. Ecological risk assessment of metals in small craft harbor sediments in Nova Scotia, Canada. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 146, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, L.; Huang, C.; Chuang, Y.H.; Chen, H.W.; Chan, Y.; Teah, H.Y.; Chen, T.; Chang, C.; Liu, Y.; Tzou, Y. Accumulation of heavy metals and trace elements in fluvial sediments received effluents from traditional and semiconductor industries. Nat. Portf. 2016, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, D.V. Seasonal Variation and Assessment of Heavy Metal Contamination in the Sediments of Selected Perennial Ponds in Kanyakumari District, Tamil Nadu, India; International Research Publication House: Delhi, India, 2020; Volume 8, p. 12. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, B.; Du, J.; Wang, T.; Shi, H.; Wang, R. Distribution, Assessment, and Source of Heavy Metals in Sediments of the Qinjiang River, China. Multidiscip. Digit. Publ. Inst. 2022, 19, 9140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaini, N.M.; Lee, H.; Mohamed, K.N.; Sabuti, A.A.; Suratman, S.; Ong, M.C. Datasets on Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Heavy Metals Concentration in Recent Sediment at Merang River System, Terengganu, Malaysia; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Volume 31, p. 105900. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Rad, S.; Xu, L.; Gui, L.; Song, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, Z.; Chen, Z. Heavy metal distribution, sources and ecological risk assessment in Huixian wetland South China. Water 2020, 12, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harikrishnan, N.; Ravishankar, R.; Chandrasekaran, A.; Gandhi, M.S.; Kanagasabapathy, K.V.; Prasad, M.V.R.; Satapathy, K.K. Assessment of heavy metal contamination in marine sediments of the east coast of Tamil Nadu affected by different pollution sources. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 121, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, S.N. PIG: A numerical index for dissemination of groundwater contamination zones. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 26, 3344–3350. [Google Scholar]
- Omwene, P.I.; Oncel, M.S.; Celen, M.; Kobya, M. Heavy metal pollution and spatial distribution in surface sediments of Mustafakemalpasa stream located in the world’s largest borate basin (Turkey). Chemosphere 2018, 208, 782–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duodu, G.O.; Goonetilleke, A.; Ayoko, G.A. Comparison of pollution indices for the assessment of heavy metal in Brisbane River sediment. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 1077–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Ghosh, P.B.; Sil, A.K.; Saha, T. Heavy metal pollution assessment through comparison of different indices in sewage fed fishery pond sediments at East Kolkata Wetland India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 63, 915–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, V.; Ghosh, S.; Pande, A.; Maldini, K.; Matic, N. Geo-Accumulation Index of Heavy Metals in Pond Water Sediment of Raipur. Environmental Communication. Biosci. Biotechnol. Res. Commun. 2019, 12, 585–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldscheider, N. A holistic approach to groundwater protection and ecosystem services in karst terrains. Carbonates Evaporites 2019, 34, 1241–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparatos, D. Soil Contamination by Heavy Metals and Metalloids. Environments 2022, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbazbegian, M.; Noori, R. Hydropolitical System Archetypes: Feedback Structures, Physical Environments, Unintended Behaviors, and a Diagnostic Checklist. Hydrology 2022, 9, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO-IHP. Protection and Sustainable Use of the Dinaric Karst Transboundary Aquifer System, Transboundary Diagnostic Analysis; UNESCO-IHP: Paris, France, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Polemio, M.; Dragone, V.; Limoni, P. Monitoring and methods to analyze the groundwater quality degradation risk in coastal karstic aquifers (Apulia, Southern Italy). Environ. Geol. 2009, 58, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUR-Lex. Water Framework Directive (WFD 2000/60/EC) of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2000 establishing a framework for Community action in the field of water policy. Off. J. Eur. Communities 2000, 327, 1–73. [Google Scholar]
- Popović, A.; Radeljak, P. Razvojni problemi pograničnog pojasa Žumberka (Development Problems of the Žumberak Border Region). Hrvat. Geogr. Glas. 2011, 73, 179–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, I.; Šimunić, N.; Živić, D. Prometna dostupnost kao čimbenik depopulacije i razvojnog zaostajanja: Primjer Žumberka (Transport Accessibility As a Factor of Depopulation and Developmental Delay: Case Study Žumberak). Društvena Istraživanja 2016, 25, 241–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzjak, N. Speleološke pojave u Parku prirode “Žumberak-Samoborsko gorje” (Speleological Features of Žumberak–Samoborsko gorje Nature Park). Geoadria 2002, 7, 31–49. [Google Scholar]
- Bognar, A.; Faivre, S.; Buzjak, N.; Pahernik, M.; Bočić, N. Recent Landform Evolution in the Dinaric and Pannonian Regions of Croatia. Recent Landform Evolution; Lóczy, D., Stankoviansky, M., Kotarba, A., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 313–334. [Google Scholar]
- Vujnović, T. Springs in the Žumberak—Samoborsko gorje Nature park. Nat. Croat. 2011, 20, 19–34. [Google Scholar]
- Brkić, Ž.; Kuhta, M.; Singer, D. Geološka i hidrogeološka Osnova Parka prirode “Žumberak—Samoborsko Gorje” (Geological and Hydrogeological Base of the “Žumberak—Samoborsko Gorje Nature Park”); JU PP Žumberak—Samoborsko gorje: Samobor, Croatia, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Peh, Z.; Miko, S. Geochemical comparison of stream and overbank sediments: A case study from the Žumberak region, Croatia. Geol. Croat. 2001, 54, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peh, Z.; Miko, S. Impact of geomorphological variables in weighting the lithoogical influence on geochemical composition of stream and overbank sediments: A regression model for the Žumberak area (NW Croatia). Geol. Croat. 2003, 56, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čović, M. Geochemical and Mineralogical Characteristics of Overbank Sediments of Žumberak—Samobor Mt. Master’s Thesis, Mining Geological Petroleum Faculty, University of Zagreb, Zagreb, Croatia, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Buzjak, N.; Trpčić, M. Mjerenje tvrdoće vode u odabranim krškim pojavama Žumberačke gore (Water hardness in selected karst features of Žumberačka Gora Mt.). Geoadria 2005, 10, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Malinar, H. Trasiranje novootvorenog ponora u Otruševcu i rekonstrukcija hidrogeološke povijesti otruševečke doline (Tracing of new ponor in Otruševec and reconstruction oh hydrogeological history of Otruševec valley). Speleolog 2010, 57, 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Frangen, T. Određivanje Značajki Krškoga Vodonosnika na Području Jugozapadnoga Žumberka Kvantitativnim Trasiranjem u Različitim Hidrološkim Uvjetima. Ph.D. Thesis, Rudarsko-geološko-naftni fakultet, Sveučilište u Zagrebu, Zagreb, Croatia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Nippgen, F.; McGlynn, B.L.; Marshall, L.A.; Emanuel, R.E. Landscape structure and climate influences on hydrologic response. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herak, M. Tectonic Interrelation of the Dinarides and the Southern Alps. Geol. Croat. 1999, 52, 83–98. [Google Scholar]
- Pamić, J.; Tomljenović, B. Basic geologic data from the Croatian part of Zagorje-Mid-Transdanubian Zone. Acta Geol. Hung. 1998, 41, 389–400. [Google Scholar]
- Buzjak, N.; Buzjak, S.; Orešić, D. Florističke, mikroklimatske i geomorfološke značajke ponikve Japage na Žumberku (Hrvatska) (Floristic, microclimatic and geomorphological features of collapsed doline Japage on the Žumberak; Croatia). Šumarski List 2011, 3–4, 127–137. [Google Scholar]
- Buzjak, N. Cave Database of Žumberak Samoborsko Gorje Mt; Caving Club Samobor: Samobor, Croatia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Šikić, K.; Basch, O.; Šimunić, A. Osnovna Geološka Karta SFRJ, 1:100.000, List Zagreb L38-80 (Basic Geological Map SFRJ, Scale 1:100.000, Sheet Zagreb L38-80); Institut za Geološka Istraživanja: Zagreb, Croatia, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Pleničar, M.; Premru, U.; Herak, M. Osnovna Geološka Karta SFRJ M 1:100.000, List Novo Mesto L 33-79 (Basic Geological Map SFRJ, Scale 1:100.000, Sheet Novo Mesto L 33-79); Savezni Geološki Zavod: Beograd, Serbia, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Premru, U.; Ogorelec, B.; Šribar, L.J. O geološkoj zgradbi Dolenjske (On the geological structure of the Lower Carniola). Geologija 1977, 20, 167–192. [Google Scholar]
- Herak, M.; Bukovac, J. Tektonsko okno Duralije u Žumberku (Tectonic window Duralije in Žumberak). Geološki Vjesn. 1988, 41, 231–236. [Google Scholar]
- Tomljenović, B.; Csontos, L. Neogene-Quaternary structures in the border zone between Alps, Dinarides and Pannonian Basin (Hrvatsko zagorje and Karlovac Basins, Croatia). Int. J. Earth Sci. (Geol. Rundsch.) 2001, 90, 560–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velić, J. Acceleration of vertical tectonic movements during the neogene and quaternary in the western part of the Sava river depression). Geološki Vjesn. 1983, 36, 225–265. [Google Scholar]
- Šegota, T.; Filipčić, A. Köppenova podjela klima i hrvatsko nazivlje (Köppen’s Classification of Climates and the Problem of Corresponding Croatian Terminology). Geoadria 2003, 8, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaninović, K.; Gajić-Čapka, M.; Perčec Tadić, M. Klimatski Atlas Hrvatske (Climate Atlas of Croatia 1961–1990, 1971–2000); Državni Hidrometeorološki Zavod: Zagreb, Croatia, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Penzar, B.; Penzar, I. Prikaz godišnjeg hoda oborine u Hrvatskoj pomoću Köppenove sheme (Analysis of annual rainfall in Croatia using the Köppen scheme). Acta Geogr. Croat. 1983, 17–18, 3–9. [Google Scholar]
- Dujmović, I. Fizičko-Geografske Značajke Samoborskog Gorja i Plješivičkog Prigorja (Physical Geographical Features of Samoborsko Gorje Mt. and Plješivica); Meridijani: Samobor, Croatia, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Vrbek, B. Tloznanstvo; Veleučilište u Karlovcu: Karlovac, Croatia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Jelaska, S.; Grgurić, Z.; Kušan, V.; Major, Z.; Mihulja, A.; Peternel, H. Vegetacijska Karta Parka Prirode “Žumberak—Samoborsko Gorje” (Vegetation Map of Žumberak-Samoborsko Gorje); Oikon d.o.o.: Zagreb, Croatia, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Velić, I.; Vlahović, I. Tumač Geološke karte Republike Hrvatske 1:300.000 (Interpreter of the Geological Map of Republic of Croatia); Croatian Geological Institute: Zagreb, Croatia, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- CGI. Geološka Karta Republike Hrvatske 1:300.000 (Geological Map of Republic of Croatia 1:300.000—In Croatian); Croatian Geological Institute: Zagreb, Croatia, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- HRN EN ISO 10523:2012; Kvaliteta Vode—Određivanje pH Vrijednosti (ISO 10523:2008; EN ISO 10523:2012); HZN Glasilo 1/2012. Croatian Standards Institute: Zagreb, Croatian, 2012.
- HRN EN 27888:2008; Kakvoća Vode—Određivanje Električne Vodljivosti (ISO7888:1985; EN 27888:1993); Glasilo 5/2008. Croatian Standards Institute: Zagreb, Croatian, 2008.
- SM: 2130—B Turbidity, 22nd ed.; Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2012.
- HRN EN ISO 10304-1:2009 en; Kakvoća Vode—Određivanje Otopljenih Aniona Ionskom Tekućinskom Kromatografijom—1. Dio (ISO 10304-1:2007, EN ISO10304-1:2009); HZN Glasilo 6/2009. Croatian Standards Institute: Zagreb, Croatian, 2009.
- HRN EN ISO 14911:2001 en; Kakvoća Vode—Određivanje Otopljenih Kationa Ionskom Kromatografijom—Metoda za Vode i Otpadne Vode. Narodne novine: Zagreb, Croatian, 2001.
- ISO/TR 11905-2:1997; Water Quality—Determination of Nitrogen. Part 2: Determination of Bound Nitrogen, after Combustion and Oxidation to Nitrogen Dioxide, Chemiluminescence Detection. ISO—International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1997.
- HRN EN 1484:2002; Ispitivanje Vode—Smjernice za Određivanje Ukupnog Organskog Ugljika i Otopljenog Organskog Ugljika; Glasilo DZNM 1-2/2002. Croatian Standards Institute: Zagreb, Croatian, 2002.
- HRN ISO 17294-2:2003; Water Quality—Application of Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS)—Part 2: Determination of Selected Elements Including Uranium Isotopes (ISO 17294-2:2023, Corrected version 2024-02; EN ISO 17294-2:2023); HZN e-Glasilo 11/2023. Croatian Standards Institute: Zagreb, Croatian, 2023.
- ISO 11466; Soil Quality—Extraction of Trace Elements Soluble in Aqua Regia. ISO—International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1995.
- HRN EN ISO 6878:2008; Water Quality—Determination of Phosphorus-Ammonium Molybdate Spectrometric Method ISO 6878:2004; EN ISO 6878:2004; HZN Glasilo 5/2008. Croatian Standards Institute: Zagreb, Croatian, 2008.
- HRN ISO 7150-1:1998; Water Quality—Determination of Ammonium—Part 1: Manual Spectrometric Method ISO 7150-1:1984; Glasilo DZNM 1-2/1998. Croatian Standards Institute: Zagreb, Croatian, 1998.
- Piper, A.M. A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water-analyses. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1944, 25, 914–923. [Google Scholar]
- Salah, E.A.M.; Zaidan, T.A.; Al-Rawi, A.S. Assessment of heavy metals pollution in the sediments of Euphrates River, Iraq. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2012, 4, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, M. The importance of enrichment factor (EF) and geoaccumulation index (Igeo) to evaluate the soil contamination. J. Geol. Geophys. 2016, 5, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, G. Schwermetalle in den Sedimenten des Rheins-Veränderun Gen Seit 1971; Deu, Umschau Wissensch. Tech., Univ., inst. sedimentforsch.: Heidelber, Germany, 1979; pp. 778–783. [Google Scholar]
- Official Gazette No. 64 (2023). Regulation on compliance parameters, methods of analysis and monitoring of water intended for human consumption 22 June 2023, Official Gazette of the Republic of Croatia 64/2023. (OG 64/2023). Available online: https://leap.unep.org/en/countries/hr/national-legislation/regulation-compliance-parameters-methods-analysis-and-monitoring (accessed on 15 September 2024).
- Matić, N.; Maldini, K.; Tomas, D.; Ćuk, R.; Milvić, S.; Miklavčić, I.; Širac, S. Geochemical characteristics of the Gacka River karstic springs (Dinaric karst, Croatia) with macroinvertebrate assemblages overview. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, R.; Batista, M.J.; Bidovec, M.; Demetriades, A.; De Vivo, B.; De Vos, W.; Duris, M.; Gilucis, A.; Gregorauskiene, V.; Halamic, J.; et al. Geochemical Atlas of Europe; Part 1—Background Information, Methodology and Maps; Geological Survey of Finland: Espoo, Finland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Frančišković-Bilinski, S. An assessment of multielemental composition in stream sediments of Kupa river drainage basin, Croatia for evaluating sediment quality guidelines. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2007, 16, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Batts, D.; Cubbage, J. Summary of Guidelines for Contaminated Freshwater Sediments; Publication No. 95-308; Washington State Department of Ecology: Olympia, WA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, Q.; Yang, S.; Song, Z.; Wang, Z.; Yu, C.; Wang, H. Vegetation Determines Lake Sediment Carbon Accumulation during Holocene in the Forest–Steppe Ecotone in Northern China. Forests 2021, 12, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sučić, H.; Damjanović, I.; Kralj, M.; Bezik, D.; Kolarić, D.; Habuda-Stanić, M.; Turić, N.; Benkotić, S.; Šveiger, B.; Ruškan, I. Seasonal Variations of the Total Organic Carbon (TOC) Concentrations in the surface waters of Kopački rit-NATURAVITA project in the period. In Proceedings of the 1st European GREEN Conference, Vodice, Croatia, 23–26 May 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Perakis, S.S.; Pett-Ridge, J.C. Nitrogen-fixing red alder trees tap rock-derived nutrients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 5009–5014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sardar, M.F.; Younas, F.; Farooqi, Z.U.R.; Li, Y. Soil nitrogen dynamics in natural forest ecosystem: A review. Front. For. Glob. Chang. 2023, 6, 1144930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frančišković-Bilinski, S.; Juračić, M.; Tibljaš, D. Rječina River sediments (Croatia): From captured spring to polluted prodelta. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 64, 1755–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frančišković-Bilinski, S.; Cuculić, V.; Bilinski, H.; Häusler, H.; Stadler, P. Geochemical and stable isotopic variability within two rivers rising under the same mountain, but belonging to two distant watersheds. Geochemistry 2013, 73, 293–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inobeme, A.; Adetunji, C.O.; Akram, M.; Munirat, M.; Inamuddin Laila, U.; Okonkwo, S.O.; Islam, S.; Inobeme, J. Benefits of Geochemistry and Its Impact on Human Health. In Geochemistry: Concepts and Applications; Mohd Imran Ahamed, I., Boddula, R., Altalhi, T., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; Chapter 2. [Google Scholar]
- Mirosevic, V.; Svagusa, T.; Matic, N.; Maldini, K.; Siljeg, M.; Milicic, D.; Gasparovic, H.; Rudez, I.; Sepac, A.; Gojmerac, L.; et al. Cardiotoxicity of Iron and Zinc and Their Association with the Mitochondrial Unfolded Protein Response in Humans. MDPI Special Issue Zinc and Manganese in Human Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).