Ecotoxicity of 2,4-Dichlorophenol to Microsorium pteropus by High Spatial Resolution Mapping of Stoma Oxygen Emission
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. Chemicals
2.3. Ecotoxicity Exposure Experiments
2.4. Stoma Oxygen Mapping by SECM
2.5. Three Conventional Ecotoxicological Assessment Methods
2.6. Calculation and Statistics
3. Results
3.1. SECM Mappings of Stoma Oxygen Emission
3.2. CLSM Images of M. pteropus Stoma
3.3. Estimation of IC50 from SECM and Other Methods
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deng, C.N.; Zhang, D.Y.; Pan, X.L.; Chang, F.Q.; Wang, S.Z. Toxic Effects of Mercury on Psi and Psii Activities, Membrane Potential and Transthylakoid Proton Gradient in Microsorium pteropus. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2013, 127, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Z.; Pan, X.L.; Zhang, D.Y. Psi Showed Higher Tolerance to Sb(V) Than Psii Due to Stimulation of Cyclic Electron Flow around Psi. Curr. Microbiol. 2015, 70, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, E.A.; Ahmed, H.M.I.; Misra, M.; Sharma, P.; Misra, A.N. Nitric Oxide Alleviates Photochemical Damage Induced by Cadmium Stress in Pea Seedlings. Phyton-Int. J. Exp. Bot. 2022, 91, 959–975. [Google Scholar]
- Ciurli; Baccio, A.; Scartazza, D.; Grifoni, A.; Pezzarossa, M.; Chiellini, B.; Mariotti, C.; Pardossi, L.A. Influence of Zinc and Manganese Enrichments on Growth, Biosorption and Photosynthetic Efficiency Ofchlorellasp. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 46764–46780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baryla, A.; Carrier, P.; Franck, F.; Coulomb, C.; Sahut, C.; Havaux, M.J.P. Leaf Chlorosis in Oilseed Rape Plants (Brassica napus) Grown on Cadmium-Polluted Soil: Causes and Consequences for Photosynthesis and Growth. Planta 2001, 212, 696–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, N.; Mohn, F.H. Use of Chlorophyll Fluorescence in Metal-Stress Research: A Case Study with the Green Microalga Scenedesmus. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2003, 55, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasukawa, T.; Kaya, T.; Matsue, T. Characterization and Imaging of Single Cells with Scanning Electrochemical Microscopy. Electroanalysis 2000, 12, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.; Li, X.; Tang, Y.; Sui, M.; Li, J.; Ma, Y.; Wang, G.; Gu, W.; Guo, X.; Yang, M. A Highly Parallel Dtt/Mb-DNA/Au Electrochemical Biosensor for Trace Hg Monitoring by Using Configuration Occupation Approach and SECM. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 234, 113391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.R.; Ning, X.M.; Ma, Q.L.; Qin, D.D.; Lu, X.Q. Recent Advances in Electrochemistry by Scanning Electrochemical Microscopy. Trends Analyt. Chem. 2016, 80, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Takahashi, Y.; Fukuma, T.; Matsue, T. Scanning Electrochemical Microscopy for Biosurface Imaging. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2021, 29, 100739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsionsky, M.; Cardon, Z.G.; Bard, A.J.; Jackson, R.B. Photosynthetic Electron Transport in Single Guard Cells as Measured by Scanning Electrochemical Microscopy. Plant Physiol. 1997, 113, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, R.K.; Macfie, S.M.; Ding, Z.F. Cadmium-Induced Plant Stress Investigated by Scanning Electrochemical Microscopy. J. Exp. Bot. 2005, 56, 2831–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaulieu, I.; Kuss, S.; Mauzeroll, J.; Geissler, M. Biological Scanning Electrochemical Microscopy and Its Application to Live Cell Studies. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 1485–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, N.; Tian, X.; Nie, Y.; Yang, C.; Zhou, Z.; Li, Y. Enhanced 2, 4-Dichlorophenol Degradation at pH 3-11 by Peroxymonosulfate Via Controlling the Reactive Oxygen Species over Ce Substituted 3d Mn2O3. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 355, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Liu, H.; Giesy, J.P.; Yu, H. pH-Dependent Aquatic Criteria for 2,4-Dichlorophenol, 2,4,6-Trichlorophenol and Pentachlorophenol. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 441, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.Q.; Jin, H.J.; Yu, L.W.; Hu, S.Q. Deriving Freshwater Quality Criteria for 2,4-Dichlorophenol for Protection of Aquatic Life in China. Environ. Pollut. 2003, 122, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Leng, H.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Duan, H.; Sun, H.; Chen, Y. Removal of 2,4-Dichlorophenol in Hydroponic Solution by Four Salix Matsudana Clones. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 86, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Jin, X.; Megharaj, M.; Naidu, R.; Chen, Z. Heterogeneous Fenton Oxidation of 2,4-Dichlorophenol Using Iron-Based Nanoparticles and Persulfate System—Sciencedirect. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 264, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makevita, M.; Athauda, S.; Pahalawattarachchi, V. Development of in Vitro Sterilization Procedure for Java Fern (Microsorum pteropus). In Proceedings of the FAuRS-2018, Peradeniya, Sri Lanka, 27 January 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chun-Nuan, D.; Tao, F. Responses of Photosystem I and Ii Activities of Microsorum pteropus Blume to Pb2+ Toxicity. Bangladesh J. Bot. 2017, 46, 1425–1428. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, X.Y.; Wang, J.J.; Yan, Y.Y.; Li, X.Y.; Xu, F.L. Hyperaccumulation Capacity and Resistance Physiology of Microsorum pteropus, an Aquatic Fern to Cadmium. Sci. Sin. Vitae 2017, 47, 1113–1123. [Google Scholar]
- Miyoshi, S.; Kimura, S.; Ootsuki, R.; Higaki, T.; Nakamasu, A. Developmental Analyses of Divarications in Leaves of an Aquatic Fern Microsorum pteropus and Its Varieties. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelini, V.A.; Agostini, E.; Medina, M.I.; González, P.S. Use of Hairy Roots Extracts for 2,4-Dcp Removal and Toxicity Evaluation by Lactuca sativa Test. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 2531–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelini, V.A.; Orejas, J.; Medina, M.I.; Agostini, E. Scale up of 2,4-Dichlorophenol Removal from Aqueous Solutions Using Brassica napus Hairy Roots. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Geng, S.; Jiao, W.; Liu, Y. Deep Oxidation Degradation of Aniline Wastewater by O3/Fe(Ⅱ) Process Enhanced Using High-Gravity Technology. Chin. J. Energetic Mater. 2018, 26, 448–454. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.Z.; Chen, F.L.; Mu, S.Y.; Zhang, D.Y.; Pan, X.L.; Lee, D.J. Simultaneous Analysis of Photosystem Responses of Microcystis aeruginoga under Chromium Stress. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 88, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.W.; Jiang, X.H.; Li, K.; Wu, M.; Zhang, R.F.; Zhang, L.; Chen, G.X. Photosynthetic Responses of Oryza sativa L. Seedlings to Cadmium Stress: Physiological, Biochemical and Ultrastructural Analyses. BioMetals 2014, 27, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthasarathy, M.; Pemaiah, B.; Natesan, R.; Padmavathy, S.R.; Pachiappan, J. Real-Time Mapping of Salt Glands on the Leaf Surface of Cynodon dactylon L. Using Scanning Electrochemical Microscopy. Bioelectrochemistry 2015, 101, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoski, C.G. Review-Advances in Scanning Electrochemical Microscopy (SECM). J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 163, 3088–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciutto, G.; Zangheri, M.; Prati, S.; Guardigli, M.; Mirasoli, M.; Mazzeo, R.; Roda, A. Immunochemical Micro Imaging Analyses for the Detection of Proteins in Artworks. Top. Curr. Chem. 2016, 374, 32–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junjie, Z.; Tong, Z.; Jinxin, L.; Wenxuan, F.; Fei, L. Recent Advances of Scanning Electrochemical Microscopy and Scanning Ion Conductance Microscopy for Single-Cell Analysis. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2020, 22, 178–185. [Google Scholar]
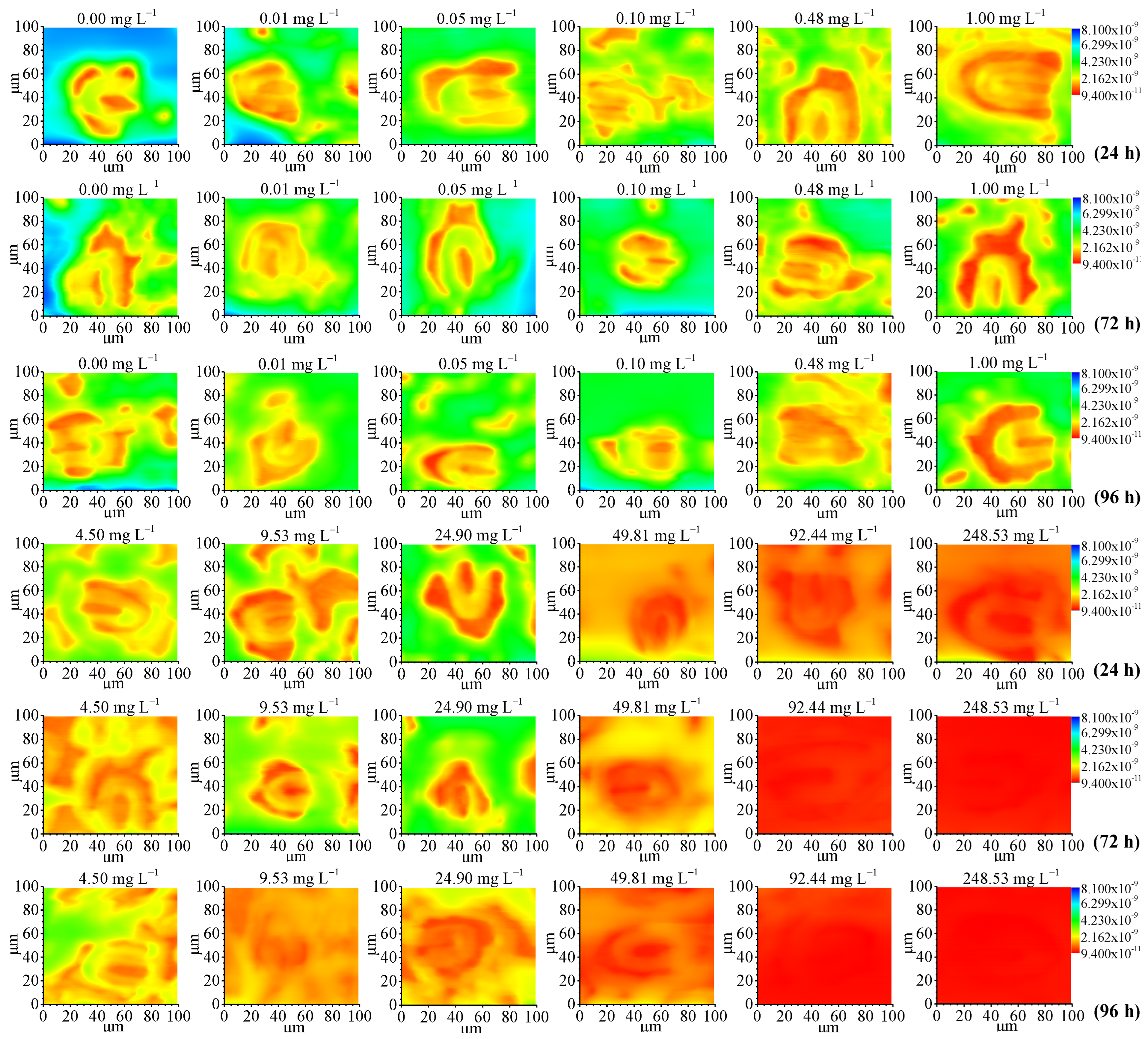
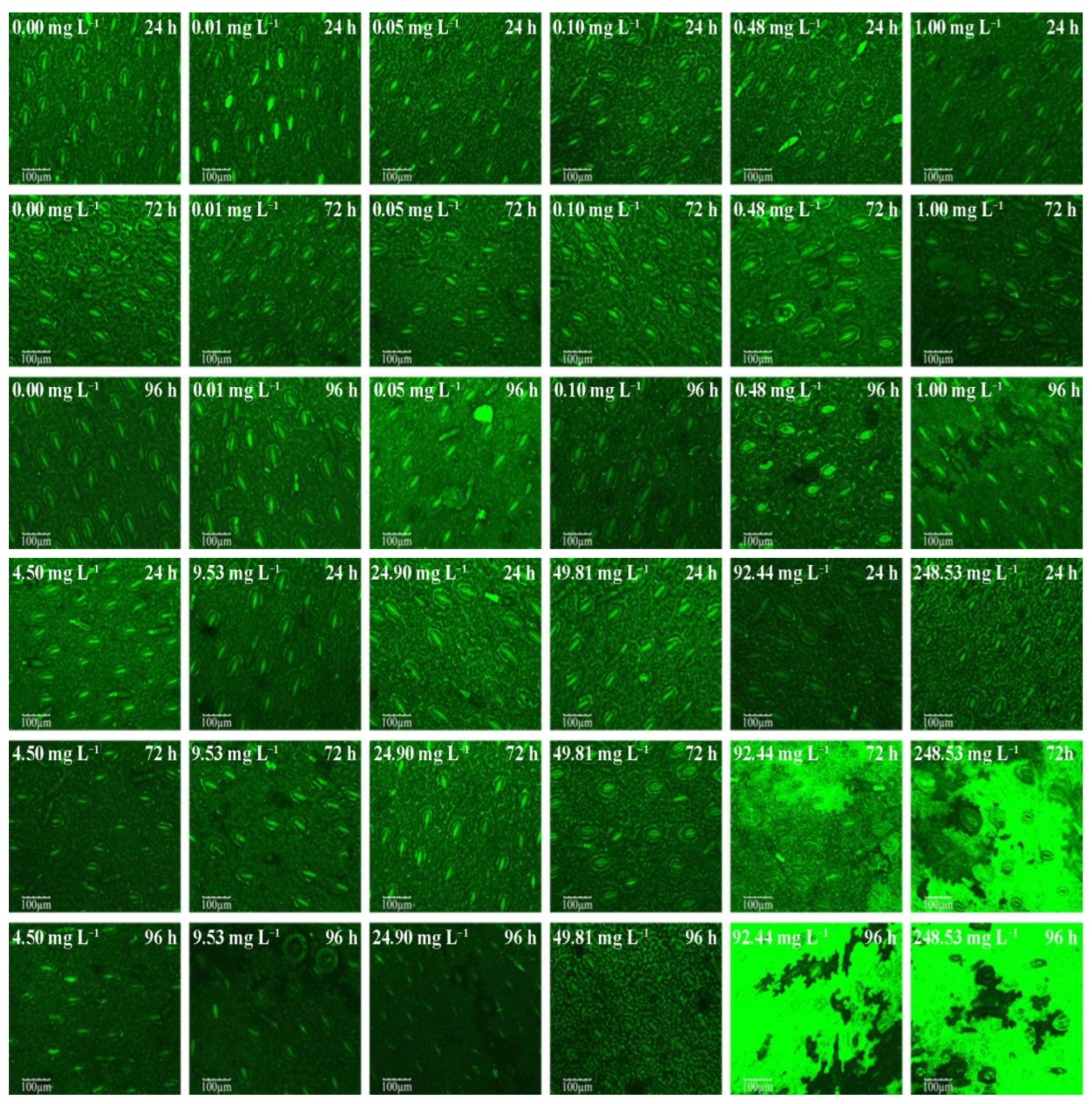
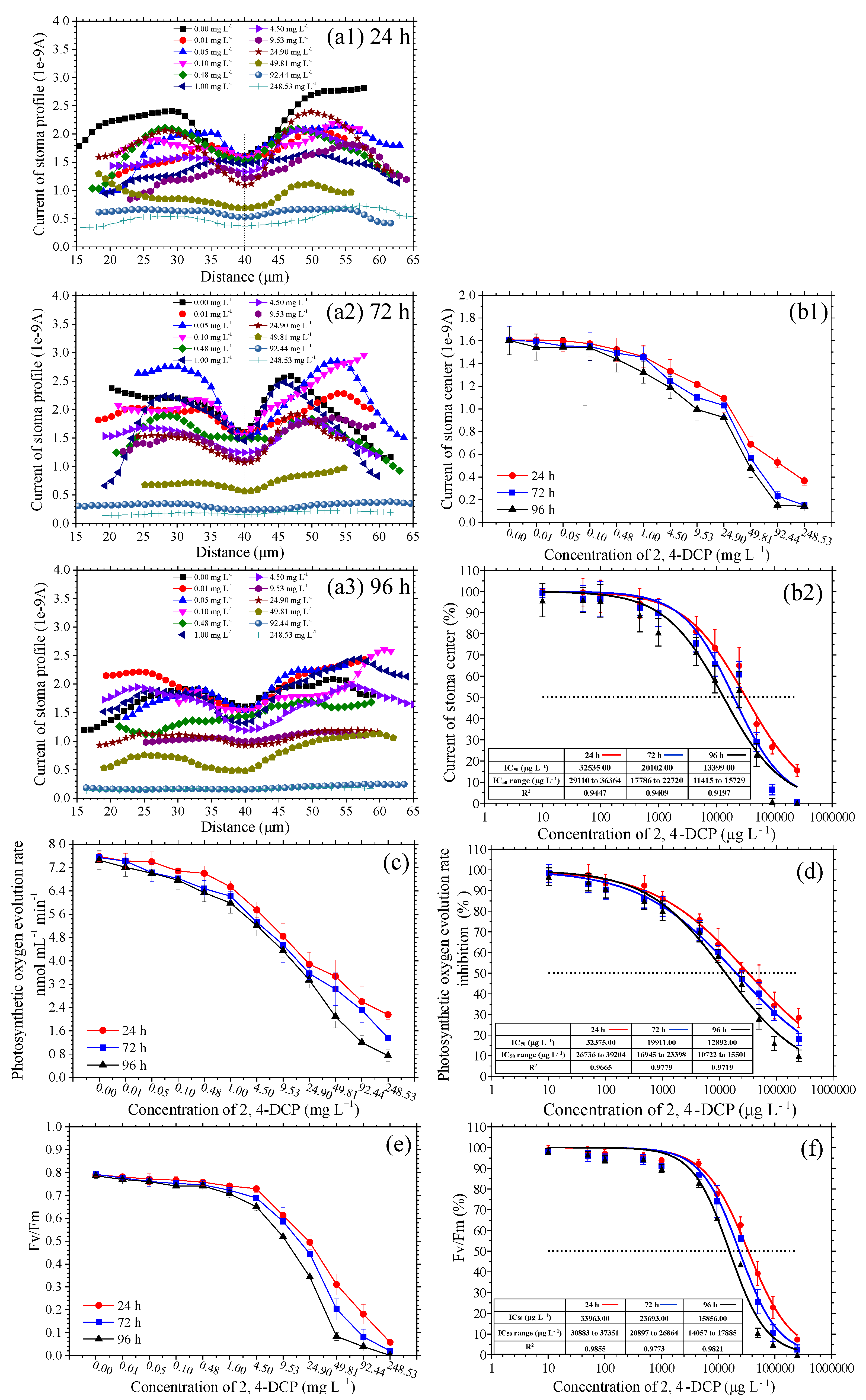
| Time | Fv/Fm (by Dual-PAM-100) | Stomatal Center Current Value (by SECM) | Photosynthetic Oxygen Evolution Rate (by Oxygraph) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24 h | IC50 (μg L−1) | 33,963 | 32,535 | 32,375 |
| IC50 range (μg −1) | 30,883 to 37,351 | 29,110 to 36,364 | 26,736 to 39,204 | |
| R2 | 0.9855 | 0.9447 | 0.9665 | |
| 72 h | IC50 (μg L−1) | 23,693 | 20,102 | 19,911 |
| IC50 range (μg L−1) | 20,897 to 26,864 | 17,786 to 22,720 | 16,945 to 23,398 | |
| R2 | 0.9773 | 0.9409 | 0.9779 | |
| 96 h | IC50 (μg L−1) | 15,856 | 13,399 | 12,892 |
| IC50 range (μg L−1) | 14,057 to 17,885 | 11,415 to 15,729 | 10,722 to 15,501 | |
| R2 | 0.9821 | 0.9197 | 0.9719 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhong, N.; Zhang, D. Ecotoxicity of 2,4-Dichlorophenol to Microsorium pteropus by High Spatial Resolution Mapping of Stoma Oxygen Emission. Water 2024, 16, 1146. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16081146
Zhong N, Zhang D. Ecotoxicity of 2,4-Dichlorophenol to Microsorium pteropus by High Spatial Resolution Mapping of Stoma Oxygen Emission. Water. 2024; 16(8):1146. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16081146
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhong, Ning, and Daoyong Zhang. 2024. "Ecotoxicity of 2,4-Dichlorophenol to Microsorium pteropus by High Spatial Resolution Mapping of Stoma Oxygen Emission" Water 16, no. 8: 1146. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16081146
APA StyleZhong, N., & Zhang, D. (2024). Ecotoxicity of 2,4-Dichlorophenol to Microsorium pteropus by High Spatial Resolution Mapping of Stoma Oxygen Emission. Water, 16(8), 1146. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16081146






