The Impact of Induced Industrial and Urban Toxic Elements on Sediment Quality
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
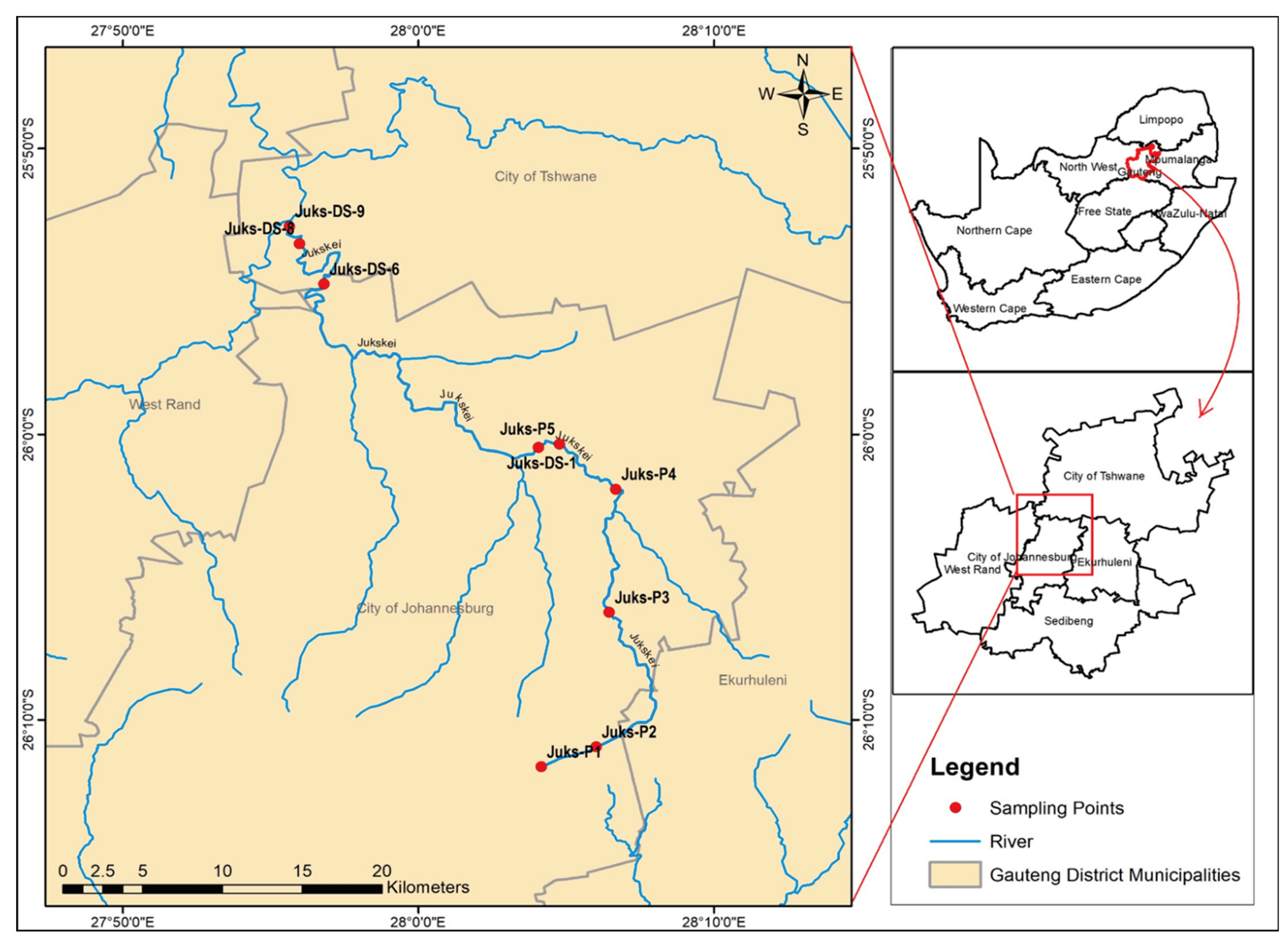
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Preparation
2.3. Reagents and Instrumentation
2.4. Mineralization of Analytes of Interest
2.5. Sediment Quality Assessment
- Cn is the concentration of element x in the sediment sample;
- Bn is the background or reference value of element n.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Assessment of Selected Toxic Elements
3.1.1. Total Quantification of Selected Toxic Elements
3.1.2. Radioactivity Determination of Thorium and Uranium
3.1.3. Pearson Correlation Coefficient
3.2. Pollution Indices for Sediment Quality Assessment
3.2.1. Enrichment Factor and Contamination Factor
3.2.2. Pollution Loan Index and Geo-Accumulation Index
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pandey, S.; Kumari, N. Assessment of Morphology and Soil Erosion Risk in Agrarian Watershed of Jharkhand India Using RUSLE, GIS and MCDA-AHP. J. Indian Soc. Remote. Sens. 2024, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, P.M.; Wang, F.; Caeiro, S.S. Assessing and managing sediment contamination in transitional waters. Environ. Int. 2013, 55, 71–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vineethkumar, V.; Sayooj, V.V.; Shimod, K.P.; Prakash, V. Estimation of pollution indices and hazard evaluation from trace elements concentration in coastal sediments of Kerala, Southwest Coast of India. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 2020, 44, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, G. A review of chemical-based sediment quality assessment methodologies for the marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 133, 218–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gqomfa, B.; Maphanga, T.; Shale, K. The impact of informal settlement on water quality of Diep River in Dunoon. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2022, 8, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel-Buitrago, N.; Rizzo, A.; Neal, W.J.; Mastronuzzi, G. Sediment pollution in coastal and marine environments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 192, 115023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska, J.B.; Mazurek, R.; Gąsiorek, M.; Zaleski, T. Pollution indices as useful tools for the comprehensive evaluation of the degree of soil contamination–A review. Environ. Geochem. Health 2018, 40, 2395–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Shao, H. Heavy Metal Pollution in Sediments from Aquatic Ecosystems in China. CLEAN–Soil Air Water 2013, 41, 878–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, N.; Ghosh, A.; Mitra, S.; Majumdar, G. Environmental issues associated with mining and minerals processing. Compr. Mater. Process. 2024, 8, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejuvenating South Africa’s economy—The Role of the Energy Sector, no. January 2022. Available online: https://www.inclusivesociety.org.za/post/rejuvenating-south-africa-s-economy-the-role-of-the-energy-sector (accessed on 28 August 2024).
- Letsoalo, M.R.; Godeto, T.W.; Magadzu, T.; Ambushe, A.A. Quantitative Speciation of Arsenic in Water and Sediment Samples from the Mokolo River in Limpopo Province, South Africa. Anal. Lett. 2018, 51, 2763–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raji, I.B.; Hoffmann, E.; Ngie, A.; Winde, F. Assessing uranium pollution levels in the rietspruit river, far west rand goldfield, South Africa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, C.K. Environmental pollution indices: A review on concentration of heavy metals in air, water, and soil near industrialization and urbanisation. Discov. Environ. 2024, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivarez, M.B.; Tovar, M.A.M.; Sánchez, J.V.; Betancourt, M.L.G.; Romero, F.M.; Arteaga, A.M.R.; Chávez, G.E.M.; Noreña, H.A.S. Mobility of Heavy Metals in Aquatic Environments Impacted by Ancient Mining-Waste. In Water Quality—Factors and Impacts; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dintsi, B.S.; Letsoalo, M.R.; Ambushe, A.A. Bioaccumulation and Human Health Risk Assessment of Arsenic and Chromium Species in Water–Soil–Vegetables System in Lephalale, Limpopo Province, South Africa. Minerals 2023, 13, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letsoalo, M.R.; Mamo, M.A.; Ambushe, A.A. Synchronous Extraction and Quantitative Speciation of Arsenic and Chromium in Sediments by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography—Inductively Coupled Plasma—Mass Spectrometry (HPLC-ICP-MS). Anal. Lett. 2020, 54, 1943–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letsoalo, M.R.; Mamo, M.A.; Ambushe, A.A. Simultaneous quantitative speciation of selected toxic elements in water using high performance liquid chromatography coupled to inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (HPLC-ICP-MS). Phys. Chem. Earth, Parts A/B/C 2021, 124, 103011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cheng, X.; Liu, K.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, Y. A new method for identifying potential hazardous areas of heavy metal pollution in sediments. Water Res. 2022, 224, 119065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chetty, S.; Pillay, L.; Humphries, M.S. Gold mining’s toxic legacy: Pollutant transport and accumulation in the Klip River catchment, Johannesburg. South Afr. J. Sci. 2021, 117, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshupya, P.M.; Mohuba, S.C.; Abiye, T.A.; Korir, I.; Nhleko, S.; Mkhosi, M. In Situ Determination of Radioactivity Levels and Radiological Doses in and around the Gold Mine Tailing Dams, Gauteng Province, South Africa. Minerals 2022, 12, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoorzook, K.B.; Pieterse, A.; Heine, L.; Barnard, T.G.; van Rensburg, N.J. Soul of the jukskei river: The extent of bacterial contamination in the jukskei river in gauteng province, South Africa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, J.; Iqani, M. Johannesburg’s shitty little river: Faecal discourse and discontent regarding the Jukskei. A J. Afr. Stud. 2024, 50, 109127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Understanding and Implementing ISO/IEC 17025 A Primer. 2009. p. 64. Available online: https://www.demarcheiso17025.com (accessed on 28 August 2024).
- Guan, Y.; Shao, C.; Ju, M. Heavy metal contamination assessment and partition for industrial and mining gathering areas. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 7286–7303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, D.; Rutherford, N. Technical Report on the Development of a Geochemical Atlas of Cyprus. Geol. Surv. Cyprus Lefkosia 2011, 1 1–104. Available online: https://www.moa.gov.cy/moa/gsd/gsd.nsf/38c34d0122ca5340c22585f300382a45/25e685022ae4ef99c2258601001e081d/$FILE/Geochemical%20Atlas%20of%20Cyprus%20FinalReport_Volume%201_Text.pdf (accessed on 28 August 2024).
- Al-Dahar, R.K.; Rabee, A.M.; Mohammed, R.J. Calculation of soil pollution indices with elements in residential areas of Baghdad city. Bionatura 2023, 8, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wu, Z.; Chen, B.; Zhou, Z.; Liang, Y.; He, M.; Hu, B. Quantification of trace heavy metals in environmental water, soil and atmospheric particulates with their bioaccessibility analysis. Talanta 2024, 276, 126284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uddin, K.; Majumder, A.K.; Hossain, S.; Al Nayeem, A. Pollution and Perceptions of Lead in Automobile Repair Shops in Dhaka, Bangladesh. J. Health Pollut. 2019, 9, 190609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiteside, T.G.; Esparon, A.J.; Bartolo, R.E. A semi-automated approach for quantitative mapping of woody cover from historical time series aerial photography and satellite imagery. Ecol. Informatics 2020, 55, 101012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, N.; Bastiansz, A.; Dórea, J.G.; Fujimura, M.; Horvat, M.; Shroff, E.; Weihe, P.; Zastenskaya, I. Our evolved understanding of the human health risks of mercury. AMBIO 2023, 52, 877–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bwapwa, J.K. A Review of Acid Mine Drainage in a Water-Scarce Country: Case of South Africa. Environ. Manag. Sustain. Dev. 2017, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radiobiology Textbook; Springer Nature: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2023.
- Rahman, M.S.; Ahmed, Z.; Seefat, S.M.; Alam, R.; Islam, A.R.M.T.; Choudhury, T.R.; Begum, B.A.; Idris, A.M. Assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediment at the newly established tannery industrial Estate in Bangladesh: A case study. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2021, 4, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, H.; Al-Azmi, D. Radioactivity concentrations in sediments and their correlation to the coastal structure in Kuwait. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2002, 56, 991–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, T.R.; Ferdous, J.; Haque, M.; Rahman, M.; Quraishi, S.B. Assessment of heavy metals and radionuclides in groundwater and associated human health risk appraisal in the vicinity of Rooppur nuclear power plant, Bangladesh. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2022, 251, 104072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masindi, V.; Foteinis, S.; Renforth, P.; Ndiritu, J.; Maree, J.; Tekere, M.; Chatzisymeon, E. Challenges and avenues for acid mine drainage treatment, beneficiation, and valorisation in circular economy: A review. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 183, 106740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.S.; Pandey, P.K.; Martín-Ramos, P.; Corns, W.T.; Varol, S.; Bhattacharya, P.; Zhu, Y. A review on arsenic in the environment: Contamination, mobility, sources, and exposure. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 8803–8821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rother, H.-A. Pesticide labels: Protecting liability or health?—Unpacking “misuse” of pesticides. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2018, 4, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.; Elahi, A.; Bukhari, D.A.; Rehman, A. Cadmium sources, toxicity, resistance and removal by microorganisms-A potential strategy for cadmium eradication. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2022, 26, 101569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | Setting |
|---|---|
| Nebulizer gas flow | 0.75 L/min |
| Auxiliary gas flow | 1.4 L/min |
| Plasma gas flow | 12 L/min |
| ICP RF power | 1400 kW |
| Sample intake | 0.8 mL/min |
| Number of replicates | 3 |
| Background Element | Reference Value (mg/kg) |
|---|---|
| As | 12.7 |
| Pb | 10 |
| Cd | 0.5 |
| Hg | 0.02 |
| Th | 10 |
| U | 10 |
| Fe | 10,000 |
| Enrichment Factor Value | Sediments Quality |
|---|---|
| <1.0 | No enrichment |
| <2.0 | Minimal enrichment |
| 3–5 | Moderate enrichment |
| 5–10 | Moderately severe enrichment |
| 10–25 | Severe enrichment |
| 25–50 | Very high enrichment |
| Contamination Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| <1.0 | Low contamination |
| <2.0 | Moderate contamination |
| 3.0–5.0 | Considerable contamination |
| >6.0 | Very high contamination |
| Geoaccumulation Index | Geoaccumulation Index Class | Pollution Intensity |
|---|---|---|
| <0 | 0 | Practically no pollution |
| >0 <1 | 1 | Uncontaminated to moderately contaminated |
| >1 <2 | 2 | Moderately contaminated |
| >2 <3 | 3 | Moderately to heavily contaminated |
| >3 <4 | 4 | Heavily contaminated |
| >4 <5 | 5 | Heavily to extremely contaminated |
| >5 <6 | 6 | Very strongly polluted |
| Sample ID | As (mg/kg) | Pb (mg/kg) | Cd (mg/kg) | Hg (µg/kg) | Th (mg/kg) | U (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Juks-P1 | 10.0 ± 0.06 | 38.8 ± 1.27 | 0.16 ± 0.03 | 77.5 ± 3.54 | 5.08 ± 0.02 | 2.02 ± 0.03 |
| Juks-P2 | 8.6 ± 0.06 | 475 ± 4.04 | 0.30 ± 0.03 | 20.7 ± 0.58 | 4.59 ± 0.09 | 1.74 ± 0.06 |
| Juks-P3 | 2.35 ± 0.29 | 12.6 ± 0.32 | <0.05 | 24.5 ± 2.12 | 3.46 ± 0.08 | 1.26 ± 0.05 |
| Juks-P4 | 5.77 ± 0.21 | 13.0 ± 0.55 | <0.05 | 10.3 ± 0.99 | 5.31 ± 0.02 | 2.86 ± 0.05 |
| Juks-P5 | 2.1 ± 0.14 | 21.2 ± 0.14 | 0.14 ± 0 | 15.0 ± 0 | 5.84 ± 0.02 | 2.25 ± 0.06 |
| Juks-DS-1 | 1.6 ± 0.14 | 21.8 ± 0.42 | 0.12 ± 0 | 16.0 ± 2.83 | 4.14 ± 0.16 | 1.67 ± 0.01 |
| Juks-DS-6 | 1.09 ± 0.16 | 15.8 ± 1.56 | <0.05 | 8.4 ± 0.85 | 4.96 ± 0.62 | 1.34 ± 0.00 |
| Juks-DS-8 | 2.1 ± 0.14 | 28.2 ± 0.42 | 0.26 ± 0.02 | 52.3 ± 4.2 | 5.35 ± 0.29 | 2.81 ± 0.00 |
| Juks-DS-9 | 1.3 ± 0.35 | 16.3 ± 0.40 | 0.12 ± 0.01 | 22.0 ± 2.83 | 4.72 ± 0.40 | 1.67 ± 0.08 |
| As | Pb | Cd | Hg | Th | U | Fe | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As | 1 | 0.3241 | 0.1546 | 0.1797 | 0.0406 | 0.0974 | 0.5068 |
| Pb | 0.3241 | 1 | 0.3831 | 0.0004 | 0.0004 | 0.0008 | 0.6521 |
| Cd | 0.1546 | 0.3831 | 1 | 0.3003 | 0.0421 | 0.2393 | 0.374 |
| Hg | 0.1797 | 0.0004 | 0.3003 | 1 | 0.0249 | 0.1357 | 0.0175 |
| Th | 0.0406 | 0.0004 | 0.0421 | 0.0249 | 1 | 0.1971 | 0.0102 |
| U | 0.0974 | 0.0008 | 0.2393 | 0.1357 | 0.1971 | 1 | 0.0606 |
| Fe | 0.5068 | 0.6521 | 0.374 | 0.0175 | 0.0102 | 0.0606 | 1 |
| Toxic Metal | Juks-P1 | Juks-P2 | Juks-P3 | Juks-P4 | Juks-P5 | Juks-DS-1 | Juks-DS-6 | Juks-DS-8 | Juks-DS-9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As | 0.40 | 0.19 | 0.14 | 0.28 | 0.13 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.08 | 0.09 |
| Pb | 1.99 | 12.98 | 1.00 | 0.80 | 1.09 | 2.12 | 2.29 | 1.29 | 1.48 |
| Cd | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.3 | 0 | 0 | 0.23 | 0 | 0.24 | 0.22 |
| Hg | 1.98 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.98 | 0.32 | 0.78 | 0.61 | 1.19 | 1.00 |
| Th | 0.26 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.28 | 0.33 | 0.40 | 0.72 | 0.24 | 0.43 |
| U | 0.16 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.10 | 0.32 | 0.16 | 0.19 | 0.13 | 0.15 |
| Toxic Metals | Juks-P1 | Juks-P2 | Juks-P3 | Juks-P4 | Juks-P5 | Juks-DS-1 | Juks-DS-6 | Juks-DS-8 | Juks-DS-9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As | 0.79 | 0.68 | 0.19 | 0.45 | 0.17 | 0.13 | 0.09 | 0.17 | 0.10 |
| Pb | 3.88 | 47.5 | 1.26 | 1.3 | 2.13 | 2.18 | 1.58 | 2.82 | 1.63 |
| Cd | 0.32 | 0.6 | 0 | 0 | 0.28 | 0.24 | 0 | 0.52 | 0.24 |
| Hg | 3.88 | 1.04 | 1.23 | 0.52 | 0.75 | 0.80 | 0.42 | 2.62 | 1.10 |
| Th | 0.51 | 0.46 | 0.35 | 0.53 | 0.58 | 0.41 | 0.50 | 0.54 | 0.47 |
| U | 0.20 | 0.17 | 0.13 | 0.29 | 0.23 | 0.17 | 0.13 | 0.28 | 0.17 |
| Sample ID | Pollution Load Index |
|---|---|
| Juks-P1 | 0.85 |
| Juks-P2 | 1.08 |
| Juks-P3 | 0 |
| Juks-P4 | 0 |
| Juks-P5 | 1.00 |
| Juks DS-1 | 0.39 |
| Juks DS-6 | 0 |
| Juks-DS-8 | 0.67 |
| Juks-DS-9 | 0.38 |
| Toxic Element | Juk-P1 | Juk-P2 | Juks-P3 | Juks-P4 | Juks-P5 | Juks-DS-1 | Juks-DS-6 | Juks-DS-8 | Juks-DS-9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As | −0.51 | −0.72 | −2.59 | −1.30 | −2.76 | −3.15 | −3.70 | −2.75 | −3.44 |
| Pb | 1.75 | 5.37 | 0.13 | 0.18 | 0.88 | 0.92 | 0.45 | 1.29 | 0.50 |
| Cd | −3.64 | −2.74 | 0 | 0 | −3.84 | −4.06 | 0 | −2.94 | −4.05 |
| Hg | −4.24 | −6.24 | −6.25 | −7.25 | −6.25 | −6.25 | −7.24 | −4.93 | −6.24 |
| Th | −1.18 | −1.33 | −1.73 | −1.11 | −0.98 | −1.47 | −1.21 | −1.10 | −1.28 |
| U | −2.51 | −2.72 | −3.19 | −2.01 | −2.35 | −2.78 | −3.10 | −2.03 | −2.78 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mukwevho, N.; Ntsasa, N.; Mkhohlakali, A.; Mabowa, M.H.; Chimuka, L.; Tshilongo, J.; Letsoalo, M.R. The Impact of Induced Industrial and Urban Toxic Elements on Sediment Quality. Water 2024, 16, 2485. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16172485
Mukwevho N, Ntsasa N, Mkhohlakali A, Mabowa MH, Chimuka L, Tshilongo J, Letsoalo MR. The Impact of Induced Industrial and Urban Toxic Elements on Sediment Quality. Water. 2024; 16(17):2485. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16172485
Chicago/Turabian StyleMukwevho, Nehemiah, Napo Ntsasa, Andile Mkhohlakali, Mothepane Happy Mabowa, Luke Chimuka, James Tshilongo, and Mokgehle Refiloe Letsoalo. 2024. "The Impact of Induced Industrial and Urban Toxic Elements on Sediment Quality" Water 16, no. 17: 2485. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16172485
APA StyleMukwevho, N., Ntsasa, N., Mkhohlakali, A., Mabowa, M. H., Chimuka, L., Tshilongo, J., & Letsoalo, M. R. (2024). The Impact of Induced Industrial and Urban Toxic Elements on Sediment Quality. Water, 16(17), 2485. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16172485






