Abstract
The ecological security of the water environment is a key element in evaluating the dynamic balance and ecological service functions in the construction of urban ecological civilizations. Through the regional study of water resources in Huizhou, we selected 24 indicators in five dimensions of the DPSIR theory, such as “driving force-pressure-state-impact-response”, and constructed an ecological evaluation index system of the water environment. Combined with the entropy weight TOPSIS model, the analysis was carried out for spatial differentiation features and spatio-temporal deduction features, and the results showed that the weight coefficients of the spatial differentiation features for the guideline layer exhibited significant stratification characteristics. The overall spatial and temporal interpretation characteristics of the water’s environmental ecology in the Huizhou region from 2016 to 2021 showed a pull-up enhancement effect. The relative proximity value showed a 63.43% increase from 0.361 in 2016 to 0.590 in 2021 over the six-year period. The region is characterized by regional differences in the ecological carrying capacity of the water environment, which is high in the south-east and low in the north-west. The top three areas in the quantitative calculation of the ecological carrying capacity of the water environment are Shexian County, Jixi County, and Qimen County, in that order.
1. Introduction
Ecological security refers to the state of survival and development of a country’s ecological environment, which holds an important position in human production and life [1] With the rapid growth of China’s social and economic sectors and the increasing frequency of cultural exchanges, it is important to note that the ecologically sustainable supply chain has been gradually breached, and the ecological security system has shown a downward trend [2,3]. As an important support and component of ecological security, the ecological security of the water environment is an important aspect of ensuring the virtuous cycle of human society and the normal functioning of the surrounding ecosphere [4,5]. The water environment and ecology are now at the core of ecological civilization development [6,7,8]. In 2022, China carried out a series of fundamental ecological environmental protection works and promoted the implementation of key tasks for the ecological protection of the water environment [9,10] According to the “14th Five-Year Plan” for water safety and security, the water environment and ecological safety are the main line of China’s safety and security, and the layout of the water network has been the focus of China’s engineering construction [11]. It can be seen that the ecological safety of the water environment is a key element in evaluating the dynamic balance and ecological service functions of urban ecological civilization construction [12].
Currently, different countries are increasingly paying attention to the water environment and ecological issues. The United Nations has released the ‘World Water Development Report’ to explore a series of global water environmental issues and management mechanisms [13]. The field of water environmental ecology is a core area of environmental ecological management, and its main research objective is to assess the level and scope of influence on the study area [14]. Multiple studies have shown that using a collaborative carrying capacity system dynamics model to conduct dynamic simulations of water ecology in regions such as the Inner Mongolia Plateau lake basins, the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei urban agglomeration, and coastal urban clusters in China can optimize the benefits of sea and lake carrying capacities [15,16,17] Therefore, simulation modeling based on the differences in the socio-economic development of different countries can provide a more accurate understanding of the characteristics of the spatial and temporal evolution of the dynamic simulation of the water environment. In the Xidiaoxi Wetland in Huzhou, Zhejiang, China, and the Hefei region in China, soft computing techniques and particle swarm K-means clustering methods were used to analyze the correlation between land cover changes and the ecology of water environments based on real-world scenarios, resulting in optimal clustering outcomes [18,19] By observing the dynamic changes in groundwater levels in typical oasis irrigation areas in North-west China, the sensitivity coefficient of water resource location changes and the relative proximity value were discussed using ArcGIS interpolation methods and the coefficient of variation method [20]. By observing the landscape pattern and ecological service value of the Manas River Basin in China’s arid inland regions, this study explores the driving role of reasonable development based on trends in water-level dynamics, providing insights into the sustainable development of water resource ecology [21]. The study of regional water resource development and protection systems uses coupled coordination and spatio-temporal difference characterization and the exploration of the mapping distribution of water resource ecology using spatial autocorrelation analysis and factor probes [22,23,24]. The water security level in Saskatchewan, Canada, has achieved alignment with sustainable development goals by combining water resource ecological security with model data, which has garnered international attention [25]. Through the assessment of the impact of geothermal energy production on underground masses in [26] European countries from 1990 to 2021, water resource ecological security has gradually become central in national environmental management [26,27] The ecological security of water resources has gradually become the core position of national environmental management, and achieving coordination between water resources and socio-economic culture has become a significant challenge and a key direction for future urban development.
The Huizhou region is located in the middle-to-low-height mountain and hilly areas of Southern China. This region is influenced by tectonic structures and crustal movements; the mountainous terrain in the western part of the region is more developed, with concentrated mountain ranges and higher elevations, while the eastern part is relatively flat, consisting mostly of low hills or plains. Due to the west-high and east-low topography of Huizhou, the water flow in this region generally follows a northwest–southeast direction, resulting in unique geographical resources and climatic conditions. In their quantitative study, Huaiyin Jiang’s team calculated the water resource carrying capacity in certain parts of Anhui Province using the entropy weight method and the CRITIC model and applied spatial kernel density estimation and Dagum analysis to interpret the results [28]. They found that there were large differences in the carrying capacity of water resources in the study area, and the Gini coefficient indicated an initial increase followed by a decrease. Ruan Jun’s team used the Normal Cloud Model to conduct a dynamic assessment of water resource sustainability across various cities in Anhui Province [29]. A comparison of indicators at the guideline level identifies key constraints to overall regional development. Chengguo Wu’s team employed the Probabilistic Coupled Risk Matrix (PCRM) model to analyze water resource carrying capacity levels in the Huizhou region, effectively exploring the average characteristic coefficients of the study area [30]. This indicates that research beginning with water resources can inform other fields on a large scale. These studies show that the water resource ecology in Huizhou exhibits regional uncertainties, and dynamic modeling in regional studies can improve the accuracy of indicator evaluation results, which is crucial for the rational development and utilization of water resources in the future.
In summary, as a typical research-oriented region for water ecological resources, Huizhou is one of the areas that promotes the rapid development of water environmental resources in China. In line with China’s “Key Basin Water Ecological Environment Protection Planning” policy, this paper selects the Huizhou region of Anhui Province as the research object. During the study, the DPSIR theoretical model was used to evaluate the residents’ perception of the ecological safety of the water environment in Huizhou from the perspective of the driving force–pressure–state–impact–response [31]. The main research implications of this paper are as follows. (1) This study selected a key region of the Yangtze River Basin as the research subject, providing specificity and enabling an in-depth exploration of water resource ecology issues in the area. Additionally, the study utilized various open-source indicators as data sources, which expanded the data coverage and enhanced the comprehensiveness of the research from multiple perspectives. The application of such comprehensive data sources is relatively rare in previous studies, addressing the limitations in data dimensions in regional water resource ecological research. (2) This study applied the entropy-weighted TOPSIS model to analyze water environment ecology samples from 2016 to 2021, specifically examining the spatial distribution of water resource utilization by residents and its spatio-temporal evolution. This combination of quantitative analysis with spatial distribution provides a new perspective for understanding the dynamic processes of water resource utilization. (3) Using ArcGIS map location analysis tools, this study further explored the significant role of the Huizhou region in ecological civilization construction and future water resource development. This holistic analysis, based on spatio-temporal dynamics, offers scientific insights for the sustainable development of regional water resources, filling a gap in existing research regarding the relationship between regional ecological civilization construction and water resource development [32]. Based on these findings, this study proposes reasonable planning recommendations for the ecological security of water resources in the Huizhou region. These recommendations not only address the current spatial distribution patterns but also consider future development needs, providing theoretical support for the region’s ecological civilization construction and water resource management.
2. Study Area and Data Sources
The Huizhou region is located in southern Anhui Province, at the junction of Anhui, Zhejiang and Gan provinces. The geographic coordinates of the area range from 117°10′ E to 118°55′ E and from 29°24′ N to 30°32′ N. The main river flowing through the region is the Xin’an River, part of the Qiantang system. Other rivers include the Qingge River, which originates on the northern slope of Huangshan Mountain and flows into the Yangtze River in the north, and the Jingyan River, which originates on the western part of the southern slope of Huangshan Mountain and flows into Poyang Lake in the south, both belonging to the Yangtze River system [33,34]. The research scope of this study covers the entire city of Huangshan, Anhui Province, and Jixi County, Xuancheng City, Anhui Province, specifically Huangshan District, Yixian County, Qimen County, Xiuning County, Huizhou District, Shexian County, Tunxi District, Jixi County (Figure 1).
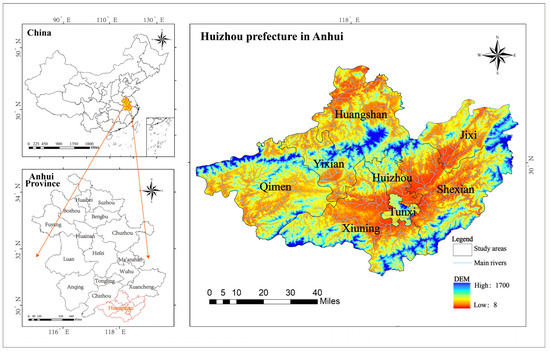
Figure 1.
Topographic map of the study area of Huizhou region.
The data in this study mainly come from various statistical yearbooks, such as Anhui Statistical Yearbook, Huangshan Statistical Yearbook, and Xuancheng City Statistical Yearbook from 2016 to 2021, and the related data come from the official websites of each regional statistical bureau and each annual statistical bulletin. We maximized data uniformity in volume by filtering, sorting, merging, and deleting data. Finally, 24 indicators were obtained for eight prefectural-level cities and counties in Anhui Province from 2016 to 2021.
3. Methodology
3.1. DPSIR Framework
The DPSIR theory was introduced by the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) in 1993 and is based on the characteristics of the PSR model, which helps in understanding system concepts and providing potential solutions to current problems [35,36] The DPSIR theory is a framework for causality correlation indices, aimed at establishing a chain of causality in the form of driver–pressure–state–impact–response. The theory integrates social, economic, environmental, and public health domains to highlight the threats to the ecological security of water environments across various sectors. It also illustrates the positive and negative feedback from the environment to society as a result of human activities and their eventual impacts, using response indicators [37]. Its broad scope makes it the most suitable method for studying the ecology of water environments (Figure 2).
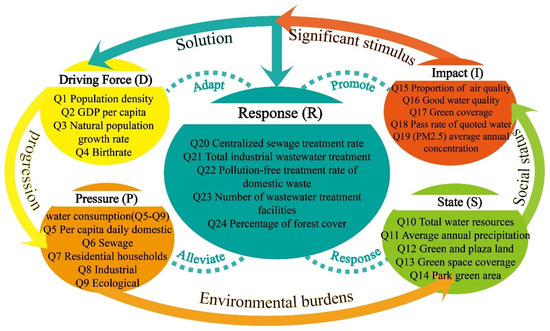
Figure 2.
DPSIR theoretical framework.
3.2. Analysis of Ecological Mechanisms of Water Environment in Huizhou under DPSIR Framework
The DPSIR theory of ecological carrying capacity of the water environment in the Huizhou region systematically presents the region’s optimal development dynamics. Among these, drivers are key factors that either promote or hinder regional socio-economic development, such as population density, gross domestic product per capita, and natural population growth rate [38,39] Pressure refers to the irreversible environmental pressure generated by social production activities or population lifestyle, such as per capita daily domestic water consumption, industrial water consumption, ecological water consumption, and total sewage discharge [40,41]. Status describes the current condition of the society under these pressures, such as total water resources, average annual precipitation, area of green space coverage, and area of green space in parks [42,43]. Impacts are significant factor changes resulting from residents’ lifestyle shifts, including the proportion of days with good air quality, the proportion of surface water sections with good water quality (Class I–III), the greening coverage rate of built-up areas, and the compliance rate of water quality standards for drinking water sources [44,45]. Responses refer to implementation plans designed to address these issues, including the centralized wastewater treatment rate, the total volume of industrial wastewater treated, and the number of wastewater treatment facilities [46,47]. These five factors are closely interconnected and are the primary elements constituting the water environment ecology in the Huizhou region (Table 1).

Table 1.
Ecological evaluation index system of water environment in Huizhou area.
3.3. Entropy Weight TOPSIS Model
The entropy weight TOPSIS model is a commonly used comprehensive evaluation method that effectively avoids the interference of subjective factors present in the traditional TOPSIS method. It makes full use of the original data samples and objectively reflects the development and changes among the influencing factors [48,49,50]. Currently, the entropy weight TOPSIS model is widely applied in assessing water environment carrying capacity [51], land use performance [52], and the level of qualitative economic development [53]. The field is widely used.
3.3.1. Standardized Evaluation Matrix and Indicator Data Matrix
We defined the standardized evaluation matrix and the indicator data matrix for the ecological sample data related to the water environment in the Huizhou region. This process evaluates the positive and negative characteristics of the indicators, reflecting the development level of the water ecological environment across various areas in Huizhou. The calculation formula is as follows:
where represents the standardization evaluation matrix, and signifies the indicator data matrix. The element index is denoted as , indicating a specific element within the matrix. ( = 1, 2, 3, …, ; = 1, 2, 3, …, y). i represents the number of units being evaluated, and denotes the quantity of evaluation indicators. Data are standardized through range normalization, which is expressed as , to address the issue of inconsistent units and dimensions in the original data samples. serves as the standardized index for the evaluation indicators of the assessed objects. is the maximum value of the indicator, and is the minimum value of the indicator.
3.3.2. Information Entropy and Weight Values
The value of information entropy considers all possible outcomes of the random variable, while the weight value reflects the amount of information carried by the indicator data. Addressing the intricacies of entropy requires a thorough examination of its conceptual foundation and historical significance, thereby underscoring its indispensable role across various domains, such as information theory, thermodynamics, computational complexity, and artificial intelligence. Fundamentally, entropy serves as a quantifier of uncertainty or disorder within a system. Its application spans diverse fields, demonstrating the versatility and depth of this concept. The calculation formula is as follows:
where represents the information entropy of each indicator, denotes the weight value, and is the proportion of the th indicator in the th year. . , .
3.3.3. Normalized Standard Matrix
Data are processed row-wise according to the feature matrix. Sample vectors are transformed into unit vectors for calculating similarity, either through dot product operations or by employing other kernel functions. Using boundary value information, the feature values are scaled to the interval , facilitating the construction of a normalized standard matrix. The specific formula is provided below:
where = .
3.3.4. Positive and Negative Ideal Solutions
The selection of positive and negative ideal solutions takes into account the decision objectives and attribute characteristics. The calculation formula is as follows:
and
where represents the positive ideal solution for each indicator, and denotes the negative ideal solution for each indicator.
3.3.5. Euclidean Distance
We determined the Euclidean distance and comprehensive score for the evaluation of the ecological development of the water environment in the Huizhou region in relation to the positive and negative ideal solutions. The specific formulas are as follows:
and
where represents the distance to the optimal (positive ideal) solution, and denotes the distance to the worst (negative ideal) solution.
3.3.6. Proximity Value
We then calculated the proximity of each evaluation object to the optimal solution. The specific formula is as follows:
where is the approximation value, which indicates the closeness of the ecological carrying capacity of the water environment of evaluation object to the ideal solution and takes a value in the range of . When , it indicates that the site has the highest ecological carrying capacity of the water environment; when , it indicates that the site has the lowest ecological carrying capacity of the water environment.
3.4. Division of Thresholds for the Level of Development of the Ecological Carrying Capacity of the Water Environment
In threshold delineation, it is challenging to define the scope of the ecological carrying capacity of the aquatic environment, as numerous scholars have adopted different research methods across various study areas. This study is based on the ‘Technical Guidelines for Water Ecological Carrying Capacity Assessment’ published by the Chinese Society for Environmental Sciences. According to the characteristics of the DPSIR model and combining it with the entropy-weighted TOPSIS model, proximity was divided into five levels to evaluate the ecological carrying capacity of the water environment in the Huizhou region (Table 2).

Table 2.
Criteria for judging the development level of ecological carrying capacity of water environment in Huizhou area.
4. Analysis of the Results
4.1. Characteristics of Spatial Differentiation in the Ecological Development of the Water Environment
Using the DPSIR model to explore the ecological development trends of the water environment in the Huizhou region from 2016 to 2021, the weighting coefficients for the spatial differentiation characteristics of the criterion layer system in the driver–pressure–state–impact–response causality chain, in descending order, are P5 (0.2711), P3 (0.2216), P2 (0.1975), P1 (0.1858), P4 (0.1340) (Table 3). Among them, the weighting coefficients of the response system and state system are above average (), indicating a significant impact on ecological governance and land resources in Huizhou. The pressure system, the driving force system, and the impact system are all below average (), indicating that population and economic development, water resource conditions, and natural ecology in the Huizhou region exert a weaker influence on the strength of implementation.

Table 3.
Weighting coefficients calculated by entropy weighting method TOPSIS.
The ecological mechanisms in the water environment of the Huizhou region generally showed a positive growth trend. The weight coefficients of the response system and state system layer are 0.2711 and 0.2216, respectively, ranking first and second among the subsystem layers. The high coefficient values of the program layer weights corresponding to the response system are mainly attributed to effective measures implemented to solve water ecosystem problems, listed in descending order as Q24, Q23, Q21, Q20, and Q22. The main reason for this is the overall improvement in ecological construction in the core of Huizhou and its district and county cities. This includes the completion and operation of a comprehensive domestic waste treatment plant and the near completion of the sewage and wastewater management and treatment system, reflecting the effectiveness of planning followed by construction and management. The high coefficient values of the programmatic layer weights corresponding to the state system are mainly derived from the current positive trends in social development, ranked in descending order, Q11, Q12, Q10, Q14, and Q13. This can be attributed to the strong implementation of the National Ecological Civilization Construction Demonstration Zone, increased green space coverage, and the effective mitigation of urban and rural land resource depletion. The advantages of ecological civilization are becoming increasingly evident.
The ecological pressure on the water environment in the Huizhou region has basically maintained a smooth dynamic change. The pressure system layer, driver system layer, and impact system layer are slightly below the average regional development level, with weighting coefficients of 0.1975, 0.1858, and 0.1340, respectively. In the pressure system layer, the high coefficient values of its programmatic layer weights are mainly derived from the environmental pressures generated by social production and daily life. In descending order, these are Q9, Q6, Q8, Q5, and Q7. The main reasons for this include the basic resolution of drinking water and water supply issues for impoverished populations, the construction of the province’s first dynamic monitoring and early-warning platform for low-income populations, and overall improvements in the quality of life. In the driver system layer, the high coefficient values of its programmatic layer weights are mainly driven by positive socio-economic development factors. In descending order, these are Q2, Q3, Q1, and Q4. This reflects the region’s unbalanced urban and rural development, weak demographic and employment functions, and insufficient livelihood resources. These factors have led to a decline in the ecological weight of the water environment, further weakening its driving force as a key factor affecting the water ecosystem. Ranked last in the subsystems tier in the impact systems tier. The high coefficient values in its programmatic tier weights are mainly derived from the significant changes. In descending order, they are Q19, Q17, Q15, Q16, and Q18. This is due to the current trend of man-made damage to the water ecological environment of the Yangtze River Economic Zone and the rectification opinions of China’s central and provincial ecological and environmental protection organizations; therefore, it is urgent to continue the battle to protect blue skies, blue water, and clean soil.
4.2. Ecological Carrying Capacity of the Water Environment
4.2.1. Temporal and Spatial Interpretation Features
Overall, the ecological spatio-temporal interpretation characteristics of the water environment in the Huizhou region from 2016 to 2021 show a pull-up enhancement effect. The relative proximity value increased from 0.361 in 2016 to 0.590 in 2021, marking a 63.43% increase over the six-year period (Table 4). The overall relative proximity value can be divided into two stages: Stage 1, from 2016 to 2019, shows minor fluctuations, with the ecological carrying capacity of the water environment remaining at the alert level. Stage 2, from 2019 to 2021, shows a rapid upward trend, as the ecological carrying capacity of the water environment gradually changes from the alert level to good status. The overall trend is one of steady development.

Table 4.
Evaluation of relative proximity by year.
Rain-cloud plots combine a variety of visualization methods, primarily to display data samples, distributions, and key peaks. As such, a rain-cloud map can be used to visualize yearly differences in the ecological carrying capacity indicator coefficients for the water environment across different region of Huizhou, China. As seen in the figure (Figure 3), the 2016–2018 period shows a wide range of dispersion peaks, with significant regional disparities represented by the dot distribution. The 2016–2017 peak was flatter, indicating weaker ecological carrying capacity in those years. In 2018, the peak began to converge toward higher values, though the range of dispersion remained large, suggesting a positive shift in the ecological carrying capacity that year. From 2019 to 2021, the number of peaks surged, the degree of dispersion gradually decreased, and the spatio-temporal characteristics of each region showed a steady upward trend. During the study period, the peaks of low-value areas in the rain-cloud plots gradually disappeared, while the width of high-value areas expanded. This indicates an improvement in the ecological carrying capacity of the water environment across the regions, suggesting both the potential for further growth and favorable development prospects.
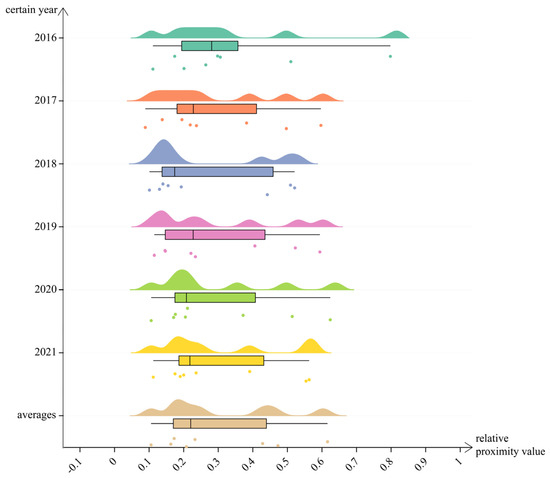
Figure 3.
Rain-cloud map of yearly differences in correlation coefficients for each region of Huizhou.
4.2.2. Trends in the Development of Temporal and Spatial Interpretation
To compare the spatial and temporal evolution characteristics of the water environment’s ecological carrying capacity in Huizhou, we analyze the trends in the differences in development across the region and propose ways to improve the overall development from the perspective of regional coordination (Table 5). According to the evaluation results of the ecological carrying capacity of the water environment in each area of Huizhou from 2016 to 2021, and using a heatmap and the ArcMap software platform (version 10.8), each area of Huizhou is graded according to the development level thresholds. These levels, from low to high, are categorized as low, alert, intermediate, good, and excellent, forming a comparative differentiation map that visualizes the type of area development.

Table 5.
Evaluation of ecological carrying capacity of water environment in Huizhou area.
From a spatial interpretation perspective, over the six years, the relative proximity evaluation index and the coefficient of variation in the spatial analysis of the Huizhou region generally showed a trend of slow fluctuation followed by a rise. To visually display the spatial variability of the water environment’s ecological carrying capacity across the counties in the Huizhou region, a heatmap was used (Figure 4). The heatmap effectively highlights the differences between counties and helps identify trends and areas of high and low distribution. Especially when the normality or distribution type of the data is unclear, the heatmap can more intuitively reveal the patterns of spatial variability. The results show that in 2016, the development levels of ecological carrying capacity, ranked from highest to lowest, were as follows: Shexian County (0.563), Jixi County (0.554), Xiuning District (0.391), Qimen County (0.236), Huangshan District (0.200), Huizhou District (0.190), Tunxi District (0.174), and Yixian County (0.112). In 2021, the ecological carrying capacity development level from high to low was Shexian County (0.798), Xiuning District (0.510), Jixi County (0.306), Qimen County (0.298), Huangshan District (0.264), Huizhou District (0.201), Tunxi District (0.175), Yixian County (0.111). These indicators quantified and ranked the development levels of water environment ecological carrying capacity across the counties in the Huizhou region based on relative proximity values, reflecting the strengths and weaknesses of each county’s ecological carrying capacity. The spatial variability in the ecological carrying capacity of the water environment in the Huizhou region is evident, with Shexian County, Xiuning District, and Jixi County showing higher levels of development. The coefficient of variation indicates that the dispersion of the relative proximity evaluation index has decreased year by year, suggesting that the spatial gap in the ecological carrying capacity of the water environment in the Huizhou region is gradually narrowing.
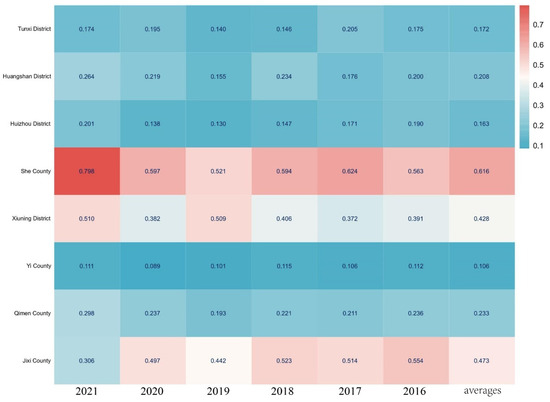
Figure 4.
Heatmap of ecological carrying capacity of water environment in Huizhou area.
From 2016 to 2021, the ecological carrying capacity of the water environment in Huizhou basically exhibited a development trend of “high in the southeast and low in the northwest” (Figure 5). Quantitative calculations of the ecological carrying capacity ranked Shexian County first, with an average value of 0.616, reaching an excellent level of ecological carrying capacity. Jixi County and Xiuning District ranked second and third, with averages of 0.473 and 0.428, respectively, both achieving intermediate standards in water environment ecological carrying capacity. The ecological carrying level of the water environment in Qimen County, Huangshan District, Tunxi District, Huizhou District, and Yixian County in the Huizhou region was low grade. The quantitative calculation results show that the ecological carrying capacity of the water environment in areas along the Xin’an River (Huangshan section) was at an intermediate level or above. This is due to the fact that the watershed area has utilized ecological protection compensation as a tool to promote upstream and downstream coordinated management, with a well-established ecological compensation mechanism and effective water environment management monitoring. In contrast, areas with low ecological carrying capacity have not yet implemented the cross-provincial horizontal ecological protection compensation mechanism, which is why their water environment ecological carrying capacity remains low.
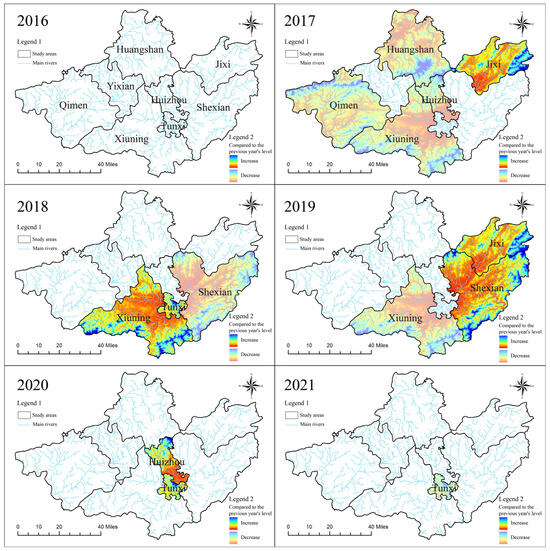
Figure 5.
Difference in ecological carrying capacity of different regions of Huizhou in different years.
5. Discussion
The DPSIR framework and TOPSIS model have proven effective in evaluating water environment ecological carrying capacity and in making scientifically sound management decisions across different geographical and ecological contexts. In Europe, the EU Water Framework Directive (WFD) uses the DPSIR model to assess the ecological status of rivers, lakes, and seas, promoting water quality improvement and sustainable use [54,55]. In this context, the TOPSIS model is employed to help weigh the effectiveness of different management options, thereby optimizing decision making. In Mediterranean coastal countries such as Italy and Spain, the DPSIR framework is used to conduct comprehensive assessments of the coastal water environment, identifying key environmental pressures such as pollution and overdevelopment [56,57,58]. The TOPSIS model is then applied to quantify the priority of different management strategies to protect sensitive ecological areas and maintain marine ecosystem health [59]. In South Asian countries like India and Bangladesh, the DPSIR model has been used to evaluate the health of wetland ecosystems, especially in the face of pressures from agricultural expansion and urbanization [60,61]. By integrating the TOPSIS model, researchers can effectively prioritize conservation efforts in different regions and propose targeted ecological restoration strategies [62]. In Malawi’s Lake Malombe area, the DPSIR model is used to analyze pressures on the lake’s ecosystem, such as overfishing, pollution, and climate change [63]. The application of the TOPSIS model enables researchers to identify the most effective strategies from a range of governance measures, improving water quality and protecting the lake’s ecological environment. These examples further illustrate the universality and effectiveness of the research methods.
In this study, the DPSIR (driving force–pressure–state–impact–response) framework was used to construct an ecological evaluation index system for the water environment in the Huizhou region. By incorporating social, economic, and ecological perspectives, the coherence factors within the DPSIR theory were introduced into the measurement of Huizhou’s water environment ecological carrying capacity. The entropy-weighted TOPSIS model was employed to coordinate the data samples, thereby revealing the impact of the “Driving Force-Pressure-State-Impact-Response” chain on the water environment ecology in Huizhou. Simultaneously, using the ArcMap software platform (version 10.8), the spatio-temporal deductive characteristics and development trends of water environment ecological carrying capacity were analyzed, overcoming the limitations of single data presentation formats and enhancing the diversity of comparative analyses of carrying capacity across different regions in Huizhou.
The results indicate that the evaluation of water environment ecological carrying capacity directly impacts the socio-economic quality and natural ecological space of the region. Although Huizhou leads the nation in ecological indicators, there is a significant asymmetry between this achievement and the environmental pressures from regional production and living activities, the degree of balance in urbanization and development, and the region’s capacity to sustainably supply resources. Therefore, Huizhou should address local ecological issues by adhering to principles of legality, scientific rigor, and precision to improve the environmental quality of residents’ production and living conditions, moving toward a more balanced and coordinated development. While the use of the DPSIR theory and entropy-weighted TOPSIS model effectively reveals the macro-level characteristics of water environment ecological carrying capacity, future research should include more micro-level field surveys and social interviews to obtain more accurate data and compensate for the lack of subjective initiative from residents in the data samples.
6. Conclusions
This study focuses on the Huizhou region and examines the ecological development trends of the water environment from 2016 to 2021, using the DPSIR (driving force–pressure–state–impact–response) framework at the criterion level. The spatio-temporal deductive characteristics and development trends were used as the focal points for analyzing the ecological carrying capacity of the water environment. The main conclusions are as follows:
First, in the DPSIR theoretical model, the weight coefficients of spatially differentiated features at the criterion level exhibit significant stratification. The weight coefficients, ranked in descending order, are as follows: response (P5), state (P3), pressure (P2), driver (P1), and impact (P4). Among these, response (P5) and state (P3), which are above the average level, dominate the region’s ecological governance and show an upward trend in positive effects. This indicates that the infrastructure for water environment management in the Huizhou region is relatively complete, including the construction and operation of domestic waste and sewage treatment plants. The continuous promotion of ecological protection and green development projects in the Xin’an River Basin has increasingly highlighted the advantages of ecological greening and efficiency actions in the region. On the other hand, pressure (P2), driver (P1), and impact (P4), which are below the average level, generally maintain stable dynamic changes. This suggests that the natural ecological compensation mechanism in the Huizhou region is not yet mature, with challenges such as unbalanced urban–rural development, insufficient resource supply for livelihoods, and ongoing human-induced damage to the water ecological environment in the Yangtze River Economic Zone. Therefore, it is necessary to continue promoting the sustainable use of the water environment and ecology.
Second, the spatio-temporal deductive characteristics of the water environment in Huizhou from 2016 to 2021 showed an overall pull-up effect. The relative proximity value increased from 0.361 in 2016 to 0.590 in 2021, a rise of 63.43% over the six-year period. The ecological carrying capacity rating of water resources improved from an alert status to a good status, maintaining a steady development form overall. The overall relative proximity value can be divided into two stages: The first stage (2016–2019) showed minor fluctuations, with the ecological carrying capacity of the water environment remaining at the alert level. The second stage (2019–2021) exhibited a rapid upward trend, with the ecological carrying capacity of the water environment gradually improving from an alert level to a good status, maintaining a steady development form overall. This is because, in order to implement the general tone of “water conservancy projects to make up for shortcomings and strengthen supervision”, the Ministry of Water Resources formulated the “Key Points of Water Resources Management Work in 2019”, which strengthened the regulatory basis of the water environment, clarified the water flow control mechanism, and highlighted water ecology management programs. Therefore, 2019 marked a turning point in the spatio-temporal interpretation of the water environment in the Huizhou region, and it was also a period of rapid increase in ecological carrying capacity.
Third, the spatio-temporal development of the water environment ecology in the Huizhou region showed a slow fluctuating downward trend followed by an upward trend from 2016 to 2021. The region exhibits regional differences in ecological carrying capacity, characterized by higher levels in the south-east and lower levels in the north-west. Quantitative calculations of water environment ecological carrying capacity ranked the top three areas as Shexian County, Jixi County, and Qimen County, with Shexian County having an average proximity value of 0.616, reaching an excellent level of ecological carrying capacity. Jixi County and Huoning District followed, with average proximity values of 0.473 and 0.428, respectively, meeting the intermediate standard of ecological carrying capacity. In contrast, the ecological carrying capacity of Qimen County, Huangshan District, Tunxi District, Huizhou District, and Yixian County in the Huizhou region was classified as low. The construction of the Xin’an River ecological corridor has elevated the ecological carrying capacity of water environments in flow-through areas to intermediate or higher levels while actively promoting the implementation of a diversified ecological compensation mechanism. However, the low-grade ecological carrying capacity in some areas indicates that the cross-provincial horizontal ecological protection compensation mechanism is still underdeveloped. Therefore, it is necessary to intensify pollution control efforts, implement a diversified ecological compensation mechanism, and continuously promote the river and lake chief system, the forest chief system, and the system of special supervisors for ecological environmental protection.
In the future, changes in water environment ecological carrying capacity and their driving factors can be explored through different spatial scales (such as watershed, regional, and national levels). Analyzing at larger spatial scales can reveal patterns and trends that cannot be detected in small-scale studies. This approach will help better explain the similarities and differences in the water environment ecological carrying capacity at different spatial scales, providing a basis for the formulation of cross-regional or cross-national ecological protection policies. By integrating the research results of domestic and international scholars, multiple datasets can be combined to improve the accuracy and predictive power of models [64,65]. For example, remote sensing data, climate data, and land use data can be integrated with existing ecological carrying capacity models for more comprehensive analysis. By referencing and drawing on the results of other studies, existing models can be validated and improved, further enhancing the reliability and scientific rigor of the research results. Utilizing global case studies, such as those from Europe, North America, and the Asia-Pacific region, where similar studies on water resource management and ecological protection have been conducted [66,67], can allow for comparisons and validations of Huizhou’s research findings on a global scale, thereby increasing the universality and applicability of the research.
By taking these specific measures, future research can not only validate and expand existing findings over a broader spatial range but also connect the research results from the Huizhou region with those from other regions globally, providing more broadly applicable ecological protection strategies and recommendations.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.G. and W.D.; methodology, X.L. and W.D.; software, X.L.; validation, J.H. and Y.G.; formal analysis, Y.G.; investigation, J.H. and Y.G.; resources, Y.G.; data curation, L.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.G. and L.Z.; writing—review X.L. and W.D.; visualization, Y.G.; supervision, Y.G.; project administration, Y.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation project “Research on the Construction of Rural Human Settlements in Huizhou Area from the perspective of Ecological Civilization” (2023M730017); Huizhou Ancient Village Digital Protection and Inheritance of Creativity, Anhui Province Key Laboratory “Huizhou Ancient Village Digital creative Product Design under the Background of Cultural and Tourism Integration” (PA2023GDSK0118).
Data Availability Statement
The experimental data used to support the findings of this study are included in the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Tian, P.; Wu, H.; Yang, T.; Jiang, F.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, Z.; Yue, Q.; Liu, M.; Xu, X. Evaluation of urban water ecological civilization: A case study of three urban agglomerations in the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 123, 107351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, W.; Li, Q.; Wang, J. Ecological security pattern construction in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region based on hotspots of multiple ecosystem services. Sustainability 2022, 14, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Zhang, X.; Ma, C.; Zhang, H.; Han, R.; Lu, X. Ecological security assessment based on remote sensing and landscape ecology model. J. Sens. 2021, 2021, 6684435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Chen, Y.; Lu, H.; Qiao, Y.; Peng, H.; He, P.; Zhao, Y. Cloud model driven assessment of interregional water ecological carrying capacity and analysis of its spatial-temporal collaborative relation. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 384, 135562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, M.; Zuo, Q.; Wu, Q.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, J. Water ecological security assessment and spatial autocorrelation analysis of prefectural regions involved in the Yellow River Basin. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Pang, Y.; Mu, R. Water environmental capacity calculation based on control of contamination zone for water environment functional zones in Jiangsu section of Yangtze River, China. Water 2021, 13, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Lv, T.; Xu, J.; Deng, X.; Liu, F.; Lam, J.S.L.; Zhang, Z.; Han, X. Evaluation of urban public transport sustainability in China based on the Driving Force-Pressure-State-Impact-Response (DPSIR) framework—A case study of 36 major cities. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2023, 103, 107263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Hu, W.-Q. A research on coordination between economy, society and environment in China: A case study of Jiangsu. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 120641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Niu, G.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Yao, H. Town-level aquatic environmental sensitivity assessment based on an improved ecological footprint model. Water Resour. Manag. 2022, 36, 763–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Zhan, H.; Huang, J. Urban green service equity in Xiamen based on network analysis and concentration degree of resources. Open Geosci. 2022, 14, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, H.; Zhang, C.; Pan, T. Variations in ecosystem service value in response to land use/land cover changes in Central Asia from 1995–2035. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, X. Construction of ecological compensation system for water environment resource in public places using grey correlation. Math. Probl. Eng. 2022, 2022, 3026588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wu, Y.; Gao, B.; Zheng, K.; Wu, Y.; Wang, M. Construction of ecological security pattern of national ecological barriers for ecosystem health maintenance. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Fu, H. Construct the future wetland ecological security pattern with multi-scenario simulation. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 153, 110473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.; Sun, B.; Shi, X.; Zhao, S.; Wang, X. Analysis of the cooperative carrying capacity of Ulan Suhai Lake based on the coupled water resources–water environment–water ecology system. Water 2022, 14, 3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, M.; Alomgir, M.; Rahman, M.A.; Monir, M.U.; Biswas, B.K.; Khan, A.S. Appraisal of groundwater quality and human health risk for water security and health safety assurance in southwest coastal zone of Bangladesh. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2023, 21, 100919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Cui, X.; Li, G.; Bao, C.; Wang, Z.; Ma, H.; Sun, S.; Liu, H.; Luo, K.; Ren, Y. Modeling regional sustainable development scenarios using the Urbanization and Eco-environment Coupler: Case study of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 689, 820–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, S.; Gao, Z. Integrating the ecological security pattern and the PLUS model to assess the effects of regional ecological restoration: A case study of Hefei City, Anhui province. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Liu, X.; Zhang, D.; Akter, F. Impact of land cover changes on the wetland ecosystem water environment using soft computing methods. Math. Probl. Eng. 2022, 2022, 3673758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Tian, H.; Yang, G.; Liu, B.; Pan, Y.; Ding, G.; Xu, X.; Dan, Y.; Cui, M.; Gao, Y. Dynamic variation of groundwater level and its influencing factors in typical oasis irrigated areas in Northwest China. Open Geosci. 2023, 15, 20220493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; He, X.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Gu, X.; Yang, G.; Li, W.; Wu, Y.; Qiu, J. Changes in landscape pattern and ecological service value as land use evolves in the Manas River Basin. Open Geosci. 2022, 14, 1092–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zhang, S.; Xu, R.; Gao, Y.; Ding, H.; Sun, P.; Liu, W. The coupling coordination measurement, spatio-temporal differentiation and driving mechanism of urban and rural water poverty in northwest China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, H.; Yang, J.; Wang, P. Study on coupling coordination relationship between urban development intensity and water environment carrying capacity of Chengdu–Chongqing Economic Circle. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Guoping, C.; Jiasheng, W.; Junsan, Z.; Kun, Y. A quantitative analysis method for the degree of coupling coordination between drinking water carrying capacity and population spatial aggregation. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2022, 24, 11392–11423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aalirezaei, A.; Khan, M.S.A.; Kabir, G.; Ali, S.M. Prediction of water security level for achieving sustainable development objectives in Saskatchewan, Canada: Implications for resource conservation in developed economies. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 311, 127521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, W.; Long, J.; Chen, M.; Nie, J.; Liu, P. Regional water resources security assessment and optimization path analysis in karst areas based on emergy ecological footprint. Appl. Water Sci. 2023, 13, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaleh, M.; Chen, T.; Abdul-Rahim, A.S. A revisit to the relationship between geothermal energy growth and underground water quality in EU economies. Environ. Technol. 2022, 45, 1271–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; He, G. Analysis of spatial and temporal evolution of regional water resources carrying capacity and influencing factors—Anhui Province as an example. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, S.O.; Kamel, A.H.; Sayl, K.N.; Alfadhel, M.Y. Water resources management and sustainability over the Western desert of Iraq. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Zhou, L.; Jin, J.; Ning, S.; Zhang, Z.; Bai, L. Regional water resource carrying capacity evaluation based on multi-dimensional precondition cloud and risk matrix coupling model. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 136324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, F.; Cole, J.; Sha, J.; Jiao, Y.; Zhou, J. The establishment of an eco-environmental evaluation model for southwest China and eastern South Africa based on the DPSIR framework. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 145, 109687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Chen, L.; Tan, S. Evolution of water environment construction and urban landscape ecological risk based on land cover change analysis. Water Sci. Technol. J. Int. Assoc. Water Pollut. Res. 2022, 85, 2097–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Wang, L.; Huang, C.; Fang, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, L. Spatio-temporal variations of ecosystem services in the urban agglomerations in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 115, 106394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Yang, H.; Ma, Y.; Hong, F.; Wang, H. Comprehensive evaluation of the hydrological health evolution and its driving forces in the river-lake system. Ecol. Inform. 2023, 75, 102117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmir, M.; Javadi, S.; Moridi, A.; Neshat, A.; Razdar, B. A new combined framework for sustainable development using the DPSIR approach and numerical modeling. Geosci. Front. 2021, 12, 101169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexakis, D.E. Linking DPSIR model and water quality indices to achieve Sustainable Development Goals in groundwater resources. Hydrology 2021, 8, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolaki, S.; Koundouri, P.; Pittis, N. Using a systemic approach to address the requirement for Integrated Water Resource Management within the Water Framework Directive. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 679, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Tian, Y.; Huang, K.; Yi, T. Spatial-temporal differentiation of the coupling coordinated development of regional energy-economy-ecology system: A case study of the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 124, 107394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.; Shao, Z.; Fang, S.; Huang, X.; Huq, M.E.; Tang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhuang, Q. Finer-scale spatiotemporal coupling coordination model between socioeconomic activity and eco-environment: A case study of Beijing, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 131, 108165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, K.; He, W.; Qiu, L. Symbiosis coordination between industrial development and ecological environment for sustainable development: Theory and evidence. Sustain. Dev. 2023, 31, 3052–3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhan, J.; Lv, T.; Wang, S.; Pan, F. Comprehensive evaluation model of the urban low-carbon passenger transportation structure based on DPSIR. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Wang, J.; Qin, T.; Liu, S.; Zhang, X.; Yan, S.; Li, C.; Feng, J. Attribution identification of terrestrial ecosystem evolution in the Yellow River Basin. Open Geosci. 2022, 14, 615–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, X.; Wang, X.; Guo, H.; Yang, C.; Zhou, Q.; Mougharbel, A. Urban ecological security evaluation and spatial correlation research-based on data analysis of 16 cities in Hubei Province of China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 311, 127613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, H.; Zhao, K.; Li, Z. Evaluation of provincial carbon-neutral capacities in the Yellow River basin using DPSIR. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Li, B.; Nan, B. An analysis framework for the ecological security of urban agglomeration: A case study of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 315, 128111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labianca, C.; De Gisi, S.; Todaro, F.; Wang, L.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Notarnicola, M. A holistic DPSIR-based approach to the remediation of heavily contaminated coastal areas. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 284, 117129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labianca, C.; De Gisi, S.; Todaro, F.; Notarnicola, M. DPSIR model applied to the remediation of contaminated sites. A case study: Mar Piccolo of Taranto. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wei, X.; Guo, Q. A three-dimensional evaluation model for regional carrying capacity of ecological environment to social economic development: Model development and a case study in China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 89, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrianto, L.; Kurniawan, F.; Romadhon, A.; Bengen, D.G.; Sjafrie, N.D.M.; Damar, A.; Kleinertz, S. Assessing social-ecological system carrying capacity for urban small island tourism: The case of Tidung Islands, Jakarta Capital Province, Indonesia. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2021, 212, 105844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Deng, H.; Peng, T.; Pan, Z. Measurement and analysis of water ecological carrying capacity in the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 95507–95524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Kong, X. Evaluation of carrying capacity on resource and environment based on improved TOPSIS method. IOP Conf. Series. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 811, 012004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.S.U.; Rai, A.K. Suitability of the Lower Ganga basin groundwater for irrigation, using hydrogeochemical parameters and land-use dynamics. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 116831–116847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, Z. High-quality development evaluation and spatial evolution analysis of urban agglomerations in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wit, R.; Leruste, A.; Le Fur, I.; Sy, M.M.; Bec, B.; Ouisse, V.; Derolez, V.; Rey-Valette, H. A multidisciplinary approach for restoration ecology of shallow coastal lagoons, a case study in south France. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 8, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hüesker, F.; Moss, T. The politics of multi-scalar action in river basin management: Implementing the EU Water Framework Directive (WFD). Land Use Policy 2015, 42, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, C.-H. Evaluation and drive mechanism of tourism ecological security based on the DPSIR-DEA model. Tour. Manag. 2019, 75, 609–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federigi, I.; Balestri, E.; Castelli, A.; De Battisti, D.; Maltagliati, F.; Menicagli, V.; Verani, M.; Lardicci, C.; Carducci, A. Beach pollution from marine litter: Analysis with the DPSIR framework (driver, pressure, state, impact, response) in Tuscany, Italy. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 143, 109395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Expósito, A.; Berbel, J. Sustainability implications of deficit irrigation in a mature water economy: A case study in Southern Spain. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfandiary Abdolmaleki, D.; Faraji Abdolmaleki, S.; Bello Bugallo, P.M. Evaluating renewable energy and ranking 17 autonomous communities in Spain: A TOPSIS method. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazarika, N.; Nitivattananon, V. Strategic assessment of groundwater resource exploitation using DPSIR framework in Guwahati city, India. Habitat. Int. 2016, 51, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, K.; Gain, A.K.; Mallick, B.; Vogt, J. Social, hydro-ecological and climatic change in the southwest coastal region of Bangladesh. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2017, 17, 1895–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rane, N.L.; Achari, A.; Choudhary, S.P.; Mallick, S.K.; Pande, C.B.; Srivastava, A.; Moharir, K.N. A decision framework for potential dam site selection using GIS, MIF and TOPSIS in Ulhas river basin, India. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 423, 138890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosamu, I.B.M.; Makwinja, R.; Kaonga, C.C.; Mengistou, S.; Kaunda, E.; Alamirew, T.; Njaya, F. Application of DPSIR and Tobit models in assessing freshwater ecosystems: The case of Lake Malombe, Malawi. Water 2022, 14, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Pang, Y. Research on narrow and generalized water environment carrying capacity, economic benefit of Lake Okeechobee, USA. Ecol. Eng. 2021, 173, 106420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Shi, W.; Fu, Y. Quantitative evaluation and optimized utilization of water resources-water environment carrying capacity based on nature-based solutions. J. Hydrol. 2019, 568, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.-Y.; Zheng, B.; Khu, S.-T. Validation of the hypothesis on carrying capacity limits using the water environment carrying capacity. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 665, 774–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świąder, M.; Lin, D.; Szewrański, S.; Kazak, J.K.; Iha, K.; van Hoof, J.; Belčáková, I.; Altiok, S. The application of ecological footprint and biocapacity for environmental carrying capacity assessment: A new approach for European cities. Environ. Sci. Policy 2020, 105, 56–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).