Graywater Treatment Efficiency and Nutrient Removal Using Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR) Systems: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
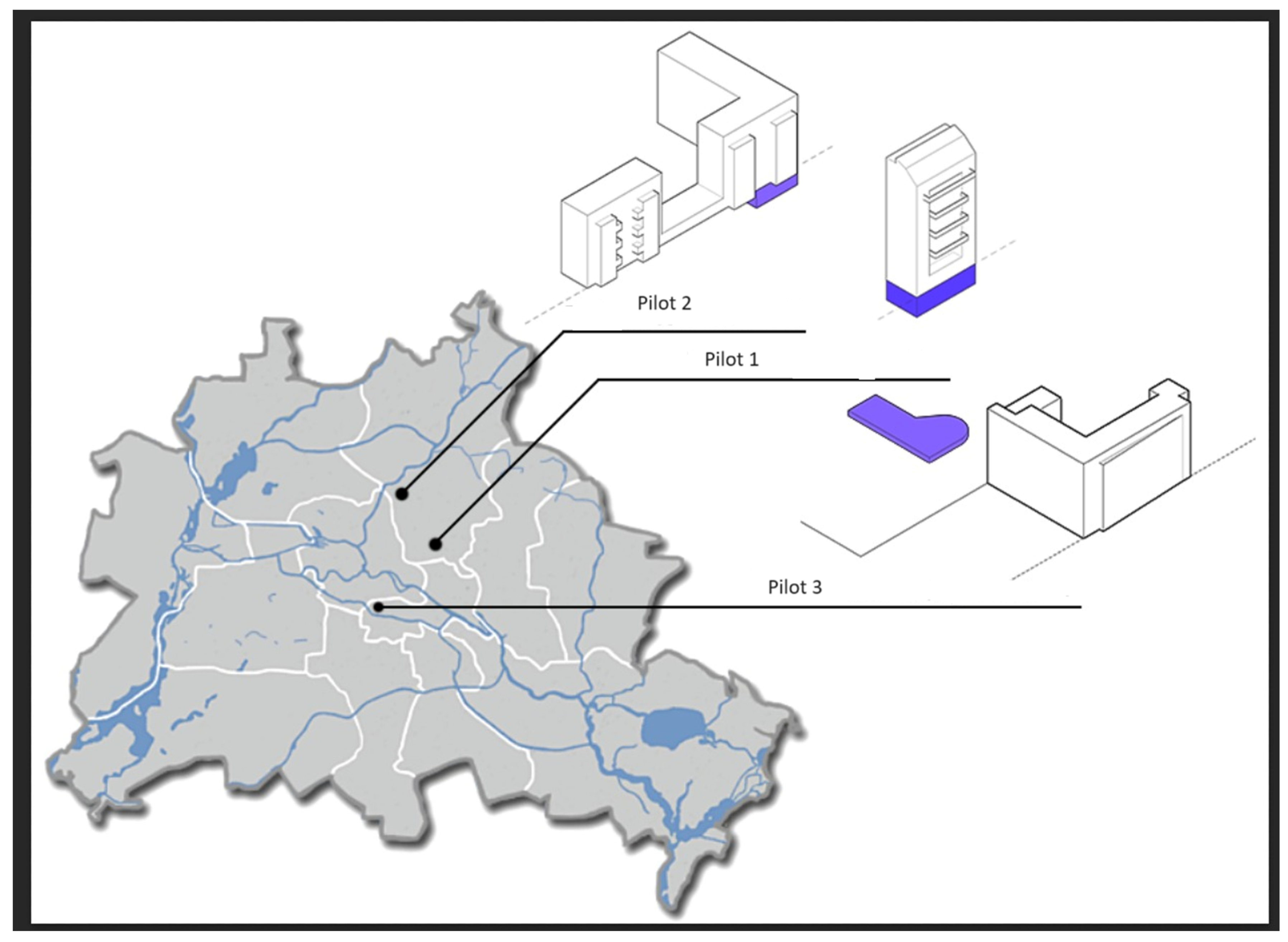
2.1. Description of the Study Area
2.2. General Description of the MBBR Treatment Plant in Case Studies
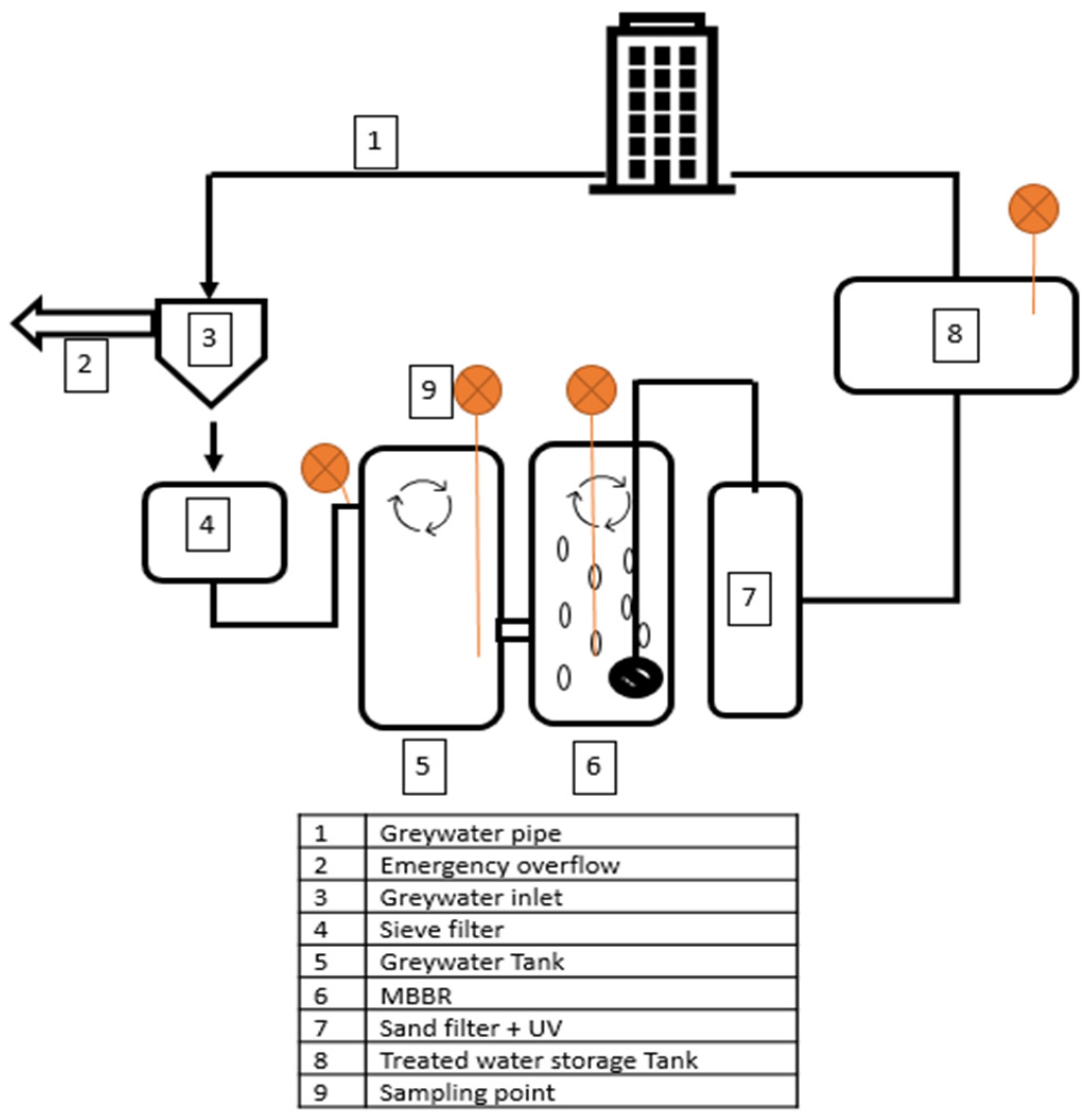
2.2.1. Description of the Treatment Plant in Pilot 1
2.2.2. Description of the Treatment Plant in Pilot 2
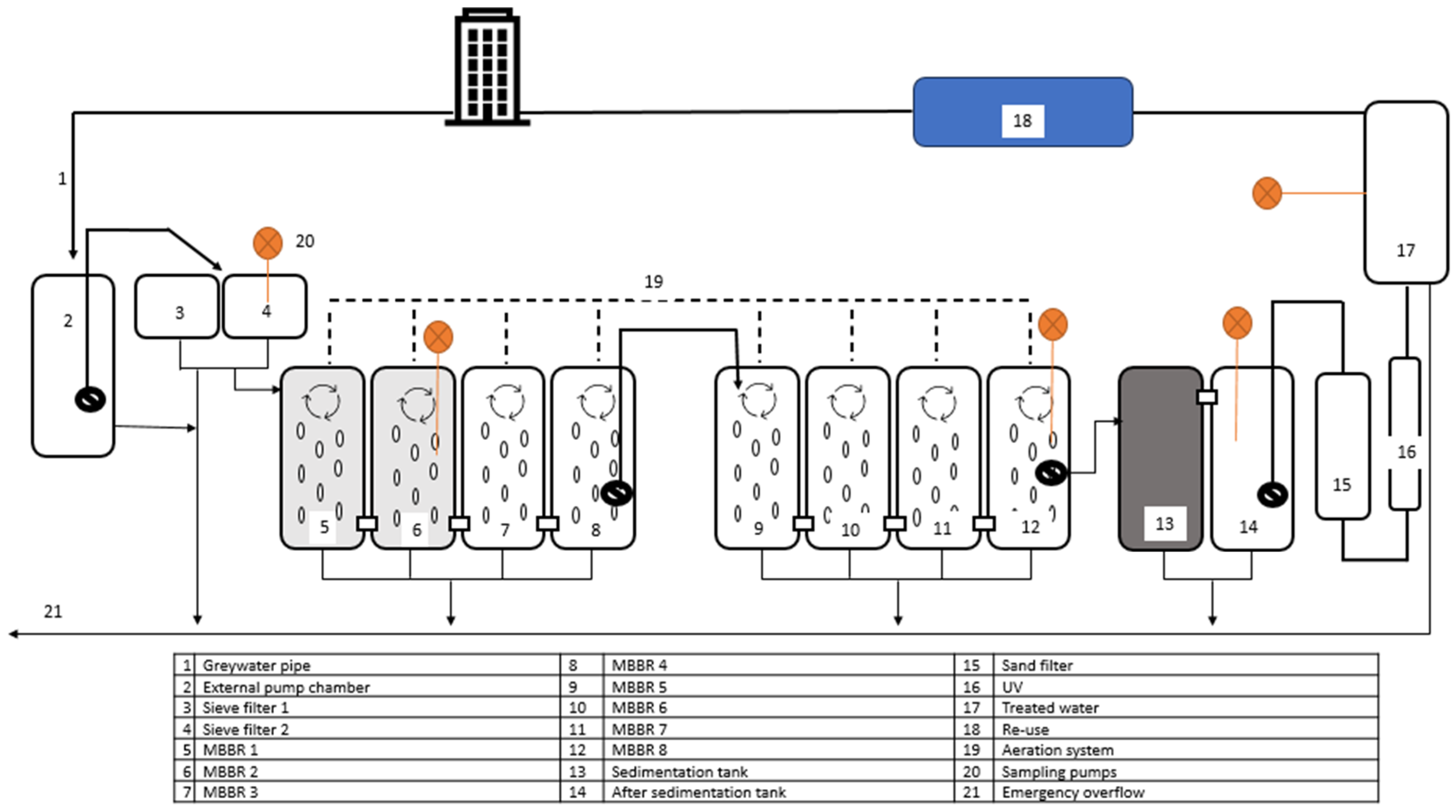
2.2.3. Description of the Treatment Plant in Pilot 3
2.3. Sampling
2.4. Analytical Procedures
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Treatment Plant in Pilot 1
| Criteria | Germany | Australia | Jordan | Spain |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Types of water | Treated graywater | Treated graywater | Treated wastewater | Treated wastewater |
| pH | NR | NR | 6.5–9 | NR |
| Turbidity | <2 NTU | NR | NR | NR |
| TSS | NR | <10 mg/L | <50 mg/L | <10 mg/L |
| BOD5 | <5 mg/L | <10 mg/L | <30 mg/L | NR |
| COD | NR | NR | <100 mg/L | NR |
| E. coli | <10.000/100 mL | NR | <10.000/100 mL | 0/100 mL |
| Parameters/Sample | CODt [mg/L] | CODs. [mg/L] | BOD5 mg/L | TSS 0.45 µm Original [mg/L] | Phosphate/Ortho/ PO43-P [mg/L] | Turbidity [FNU] | Ammonium NH4+-N [mg/L] | Nitrate NO3−-N [mg/L] | Temperature (°C) | Dissolved Oxygen [mg/L] | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Graywater | 122.4 | 76 | 69 | 29.3 | 0.1 | 31.9 | 2.3 | 0.75 | 25.4 | 4.1 | 8 |
| Graywater Tank | 104.3 | 63 | 51.8 | 24.4 | 0.3 | 73.9 | 8.3 | 0.3 | 24.2 | 1.03 | 7.3 |
| MBBR2 | 41.7 | 19.4 | 15.2 | 18.8 | 0.2 | 16.2 | 0.6 | 6.9 | 24.1 | 5.5 | 8.2 |
| Treated water | 19.8 | 17.9 | 3.6 | 0.25 | 0.21 | 1.4 | 0.1 | 7.1 | 22.2 | 6.9 | 7.8 |
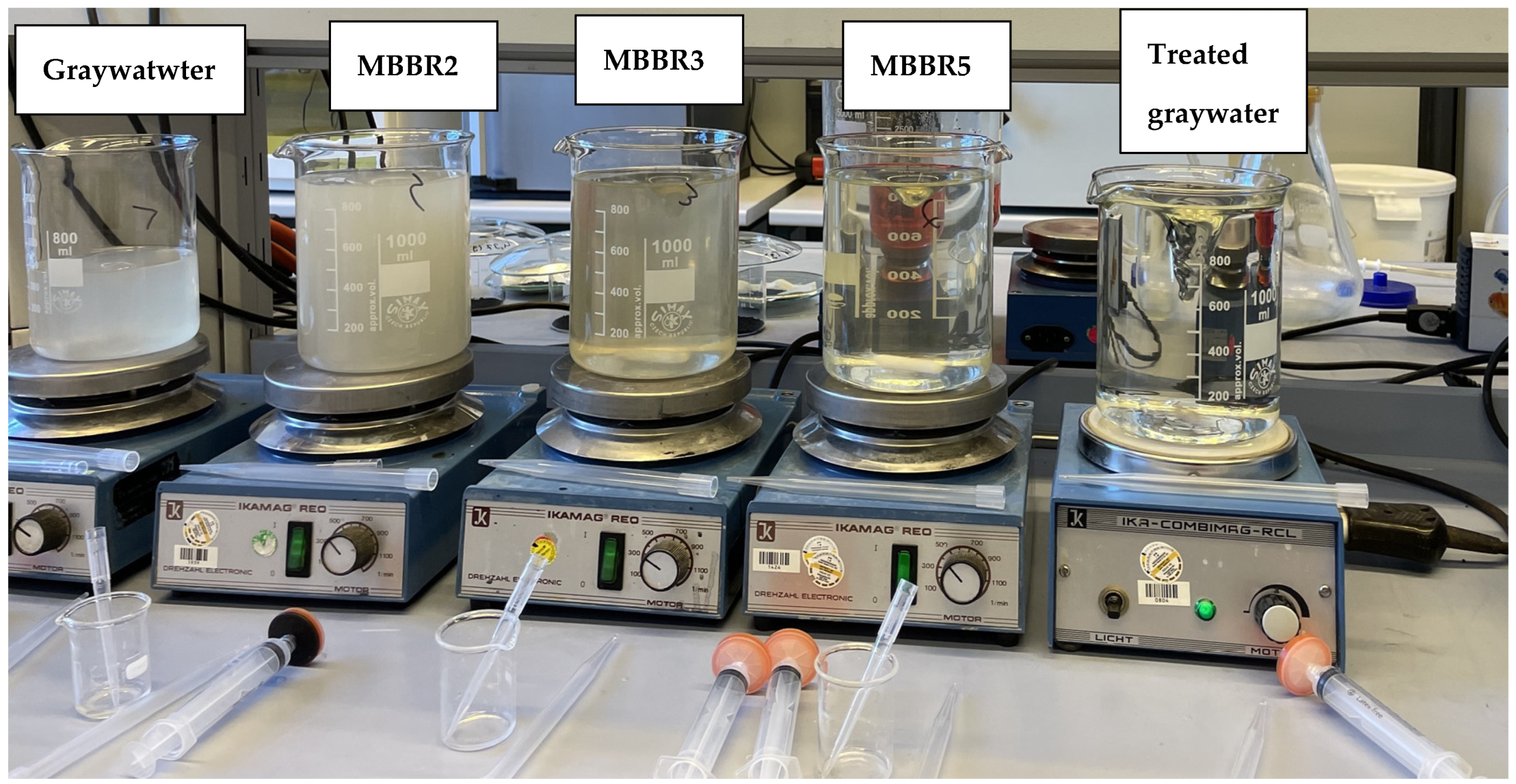
3.2. Treatment Plant in Pilot 2
3.3. Treatment Plant in Pilot 3
4. General Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bogardi, J.J.; Gupta, J.; Nandalal, K.D.W.; Salamé, L.; van Nooijen, R.R.P.; Kumar, N.; Tingsanchali, T.; Bhaduri, A.; Kolechkina, A.G. Handbook of Water Resources Management: Discourses, Concepts and Examples; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; ISBN 978-3-030-60147-8. [Google Scholar]
- Penserini, L.; Moretti, A.; Mainardis, M.; Cantoni, B.; Antonelli, M. Tackling climate change through wastewater reuse in agriculture: A prioritization methodology. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 914, 169862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobsen, M.; Webster, M.; Vairavamoorthy, K. The Future of Water in African Cities: Why Waste Water? World Bank Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; ISBN 978-0-8213-9722-0. [Google Scholar]
- Akpan, V.E. Assessing the public perceptions of treated wastewater reuse: Opportunities and implications for urban communities in developing countries. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holcomb, F.H.; Deliman, P.N.; Ringelberg, D.B. Sustainability-Related Publications Calendar Years 2015–2016; Technical Report; Construction Engineering Research Laboratory (CERL): Champaign, IL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Shaikh, I.N.; Ahammed, M.M. Quantity and quality characteristics of greywater from an Indian household. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delhiraja, K.; Philip, L. Characterization of segregated greywater from Indian households: Part A—Physico-chemical and microbial parameters. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaly, A.; Rahman, E.; Hassanien, R.; Mahmoud, N.; Ibrahim, M.; Mostafa, E.; Kassem, M.; Hatem, M. Overview of Biological Treatment Technologies for Greywater Reuse. Adn. Environ. Waste Manag. Recycl. 2021, 4, 165–191. [Google Scholar]
- Hellman, J. Re-Sourcing Soil Fertility. Available online: https://stud.epsilon.slu.se/15313/ (accessed on 8 February 2024).
- Cecconet, D.; Bolognesi, S.; Piacentini, L.; Callegari, A.; Capodaglio, A. Bioelectrochemical Greywater Treatment for Non-Potable Reuse and Energy Recovery. Water 2021, 13, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.; Santos, C.; Imteaz, M.A.; Matos, C. Hybrid Decentralized Systems of Non-potable Water Supply: Performance and Effectiveness Analysis. Water Resour. Manag. 2023, 37, 3897–3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, G.; Pino, V.; Brambilla, A.; Alonso-Marroquin, F. Staircase Wetlands for the Treatment of Greywater and the Effect of Greywater on Soil Microbes. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drangert, J.-O.; Kjerstadius, H. Recycling—The future urban sink for wastewater and organic waste. City Environ. Interact. 2023, 19, 100104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasciucco, F.; Pecorini, I.; Iannelli, R. Planning the centralization level in wastewater collection and treatment: A review of assessment methods. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 375, 134092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meney, K.A.; Pantelic, L. Decentralized Water and Wastewater Systems for Resilient Societies: A Shift towards a Green Infrastructure-Based Alternate Economy. In The Palgrave Handbook of Climate Resilient Societies; Brears, R.C., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 157–184. ISBN 978-3-030-42461-9. [Google Scholar]
- Schwetschenau, S.E.; Kovankaya, Y.; Elliott, M.A.; Allaire, M.; White, K.D.; Lall, U. Optimizing Scale for Decentralized Wastewater Treatment: A Tool to Address Failing Wastewater Infrastructure in the United States. ACS Environ. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2023, 3, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buller, L.S.; Sganzerla, W.G.; Berni, M.D.; Brignoli, S.C.; Forster-Carneiro, T. Design and techno-economic analysis of a hybrid system for energy supply in a wastewater treatment plant: A decentralized energy strategy. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 305, 114389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albalawneh, A.; Perilli, N. The Efficiency of Natural Decentralized Greywater Treatment Systems in Resolving the Wastewater Problems in the Rural Areas of Developing Countries. In Recent Advances in Environmental Science from the Euro-Mediterranean and Surrounding Regions, 2nd ed.; Ksibi, M., Ghorbal, A., Chakraborty, S., Chaminé, H.I., Barbieri, M., Guerriero, G., Hentati, O., Negm, A., Lehmann, A., Römbke, J., et al., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 147–151. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez, C.; Sánchez, R.; Rebolledo, N.; Schneider, N.; Serrano, J.; Leiva, E. Cost–Benefit Evaluation of Decentralized Greywater Reuse Systems in Rural Public Schools in Chile. Water 2020, 12, 3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, A.; Gandhi, K.; Rayalu, S. Greywater treatment technologies: A comprehensive review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 21, 1053–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greywater Reuse as a Key Enabler for Improving Urban Wastewater Management—ScienceDirect. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S266649842300042X (accessed on 8 February 2024).
- Aldris, B.; Farhoud, N. Wastewater treatment efficiency of an experimental MBBR system under different influent concentrations. DYSONA-Appl. Sci. 2020, 1, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawan, J.A.; Suja’, F.; Pramanik, S.K.; Yusof, A.; Abdul Rahman, R.; Abu Hasan, H. Effect of Hydraulic Retention Time on the Performance of a Compact Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor for Effluent Polishing of Treated Sewage. Water 2022, 14, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohnungsbestand Steigt Kontinuierlich. Available online: https://www.statistik-berlin-brandenburg.de/142-2022 (accessed on 12 February 2024).
- Saidi, A.; Masmoudi, K.; Nolde, E.; El Amrani, B.; Amraoui, F. Organic matter degradation in a greywater recycling system using a multistage moving bed biofilm reactor (MBBR). Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 76, 3328–3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolde, E. Grey Water Reuse Systems for Toilet Flushing in Multi-Storey Buildings—Over Ten Years Experience in Berlin. Urban Water 2000, 1, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masmoudi Jabri, K.; Nolde, E.; Ciroth, A.; Bousselmi, L. Life cycle assessment of a decentralized greywater treatment alternative for non-potable reuse application. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 17, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievers, J.C.; Londong, J.; Albold, A.; Oldenburg, M.; Lohaus, J. Characterisation of Greywater—Estimation of Design Values. In Proceedings of the 17th International EWA Symposium “WatEnergyResources—Water, Energy and Resources: Innovative Options and Sustainable Solutions” during IFAT, Munich, Germany, 5–9 May 2014; pp. 5–9. [Google Scholar]
- Labrador-Rached, C.J.; Browning, R.T.; Braydich-Stolle, L.K.; Comfort, K.K. Toxicological Implications of Platinum Nanoparticle Exposure: Stimulation of Intracellular Stress, Inflammatory Response, and Akt Signaling In Vitro. J. Toxicol. 2018, 2018, e1367801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DIN EN ISO 5667-1:2019-09; Water Quality—Sampling—Part 1: Guidance on the Design of Sampling Programs and Sampling Techniques (ISO/DIS 5667-1:2019); German and English Version prEN ISO 5667-1:2019. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019.
- Sievers, J.C.; Londong, J. Characterization of domestic graywater and graywater solids. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 77, 1196–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Ngo, H.H.; Nghiem, L.D.; Hai, F.I.; Price, W.E.; Wang, J.; Guo, W. Evaluation of micropollutant removal and fouling reduction in a hybrid moving bed biofilm reactor-membrane bioreactor system. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 191, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recent Technologies for Nutrient Removal and Recovery from Wastewaters: A Review—ScienceDirect. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0045653521007980 (accessed on 15 April 2024).
- Noutsopoulos, C.; Andreadakis, A.; Kouris, N.; Charchousi, D.; Mendrinou, P.; Galani, A.; Mantziaras, I.; Koumaki, E. Greywater characterization and loadings—Physicochemical treatment to promote onsite reuse. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 216, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- fbr-Hinweisblatt H 202|Presse|FBR.de. Available online: https://www.fbr.de/presse/fbr-hinweisblatt-h-202/index.html (accessed on 3 June 2024).
- Filali, H.; Barsan, N.; Souguir, D.; Nedeff, V.; Tomozei, C.; Hachicha, M. Greywater as an Alternative Solution for a Sustainable Management of Water Resources—A Review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enhancing Anaerobic Treatment of Domestic Wastewater: State of the Art, Innovative Technologies and Future Perspectives—ScienceDirect. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S004896971831235X (accessed on 15 April 2024).
- Shi, C.; Yan, B.; Zuo, X.; Wang, C.; Li, Z.; Zhu, L. The effect of aeration mode on the operational effectiveness and membrane bioreactors for greywater treatment and membrane fouling. Environ. Eng. Res. 2022, 28, 210637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajit, K. A Review on Grey Water Treatment and Reuse. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. 2016, 3, 2665–2668. [Google Scholar]
- Oron, G.; Adel, M.; Agmon, V.; Friedler, E.; Halperin, R.; Leshem, E.; Weinberg, D. Greywater use in Israel and worldwide: Standards and prospects. Water Res. 2014, 58, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oteng-Peprah, M.; Acheampong, M.A.; deVries, N.K. Greywater Characteristics, Treatment Systems, Reuse Strategies and User Perception—A Review. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2018, 229, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolde, E.; Partner, N. Greywater Recycling in Buildings. In Water Efficiency in Buildings; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 169–189. ISBN 978-1-118-45661-3. [Google Scholar]
- Ultrafiltration as Tertiary Treatment for Municipal Wastewater Reuse—ScienceDirect. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1383586621006328?casa_token=6FZmF6nW1moAAAAA:MjYdRlTgR7EW01-eI5FTsQR09-Gl7AB-SctNzGjKgbU6fbx1lPIHygVHF6h5Si2LrpjLJfDUZ6Q (accessed on 28 March 2024).
- Zhou, Y.; Li, R.; Guo, B.; Zhang, L.; Zou, X.; Xia, S.; Liu, Y. Greywater treatment using an oxygen-based membrane biofilm reactor: Formation of dynamic multifunctional biofilm for organics and nitrogen removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 386, 123989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albalawneh, A. Review of the greywater and proposed greywater recycling scheme for agricultural irrigation reuses. Int. J. Res. Int. J. Res. Granthaalayah 2015, 3, 16–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Graywater Treatment System | Graywater Characteristics | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerobic MBR (pilot-scale) | Parameter | Feed (mg/L) | Permeate (mg/L) |
| CODt | 99–200 | 15–20 | |
| BOD5 | 40–60 | 3–4 | |
| Ammonia | 21–4 | 0.3–0.5 | |
| Nitrate | 1–7 | 8.5–9.3 | |
| Aerobic membrane sequencing batch reactor (pilot-scale) | CODt | 310 | NR |
| BOD5 | 117 | <5 | |
| Ammonia | 1.9 | 0.2 | |
| Nitrate | 7.6 | NR | |
| SBR + Ultrafiltration (pilot-scale) | CODt | 543 | 37 |
| BOD5 | 212 | 4 | |
| Ammonia | NR | NR | |
| Nitrate | 0.6 | 6.5 | |
| Aerobic MBBR (pilot-scale) | CODt | 246.63 | 23.86 |
| TN | 2.81 | 4.17 | |
| Total P | 6.59 | 0.8 | |
| BOD5 | 44.37 | 2 | |
| Pilot 2 | Storage tank | MBBR2 | MBBR3 | MBBR5 | Treated water storage tank | 02.02.23—17.02.23 |
| Pilot 1 | After the sieve (pipe) | Graywater tank | MBBR2 | Treated water tank | 06.06.23—15.06.23 | |
| Pilot 3 | Sieve 2 | MBBR 2 | MBBR 8 | After sedimentation tank | Treated water storage tank | 01.11.23—14.11.23 |
| Sampling method | 24-h systematic sampling volume proportional | Random sampling | ||||
| average concentration values | Parameters/Sample | CODt [mg/L] | CODs. [mg/L] | BOD5 mg/L | TSS 0.45 µm original [mg/L] | Phosphate/ortho/ PO43-P [mg/L] | Turbidity [FNU] | Ammonium NH4+-N [mg/L] | Nitrate NO3−-N [mg/L] | Temperature (°C) | Dissolved Oxygen [mg/L] | pH |
| Graywater | 359.6 | 243.2 | 126.9 | 80 | 1.1 | 76.5 | 4.1 | 0.5 | 22.6 | 4.1 | 7.6 | |
| MBBR2 | 521.2 | 133.8 | 125.3 | 328.3 | 1.8 | 405.8 | 4.9 | 0.4 | 20.6 | 4.2 | 7.9 | |
| MBBR3 | 480.1 | 107 | 103.5 | 303 | 0.2 | 441.3 | 4.1 | 0.6 | 20.3 | 7.9 | 8.1 | |
| MBBR5 | 420.7 | 86 | 74.1 | 295.5 | 0.1 | 373.2 | 0.1 | 5 | 19.9 | 8.7 | 8.2 | |
| Treated water | 37.2 | 35.1 | 2.1 | 1.7 | 0.2 | 2.3 | <0.01 | 4.6 | 17.3 | 5.6 | 7.9 | |
| Drink Water | 10.2 | 10.8 | 0.7 | <0.01 | 0.1 | 0.5 | <0.01 | 0.9 | 12.2 | 8.3 | 7.3 |
| average concentration values | Parameters/Sample | CODt [mg/L] | CODs. [mg/L] | BOD5 mg/L | TSS 0.45 µm original [mg/L] | Phosphate/ortho/ PO43-P [mg/L] | Turbidity [FNU] | Ammonium NH4+-N [mg/L] | Nitrate NO3−-N [mg/L] | Temperature (°C) | Dissolved Oxygen [mg/L] | pH |
| Graywater | 492.5 | 218 | 248.7 | 167.7 | 0.08 | 126.8 | 5.5 | 0.3 | 22.6 | 4.1 | 7.6 | |
| MBBR2 | 416.2 | 115.4 | 213.5 | 185.2 | 0.261 | 624.8 | 5 | 0.2 | 20 | 0.8 | 9.1 | |
| MBBR8 | 123.8 | 37.9 | 36.4 | 71.7 | 0.6 | 77.5 | 0.1 | 8.0 | 21.1 | 7.6 | 8 | |
| After Sedimentation Tank | 46.7 | 32.2 | 7.2 | 10.3 | 0.5 | 14.8 | <0.01 | 7.9 | 20.9 | 8.3 | 8 | |
| Treated water | 29.1 | 28.5 | 2.7 | 1.1 | 0.6 | 1.5 | <0.01 | 8.1 | 20.7 | 5.4 | 7.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nourredine, H.; Barjenbruch, M. Graywater Treatment Efficiency and Nutrient Removal Using Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR) Systems: A Comprehensive Review. Water 2024, 16, 2330. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16162330
Nourredine H, Barjenbruch M. Graywater Treatment Efficiency and Nutrient Removal Using Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR) Systems: A Comprehensive Review. Water. 2024; 16(16):2330. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16162330
Chicago/Turabian StyleNourredine, Hajar, and Matthias Barjenbruch. 2024. "Graywater Treatment Efficiency and Nutrient Removal Using Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR) Systems: A Comprehensive Review" Water 16, no. 16: 2330. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16162330
APA StyleNourredine, H., & Barjenbruch, M. (2024). Graywater Treatment Efficiency and Nutrient Removal Using Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR) Systems: A Comprehensive Review. Water, 16(16), 2330. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16162330






