Sedimentological, Geochemical, and Environmental Assessment in an Eastern Mediterranean, Stressed Coastal Setting: The Gialova Lagoon, SW Peloponnese, Greece
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
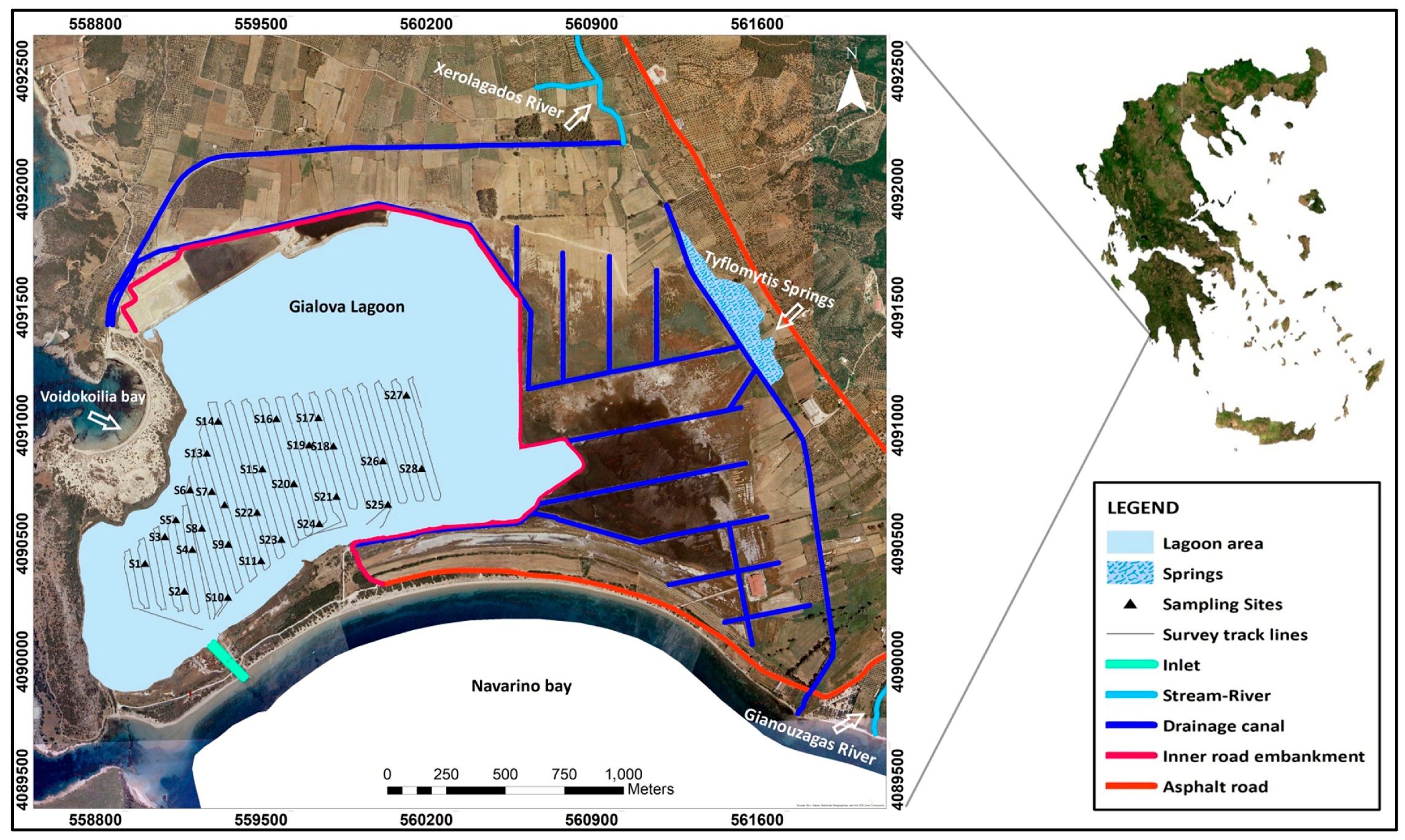
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Fieldwork
2.3. Laboratory Analyses
2.3.1. Sedimentology
2.3.2. Geochemistry
2.3.3. Benthic Foraminifera
2.4. Contamination Assessement
2.5. Statistical Treatment—Hierarchical Clustering and Factor Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
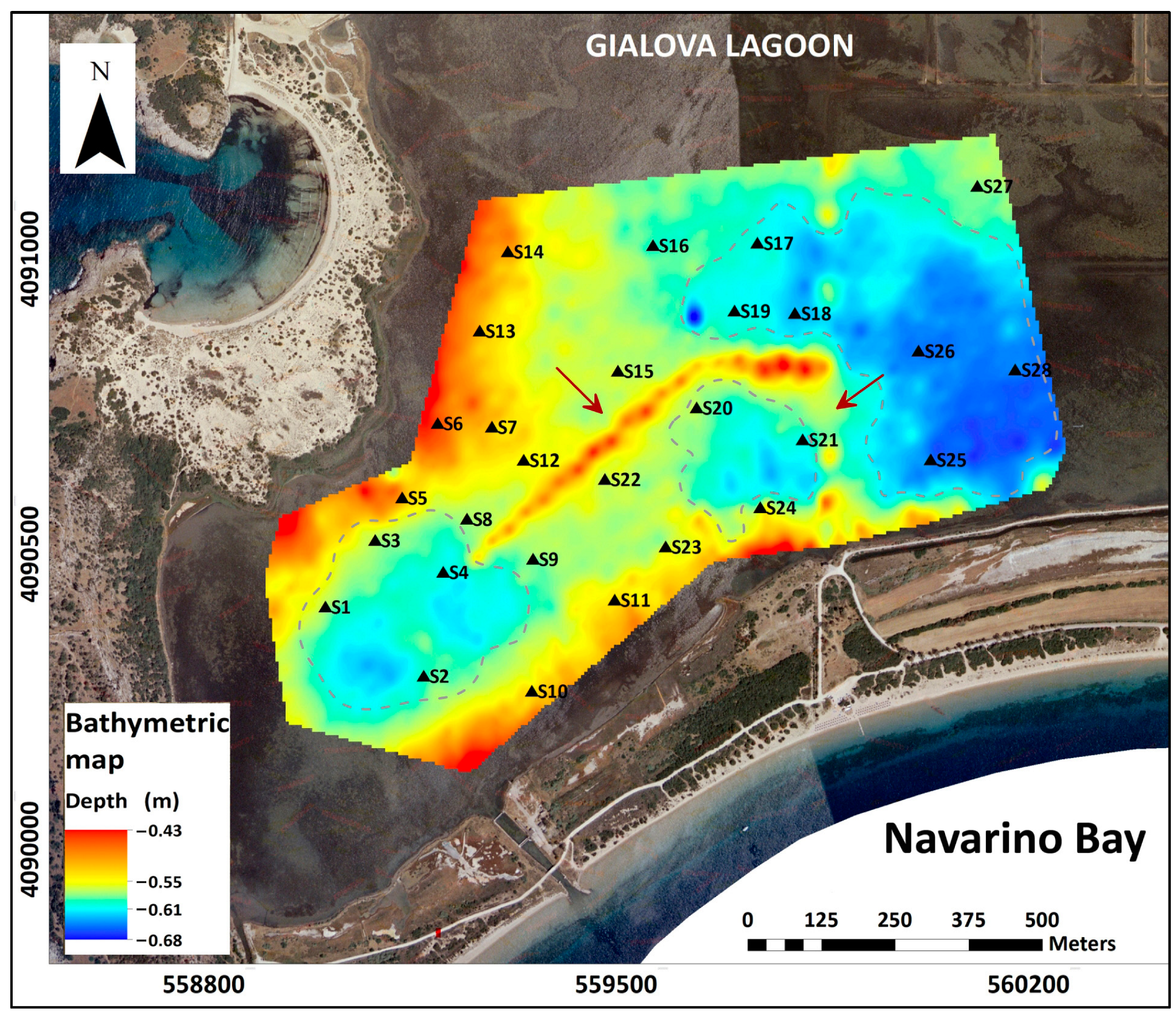
3.1. Bathymetry
3.2. Sedimentology
3.2.1. Grain Size Distribution
3.2.2. Sand Composition
3.2.3. Insights on the Depositional Environment
3.3. Geochemistry
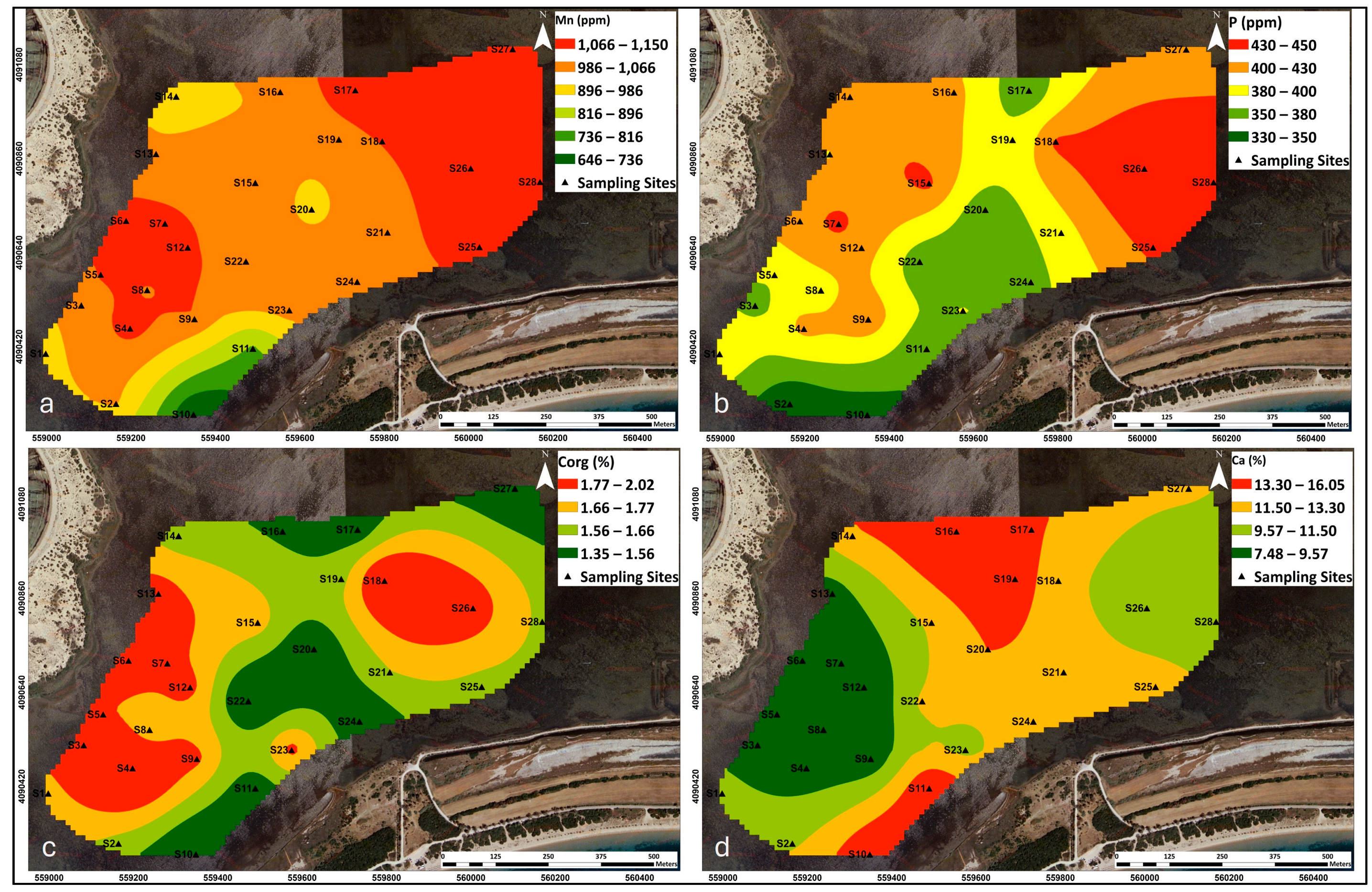
3.3.1. Elemental Concentrations in Gialova Lagoon Sediments
3.3.2. Geochemical Comparison with Other Greek Lagoons
3.4. Benthic Foraminifera
3.5. Geochemical Processes—Elemental Source Identification
3.6. Contamination Assessment (Environmental Indices)
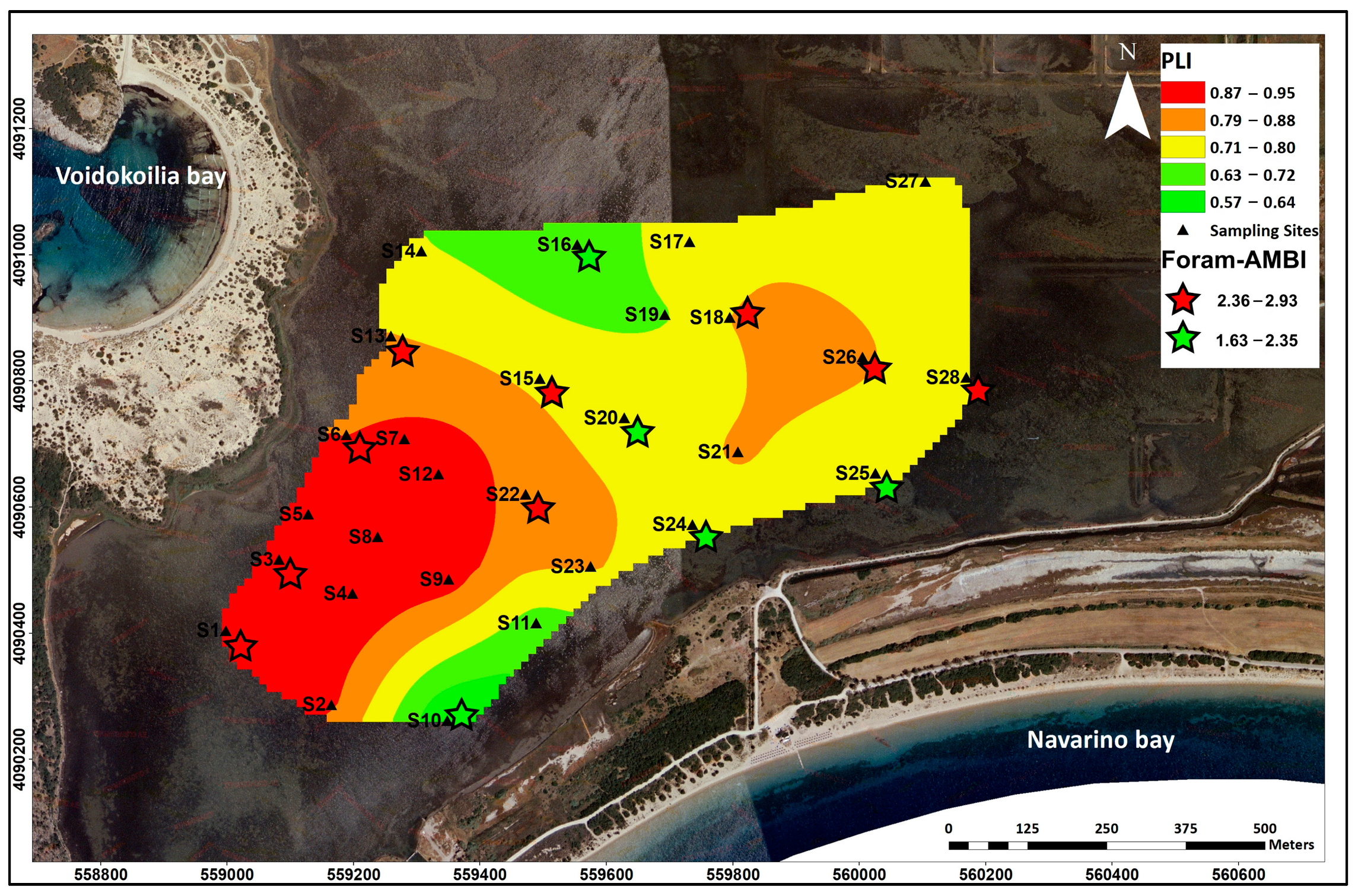
3.6.1. Heavy Metal Pollution Indices (EF, I-geo, PLI)
3.6.2. Q-mode Factor Analysis
3.6.3. Microfaunal Index (Foram-AMBI)
3.7. Depositional and Environmental Variations of the Last 30 Years
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kjerfve, B. Coastal Lagoon Processes; Elsevier Science B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1994; ISBN 0444882588. [Google Scholar]
- Sousa, A.; García-Murillo, P.; Morales, J.; García-Barrón, L. Anthropogenic and Natural Effects on the Coastal Lagoons in the Southwest of Spain (Doñana National Park). ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2009, 66, 1508–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, P.M. Management of Coastal Lagoons under Climate Change. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 110, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madkour, H.; Abdelhalim, M.A.K.; Branch, R.S.; Obirikorang, K.A.; El-taher, A. Environmental Implications of Surface Sediments from Coastal Lagoons in the Red Sea Coast. J. Environ. Biol. 2015, 36, 1421–1427. [Google Scholar]
- Inda, H.; García-Rodríguez, F.; del Puerto, L.; Stutz, S.; Lopes Figueira, R.C.; de Lima Ferreira, P.A.; Mazzeo, N. Discriminating between Natural and Human-Induced Shifts in a Shallow Coastal Lagoon: A Multidisciplinary Approach. Anthropocene 2016, 16, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana, X.D.; Boix, D.; Gascón, S.; Sala, J. Management and Restoration of Mediterranean Coastal Lagoons in Europe; Càtedra d’Ecosistemes Litorals Mediterrànis i LIFE Pletera: Torroella de Montgrí, Spain, 2018; Volume 220. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Ruzafa, A.; Marcos, C.; Pérez-Ruzafa, I.M. Mediterranean Coastal Lagoons in an Ecosystem and Aquatic Resources Management Context. Phys. Chem. Earth 2011, 36, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillebø, A.I.; Stålnacke, P.; Gooch, G.D.; Krysanova, V.; Bielecka, M. Pan-European Management of Coastal Lagoons: A Science-Policy-Stakeholder Interface Perspective. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017, 198, 648–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria, J.; Pérez, R.; Sòria-Pepinyà, X. Mediterranean Coastal Lagoons Review: Sites to Visit before Disappearance. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sammak, A.A. Textural Facies of Recent Sediments North of Sinai, Southeastern Mediterranean, Egypt. J. Coast. Res. 1995, 11, 904–910. [Google Scholar]
- Chevillon, C. Skeletal Composition of Modern Lagoon Sediments in New Caledonia: Coral, a Minor Constituent. Coral Reefs 1996, 15, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boggs, S. Principles of Sedimentology and Stratigraphy, 4th ed.; Pearson Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2006; ISBN 9788490225370. [Google Scholar]
- Molinaroli, E.; Sarretta, A.; Ferrarin, C.; Masiero, E.; Specchiulli, A.; Guerzoni, S. Sediment Grain Size and Hydrodynamics in Mediterranean Coastal Lagoons: Integrated Classification of Abiotic Parameters. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 123, 1097–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christophoridis, A.; Stamatis, N.; Orfanidis, S. Sediment Heavy Metals of a Mediterranean Coastal Lagoon: Agiasma, Nestos Delta, Eastern Macedonia (Greece). Transitional Waters Bull. 2007, 1, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prudêncio, M.I.; Gonzalez, M.I.; Dias, M.I.; Galan, E.; Ruiz, F. Geochemistry of Sediments from El Melah Lagoon (NE Tunisia): A Contribution for the Evaluation of Anthropogenic Inputs. J. Arid Environ. 2007, 69, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karageorgis, A.P.; Sioulas, A.; Krasakopoulou, E.; Anagnostou, C.L.; Hatiris, G.A.; Kyriakidou, H.; Vasilopoulos, K. Geochemistry of Surface Sediments and Heavy Metal Contamination Assessment: Messolonghi Lagoon Complex, Greece. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 65, 1619–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Crespo, C.; Martín, M. Determination of Background Levels and Pollution Assessment for Seven Metals (Cd, Cu, Ni, Pb, Zn, Fe, Mn) in Sediments of a Mediterranean Coastal Lagoon. Catena 2015, 133, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maanan, M.; Saddik, M.; Maanan, M.; Chaibi, M.; Assobhei, O.; Zourarah, B. Environmental and Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Sediments of Nador Lagoon, Morocco. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 616–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasileiadou, K.; Pavloudi, C.; Kalantzi, I.; Apostolaki, E.T.; Chatzigeorgiou, G.; Chatzinikolaou, E.; Pafilis, E.; Papageorgiou, N.; Fanini, L.; Konstas, S.; et al. Environmental Variability and Heavy Metal Concentrations from Five Lagoons in the Ionian Sea (Amvrakikos Gulf, W Greece). Biodivers. Data J. 2016, 4, e8233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsaros, D.; Panagiotaras, D.; Kontopoulos, N.; Avramidis, P. Sediments Characteristics and Heavy Metals Distribution of a Very Shallow Protected Coastal Lagoon, Prokopos Lagoon, Mediterranean Sea Western Greece. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2017, 26, 6093–6103. [Google Scholar]
- Zonta, R.; Botter, M.; Cassin, D.; Bellucci, L.G.; Pini, R.; Dominik, J. Sediment Texture and Metal Contamination in the Venice Lagoon (Italy): A Snapshot before the Installation of the MOSE System. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2018, 205, 131–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Zrelli, R.; Yacoubi, L.; Wakkaf, T.; Castet, S.; Grégoire, M.; Mansour, L.; Courjault-Radé, P.; Rabaoui, L. Surface Sediment Enrichment with Trace Metals in a Heavily Human-Impacted Lagoon (Bizerte Lagoon, Southern Mediterranean Sea): Spatial Distribution, Ecological Risk Assessment, and Implications for Environmental Protection. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 169, 112512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoidou, M.; Sylaios, G. Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in the Sediments of a Mediterranean Lagoon Complex. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2021, 19, 1835–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lacerda, L.D. Chapter 8 Biogeochemistry of Heavy Metals in Coastal Lagoons. In Elsevier Oceanography Series; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1994; Volume 60, pp. 221–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramiro Pastorinho, M.; Telfer, T.C.; Nogueira, A.J.A.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Ranville, J.F. An Evaluation of Trace Metal Distribution, Enrichment Factors and Risk in Sediments of a Coastal Lagoon (Ria de Aveiro, Portugal). Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 67, 2043–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tnoumi, A.; Angelone, M.; Armiento, G.; Caprioli, R.; Crovato, C.; De Cassan, M.; Montereali, M.R.; Nardi, E.; Parrella, L.; Proposito, M.; et al. Heavy Metal Content and Potential Ecological Risk Assessment of Sediments from Khnifiss Lagoon National Park (Morocco). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alve, E.; Korsun, S.; Schönfeld, J.; Dijkstra, N.; Golikova, E.; Hess, S.; Husum, K.; Panieri, G. Foram-AMBI: A Sensitivity Index Based on Benthic Foraminiferal Faunas from North-East Atlantic and Arctic Fjords, Continental Shelves and Slopes. Mar. Micropaleontol. 2016, 122, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorissen, F.; Pia, M.; Almogi-labin, A.; Barras, C.; Bergamin, L.; Bicchi, E.; El, A.; Ferraro, L.; Mcgann, M.; Morigi, C.; et al. Developing Foram-AMBI for Biomonitoring in the Mediterranean: Species Assignments to Ecological Categories. Mar. Micropaleontol. 2018, 140, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchet, V.M.P.; Frontalini, F.; Francescangeli, F.; Sauriau, P.G.; Geslin, E.; Martins, M.V.A.; Almogi-Labin, A.; Avnaim-Katav, S.; Di Bella, L.; Cearreta, A.; et al. Relative Abundances of Benthic Foraminifera in Response to Total Organic Carbon in Sediments: Data from European Intertidal Areas and Transitional Waters. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 164, 112071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maneas, G.; Makopoulou, E.; Bousbouras, D.; Berg, H.; Manzoni, S. Anthropogenic Changes in a Mediterranean Coastal Wetland during the Last Century-The Case of Gialova Lagoon, Messinia, Greece. Water 2019, 11, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontopoulos, N.; Bouzos, D. The Sedimentology of the Modern Lagoons in the Western Peloponnesus. Bull. Geol. Soc. Greece 2011, 44, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avramidis, P.; Iliopoulos, G.; Kontopoulos, N.; Panagiotaras, D.; Barouchas, P.; Nikolaou, K.; Papadopoulou, P. Depositional Environments, Sediment Characteristics, Palaeoecological Analysis and Environmental Assessment of an Internationally Protected Shallow Mediterranean Lagoon, Gialova Lagoon—Navarino Bay, Greece14. Earth Environ. Sci. Trans. R. Soc. Edinb. 2015, 105, 189–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, L.; Faulwetter, S.; Kaberi, H.; Karageorgis, A.P.; Kastanidi, E.; Katsiaras, N.; Pavlidou, A.; Providakis, N.; Sigala, K.; Voutsinas, E.; et al. Assessing Pressure Drivers on the Benthic Ecosystem in the Coastal Zone of Western Messinia, Greece. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2022, 274, 107935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsoubas, D.; Arvanitidis, C.; Dounas, C.; Drummond, L. Community Structure and Dynamics of the Molluscan Fauna in a Mediterranean Lagoon (Gialova Lagoon, SW Greece). Belg. J. Zool. 2000, 130, 131–138. [Google Scholar]
- Chatzigeorgiou, G.; Reizopoulou, S.; Maidanou, M.; Naletaki, M.; Orneraki, E.; Apostolaki, E.; Arvanitidis, C. Macrobenthic Community Changes Due to Dystrophic Events and Freshwater Inflow: Changes in Space and Time in a Mediterranean Lagoon (Gialova Lagoon, SW Greece). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 94, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoni, S.; Maneas, G.; Scaini, A.; Psiloglou, B.E.; Destouni, G.; Lyon, S.W. Understanding Coastal Wetland Conditions and Futures by Closing Their Hydrologic Balance: The Case of the Gialova Lagoon, Greece. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 24, 3557–3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willershäuser, T.; Vött, A.; Hadler, H.; Ntageretzis, K.; Emde, K.; Brückner, H. Holocene Palaeotsunami Imprints in the Stratigraphical Record and the Coastal Geomorphology of the Gialova Lagoon near Pylos (Southwestern Peloponnese, Greece). Z. Geomorphol. 2015, 59, 215–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmanouilidis, A.; Katrantsiotis, C.; Norström, E.; Risberg, J.; Kylander, M.; Sheik, T.A.; Iliopoulos, G.; Avramidis, P. Middle to Late Holocene Palaeoenvironmental Study of Gialova Lagoon, SW Peloponnese, Greece. Quat. Int. 2018, 476, 46–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katrantsiotis, C.; Kylander, M.E.; Smittenberg, R.; Yamoah, K.K.A.; Hättestrand, M.; Avramidis, P.; Strandberg, N.A.; Norström, E. Eastern Mediterranean Hydroclimate Reconstruction over the Last 3600 Years Based on Sedimentary N-Alkanes, Their Carbon and Hydrogen Isotope Composition and XRF Data from the Gialova Lagoon, SW Greece. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2018, 194, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papakonstantinou, M. Side Scan Sonar Bottom Relief Interpretation and Ecological Evaluation of Gialova Lagoon, Pref. of Messinia, Greece, as Well as Land Cover Land Use (LCLU) Digital Mapping in the Wider Protected Area. Master’s Thesis, University of Patras, Patras, Greece, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bouzos, D.; Kontopoulos, N.; Avramidis, P. Oceanographic Observations in the Lagoon of Gialova, (SW Peloponnese). In Proceedings of the 6th Pan-Hellenic Geographical Conference of the Hellenic Geographical Society, Thessaloniki, Greece, 3–6 October 2002; pp. 247–254. [Google Scholar]
- Papakonstantinou, M.; Papatheodorou, G.; Christodoulou, D.; Papastergiadou, E. Seasonal Variations of Water Quality and Aquatic Macrophytes Survey Based on Side Scan Sonar, in a Shallow Coastal Lagoon (Gialova, SW Peloponnesus, Greece). In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology, Rhodes, Greece, 4–7 September 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papakonstantinou, M.; Fakiris, E.; Geraga, M.; Papatheodorou, G. Exploring Shallow Lagoons with USV Mapping Technology. Hydro Int. 2023, 27, 30–34. [Google Scholar]
- Folk, R.L.; Ward, W. Brazos River Bar: A Study in the Significance of Grain Size Parameters. J. Sediment. Pet. 1957, 27, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blott, S.J.; Pye, K. Gradistat: A Grain Size Distribution and Statistics Package for the Analysis of Unconsolidated Sediments. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2001, 26, 1237–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folk, R.L. Petrology of Sedimentary Rocks; Hemphill Publishing Company: Austin, TX, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, H. Sedimentary Reflections of Depositional Environment in San Miguel Lagoon, Baja California, Mexico. Am. Assoc. Pet. Geol. Bull. 1958, 42, 2587–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, B.K. Depositional Mechanisms from the Size Analysis of Clastic Sediments. SEPM J. Sediment. Res. 1964, 34, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhat, H.I. Textural Features and Transportation Mode of Nile Delta Coastal Lagoon Surficial Sediments (Lake Burullus, Ramsar Site). SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tnoumi, A.; Khalidi, K.E.; Zourarah, B.; Angelone, M.; Armiento, G.; Caprioli, R.; Crovato, C.; De Cassan, M.; Montereali, M.R.; Proposito, M.; et al. Studies on the Textural Characteristics of Sediments From Khnifiss Lagoon (Southern Coast of Morocco). Int. J. Adv. Res. Eng. Technol. 2020, 11, 2299–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botziolis, C.; Bourli, N.; Zoumpouli, E.; Papadopoulou, P.; Dimopoulos, N.; Kovani, A.; Zelilidis, P.; Aspioti, D.C.; Iliopoulos, G.; Zelilidis, A. The Knowledge and Application of Sedimentary Conditions of Shallow Marine and Tidal Waters of Ionian Islands, Greece: Implications for Therapeutic Use. Geosciences 2024, 14, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azidane, H.; Michel, B.; Bouhaddioui, M.E.; Haddout, S.; Magrane, B.; Benmohammadi, A. Grain Size Analysis and Characterization of Sedimentary Environment along the Atlantic Coast, Kenitra (Morocco). Mar. Georesour. Geotechnol. 2021, 39, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turekian, K.K.; Wedepohl, K.H. Distribution of the Elements in Some Major Units of the Earth’s Crust. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1961, 72, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, G.F. An Assessment of Aluminum and Iron in Normalisation and Enrichment Procedures for Environmental Assessment of Marine Sediment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 727, 138123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.W.; Kao, C.M.; Chen, C.F.; Dong, C. Di Distribution and Accumulation of Heavy Metals in the Sediments of Kaohsiung Harbor, Taiwan. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 1431–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, G. Schwermetalle in Den Sedimenten Des Rheins Veranderungen Selt 1971. Umschau 1979, 79, 778–783. [Google Scholar]
- Tomilson, D.L.; Wilson, J.G.; Harris, C.; Jeffrey, D. Problems in the Assessment of Heavy Metal Levels in Estuaries and the Formation of a Pollution Index. Helgol. Meeresunters. 1980, 33, 566–575. [Google Scholar]
- Borja, A.; Franco, J.; Pérez, V. A Marine Biotic Index to Establish the Ecological Quality of Soft-Bottom Benthos within European Estuarine and Coastal Environments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2000, 40, 1100–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyment, R.A.; Joreskog, K.G. Applied Factor Analysis in the Natural Sciences; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Papatheodorou, G.; Hotos, G.; Geraga, M.; Avramidou, D.; Vorinakis, T. Heavy Metal Concentrations in Sediments of Klisova Lagoon (Southeast Mesolonghi-Aetolikon Lagoon Complex), W. Greece. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2002, 11, 951–956. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, Z.; Yinghui, J.; Tao, Y.; Min, W.; Guangxun, S.; Mingjun, D. Heavy Metal Concentrations and Risk Assessment of Sediments and Surface Water of the Gan River, China. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2016, 25, 1529–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraj, K.; Ram Mohan, V.; Szefer, P. Evaluation of Metal Contamination in Coastal Sediments of the Bay of Bengal, India: Geochemical and Statistical Approaches. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2004, 49, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papatheodorou, G.; Demopoulou, G.; Lambrakis, N. A Long-Term Study of Temporal Hydrochemical Data in a Shallow Lake Using Multivariate Statistical Techniques. Ecol. Model. 2006, 193, 759–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, J.D.; Chambers, P.A.; James, W.F.; Koch, E.W.; Westlake, D.F. The Interaction between Water Movement, Sediment Dynamics and Submersed Macrophytes. Hydrobiologia 2001, 444, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontopoulos, N.; Avramidis, P. A Late Holocene Record of Environmental Changes from the Aliki Lagoon, Egion, North Peloponnesus, Greece. Quat. Int. 2003, 111, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Falco, G.; Molinaroli, E.; Conforti, A.; Simeone, S.; Tonielli, R. Biogenic Sediments from Coastal Ecosystems to Beach-Dune Systems: Implications for the Adaptation of Mixed and Carbonate Beaches to Future Sea Level Rise. Biogeosciences 2017, 14, 3191–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valia, H.; Cameron, B. Skewness as a Paleoenvironmental Indicator. SEPM J. Sediment. Res. 1977, 47, 784–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, L.R. Recent Sediments and Grain-Size Analysis. Gravel 2003, 1, 90–105. [Google Scholar]
- Magni, P.; De Falco, G.; Como, S.; Casu, D.; Floris, A.; Petrov, A.N.; Castelli, A.; Perilli, A. Distribution and Ecological Relevance of Fine Sediments in Organic-Enriched Lagoons: The Case Study of the Cabras Lagoon (Sardinia, Italy). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2008, 56, 549–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karageorgis, A.P.; Katsanevakis, S.; Kaberi, H. Use of Enrichment Factors for the Assessment of Heavy Metal Contamination in the Sediments of Koumoundourou Lake, Greece. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2009, 204, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotaras, D.; Papoulis, D.; Kontopoulos, N.; Avramidis, P. Geochemical Processes and Sedimentological Characteristics of Holocene Lagoon Deposits, Alikes Lagoon, Zakynthos Island, Western Greece. Geol. J. 2012, 47, 372–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dassenakis, M.; Krasakopoulou, E.; Matzara, B. Chemical Characteristics of Aetoliko Lagoon, Greece, after an Ecological Shock. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1994, 28, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karageorgis, A.P. Geochemical Study of Sediments from the Amvrakikos Gulf Lagoon Complex, Greece. Transitional Water Bull. 2007, 1, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varnavas, S.P.; Panagos, A.G.; Laios, G. Trace Elements in Surface Sediments of Navarino Bay, Greece. Environ. Geol. Water Sci. 1987, 10, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geslin, E.; Debenay, J.P.; Lesourd, M. Abnormal Wall Textures and Test Deformation in Ammonia (Hyaline Foraminifer). J. Foraminifer. Res. 1998, 28, 148–156. [Google Scholar]
- Frontalini, F.; Buosi, C.; Da Pelo, S.; Coccioni, R.; Cherchi, A.; Bucci, C. Benthic Foraminifera as Bio-Indicators of Trace Element Pollution in the Heavily Contaminated Santa Gilla Lagoon (Cagliari, Italy). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 858–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothwell, R.G.; Croudace, I.W. Twenty Years of XRF Core Scanning Marine Sediments: What Do Geochemical Proxies Tell Us? In Micro-XRF Studies of Sediment Cores. Developments in Paleoenvironmental Research; Croudace, I., Rothwell, R., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 17, ISBN 978-94-017-9848-8. [Google Scholar]
- Veizer, J.; Mackenzie, F.T. Evolution of Sedimentary Rocks, 2nd ed.; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 9, ISBN 9780080983004. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, M.W.; Davies-Mcconchie, F.; McConchie, D.; Birch, G.F. Selective Chemical Extraction and Grainsize Normalisation for Environmental Assessment of Anoxic Sediments: Validation of an Integrated Procedure. Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 258, 149–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksu, A.E.; Yaşar, D.; Uslu, O. Assessment of Marine Pollution in Izmir Bay: Heavy Metal and Organic Compound Concentrations in Surficial Sediments. Turk. J. Eng. Environ. Sci. 1998, 22, 387–415. [Google Scholar]
- Löffler, A.; Leipe, T.; Emeis, K.C. The “Fluffy Layer” in the Pomeranian Bight (Western Baltic Sea): Geochemistry, Mineralogy and Environmental Aspects. Meyniana 2000, 52, 85–86. [Google Scholar]
- Glasby, G.P.; Szefer, P.; Geldon, J.; Warzocha, J. Heavy-Metal Pollution of Sediments from Szczecin Lagoon and the Gdansk Basin, Poland. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 330, 249–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langmuir, D. Uranium Solution-Mineral Equilibria at Low Temperatures with Applications to Sedimentary Ore Deposits. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1978, 42, 547–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borovec, Z. Trace Element Levels in Sediments of the Czech Part of the Elbe River. GeoJournal 1996, 40, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickard, D.; Morse, J.W. Acid Volatile Sulfide (AVS). Mar. Chem. 2005, 97, 141–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milliman, J.D. Marine Carbonates. Recent Sedimentary Carbonates Part 1. Marine Carbonates; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.-M.; Gao, J.-b.; Yuan, Y.-Q.; Ma, J.; Yu, S. Relationship between Heavy Metal Contents and Clay Mineral Properties in Surface Sediments: Implications for Metal Pollution Assessment. Cont. Shelf Res. 2016, 124, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aires, T.; Muyzer, G.; Serrão, E.A.; Engelen, A.H. Seaweed Loads Cause Stronger Bacterial Community Shifts in Coastal Lagoon Sediments than Nutrient Loads. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 3283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fielding, J.J.; Croudace, I.W.; Kemp, A.E.S.; Pearce, R.B.; Cotterill, C.J.; Langdon, P.; Avery, R. Tracing Lake Pollution, Eutrophication and Partial Recovery from the Sediments of Windermere, UK, Using Geochemistry and Sediment Microfabrics. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 722, 137745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huerta-Diaz, M.A.; Morse, J.W. Pyritization of Trace Metals in Anoxic Marine Sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1992, 56, 2681–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolin, A.; Frizzo, P.; Rampazzo, G. Sulphide Speciation in Surface Sediments of the Lagoon of Venice: A Geochemical and Mineralogical Study. Mar. Geol. 1995, 123, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prange, A.; Kremling, K. Distribution of Dissolved Molybdenum, Uranium and Vanadium in Baltic Sea Waters. Mar. Chem. 1985, 16, 259–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellwig, O.; Beck, M.; Lemke, A.; Lunau, M.; Kolditz, K.; Schnetger, B.; Brumsack, H.J. Non-Conservative Behaviour of Molybdenum in Coastal Waters: Coupling Geochemical, Biological, and Sedimentological Processes. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2007, 71, 2745–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, C.; Beck, M.; Striebel, M.; Merder, J.; Schnetger, B.; Dittmar, T.; Pahnke, K.; Brumsack, H.J. Biogeochemical Cycling of Molybdenum and Thallium during a Phytoplankton Summer Bloom: A Mesocosm Study. Mar. Chem. 2021, 229, 103910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bau, M.; Koschinsky, A. Oxidative Scavenging of Cerium on Hydrous Fe Oxide: Evidence from the Distribution of Rare Earth Elements and Yttrium between Fe Oxides and Mn Oxides in Hydrogenetic Ferromanganese Crusts. Geochem. J. 2009, 43, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, P.; Prego, R.; Mil-Homens, M.; Caçador, I.; Caetano, M. Sources and Distribution of Yttrium and Rare Earth Elements in Surface Sediments from Tagus Estuary, Portugal. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, B.; Jeppesen, E.; Søndergaard, M.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Liu, Z. Nitrogen, Macrophytes, Shallow Lakes and Nutrient Limitation: Resolution of a Current Controversy? Hydrobiologia 2013, 710, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thin, M.M.; Sacchi, E.; Setti, M.; Re, V. A Dual Source of Phosphorus to Lake Sediments Indicated by Distribution, Content, and Speciation: Inle Lake (Southern Shan State, Myanmar). Water 2020, 12, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khourchi, S.; Delaplace, P.; Bargaz, A. Polyphosphate Fertilizer Use Efficiency Strongly Relies on Soil Physicochemical Properties and Root-Microbial Activities. Geoderma 2023, 429, 116281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louda, J.W.; Li, J.; Liu, L.; Winfree, M.N.; Baker, E.W. Chlorophyll-a Degradation during Cellular Senescence and Death. Org. Geochem. 1998, 29, 1233–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Degryse, F.; Huang, C.; Hou, C.; Wu, L.; Jiang, R.; McLaughlin, M.J.; Zhang, F. Magnesium-Fortified Phosphate Fertilizers Improve Nutrient Uptake and Plant Growth without Reducing Phosphorus Availability. Pedosphere 2022, 32, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leybourne, M.I.; Johannesson, K.H. Rare Earth Elements (REE) and Yttrium in Stream Waters, Stream Sediments, and Fe-Mn Oxyhydroxides: Fractionation, Speciation, and Controls over REE + Y Patterns in the Surface Environment. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2008, 72, 5962–5983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briffa, J.; Sinagra, E.; Blundell, R. Heavy Metal Pollution in the Environment and Their Toxicological Effects on Humans. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd Elnabi, M.K.; Elkaliny, N.E.; Elyazied, M.M.; Azab, S.H.; Elkhalifa, S.A.; Elmasry, S.; Mouhamed, M.S.; Shalamesh, E.M.; Alhorieny, N.A.; Abd Elaty, A.E.; et al. Toxicity of Heavy Metals and Recent Advances in Their Removal: A Review. Toxics 2023, 11, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Sultana, K.W.; Ndhlala, A.R.; Mondal, M.; Chandra, I. Heavy Metal Pollution in the Environment and Its Impact on Health: Exploring Green Technology for Remediation. Environ. Health Insights 2023, 17, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prochaska, C.; Zouboulis, A. A Mini-Review of Urban Wastewater Treatment in Greece: History, Development and Future Challenges. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarbu, N.D.; Mihai, D.; Panter, Z.; Salcianu, R.; Mudura, R.; Mircea, L.C.; Konvalina, P. Research on the Efficiency of Wastewater Treatment Facility in Heavy Metal Removal from Leachate. Rom. Biotechnol. Lett. 2020, 25, 1768–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkaragkouni, A.; Sergiou, S.; Geraga, M.; Christodoulou, D.; Dimas, X.; Papatheodorou, G. Metal Pollution Chronology and Ecological Risk Assessment in Marine Sediments of Perama—Salamina Strait, Saronikos Gulf, Greece. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2024, 76, 103584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasem, N.A.A.; Mohammed, R.H.; Lawal, D.U. Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Wastewater: A Comprehensive and Critical Review. NPJ Clean Water 2021, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, L.; Gong, H.; Dai, L.; Dai, X. An Overview of Removing Heavy Metals from Sewage Sludge: Achievements and Perspectives. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Index | Procedures of Calculation | Values | Description-Classification | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EF | EF = (Metal/RE)sample/(Metal/RE)background. “RE” stands for the Reference Element. Aluminum (Al) was selected as the most suitable reference element, as it is mostly indicative of the natural, lithogenic fraction of the sediments [54]. | EF ≤ 1 1 < EF ≤ 3 3 < EF ≤ 5 5 < EF ≤ 10 10 < EF ≤ 25 25 < EF ≤ 50 EF > 50 | No enrichment Minor enrichment Moderate enrichment Moderate to severe enrichment Severe enrichment Very severe enrichment Extremely severe enrichment | [55] |
| I-geo | I-geo = log2 (Cn/1.5Bn), where Cn is the measured content of element “n”, and Bn is the background content of the “n” element. | Igeo ≤ 0 0 < Igeo < 1 1 < Igeo < 2 2 < Igeo < 3 3 < Igeo < 4 4 < Igeo < 5 Igeo ≥ 5 | Unpolluted Unpolluted to moderately polluted Moderately polluted Moderately to heavily polluted Heavily polluted Heavily to extremely polluted Extremely polluted | [56] |
| PLI | PLI = (CF1 × CF2 × CF3 × … × CFn)1/n where CFmetals is the ratio between the content of each metal to the background values in sediment; CFmetals = Cmetal/Cbackground. The PLI ascribes an evaluation of the overall toxicity status of the sediments. | PLI < 1 PLI = 1 PLI > 1 | Unpolluted sediments Baseline level of contamination Progressive deterioration of the environmental conditions and increasing pollution | [57] |
| Foram-AMBI | AMBI = {(0*%GI) + (1.5*%GII) + (3*%GIII) + (4.5*%GIV) + (6*%GV)}/100 Where GI-GV the relative abundance of each ecological group. Specifically, GI is the “sensitive species”, GII “Indifferent species”, GIII “3rd-order opportunistic species”, GIV “2nd-order opportunistic species” and GV “1st-order opportunistic species” | 0 < AMBI ≤ 1.2 1.2 < AMBI ≤ 3.3 3.3 < AMBI ≤ 4.3 4.3 < AMBI ≤ 5.5 5.5 < AMBI ≤ 7 | High Ecological Quality Status (EcoQs) Good EcoQs Moderate EcoQs Poor EcoQs Bad EcoQs | [28,58] |
| Element | Unit | Mean | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ag | ppm | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.05 |
| Al | % | 4.47 | 3.11 | 5.33 |
| As | ppm | 8.40 | 6.20 | 10.00 |
| Ba | ppm | 136.79 | 110.00 | 160.00 |
| Be | ppm | 1.22 | 0.87 | 1.50 |
| Ca | % | 11.18 | 7.48 | 16.05 |
| Cd | ppm | 0.13 | 0.10 | 0.16 |
| Ce | ppm | 37.99 | 35.40 | 40.80 |
| Co | ppm | 14.81 | 10.30 | 17.40 |
| Cr | ppm | 122.50 | 91.00 | 151.00 |
| Cs | ppm | 4.06 | 2.70 | 4.93 |
| Cu | ppm | 30.50 | 20.50 | 36.50 |
| Fe | % | 3.20 | 2.13 | 3.84 |
| Ga | ppm | 10.61 | 7.14 | 12.65 |
| Hf | ppm | 1.33 | 1.00 | 1.60 |
| In | ppm | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.05 |
| K | % | 1.40 | 1.00 | 1.63 |
| La | ppm | 20.09 | 18.00 | 22.90 |
| Li | ppm | 43.01 | 31.20 | 50.20 |
| Mg | % | 1.97 | 1.27 | 2.25 |
| Mn | ppm | 1026.32 | 646.00 | 1150.00 |
| Mo | ppm | 6.32 | 3.26 | 8.90 |
| Na | % | 2.72 | 1.82 | 3.61 |
| Nb | ppm | 7.46 | 5.10 | 8.80 |
| Ni | ppm | 103.20 | 66.50 | 123.50 |
| P | ppm | 395.71 | 330.00 | 450.00 |
| Pb | ppm | 35.46 | 26.30 | 44.40 |
| Rb | ppm | 80.07 | 55.20 | 95.20 |
| S | % | 1.50 | 0.99 | 1.84 |
| Sb | ppm | 0.49 | 0.36 | 0.57 |
| Sc | ppm | 10.60 | 7.00 | 12.70 |
| Sn | ppm | 1.62 | 1.10 | 2.00 |
| Sr | ppm | 713.00 | 434.00 | 1145.00 |
| Ta | ppm | 0.48 | 0.33 | 0.57 |
| Th | ppm | 5.91 | 4.54 | 7.55 |
| Ti | % | 0.22 | 0.16 | 0.26 |
| Tl | ppm | 0.42 | 0.31 | 0.51 |
| U | ppm | 2.94 | 2.10 | 3.90 |
| V | ppm | 69.18 | 46.00 | 83.00 |
| W | ppm | 0.85 | 0.60 | 1.00 |
| Y | ppm | 16.97 | 13.50 | 18.70 |
| Zn | ppm | 64.50 | 45.00 | 79.00 |
| Zr | ppm | 48.38 | 32.70 | 59.80 |
| Corg | % | 1.67 | 1.35 | 2.02 |
| Element | Cd | Cr | Cu | Fe | Mn | Ni | Pb | V | Zn | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Element Unit | ppm | ppm | ppm | % | ppm | ppm | ppm | ppm | ppm | |
| Gialova lagoon | 0.13 | 122.50 | 30.50 | 3.20 | 1026.32 | 103.20 | 35.46 | 69.18 | 64.50 | This study |
| Gialova lagoon | 0.81 | 118.20 | 57.51 | 4.76 | 1549 | 172.11 | 36.29 | 69.24 | 98.47 | [32] |
| Messolonghi Lagoon | – | 101.00 | 20.00 | 2.36 | 630.00 | 84.00 | 16.00 | 75.00 | 60.00 | [16] |
| Koumoundourou Lake | – | 58.00 | 21.00 | 0.58 | 155.00 | 28.00 | 53.00 | 23.00 | 83.00 | [70] |
| Alikes Lagoon | – | 251.67 | 29.17 | 3.59 | 630.00 | 134.17 | 9.88 | 109.33 | 68.89 | [71] |
| Aetoliko Lagoon | – | 140 | 88 | 4.17 | 837 | 75.6 | – | – | 122.2 | [72] |
| Kleisova Lagoon | – | – | 13.00 | 1.64 | 562.00 | 62.00 | – | – | 29.00 | [60] |
| Rhodia Lagoon | – | 231 | 37 | 2.83 | 867 | 124 | 36 | 112 | 72 | [73] |
| Tsoukalio Lagoon | – | 274 | 31 | 3.16 | 1191 | 131 | 26 | 108 | 76 | [73] |
| Logarou Lagoon | – | 302 | 44 | 4.74 | 922 | 221 | 25 | 153 | 105 | [73] |
| Tsopeli Lagoon | – | 295 | 48 | 3.98 | 665 | 168 | 26 | 129 | 100 | [73] |
| Navarino Bay—upper sediments | – | – | 66.00 | – | – | 151.00 | – | – | 352.00 | [74] |
| Mean | 196.76 | 38.87 | 3.18 | 800.8 | 119.99 | 28.52 | 97.32 | 81.45 | ||
| (min-max) | (58–302) | (13–88) | (0.58–4.76) | (155–1549) | (28–221) | (16–36.3) | (23–109.3) | (29–122.2) | ||
| Average Shales | 0.3 | 90 | 45 | 4.72 | 850 | 68 | 20 | 130 | 95 | [53] |
| Variable | Communalities | Rotated Component Matrix | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factor 1 | Factor 2 | Factor 3 | Factor 4 | ||
| Ag | 0.646 | 0.731 | 0.299 | −0.141 | 0.046 |
| Al | 0.995 | 0.927 | 0.257 | 0.253 | 0.074 |
| As | 0.796 | 0.242 | 0.736 | 0.374 | −0.236 |
| Ba | 0.947 | 0.901 | 0.249 | 0.268 | 0.028 |
| Be | 0.977 | 0.943 | 0.218 | 0.197 | 0.044 |
| Ca | 0.928 | −0.898 | −0.106 | −0.191 | −0.272 |
| Cd | 0.789 | 0.650 | 0.605 | 0.027 | −0.010 |
| Ce | 0.856 | 0.494 | −0.102 | 0.304 | −0.713 |
| Co | 0.971 | 0.862 | 0.359 | 0.311 | 0.039 |
| Cr | 0.876 | 0.929 | −0.038 | −0.029 | −0.101 |
| Cs | 0.993 | 0.917 | 0.294 | 0.248 | 0.058 |
| Cu | 0.982 | 0.899 | 0.292 | 0.274 | 0.110 |
| Fe | 0.995 | 0.903 | 0.264 | 0.319 | 0.095 |
| Ga | 0.994 | 0.913 | 0.275 | 0.273 | 0.102 |
| Hf | 0.918 | 0.904 | 0.231 | 0.210 | 0.060 |
| In | 0.906 | 0.790 | 0.339 | 0.362 | 0.186 |
| K | 0.990 | 0.897 | 0.280 | 0.277 | 0.177 |
| La | 0.881 | 0.556 | 0.162 | 0.544 | −0.500 |
| Li | 0.935 | 0.860 | 0.380 | 0.221 | 0.048 |
| Mg | 0.958 | 0.677 | 0.186 | 0.432 | 0.527 |
| Mn | 0.911 | 0.297 | 0.144 | 0.800 | 0.403 |
| Mo | 0.926 | 0.369 | 0.884 | 0.036 | −0.086 |
| Na | 0.757 | 0.265 | −0.016 | 0.191 | 0.806 |
| Nb | 0.989 | 0.902 | 0.254 | 0.313 | 0.113 |
| Ni | 0.993 | 0.894 | 0.334 | 0.279 | 0.061 |
| P | 0.829 | 0.183 | −0.169 | 0.212 | 0.850 |
| Pb | 0.973 | 0.927 | 0.239 | 0.236 | −0.014 |
| Rb | 0.994 | 0.910 | 0.304 | 0.260 | 0.072 |
| S | 0.919 | 0.780 | 0.403 | 0.386 | 0.003 |
| Sb | 0.868 | 0.126 | 0.883 | 0.171 | 0.209 |
| Sc | 0.992 | 0.914 | 0.285 | 0.260 | 0.086 |
| Sn | 0.974 | 0.928 | 0.188 | 0.237 | 0.146 |
| Sr | 0.904 | −0.908 | −0.064 | −0.246 | −0.123 |
| Ta | 0.976 | 0.911 | 0.239 | 0.288 | 0.075 |
| Th | 0.897 | 0.849 | 0.105 | 0.406 | 0.006 |
| Ti | 0.996 | 0.924 | 0.254 | 0.264 | 0.090 |
| Tl | 0.972 | 0.938 | 0.267 | 0.129 | 0.059 |
| U | 0.830 | 0.387 | 0.824 | −0.007 | −0.027 |
| V | 0.975 | 0.890 | 0.361 | 0.219 | 0.067 |
| W | 0.945 | 0.889 | 0.204 | 0.322 | 0.093 |
| Y | 0.934 | 0.485 | 0.169 | 0.813 | 0.098 |
| Zn | 0.986 | 0.925 | 0.308 | 0.187 | 0.041 |
| Zr | 0.854 | 0.733 | 0.217 | 0.519 | 0.015 |
| Corg | 0.702 | 0.597 | 0.295 | −0.033 | 0.508 |
| Explained Variance (%) | 61.506 | 12.784 | 10.215 | 7.378 | |
| Enrichment Factor (EF) | Geoaccumulation Index (I-geo) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metal | Min | Max | Mean | Class | State | Min | Max | Mean | Class | State |
| Sn | 0.45 | 0.52 | 0.48 | EF ≤ 1 | No enrichment | −3.03 | −2.17 | −2.49 | I-geo ≤ 0 | Unpolluted |
| Cd | 0.64 | 0.87 | 0.76 | EF ≤ 1 | No enrichment | −2.17 | −1.49 | −1.84 | I-geo ≤ 0 | Unpolluted |
| Ag | 0.55 | 1.13 | 0.86 | EF ≤ 1 | No enrichment | −2.39 | −1.07 | −1.68 | I-geo ≤ 0 | Unpolluted |
| V | 0.87 | 1.00 | 0.95 | EF ≤ 1 | No enrichment | −2.08 | −1.23 | −1.51 | I-geo ≤ 0 | Unpolluted |
| As | 0.93 | 1.48 | 1.17 | 1 < EF ≤ 3 | Minor enrichment | −1.65 | −0.96 | −1.23 | I-geo ≤ 0 | Unpolluted |
| Cu | 1.15 | 1.25 | 1.21 | 1 < EF ≤ 3 | Minor enrichment | −1.72 | −0.89 | −1.16 | I-geo ≤ 0 | Unpolluted |
| Zn | 1.17 | 1.28 | 1.21 | 1 < EF ≤ 3 | Minor enrichment | −1.66 | −0.85 | −1.16 | I-geo ≤ 0 | Unpolluted |
| Co | 1.32 | 1.47 | 1.40 | 1 < EF ≤ 3 | Minor enrichment | −1.47 | −0.71 | −0.95 | I-geo ≤ 0 | Unpolluted |
| U | 1.03 | 1.69 | 1.43 | 1 < EF ≤ 3 | Minor enrichment | −1.40 | −0.51 | −0.93 | I-geo ≤ 0 | Unpolluted |
| Mn | 1.77 | 2.69 | 2.18 | 1 < EF ≤ 3 | Minor enrichment | −0.98 | −0.15 | −0.32 | I-geo ≤ 0 | Unpolluted |
| Cr | 2.13 | 3.43 | 2.45 | 1 < EF ≤ 3 | Minor enrichment | −0.57 | 0.16 | −0.15 | I-geo ≤ 0 | Unpolluted |
| Ni | 2.52 | 2.79 | 2.71 | 1 < EF ≤ 3 | Minor enrichment | −0.62 | 0.28 | 0.00 | I-geo ≤ 0 | Unpolluted |
| Pb | 3.03 | 3.38 | 3.17 | 3 < EF ≤ 5 | Moderate enrichment | −0.19 | 0.57 | 0.23 | 0 < Igeo < 1 | Unpolluted to moderately polluted |
| Mo | 2.18 | 5.49 | 4.36 | 3 < EF ≤ 5 | Moderate enrichment | −0.26 | 1.19 | 0.66 | 0 < Igeo < 1 | Unpolluted to moderately polluted |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Papakonstantinou, M.; Sergiou, S.; Geraga, M.; Prandekou, A.; Dimas, X.; Fakiris, E.; Christodoulou, D.; Papatheodorou, G. Sedimentological, Geochemical, and Environmental Assessment in an Eastern Mediterranean, Stressed Coastal Setting: The Gialova Lagoon, SW Peloponnese, Greece. Water 2024, 16, 2312. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16162312
Papakonstantinou M, Sergiou S, Geraga M, Prandekou A, Dimas X, Fakiris E, Christodoulou D, Papatheodorou G. Sedimentological, Geochemical, and Environmental Assessment in an Eastern Mediterranean, Stressed Coastal Setting: The Gialova Lagoon, SW Peloponnese, Greece. Water. 2024; 16(16):2312. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16162312
Chicago/Turabian StylePapakonstantinou, Maria, Spyros Sergiou, Maria Geraga, Amalia Prandekou, Xenophon Dimas, Elias Fakiris, Dimitris Christodoulou, and George Papatheodorou. 2024. "Sedimentological, Geochemical, and Environmental Assessment in an Eastern Mediterranean, Stressed Coastal Setting: The Gialova Lagoon, SW Peloponnese, Greece" Water 16, no. 16: 2312. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16162312
APA StylePapakonstantinou, M., Sergiou, S., Geraga, M., Prandekou, A., Dimas, X., Fakiris, E., Christodoulou, D., & Papatheodorou, G. (2024). Sedimentological, Geochemical, and Environmental Assessment in an Eastern Mediterranean, Stressed Coastal Setting: The Gialova Lagoon, SW Peloponnese, Greece. Water, 16(16), 2312. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16162312











