Abstract
Modern humans are mineral deficient; thus, considerable attention has been focused on vitamins and polyphenols taken in supplements. However, in the case of minerals, only a few are known, such as calcium, zinc, and iron. As minerals are essential for proper physiologic function, mineral deficiencies are a risk factor for various serious diseases. For a variety of reasons, it has become difficult in recent years for humans to ingest the required amounts of minerals through diet alone, creating the need for a means of easy mineral replenishment. In this study, we measured changes in various physiologic parameters when 36 healthy individuals drank one bottle (550 mL) of water per day for one month containing minerals extracted from deep-sea water and adjusted to a hardness of 300. Although there were no changes in body weight or body mass index, body fat percentage decreased significantly, and basal metabolic rate and muscle mass increased significantly. Although the mechanism behind these changes is unknown, continuous intake of water amended with minerals extracted from deep-sea water may be an excellent approach to replenishing essential minerals.
1. Introduction
Humans obtain required minerals from their diet. For example, adult males aged in their 20s require 3000 mg potassium, 800 mg calcium, and 340 mg magnesium per day [1]. Most minerals are obtained from vegetables, but minerals are also obtained indirectly through the consumption of meat and fish. It is said that there are more than 100 types of minerals in nature, and those that provide nutrients to living organisms in various forms are called essential minerals [2]. Sixteen types of essential minerals have been described, and reportedly constitute 5% of the minerals in the body other than oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen [3,4]. For a variety of reasons, however, people of all ages no longer take in sufficient amounts of minerals. As mineral deficiencies are a risk factor for various diseases, this issue is of public health concern [5].
Missing minerals can be taken in through a variety of means, including supplements. However, as supplements are expensive, not everyone can afford them. Mineral water is an easy way to ingest minerals. More than 100 types of mineral water are sold in Japan, but all of them are classified as soft water [6]. Generally, hardness is calculated from the amount of magnesium and calcium, but since mineral water in Japan is soft, it is difficult to claim that it is rich in minerals [7,8]. Isotonic drinks are another means of obtaining minerals. Although these drinks are popular as a mineral supplement after intense exercise, sodium represents >90% of the minerals in isotonic drinks [9]. In addition, these drinks are high in sugar, which precludes their use as a daily mineral supplement.
Our research focused on the use of deep-sea water (DSW) as a means of addressing mineral deficiencies. DSW is pumped from a depth of at least 200 m, and it is used not only as drinking water but also for various industrial purposes [10,11]. DSW is characterized by high purity, low temperature (the surface water temperature is typically about 15–30 °C, but the temperature of DSW at the intake depth is constant at 10 °C throughout the year), and high content of minerals, such as potassium, calcium, and magnesium [11,12,13]. In our previous study, we found that when mice were given water that had been adjusted to a hardness of 300 by adding minerals extracted from DSW, their cognitive function in the Morris water maze test significantly improved [14]. Previous component analyses have shown that minerals extracted from DSW are high in magnesium [14]. Why water supplemented with minerals extracted from DSW has exhibited beneficial effects in past studies remains unclear. However, this water does not contain sugar or artificially synthesized substances. Previous studies conducted by other researchers have reported that ingesting minerals extracted from DSW affects the intestinal flora [10], hyperlipemia [15] and exercise training [16]. Therefore, it is strongly believed that consuming water with concentrated minerals extracted from DSW has a variety of beneficial health effects. However, there is still very little experimental data on chronic administration in humans, including basic data on body composition. In the present study, participants drank water containing minerals extracted from DSW that had been adjusted to a hardness of 300, equivalent to one plastic bottle (550 mL) every day for one month. At that time, various indicators were measured, such as body weight and body mass index (BMI), and the beneficial effects of consuming water with minerals extracted from DSW were investigated further.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement and Research Subjects
The experimental protocol was approved by the Ethical Committee of the Shibaura Institute of Technology and conducted per their guidelines (approval number: 21-05, 30 September 2021) and according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and the Ethical Guidelines for Medical and Health Research Involving Human Subjects (Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare Japan). Healthy males and females (10–47 years old) were enrolled in this study (Figure 1). The gender breakdown was 20 males and 16 females. Participants were excluded from the study if they were already taking medications such as antihypertensive drugs or taking mineral supplements. The experiment was conducted three times: the first group from early October 2021 to mid-November 2021 (n = 14), the second group from mid-February 2022 to the end of March 2022 (n = 12), and the third group from early January 2023 to the end of February 2023 (n = 10).
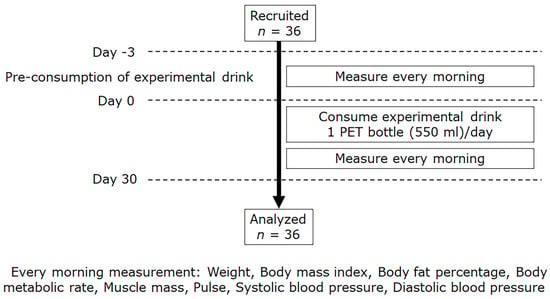
Figure 1.
Flow chart of the experimental design.
2.2. Experimental Design
Prior to the start of the experiment, each participant was supplied with experimental drinks, a body composition analyzer (BC-767, TANITA Corp., Tokyo, Japan), and a sphygmomanometer (BP-213, TANITA Corp.). Each participant drank one plastic bottle (550 mL) of the experimental drink each day for a total of 30 days. Participants were not required to finish the experimental beverage in one sitting, and they were free to decide when to drink it during the day.
To verify the effects of the experimental drink, various physiologic parameters were measured for three days before the start of the experiment. These parameters were measured once per day. To obtain stable values, each measurement was performed within 30 min after waking and before breakfast. In addition, participants were asked to urinate before the measurement. The following parameters were measured: weight, BMI, body fat percentage, body metabolic rate, muscle mass, pulse, systolic blood pressure, and diastolic blood pressure. The hardness of the beverage used in this experiment was 300. Water with a hardness of 300 differs markedly from tap water and natural water in Japan, where soft water is typical. It was not possible to set up a placebo group for this study because tasting the product would immediately enable the participant to know the water was hard.
2.3. Experimental Drink
The DSW extract-supplemented water with a hardness of 300 was provided by Dydo-Takenaka Beverage Co., Ltd. DSW was obtained from the Muroto Deep-Sea Water Aqua Farm operated by Muroto-City (Kochi, Japan); the DSW was collected offshore of Cape Muroto in Kochi Prefecture (depth: approximately 350 m; length of water intake pipe from land: approximately 3000 m) [11]. The DSW was concentrated using a filter membrane (details unknown due to trade secrets), and the resulting extract was diluted with filtered tap water to create DSW extract-supplemented water (hardness 300). Results of analyses of the dissolved elements in the experimental water are available in a previous report [14].
2.4. Statistical Analysis
The ratios of physical characteristics before and after consumption of the experimental drink were compared using the Wilcoxon single-rank sum test. Two types of calculations were performed: statistical processing using actual values, and calculation of the before and after ratios by statistical processing. Values are expressed as the means ± SE. Differences between means were significant at p < 0.05. All statistical analyses were carried out using GraphPad Prism software (ver.9.2.0, GraphPad Software LLC., San Diego, CA, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Continuous Intake of DSW-Derived Minerals Significantly Reduced Body Fat Percentage, Accelerated Metabolism, and Increased Muscle Mass, although Body Weight Was Not Affected
Each day for one month, 36 participants consumed water amended with minerals extracted from DSW with a hardness of 300. The results of the daily measurements are shown in Table 1. There was no difference in body weight or BMI before and after the study period, but body fat percentage, basal metabolic rate, and muscle mass were significantly different compared with the pre-consumption period. Considering the results based on participant sex, basal metabolic rate and muscle mass were significantly increased in males.

Table 1.
Values of body composition indices before and after the DSW-supplemented water regimen.
3.2. Continuous Intake of Minerals Derived from DSW Had No Effect on Blood Pressure but Significantly Increased Pulse Rate
Blood pressure and pulse rate were also measured at the same time as other daily measurements using a body composition monitor (Table 2). At the end of the 30-day study period, no changes were observed in systolic or diastolic blood pressure, but pulse rate was significantly increased in both males and females.

Table 2.
Blood pressure and pulse rate before and after the DSW-supplemented water regimen.
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect on Humans of Continuous Intake of Minerals Extracted from DSW
There have been several reports of human consumption of water supplemented with minerals extracted from DSW, with scientific evidence showing various benefits, including enhanced exercise training and reduced risk of cardiovascular disease [12,17]. The present study examined the effects of daily consumption (550 mL per day) for one month of water supplemented with minerals extracted from DSW and adjusted to a hardness of 300. The hardness was set at 300 because previous studies using mice found that a hardness of 300 yielded better data than water with a hardness of 200 or 500 [14]. The hardness was also set at 300 because if it exceeded 300, many participants would likely quit the study because the taste would be too harsh, or they would not be able to drink it unless it was diluted. A total of 36 individuals participated in the present study, and except for a technical issue which meant data could not be used due to a measurement error, no participants left the study. Unfortunately, even at a hardness of 300, the taste of the water clearly differed from that of regular tap water (which has a standard hardness of ~50), so we were unable to set up a placebo group.
After drinking the test water for one month, no changes in the study participants’ weight or BMI were observed, but their body fat percentage decreased significantly, and their basal metabolic rate and muscle mass increased significantly. Participants made no changes to their life routines except for drinking the experimental water. In addition, there was no change in blood pressure, but pulse rate increased significantly. There are some reports that the continued consumption of beverages can reduce body fat percentage. Aizawa et al. [18] showed that 10 weeks of administration of theaflavin significantly reduced body fat percentage by 5%. Another study reported that three months of coffee consumption in young adults reduced body fat by 7.98% [19]. However, most of these studies are related to polyphenols. The administration period is also much longer than ours. Coffee and green tea contain caffeine and have a bitter taste, so not everyone can drink them. On the other hand, our DSW is made of water, so it has the advantage that anyone can drink it easily. These results strongly suggest that continuous consumption of water supplemented with minerals extracted from DSW has beneficial effects in humans.
4.2. Which Components of the Minerals Extracted from DSW Are Related to These Results?
Our previous research showed that a large amount of magnesium is contained in water adjusted to a hardness of 300 by redissolving minerals extracted from DSW [14]. Natural mineral water is usually collected as spring water from mountain snowmelt that sinks underground. Therefore, these waters contain large amounts of calcium. Interestingly, when we investigated the composition of commercially available natural mineral water products, which have almost the same hardness as the water used in this experiment, we found that the ratio of magnesium to calcium was 1:3. Natural mineral waters of other hardness levels contain 3 to 5 times more calcium than magnesium. This was the opposite of the water used in the present study (magnesium: calcium = 3:1). Although the water used in this present study contained a relatively high amount of magnesium, study participants did not report any health problems, such as diarrhea. This suggests that magnesium contained in minerals extracted from DSW may have impacted the results.
Several studies have examined the effects of magnesium deficiency on living organisms. Killilea et al. reported that magnesium deficiency accelerated cellular senescence of cultured human fibroblasts [20]. Magnesium deficiency is also associated with exercise-induced muscle damage and inflammation through increased production of pro-inflammatory cytokines [21,22]. It is unclear whether the daily intake of magnesium was insufficient in the participants of the present study. However, the observations that the basal metabolic rate increased, muscle mass increased, and body fat percentage decreased suggest that magnesium intake affected the results. Of course, the experimental water used in this study contained a large amount of potassium in addition to other trace elements, albeit in smaller amounts, so it is possible that these had an effect as well. To fully elucidate the mechanism by which water supplemented with minerals extracted from DSW exerts its effects, it will be necessary to feed mice a magnesium-deficient or magnesium-supplemented diet and examine the effects in detail.
4.3. Significance of Continuous Intake of Water Supplemented with Minerals Extracted from DSW
Our experimental results revealed that continuous intake of water supplemented with minerals extracted from DSW may have beneficial effects in humans. Of course, as seawater is mineral-concentrated, it also contains sodium. However, the water used in the present study was 15 to 20 times more concentrated in terms of potassium and magnesium, but only 4 times more concentrated in terms of sodium [14]. In another experiment, mice were given the same water for two months, and blood was collected after the administration period for measurement of sodium ion concentration in the serum, but no significant increase was observed. Based on this result, it is thought that continuous consumption of the experimental water used in this study would not lead to excessive salt intake. (Of course, in the future, it will be necessary to measure sodium ion concentrations in human blood and urine.) Although concentrated, the total intake of minerals from the water used in this study was not high. In Japan, the recommended intake of magnesium for people in their 20s is 340 mg, but with the water used in this experiment, their intake would only be 34 mg per day (bottle) [1]. In other words, it is not possible to ingest a day’s worth of minerals by consuming one bottle of this experimental water. After all, the experimental water would be replenishing what is absent in the daily diet. Therefore, this would not be likely to lead to an overdose any more than could occur with supplements
5. Conclusions
Our current study revealed that continuous intake of water supplemented with minerals extracted from DSW significantly lowers body fat percentage and significantly increases basal metabolic rate and muscle mass. Although minerals are essential for survival, many unknowns remain regarding their effects as well as their mechanisms of action. It is unclear why there was a gender difference in effectiveness in the present study. However, a clear statistically significant difference was observed, so it will be necessary to continue investigating the benefits and underlying mechanisms of consuming water supplemented with minerals extracted from DSW.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.K. and K.F.; Data curation, S.Y., M.I., Y.K. and K.F.; Formal analysis, K.F.; Investigation, M.K. and K.F.; Resources, N.T. and H.T.; Project administration, M.K. and K.F.; Supervision, K.F.; Writing, review and editing, K.F.; All other contributions to the research, K.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research funding was provided by Dydo-Takenaka Beverage Co., Ltd.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be disclosed individually upon request if necessary.
Conflicts of Interest
N.T. and H.T. are employees of Dydo-Takenaka Beverage Co., Ltd., and prepared the DSW-extract supplemented water (hardness 300). The water used in this study was produced by Dydo-Takenaka Beverage Co., Ltd. for research purposes and is not commercially available. Dydo-Takenaka Beverage Co., Ltd., N.T. and H.T. participated in the conceptualization of this study, but were not involved in the experimentation, data interpretation, writing, or publication of this study at Shibaura Institute of Technology. The other authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose. K.F., S.Y., M.I., Y.K., and M.K. did not receive payment for consultation or expert testimony and do not own stock or stock options from Dydo-Takenaka Beverage Co., Ltd.
References
- Overview of the Dietary Reference Intakes for Japanese. 2020. Available online: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/content/10900000/000862500.pdf (accessed on 20 December 2023).
- Colotti, G.; Ilari, A.; Boffi, A.; Morea, V. Metals and metal derivatives in medicine. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacar, B.; Garcia, A.K.; Anbar, A.D. Evolutionary history of bioessential elements can guide the search for life in the universe. Chembiochem 2021, 22, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoroddu, M.A.; Aaseth, J.; Crisponi, G.; Medici, S.; Peana, M.; Nurchi, V.M. The essential metals for humans: A brief overview. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2019, 195, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, A.; Ortega, R.M. Introduction and executive summary of the supplement, role of milk and dairy products in health and prevention of noncommunicable chronic diseases: A series of systemic reviews. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10 (Suppl. 2), S67–S73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Mineral Water Association of Japan. Changes in per Capita Consumption of Mineral Water. 2020. Available online: https://minekyo.net/relays/download/5/123/2/454/?fle=/fles/libs/454/20210421412161245.pdf (accessed on 21 December 2023).
- Klevay, L.M. Some bottled water may be salubrious. J. Trace. Elem. Med. Biol. 2018, 48, 188–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hori, M.; Shozugawa, K.; Sugimori, K.; Watanabe, Y. A survey of monitoring tap water hardness in Japan and its distribution patterns. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowlands, D.S.; Kopetschny, B.H.; Badenhorst, C.E. The hydrating effects of hypertonic, isotonic and hypotonic sports drinks and waters on central hydration during continuous exercise: A systematic meta-analysis and perspective. Sports Med. 2022, 52, 349–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, H.; Higuchi, K.; Yoshikane, Y.; Takagi, R.; Tokuhiro, S.; Takenaka, K.; Oboshi, W.; Kimura, A.; Islam, J.M.; Kaneko, A.; et al. Drinking refined deep-sea water improves the gut ecosystem with beneficial effects on intestinal health in humans: A randomized double-blind controlles trial. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muroto Deep Seawater. Available online: https://www.kochi-seizou.jp/introduction/index.php?lang=en&mid=34 (accessed on 28 March 2024).
- Nani, S.Z.M.; Majid, F.A.A.; Jaafar, A.B.; Mahdzir, A.; Musa, M.N. Potential health benefits of deep-sea water: A review. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2016, 6520475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.Y.; Lee, C.L. Comparison of the Improvement Effect of Deep Ocean Water with Different Mineral Composition on the High Fat Diet-Induced Blood Lipid and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in a Mouse Model. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Kato, Y.; Takeuchi, N.; Takenaka, H.; Kohno, M. Effect of extract-added water derived from deep-sea water with different hardness on cognitive function, motor ability and serum indexes of obese mice. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshioka, S.; Hamada, A.; Cui, T.; Yokota, J.; Yamamoto, S.; Kusunose, M.; Miyamura, M.; Kyotani, S.; Kaneda, R.; Tsutsui, Y.; et al. Pharmacological activity of deep-sea water: Examination of hyperlipemia prevention and medical treatment effect. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2003, 26, 1152–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.; Tan, Z.; Hua, Y.; Huang, X.; Gao, X.; Wu, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhou, Y. Deep sea water improves exercise and inhibits oxidative stress in a physical fatigue mouse model. Biomed. Rep. 2016, 4, 751–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.L.; Chang, Y.Y.; Chiu, C.H.; Yang, K.T.; Wang, Y.; Fu, S.G.; Chen, Y.C. Cardiovascular protection of deep-seawater drinking water in high-fat/cholesterol fed hamsters. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 1146–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aizawa, T.; Yamamoto, A.; Ueno, T. Effect of theaflavin administration on body weight, fat, and muscle in healthy subjects: A randomized pilot study. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2017, 81, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran-Lev, H.; Cohen, S.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Mazkeret Mayer, E.; Anafy, A.; Yerushalmy-Feler, A.; Lubetzky, R. Effect of coffee and tea consumption on adolescent weight control: An interventional pilot study. Child. Obes. 2023, 19, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Killilea, D.W.; Ames, B.N. Magnesium deficiency accelerates cellular senescence in cultured human fibroblasts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 5768–5773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, F.H. Magnesium deficiency and increased inflammation: Current perspectives. J. Inflamm. Res. 2018, 11, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aragón-Vela, J.; González-Acevedo, O.; Plaza-Diaz, J.; Casuso, R.A.; Huertas, J.R. Physiological Benefits and Performance of Sea Water Ingestion for Athletes in Endurance Events: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).