Early Warning of Sudden Water Pollution Accident Risks Based on Water Quality Models in the Three Gorges Dam Area
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methodology
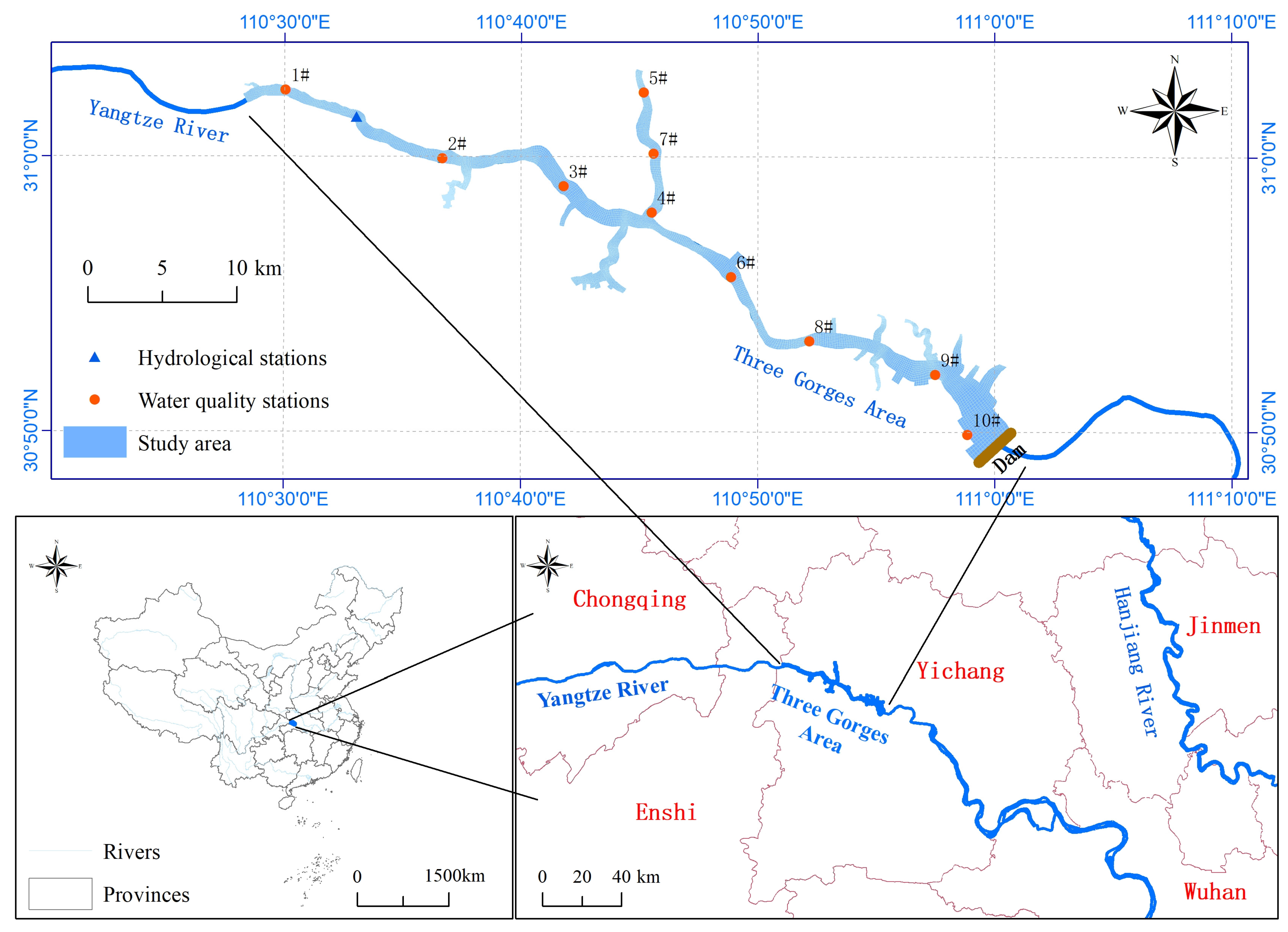
2.1. Study Area and Data Sources
2.2. Technical Framework of Risk Warning for Water Quality Pollution
2.3. Hydrodynamic Water Quality Model
2.4. Risk Early Warning Assessment Model
2.4.1. Classification of Different Receptors
2.4.2. Risk Warning Level of Water Pollution Accidents
2.4.3. Model Calibration and Verification Methodology
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Model Construction and Verification
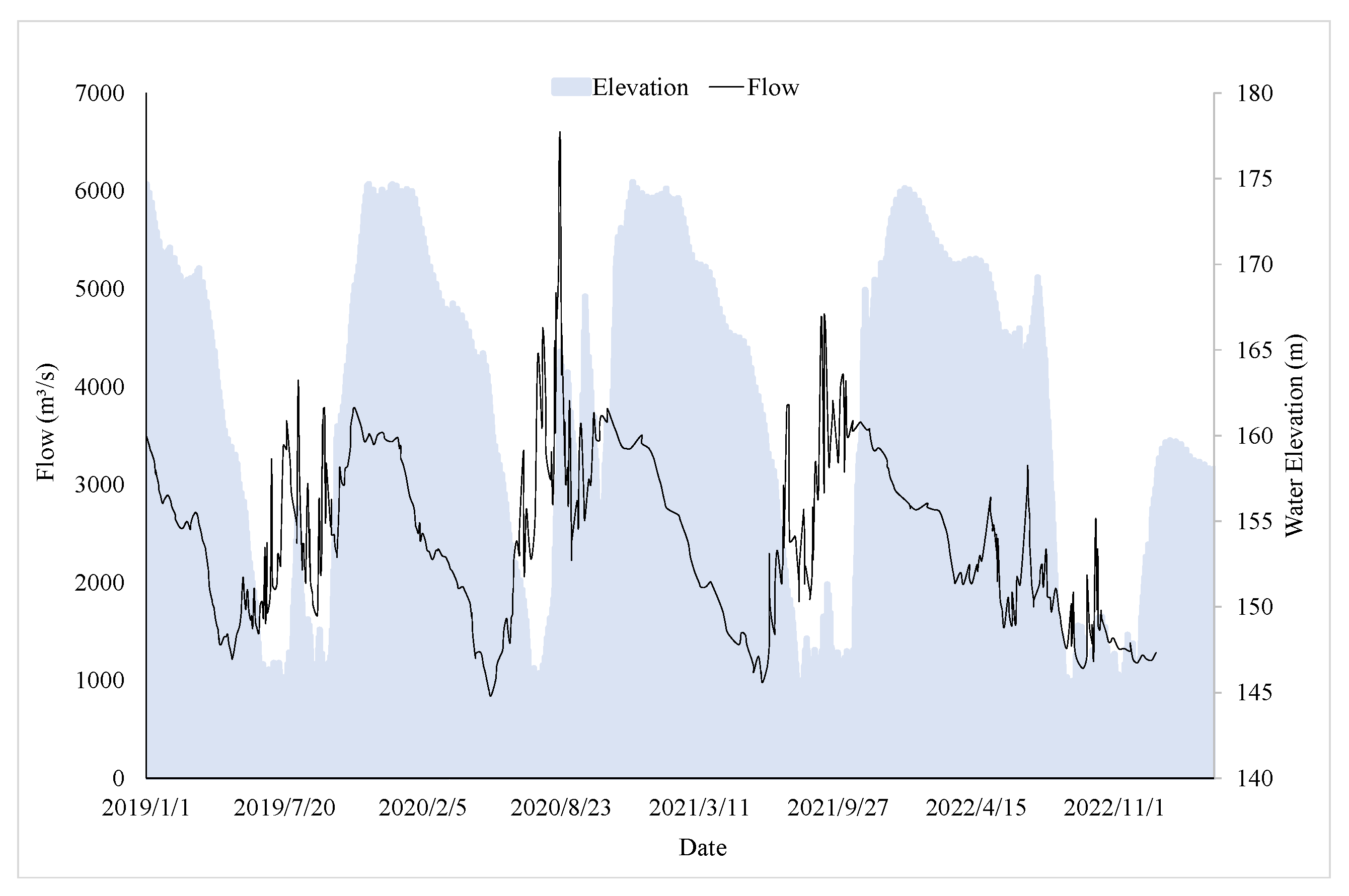
3.1.1. Boundary Conditions
- (1)
- Upstream flow
- (2)
- Downstream water level
3.1.2. Initial Conditions
3.1.3. Model Calculation Steps
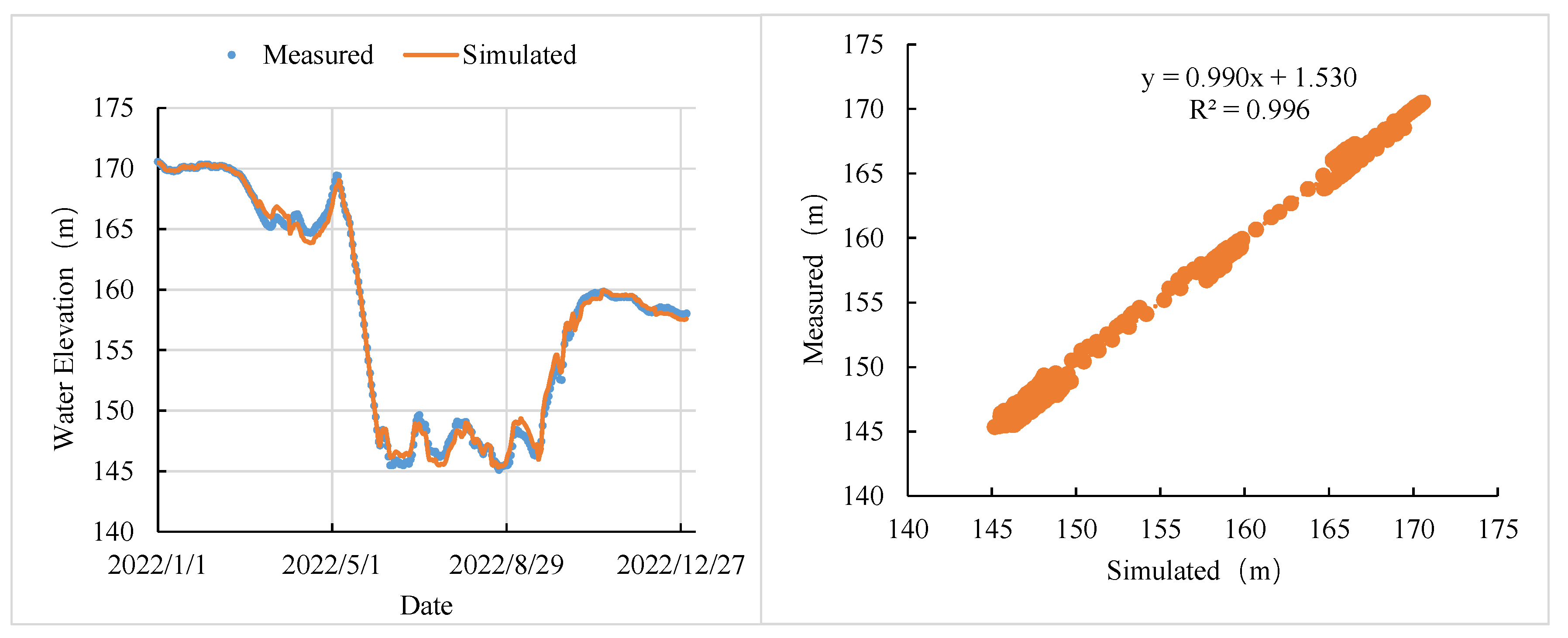
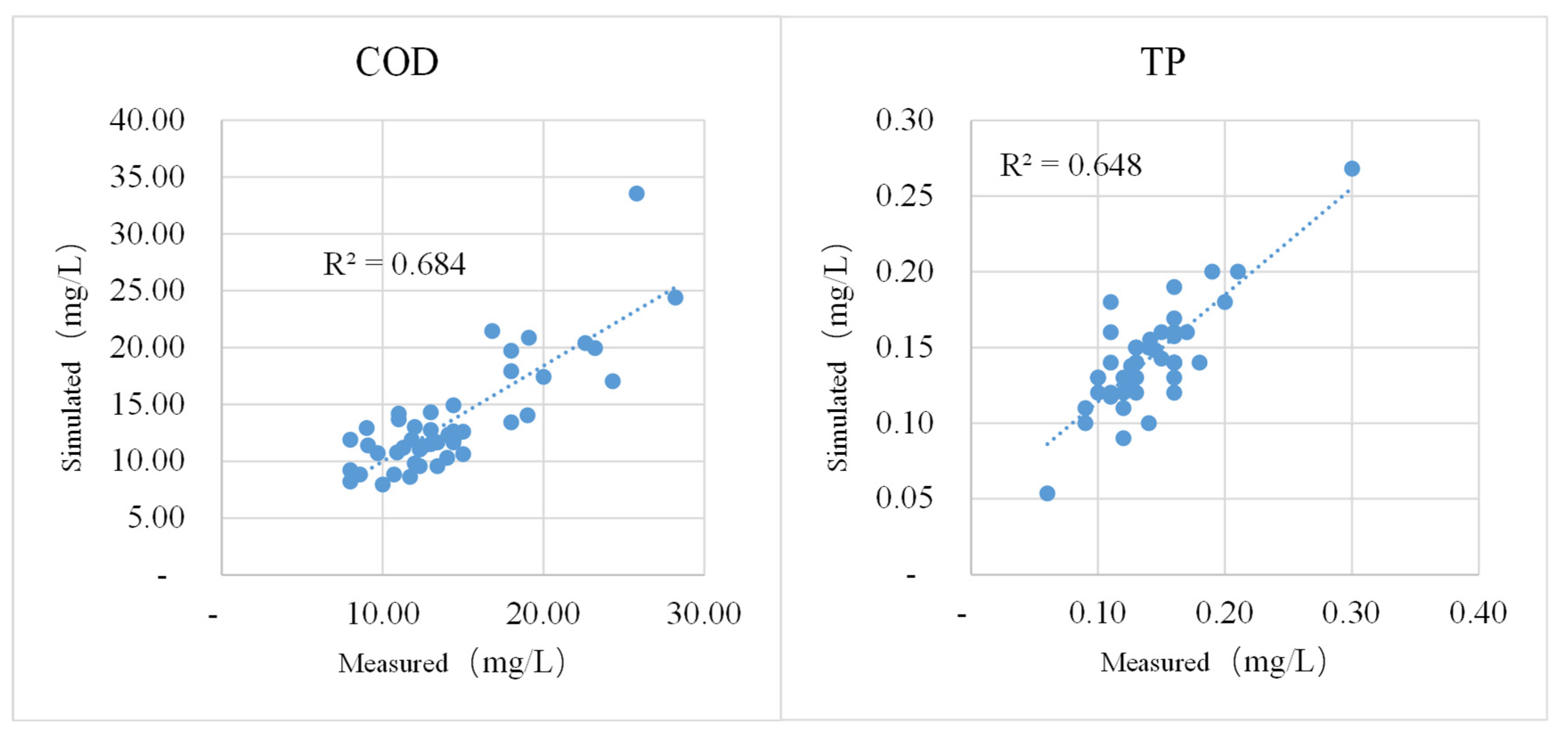
3.1.4. Model Calibration and Verification
- (1)
- Water Level
- (2)
- Water Quality
3.2. Application for Accident Early Warning
3.2.1. Accident Scenario
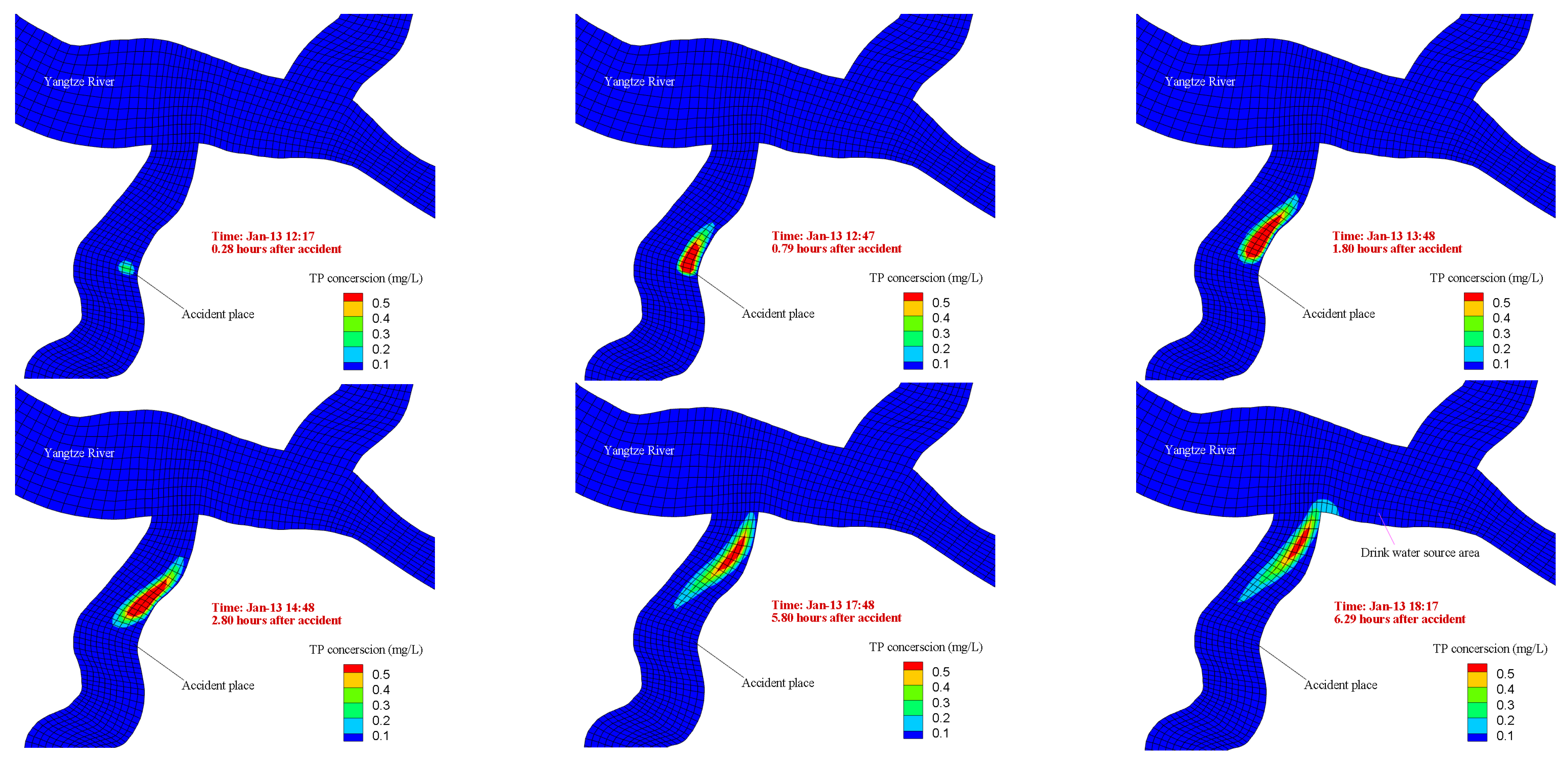
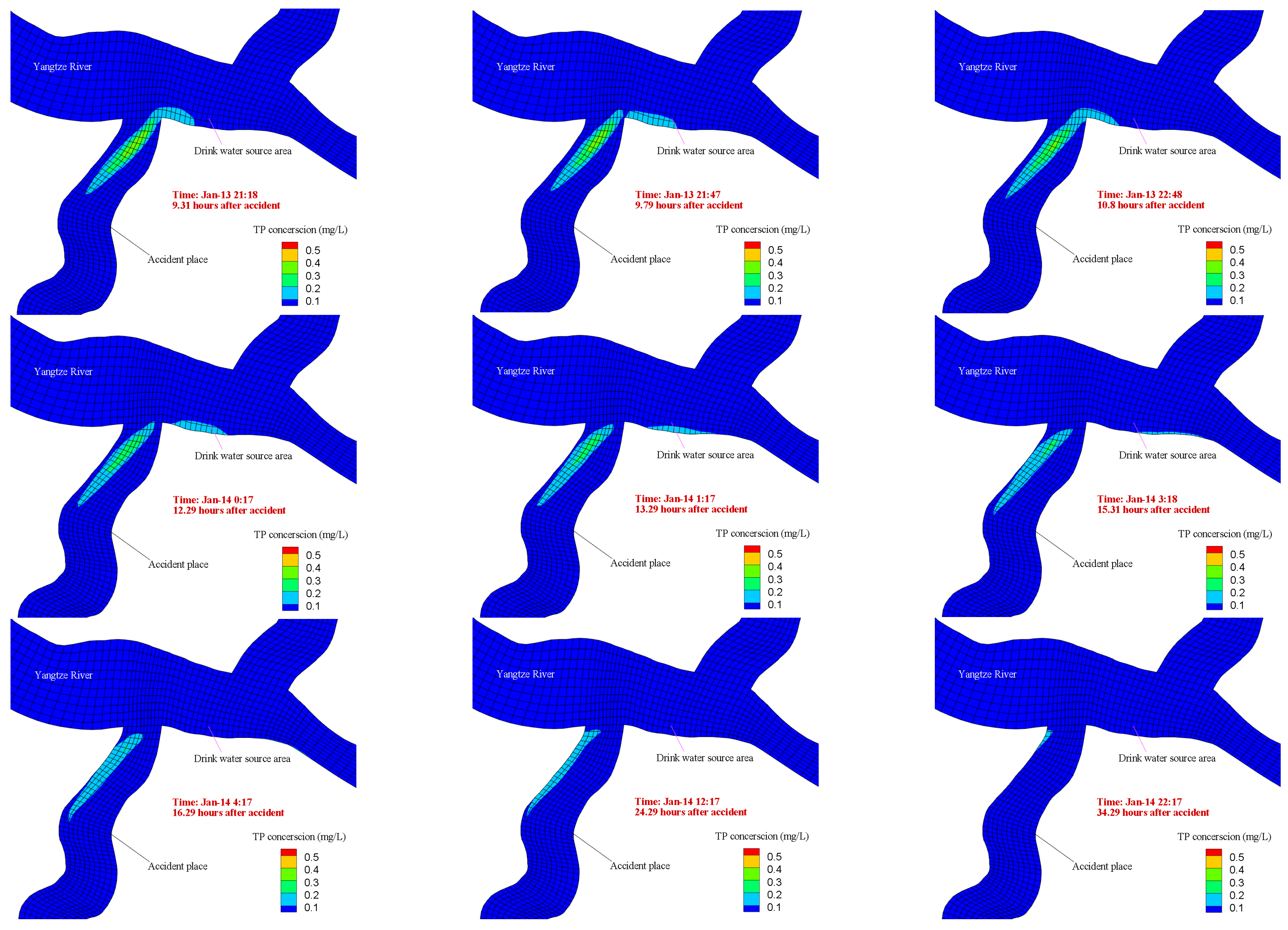
3.2.2. Pollutant Concentrations Changes after the Accident
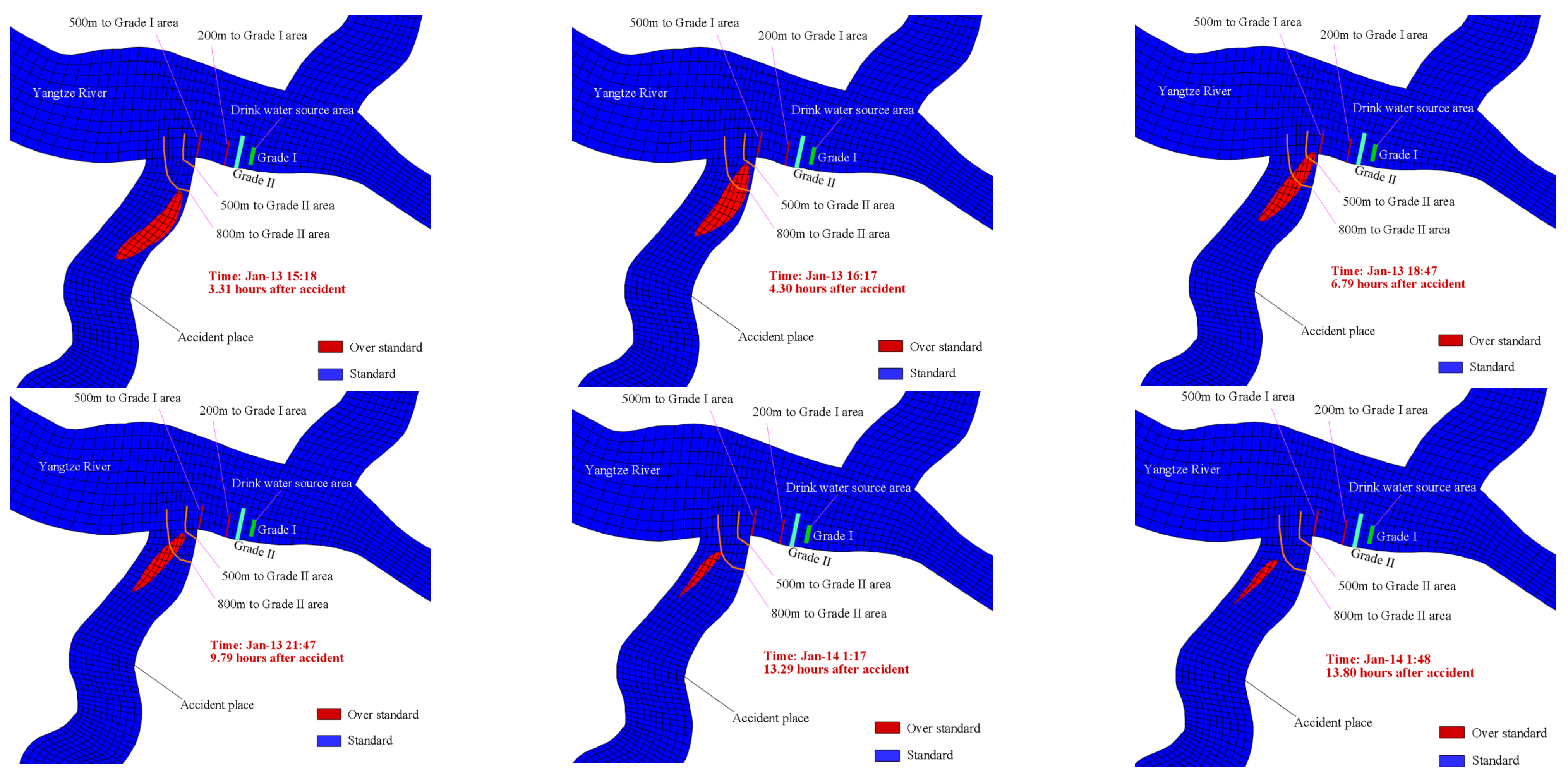
3.2.3. Impact Analysis of the Accident
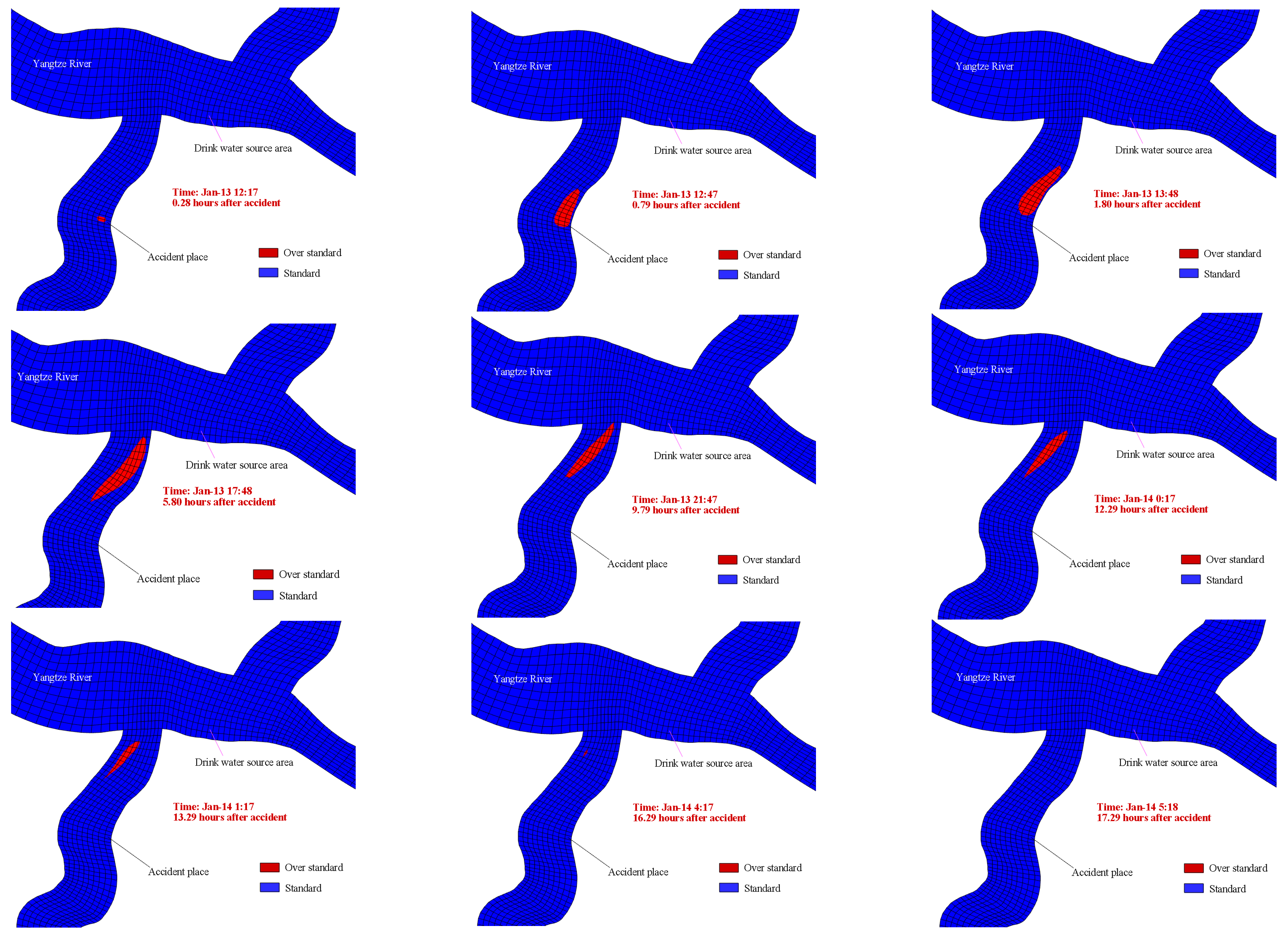
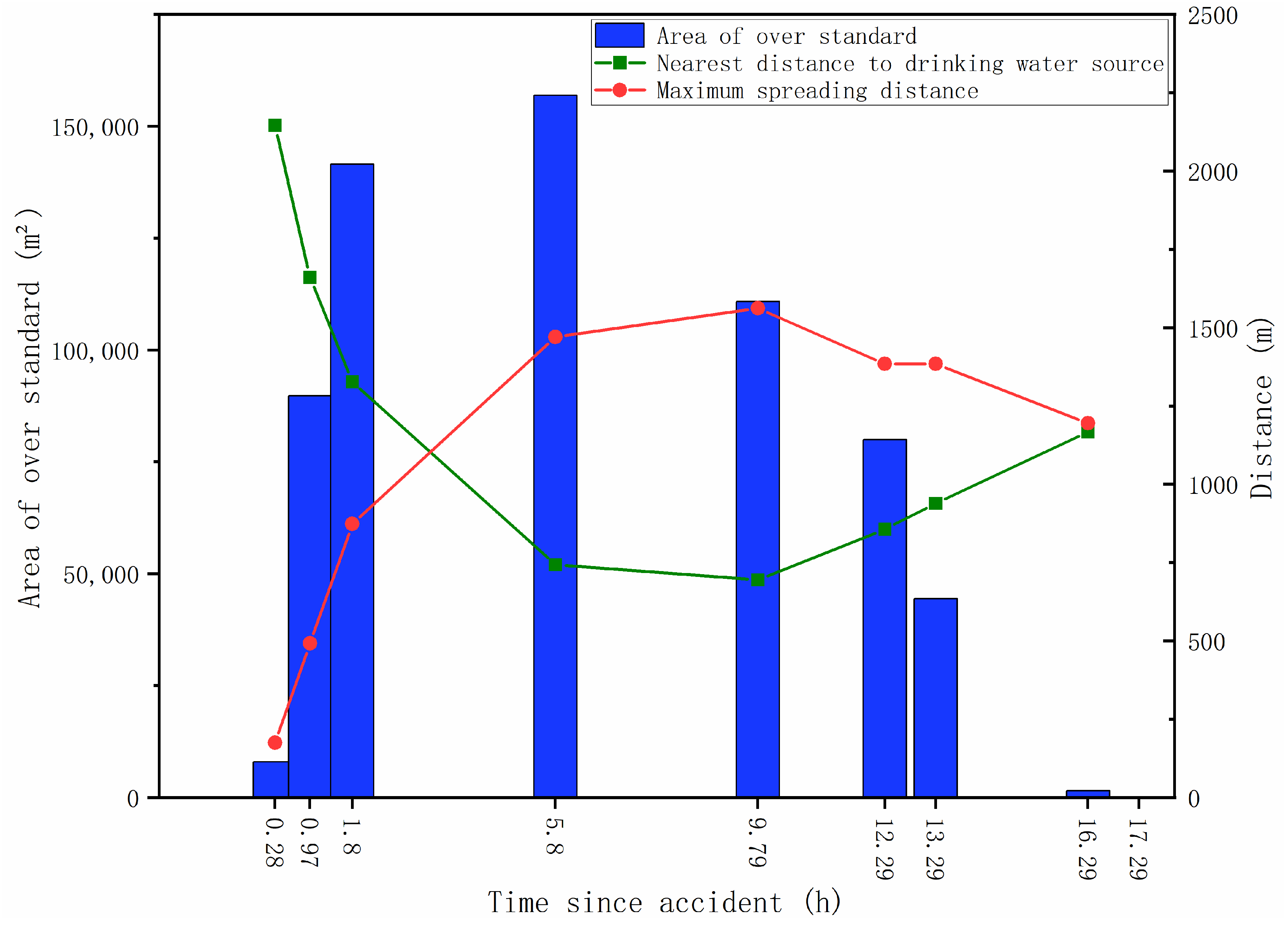
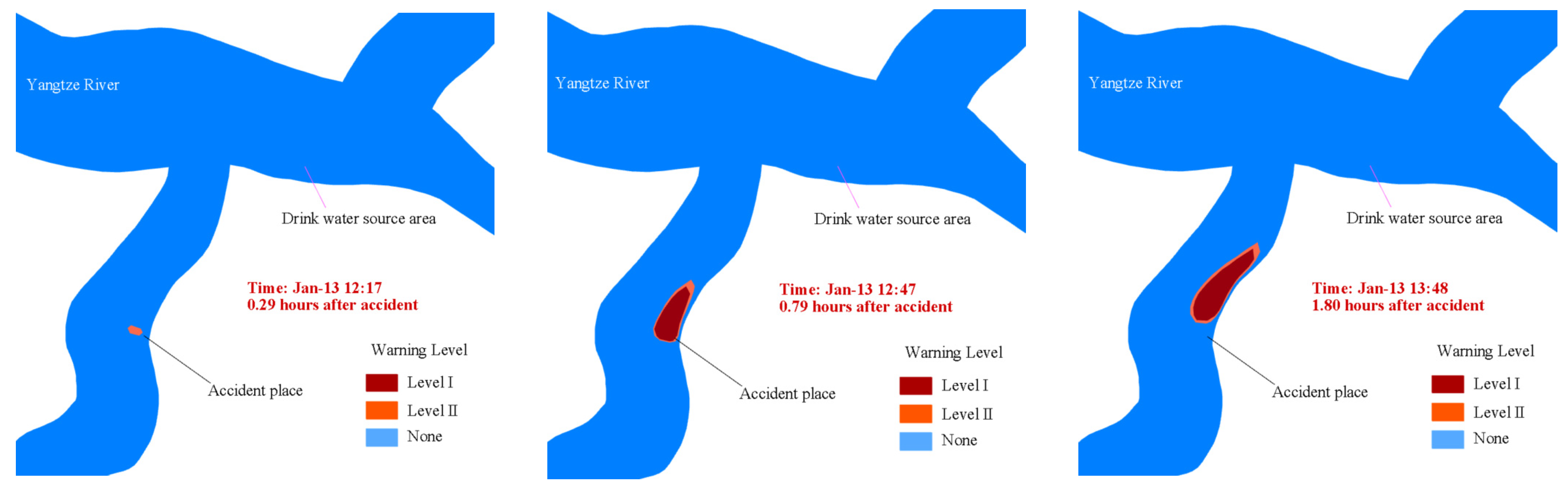
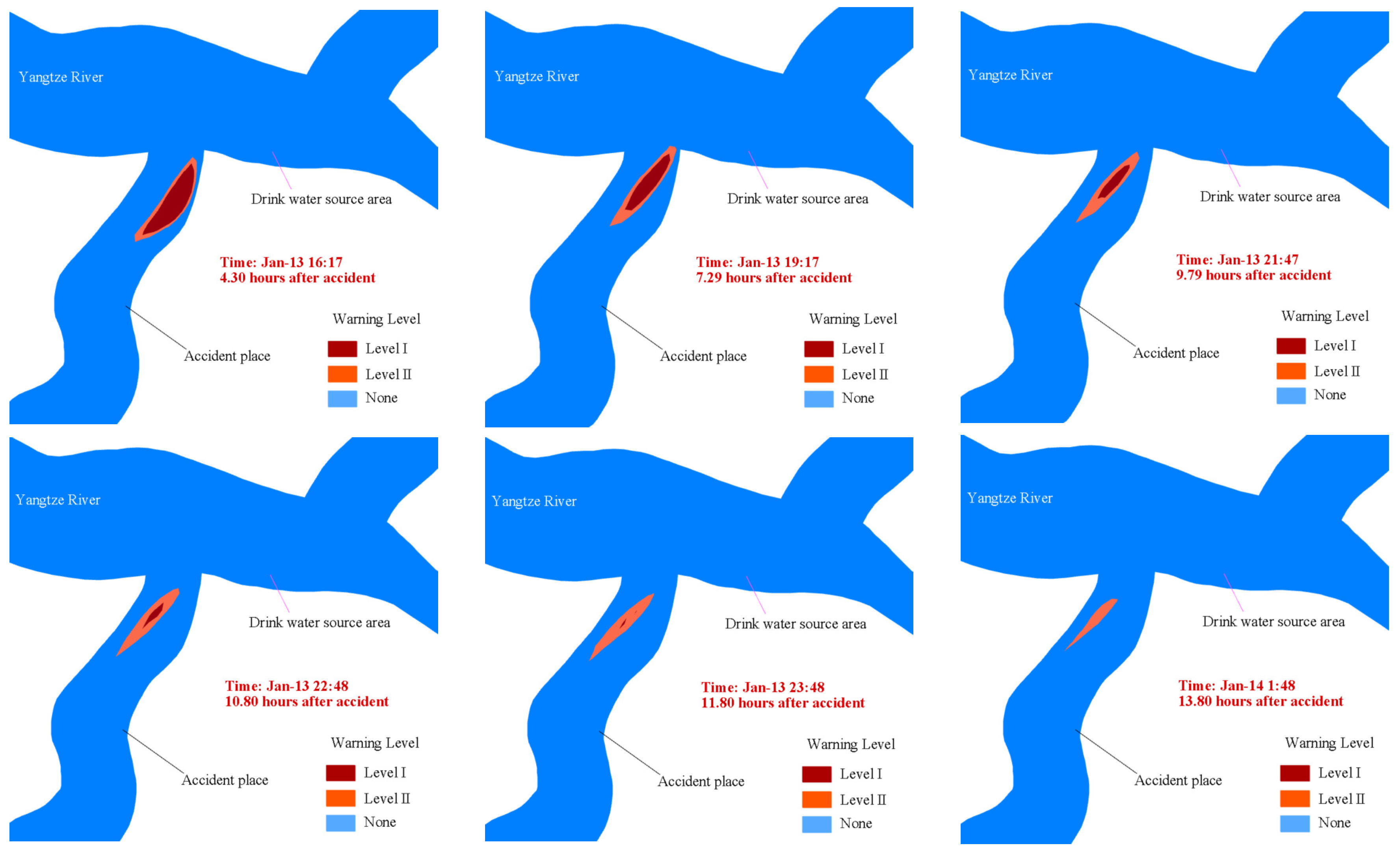
3.2.4. Risk Early Warning Assessment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, J.; Xu, M.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, S.; Tao, M.; Wang, Y. Spatial-Temporal Distribution and Evolutionary Characteristics of Water Environment Sudden Pollution Incidents in China from 2006 to 2018. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 801, 149677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, H.; Mei, Y.; Chen, J.; Wu, Z.; Lan, L.; Zhu, D. An Analysis of the Relation between Water Pollution and Economic Growth in China by Considering the Contemporaneous Correlation of Water Pollutants. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 276, 122783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; He, H.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, L. Water Exchange and Pollutant Diffusion Law in Gangnan Reservoir. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 12259–12269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Peng, B.; Wei, G.; Wan, A. Dynamic Assessment and Early Warning of Ecological Security: A Case Study of the Yangtze River Urban Agglomeration. Nat. Hazards 2021, 107, 2441–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; Song, X.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, H.; Loaiciga, H. An Early Warning and Control System for Urban, Drinking Water Quality Protection: China’s Experience. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 4496–4508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, G.; Zhang, S. Early Warning and Forecasting System of Water Quality Safety for Drinking Water Source Areas in Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Water 2017, 9, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, S. Water Quality Prospective in Twenty First Century: Status of Water Quality in Major River Basins, Contemporary Strategies and Impediments: A Review. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 271, 116332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streeter, H.W. A Study of the Pollution and Natural Purification of Ohio River. Health Bull. Dep. Health Educ. Welf. 1958, 146, 1436–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotovtsev, A.V. Evaluating BOD and the Coefficient of Oxidation Rate: Monitoring, Direct and Inverse Problems, Formulas, Calculations and Tables. Water Resour. 2016, 43, 885–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejigu, M.T. Overview of Water Quality Modeling. Cogent Eng. 2021, 8, 1891711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żelazny, M.; Bryła, M.; Ozga-Zielinski, B.; Walczykiewicz, T. Applicability of the WASP Model in an Assessment of the Impact of Anthropogenic Pollution on Water Quality—Dunajec River Case Study. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Merritt, W.S.; Croke, B.F.W.; Weber, T.R.; Jakeman, A.J. A Review of Catchment-Scale Water Quality and Erosion Models and a Synthesis of Future Prospects. Environ. Model. Softw. 2019, 114, 75–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.-J.; Chen, H.-X.; Sun, H.-H.; Yazdi, M.; Nedjati, A.; Adesina, K.A. An Improved Multi-Criteria Emergency Decision-Making Method in Environmental Disasters. Soft Comput. 2021, 25, 10351–10379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zyoud, S.H.; Kaufmann, L.G.; Shaheen, H.; Samhan, S.; Fuchs-Hanusch, D. A Framework for Water Loss Management in Developing Countries under Fuzzy Environment: Integration of Fuzzy AHP with Fuzzy TOPSIS. Expert Syst. Appl. 2016, 61, 86–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sermet, Y.; Demir, I.; Muste, M. A Serious Gaming Framework for Decision Support on Hydrological Hazards. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiannakoulias, N.; Gordon, J.N.; Darlington, J.C. The Decision Game: A Serious Game Approach to Understanding Environmental Risk Management Decisions. J. Risk Res. 2020, 23, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y. Three-Way Decision Approach for Water Ecological Security Evaluation and Regulation Coupled with VIKOR: A Case Study in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 379, 134666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chen, Z. A Hybrid Approach Based on Monte Carlo Simulation-VIKOR Method for Water Quality Assessment. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 150, 110202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Pablo, H.; Sobrinho, J.; Garcia, M.; Campuzano, F.; Juliano, M.; Neves, R. Validation of the 3D-MOHID Hydrodynamic Model for the Tagus Coastal Area. Water 2019, 11, 1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagos, M.S.; Muñoz, J.F.; Suárez, F.I.; Fuenzalida, M.J.; Yáñez-Morroni, G.; Sanzana, P. Investigating the Effects of Channelization in the Silala River: A Review of the Implementation of a Coupled MIKE -11 and MIKE-SHE Modeling System. WIREs Water 2024, 11, e1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pak, G.; Mallari, K.J.B.; Baek, J.; Kim, D.; Kim, H.; Jung, M.; Kim, Y.; Yoon, J. Modelling of Suspended Sediment in a Weir Reach Using EFDC Model. Water Sci. Technol. 2015, 73, 1583–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.; Her, Y.; Muñoz-Carpena, R.; Yu, X. Quantifying the Contribution of External Loadings and Internal Hydrodynamic Processes to the Water Quality of Lake Okeechobee. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 883, 163713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villota-López, C.; Rodríguez-Cuevas, C.; Torres-Bejarano, F.; Cisneros-Pérez, R.; Cisneros-Almazán, R.; Couder-Castañeda, C. Applying EFDC Explorer Model in the Gallinas River, Mexico to Estimate Its Assimilation Capacity for Water Quality Protection. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arifin, R.R.; James, S.C.; de Alwis Pitts, D.A.; Hamlet, A.F.; Sharma, A.; Fernando, H.J.S. Simulating the Thermal Behavior in Lake Ontario Using EFDC. J. Great Lakes Res. 2016, 42, 511–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, T.; Seo, D. Algal Bloom Prediction of the Lower Han River, Korea Using the EFDC Hydrodynamic and Water Quality Model. Ecol. Model. 2017, 366, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camp, J.S.; LeBoeuf, E.J.; Abkowitz, M.D. Application of an Enhanced Spill Management Information System to Inland Waterways. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 175, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LI, C.; Tian, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, X. Research progress on risk assessment and emergency countermeasures of sudden water pollution. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2020, 39, 1161–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobban, F.; Solis-Trapala, I.; Symes, W.; Morriss, R. Early Warning Signs Checklists for Relapse in Bipolar Depression and Mania: Utility, Reliability and Validity. J. Affect. Disord. 2011, 133, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunjó, J.; Fthenakis, V.; Vílchez, J.A.; Arnaldos, J. Hazard and Operability (HAZOP) Analysis. A Literature Review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 173, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebelo, A.; Ferra, I.; Gonçalves, I.; Marques, A.M. A Risk Assessment Model for Water Resources: Releases of Dangerous and Hazardous Substances. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 140, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Lei, X.; Long, Y.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Hou, X.; Shi, M.; Wang, P.; Zhang, C.; et al. A Novel Comprehensive Risk Assessment Method for Sudden Water Accidents in the Middle Route of the South–North Water Transfer Project (China). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 698, 134167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Alba, J.; Bárcena, J.F.; Ugarteburu, C.; García, A. Artificial Neural Networks as Emulators of Process-Based Models to Analyse Bathing Water Quality in Estuaries. Water Res. 2019, 150, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, W.; Miao, P.; Sun, B.; Kong, F. Risk Grade Assessment of Sudden Water Pollution Based on Analytic Hierarchy Process and Fuzzy Comprehensive Evaluation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 469–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Zhang, C. Early Warning of Water Quality Degradation: A Copula-Based Bayesian Network Model for Highly Efficient Water Quality Risk Assessment. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 292, 112749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.N.; Othman, F.B.; Afan, H.A.; Ibrahim, R.K.; Fai, C.M.; Hossain, S.; Ehteram, M.; Elshafie, A. Machine Learning Methods for Better Water Quality Prediction. J. Hydrol. 2019, 578, 124084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Lou, Z. The Environmental Changes and Mitigation Actions in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region, China. Environ. Sci. Policy 2011, 14, 1132–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China. Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water (GB 3838-2002). 2002. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/shjbh/shjzlbz/200206/t20020601_66497.shtml (accessed on 1 April 2024).
- Zhu, Y.-C.; Tang, M.-K.; Du, M. An Emergency Monitoring about Sudden Water Pollution Accident in Drinking Water Sources. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Emergency Management and Management Sciences, Beijing, China, 8–10 August 2010; pp. 99–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wei, G.; Shen, Z. Incorporating Water Quality Responses into the Framework of Best Management Practices Optimization. J. Hydrol. 2016, 541, 1363–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Liu, Y.; Gao, Z.; Liu, D. Simulation of Sudden Water Pollution Accidents in Hunhe River Basin Upstream of Dahuofang Reservoir. Water 2022, 14, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, L. Simulation of Sudden Benzene Leakage Water Pollution Events. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 208, 012035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; Ge, X.; Huang, P.; Zhang, G.; Loáiciga, H. A Real-Time, Dynamic Early-Warning Model Based on Uncertainty Analysis and Risk Assessment for Sudden Water Pollution Accidents. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 8878–8892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, N.; Jamil, N.R.; Looi, L.J.; Yap, N.K. A Management Framework for Sudden Water Pollution: A Systematic Review Output. Water Environ. Res. 2024, 96, e11012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Yan, X.; Tian, Y.; Pu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Yi, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, Q. Risk Assessment of Sudden Water Pollution Accidents Associated with Dangerous Goods Transportation on the Cross-Tributary Bridges of Baiyangdian Lake. Water 2023, 15, 2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posthuma, L.; Wahlstrom, E.; Nijenhuis, R.; Dijkens, C.; de Zwart, D.; van de Meent, D.; Hollander, A.; Brand, E.; den Hollander, H.A.; van Middelaar, J.; et al. The Flash Environmental Assessment Tool: Worldwide First Aid for Chemical Accidents Response, pro Action, Prevention and Preparedness. Environ. Int. 2014, 72, 140–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Pan, Y.; Wang, W.; Guo, L. A Brain-Inspired Dynamic Environmental Emergency Response Framework for Sudden Water Pollution Accidents. Water 2021, 13, 3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Serial Number | Data Types | Data Content and Role | Data Sources |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Geographic Data | Administrative boundary data, roads, etc. 1:250,000 national basic geographic database. | National Center for Basic Geographic Information (NCBGI) https://www.webmap.cn/ (accessed on 1 April 2024) |
| 2 | Shoreline Data | Defining the grid boundaries of the model. | Geospatial Data Cloud (GDC) https://www.gscloud.cn/ (accessed on 1 April 2024) |
| 3 | Reservoir Bottom Topography | Defining the grid elevation of the model | Yangtze River Commission (PRC) |
| 4 | Hydrographic Data | Upstream inflow, tributary inflow, water level in the reservoir, etc., used for model boundary condition setting and model rate validation. | Ministry of Water Resources official website http://xxfb.mwr.cn/sq_dxsk.html (accessed on 1 April 2024) |
| 5 | Water Quality Data | Pollutant concentrations at monitoring stations for model boundary condition setting and model rate validation. | Ministry of Ecology and Environment official website https://www.mee.gov.cn/ (accessed on 1 April 2024) |
| 6 | Dam Data | Data related to the dam’s flood relief equipment and facilities, and the dam’s scheduling and operation rules. | Ministry of Water Resources official website Three Gorges (Normal Operation Period)—Gezhouba Dam Water Conservancy Hub Gradient Scheduling Regulations |
| Typology | Receptor Type | Classification Criteria | Level of Protected Area | Basis of Delineation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water source area | Drinking water source area | Protection Grade | Level I | The primary water source protection area |
| Level II | The secondary water source protection area | |||
| Agricultural water use area | Service Cultivated Land Area | Level I | >200 km2 | |
| Level II | ≤1200 km2 | |||
| Non-water source area | Other water bodies | Water Environment Functional Category | Judged according to the Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water [37] | |
| Standard Value | Class I | Class II | Class III | Class IV | Class V |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total phosphorus concentration (measured as P, mg/L) | 0.02 (Lakes, reservoirs 0.01) | 0.1 (Lakes, reservoirs 0.025) | 0.2 (Lakes, reservoirs 0.05) | 0.3 (Lakes, reservoirs 0.1) | 0.4 (Lakes, reservoirs 0.2) |
| Receptor Types | Level | Color | Criteria | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water source area | Level I | Red | Satisfy anyone | H = 1 H = 0 and L1 ≤ 200 H = 0 and 200 < L1 ≤ 500 and R = 1 |
| Level II | Orange | Except Level I, Satisfy anyone | H = 0 and L2 ≤ 500 H = 0 and 500 < L2 ≤ 800 and R = 1 | |
| Non-water source area | Level I | Red | Satisfy all | Q′ ≤ Q − 1 and Q′ < 3 Q′ < T W = 0 |
| Level II | Orange | Satisfy all | Q′ ≤ Q − 2 and Q′ < 3 Q′ < T | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, N.; Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Chen, R.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y. Early Warning of Sudden Water Pollution Accident Risks Based on Water Quality Models in the Three Gorges Dam Area. Water 2024, 16, 2679. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16182679
Zhao N, Wang Y, Yang J, Chen R, Wang X, Yang Y. Early Warning of Sudden Water Pollution Accident Risks Based on Water Quality Models in the Three Gorges Dam Area. Water. 2024; 16(18):2679. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16182679
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Na, Yonggui Wang, Jun Yang, Ruikai Chen, Xiaoyu Wang, and Yinqun Yang. 2024. "Early Warning of Sudden Water Pollution Accident Risks Based on Water Quality Models in the Three Gorges Dam Area" Water 16, no. 18: 2679. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16182679
APA StyleZhao, N., Wang, Y., Yang, J., Chen, R., Wang, X., & Yang, Y. (2024). Early Warning of Sudden Water Pollution Accident Risks Based on Water Quality Models in the Three Gorges Dam Area. Water, 16(18), 2679. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16182679





