Abstract
This study explores the enhanced removal of refractory organic compounds from coking wastewater using polyaluminum chloride (PACl) with two different basicity levels (0.5 and 2.5), in combination with coagulant aids such as cationic polyacrylamide (CPAM) and iron ions. The results demonstrated that both PACl formulations significantly outperformed commercial PACl in terms of COD and color removal, with PACl at the basicity of 2.5 achieving slightly higher efficiency than PACl at the basicity of 0.5. The improved performance was attributed to the higher content of polymeric aluminum species, enhancing charge neutralization and bridging adsorption. The addition of coagulant aids further improved the performance, with PACl at the basicity of 2.5 combined with iron ions achieving the highest COD (48.41%) and color removal (80.77%), due to sweep coagulation and complexation. Organic composition analysis using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC-MS), three-dimensional excitation–emission matrix (3D-EEM) fluorescence spectroscopy, and ultraviolet (UV) spectroscopy indicated that PACl combined with iron ions was the most effective in removing polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and nitrogen-, oxygen-, and sulfur-containing heterocyclic compounds. Additionally, a floc analysis showed that the flocs formed with iron ions were more compact and had better settleability compared to those formed with CPAM, further contributing to the improved coagulation efficiency. These results highlight the importance of optimizing the PACl basicity and coagulant aid selection for the enhanced removal of refractory organic compounds from coking wastewater, offering a promising strategy for advanced wastewater treatment.
1. Introduction
Coking wastewater is a complex and toxic byproduct produced during coal coking, gas purification, and by-product recovery processes. It contains a mixture of inorganic pollutants (such as ammonia, sulfate, cyanide, and thiocyanate), alongside organic contaminants including phenolic compounds, polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), and nitrogen-, oxygen-, and sulfur-containing heterocyclic compounds [1,2,3]. These pollutants are typically present in high concentrations and exhibit refractory, toxic, mutagenic, and carcinogenic properties, making their removal particularly challenging. Their presence in coking wastewater not only severely inhibits microbial activities like anaerobic digestion and nitrification but also leads to strong biological inhibition and genotoxicity. Furthermore, the low biodegradability (BOD5/COD < 0.3) of coking wastewater limits the effectiveness of conventional biological treatment processes, preventing them from meeting discharge standards [4,5,6]. This underscores the need for advanced treatment methods that can enable wastewater reuse or safe discharge.
Coagulation has been recognized as one of the most effective and widely used advanced treatment processes for both drinking water and industrial wastewater, offering advantages such as low investment costs, simple operation, and efficient contaminant removal [7,8,9]. Despite its benefits, coagulation faces significant challenges in coking wastewater treatment due to the complex nature of the contaminants, which include high residual organic polarity and large coagulant dosage requirements, typically leading to poor removal efficiency, low floc settleability, and difficult sludge management [10,11,12]. These issues limit the broader application of conventional coagulants in coking wastewater treatment. Among the various coagulants, inorganic polyaluminum chloride (PACl) has become one of the most widely used due to its lower causticity to equipment, reduced sludge production, and strong charge neutralization and bridging adsorption capabilities, as well as its relatively low sensitivity to temperature fluctuations. Despite these advantages, PACl’s efficiency in removing refractory organic compounds remains limited, and its performance is highly dependent on the pH, which constrains its broader industrial application [13,14,15,16].
Recent research has explored the use of PACl combined with coagulant aids for the enhanced treatment of coking wastewater. For instance, cationic polyacrylamide (CPAM) could enhance floc formation through strong bridging adsorption and charge neutralization, particularly effective in adsorbing negatively charged organic pollutants like phenols and long-chain hydrocarbons due to its high molecular weight and cationic nature [17]. Iron ions could improve the removal of refractory organic compounds by forming hydroxide precipitates that aid in sweep coagulation and complexation, leading to the formation of denser and more stable flocs [18]. However, these studies mainly focused on optimizing the operational conditions, such as the coagulant dosage and pH, while giving limited attention to the combined effects of PACl with CPAM or iron ions on the removal of refractory organic compounds in coking wastewater [19,20].
Another key factor in the success of the coagulation process is the behavior of flocs—particularly their stability during breakup and regrowth cycles [21]. These properties play a critical role in determining the overall efficiency of coagulation, as flocs that break down too easily may lead to reduced removal efficiency. Additionally, the basicity of PACl significantly influences its coagulation performance. PACl with higher basicity tends to have a greater proportion of polymeric aluminum species, which enhances charge neutralization and bridging adsorption, resulting in more stable flocs and improved contaminant removal [22]. Conversely, lower-basicity PACl contains more monomeric aluminum species, which may limit its ability to form strong and stable flocs [23]. Therefore, it is crucial to study the role of PACl’s basicity and coagulant aids to optimize the coagulation process and enhance the pollutant removal efficiency in coking wastewater treatment under operational conditions.
In this study, PACl with different basicity levels ([OH]/[Al] molar ratios of 0.5 and 2.5) was synthesized using a micro-alkaline dropping method. Coagulant aids, including CPAM and iron ions, were added at varying dosages to evaluate their effects on the removal of the chemical oxygen demand (COD) and color from coking wastewater. Changes in the organic composition of the wastewater after treatment with PACl + CPAM or PACl + iron ions were analyzed using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC-MS), three-dimensional excitation–emission matrix (3D-EEM) fluorescence spectroscopy, and ultraviolet (UV) spectroscopy. Additionally, the floc properties were studied using laser diffraction to better understand the removal mechanisms of refractory organic compounds. The aim of this research is to provide a better understanding of the coagulation mechanisms involved in the treatment of coking wastewater, offering a practical approach to enhancing the removal of refractory organic compounds in industrial wastewater treatment.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Wastewater Characteristics
Wastewater was collected from a coking wastewater treatment plant employing an anaerobic/anoxic/oxic (A2/O) process in Shanxi, China. The effluent quality characteristics after biological treatment are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Characteristics of the coking wastewater after biological treatment.
2.2. Preparation and Characterization of PACl
PACl was synthesized by slowly adding a sodium hydroxide (NaOH) solution (0.5 mol/L) to an aluminum chloride (AlCl3) solution (0.5 mol/L) under rapid stirring at 70 °C to achieve the target basicity values of 0.5 and 2.5. The preparation of PACl is illustrated in Figure 1. The Ferron method was used to analyze the distribution of hydrolyzed Al (III) species in PACl [24]. For PACl with basicity of 0.5, the proportions of Ala (monomeric aluminum), Alb (polymeric aluminum), and Alc (colloidal aluminum) were 72.22%, 20.18%, and 7.60%, respectively. In comparison, for PACl with basicity of 2.5, the corresponding values were 5.56%, 73.68%, and 20.76%. For commercially available PACl, with the approximate basicity of 2.2, the Ala, Alb, and Alc content was 10.62%, 60.16%, and 29.22%, respectively.
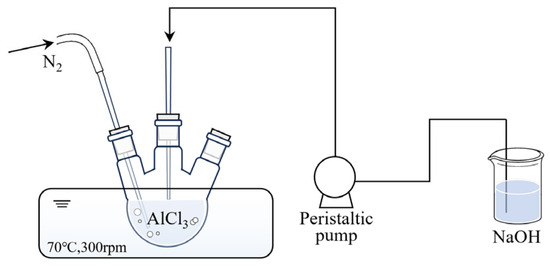
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the preparation of PACl.
2.3. Coagulation Process
Coagulation experiments were performed using a jar-test apparatus (ZR4-6, Zhongrun Water Industry Technology Development Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, China). A 200 mL sample of coking wastewater was subjected to rapid stirring for 30 s, followed by the addition of a predetermined amount of PACl and an additional 1.5 min of rapid mixing at 200 rpm. The stirring speed was then reduced to 40 rpm for 10 min, after which the mixture was allowed to settle quiescently for 30 min. Coagulant aids, including CPAM and iron ions, were added 20 s before the slow mixing phase. Water samples were collected 1.0 cm below the liquid surface for further analysis.
2.4. GC-MS
The organic composition in the biochemical effluent of coking wastewater was analyzed using GC-MS with a 7890B GC-5977A MSD system (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). Sample pretreatment was as follows. First, 50 mL collected samples of coking wastewater biochemical effluent before and after coagulation were filtered through 0.45 μm membranes (PTFE, Merck Millipore, Burlington, MA, USA). Organic compound extraction was conducted through a syringe-like C18-SPE cartridge (C18-SPE Bond Elut, Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) sequentially preconditioned with 10 mL methylene dichloride, 10 mL methanol, and 10 mL MilliQ water at a flow rate of 4 mL/min. The filtered water samples were delivered directly into the headspace of the activated C18-SPE cartridge and forced by pressure through the sorbent at a flow rate of 3~4 mL/min. Organic pollutants were subsequently eluted with an organic mixture (5 mL methylene dichloride and 5 mL methanol), after which the eluent was collected in a glass flask and concentrated to 1.5 mL using a rotary evaporator (RV-211M, Shanghai Yiheng Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) and the nitrogen blow method.
The initial oven temperature of the GC was maintained for 3 min at 40 °C, increased to a maximum of 240 °C at a gradient of 5 °C/min, and kept at 240 °C for 2 min. Helium (>99.999%) was used as a carrier gas, with a constant flow rate of 1 mL/min. The automatic injector temperature was set at 280 °C, 1 μL samples were injected, and the shunt ratio was 10:1. The MS was operated in EI mode (70 eV).
2.5. 3D-EEM
The 3D-EEM fluorescence spectra were measured using a Cary Eclipse spectrofluorometer (Agilent), equipped with a 150 W xenon lamp as the excitation source and a photomultiplier tube (PMT) set at 600 V. Both the excitation and emission slit widths were 5 nm. The excitation wavelength (λEx) ranged from 200 to 450 nm with 10 nm increments, and the emission wavelength (λEm) ranged from 250 to 550 nm with 1 nm intervals. The scanning speed was set at 600 nm/min. Water samples were diluted to a TOC concentration of 2 mg/L, filtered through a 0.45 μm membrane, and measured in a 1 cm quartz cuvette. Ultrapure water was used as a blank to correct the Raman scattering of the samples. The fluorescence regional integration (FRI) method, as described by Wang et al. [25], was employed to quantitatively evaluate the changes in dissolved organic matter.
2.6. Floc Size, Strength, and Fractal Structure Analysis
The floc growth, breakage, and regrowth processes were monitored online using a laser diffraction instrument (Mastersizer 2000, Malvern Instruments Ltd., Malvern, UK). A 5-mm-diameter silicone tube was used to connect the jar tester, laser diffraction instrument, and peristaltic pump. The peristaltic pump was set at a flow rate of 1.5 L/h, drawing water samples containing flocs from the beaker through the laser diffraction instrument and then back into the beaker. The laser diffraction instrument, controlled by a computer, continuously measured the water samples and automatically recorded the results at 16 s intervals. After adding the coagulants, rapid mixing at 200 rpm was conducted for 1.5 min to ensure uniform mixing, followed by slow mixing at 40 rpm for 10 min to allow floc growth. Subsequently, the stirring speed was increased to 200 rpm for 5 min to induce floc breakage under high shear force. Finally, the speed was reduced to 40 rpm for 10 min to allow floc recovery. The online monitoring setup for the floc size during the coagulation process is shown in Figure 2.
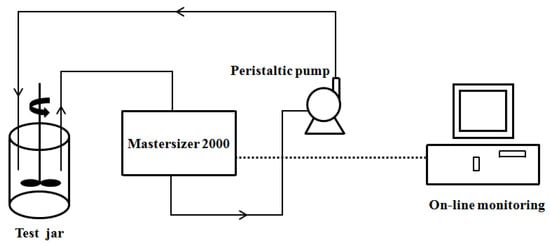
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of the dynamic floc size online monitoring system.
The 50th percentile d50 (μm) was used to denote the floc size. Small-angle laser light scattering was employed to calculate the fractal dimension (Df) to evaluate the structure of the flocs [26]. The strength factor (Sf) and recovery factor (Rf) were used to quantitatively investigate the floc strength and regrowth ability [27], as defined by
where d1 (μm), d2 (μm), and d3 (μm) are the sizes of the flocs at the plateau before applying the shear force, after breakage, and after regrowth, respectively.
Sf = d2/d1 × 100%
Rf = (d3 − d2)/(d1 − d2) × 100%
2.7. Other Measurements
The color of the water samples was measured using a colorimeter (XS-1, Shanghai Haiheng Electromechanical Instrument Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China). Total organic carbon (TOC) was determined with a TOC analyzer (Aurora 1030W, OI Analytical, College Station, TX, USA), while CODCr was measured using the potassium dichromate method. UV absorption spectra were obtained using a UV–vis spectrophotometer (UV-1601, Beijing Beifen-Ruili analytical instrument Co., Ltd., Beijing, China). All experiments in this study were conducted in triplicate.
3. Results
3.1. Coagulation with PACl
This study conducted a comparative analysis of the coagulation performance of PACl with varying basicity on the removal of refractory organic compounds from coking wastewater. The results indicated that, at a fixed PACl dosage of 200 mg/L, the optimal pH values for organic pollutant removal using commercial PACl, PACl with basicity of 0.5, and PACl with basicity of 2.5 were 4, 8, and 6, respectively (Figure 3a). Under these conditions, the CODCr removal efficiency was 36.51%, 38.89%, and 44.44%, with corresponding residual CODCr concentrations of 80, 77, and 70 mg/L (Figure 3a). Further experiments were conducted to adjust the pH to the optimal values for each PACl type and to investigate the effects of varying dosages (25 to 400 mg/L) on CODCr removal (Figure 3b,c). Commercial PACl and PACl with basicity of 0.5 exhibited the best coagulation performance near their isoelectric points, with optimal dosages of 200 mg/L and 100 mg/L, yielding residual CODCr concentrations of 80 and 78 mg/L, respectively. Although PACl with basicity of 2.5 exhibited a higher positive charge at a dosage of 50 mg/L, its optimal dosage was 200 mg/L, resulting in a residual CODCr concentration of 70 mg/L.
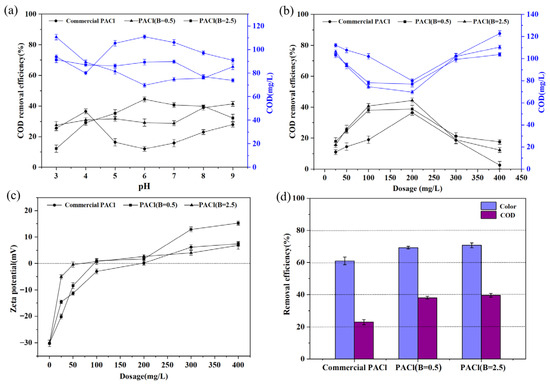
Figure 3.
(a) CODCr removal efficiency with different pH levels; CODCr (b) and color (c) removal efficiency with different PACl doses; (d) CODCr and color removal efficiency with different PACl.
Previous studies have demonstrated that when the pH is below 5, the primary hydrolysis products of PACl are highly charged, low-polymerized multinuclear complexes that remove pollutants primarily via charge neutralization [28]. For PACl with basicity of 0.5, despite Ala being the main component, the hydrolysis products partially convert to Alb and Alc at pH levels between 5 and 8, suggesting a coagulation mechanism involving charge neutralization, sweep flocculation, and bridging adsorption [29,30]. In contrast, PACl with basicity of 2.5, which contains higher levels of Alb, exhibited multiple coagulation mechanisms, resulting in the highest removal efficiency, and its performance was not limited to the isoelectric point.
For industrial applications, tests were conducted without adjusting the pH (approximately 7.8) using a PACl dosage of 100 mg/L. The CODCr removal efficiency for commercial PACl, PACl with basicity of 0.5, and PACl with basicity of 2.5 was 23%, 38.10%, and 39.68%, respectively, representing a 1.66-fold and 1.73-fold improvement over commercial PACl. Similarly, the color removal efficiency was 61%, 69.23%, and 70.77%, with the PACl variants showing 1.13-fold and 1.16-fold improvements, respectively, reducing the remaining color to 51, 40, and 38° (Figure 3d). These findings highlight that adjusting PACl’s basicity can optimize the aluminum hydrolysis species and enhance the coagulation efficiency. Notably, PACl with basicity of 2.5 exhibited better pH adaptability, reinforcing its potential for broader industrial use.
3.2. Effect of Coagulation Aid Addition on PACl with Basicity of 0.5 and 2.5
3.2.1. Effect of CPAM on CODCr and Color Removal
The removal of CODCr and color from the coking wastewater biochemical effluent was investigated using a fixed dosage of 100 mg/L PACl, without adjusting the initial pH. The CPAM dosage was varied from 0.25 to 10 mg/L. As shown in Figure 4, the color removal efficiency increased with the rising CPAM dosage, reaching a plateau beyond which no further significant reduction was observed (Figure 4a). However, the CODCr removal efficiency decreased when the CPAM dosage exceeded 1 mg/L (Figure 4b). This decline may be attributed to the formation of excessively dense flocs or increased electrostatic repulsion between particles, inhibiting the further aggregation or adsorption of fine particles. Moreover, the more pronounced decline in the removal efficiency for PACl with basicity of 2.5 is mainly due to its higher content of polymeric aluminum, particularly Alb. Alb tends to form larger and denser flocs, and, at higher CPAM dosages, these dense flocs increase the electrostatic repulsion between particles. This reduces the available surface area for adsorption and makes bridging adsorption more difficult, resulting in a significant decrease in the removal efficiency. Additionally, the excessive polymer chains covering the particles likely reduced the effectiveness of bridging adsorption, further decreasing the overall flocculation efficiency [31]. The residual CPAM in the water may also have contributed to the increase in the CODCr values.
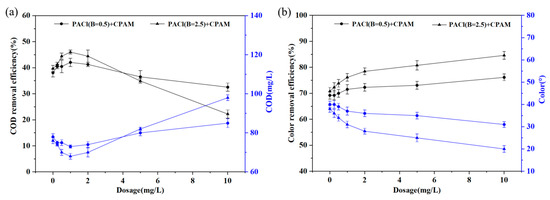
Figure 4.
CODCr (a) and color (b) removal efficiency with different CPAM doses.
The more pronounced decrease in PACl (B = 2.5) can be attributed to its higher polymeric aluminum content (Alb), which leads to stronger initial floc formation. However, at higher CPAM dosages, dense flocs and increased electrostatic repulsion between particles are more likely to occur in PACl (B = 2.5), as Alb has a greater tendency to form larger and more compact flocs. This results in a reduction in the available surface area for adsorption, making the system more sensitive to excessive polymer dosing, thereby causing a more significant decline in the removal efficiency.
The results in Figure 3d and Figure 4 also indicate that combining PACl with CPAM yielded superior coagulation performance in treating coking wastewater compared to using PACl alone. Notably, the combination of PACl with basicity of 2.5 and CPAM showed optimal performance. A CPAM dosage of approximately 1 mg/L improved the CODCr and color removal efficiency from 39.68% and 70.77% when using PACl alone to 46.03% and 76.15%, respectively. For PACl with basicity of 0.5, the CODCr and color removal efficiency also increased to 42.06% and 71.54%, respectively. These findings clearly demonstrate that CPAM addition enhanced the coagulation efficiency, as its three-dimensional polymer network and polar amide groups promoted the formation of larger flocs, improving the particulate removal through sweep flocculation and precipitation [32].
3.2.2. Effect of Iron Ions on CODCr and Color Removal
The effect of iron ions on the coagulation performance of PACl was investigated under a fixed PACl dosage of 100 mg/L without pH adjustment. As shown in Figure 5a,b, for PACl with the basicity of 0.5 and 2.5, the CODCr and color removal efficiency initially increased and then declined as the FeCl3 dosage increased. This trend can be attributed to the rapid hydrolysis of FeCl3 in water, forming trivalent hydrated ions (Fe(H2O)63+), which subsequently condense into dinuclear complexes (Fe2(OH)24+). As the FeCl3 dosage increases, the concentration of hydrolyzed complex ions rises. These ions react with the functional groups of organic compounds, forming insoluble organometallic salts or complexes. Some organics are removed by co-precipitation with metal hydroxide flocs, while sweep flocculation enhances the removal of smaller particles [33]. However, due to the yellowish color of ferric ions in solution, excessive dosing can lead to a rise in color levels. Moreover, the formation of highly charged, low-polymerization complexes may cause colloidal restabilization, resulting in an increase in the COD levels [34].
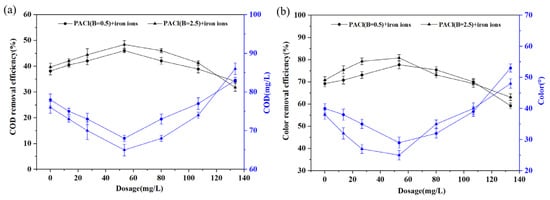
Figure 5.
CODCr (a) and color (b) removal efficiency with different iron ion doses.
As shown in Figure 5, the optimal dosage of FeCl3 for both types of PACl is 53.4 mg/L. However, the combination of PACl at basicity of 2.5 with iron ions exhibited better performance, achieving CODCr and color removal efficiency of 48.41% and 80.77%, respectively. For PACl with basicity of 0.5, the CODCr and color removal efficiency was 46.03% and 77.69%, respectively. It is worth noting that the combined treatment of PACl and FeCl3 not only outperformed the use of PACl alone but also showed better results compared to the combination of PACl and CPAM (Figure 3d, Figure 4 and Figure 5). This is mainly due to the synergistic effect between PACl and FeCl3. The further removal of organics by FeCl3 occurs primarily through chemical precipitation, where Fe3+ and its hydrolysis products form complexes with the organic compounds in the system, producing insoluble metal–organic complexes that precipitate and remove organics. Additionally, the coagulation process with PACl reduces the pH before the addition of FeCl3, rapidly increasing the protonation of organic compounds in the water, facilitating their adsorption onto the hydrolysis products of the coagulant [35]. Therefore, iron salts play a more effective role in promoting the removal of organic matter.
3.3. Organic Compound Removal
3.3.1. GC-MS Analysis
Given that PACl with basicity of 2.5 exhibited superior performance in organic matter removal, GC-MS was employed to analyze the composition and transformation of organic compounds before and after coagulation. As presented in Table 2 and Figure 6, 28 distinct organic compounds were identified in the water samples. These compounds were classified into eight categories based on their functional groups: polymeric aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs); long-chain alkanes (LCAs); nitrogen-, oxygen-, and sulfur-containing heterocyclic compounds (NOSs); benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, and xylene (BTEX); phenols (ArOH); esters (R-COO-R’); alcohols and carboxylic acids (R-OH and R-COOH); and halohydrocarbons (R-X). BTEX, PAHs, and R-OH and R-COOH were the predominant organic compounds before coagulation, comprising 26.70%, 24.98%, and 21.36% of the total peak area, respectively. The remaining 26.96% was attributed to LCAs, NOSs, ArOH, and R-COO-R’. Some of these compounds originated directly from the wastewater, while others were intermediates of biodegradation. However, the majority were resistant to microbial degradation.

Table 2.
Organic composition in biochemical effluent of coking wastewater before and after coagulation.
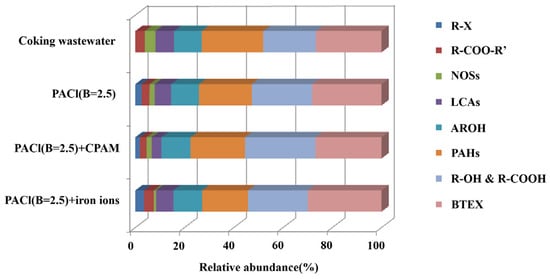
Figure 6.
Relative content of different organic compounds in coking wastewater biochemical effluent before and after coagulation.
After coagulation with PACl at the basicity of 2.5 and CPAM, esters and long-chain alkanes were efficiently removed, with their relative concentrations dropping from 3.87% and 7.61% to 2.71% and 3.96%, respectively. This can be attributed to the immediate hydrolysis of PACl upon its addition to the water, allowing the hydrolysis products to react with the active functional groups of the organic molecules [36]. Additionally, the strong bridging adsorption and sweep flocculation properties of CPAM further enhanced the removal of these compounds [37].
In contrast, the combination of PACl and iron ions proved more effective in eliminating PAHs; nitrogen-, oxygen-, and sulfur-containing NOSs; alcohols; carboxylic acids; and phenols. The relative content of PAHs decreased significantly from 24.98% to 18.66%, indicating that iron ions facilitated the more thorough removal of macromolecules. NOSs were reduced from 4.30% to 0.92%, and the concentrations of alcohols, carboxylic acids, and phenols dropped to 24.21% and 11.64%, compared to 28.60% and 11.83% with PACl and CPAM. This demonstrates the superior effectiveness of iron ions in removing these compounds, likely due to their ability to readily bind with functional groups such as carboxyl (-COOH) and hydroxyl (-OH) groups [38]. Additionally, the relative content of halohydrocarbons increased to 3.55% after coagulation with iron ions, compared to 2.59% after treatment with PACl alone. This suggests that ferric chloride introduced additional chloride ions, which reacted with the alkanes in the wastewater, leading to the formation of halohydrocarbons.
3.3.2. EEM Analysis
As outlined earlier, the fluorescence spectra were divided into five distinct regions: Peak I, with excitation/emission wavelengths (λEx/λEm) of 200–250/250–330 nm, corresponding to aromatic protein I (tyrosine-like compounds); Peak II (200–250/330–380 nm), representing aromatic protein II (tryptophan-like compounds); Peak III (200–250/380–550 nm), associated with fulvic acid-like substances; Peak IV (250–450/250–380 nm), indicating soluble microbial byproduct-like materials; and Peak V (250–450/380–550 nm), representing humic acid-like substances. The EEM analysis and corresponding semi-quantitative results revealed that the humic acid-like fluorescence peak was the most prominent, reaching 164,226 a.u. and accounting for 51.23% of the total fluorescence. The fulvic acid-like peak followed with an intensity of 56,434 a.u. or 18.60% (Figure 7 and Figure 8). These humic and fulvic acid-like substances, primarily originating from raw wastewater and microbial by-products, are refractory organics that are resistant to conventional biochemical treatments [39,40]. The fluorescence intensities of soluble microbial by-products, aromatic protein II, and aromatic protein I were 55,972 a.u., 37,785 a.u., and 6167 a.u., respectively.
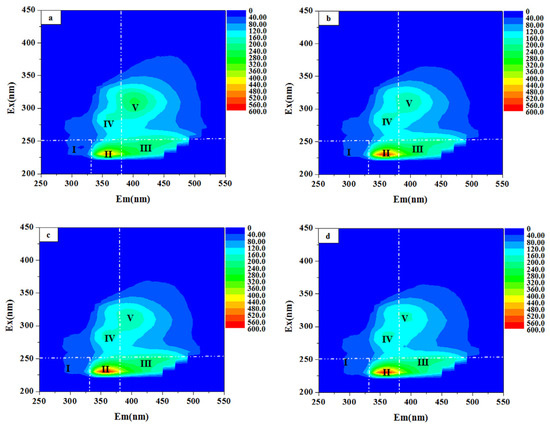
Figure 7.
The 3D-EMM fluorescence spectra of the coking wastewater biochemical effluent before and after coagulation: (a) biochemical effluent and after coagulation with (b) PACl (B = 2.5), (c) PACl (B = 2.5) + CPAM, and (d) PACl (B = 2.5) + iron ions.
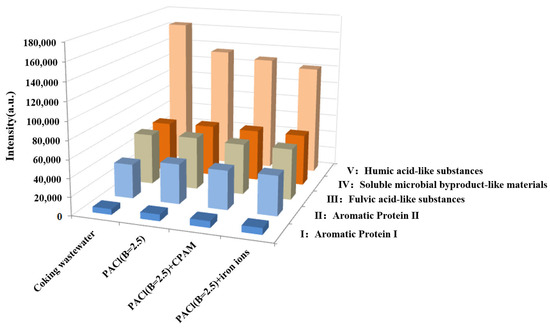
Figure 8.
Fluorescence components identified by EEM and FRI in the coking wastewater biochemical effluent before and after coagulation.
After coagulation with PACl with basicity of 2.5, the fluorescence intensity of humic acid-like substances decreased to 134,651 a.u., reflecting a 44.68% reduction and indicating efficient removal. However, the level of fulvic acid-like substances remained largely unchanged. In contrast, the fluorescence intensities of soluble microbial by-products and aromatic protein II increased to 57,489 a.u. and 43,947 a.u., with their relative proportions rising to 19.07% and 14.58%. This increase may be attributed to the chelation of aluminum ions from PACl with soluble microbial by-products and aromatic proteins in the coking wastewater [41].
When coagulated with PACl combined with either CPAM or iron ions, the fluorescence intensities of humic acid-like substances decreased further to 128,456 a.u. and 121,629 a.u., showing reductions of 44.67% and 42.64%, respectively. This suggests that iron ions were more effective in removing humic acid-like substances. Additionally, the fluorescence peak in Region V showed a blue shift of 11 nm after treatment with PACl and iron ions, indicating a shift to a lower emission wavelength. Previous studies suggest that humic acid-like substances consist of carboxyl and hydroxyl groups attached to benzene rings or polycyclic organic matter [38]. The observed blue shift, together with the results of the GC-MS analysis, suggests a reduction in polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and the degradation of hydroxyl and carboxyl groups [42,43].
For fulvic acid-like substances, the fluorescence intensities after coagulation with PACl combined with CPAM or iron ions were 56,032 a.u. and 56,133 a.u., similar to the pre-coagulation levels. However, the relative content of soluble microbial by-products increased to 19.07% and 19.95%, with the peak position in Region V shifting and the fluorescence intensity in Region IV increasing, particularly with iron ions. Furthermore, the fluorescence intensity of aromatic protein II rose to 42,911 a.u. and 43,489 a.u., with relative proportions of 14.72% and 15.24%. These results are consistent with previous studies that reported low protein removal efficiency for both aluminum and iron salts [44].
Overall, these findings highlight the superior performance of iron ions compared to PACl with CPAM in removing humic acid-like substances. They also provide insights into the molecular changes occurring during coagulation, including the degradation of refractory organic compounds, reinforcing the importance of advanced coagulation strategies in improving the removal of persistent organic matter in wastewater treatment processes.
3.3.3. UV Spectra Analysis
Figure 9 presents the UV spectra of the coking wastewater biochemical effluent before and after coagulation. The absorbance trends before and after coagulation were similar, although the intensity at certain wavelengths decreased after the coagulants were added. Strong absorption peaks were observed between 200 and 250 nanometers, with additional peaks in the 250 to 370 nanometer range. This suggests the presence of monocyclic aromatic compounds, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, and nitrogenous heterocyclic compounds in the effluent [45]. Organic pollutants with strong absorption peaks between 230 and 400 nanometers were effectively removed, indicating that the coagulation treatment successfully eliminated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and nitrogenous heterocyclic compounds. However, residual contaminants with high absorbance between 200 and 230 nanometers remained unaffected by the treatment.
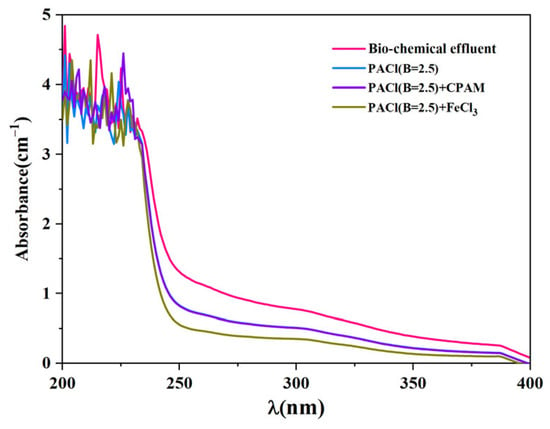
Figure 9.
UV spectra of the coking wastewater biochemical effluent before and after coagulation.
When CPAM was used as a coagulant aid, the UV spectra were almost identical to those of the effluent treated with PACl with the basicity of 2.5 alone, indicating that CPAM did not enhance the removal efficiency of organic compounds. In contrast, the addition of iron ions significantly reduced the intensity of the ultraviolet absorption peaks compared to treatment with PACl alone, demonstrating that the combination of PACl and iron ions was more effective in coagulating the coking wastewater.
Specific ultraviolet absorption (SUVA), calculated as the UV254 divided by dissolved organic carbon (DOC) and multiplied by 100, reflects the content of humic-like organic compounds in water systems [46]. Humic-like and highly hydrophobic organic compounds are predominant when the SUVA exceeds 4 L·mg−1·m−1. When the SUVA falls between 2 and 4 L·mg−1·m−1, the organic matter consists of a mixture of humic-like and other natural organic compounds, including both hydrophobic and hydrophilic substances. When the SUVA is less than 2 L·mg−1·m−1, mainly hydrophilic organic matter and other contaminants are present. The results of this study indicate that the organic compounds in the coking wastewater biochemical effluent were primarily humic-like and hydrophobic, with a SUVA value of 4.06 L·mg−1·m−1. After coagulation treatment with PACl, PACl combined with CPAM, and PACl combined with iron ions, the SUVA values were reduced to 3.57, 3.55, and 3.24 L·mg−1·m−1, respectively. This reduction suggests that the hydrophobicity of the organic compounds decreased, as the reduction in dissolved organic carbon was less pronounced than the decrease in UV254. These findings indicate that the coagulation processes used in this study effectively removed the hydrophobic organic compounds from the effluent.
3.4. Floc Characteristics
The floc characteristics are largely influenced by the performance of the coagulants and the mechanisms involved in the coagulation process [47]. The variations in floc growth, breakage, and regrowth are depicted in Figure 10a. During the floc growth stage at 40 rpm, the floc size increased and reached a plateau after the addition of the coagulants. The stable floc sizes were approximately 767, 656, 579, 256, 245, and 147 μm, following the order PACl (basicity 0.5) + CPAM > PACl (basicity 2.5) + CPAM > PACl (basicity 0.5) > PACl (basicity 2.5) > PACl (basicity 0.5) + iron ions > PACl (basicity 2.5) + iron ions. This trend is likely due to the strong bridging adsorption of CPAM, which promoted floc growth. After the introduction of shear force at 200 rpm, the floc sizes decreased to 436, 433, 347, 206, 153, and 99 μm, respectively. The regrowth stage at 40 rpm resulted in floc sizes of 487, 543, 366, 209, 155, and 101 μm, depending on whether CPAM or iron ions were used.
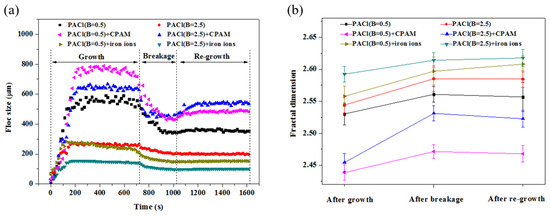
Figure 10.
Floc characteristics under various conditions: (a) floc size and (b) fractal dimension.
Figure 10b illustrates that the Df of the flocs was the highest when formed with iron ions and lowest when generated with CPAM. This indicates that the flocs formed in the presence of CPAM were loosely connected, likely due to bridging adsorption between smaller flocs, while iron ions produced more compact flocs. During the breakage stage, the Df values increased to varying extents, suggesting that the flocs became more compact under high shear conditions. However, the Df values during the regrowth phase did not fully recover to the pre-breakage levels. A comparison of Figure 10a,b reveals a negative correlation between the Df and the floc size.
The Sf and Rf are shown in Figure 11. The Sf of the flocs formed with PACl and CPAM was relatively low, indicating that although the coagulant promoted visible floc formation during growth, the bridging effect and the chemical bonds of the organic matter were easily disrupted. However, the regrowth ability of these flocs was better, suggesting that CPAM accelerated the reaggregation of broken floc fragments. This may be because the flocs broke at weak points under shear force and reformed at more favorable locations with stronger attractive forces or weaker repulsive forces [48]. CPAM exhibited strong adsorption capabilities, and the number of clusters between the flocs increased after breakage, enhancing their recovery potential [49].
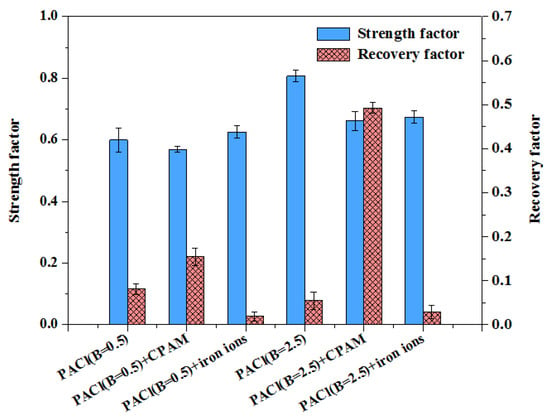
Figure 11.
Strength and recovery factors in coagulation process under various conditions.
The Sf of the flocs formed with PACl and iron ions was significantly higher, which contrasts with the floc size results. The smaller flocs generated by PACl and iron ions were less affected by surface erosion caused by eddy splitting [50,51]. However, the Rf was lower, indicating inferior regeneration performance. This is likely because charge neutralization was not the sole coagulation mechanism for PACl combined with iron ions. Other mechanisms, such as complexation and sweep flocculation, also contributed to the removal of inorganic colloidal particles and organic pollutants. Previous studies have shown that the floc recovery performance diminishes as the flocs break into smaller particles [33,37].
3.5. Floc Settleability
The floc settleability significantly influences the overall cost and efficiency of effluent treatment. In engineering applications, rapid and efficient floc settling not only enhances the treatment capacity but also reduces the footprint and operating costs of sedimentation tanks. In this study, after coagulation, the coking wastewater was collected into a settlement cup, and the settling volume of the flocs over a 30 min sedimentation period was recorded, as shown in Figure 12. Following half an hour of sedimentation, the residual floc volumes after treatment with PACl at basicity of 0.5 and 2.5 were 94 mL and 39 mL, respectively, indicating that an increase in basicity significantly improved the floc settleability.
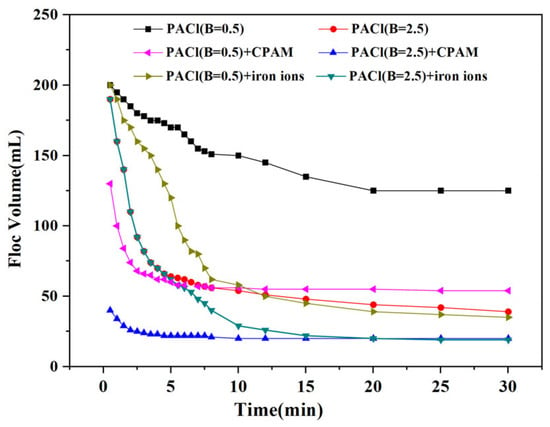
Figure 12.
Residual floc volume with settling time under various conditions.
The combination of PACl with either CPAM or iron ions resulted in faster settling speeds compared to PACl alone, demonstrating the effectiveness of coagulant aids in enhancing the coagulation performance. The flocs produced by PACl combined with CPAM required less than 5 min of settling time, and the residual floc volumes after treatment with PACl at basicity of 0.5 and 2.5 combined with CPAM were reduced to 54 mL and 20 mL, respectively. The increase in floc size improved the settling speed, thereby significantly reducing the overall sedimentation time. Additionally, the chain structure of CPAM accelerated floc growth. After 10 min of sedimentation, the flocs formed by PACl combined with iron ions had nearly reached their optimal settling state. The residual floc volumes after treatment with PACl at basicity of 0.5 and 2.5 combined with iron ions were reduced to 35 mL and 19 mL, respectively. These results suggest that the flocs generated by PACl combined with iron ions were more compact than those formed with CPAM, as indicated by the higher Df values shown in Figure 10.
While this study demonstrates that the combination of PACl with iron ions significantly improves the settling speed and floc compactness, the complexity of real industrial wastewater could affect its performance in practice. For instance, the presence of other impurities or high concentrations of organic pollutants in wastewater may reduce the effectiveness of the coagulants. To optimize the coagulation efficiency for large-scale engineering applications, future studies should investigate the effectiveness of PACl combined with various coagulant aids in treating wastewater. Moreover, efforts should focus on maintaining high settling efficiency while reducing the dosage of chemical agents to minimize the costs and environmental impact. Improving the regeneration performance of the flocs will also be a critical area for future research.
4. Conclusions
This study demonstrates that PACl with basicity of 2.5 and 0.5, in combination with coagulant aids, provides an effective approach for the treatment of coking wastewater. Both PACl formulations significantly outperformed commercial PACl in COD and color removal. Specifically, PACl with the basicity of 2.5 achieved 44.44% COD and 70.77% color removal, which was approximately 1.93 times higher for COD and 1.16 times higher for color removal compared to commercial PACl. This enhanced performance is attributed to the higher content of polymeric aluminum species, improving the charge neutralization and bridging adsorption. The addition of coagulant aids, particularly iron ions, further boosted the performance, with PACl at the basicity of 2.5 and iron ions achieving the highest COD (48.41%) and color removal (80.77%) through sweep coagulation and complexation. Organic composition analysis confirmed the superior removal of PAHs and other complex organics when iron ions were used. Moreover, the floc analysis revealed that the iron ions formed more compact, settleable flocs than CPAM, further improving the coagulation efficiency. These findings underscore the significant improvement in the removal rates achieved by optimizing the PACl basicity and coagulant aid selection, offering a practical and efficient solution for advanced coking wastewater treatment.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.D.; data curation, H.S., Y.Z. and M.D.; formal analysis, Y.Z.; funding acquisition, H.S. and Z.D.; investigation, H.S. and M.D.; methodology, H.S. and Y.Z.; supervision, Z.D.; writing—original draft, H.S.; writing—review and editing, Z.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 22108163) and the Key Research and Development Plan in Shanxi (No. 202102090301028).
Data Availability Statement
All the data have been provided in the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Li, Z.; Wei, T.; Pan, J.; Liang, Y.; Ban, Z.; Ke, X.; Kong, Q.; Qiu, G.; Hu, Y.; Preis, S.; et al. Physicochemical pre- and post-treatment of coking wastewater combined for energy recovery and reduced environmental risk. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 447, 130802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Ni, J.; Lai, P. Advanced treatment of biologically pretreated coking wastewater by electrochemical oxidation using boron-doped diamond electrodes. Water Res. 2009, 43, 4347–4355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, L.; Paul, K.K.; Jena, S. Coke wastewater treatment methods: Mini review. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2021, 98, 100133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.; Wei, T.; Li, Z.; Wei, C.; Kong, Q.; Guan, X.; Qiu, G.; Hu, Y.; Wei, C.; Zhu, S.; et al. BOD/COD ratio as a probing index in the O/H/O process for coking wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 466, 143257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, X.; Li, Y.; Su, P.; Paidar, M.; Bouzek, K. Cost-efficient improvement of coking wastewater biodegradability by multi-stages flow through peroxi-coagulation under low current load. Water Res. 2019, 154, 336–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.M.; Wang, B.; Li, W.; Cui, L.; Guo, Y.; Cheng, F. High-efficiency leaching of Al and Fe from fly ash for preparation of polymeric aluminum ferric chloride sulfate coagulant for wastewater treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 306, 122545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Hu, Z.; Li, H.; Zheng, H.; Yang, S.; Yu, W.; Tang, B.; Yang, H.; He, R.; Guo, W.; et al. Recent advances in microplastic removal from drinking water by coagulation: Removal mechanisms and influencing factors. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 349, 123863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Li, M.; Zhang, G.H.; Liu, W.; Xu, J.Y.; Tian, Y.S.; Wang, Y.F.; Xie, X.Y.; Peng, Z.Q.; Li, A.M.; et al. Efficient treatment of the starch wastewater by enhanced flocculation-coagulation of environmentally benign materials. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 307, 122788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.P.; Gong, Z.P.; Qi, W.H.; Li, E.Z.; Shen, J.; Li, J.F.; Zhao, H.Z. Coagulation performance and floc characteristics of poly-ferric-titanium-silicate-chloride in coking wastewater treatment. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 642, 128413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, P.; Zhao, H.Z.; Wang, C.; Ni, J.R. Advanced treatment of coking wastewater by coagulation and zero-valent iron processes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 147, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, E.; Li, J.; Du, Z.; Cheng, F. Preparation and coagulation-flocculation performance of covalently bound organic hybrid coagulant with excellent stability. Colloids Surf. A. 2020, 600, 124966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.; Kim, Y.M.; Lee, D.S.; Park, J.M. Chemical treatment for treating cyanides-containing effluent from biological cokes wastewater treatment process. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 143, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.B.; Xu, R.H.; Wei, C.H.; Wu, H.Z. Removal of cyanide compounds from coking wastewater by ferrous sulfate: Improvement of biodegradability. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 302, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zouboulis, A.I.; Tzoupanos, N. Alternative cost-effective preparation method of polyaluminium chloride (PAC) coagulant agent: Characterization and comparative application for water/wastewater treatment. Desalination 2010, 250, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.J.; Xie, Y.; Chen, Q.H.; Wang, W.X.; Li, X. Investigation of polyaluminum chloride (PACl) coagulation to remove cyanobacteria from maintenance to decay stage: Performance and mechanism. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mccurdy, K.; Carlson, K.; Gregory, D. Floc morphology and cyclic shearing recovery: Comparison of alum and polyaluminum chloride coagulants. Water Res. 2004, 38, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.L.; Zhou, J.Y.; Yan, Y.; Yang, L.W.; Xing, G.H.; Li, H.Y.; Wu, P.; Wang, M.Y.; Zheng, H.L. Application of coagulation/flocculation in oily wastewater treatment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 765, 142795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Li, Y.; Yong, T.; Cao, W.; Wu, J.; Shen, Y. Synergistic effects of oxidation, coagulation and adsorption in the integrated fenton-based process for wastewater treatment: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 306, 114460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.Q.; Wang, D.S.; Yu, J.F.; Ni, J.R.; Edwards, M.; Qu, J.H. Enhanced coagulation with polyaluminum chlorides: Role of pH/Alkalinity and speciation. Chemosphere 2008, 71, 1665–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillanpää, M.; Ncibi, M.C.; Matilainen, A.; Vepslainend, M. Removal of natural organic matter in drinking water treatment by coagulation: A comprehensive review. Chemosphere 2018, 190, 54–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.L.; Zhang, H.L.; Liu, G.; Chen, X.Y.; Yang, Y.H.; Sun, Z.N.; Tang, L.; Dong, L.; Wang, Y.J.; Liu, H.S. Preparation of microencapsulated coagulants and application to oil–water separation under gravity coagulation conditions. Fuel 2024, 363, 131022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Song, Z.; Zhang, W.; Li, L.; Liao, G.; Wang, D. Impact of hydroxyl aluminum speciation on dewaterability and pollutants release of dredged sludge using polymeric aluminum chloride. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 49, 103051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.W.; Shi, L.L.; Chen, X.; Huang, X.Y.; Wang, X.K.; Chen, S.X.; Hua, Y.; Gong, H.; Dong, H.; Liu, H.L.; et al. Systematic review on the residual chemicals in wastewater treatment sludge: Specifically focusing on the occurrence state and anaerobic bioprocess. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 151563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.X.; Xiao, F.; Wang, D.S. Speciation, stability, and coagulation mechanisms of hydroxyl aluminum clusters formed by PACl and alum: A critical review. Adv. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2015, 226, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.M.; Meng, Y.J.; Ma, D.F.; Wang, Y.; Li, F.L.; Xu, X.; Xia, C.F.; Gao, B.Y. Integration of coagulation and adsorption for removal of N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA) precursors from biologically treated municipal wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 12426–12436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.H.; Gao, B.Y.; Sun, J.Z.; Yue, Q.Y. Coagulation behavior of kaolin-anionic surfactant simulative wastewater by polyaluminum chloride-polymer dual coagulants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 7382–7390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.H.; Qi, X.H.; Wang, W.Y.; Cheng, M.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhang, P.; Song, G.F. Floc Kinetics in Dual-coagulation for the Treatment of High-concentration Surfactant-kaolin Wastewater. J. Polym. Environ. 2024, 32, 1706–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Tang, H.X.; Wang, D.S.; Wang, S.F.; Deng, Z.J. Al (III) speciation distribution and transformation in high concentration PACl solutions. J. Environ. Sci. 2006, 18, 872–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.Z.; Ke, S.Z.; Tu, J.Y.; Zhu, J.; Wei, W.; Gao, J.S. Influences of pH on polyaluminium chloride species distribution and coagulation effect. Ind. Water Treat. 2016, 36, 50–53. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xue, S.; Wen, Y.; Tie, M.; Zhao, Q.L.; Wei, L.L.; Zhang, Z.H.; Jin, W.; Zhang, L.N. Effect of enhanced coagulation on the characteristics of dissolved organic matter in secondary treated effluents. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2013, 33, 2199–2208. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Xiao, F.; Wang, D.S. Effects of Al2O3 and TiO2 on the coagulation process by Al2(SO4)3 (AS) and poly-aluminum chloride (PACl) in kaolin suspension. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 124, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Gao, B.Y.; Guo, K.Y.; Yue, Q.Y. Characterization and influence of floc under different coagulation systems on ultrafltration membrane fouling. Chemosphere 2020, 238, 124659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, B.; Gao, B.; Liu, X.; Wang, M.; Yang, Z.; Yue, Q. The impact of pH on floc structure characteristic of polyferric chloride in a low DOC and high alkalinity surface water treatment. Water Res. 2011, 45, 6181–6188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Gao, B.Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Xu, W.; Yue, Q. Effect of pH on humic acid removal performance in coagulation-ultrafiltration process and the subsequent effects on chlorine decay. Sep. Purif. 2011, 80, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Sen, G.; Jha, U.; Pal, S. Novel biodegradable polymeric flocculant based on polyacrylamide-grafted tamarind kernel polysaccharide. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 9638–9644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngadi, N.; Yahya, N.Y.; Muhamad, N. Treatment of industrial textile wastewater using polyarcrylamide (PAM) and polyaluminium chloride (PAC). J. Teknol. 2012, 60, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, P.; Jefferson, B.; Parsons, S.A. Breakage, regrowth, and fractal nature of natural organic matter flocs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 2307–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.L.; Zhang, Y.J.; Li, L.H.; Li, G.B. Characteristic of natural organic matter removal by ferric and aluminium coagulation. Environ. Sci. 2008, 29, 1187–1191. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wan, J.L.; Wang, X.C.; Jin, P.K. Comparison of the properties of coagulation between alum sulfate and ferric chloride thhumic acids. Water Purif. Technol. 2008, 27, 16–19. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.B.; Song, Y.H.; Tu, X.; Du, E.D.; Liu, R.X.; Peng, J.F. Assessing removal efficiency of dissolved organic matter in wastewater treatment using fluorescence excitation emission matrices with parallel factor analysis and second derivative synchronous fluorescence. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 144, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.H.; Hou, D.Y.; Yu, Y. Development of a novel integrated membrane system incorporated with an activated coke adsorption unit for advanced coal gasification wastewater treatment. Colloid. Surf. A 2015, 484, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkins, K.M.; Nelson, D.J. Spectroscopic approaches to the study of the interaction of aluminum with humic substances. Coordin. Chem. Rev. 2002, 228, 205–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carstea, E.M.; Bridgeman, J.; Baker, A.; Reynolds, D.M. Fluorescence spectroscopy for wastewater monitoring: A review. Water Res. 2016, 95, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.F.; Liu, X.Y.; Cheng, F.Q. Bio-refractory organics removal and floc characteristics of poly-siliciccation coagulants in tertiary-treatment of coking wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 324, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gone, D.L.; Seidel, J.L.; Batiot, C.; Bamory, K.; Ligban, R.; Biemi, J. Using fluorescence spectroscopy EEM to evaluate the efficiency of organic matter removal during coagulation–flocculation of a tropical surface water (Agbo reservoir). J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 172, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.H.; Wei, C.H.; Yan, B.; Ren, M.; Peng, P.A. Composition characterization of dissolved organic matters in coking wastewater. Environ. Chem. 2012, 31, 702–707. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.C.; Lee, S. Pump diffusion flash mixing (PDFM) for improving coagulation process in drinking water treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 52, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Melia, C.R. Coagulation and sedimentation in lakes, reservoirs and water treatment plants. Water Sci. Technol. 1998, 37, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.Y.; Gao, B.Y.; Yue, Q.Y.; Wang, Q. Effect of preformed and non-preformed Al13 species on evolution of floc size, strength and fractal nature of humic acid flocs in coagulation process. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 78, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Xu, H.; Wang, D.S.; Duan, J.M. Effects of Pam on coagulation process in kaolin system using composite coagulants. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2017, 11, 1431–1436. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis, P.; Jefferson, B.; Gregory, J.; Parsons, S.A. A review of floc strength and breakage. Water Res. 2005, 39, 3121–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).