Abstract
Variations in species distribution, population structure, and behavior can provide a portfolio effect that buffers populations against rapid environmental change. Although diversity has been identified as a goal for effective resource management and genetic and demographic tools have been developed, life history remains challenging to quantify. In this study, we demonstrate a novel metric of life history diversity using telemetry data from migratory fish. Here, we examined diversity in the outmigration behavior of juvenile Chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha) released in the Sacramento River, California, between 2007 and 2017. In this synthesis, we examined a wide variety of landscape and demographic drivers at high resolution by incorporating many individual telemetry studies, with variability in release location by year, environmental conditions, and all runs of salmon that are present in the watershed. When years were grouped by shared hydrologic conditions, variation in travel time was significantly higher in wet years. Further, our model showed a negative effect of warm temperatures at low flows on the variation in migration movements. This suggests that enhanced hydrologic connectivity increases the variation in migration time, a representation of habitat complexity and biocomplexity, despite the degraded state of this watershed and the weakened state of these populations. Variation in migration behavior could buffer species from current and future environmental changes, such as climate effects on precipitation and temperature. Hence, behavioral metrics generated from telemetry studies can be used to understand life history diversity and the potential effects of environmental fluctuations.
1. Introduction
Migration is a recurring behavior within the animal kingdom in which animals benefit through increased growth or reproductive opportunities by coordinating their movements between spatially segregated resources. Many resources are not static, and therefore, the timing of migration is an important component of resource acquisition. The match-mismatch hypothesis suggests that growth and survival are highest when cooccurring with prey production, and this match or mismatch with peak production may in part explain variability in recruitment [1], although temperature and developmental phase may mediate that response [2]. For example, the size and timing of juvenile anadromous Pacific salmon (Oncorhynchus spp.) seaward migration is critical for survival and has been implicated in stock collapse [3,4].
Anadromous migration is thought to balance mortality risks and growth opportunities across rearing habitats. However, in altered systems, these tradeoffs may be impacted by invasive predators inflating mortality risks and the degradation of the food web by landscape and water quality modification, thereby limiting growth benefits. Similarly, altered landscapes disconnect migratory routes and migratory cues in which mismatches become potentially catastrophic [5,6]. For example, the magnitude of maximum spring freshet in the Columbia River has decreased by more than 40% and shifted two weeks earlier, and 75% of the decrease is linked to flow regulation [7]. Bottom et al. [7] suggests that these changes in the historical template of the Columbia River ecosystem may have created mismatches with established salmon behaviors through the suppression of overbank flows. The reduction of high-flow events limits rearing opportunities and disrupts sediment and woody debris transport, causing a shift in the physical state of the ecosystem.
Effective resource management requires a clear understanding of the environmental processes and habitat features that impact migration. It is possible to characterize the optimal timing for organisms to undergo key migratory events [8], which may be particularly useful when managing a species through artificial propagation. However, another resource management strategy is the maintenance of diversity across a connected migratory landscape. Specifically, variation in migration and rearing behavior could buffer species from disastrous losses, when mismatches occur. While metrics such as growth, condition, health, abundance, and survival are commonly used to measure the responses of organisms to environmental conditions (e.g., [9]), diversity is an equally important attribute for measuring species viability [10,11]. Diversity can therefore enhance the ability of organisms to adapt to changing physical (e.g., high temperatures), chemical (e.g., contaminants), and biological factors (e.g., predation and food resources). Similarly, variation in species distribution, population structure, and behavior can provide a portfolio effect that buffers populations against rapid environmental change [12]. Hence, populations with demographic diversity are less likely to be seriously compromised by local extinction events [11].
Although diversity has been identified as a goal for effective management of fisheries [13], it was historically underappreciated by resource managers. By using oversimplified conceptual models, aspects of diversity that may be important to resilience and conservation were generalized. For example, in Pacific salmon, reliance on hatchery supplementation has been identified as one of the major drivers of changes in salmon diversity and is thought to be a key factor contributing to regional declines in salmon resilience [14,15]. In response to this issue, managing diversity for species of concern is now widely supported in federal and state regulatory conservation plans. For salmonids, one product of this effort has been improved management of hatchery stocks through Hatchery and Genetic Management Plans, a strategy to reduce the genetic and demographic effects of supplementation on wild fish and the overall population. A complementary approach is the development of conservation hatcheries, programs specifically targeted at maintenance of diversity in imperiled populations [16].
Genetic tools have traditionally been used to measure diversity, such as the estimation of effective population size [17], evaluation of population structure [18], use of specific genetic markers to measure adaptive variation [19], and association mapping [20]. More recently, otolith methods have also been used to identify run origin across tributaries [21] and to describe the timing, location, and duration of rearing during seaward migration [22,23,24]. Finally, data from fisheries field surveys have been used to develop demographic metrics of variation. For example, Satterthwaite and Carlson [8] used demographic metrics to show a weakening portfolio effect in the magnitude and timing of salmon runs across multiple rivers in California, likely due to the influence of hatchery practices.
Despite the progress in quantifying different aspects of life history variation, there remains a need for techniques that provide better temporal and spatial information. For highly mobile species such as salmonids, one of the highest-resolution tools is acoustic telemetry, the use of micro-transmitters to track the timing, duration, and location of movements across landscapes [25]. This is an area of substantial innovation, with miniaturization of transmitters [26] and the widespread use of multiple receiver technologies to track the movements of many types of fish and wildlife. To our knowledge, these types of data have not been used to quantify the variation in life history patterns. In altered systems, understanding what environmental processes and habitat features promote diversity is a key information need, and researchers and mangers can use advances in telemetry to inform restoration and conservation activities, such as land use change that poses constraints on migration.
Here, we leveraged 11 years of juvenile Chinook salmon (Oncoryhnchus tschawytscha) acoustic telemetry detections, initially collected for estimating survival, to describe variation in seaward migration behavior. Specifically, we used route selection and the standard deviation of both migration time to the estuary and daily individual movements to describe diversity in the seaward migration of acoustic tagged fish in the San Francisco Estuary, the Sacramento River, and its tributaries. Standard deviation provides a measure of dispersion in migration outcomes and is a common measure of diversity. In altered systems, habitats that respond to natural hydrologic variability and maintain habitat complexity may be particularly important for maintaining diversity within a population. Therefore, we hypothesized that variation in migration time to the estuary would increase with increased access across the landscape. Access was described by water year (year according to an October 1-to-September 30 calendar, which parallels the accumulation of precipitation in California), release group and route, representing the influences of hydrology, study design and behavior, respectively.
With the standard deviation in daily individual movements, we had the opportunity to investigate finer-resolution patterns in individual trends in seaward migration. Here, we hypothesized that there may be complex relationships between the influences of season (water temperature), climate, hydrology (river outflow, tidal extent, and floodplain inundation), and behavior (route) on the variation in the seaward migration of acoustic tagged fish. We also considered that variation in trends in downstream migration could be impacted by the experimental design of individual studies. Therefore, the same variables shown to influence variation in straying rate from Sturrock et al. [27], we also summarized here: run, origin, transport distance, size (fork length in millimeters and weight in grams, as a proxy for age), and release (date, temperature, and location).
This is a logical next step for the application of acoustic telemetry data as a tool for both basic ecology and resource management. In our case, one goal was to improve our understanding of how juvenile salmon use routing to navigate the risks and rewards of freshwater residency. In addition, this approach can help resource managers identify factors (e.g., environmental variables, geographic areas, and habitats) that enhance or inhibit behavioral variation, an important component of overall life history diversity.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study System
In California’s Central Valley (CCV), adult salmon spawn in the upper reaches of the Sacramento and San Joaquin Rivers (and their tributaries). These two rivers join to form a freshwater delta (the Delta) and exit toward the ocean through a series of large bays (Suisun Bay, San Pablo Bay, and San Francisco Bay). CCV Chinook salmon are commonly described as four runs, which signify the season in which adults return to the freshwater system from which they emerge to spawn: winter, spring, fall, and late fall [28]. Historically, the range of salmon encompassed a drainage area roughly two-thirds the state of California [29]. Currently, impassable dams block 72% of upstream historical salmon spawning habitat [30]. The Central Valley is at the southern end of the Chinook salmon species’ native range, and the species has experienced major long-term declines, with both the winter and spring runs listed under the Endangered Species Act (ESA) as the endangered and the threatened, respectively. Declines in salmon fisheries have given rise to artificial spawning and rearing of juveniles in hatcheries, first established in California in 1872, to improve growth and survival in the first year of life [30]. Millions of hatchery-reared CCV Chinook salmon have been released each year since the mid-1940s [31]. Concerns with in-stream survival have also led to extensive monitoring studies, consisting of an acoustic telemetry receiver array, which is broadly used to track reach-specific outmigration survival of wild and hatchery salmon throughout the CCV (primarily O. tshawytscha and O. mykiss). These studies, which began in the mid-2000s, have demonstrated that outmigration survival is generally low and that the interaction between river flow and tides can influence routing and survival [32,33,34]. Here, we leveraged this rich data resource to examine diversity in the outmigration behavior of juvenile Chinook salmon released in the Sacramento River (and its tributaries) between 2007 and 2017. This period encompassed a wide range of environmental conditions, including both an historic drought (2012–2016) and an extreme precipitation season for this region. The average precipitation for 2016/2017 was the highest on record and over 15 centimeters higher than the previous record set in 1982/1983 ([35].
2.2. Data Source and Integration
In the collection of studies assembled here, fish were either reared to a taggable size (between 79 and 218 mm in fork length for this study) at a state or federal hatchery and tagged on site or captured in a rotary screw trap after initiating their downstream migration and tagged in the field. There are slight variations in the tagging procedures among research groups (see Supplementary S1), but coordination efforts exist to standardize methods [36]. Detailed explanations of the tagging procedure can be found in the individual manuscripts (Supplementary S2; Table S1) and generally follow the methods described in Ammann et al. [37]. Several studies required transport from the tagging site to the release site (e.g., from the hatchery to the river), and detailed methods can be found in Singer et al. [38].
Juvenile Chinook salmon detection data were compiled from four sources: (1) real-time/data/accessing_ERDDAP_via_R_autonomous.R (https://github.com/CalFishTrack/real-time). (uploaded 15 January 2020); (2) Johnston et al. [39] (https://github.com/Myfanwy/Johnstonetal2018SFEWS). (uploaded 23 May 2020); (3) Michel et al. [32] (available from National Marine Fisheries Service Southwest Fisheries Science Center Santa Cruz Laboratory on request); (4) Liedtke et al. [40] and Pope et al. [41] (available from the Department of Water Resources on request). Once compiled, all data were screened for false detections and backwards movements using the criteria outlined in Johnston et al., 2018. Individuals were discarded, when detections occurred prior to their recorded release time (n = 3) and when fish were detected above river kilometer 153.14 (Freeport, Figure 1) after being detected at or below tidal river kilometers (n = 8). These backwards movements within the fluvial reaches of the river were assumed to represent predator movements; however, we assumed upstream movements in the tidal reaches were legitimate. Release locations were grouped into three release location groups: the upper Sacramento River, the middle Sacramento River and the Tidal Delta, and Bays, defined by Johnson et al. [42] (Figure 1).
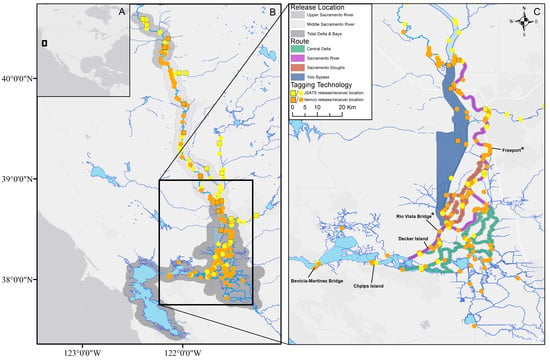
Figure 1.
(A) Map of North America, with the location of California’s Central Valley. (B) Map of fish release and receiver locations for individual studies synthesized here (Supplementary S2, Table S1), colored by technology type, as well as release groups from Johnson et al. [42]. (C) Map of routes and locations used for the routing analysis denoted by color and labels, respectively. Labels for locations of data collection describing environmental conditions are marked by *.
Juvenile Chinook salmon data sources included in this study represented the detection histories of all individual juvenile Chinook salmon acoustic tagged and released into the Sacramento River or its tributaries between 2007 and 2017 (n = 11,185). However, only those individuals detected in the estuary (e.g., Chipps Island or the Benicia–Martinez Bridge) and at least one other location during migration were included in analysis (n = 1806; Supplementary S2; Table S1). Therefore, our study was limited to those fish that successfully exited the Sacramento River watershed. These studies included all four runs of CCV Chinook salmon (fall, late-fall, spring, and winter) and nearly all populations, including hatchery (Livingston Stone National Fish Hatchery, Coleman National Fish Hatchery, Feather River Fish Hatchery, and Nimbus Fish Hatchery) and wild origin (Deer Creek, Mill Creek, and Butte Creek) salmon.
Data describing environmental conditions included water temperature and river stage measured at Rio Vista Bridge on the tidal Sacramento River (https://cdec.water.ca.gov/ [43] (accessed on 27 September 2022) and Sacramento River outflow at Freeport (https://data.cnra.ca.gov/dataset/dayflow) (accessed on 27 September 2022), inundation of the Yolo Bypass [44], Figure 1) and the Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO; [45] Water year (year according to an October 1-to-September 30 calendar, which parallels the accumulation of precipitation in California) and water year type (defined as wet, below normal, dry, and critically dry) were also included in analyses. The water year type was defined by the Sacramento Valley water year hydrologic classification indices, which are based on measured unimpaired runoff (https://cdec.water.ca.gov/reportapp/javareports?name=WSIHIST) (accessed on 15 January 2020).
2.3. Outmigration Routing Assignment
Juvenile Chinook salmon emigrating from the Sacramento River can take a variety of routes through the Delta. To determine which routes were used, receivers were grouped into the following routes: the mainstem Sacramento River, the Yolo Bypass, Sacramento River Sloughs (Sutter, Steamboat, and Miner Sloughs), and the Central Delta (Georgiana Slough, Three Mile Slough, and the Delta Cross Channel; Figure 1C). For non-mainstem routes (the Yolo Bypass, Sacramento River Sloughs, and Central Delta), each receiver was assigned a categorical value by visual inspection: entrance of a route, exit of a route, and location within the alternative route (route site). Fish detected at fewer than two non-mainstem route sites were considered to have traveled through the Sacramento River exclusively. All fish detected at two or more non-mainstem route sites were then sorted by route to determine whether those fish had greater than two detections in each route site within the same complex (the Yolo Bypass, Sacramento River Sloughs, and Central Delta). Those individuals also needed to be detected within a logically paired order of route sites (entrance and within slough, within slough and exit, entrance, and exit) and not detected at any adjacent site within the mainstem Sacramento River, to then be assigned a route other than the Sacramento River.
2.4. Estimating Travel Time to the Estuary
Travel time was estimated by subtracting the date and time of release from the date and time of the individual’s first detection at Chipps Island (in days; Figure 1). Acoustic data were collected using two receiver technologies, Vemco and Juvenile Salmon Acoustic Telemetry System (JSATS; [45], and receiver locations were generally consistent across years but varied by technology (Figure 1). For example, a Chipps Island JSATS receiver array was not installed until 2016 (river kilometer: 71.244). Therefore, for JSATS data prior to 2016, an alternative travel time was calculated by taking the average travel time of individual’s first detection at Decker Island (river kilometer: 86.078) or Antioch Bridge (river kilometer: 86.948) and that same individual’s first detection at Benicia (river kilometer: 52.048).
To examine the variation in juvenile Chinook salmon travel time and our hypothesis that variation would increase with hydrologic connectivity (e.g., access across the landscape), individual travel times were grouped by water year, location of release and number of routes used, representing the influences of hydrology, study design, and behavior, respectively.
2.5. Variation in Downstream Movement
We defined a “movement” as the last chronological detection at one receiver location that is followed by the first detection at the next receiver location. Each movement that each fish made was associated with its calculated distance in meters. This association was performed with a distance matrix constructed from the receiver array. The total distance in meters of a movement was then divided equally by the duration of the movement in hours, creating a proportional time/distance ledger for each movement and fish. We summarized this by day (24 h), yielding the total meters traveled by each fish for each day. All code used to clean and analyze fish detection histories are available at https://github.com/goertler/migration_diversity_metrics.
Here, we investigated the variation in migration across changes in environmental conditions, behavior (e.g., route), demographics, and release strategies by estimating the standard deviation in the individual daily detection time series (spread in individual daily travel distances) and applying a hierarchical generalized additive model (HGAM), following methods in Pedersen et al. [46] and R package mgcv [47]. Behavioral metrics generated from telemetry studies can be used to understand life history diversity and the potential effects of environmental fluctuations. We hypothesized that there may be complex relationships between the influences of season (water temperature), climate, hydrology (river outflow, tidal extent, and floodplain inundation), and behavior (route) on the variation in the seaward migration of acoustic tagged fish. The HGAM model formula included a single common smoother plus group-level smoothers (allowing each group-specific smoother to have its own smoothing parameter; Supplementary S6). This global smoother with individual effects and penalties constrains the information shared between groups to the global smoother and the common error term [46]. Group was described by the three release location groups, the upper Sacramento River, the middle Sacramento River and the Tidal Delta, and Bays.
where fglobal is the global smoother and fgroup-specific is the smoother for a given release location group. This model allows each group-specific smoother to have its own smoothing parameter (e.g., differing slightly in the shape of their responses). This model formula was chosen, because homogeneity of variance was not achieved across release groups due to the imbalance in release sites within the data compiled here (e.g., it was most appropriate to consider release group as a “treatment” due to the nested data).
loge(y) = β0 + β1 + β2 + fglobal(x1, x2) + fgroup-specific(x1, x2) + ϵ
We evaluated the impact of river conditions by testing the influence of both the mean daily and standard deviation in Sacramento River outflow, water temperature, and standard deviation in the tidal extent (i.e., stage). To address composite changes in climate over our time series, monthly mean PDO was also included in our model. PDO describes broad patterns in the Pacific climate and is characterized by distinct patterns in sea surface temperature, sea level pressure, and the direction and intensity of surface wind stress [45]. The total and maximum floodplain inundation days during migration were also included as environmental covariates (i.e., in some years, multiple inundation events occurred; the maximum inundation days represents the longest continuous flood event, while the total summarizes all days of inundation between an individual’s release and first detection in the estuary). Floodplain inundation duration of the Yolo Bypass incorporated the influence of both access to an alternative route (for fish released in the upper and middle Sacramento River), and opportunities for increased productivity and habitat complexity caused by Sacramento River flooding [48,49]. All environmental variables were constrained to the days between the release and the first detection in the estuary for each individual fish.
We considered that variation in migration could be impacted by the same variables shown to influence variation in straying rate from Sturrock et al. [27], and therefore, in addition to run and origin, we also summarized each fish’s transport distance, size (fork length in millimeters and weight in grams, as a proxy for age), and release date. Release strategies, which varied across studies, were also investigated. Release strategy encompassed date, water temperature, and location of release.
3. Results
3.1. Routing
In total, seven routes were observed for JSATS fish (Supplementary S3; Table S2): (1) Sacramento River only (n = 490); (2) the Yolo Bypass (n = 77); (3) Sacramento River Sloughs (n = 138); (4) Central Delta (n = 55); (5) the Yolo Bypass and Sacramento River Sloughs (n = 16); (6) Sacramento River Sloughs and the Central Delta (n = 8); and (7) the Yolo Bypass, Sacramento River Sloughs, and the Central Delta (n = 1). Fish detected by the Vemco receiver array displayed five routing alternatives (Supplementary S3; Table S2): (1) Sacramento River only (n = 559); (2) the Yolo Bypass (n = 205); (3) Sacramento River Sloughs (n = 129); (4) the Central Delta (n = 117); and (5) Sacramento River Sloughs and the Central Delta (n = 11).
Release location impacted routing, as the Yolo Bypass is not available to fish released below the City of Sacramento. Access to the Yolo Bypass is limited by the Fremont Weir, at its northernmost upstream end or in years when flooding occurs (when the Sacramento River height exceeds the height of the Fremont Weir). Seven routes were observed for individuals in the upper Sacramento River release group. Whereas only five routes were assigned to fish released in the middle Sacramento River and the Tidal Delta (e.g., not the most complex routes in which individuals traveled through both the Yolo Bypass and Sacramento River Sloughs).
3.2. Travel Time to the Estuary
A total of 1806 Chinook salmon were detected in the estuary and therefore yielded travel time estimates (n = 785 JSATS and n = 1021 Vemco). The majority (86%) of the travel time estimates were derived from detection data recorded at Chipps Island (JSATS: 567 from Chipps, 31 from Antioch, and 187 from Decker; Vemco: 994 from Chipps, 1 from Antioch, and 26 from Decker). Travel time estimates were not significantly different when comparing the three estuarine locations with a Tukey’s multiple comparison of means (adjusted p-values of 0.92, 0.94, and 0.15 for Chipps−Antioch, Decker−Antioch, and Chipps−Decker, respectively). In the JSATS array, individual juvenile Chinook salmon were detected at 100 receiver locations over the study period, while studies employing Vemco technology included 184 receiver locations (Figure 1).
Juvenile Chinook salmon travel time to the estuary varied from 1.76 to 70.55 days (median travel time = 9.3 days). No outliers were observed; however, as a synthesis of many disparate studies, some aspects of the sampling design were not well balanced. For example, homogeneity of variance exists for tagging technology used and water year type, but 96% of all Chinook salmon in this study were of hatchery origin. Further, a similar number of individuals detected in the estuary were released in the upper (n = 767) and the middle (n = 744) Sacramento River, but less than 20% were released into the Tidal Delta (n = 295).
Travel time varied by water year and, when years were grouped, by shared hydrologic conditions defined by the Sacramento valley water year indices (p-value < 2 × 10−16). Variation in travel time was higher in wet years (Figure 2), and travel times were significantly different across all water year types except dry and critically dry years (Table 1). Wet years may represent conditions which maintain diversity across a connected migratory landscape.
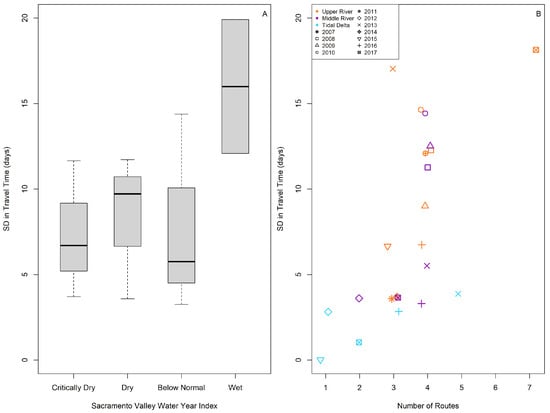
Figure 2.
(A) Box plot of the standard deviation in travel time (days) to the estuary, grouped by the water year type in which juvenile Chinook salmon were released (Sacramento Valley water year index); and (B) the standard deviation in travel time (days) grouped by release year and location (the upper Sacramento River, the middle Sacramento River, and the Tidal Delta, from Johnson et al. [42] plotted against the number of routes used. The box plot displays the distribution of the data based on a five-number summary: the minimum (the lowest horizontal line), the first quartile (the bottom of gray box), the median (the thick line), the third quartile (the top of gray box), and the maximum (the highest horizontal line).

Table 1.
Results from the Tukey’s honestly significant difference test of travel time by water year type. The adjusted p-value was adjusted for multiple comparisons.
3.3. Variation in Downstream Movement
Individual daily detection time series were produced for all fish detected in the estuary (n = 1806), and the standard deviation across those individual movements (spread in individual daily travel distances) was used to describe their variation. Here, we had the opportunity to investigate finer-resolution patterns in individual trends in seaward migration and hypothesized that there may be complex relationships between the influences of season (water temperature), climate, hydrology (river outflow, tidal extent, and floodplain inundation), and behavior (route). We also considered that variation in trends in downstream migration could be impacted by the experimental design of individual studies. Data diagnostics were assessed following the methods in Zuur et al. [50]. No outliers were determined, but collinearity did exist among some covariates (e.g., variation inflation factor greater than three) and was accounted for (Supplementary S4; Table S3). For example, transport distance could not be investigated due to the imbalance in the data compiled (all individuals released in the upper watershed had a transport distance of 0, while fish released in the middle Sacramento River ranged from 0 to 253 km and the lower watershed ranged from 3 to 345 km). Further, run and origin inferred similar information and were not included in the same models. Models were ranked using AIC and deviance explained.
To explore our hypothesis that there may be complex relationships between the influences of season (water temperature), climate (PDO), hydrology (river outflow, tidal extent, and floodplain inundation), and behavior (route) on the variability in the seaward migration of acoustic tagged fish, we used an HGAM model formula with a single common smoother plus group-level smoothers. The best model included Sacramento River outflow and water temperature (deviance explained = 70.3%; Figure 3; see Supplementary 2; Table S1 for top 10 model comparisons).
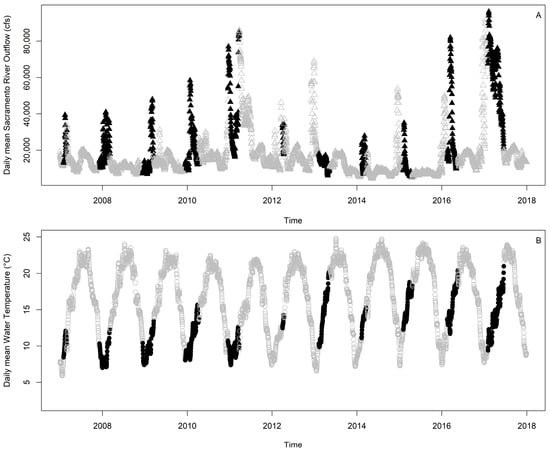
Figure 3.
(A) Mean daily Sacramento River outflow (cfs) and (B) water temperature between 2007 and 2017. Black symbols represent the conditions, when tagged fish were present.
Sacramento River outflow and water temperature had a variable effect on the variation in individual daily travel distances (Figure 4). The observed water temperature ranged from 7.5 °C to 19.9 °C (Figure 3). The general smoother showed a negative effect of warm temperatures (~16–19 °C) at low flows on the variation in movements. Contrastingly, moderate temperatures (~12–16 °C) at high flows showed a high positive effect on the standard deviation in downstream migration. The release group-level smoothers showed variable and nonparametric effects (Supplementary S7; Figure S1). For individuals released in the tidal Delta, there was a positive relationship with the standard deviation in downstream migration at moderate temperatures (~12–16 °C) and low flow. Whereas those fish originating from the middle Sacramento River showed a positive effect on the standard deviation in migration at warmer temperatures (~16–19 °C) and high flow. While the upper Sacramento River release group exhibited a complex relationship between flow and temperature on the standard deviation in downstream migration. Several intersections between flow and temperature produced a large effect on the standard deviation in downstream migration: low temperatures (~less than 9 °C) at a wide range of flows (~less than 70,000 cfs), moderate temperature with high flow, and high temperature with low flow.
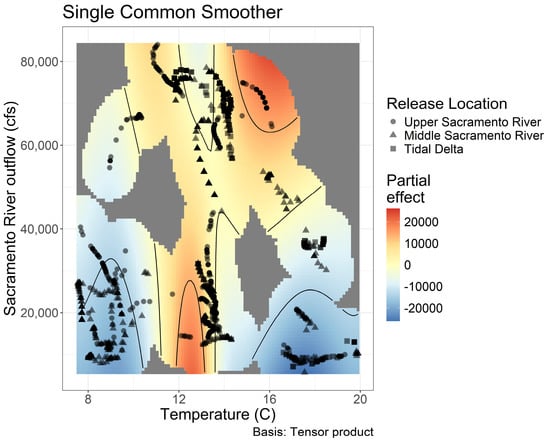
Figure 4.
Data and partial residuals from the best hierarchical generalized additive model, which included release group (symbol), the mean in daily water temperature, and the mean in daily outflow of the Sacramento River between the release and the first detection in the estuary for each individual fish. The global smoother is shown here, while plots for each group-level smoother are in Supplemental Materials (Supplementary S7; Figure S1). This plot shows the relationship between water temperature and the standard deviation in individual daily detection time series (spread in individual daily travel distances) while adjusting for the influence of outflow. Solid grey represents no data.
4. Discussion
Life history variability is increasingly understood to be a key attribute to support healthy populations for many species. Variations in species distribution, population structure, and behavior can provide a portfolio effect that buffers populations against rapid environmental change [12]. This recognition has led to the development of various tools to understand diversity in fish populations including genetics (e.g., [17,18,19]), otolith analysis (e.g., [21,23,24]), and metrics of demographic data (e.g., [15]). Here, we used telemetry data to describe a novel life history metric, variability in migration time. In presenting this new approach, we included examples of how telemetry data can be used to provide insights into variability in migration behavior and its potential ecological consequences. Here, we showed that river outflow and temperature, both sources of hydrologic connectivity and habitat complexity, diversify the routing, travel time, and movement of juvenile Chinook salmon. In this synthesis, we examined a wide variety of landscape and demographic drivers at high resolution by incorporating many individual acoustic telemetry studies over 11 years, with highly variable environmental conditions and all runs of salmon that are present in the Sacramento River watershed.
In our study, we explored the landscape drivers of several metrics for diversity in migration time. We found that when years were grouped by shared hydrologic conditions, variation in travel time was significantly higher in wet years (Figure 2). Further, routing diversity increased in wetter years; seven, five, and four routes were used in wet, below normal/dry, and critically dry years, respectively (Supplementary S3; Table S2). This suggests that increased routing opportunities, with enhanced hydrologic connectivity, increases the variation in migration time. Chinook salmon are impacted by anthropogenic alterations to the landscape, particularly the timing and distribution of river flow below dams [51]. The operation of hydropower dams delays migration and disrupts migration routes of juvenile anadromous salmon to the ocean with consequences for survival to adulthood [52].
Migration timing has implications for resource acquisition, life-history transitions, growth, and survival for many species. Human modifications and resource use have impacted the timing and outcomes of migration in terrestrial and aquatic communities. For example, in some bird species, climate impacts on migration have shifted the departure date, progression and stopover frequency and duration with phenological consequences, such as size of returning population, body condition and molting [53]. A match or mismatch with peak production may in part explain the impact of disruptions in the timing of migration when resources are spatially and temporally variable across the migratory landscape. Understanding the consequences of human-modified landscapes and how variation in migration timing may ensure long-term stability is critical for species persistence and resource management.
Increased routing opportunities during seaward migration may be one representation of habitat complexity and biocomplexity for juvenile Chinook salmon. Further, variation in seaward migration time may be one measurable characteristic that balances growth opportunities and mortality risk for juvenile salmon [54]. For example, Scheuerell et al. [55] provided support for the importance of migration timing on survival to adulthood, but also peak survival timing varied from year to year, so the maintenance of diversity in timing may play a key role in survival dynamics. Similarly, Achord et al. [56] showed diversity of migration times results in different salmon populations encountering different prey abundances in the estuary. These results illuminate the importance of maintaining a diversity of migratory routes.
Asynchrony in these populations is likely gained by a combination of run diversity and habitat complexity, which is most evident in the upper Sacramento River release in the wettest year in our dataset (e.g., 2017). However, it is challenging to separate the influence of hydrology on habitat complexity (e.g., extensive access to the Yolo Bypass) and juvenile salmon behavior (e.g., increased foraging opportunities and pulse flows that have been shown to initiate seaward migration). The three years with the highest standard deviation in travel time were 2017 (19.9 days), 2010 (14.4 days), and 2011 (12.1 days), which were classified as wet, below normal, and wet, respectively, according to the hydrologic classification index. In all three years, the Yolo Bypass was inundated for 20 consecutive days or more, representing enhance habitat complexity and alternative routing opportunities in wet years. Further, each run was released at different times and may experience different environmental conditions (e.g., the fall run experienced warmer river temperatures than the winter run). This was further exemplified by the influence of water temperature and river flow on the global HGAM smoother (Figure 4; when flows were above ~60,000 cfs and temperatures were between 14 and 17 °C). Variation in estuary arrival date was investigated (Supplementary S5; Table S4) and showed a similar pattern to the variation in travel time (Supplementary S8; Figure S2; e.g., higher standard deviation in wet years and with four or more routes) but was influenced by release date (r = 0.917; Supplementary S4; Table S3).
Salmon populations in the CCV experienced drastic changes in year-to-year precipitation and stream flow (Figure 3). This variation in hydrology impacted migration cues and routing alternatives. For example, seaward migration through the Yolo Bypass is only accessible, when the Sacramento River height exceeds the height of the Fremont Weir (during flooding events) or to those individuals spawned in westside tributaries of the middle Sacramento River. In developed watersheds, floodplain−tidal slough complexes, like the Yolo Bypass, represent remnant habitats in which established salmon behaviors can respond to landscape drivers, such as overbank flows which enhance food web resources (e.g., avoid mismatches with productivity in the estuary and the ocean). However, inundation duration was not included in the top model examining the drivers of standard deviation in individual daily movements (Figure 4; Supplementary S5; Table S4). The maximum and the sum of inundation (in days) were somewhat correlated with Sacramento River outflow (0.536 and 0.523, respectively; Supplementary S4; Table S3), which did influence the variation in trends in downstream migration. Further, the complexity of the route was not indicative of greater travel time. The greatest average travel time was exhibited by the winter run individuals released in 2017 from the upper Sacramento River who traveled through the Yolo Bypass (mean of 51.2 days). The Yolo Bypass is a unique feature in the Central Valley seaward migration landscape for juvenile Chinook salmon. Studies have shown that a flooded Yolo Bypass represents both an alternate route to the estuary and offers substantial growth benefits for juvenile salmon and other native species [49,57].
In addition to Sacramento River outflow, mean water temperature was also included in the best model and had a variable effect on model predictions (Figure 4). Warm temperatures at high flows showed a high positive effect on the standard deviation in downstream migration (Figure 4). These conditions typically coincide with seasonal spring flooding and likely offer the greatest landscape heterogeneity and connectivity for outmigrating juvenile Chinook salmon [48]. In contrast, the general smoother (Figure 4) showed a negative effect of warm temperatures at low flows. Drought conditions may offer very little suitable habitat and constrain outmigration alternatives. Additionally, some portion of this relationship could be explained by lower survival, when flows are low and temperatures are high, which would eliminate slower-moving individuals from the observations of travel time. Further, the warmest years in this study encompassed the most recent drought (2014, 2015, 2016, and 2013), while the coolest years were also wetter years (2011, 2006, 2010, and 2017). The three years with the lowest standard deviation in travel time were 2012 (3.26), 2007 (3.58), and 2014 (3.71), representing the dry, below normal, and critically dry water year types, respectively, with no flooding. Travel time was also significantly different across all water year types except dry and critically dry (Table 1). However, the importance of water temperature is likely a representation of both seasonality and the habitat complexity produced during spring inundation. The standard deviation in migration movements was generally high across most Sacramento River outflow values at 12 °C (Figure 4). These conditions typically occur in February and March, or the beginning of spring, and season is a well-established driver of migration in many species. Water temperature was also highly correlated with date of release (r = 0.892; Supplementary S4; Table S3), and release date was included in the second-best model (along with outflow; Supplementary S4; Table S3). We suspect that the outputs from the HGAM represented both a direct mechanistic response for water temperature and integrated effects of seasonal and hydrologic conditions during the time in which each individual juvenile salmon was experiencing the Sacramento River watershed.
In California, climate warming is expected to increase both air temperature and variability in precipitation [58], which may have cascading ecosystem impacts. Air temperature in California is projected to increase by 1.5–4.5 °C this century [59]. Studies suggest that animal responses to climate change correspond to seasonality rather than to temperature [60]. This conclusion is complicated by changes in temperature and photoperiod interacting with other environmental conditions, such as food supply [61]. Therefore, temperature may represent composite climatic trends acting on migration timing and prey resources in the estuary and the ocean. For example, Munsch et al. [62] showed that for every 1 °C cooler April water temperature, juveniles inhabited the watershed 4–7 days longer and entered marine waters, where survival is size-selective, up to 2.1 mm larger. It has been suggested that recent climate stress concurrent with past human actions has eroded resilience in this system and building climate-resilience fisheries includes prioritizing complex, less-modified ecosystems [63].
Both release region and the number of routes used by juvenile Chinook salmon are likely influencing access to habitat complexity and cannot be easily disentangled. The winter run and the late-fall run had the longest travel times. This could be due to non-natal rearing, which has been documented for the winter run [23]. However, this observation for the winter run may have been affected by release location. Carr-Harris et al. [64] showed that juvenile sockeye salmon (Oncorhynchus nerka) arrive three days later for every 100 km of river distance traveled. Achord et al. [56] showed a similar pattern where juvenile salmon rearing at lower elevations arrive earlier than those rearing at higher elevations. Both studies suggested that this was due to growth opportunities, such as warmer thermal regimes at varying elevations, attaining an adequate size prior to migration and different salmon populations encountering different prey abundances. In our study, the fall run and the winter run release locations in the upper Sacramento River were approximately 90 km apart, and we observed an up to 37-day difference between the fall run and the winter run travel times in the same year and route. Finally, the fall run typically exhibited a subyearling life history and may be predisposed to enter the estuary quickly at a relatively large size (due to minimum size criteria for tagging) in this study. The shortest average travel times described in this study were fall-run individuals released into the tidal Sacramento River in 2017. These individuals entered the estuary through the Sacramento River Sloughs (3.8 days) and the mainstem Sacramento River (4.0 days). Although landscape-scale environmental drivers were best supported by the HGAM, individual demographic variation and inconsistencies in study design may have impacted our estimates of travel time, movement, and routing. As tagging technology inevitably gets smaller, we will be able to glean more information on migration diversity from smaller juveniles, which are more likely to capitalize on rearing opportunities.
5. Conclusions
Environmental heterogeneity is thought to promote life history diversity and resilience. Increased spatial variation in habitat use and decreased interannual variation in production is apparent for both juvenile [65] and adult [12] life stages. Some aspects of population diversity are dependent upon the maintenance of a range of habitats [12,66,67]. Here, we demonstrated that seaward migration is one aspect of life history diversity that is likely supported by habitat complexity, in terms of both hydrology and temperature, which impacts access, timing, and routing (Figure 2). Despite the degraded state of this watershed and the weakened state of these populations [66], juvenile salmon used a diversity of migratory routes when available (e.g., the remnant floodplain−tidal slough complex, the Yolo Bypass). Migration timing has important implications for match−mismatch dynamics and later growth and survival [55,56,64]. Maintaining a diversity of routes and increased hydrologic connectivity and habitat complexity should be a management priority when addressing goals of long-term stability.
Finally, we found that useful metrics of life history variability can be generated using telemetry data. Telemetry data are widely collected for a broad range of species, allowing scientists to gain insights into many factors such as habitat use, distribution, and life history timing. Further, telemetry studies are expensive, and our approach provides a valuable additional use for these telemetry data. To our knowledge, telemetry data have not previously been used for the purposes of quantifying life history variability. Our hope is that other researchers may find this approach to be helpful to understand other species and populations. We anticipate that many other useful variability metrics will be possible using telemetry data.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/w16172529/s1. Supplementary S1. Tagging procedure and transport supplementary methods. Supplementary S2, Table S1. Data included in analyses and source publications for those data, arranged by release group, year, run and origin. The sample size, n, describes those individuals who were detected in the estuary (e.g., Chipps Island or the Benicia Bridge) and at least one other location during migration. Supplementary S3, Table S2. Results from the routing analysis. All individuals detected at Chipps Island or Benicia and Decker or Antioch were analyzed for routing to the estuary. Receivers were grouped into four routes: the Sacramento River only, the Sacramento River sloughs, the Central Delta, and the Yolo Bypass. To be assigned a route, an individual must have been detected at least twice in at least two locations in logical order (e.g., entrance, internal slough site, exit) and not detected at a site adjacent to the route in the Sacramento River. Supplementary S4, Table S3. Correlation matrix (values range from −1 to 1). Correlations greater than 0.5 or less than -0.5 are in bold. Supplementary S5, Table S4. AIC and deviance explained for the top ten models. The hierarchical generalized additive models (HGAMs) examined the drivers of variation in migration (the standard deviation in the individual daily detection time series). The HGAM model formula included a single common smoother plus group-level smoothers, allowing each release group-specific smoother to have its own smoothing parameter (released in the upper Sacramento River, middle Sacramento River, and Tidal Delta). Drivers included in the top ten models were mean and the standard deviation in daily Sacramento River outflow (outflow), mean and standard deviation in daily Sacramento River water temperature (temperature), standard deviation in daily Sacramento River stage (stage), water temperature at the release site (release temperature), Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO), release date (release), and date of first detection in the estuary (estuary entry). To best describe conditions experienced by each individual fish, environmental variables were summarized between the date of release and first detection in the estuary. Supplementary S6. Model formula. Supplementary S7, Figure S1. Group-level smoother plots from the best HGAM, which included release group, the mean in daily water temperature and mean in daily outflow of the Sacramento River (color) between release and first detection in the estuary for each individual fish. These plots show the group-level relationship between water temperature and the standard deviation in downstream movements while adjusting for the influence of outflow. The gray ribbon denotes the model confidence interval, the black shows the model estimate and the colored points represent the data (colored by outflow values). Supplementary S8, Figure S2. (A) Box plot of the standard deviation in estuary arrival date grouped by the water year type in which juvenile Chinook salmon were released (Sacramento Valley water year index), and (B) standard deviation in estuary arrival date grouped by release year and location (upper Sacramento River, middle Sacramento River and Tidal Delta) and plotted against the number of routes used. The box plot displays the distribution of the data based on a five-number summary: minimum (lowest horizontal line), first quartile (bottom of gray box), median (thick line), third quartile (top of gray box) and maximum (highest horizontal line). References [68,69,70,71,72] are cited in Supplementary S2, Table S1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.A.L.G. and T.S.; Formal analysis, P.A.L.G. and M.J.; Investigation, C.J.M. and T.G.; Data curation, P.A.L.G., M.J., C.J.M., T.G., G.S. and J.N.; Writing—original draft, P.A.L.G. and T.S.; Writing—review & editing, M.J., C.J.M., T.G., G.S. and J.N.; Project administration, P.A.L.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Funding for the UC Davis study included in this synthesis was provided by the Ecosystem Restoration Program (grant numbers: E1183012 and E1183008; to A.P.K) and provided by the US Bureau of Reclamation for the UC Santa Cruz/NMFS study (grant number: R18AC00039) and the CALFED Bay Delta Program (grant number: U-05-SC-047).
Data Availability Statement
Data and codes that are in GitHub (https://github.com/goertler/migration_diversity_metrics). The manuscript tables and figures are all reproducible within our GitHub repository.
Acknowledgments
The data used in this study were collected by many individuals, and we would like to thank all the past and present staff at the U.S. Bureau of Reclamation, U. S. Geological Survey, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, California Department of Fish and Wildlife, California Department of Water Resources, East Bay Municipal Utilities District, Cramer Fish Sciences and U.S. Army Corps of Engineers who collected the data used in this study. Additionally, we would like to thank Russell Perry and Arnold Ammann whose helpful input improved earlier versions of this study. We would also like to acknowledge individuals who compiled and provided data: Adam Pope and Theresa Liedtke. We would like to thank the members of the UC Davis Biotelemetry Laboratory and the UC Santa Cruz/NMFS SWFSC Salmon Ecology Team that helped with fish care, transmitter implantations, fish releases, and receiver downloads. An additional debt of gratitude is extended to the staff at Coleman National Fish Hatchery and the Feather River Fish Hatchery, for providing the research subjects and allowing us to work on site to implant the acoustic transmitters. Coordination for the data collection occurred through the Interagency Acoustic Telemetry Group (ITAG).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Cushing, D.H. Plankton Production and Year-Class Strength in Fish Populations: An Update of the Match/Mismatch Hypothesis. Adv. Mar. Biol. 1990, 26, 249–293. [Google Scholar]
- Laurel, B.J.; Hurst, T.P.; Ciannelli, L. An Experimental Examination of Temperature Interactions in the Match—Mismatch Hypothesis. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2011, 68, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindley, S.T.; Grimes, C.B.; Mohr, M.S.; Peterson, W.; Stein, J.E.; Anderson, J.T.; Botsford, L.W.; Bottom, D.L.; Busack, C.A.; Collier, T.K.; et al. What Caused the Sacramento River Fall Chinook Stock Collapse? 2009. Available online: https://www.waterboards.ca.gov/waterrights/water_issues/programs/bay_delta/deltaflow/docs/exhibits/nmfs/spprt_docs/nmfs_exh4_lindley_etal_2009.pdf (accessed on 15 January 2020).
- Woodson, L.E.; Wells, B.K.; Weber, P.K.; Macfarlane, R.B.; Whitman, G.E.; Johnson, R.C. Size, Growth, and Origin-Dependent Mortality of Juvenile Chinook Salmon Oncorhynchus tshawytscha during Early Ocean Residence. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2013, 487, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budy, P.; Thiede, G.P.; Bouwes, N.; Petrosky, C.E.; Schaller, H. Evidence Linking Delayed Mortality of Snake River Salmon to Their Earlier Hydrosystem Experience. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2002, 22, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crozier, L.G.; Bowerman, T.E.; Burke, B.J.; Keefer, M.L.; Caudill, C.C. High-stakes steeplechase: A behavior-based model to predict individual travel times through diverse migration segments. Ecosphere 2017, 8, e01965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottom, D.L.; Jones, K.K.; Cornwell, T.J.; Gray, A.; Simenstad, C.A. Patterns of Chinook Salmon Migration and Residency in the Salmon River Estuary (Oregon). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2005, 64, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satterthwaite, W.H.; Carlson, S.M.; Allen-Moran, S.D.; Vincenzi, S.; Bograd, S.J.; Wells, B.K. Match-Mismatch Dynamics and the Relationship between Ocean-Entry Timing and Relative Ocean Recoveries of Central Valley Fall Run Chinook Salmon. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2014, 511, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreck, C.B.; Moyle, P.B. (Eds.) Methods for Fish Biology; American Fisheries Society: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Greene, C.M.; Hall, J.E.; Guilbault, K.R.; Quinn, T.P. Improved Viability of Populations with Diverse Life-History Portfolios. Biol. Lett. 2010, 6, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.W.; Yeakel, J.D.; Peard, D.; Lough, J.; Beere, M. Life-History Diversity and Its Importance to Population Stability and Persistence of a Migratory Fish: Steelhead in Two Large North American Watersheds. J. Anim. Ecol. 2014, 83, 1035–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, D.E.; Hilborn, R.; Chasco, B.; Boatright, C.P.; Quinn, T.P.; Rogers, L.A.; Webster, M.S. Population Diversity and the Portfolio Effect in an Exploited Species. Nature 2010, 465, 609–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Marine Fisheries Service. Biological and Conference Opinion on the Long-Term Operations of the Central Valley Project and State Water Project; National Marine Fisheries Service: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2009.
- Rand, P.S.; Goslin, M.; Gross, M.R.; Irvine, J.R.; Augerot, X.; Mchugh, P.A.; Bugaev, V.F. Global Assessment of Extinction Risk to Populations of Sockeye Salmon Oncorhynchus nerka. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satterthwaite, W.H.; Carlson, S.M. Weakening Portfolio Effect Strength in a Hatchery-Supplemented Chinook Salmon Population Complex. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2015, 72, 1860–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, D.A.; Harstad, D.L.; Fuhrman, A.E.; Knudsen, C.M.; Schroder, S.L.; Bosch, W.J.; Galbreath, P.F.; Fast, D.E.; Beckman, B.R. Maintaining a Wild Phenotype in a Conservation Hatchery Program for Chinook Salmon: The Effect of Managed Breeding on Early Male Maturation. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedrick, P.W.; Hedgecock, D.; Hamelberg, S. Effective Population Size in Winter-Run Chinook Salmon. Conserv. Biol. 1995, 9, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utter, F.; Milner, G.; Stahl, G.; Teel, D. Genetic Population Structure of Chinook Salmon, Oncorhynchus tshawytscha, in the Pacific Northwest. Fish. Bull. 1989, 87, 239–264. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, T.Q.; Bellinger, M.R.; O’Rourke, S.M.; Prince, D.J.; Stevenson, A.E.; Rodrigues, A.T.; Sloat, M.R.; Speller, C.F.; Yang, D.Y.; Butler, V.L.; et al. Anthropogenic Habitat Alteration Leads to Rapid Loss of Adaptive Variation and Restoration Potential in Wild Salmon Populations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narum, S.R.; Genova, A.D.; Micheletti, S.J.; Maass, A. Genomic Variation Underlying Complex Life-History Traits Revealed by Genome Sequencing in Chinook Salmon. Proc. R. Soc. B 2018, 285, 20180935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.C.; Garza, J.C.; Macfarlane, R.B.; Grimes, C.B.; Phillis, C.C.; Koch, P.L.; Weber, P.K.; Carr, M.H. Isotopes and Genes Reveal Freshwater Origins of Chinook Salmon Oncorhynchus tshawytscha Aggregations in California’s Coastal Ocean. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2016, 548, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordoleani, F.; Phillis, C.C.; Sturrock, A.M.; FitzGerald, A.M.; Malkassian, A.; Whitman, G.E.; Weber, P.K.; Johnson, R.C. Threatened salmon rely on a rare life history strategy in a warming landscape. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2021, 11, 982–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillis, C.C.; Sturrock, A.M.; Johnson, R.C.; Weber, P.K. Endangered Winter-Run Chinook Salmon Rely on Diverse Rearing Habitats in a Highly Altered Landscape. Biol. Conserv. 2018, 217, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturrock, A.M.; Wikert, J.D.; Heyne, T.; Mesick, C.; Hubbard, A.E.; Hinkelman, T.M.; Weber, P.K.; Whitman, G.E.; Glessner, J.J.; Johnson, R.C. Reconstructing the Migratory Behavior and Long-Term Survivorship of Juvenile Chinook Salmon under Contrasting Hydrologic Regimes. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, N.S.; Beeman, J.W.; Eiler, J.H. (Eds.) Telemetry Techniques: A User Guide for Fisheries Research; American Fisheries Society: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- McMichael, G.A.; Eppard, M.B.; Carlson, T.J.; Carter, J.A.; Ebberts, B.D.; Brown, R.S.; Weiland, M.; Ploskey, G.R.; Harnish, R.A.; Deng, Z.D. The Juvenile Salmon Acoustic Telemetry System: A New Tool. Fisheries 2010, 35, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturrock, A.M.; Satterthwaite, W.H.; Yoshida, K.M.; Huber, E.R.; Sturrock, H.J.W.; Nusslé, S.; Carlson, S.M. Eight Decades of Hatchery Salmon Releases in the California Central Valley: Factors Influencing Straying and Resilience. Fisheries 2019, 44, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshiyama, R.M.; Moyle, P.B.; Gerstung, E.R.; Fisher, F.W. Chinook Salmon in the California Central Valley: An Assessment. Fisheries 2000, 25, 6–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whipple, A.; Grossinger, R.; Rankin, D.; Stanford, B.; Askevold, R. Sacramento-San Joaquin Delta Historical Ecology Investigation: Exploring Pattern and Process; San Franciso Estuary Institute: Richmond, CA, USA, 2012; Available online: https://www.sfei.org/documents/sacramento-san-joaquin-delta-historical-ecology-investigation-exploring-pattern-and-proces (accessed on 15 January 2020).
- Yoshiyama, R.M.; Gerstung, E.R.; Fisher, F.W.; Moyle, P.B. Historical and Present Distribution of Chinook Salmon in the Central Valley Drainage of California. Fish Bull. 2001, 179, 71–176. [Google Scholar]
- Huber, E.R.; Carlson, S.M. Temporal Trends in Hatchery Releases of Fall-Run Chinook Salmon in California’s Central Valley. San Fr. Estuary Watershed Sci. 2015, 13, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Michel, C.J.; Ammann, A.J.; Lindley, S.T.; Sandstrom, P.T.; Chapman, E.D.; Thomas, M.J.; Singer, G.P.; Klimley, A.P.; Macfarlane, R.B. Chinook Salmon Outmigration Survival in Wet and Dry Years in California’s Sacramento River. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2015, 72, 1749–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, R.W.; Pope, A.C.; Romine, J.G.; Brandes, P.L.; Burau, J.R.; Blake, A.R.; Ammann, A.J.; Michel, C.J. Flow-Mediated Effects on Travel Time, Routing, and Survival of Juvenile Chinook Salmon in a Spatially Complex, Tidally Forced River Delta. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2018, 75, 1886–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, R.W.; Skalski, J.R.; Brandes, P.L.; Sandstrom, P.T.; Klimley, A.P.; Ammann, A.; MacFarlane, B. Estimating Survival and Migration Route Probabilities of Juvenile Chinook Salmon in the Sacramento-San Joaquin River Delta. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2010, 30, 142–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Liberto, T. Very Wet 2017 Water Year Ends in California. Science & Information for a Climate-Smart Nation. 2017. Available online: https://www.climate.gov/news-features/featured-images/very-wet-2017-water-year-ends-california (accessed on 15 January 2020).
- Liedtke, T.L.; Beeman, J.W.; Gee, L.P. A Standard Operating Procedure for the Surgical Implantation of Transmitters in Juvenile Salmonids: U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 2012–1267. 2012; 50p. Available online: https://pubs.usgs.gov/of/2012/1267/pdf/ofr20121267.pdf (accessed on 15 January 2020).
- Ammann, A.J.; Michel, C.J.; Macfarlane, R.B. The Effects of Surgically Implanted Acoustic Transmitters on Laboratory Growth, Survival and Tag Retention in Hatchery Yearling Chinook Salmon. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2013, 96, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, G.P.; Chapman, E.D.; Ammann, A.J.; Klimley, A.P.; Rypel, A.L.; Fangue, N.A. Historic Drought Influences Outmigration Dynamics of Juvenile Fall and Spring-Run Chinook Salmon. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2020, 103, 543–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, M.E.; Steel, A.E.; Espe, M.; Sommer, T.; Klimley, A.P.; Sandstrom, P.; Smith, D. Survival of Juvenile Chinook Salmon in the Yolo Bypass and the Lower Sacramento River, California. San Fr. Estuary Watershed Sci. 2018, 16, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liedtke, T.L.; Hurst, W.R. Yolo Bypass Juvenile Salmon Utilization Study 2016—Summary of Acoustically Tagged Juvenile Salmon and Study Fish Releases, Sacramento River, California. 2017. Available online: https://pubs.usgs.gov/ds/1066/ds1066.pdf (accessed on 15 January 2020).
- Pope, A.C.; Perry, R.W.; Harvey, B.N.; Hance, D.J.; Hansel, H.C. Juvenile Chinook Salmon Survival, Travel Time, and Floodplain Use Relative to Riverine Channels in the Sacramento–San Joaquin River Delta. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2021, 150, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.C.; Nmfs, N.; Windell, S.; Brandes, P.L.; Conrad, J.L.; Ferguson, J.; Goertler, P.A.L.; Harvey, B.N.; Heublein, J.; Israel, J.A.; et al. Science Advancements Key to Increasing Management Value of Life Stage Monitoring Networks for Endangered Sacramento River Winter-Run Chinook Salmon in California. San Fr. Estuary Watershed Sci. 2017, 15, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goertler, P.; Pien, C. Daily water temperature (°C) in the Yolo Bypass and Sacramento River, 1998–2019 ver 1. Environmental Data Initiative. 2022. Available online: https://portal.edirepository.org/nis/mapbrowse?packageid=edi.1178.1 (accessed on 23 May 2023). [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.; Goertler, P. Inundation. Zenodo. 2022. Available online: https://zenodo.org/records/6450272 (accessed on 23 May 2023). [CrossRef]
- Mantua, N.J.; Hare, S.R. The Pacific Decadal Oscillation. J. Oceanogr. 2002, 58, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, E.J.; Miller, D.L.; Simpson, G.L.; Ross, N. Hierarchical Generalized Additive Models in Ecology: An Introduction with Mgcv. PeerJ 2019, 7, e6876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, S. Fast stable restricted maximum likelihood estimation of semiparametric generalized linear models. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Stat. Methodol.) 2011, 78, 3–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goertler, P.; Sommer, T.R.; Satterthwaite, W.H.; Schreier, B.M. Seasonal Floodplain-Tidal Slough Complex Supports Size Variation for Juvenile Chinook Salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha). Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2017, 27, 580–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, T.R.; Nobriga, M.L.; Harrell, W.C.; Batham, W.; Kimmerer, W.J. Floodplain Rearing of Juvenile Chinook Salmon: Evidence of Enhanced Growth and Survival. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2001, 58, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuur, A.F.; Ieno, E.N.; Elphick, C.S. A Protocol for Data Exploration to Avoid Common Statistical Problems. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2010, 1, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, R.W.; Brandes, P.L.; Burau, J.R.; Klimley, A.P.; MacFarlane, B.; Michel, C.; Skalski, J.R. Sensitivity of survival to migration routes used by juvenile Chinook salmon to negotiate the Sacramento−San Joaquin River Delta. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2013, 96, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skalski, J.R.; Townsend, R.; Lady, J.; Giorgi, A.E.; Stevenson, J.R.; McDonald, R.D. Estimating route-specific passage and survival probabilities at a hydroelectric project from smolt radiotelemetry studies. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2002, 59, 1385–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordo, O. Why Are Bird Migration Dates Shifting? A Review of Weather and Climate Effects on Avian Migratory Phenology. Clim. Res. 2007, 35, 37–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrice, K.J.; Baptista, A.M.; Burke, B.J. Environmental and behavioral controls on juvenile Chinook salmon migration pathways in the Columbia River estuary. Ecol. Model. 2020, 427, 109003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheuerell, M.D.; Zabel, R.W.; Sandford, B.P. Relating Juvenile Migration Timing and Survival to Adulthood in Two Species of Threatened Pacific Salmon (Oncorhynchus spp.). J. Appl. Ecol. 2009, 46, 983–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achord, S.; Zabel, R.W.; Sandford, B.P. Migration Timing, Growth, and Estimated Parr-to-Smolt Survival Rates of Wild Snake River Spring—Summer Chinook Salmon from the Salmon River Basin, Idaho, to the Lower Snake River. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2007, 136, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goertler, P.; Jones, K.; Cordell, J.; Schreier, B.; Sommer, T. Effects of Extreme Hydrologic Regimes on Juvenile Chinook Salmon Prey Resources and Diet Composition in a Large River Floodplain. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2017, 147, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dettinger, M.; Udall, B.; Georgakakos, A. Western Water and Climate Change. Ecol. Appl. 2015, 25, 2069–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloern, J.E.; Knowles, N.; Brown, L.R.; Cayan, D.; Dettinger, M.D.; Morgan, T.L.; Schoellhamer, D.H.; Stacey, M.T.; van der Wegen, M.; Wagner, R.W.; et al. Projected Evolution of California’s San Francisco Bay-Delta-River System in a Century of Climate Change. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradshaw, W.E.; Holzapfel, C.M. Evolutionary Response to Rapid Climate Change. Science 2006, 312, 1477–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studds, C.E.; Marra, P.P. Linking Fluctuations in Rainfall to Nonbreeding Season Performance in a Long-Distance Migratory Bird, Setophaga ruticilla. Clim. Res. 2007, 35, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munsch, S.H.; Greene, C.M.; Johnson, R.C.; Satterthwaite, W.H.; Imaki, H.; Brandes, P.L. Warm, Dry Winters Truncate Timing and Size Distribution of Seaward-Migrating Salmon across a Large, Regulated Watershed. Ecol. Appl. 2019, 29, e01880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munsch, S.H.; Greene, C.M.; Mantua, N.J.; Satterthwaite, W.H. One Hundred–seventy Years of Stressors Erode Salmon Fishery Climate Resilience in California’s Warming Landscape. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2022, 28, 2183–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr-Harris, C.N.; Moore, J.W.; Gottesfeld, A.S.; Gordon, J.A.; Shepert, W.M.; Henry, J.D.J., Jr.; Russell, H.J.; Helin, W.N.B.; Doolan, D.J.; Beacham, T.D. Phenological Diversity of Salmon Smolt Migration Timing within a Large Watershed. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2018, 147, 775–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorson, J.T.; Scheuerell, M.D.; Buhle, E.R.; Copeland, T. Spatial Variation Buffers Temporal Fluctuations in Early Juvenile Survival for an Endangered Pacific Salmon. J. Anim. Ecol. 2014, 83, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, S.M.; Satterthwaite, W.H. Weakened Portfolio Effect in a Collapsed Salmon Population Complex. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2011, 68, 1579–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, B.; Skúlason, S.; Snorrason, S.S.; Sandlund, O.T.; Malmquist, H.J.; Jónasson, P.M.; Cydemo, R.; Lindem, T. Life History Variation of Polymorphic Arctic Charr (Salvelinus alpinus) in Thingvallavatn, Iceland. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1988, 45, 1537–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, E.D.; Singer, G.P.; Hayes, S.; Merz, A.J.; Zueg, S.; Hassrick, J.; Null, R.; Kurt, R.; Kindopp, J.; Klimley, A.P. Evaluating the Effects of Release Strategy on Movement and Survival of Fall and Spring Run Chinook Salmon Tagged with JSATS Transmitters in the Sacramento-San Joaquin Delta; Interagency Ecolicigal Program Workshop: Folsom, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cordoleani, F.; Notch, J.; McHuron, A.S.; Ammann, A.J.; Michel, C.J. Movement and Survival of Wild Chinook Salmon Smolts from Butte Creek During Their Out-Migration to the Ocean: Comparison of a Dry Year versus a Wet Year. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2018, 147, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassrick, J.L.; Ammann, A.J.; Perry, R.W.; John, S.N.; Daniels, M.E. Factors Affecting Spatiotemporal Variation in Survival of Endangered Winter-Run Chinook Salmon Out-Migrating from the Sacramento River. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2022, 42, 375–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notch, J.J.; McHuron, A.S.; Michel, C.J.; Cordoleani, F.; Johnson, M.; Henderson, M.J.; Ammann, A.J. Outmigration Survival of Wild Chinook Salmon Smolts through the Sacramento River during Historic Drought and High Water Conditions. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2020, 103, 561–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeug, S.C.; Null, R.; Brodsky, A.; Johnston, M.; Ammann, A.J. Effect of Release Timing on Apparent Survival of Juvenile Fall Run Chinook Salmon from Coleman National Fish Hatchery. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2020, 103, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).