Highly Efficient Reduction of Vanadium (V) with Histidine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental Procedure
2.3. Response Surface Optimization
3. Results
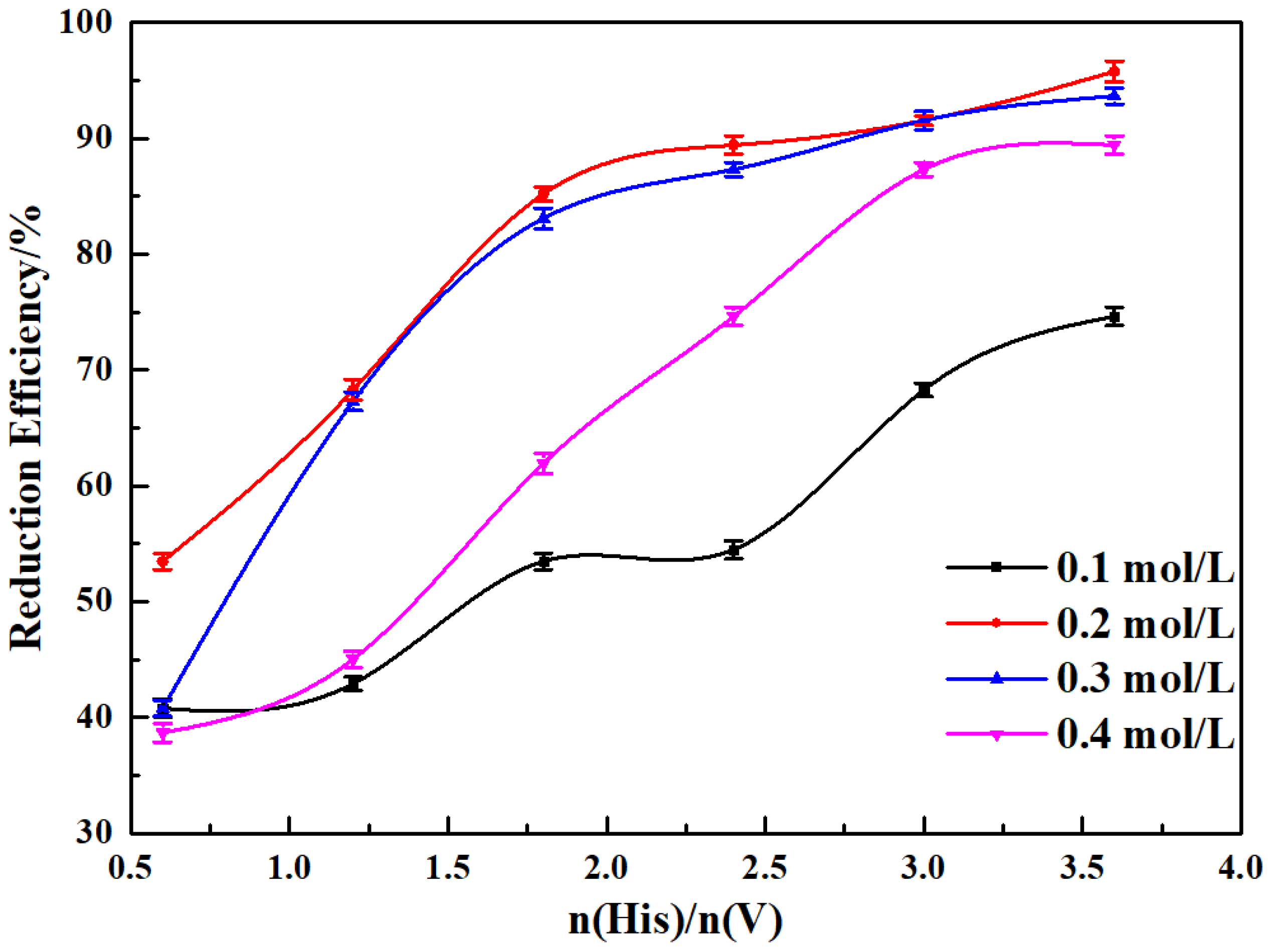
3.1. Single Factor Experiments
3.2. Response Surface Methodology
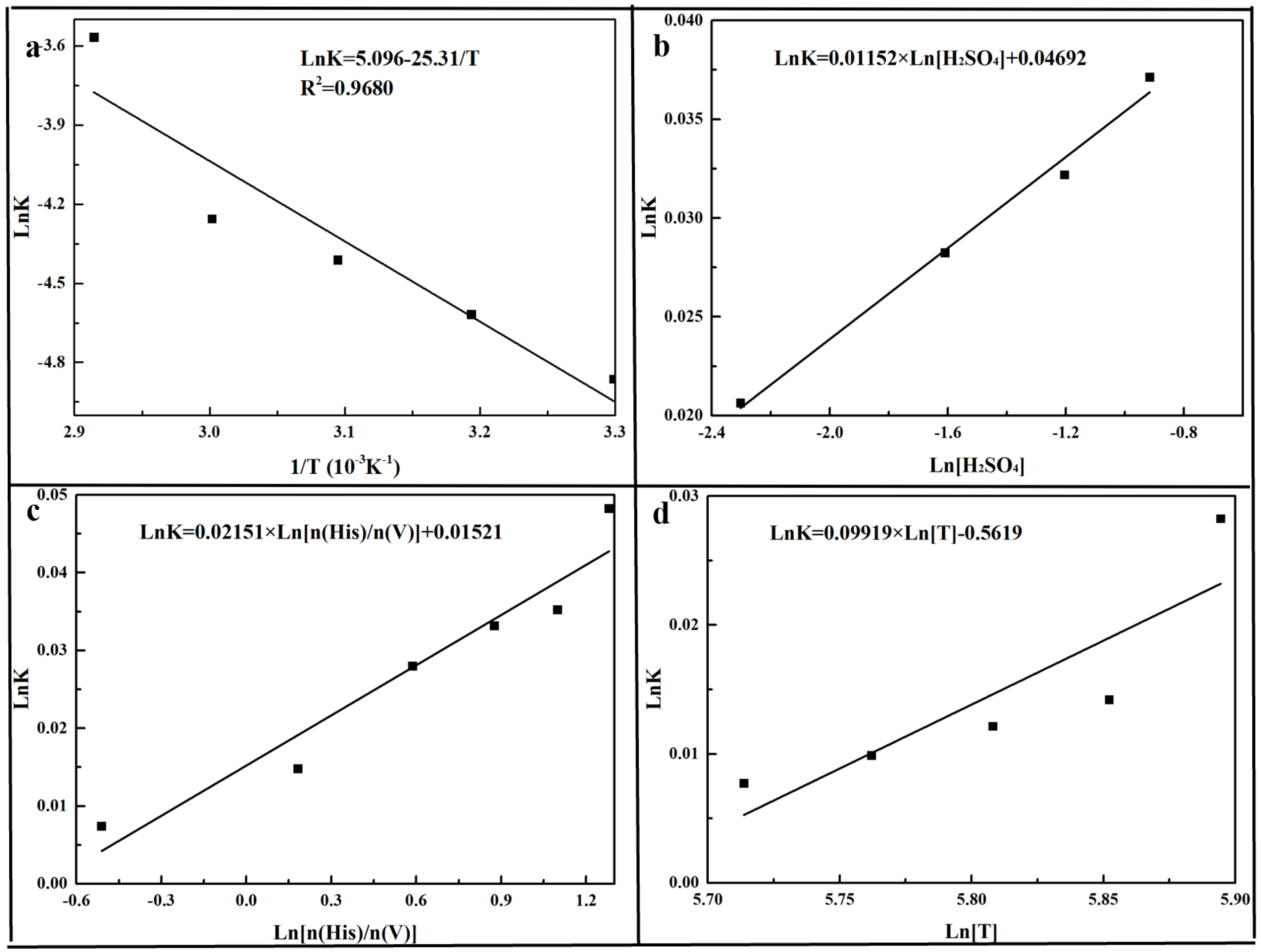
3.3. Reduction Kinetics Analysis
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Histidine was an efficient reductant for vanadium reduction. Increasing the dosage of histidine and raising the reaction temperature could promote the reduction process.
- (2)
- All the experimental factors showed a positive effect on the reduction process and the response surface methodology confirmed that the influence of each parameter on the reduction efficiency decreased in the following order: dosage of histidine > reaction temperature > reaction time. The reduction efficiency of vanadium could be achieved at 95.77% at H2SO4 concentration of 0.2 mol/L, the dosage of histidine at n(His)/n(V) = 3.6, reaction temperature of 90 °C, reaction time of 60 min and stirring rate at 500 rpm.
- (3)
- The reduction kinetics was followed with the pseudo-first-order kinetics model with an Ea of 25.31 kJ/mol. The reduction kinetics affected by the factors and the kinetics model could be described as follows:
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mubula, Y.; Yu, M.; Yang, D.; Lin, B.; Guo, Y.; Qiu, T. Recovery of valuable elements from solid waste with the aid of external electric field: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 111237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xing, Z.; Wang, X.; Cheng, G.; Xue, X. Effect of V2O5 on Consolidation, Reduction, and Softening-Melting Behavior of High-Cr Vanadium Titanomagnetite. Metals 2023, 13, 1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.; Chen, B.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, L.; Xin, C.; Ding, W.; Yang, S.; Zhang, W. A comprehensive review on the ultrasound-enhanced leaching recovery of valuable metals: Applications, mechanisms and prospects. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2023, 98, 106525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, K.-H.; Jin, C.-S.; So, J.-Y.; Park, S.-K.; Kim, D.-H.; Yeon, S.-H. Real-time monitoring of the state of charge (SOC) in vanadium redox-flow batteries using UV–Vis spectroscopy in operando mode. J. Energy Storage 2020, 27, 101066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Pu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H. In-situ and ex-situ degradation of sulfonated polyimide membrane for vanadium redox flow battery application. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 526, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, H.; He, J.; Zhou, S.; Dong, H.; Rinklebe, J.; Ok, Y.S. Vanadium in the Environment: Biogeochemistry and Bioremediation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 14770–14786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basit, F.; Bhat, J.A.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Shah, T.; Ahmad, P. Nitric oxide mitigates vanadium toxicity in soybean (Glycine max L.) by modulating reactive oxygen species (ROS) and antioxidant system. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 451, 131085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwolak, I. Vanadium carcinogenic, immunotoxic and neurotoxic effects: A review of in vitro studies. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2014, 24, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, M.R.; Kale, P.P. Mini review–vanadium-induced neurotoxicity and possible targets. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 41, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Yang, L.; Chen, Y.; Guo, J.; Li, B. Recovery and Separation of Vanadium and Chromium by Two-Step Alkaline Leaching Enhanced with an Electric Field and H2O2. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 5340–5345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Shang, Q.; Chen, R.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Guo, J. Step-Adsorption of Vanadium (V) and Chromium (VI) in the Leaching Solution with Melamine. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilligan, R.; Nikoloski, A.N. The extraction of vanadium from titanomagnetites and other sources. Miner. Eng. 2020, 146, 106106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Jiang, T.; Gao, H.; Zhou, W.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, X.; Liu, Y.; Xue, X. An efficient utilization of chromium-containing vanadium tailings: Extraction of chromium by soda roasting-water leaching and preparation of chromium oxide. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 244, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, B.; Li, S.; Yang, M.; Yin, C. Simultaneous microbial reduction of vanadium (V) and chromium (VI) by Shewanella loihica PV-4. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 227, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Liu, H. Understanding the Reduction Kinetics of Aqueous Vanadium(V) and Transformation Products Using Rotating Ring-Disk Electrodes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 11643–11651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Li, P.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Liu, W.; Luo, L.; Han, Y.; Fan, B.; Zheng, S.; Wang, Z.; et al. Removal of vanadium and chromium from vanadium wastewaters with amino-functionalized γ-AlOOH. Hydrometallurgy 2022, 210, 105841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kologrieva, U.; Volkov, A.; Krasnyanskaya, I.; Stulov, P.; Wainstein, D. Analysis of Hydrometallurgical Methods for Obtaining Vanadium Concentrates from the Waste by Chemical Production of Vanadium Pentoxide. Materials 2022, 15, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Naggar, A.; Shaheen, S.M.; Chang, S.X.; Hou, D.; Ok, Y.S.; Rinklebe, J. Biochar Surface Functionality Plays a Vital Role in (Im)Mobilization and Phytoavailability of Soil Vanadium. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 6864–6874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, D.; Zhang, X.; Dong, M.; Xue, X. A novel method to remove chromium, vanadium and ammonium from vanadium industrial wastewater using a byproduct of magnesium-based wet flue gas desulfurization. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 336, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Diao, M.; Zhang, B.; Liu, H.; Wang, S.; Yang, M. Spatial distribution of vanadium and microbial community responses in surface soil of Panzhihua mining and smelting area, China. Chemosphere 2017, 183, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghouti, M.A.; Ashfaq, M.Y.; Khan, M.; Al Disi, Z.; Da’na, D.A.; Shoshaa, R. State-of-the-art adsorption and adsorptive filtration based technologies for the removal of trace elements: A critical review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 895, 164854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.; Guo, J.; Li, B.; Huang, H.; Shi, W.; Liu, Z. Removal and recovery of vanadium from waste by chemical precipitation, adsorption, solvent extraction, remediation, photo-catalyst reduction and membrane filtration. A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 1763–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yang, Q. Study on Precipitation Kinetics of Calcium Pyro-Vanadate and Thermodynamics of Vanadium Water System. Metals 2022, 13, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, T.A.; Mustaqeem, M.; Khaled, M. Water treatment technologies in removing heavy metal ions from wastewater: A review, Environmental Nanotechnology. Monit. Manag. 2022, 17, 100617. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Li, W.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, C.; Chen, L. Separation characteristics of vanadium from leach liquor of red mud by ion exchange with different resins. Hydrometallurgy 2018, 176, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Li, J.; Li, Z.; Li, S.; Zhang, B. Electrical stimulation promotes synchronous nitrobenzene bio-degradation and vanadate bio-reduction. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 475, 146119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, B.; Li, L.; Sun, W. Synergy between pyridine anaerobic mineralization and vanadium (V) oxyanion bio-reduction for aquifer remediation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 418, 126339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, N.; Hao, X.; Zhang, B.; Feng, C. Microbial removal of vanadium (V) from groundwater by sawdust used as a sole carbon source. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 751, 142161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Low, G.K.C.; Scott, J.A.; Amal, R. Microbial reduction of hexavalent chromium by landfill leachate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 142, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reijonen, I.; Metzler, M.; Hartikainen, H. Impact of soil pH and organic matter on the chemical bioavailability of vanadium species: The underlying basis for risk assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 210, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suman, N.; Rangabhashiyam, S.; Balasubramanian, P.; Paresh, K. A review of chromite mining in Sukinda Valley of India: Impact and potential remediation measures. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2020, 22, 804–818. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.; Liu, J.; Dong, Y.; He, Y. The effect of substrates on the removal of low-level vanadium, chromium and cadmium from polluted river water by ecological floating beds. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 169, 856–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levina, A.; Lay, P.A. Stabilities and Biological Activities of Vanadium Drugs: What is the Nature of the Active Species? Chem.–Eur. J. 2017, 12, 1692–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, S.M.; Rinklebe, J.; Rupp, H.; Meissner, R. Lysimeter trials to assess the impact of different flood–dry-cycles on the dynamics of pore water concentrations of As, Cr, Mo and V in a contaminated floodplain soil. Geoderma 2014, 228–229, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, S.M.; Rinklebe, J.; Frohne, T.; White, J.R.; DeLaune, R.D. Redox effects on release kinetics of arsenic, cadmium, cobalt, and vanadium in Wax Lake Deltaic freshwater marsh soils. Chemosphere 2016, 150, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nancharaiah, Y.V.; Mohan, S.V.; Lens, P.N. Metals removal and recovery in bioelectrochemical systems: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 195, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.F.; Zhang, Z.M.; Guo, Z.C.; Tang, H.Q. Direct electrochemical reduction of solid vanadium oxide to metal vanadium at low temperature in molten CaCl2-NaCl. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2012, 19, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Guo, J.; Zhang, X. Leaching Kinetics of Vanadium from Calcium-Roasting High-Chromium Vanadium Slag Enhanced by Electric Field. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 17664–17671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangini, L.F.K.; Valt, R.B.G.; Ponte, M.J.J.d.S.; Ponte, H.d.A. Vanadium removal from spent catalyst used in the manufacture of sulfuric acid by electrical potential application. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 246, 116854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, C.; Lin, M.; Guo, Y.; Xie, B. Green one-step roasting method for efficient extraction of vanadium and chromium from vanadium-chromium slag. Powder Technol. 2020, 360, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Ye, Z.; Chen, L.; Chen, X.; Liu, C.; Yin, Y.; Wang, X.; Wei, Y. Removal of V(V) From Solution Using a Silica-Supported Primary Amine Resin: Batch Studies, Experimental Analysis, and Mathematical Modeling. Molecules 2020, 25, 1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, B.; Yuan, H.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, S.; He, Z. Microbial reduction of vanadium (V) in groundwater: Interactions with coexisting common electron acceptors and analysis of microbial community. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 1362–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Guo, J. Reduction behavior of chromium(VI) with oxalic acid in aqueous solution. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.; Leng, Y.; Guo, J. Electrochemical Removal of Chromium (VI) from Wastewater. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Leng, Y.; Cheng, Q.; Shang, Q.; Shu, J.; Guo, J. Efficient Removal of Hexavalent Chromium from Wastewater with Electro-Reduction. Processes 2019, 7, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Shang, Q.; Chen, R.; Leng, Y.; Guo, J.; Liu, Z.; Tao, C. Oxidative Leaching Kinetics of Vanadium from the Vanadium-Chromium-Reducing Residue with K2Cr2O7. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 8777–8783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Wang, F.; Li, G.; Guo, J.; Li, B. Highly Efficient Recovery of Vanadium and Chromium: Optimized by Response Surface Methodology. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 904–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, Z.; Fan, X.; Lian, X.; Tao, C. Optimization of reaction conditions for the electroleaching of manganese from low-grade pyrolusite. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2015, 22, 1121–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okello, V.A.; Mwilu, S.; Noah, N.; Zhou, A.; Chong, J.; Knipfing, M.T.; Doetschman, D.; Sadik, O.A. Reduction of hexavalent chromium using naturally-derived flavonoids. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 46, 10743–10751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Fu, W.; Yin, Y.; Chen, Z.; Qiu, R.; Simonnot, M.-O.; Wang, X. Adsorption-reduction removal of Cr(VI) by tobacco petiole pyrolytic biochar: Batch experiment, kinetic and mechanism studies. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 268, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Han, J.; Mu, Y.; Yu, H.; Qin, L. Two-stage chromium isotope fractionation during microbial Cr(VI) reduction. Water Res. 2019, 148, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langeslay, R.R.; Kaphan, D.M.; Marshall, C.L.; Stair, P.C.; Sattelberger, A.P.; Delferro, M. Catalytic Applications of Vanadium: A Mechanistic Perspective. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 2128–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.; Tang, D.; Liao, M.; Wu, Y.; Fan, X.; Li, B.; Huang, H.; Shi, W. A Clean Method for Vanadium (V) Reduction with Oxalic Acid. Metals 2022, 12, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Independent Variable | Unit | Level | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| A: reaction temperature | °C | 30.00 | 60.00 | 90.00 |
| B: reaction time | min | 10.00 | 35.00 | 60.00 |
| C: n(His)/n(V) | - | 0.60 | 2.10 | 3.60 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | Df | Mean Square | F Value | p Value Prob > F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 3.14 | 9 | 0.35 | 118.63 | <0.0001 |
| A | 0.96 | 1 | 0.96 | 324.93 | <0.0001 |
| B | 0.50 | 1 | 0.50 | 169.78 | <0.0001 |
| C | 1.32 | 1 | 1.32 | 448.08 | <0.0001 |
| A × B | 0.001743 | 1 | 0.001743 | 0.59 | 0.4666 |
| A × C | 0.032 | 1 | 0.032 | 10.97 | 0.0129 |
| B × C | 0.00012 | 1 | 0.00012 | 0.041 | 0.8456 |
| A × A | 0.00315 | 1 | 0.00315 | 1.07 | 0.3352 |
| B × B | 0.00384 | 1 | 0.00384 | 1.30 | 0.2909 |
| C × C | 0.32 | 1 | 0.32 | 110.26 | <0.0001 |
| Residual | 0.021 | 7 | 0.00294 | - | - |
| Lack-of-fit | 0.021 | 3 | 0.00686 | - | - |
| Pure error | 0.000 | 4 | 0.000 | - | - |
| Cor Total | 3.16 | 16 |
| Temperature (K) | K (min−1K−1) | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| 303 | 0.00773 | 0.9694 |
| 318 | 0.00988 | 0.9832 |
| 333 | 0.01214 | 0.9818 |
| 348 | 0.01420 | 0.9869 |
| 363 | 0.02824 | 0.9673 |
| Parameters | K (min−1K−1) | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| [H2SO4] (mol/L) | ||
| 0.1 | 0.02064 | 0.9823 |
| 0.2 | 0.02824 | 0.9673 |
| 0.3 | 0.03218 | 0.9638 |
| 0.4 | 0.03712 | 0.9609 |
| n(His)/n(V) | ||
| 0.6 | 0.00738 | 0.9643 |
| 1.2 | 0.01479 | 0.9814 |
| 1.8 | 0.02801 | 0.9896 |
| 2.4 | 0.03319 | 0.9783 |
| 3.0 | 0.03522 | 0.9864 |
| 3.6 | 0.04824 | 0.9673 |
| Temperature (K) | ||
| 303 | 0.00773 | 0.9694 |
| 318 | 0.00988 | 0.9832 |
| 333 | 0.01214 | 0.9818 |
| 348 | 0.0142 | 0.9869 |
| 363 | 0.02824 | 0.9673 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, H.; Wang, L.; Pan, W.; Yang, S.; Wang, J.; Qin, J.; Ao, L.; Lin, Y.; Tang, J. Highly Efficient Reduction of Vanadium (V) with Histidine. Water 2024, 16, 2227. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16162227
Peng H, Wang L, Pan W, Yang S, Wang J, Qin J, Ao L, Lin Y, Tang J. Highly Efficient Reduction of Vanadium (V) with Histidine. Water. 2024; 16(16):2227. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16162227
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Hao, Laixin Wang, Wenjing Pan, Sisi Yang, Jingjing Wang, Jielin Qin, Lihua Ao, Yinhe Lin, and Jinzhu Tang. 2024. "Highly Efficient Reduction of Vanadium (V) with Histidine" Water 16, no. 16: 2227. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16162227
APA StylePeng, H., Wang, L., Pan, W., Yang, S., Wang, J., Qin, J., Ao, L., Lin, Y., & Tang, J. (2024). Highly Efficient Reduction of Vanadium (V) with Histidine. Water, 16(16), 2227. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16162227







