Effects of Domestic Pollution on European Brook Lamprey Ammocoetes in a Lowland River: Insights from Microbiological Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Microbiological Study of Lamprey Gut Content and Water
2.2.1. Water and Larval Lamprey Sampling
2.2.2. Collection of Gut Content from Lampreys
2.2.3. Estimation of TVC of Microorganisms
2.2.4. Estimation of the IMs Numbers
2.3. European Brook Lamprey Larval Condition
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
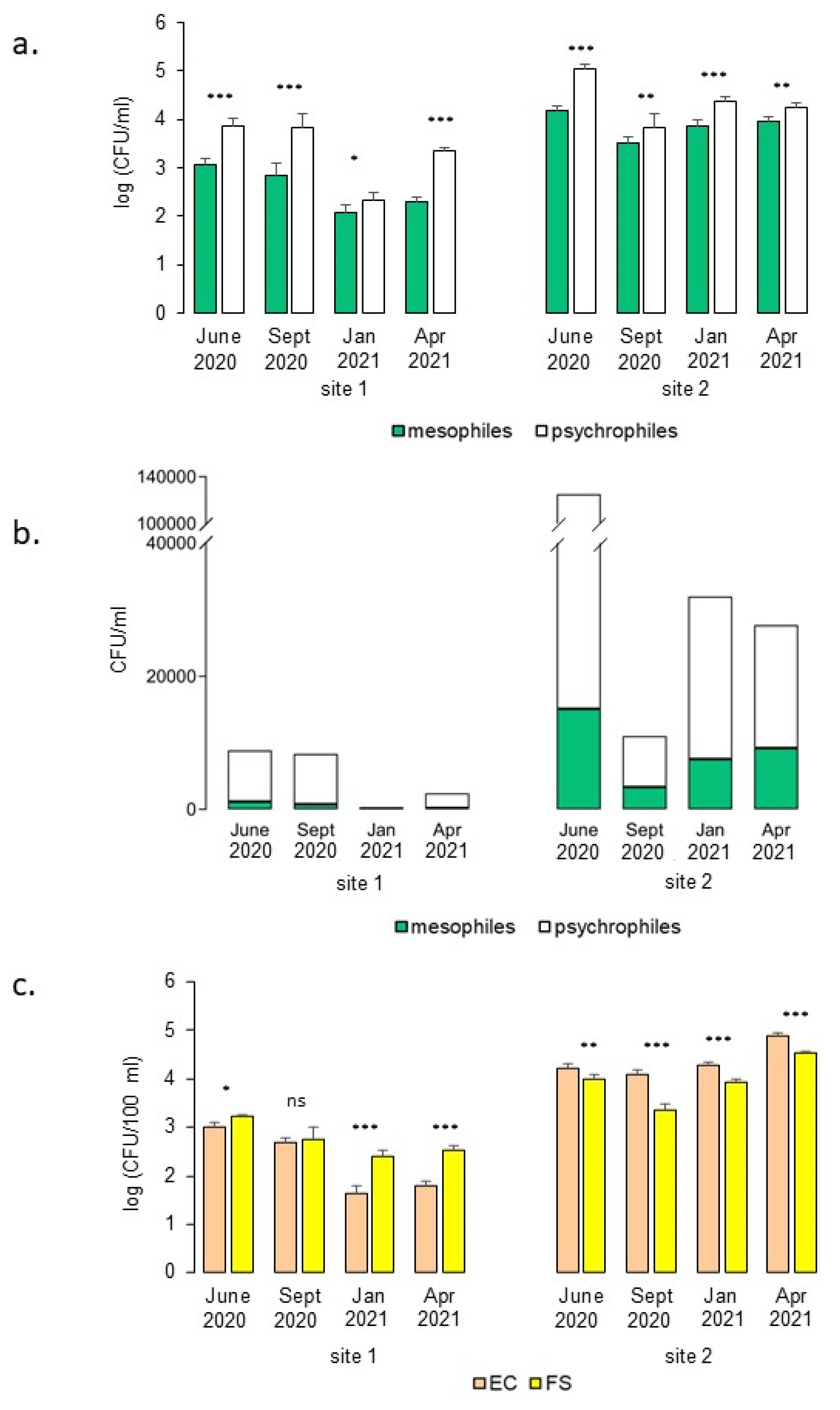
3.1. TVC and IM Estimation in Water
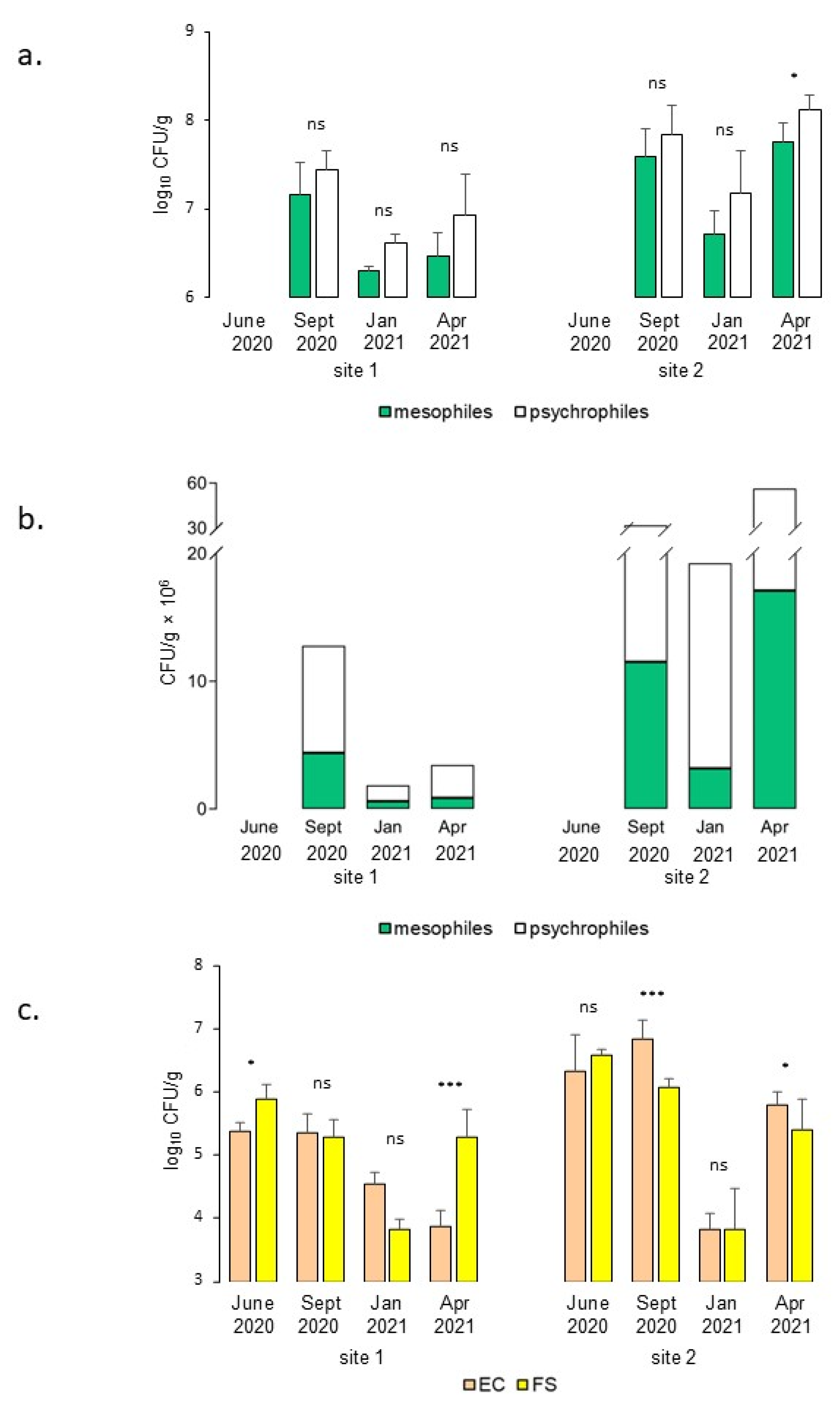
3.2. TVC and IM Estimation in the Midgut Content of Ammocoetes
3.3. Condition of Lamprey Ammocoetes
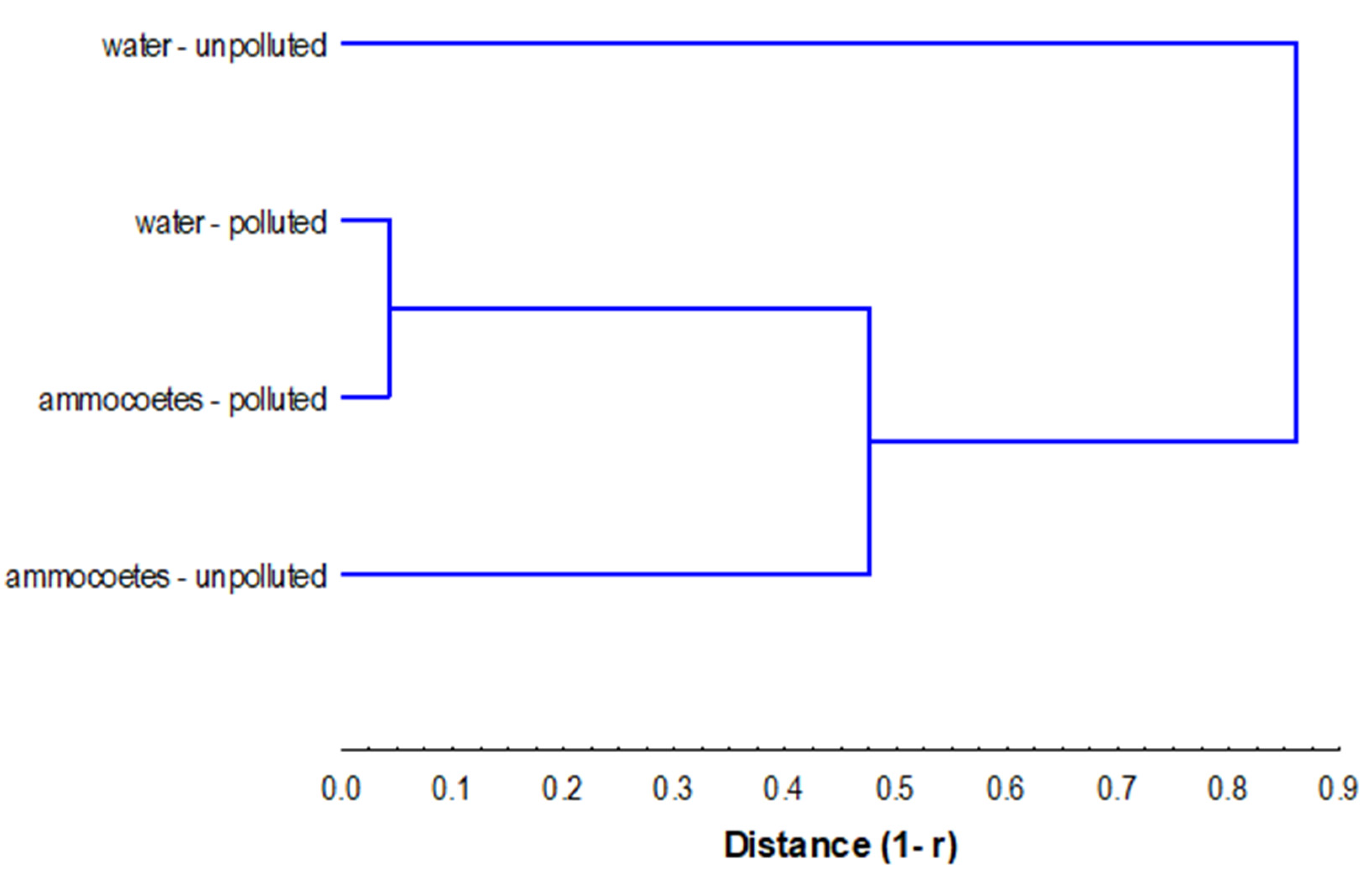
4. Discussion
4.1. Water Microbiological Quality
4.2. TVC and IMs in Lamprey Ammocoete Midgut Content
4.3. Lamprey Condition in Polluted Water
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maitland, P.S. Ecology of the River, Brook and Sea Lamprey; Conserving Natura 2000 Rivers Ecology Series No. 5; The Enquiry Service, English Nature, Northminster House: Peterborough, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, N.S.; Buchinger, T.J.; Li, W. Reproductive ecology of lampreys. In Lampreys: Biology, Conservation and Control; Docker, M.F., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 1, pp. 265–303. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, S.; Gooderham, A.; Forty, M.; Morland, B.; Lucas, M.C. Egg drift and hatching success in European river lamprey Lampetra fluviatilis: Is egg deposition in gravel vital to spawning success. Aquat. Conserv. 2015, 25, 534–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirakawa, H.; Yanai, S.; Goto, A. Lamprey larvae as ecosystem engineers: Physical and geochemical impact on the streambed by their burrowing behavior. Hydrobiologia 2013, 701, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeker, C.; Geist, J. Lampreys as ecosystem engineers: Burrows of Eudontomyzon sp. and their impact on physical, chemical, and microbial properties in freshwater substrates. Hydrobiologia 2016, 777, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeker, C.; Lueders, T.; Mueller, M.; Pander, J.; Geist, J. Alteration of physico-chemical and microbial properties in freshwater substrates by burrowing invertebrates. Limnologica 2016, 59, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, H.A.; Quintella, B.R.; Almeida, P.R.; Treble, A.J.; Jolley, J.C. The ecology of larval and metamorphosing lampreys. In Lampreys: Biology, Conservation and Control; Docker, M.F., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 1, pp. 75–137. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, J.W.; Potter, I.C. A laboratory study on the feeding of larvae of the brook lamprey Lampetra planeri (Bloch). J. Anim. Ecol. 1976, 45, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardisty, M.W. Lampetra planeri (Bloch, 1784). In The Freshwater Fishes of Europe. Petromyzontiformes; Holčík, J., Ed.; AULA-Verlag: Wiesbaden, Germany, 1986; pp. 249–278. [Google Scholar]
- Kottelat, M.; Freyhof, J. Handbook of European Freshwater Fishes; Publications Kottelat: Cornol, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Renaud, C.B. Conservation status of northern hemisphere lampreys (Petromyzontidae). J. Appl. Ichthyol. 1997, 13, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkowski, A.; Kotusz, J.; Przybylski, M. The degree of threat to the freshwater ichthyofauna of Poland: Red list of fishes and lampreys—Situation in 2009. Chrońmy Przyr. Ojczystą 2009, 65, 33–52. [Google Scholar]
- Witkowski, A. Threats and protection of freshwater fishes in Poland. Neth. J. Zool. 1992, 42, 243–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateus, C.S.; Rodríguez-Muñoz, R.; Quintella, B.R.; Alves, M.J.; Almeida, P.R. Lampreys of the Iberian Peninsula: Distribution, population status and conservation. Endanger Species Res. 2012, 16, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateus, C.S.; Beaulaton, L.; Bochechas, J.; Bruxelas, S.; Cobo, F.; Franco, A.; Nachón, D.J.; Quintella, B.R.; Rosa, C.; Rougier, T.; et al. Habitat Recovery and Related Conservation Efforts: 4. Report of the ICES Workshop on Lampreys and Shads; WKLS: Libone, Portugal, 2015; pp. 106–150. Available online: https://hal.inrae.fr/hal-02602615 (accessed on 5 December 2023).
- Marszał, L. Minóg strumieniowy Lampetra planeri. In Monitoring Gatunków Zwierząt. Przewodnik Metodyczny. Część III; Makomaska-Juchiewicz, M., Baran, P., Eds.; GIOŚ: Warszawa, Poland, 2012; pp. 101–117. [Google Scholar]
- Kappus, B.; Janse, W.; Fok, P.; Rahman, H. Threatened lamprey (Lampetra planeri) populations of the Danube Basin within Baden-Wuerttemberg, Germany. Miscnea. Zoo. Hung. 1995, 10, 85–98. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, P.K.; Kass, P.H.; Soupir, M.L.; Biswas, S.; Singh, V.P. Contamination of water resources by pathogenic bacteria. Amb. Express 2014, 4, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, G.; Bharagava, R.N.; Kaithwas, G.; Raj, A. Microbial indicators, pathogens and methods for their monitoring in water environment. J. Water Health 2015, 13, 319–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, R.; Wrzesiński, D. Detecting patterns of changes in river water temperature in Poland. Water 2020, 12, 1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łaszewski, M. Seasonal differentiation of water temperature on the example of lowland Mazovian rivers. Przegląd Geogr. 2020, 92, 391–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiraldi, C.; De Rosa, M. Mesophilic Organisms. In Encyclopedia of Membranes; Drioli, E., Giorno, L., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Ganesh, A. Water quality indicators: Bacteria, coliphages, enteric viruses. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2013, 23, 484–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rompré, A.; Servais, P.; Baudart, J.; de-Roubin, M.R.; Laurent, P. Detection and enumeration of coliforms in drinking water: Current methods and emerging approaches. J. Microbiol. Methods 2002, 49, 31–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoh, A.I.; Sibanda, T.; Gusha, S.S. Inadequately Treated Wastewater as a Source of Human Enteric Viruses in the Environment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 2620–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korajkic, A.; Wanjugi, P.; Brooks, L.; Cao, Y.; Harwood, V.J. Persistence and decay of fecal microbiota in aquatic habitats. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2019, 83, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeBruyn, A.M.; Marcogliese, D.J.; Rasmussen, J.B. The role of sewage in a large river food web. Can. J. Fish Aquat. Sci. 2003, 60, 1332–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcogliese, D.J.; Blaise, C.; Cyr, D.; de Lafontaine, Y.; Fournier, M.; Gagné, F.; Gagnon, C.; Hudon, C. Effects of a major municipal effluent on the St. Lawrence River: A case study. Ambio 2015, 44, 257–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalan, P.; Steinbeck, J.; Otte, F.; Lema, S.C.; White, C. Filter-feeding Pacific Lamprey (Entosphenus tridentatus) ammocetes can reduce suspended concentrations of E. coli Bacteria. Fishes 2023, 8, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geldreich, E.E.; Clarke, N.A. Bacterial pollution indicators in the intestinal tract of freshwater fish. Appl. Microbiol. 1966, 14, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Rio-Rodriguez, R.E.; Inglis, V.; Millar, S.D. Survival of Escherichia coli in the intestine of fish. Aquac. Res. 1997, 28, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 6222:1999; Water quality—Enumeration of culturable micro-organisms—Colony count by inoculation in a nutrient agar culture medium. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1999.
- ISO 9308-1:2014; Water quality—Enumeration of Escherichia coli and coliform bacteria. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014.
- ISO 7899-2:2000; Water quality—Detection and enumeration of intestinal enterococci. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2000.
- Lambooij, B.; Pilarczyk, M.; Bialowas, H.; Reimert, H.; Andre, G.; Van De Vis, H. Anaesthetic properties of Propiscin (Etomidaat) and 2-phenoxyethanol in the common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.), neural and behavioural measures. Aquac. Res. 2009, 40, 1328–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricker, W.E. Computation and interpretation of biological statistics of fish populations. J. Fish Res. Board Can. 1975, 191, 1–382. [Google Scholar]
- Weatherley, A.H. Growth and Ecology of Fish Population; Academic Press: London, UK, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Zar, J.H. Biostatistical Analysis; Pearson Prentice Hall: Upper Sadde River, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Regulation of the Minister of Health on the Supervision of Sater Quality in the Bathing Area and Place Occasionally Used for Bathing. Dz. U. 2019 poz. 255. Available online: https://isap.sejm.gov.pl/isap.nsf/DocDetails.xsp?id=WDU20190000255 (accessed on 5 December 2023).
- Wen, X.; Chen, F.; Lin, Y.; Zhu, H.; Yuan, F.; Kuang, D.; Jia, Z.; Yuan, Z. Microbial indicators and their use for monitoring drinking water quality—A review. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solaiman, S.; Allard, S.M.; Callahan, M.T.; Jiang, C.; Handy, E.; East, C.; Haymaker, J.; Bui, A.; Craddock, H.; Murray, R.; et al. Longitudinal assessment of the dynamics of Escherichia coli, total coliforms, Enterococcus spp., and Aeromonas spp. in alternative irrigation water sources: A CONSERVE study. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e00342-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latosińska, J.; Żek, M. Funkcja turystyczna Spały. In Warsztaty z Geografii Turyzmu; Lodz University Press: Łódź, Poland, 2011; pp. 93–114. [Google Scholar]
- Ruppé, E.; Lixandru, B.; Cojocaru, R.; Büke, Ç.; Paramythiotou, E.; Angebault, C.; Visseaux, C.; Djuikoue, I.; Erdem, E.; Burduniuc, O.; et al. Relative fecal abundance of extend-ed-spectrum-β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli strains and their occurrence in urinary tract infections in women. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother 2013, 57, 4512–4517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, A.B.; Sassoubre, L.M. Enterococci as indicators of environmental fecal contamination. In Enterococci: From Commensals to Leading Causes of Drug Resistant Infection; Gilmore, S., Clewell, D.B., Ike, Y., Shankar, N., Eds.; Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary: Boston, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Edwards, D.R.; Coyne, M.S.; Daniel, T.C.; Vendrell, P.F.; Murdoch, J.F.; Moore, P.A. Indicator bacteria concentrations of two Northwest Arkansas streams in relation to flow and season. Trans. ASABE 1997, 40, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, C.M.; Long, J.A.; Donald, M.; Ashbolt, N.J. Survival of fecal microorganisms in marine and freshwater sediments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 1888–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Armisen, T.; Touron, A.; Petit, F.; Servais, P. Sources of faecal contamination in the Seine estuary (France). Estuaries 2005, 28, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popović, N.T.; Strunjak-Perović, I.; Klobučar, R.S.; Barišić, J.; Babić, S.; Jadan, M.; Kepec, S.; Kazazić, S.P.; Matijatko, V.; Ljubić, B.B.; et al. Impact of treated wastewater on organismic biosensors at various levels of biological organisation. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 538, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cazenave, J.; Bacchetta, C.; Rossi, A.; Ale, A.; Campana, M.; Parma, M.J. Deleterious effects of wastewater on the health status of fish: A field caging study. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 38, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crabill, C.; Donald, R.; Snelling, J.; Foust, R.; Southam, G. The impact of sediment fecal coliform reservoirs on seasonal water quality in Oak Creek, Arizona. Water Res. 1999, 33, 2163–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devane, M.L.; Moriarty, E.; Weaver, L.; Cookson, A.; Gilpin, B. Fecal indicator bacteria from environmental sources: Strategies for identification to improve water quality monitoring. Water Res. 2020, 185, 116204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Docker, M.F. Lampreys: Biology, Conservation and Control; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, J.W.; Mallatt, J.M. Feeding of larval lamprey. Can. J. Fish Aquat. Sci. 1980, 37, 1658–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, B.; Ferron, M.; Cunjak, R.A.; Samways, K. Fruit of the forest-larval sea lamprey Petromyzon marinus are fuelled by allochthonous resources. J. Fish Biol. 2019, 95, 781–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mundahl, N.D.; Erickson, C.; Johnston, M.R.; Sayeed, G.A.; Taubel, S. Diet, feeding rate, and assimilation efficiency of American brook lamprey. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2005, 72, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitland, P.S.; Renaud, C.B.; Quintella, B.R.; Close, D.A.; Docker, M.F. Conservation of native lampreys. In Lampreys: Biology, Conservation and Control; Docker, M.F., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 1, pp. 375–428. [Google Scholar]
- David, L.A.; Maurice, C.F.; Carmody, R.N.; Gootenberg, D.B.; Button, J.E.; Wolfe, B.E.; Ling, A.V.; Devlin, A.S.; Varma, Y.; Fischbach, M.A.; et al. Diet rapidly and reproducibly alters the human gut microbiome. Nature 2014, 505, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, P.A.; Glenn, A.R.; Potter, I.C. The bacterial flora of the gut contents and environment of larval lampreys. Acta Zool. 1980, 61, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetlock, A.; Yost, C.K.; Stavrinides, J.; Manzon, R.G. Changes in the gut microbiome of the sea lamprey during metamorphosis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 7638–7644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Xie, W.; Pang, Y.; Li, T.; Li, Q.; Li, Y. Bacterial community composition in the gut content of Lampetra japonica revealed by 16S rRNA gene pyrosequencing. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hejkal, T.W.; Gerba, C.P.; Henderson, S.; Freeze, M. Bacteriological, virological and chemical evaluation of a wastewater-aquaculture system. Water Res. 1983, 17, 1749–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattal, B.; Dotan, A.; Tchorsh, Y. Rates of experimental microbiological contamination of fish exposed to polluted water. Water Res. 1992, 26, 1621–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, D.; Gupta, C.D. Microbial pollution in water and its effect on fish. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 1992, 4, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán, M.C.; de los Angeles Bistoni, M.; Tamagnini, L.M.; González, R.D. Recovery of Escherichia coli in fresh water fish, Jenynsia multidentata and Bryconamericus iheringi. Water Res. 2004, 38, 2368–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakuta, I. Effect of sewage on blood parameters and the resistance against bacterial infection of goldfish, Carassius auratus. Environ. Toxicol. Water Qual. 1997, 12, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giulio, R.T.; Hinton, D.E. The Toxicology of Fishes; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Giang, P.T.; Burkina, V.; Sakalli, S.; Schmidt-Posthaus, H.; Rasmussen, M.K.; Randak, T.; Grabic, R.; Grabicova, K.; Fedorova, G.; Koba, O.; et al. Effects of multi-component mixtures from sewage treatment plant effluent on common carp (Cyprinus carpio) under fully realistic condition. Environ. Manag. 2019, 63, 466–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hume, J.B.; Bracken, F.S.; Mateus, C.S.; Brant, C.O. Synergising basic and applied scientific approaches to help understand lamprey biology and support management actions. J. Great Lakes Res. 2021, 47, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanel, L.; Andreska, J. Lampreys in Central Europe: History and Present State. In Jawless Fishes of the World; Orlov, A., Beamish, R., Eds.; Cambridge Scholars Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2016; Volume 2, pp. 2–31. [Google Scholar]
- Madenjian, C.P.; Unrein, J.R.; Pedro, S. Trends and biological effects of environmental contaminants in lamprey. J. Great Lakes Res. 2021, 47, 112–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coxon, S.; Harding, J.S.; Gilpin, B. Faecal indicator bacteria in New Zealand freshwater fish: A pilot study. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshwater Res. 2019, 53, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sampling Location | Site 1 (Relatively Unpolluted) | Site 2 (Polluted) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sampling date | 28 September 2020 | 16 January 2021 | 10 April 2021 | 28 September 2020 | 16 January 2021 | 10 April 2021 |
| Water temperature [°C] | 12.8 | 1.4 | 6.1 | 10.9 | 1.5 | 6.5 |
| Dissolved oxygen [mgL−1] | 5.15 | 11.61 | 11.35 | 12.7 | 12.97 | 12.5 |
| Specific conductance [µSL−1] | 304 | 314 | 313 | 291 | 331 | 331 |
| pH | 8.61 | 7.54 | 7.34 | 6.19 | 6.98 | 7.02 |
| Bacteria | Effect | F | df | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| water | TVC | site | 1034.20 | 1, 68 | >0.0001 |
| season | 81.85 | 3, 68 | >0.0001 | ||
| TVC | 300.57 | 1, 68 | >0.0001 | ||
| site × season | 88.91 | 3, 68 | >0.0001 | ||
| site × TVC | 13.27 | 1, 68 | >0.0001 | ||
| season × TVC | 5.94 | 3, 68 | >0.001 | ||
| site × season × TVC | 12.46 | 3, 68 | >0.0001 | ||
| IMs | site | 3510.29 | 1, 80 | >0.0001 | |
| season | 65.59 | 3, 80 | >0.0001 | ||
| IMs | 0.48 | 1, 80 | 0.4921 | ||
| site × season | 212.06 | 3, 80 | >0.0001 | ||
| site × IMs | 228.91 | 1, 80 | >0.0001 | ||
| season × IMs | 23.65 | 3, 80 | >0.0001 | ||
| site × season × IMs | 5.96 | 3, 80 | >0.001 | ||
| ammocoetes | TVC | site | 15.22 | 2, 23 | >0.0001 |
| season | 48.05 | 1, 23 | >0.0001 | ||
| TVC | 7.07 | 1, 23 | 0.0140 | ||
| site × season | 9.24 | 2, 23 | 0.0011 | ||
| site × TVC | 0.53 | 2, 23 | 0.5958 | ||
| season × TVC | 0.27 | 1, 23 | 0.6086 | ||
| site × season × TVC | 0.33 | 2, 23 | 0.7234 | ||
| IMs | site | 114.38 | 1, 31 | >0.0001 | |
| season | 81.93 | 3, 31 | >0.0001 | ||
| IMs | 0.67 | 1, 31 | 0.4203 | ||
| site × season | 5.68 | 3, 31 | 0.0032 | ||
| site × IMs | 13.81 | 1, 31 | 0.0008 | ||
| season × IMs | 17.33 | 3, 31 | >0.0001 | ||
| site × season × IMs | 3.74 | 3, 31 | 0.0210 |
| Location | a | se a | b | se b | r2 | n | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Site 1 | −5.527 | 0.263 | 2.878 | 0.122 | 0.957 | 27 | <0.001 |
| Site 2 | −5.594 | 0.234 | 2.883 | 0.110 | 0.965 | 27 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zięba, G.; Moryl, M.; Drzewiecka, D.; Przybylski, M.; Pyrzanowski, K.; Grabowska, J. Effects of Domestic Pollution on European Brook Lamprey Ammocoetes in a Lowland River: Insights from Microbiological Analysis. Water 2024, 16, 2349. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16162349
Zięba G, Moryl M, Drzewiecka D, Przybylski M, Pyrzanowski K, Grabowska J. Effects of Domestic Pollution on European Brook Lamprey Ammocoetes in a Lowland River: Insights from Microbiological Analysis. Water. 2024; 16(16):2349. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16162349
Chicago/Turabian StyleZięba, Grzegorz, Magdalena Moryl, Dominika Drzewiecka, Mirosław Przybylski, Kacper Pyrzanowski, and Joanna Grabowska. 2024. "Effects of Domestic Pollution on European Brook Lamprey Ammocoetes in a Lowland River: Insights from Microbiological Analysis" Water 16, no. 16: 2349. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16162349
APA StyleZięba, G., Moryl, M., Drzewiecka, D., Przybylski, M., Pyrzanowski, K., & Grabowska, J. (2024). Effects of Domestic Pollution on European Brook Lamprey Ammocoetes in a Lowland River: Insights from Microbiological Analysis. Water, 16(16), 2349. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16162349






