Abstract
Hydra is known for its natural occurrence, anatomical simplicity, intricate physiology, regenerative capacity, and ease of maintenance and manipulation in laboratory environments. It has proven to be a valuable model organism in various disciplines. Its applications range from developmental biology, stem cell research, animal physiology to environmental toxicology including ecotoxicology. The sensitivity of Hydra to a variety of environmental stressors and chemical agents such as metals, nanomaterials, and toxic organic compounds provides valuable insights into physiological mechanisms affected by environmental stressors and pollution, and Hydra can be of great use in environmental monitoring. Furthermore, since green Hydra lives in a symbiotic relationship with unicellular photoautotrophic algae, it is a suitable model organism for symbiosis research. Recently, it has become a popular model in holobiont research. The adaptability and importance of Hydra also extends to aquatic science and aquatic ecology, particularly in the context of monitoring and water pollution. Since the 1980s, Hydra has been increasingly used in various fields of research and has established itself as an important versatile model organism in numerous scientific studies. Hydra also represents an outstanding model in the fields of education and STEM. Hydra continues to be an important model in the 21st century, contributing significantly to our understanding of the biology of water and advancing freshwater research, and possibly finding its way to regenerative medicine and tumor pathobiology research.
Keywords:
hydra; endosymbiosis; microscopy; aquatic ecology; ecotoxicology; holobiont; nanomaterials; myc; comet assay 1. Introduction
Hydra, a genus of small, freshwater invertebrates, holds a significant position in biological and ecological research due to its unique characteristics and evolutionary relevance. Known for its natural occurrence, anatomical simplicity, and intricate physiology, Hydra has become a cornerstone of studies in various scientific fields [1]. Its robust regenerative capacity and genetic conservation [2] make it an invaluable model in developmental biology, stem cell research, and environmental toxicology, including ecotoxicology. Extensive and diverse research on Hydra and its algal endosymbionts spans areas such as microscopy, ecotoxicology, endosymbiosis, educational applications, and microcosm research [3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13].
Our studies have demonstrated that environmental influences, such as industrial salt, cause damage to the tentacles of both green and brown Hydra, with green Hydra exhibiting greater adaptability to these stressors (3). We also recorded different responses of Hydra to herbicide norflurazon and UV radiation (4). Our previous studies show that symbiotic relationships can be studied using the Hydra as a model organism, on many levels, e.g., describing the new mechanisms of symbiosis and isolation and biodiversity of endosymbionts [6,7,8,9,10]. In microcosm research that includes Hydra, we studied predator–prey interactions, the formation of microalgal hunting nets and the defensive mechanisms of Hydra’s prey Daphnia magna [12,13]. Additionally, our research indicates that Hydra can be effectively used in educational settings, such as school-level studies to estimate the impact of flavonoids on freshwater organisms [11]. In our current studies, we are aiming to analyze genes conserved during evolution that have a role in tumorigenesis, using Hydra as a model for the earliest known organisms that develop neoplastic tissue. This ongoing research underscores Hydra’s relevance not only to morphological and toxicological studies but also to human health research. We believe that Hydra holds significant promise for numerous fields in 21st-century research.
This paper aims to systematize the extensive information on the freshwater hydrozoan polyps of the genus Hydra, which have proven to be invaluable model organisms in various fields of biology. By organizing the existing literature and highlighting the central role of Hydra in advancing our understanding of biological processes, this review serves as a fundamental resource for researchers and educators. Key topics include ecotoxicology research, microscopy techniques, comet assays, nanoparticles, and the role of Hydra in studying myc genes. Through this comprehensive overview, we aim to underscore Hydra’s ongoing and future contributions to science, showcasing its versatility and importance in modern research.
This review begins with a detailed introduction describing the phylogenetic position, taxonomy, body plan, tissues, biology, ecology and life cycle of Hydra. This foundational information is followed by a description of fields where Hydra has been used as an efficient model organism for many biological fields and concepts. Each section is designed to demonstrate how Hydra serves as an effective model organism, culminating in a summary of conclusions.
2. Hydra: A Model Organism for Biological and Ecological Research
Hydra, which belongs to the phylum Cnidaria and the class Hydrozoa, is a simple, radially symmetrical organism known primarily for its regenerative capacity and relative simplicity. Hydra is characterized by a simple body plan and life cycle and exists exclusively in the polyp form, which distinguishes it from many of its cnidarian relatives, which often have both polyp and medusa stages. The body of a Hydra is usually up to 10 mm. It consists of a basal disk for attachment, a cylindrical body, and a hypostome surrounded by tentacles at the oral end. The tentacles of Hydra have stinging cells, nematocysts, which shoot poisonous barbs into the prey. The body wall consists of two main layers: an outer ectoderm and an inner endoderm with a gelatinous mesoglea in between. These layers contain specialized cells, including stinging cells (nematocytes) for prey capture and epithelial cells for structural integrity.
The morphology and function of nematocysts were only discovered in the middle of the 19th century, after suitable microscopic and histological techniques had been developed. The stinging cells are small, oval or pear-shaped, firmly anchored in the cytoplasm of the nematocyst by a microtubular basket surrounding the capsule [14], and are scattered throughout the body of Hydra. Hydra possesses four different types of capsules [15]: the large stenoteles, which have conspicuous spines at the base of their tubes [16], the atrichous and holotrichous isorhizae, which serve to attach to surfaces and prey organisms, and the small desmonemes, which wrap tightly around the appendages of prey after discharge [17]. In addition, the tentacle bends to bring the food to the center of the hypostome, where the mouth is located, with the help of other tentacles. The mouth opening has been visualized in transgenic animals using epifluorescence microscopy. Carter et al. [18] investigated the dynamics of mouth opening in Hydra using live imaging of hypostomes in transgenic Hydra expressing fluorescent proteins in the two epithelial layers and quantitative image analysis. The authors showed that mouth opening in Hydra requires the activity of radially arranged ectodermal myonemes, musculoepithelial cells with muscle filaments.
Hydra has two epithelial layers, an outer ectoderm and a thicker inner endoderm. In 1959, Wood used transmission electron microscopy to show that in Hydra, adjacent epithelial cells are firmly connected by desmosomes, which bridge the intercellular space with a series of parallel lamellae and directly connect the two adjacent cell surfaces [19]. Wood hypothesized that the septate desmosomes in Hydra not only firmly connect the cells, but also form barriers against the penetration of water into the intercellular spaces, thus helping to protect the internal environment of the organism. Between the ectoderm and the endoderm is a layer of extracellular matrix, the mesoglea. The mesoglea has the structural and molecular organization of basement membranes in higher animals and is synthesized by epithelial cells of both layers [20,21]. To address these questions of whether the mesoglea is recruited from the mother like the epithelial cells and how the mesoglea is reorganized during bud growth while maintaining a functional epithelial basement membrane, Aufschnaiter et al. [22] microinjected monoclonal antibodies against Hydra-laminin and collagen-1 into the mesoglea. Their results show that the mesoglea is a very dynamic structure, except in the head region. In the adjacent body column and tentacles, it was continuously shifted towards the ends of the animal. During the evagination of the buds, it was stretched and reshaped to produce the morphology of the buds. The dynamic displacement of the mesoglea along the body column and tentacles largely overlapped with the movement of the epithelial cells. However, where the tissue expanded, the mesoglea was drastically remodeled, and the epithelial cells moved relative to the mesoglea.
Hydra is very flexible, mainly due to the unique composition of its extracellular matrix [23]. The more complex forms of locomotion in Hydra utilize the neuromuscular system. The muscle cells are controlled by various neural circuits to achieve a range of coordinated behavioral activities [24,25,26]. This ability of Hydra to coordinate contraction and relaxation helps the polyp to perform a range of movements, such as swings, loops, and somersaults [27]. To understand the biomechanics of somersaulting, Naik et al. [28] created a spatially resolved elasticity profile of Hydra’s body column using an atomic force microscope. They observed that polyps with uniform stiffness along the body column lose their ability to somersault. They showed that somersaulting depends primarily on the varying tissue stiffness of the body column. They show that disrupting the observed stiffness differences in the body column by modulating extracellular matrix polymerization impairs somersaulting ability. The stiffness difference mediated by the extracellular matrix is likely an ancient mechanism for achieving specialized tissue functions. To further investigate the role of tissue stiffness as a function of collagen cross-linking, they observed the ultrastructure of the extracellular matrix in mesoglea using scanning electron microscopy. These observations suggest that the stiffness differences observed between the shoulder region and the body column are due to the different packing of collagen fibers in the extracellular matrix [28].
Hydra is known for its remarkable regenerative abilities, allowing it to regenerate its entire body from small fragments, as it has multipotent stem cells distributed throughout its body. This regenerative ability is a focus of research in developmental biology [29,30]. Hydra feeds on small aquatic organisms such as crustaceans and larvae, using its tentacles to capture prey.
Hydra inhabit a variety of freshwater environments, including ponds, lakes and slow-moving streams, attaching to submerged vegetation, rocks or debris where they can effectively capture passing prey. As both predator and prey, Hydra play an important role in aquatic ecosystems, helping to regulate populations of small invertebrates and serving as indicators of environmental health. The life cycle of Hydra primarily involves asexual reproduction by budding, in which new individuals develop as outgrowths from the mother’s body and eventually detach to become independent organisms. Under certain conditions, Hydra can also reproduce sexually by producing gametes that lead to the formation of hardy, dormant eggs that can withstand adverse conditions [31].
The biology of Hydra, combined with its ecological importance and evolutionary position, makes it an invaluable model organism for the study of fundamental biological processes, environmental interactions, and basic cellular and developmental mechanisms underlying the evolution of eumetazoans [16,32]. As it is well characterized by both light and electron microscopy, it is used in various research areas that investigate the morphological level of biological processes and provide histological insights into multicellular development.
3. Hydra in Morphological Studies
Microscopy is essential for the structural and morphological study of small aquatic organisms. In recent years, new genetic manipulations such as stable transgenesis, gene silencing, genome editing, the accumulation of high-throughput omics data, and improved and new imaging systems and preparation methods have expanded the possibilities for utilizing Hydra. Cryoprocessing, e.g., high-pressure freezing/freeze substitution, offers excellent preservation of Hydra tissue. The high spatial and temporal resolution achieved with these methods may be important for deciphering minute ultrastructural details and dynamic features [33]. In our recent work, cryofixation of the endosymbiotic microalga Desmodesmus subspicatus isolated from the green Hydra H. viridissima allowed us to obtain and visualize many small rod-like structures on the cell wall of the isolated microalga, suggesting the possibility of the microalgal net formation using these rod structures. Indeed, it has been observed that D. subspicatus tends to cluster together in the presence of predators such as Daphnia magna and Polycelis felina to protect themselves from being eaten by predators due to their increased size [12]. Similarly, Wiltshire et al. 2003 [34] showed that the presence of D. magna individuals stimulates the production of mucus by the alga Staurastrum and that the cells use the mucus produced to form algal clusters that are too large for D. magna individuals to eat. These algal clusters are thought to be a mechanism that protects the algae from predatory attacks by D. magna. In addition, the microalgae nets were also observed in the microcosms with H. viridissima [12]. The link between the isolated microalgae and the hunting nets illustrates the potential role of microalgae as part of the predatory chain. On the other hand, the Hydra, which lives in a symbiotic relationship with unicellular photoautotrophic algae located in the gastrodermal myoepithelial cells, actively encounters endosymbiotic algal cells during predatory feeding on Artemia sp. [29]. This phenomenon could be a mechanism by which the Hydra can expel excess symbiotic algae when an alternative form of nutrition is available in the form of prey, as well as the way in which the host regulates the population density of its symbionts, as an overpopulation of algae can damage the host through an excessive accumulation of photosynthetically produced reactive oxygen species [35].
Hydra as the oldest model system in experimental developmental biology has been studied for more than 250 years, especially in evolutionary and ecotoxicological research [16,36,37,38,39,40,41] and in research into the mechanisms and evolution of endosymbiotic relationships. The Hydra–algal symbiosis represents an important model for the investigation of the specificity between host and symbiont in the invertebrate–algal system [42]. Symbiotic algae have been shown to protect the host under temperature stress conditions [43,44] and play a role in controlling an invasive species in a metacommunity, thereby shaping the microbiome in Hydra [45]. In addition, the symbiotic Hydra benefits from the association with algae, which enables them to better tolerate the toxin. At low concentrations, the copper absorbed by the symbiotic Hydra can be sequestered by the algae, which provides a degree of protection for the polyp itself [46]. Zinc, which is not so toxic to algae, also has a less harmful effect on green Hydra than on a free-living Hydra species [47]. Also, endosymbiotic algae in green Hydra are not bleached by norflurazon, i.e., the “bleaching effect” does not take place [4,48]. Hydra is also a powerful model system for the study of conditions affecting wound healing, the reactivation of a developmental process, the regeneration of an amputated body part, aging and the nervous system [49,50,51,52,53].
It is also an excellent system for the study of biomechanics and hydrodynamics. Le et al. 2023 [54] developed a DIY microscope, GLUBscope, which allows the organisms to be viewed from two orthogonal imaging planes—a top view and a side view. With this approach, an organism can move out of the plane in one view, but remain visible in the orthogonal view. Due to their complex 3D shapes, viewing organisms from multiple angles could be crucial to answer questions about biomechanics and hydrodynamics (e.g., surface attachment, elongation or stretching in multiple planes). Hedde et al. 2023 [55] developed SPIM-Flow, a simple and inexpensive system that easily integrates light sheet microscopy and fluidics. Using Hydra, they showed that this system offers exciting possibilities for studying the hydrodynamics of freely moving model organisms.
4. Hydra as a Model Organism in Ecotoxicological Research
The sensitivity of Hydra to a spectrum of pollutants, particularly heavy metals, underscores its importance in toxicological research and provides valuable insights into physiological mechanisms affected by environmental stressors [56,57,58,59,60]. The historical importance of Hydra coincides seamlessly with its utility in toxicological studies, as it has often been used as an alternative model organism for toxicity testing [61,62]. Despite its natural habitat in slow-moving waters, the ease of maintenance and manipulation of Hydra in laboratory environments has driven its application in the evaluation of pharmaceutical compounds and contributed significantly to advances in pharmacology and toxicology [63,64].
The diploblastic organization of Hydra, combined with its rapid proliferation and sensitivity to environmental pollutants, makes it an ideal candidate for ecotoxicological assessments. Moreover, the growing scientific interest in Hydra, as evidenced by an increase in publications since the 1980s, underscores its continued importance to toxicological research amidst general scientific advancements [65,66] (Figure 1). Hydra has proven to be a versatile model organism in toxicity studies dealing with a wide range of environmental stressors and chemical agents. Its application ranges from the response assessment of Hydra to stressors such as temperature fluctuations and metal contamination, shedding light on its interactive effects in aquatic ecosystems [67,68], the effects of heavy metals such as copper, cadmium, and zinc [36,68,69,70] to the assessment of the toxicity of organic compounds, including pharmaceuticals such as carbamazepine and endocrine disrupting compounds such as 4-nonylphenol and bisphenol A [71,72,73]. In addition, the sensitivity of Hydra to nanomaterials, including copper and zinc iron oxides, emphasizes its usefulness in studying the toxicity of emerging contaminants [74,75]. Its unique properties enable studies of genotoxicity induced by metals such as aluminum and highlight its role in elucidating molecular toxicity mechanisms [76]. In addition, Hydra has retained its place in ecotoxicological research in the era of microplastic pollution [77,78], further highlighting the versatility of Hydra as a model organism.
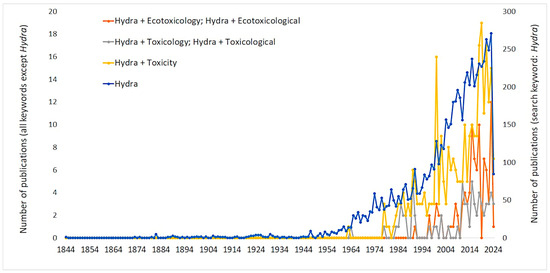
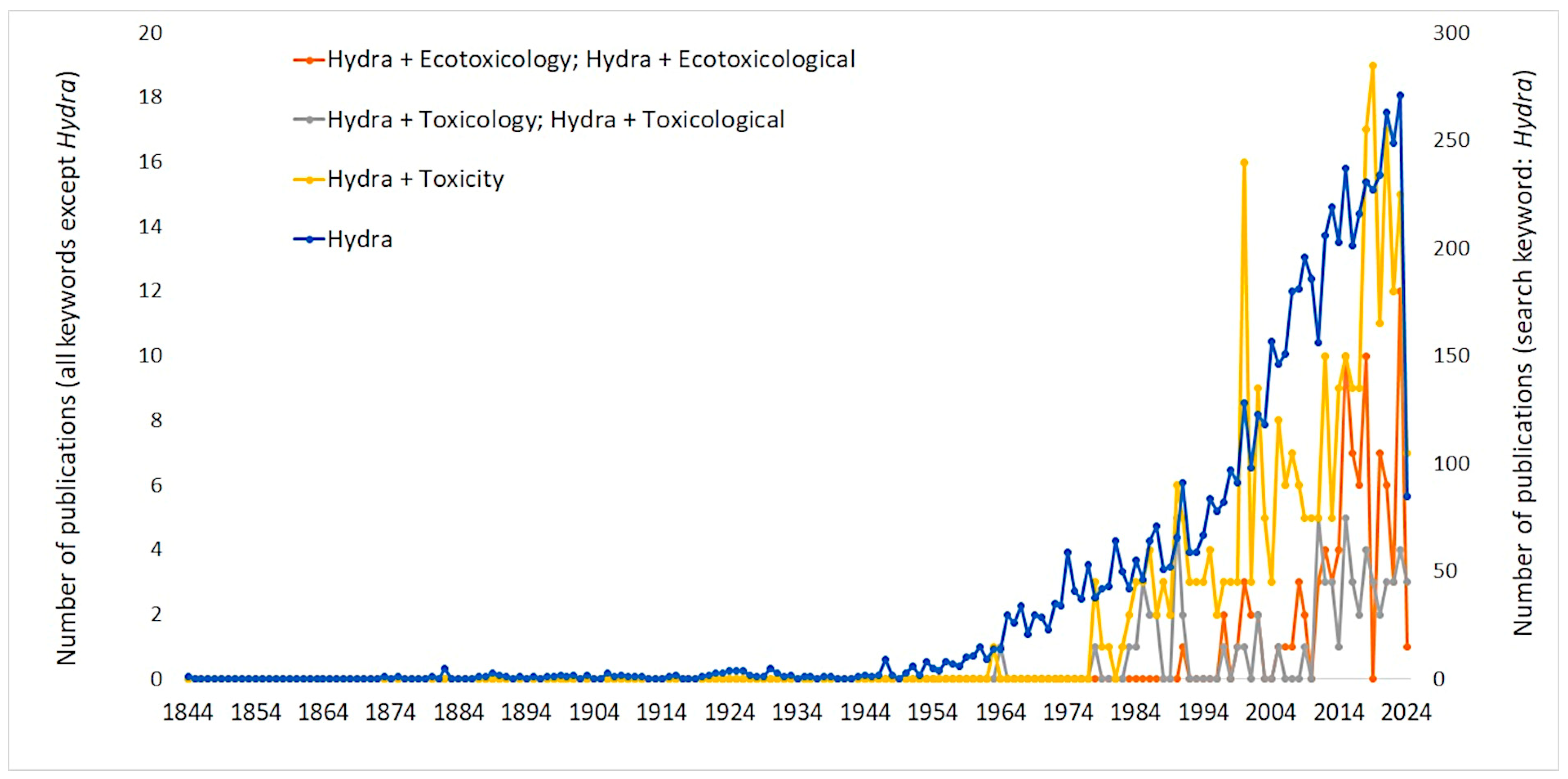
Figure 1.
Trends in Hydra-related publications in ecotoxicology over time. The graph illustrates the number of scientific publications retrieved from the Scopus database spanning from 1844 to 2024, focusing on studies related to Hydra in the context of ecotoxicology. The data were generated by conducting searches in the Scopus database using specific keywords (Hydra, Hydra + Ecotoxicology, Hydra + Ecotoxicological, Hydra + Toxicology, Hydra + Toxicological, Hydra + Toxicity) in the article title, abstract, and keywords sections of publications. The left y-axis represents the number of publications that use the following keyword combinations: “Hydra + Ecotoxicology”, “Hydra + Ecotoxicological”, “Hydra + Toxicology”, “Hydra + Toxicological”, and “Hydra + Toxicity”. The right y-axis represents the total number of publications that use the keyword “Hydra”. The graph showcases the increasing trend in Hydra-related publications within the field of ecotoxicology over the years, reflecting the growing interest and research focus on model organisms in toxicological studies.
Hydra inhabit surface waters of the highest clarity and are highly sensitive to organic and inorganic pollution. These characteristics qualify them as optimal indicator organisms, both as bioindicators for the assessment of pollution levels in aquatic ecosystems and as experimental model organisms for controlled exposure to potential pollutants. Due to its intolerance to cytotoxic levels of pollutants, Hydra is ideal for the study of genotoxic substances in freshwater, as the levels that trigger genotoxicity are far below those that cause toxic effects. Inorganic substances, as well as pesticides and their metabolites formed in the environment, are bioaccumulative and can often exceed ecotoxic levels for non-target organisms in aquatic systems [79]. Hydra is an important indicator organism for the assessment of acute and chronic genotoxic effects of inorganic pollution and other chemicals released into the environment [59,76]. It is also capable of forming tumors similar to human cells and tissues, further highlighting its importance in toxicological studies [80]. Hydra possesses the same protooncogenes as humans, which makes it an even more suitable model organism for evaluating the genotoxic potential of the chemical substances in question [81,82] and the transcription factors relevant to human carcinogenesis [83]. In addition, Hydra has been shown to be an excellent bioindicator of water pollution by organic chemicals, especially pesticides and their metabolites [84,85,86]. Due to their bioaccumulative properties, pollutant concentrations in these organisms can exceed ecotoxic levels for non-target organisms in aquatic systems [59,87].
Furthermore, Hydra has been used to monitor wastewater quality and the genotoxicity of various nanomaterials and pharmaceuticals [59]. Both symbiotic and free-living Hydra have been shown to be sensitive biomarkers for the genotoxicity of inorganic chemical substances, such as aluminum salts [76,88]. Recently, promising attempts have been made to use Hydra as model organisms for the assessment of endocrine disruption [73]. The presence of cations such as Al3+, Cd2+ and Cu2+ in Hydra leads to significantly increased genotoxicity levels, altered molecular defense mechanisms, disrupted cell cycle progression, and increased apoptosis [14]. The alkaline comet assay has proven to be the best known and most reliable method for the detection of genotoxic effects in Hydra cells [60,76,89].
When assessing genotoxicity in free-living Hydra cells from surface waters or in Hydra cells that have been cultured and treated with various potential contaminants, two descriptors of the alkaline comet assay are considered: the length of the comet tail and the intensity of the comet tail (i.e., the percentage of DNA in the tail). In the assay, the entire Hydra is immersed in a homogenization buffer containing high doses of Na2EDTA to chelate divalent cations and inhibit their catalytic activity, preventing additional DNA damage. The Hydra is then mechanically separated on ice to obtain a cell suspension. The separated cells are mixed with agarose gel, and the protocol for the alkaline comet assay is performed [62]. As previously mentioned, two different descriptors of the comet assay are used to assess primary DNA damage: comet tail length and tail intensity (% DNA in the tail). The free-living brown Hydra (Hydra oligactis) and the green symbiotic Hydra (Hydra viridissima) differ significantly in the size of the nucleus and, consequently, in the size of the nucleoid and the first descriptor of the comet assay—tail length [60]. However, the intensity of tail fluorescence (% of tail DNA) directly reflects the percentage of DNA that has migrated from the nucleoid core into the tail, indicating primary damage to the DNA. This metric is comparable across different Hydra species, regardless of whether they are symbiotic or free-living [87].
In addition, the incomparable regenerative capacity of Hydra makes it an ideal model for assessing teratogenic potential and effects on stem cells [56]. They are recognized as relevant indicators in ecotoxicological studies [90]. Numerous studies have shown that Hydra are reliable indicator organisms to determine the presence of genotoxic chemical substances in surface waters. They also serve as model organisms for testing genotoxicity under microcosm or controlled experimental conditions in vivo.
5. Hydra as a Test Organism for More Successful Environmental Decision-Making
In the last two decades, Hydra has reshaped the classical model of the test organism in environmental assessment protocols due to its simplicity, sensitivity, multifunctionality, and versatility in different, even simultaneous tests [63,73,91]. As a ubiquitous organism, Hydra is a highly adaptable and widespread animal in all types of aquatic ecosystems, inhabiting flowing, slow-flowing, stagnant, surface and subterranean, fresh, and even slightly brackish waters. Those small freshwater cnidarians are one of the most fragile aquatic organisms, simple in body structure and biology [56,92], with an extremely short life cycle (only 3 days on average) and rapid growth rate through clonal reproduction [78,93] with extreme regenerative capabilities in which they can fully regenerate their body even when most body and tissue structures are destroyed [93,94], making them ideal model organisms for environmental assessment protocols. Although Hydra is not used in formalized monitoring programs, the above list has shown that it has been used extensively and for a long time [95]. All these facts have made Hydra an excellent model organism in classical aquatic toxicology [56,63,73,91], in developmental biology research as a consequence of pollution impacts [61,62,95], in reproductive biology through effects of pollutants [96], and in the monitoring protocols of morphology, feeding, growth, and tissue regeneration [12,59] for more successful environmental decision-making.
Various Hydra species have been studied for a variety of environmental assessment protocols, from toxicity testing of freshwater pollutants (heavy metals, organic toxicants, and nano-materials) [36,59] to analysis of polyp survival, body structure, regeneration, and mortality [12,92]. Hydra, as a multifunctional test organism in environmental bioindication, meets the following primary prerequisites: (1) it has been thoroughly tested on different types of chemical substances, (2) it is well understood at different functional and physiological levels, and (3) it has been suitably used for the intended purpose of testing.
Hydra has proven to be an important alternative organism for preliminary environmental and health studies as it avoids the use of sensitive and rare vertebrate species. To minimize the unnecessary use of animals in experiments by finding ideal alternative methods and protocols for toxicity testing, it has proven to be a powerful model organism for toxicity testing at the organic and cellular levels. We live in a time of rapid global economic growth and increasing accumulation of toxic chemicals in the aquatic environment. Therefore, we propose to include Hydra as a more suitable organism in the regular methodological principles for environmental biomonitoring of hazardous toxic chemical contaminants, thus reducing mortality testing on vertebrates or rare and hard-to-test invertebrates. With these proposals, we are attempting to present the Hydra in more detail and better recognize it as an excellent test organism for monitoring environmental quality. This is in line with the EU Biodiversity Strategy for 2030, which is a comprehensive, ambitious, and long-term plan for nature conservation and a significant reversal of ecosystem degradation [97].
Environmental impact assessment and nature evaluation using Hydra species should be of great interest to researchers and decision-makers around the world to reduce the impact on rare and sensitive species and those for which the code of ethics does not even allow testing with various toxic substances.
6. Hydra as a Holobiont
As already stated, Hydra is a simple symbiotic organism and, as such, is a good model for studying many physiological mechanisms of more complex organisms [98] and is an excellent model for studying the holobiont. The holobiont is a relatively new view of the community of organisms in symbiosis that depend on each other and mutually determine not only the balance of physiological processes, i.e., health, but also the phenotype of each of them and the evolution of the organisms that participate in it [99].
The holobiont consists of a host individual and its microbial community. As a framework for understanding and describing the holobiont, the concept of the hologenome was presented in 2007 and 2008 [100,101]. The hologenome includes the genome of the host and the associated microbiome, i.e., the genome of all the belonging microorganisms. According to the hologenomic theory of evolution, the holobiont is considered the unit of selection in evolution [101]. The influence of an individual on the environment in which it lives does not only change the conditions for it, but also for other organisms that live in that environment, so organisms that live in the same space are very dependent on each other. In the case when organisms live on each other or in others at the organismal level, and especially at the tissue or cellular level, the interdependencies are even more pronounced. In organisms where this coexistence is long-term and de facto permanent, the dependence of organisms goes to the level that they regulate each other’s physiological processes, gene expression, and even evolution, i.e., to the level that the evolution of an individual can/should be observed through the evolution of the holobiont [99,102,103].
Hydra as a holobiont includes the host Hydra, endosymbiotic algae and bacterial microbiota. A simple structure with only one layer of cells on each side of the mesoglea, which limit the organism from the environment and perform numerous functions, including active immune defense and interactions with microorganisms [104,105], the well-researched physiology and genome, as well as the relatively small number of bacterial genera participating as microbiota [106,107] are a good basis for researching Hydra as a holobiont. In addition, the rather well-studied mechanisms of Hydra microbial population regulation are very similar to those of vertebrates [106] and allow Hydra to be used as a model organism to study the interrelationships of holobionts most interesting to humans. However, not all the mechanisms of regulation and communication of the partners in the very complex relationship of the holobiont which enable the achievement of stability are completely clear. Due to the clarification of these important mechanisms, the Hydra is an organism/holobiont that needs to be intensively researched further, not only at the level of the relationship between the Hydra and its bacterial microbiome, but also at the level of the relationship with viruses that, according to some results, have a regulatory role in maintaining the holobiont [104].
7. Hydra in Tumorigenesis Research
In recent years, it became evident that Hydra is a valuable asset in other areas, and not only in ecological research. It is a well-known model organism for pattern formation, regeneration, and stem cell research. Even though its regeneration potential was recognized a few hundred years ago, extensive studies concerning the underlying molecular mechanism began almost a few decades ago, and have shown that it is useful in human health studies.
For example, the Wnt signaling cascade, which is a key signaling pathway in embryonic development, is guided by Wnt-proteins, one of the morphogenes that trigger canonical (β-catenin-dependent) or non-canonical (β-catenin-independent) pathways and through which signaling process guide the pattern formation found in Hydra. These pathways are well-conserved through evolution, and it was recognized that in Hydra, they are responsible for head formation, oral-aboral axis pattern formation, tentacle and bud formation, and cell proliferation [36,67,68,69,70,71,72]. In human cancers, one of the consequences of a disrupted WNT-canonical pathway involves changes in MYC gene expression. The MYC gene codes for phosphoprotein MYC that forms dimers with the protein MAX and, in that way, acts as a transcriptional factor that regulates cell cycle progression, apoptosis, and even cellular transformation (Figure 2a) [83]. In 2010, Hartl et. al. [81] characterized myc and max genes in Hydra. They found myc1 and max gene expression in interstitial stem cells, which confirmed that the known myc and max biochemical properties known from human-based research existed as early as in the metazoan era, and showed that, because of conserved protein carboxyl and amino-terminal domains, Hydra myc1 shows similar transformation properties as its vertebrate descendent (Figure 2b) [81]. In 2014, the same group characterized Hydra myc2 in detail. They proved that although myc1 and myc2 have many similarities, myc2 gene expression can be found in proliferating epithelial cells, and is expressed during the gametogenesis. Moreover, myc2 also forms a complex with max proteins and can trigger avian fibroblast transformation (Figure 2b) [105]. A few years ago, Hartl et al. further proposed that in cnidarian Hydra, myc1 expression is suppressed by the induction of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, while myc2 might represent a c-MYC ortholog [106]. In 2023, Lechable M. et al. [107] characterized the third myc gene in Hydra—myc3. They showed that although the protein that it codes for does not have the usual myc-box-domain, it binds to max and has oncogenic potential (Figure 2b). They hypothesized that myc3 acts as a competitor for myc1 and myc2 in max binding and that through such a mechanism, it has a very specific role in nerve and gland differentiation [108]. Another paper from 2014 revealed that Hydra oligactis and Pelmatohydra robusta can develop naturally occurring tumors that reduce polyp fitness and arise because of differentiation arrest [80].
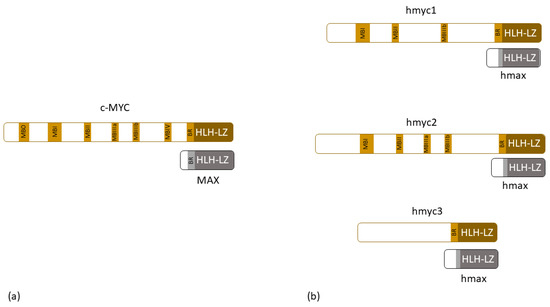
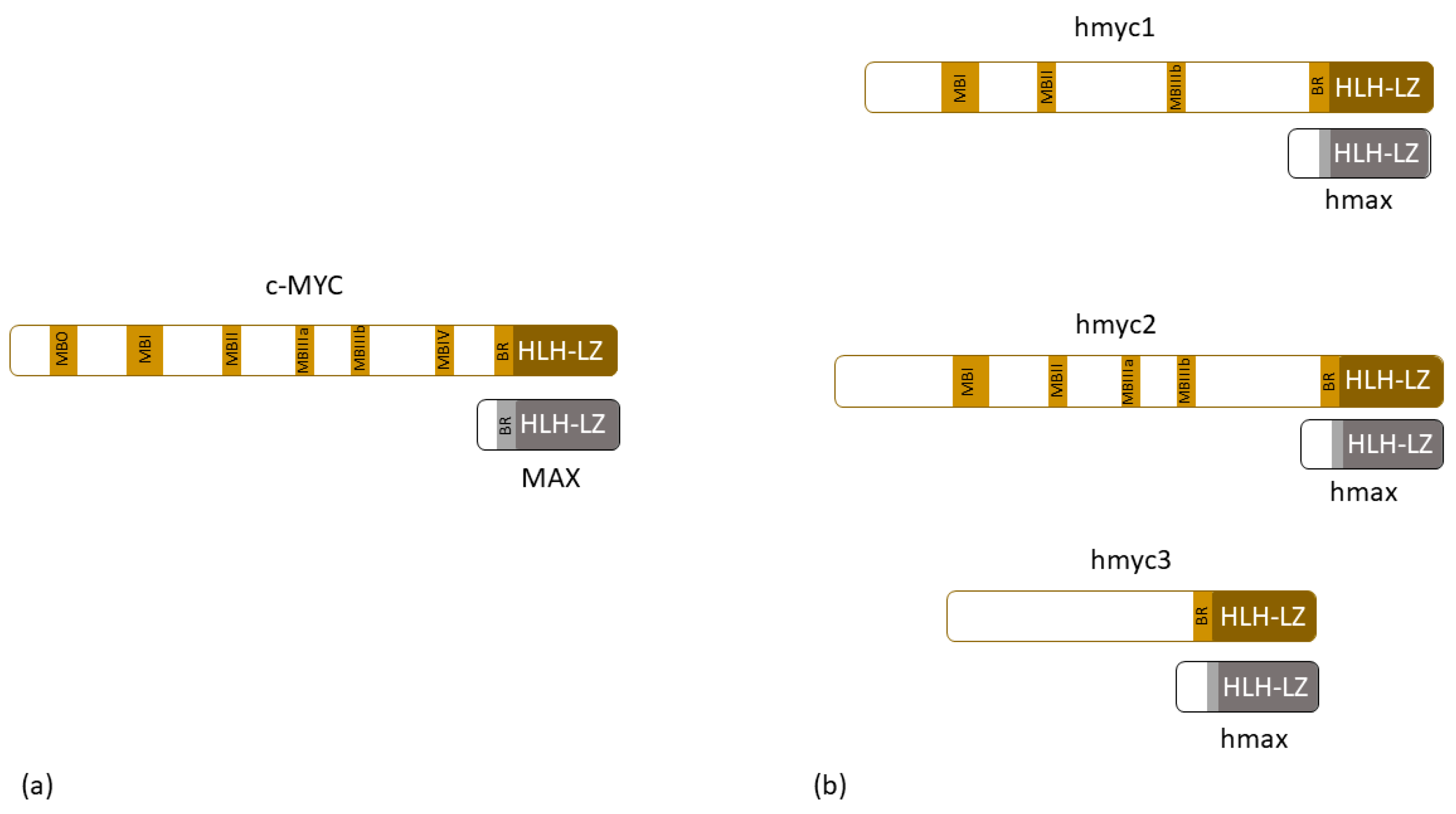
Figure 2.
(a) Schematic structure of human c-MYC protein and its dimer partner MAX; (b) schematic structure of hydra myc proteins and their dimer partner max. MB—myc box, BR—basic region, HLH-LZ—helix-loop-helix/leucine zipper domain.
Taken together, so far, the published data about Hydra tumor development and the myc gene family might direct further research about tumor evolution and even make Hydra a model for studies concerning evolutionary conserved oncogenetic mechanisms that can help in the understanding of human tumor development.
8. Conclusions
Based on extensive literature searches, we confirmed that Hydra has been a studied model organism in various biological fields for centuries, with particular emphasis on ecological and ecotoxicological studies. Its ease of manipulation and numerous properties, including cellular and organismal adaptations and differentiations, have, over time, made Hydra an invaluable model in education and STEM subjects. Due to its remarkable regenerative properties and the evolutionary origins of tumorigenesis, Hydra is also an emerging model for human biology and health studies. After many decades of studying symbiotic relationships, a new view on communities of organisms in symbiosis emerged from the perspective of the holobiont and the hologenome. Due to its particularities as an individual, but also due to the well-researched microbiota, Hydra quickly stood out as an excellent research model, with great prospects in scientific research.
The unique characteristics of Hydra, such as its simple body plan, robust regenerative capacity, and the presence of multipotent stem cells, have made it a cornerstone of developmental biology research. Its sensitivity to pollutants has also made Hydra an important bioindicator for assessing environmental health and genotoxicity in aquatic ecosystems. The use of techniques, such as the alkaline comet assay, illustrates its utility in detecting DNA damage and in studying the genotoxic effects of various substances.
In addition to its ecological and toxicological significance, the ability of Hydra to form tumors that resemble human tissue has opened new avenues for research into cancer and stem cell biology. This evolutionary perspective on tumorigenesis offers valuable insights into the fundamental mechanisms of carcinogenesis and the potential for regenerative medicine. Moreover, its regenerative properties and prospect of being the earliest known case of tumorigenesis make it a fascinating emerging model in human biology and health studies.
Overall, the broad applicability of Hydra in various scientific disciplines underscores its continued importance and versatility as a model organism. It promises to improve our understanding of biological processes, environmental interactions and human health.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.K., P.K., D.Ž., M.S.P. and S.G.; methodology, P.K. and M.S.P.; validation, G.K. and P.K.; formal analysis, P.K., M.S.P. and D.S.; investigation, G.K., P.K., D.Ž., M.S.P., P.P.Š., D.S., M.N. and S.G.; resources, G.K., P.K., D.Ž., M.S.P., P.P.Š., D.S., M.N. and S.G.; data curation, M.S.P.; writing—original draft preparation, G.K., P.K., D.Ž., M.S.P., P.P.Š., D.S., M.N. and S.G.; writing—review and editing, G.K., P.K. and D.Ž.; visualization, G.K., P.K., D.Ž., M.S.P., P.P.Š., D.S., M.N. and S.G.; supervision, G.K.; project administration, G.K.; funding acquisition, G.K. and D.Ž. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the University of Zagreb, support number 20286656. The paper is partially part of the project of the Institute for Medical Research and Occupational Health “Evaluation of Efficacy and Toxicity of Biologically Active Substances WP5: Ecogenetic Research in Biomonitoring of Populations in vivo and in vitro” by Institute for Medical Research and Occupational Health, support number 533-03-23-0006.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Nykolay, A.; Shahid, A. Immortal Hydra as a Model Organism for Metal Toxicity Studies. Sci. McMaster Undergrad. Sci. J. 2019, 1, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barve, A.; Galande, A.A.; Ghaskadbi, S.S.; Ghaskadbi, S. DNA Repair Repertoire of the Enigmatic Hydra. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 670695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovačević, G.; Gračan, R.; Gottstein, S. Ecotoxicological Effects of Sodium Metasilicate on Two Hydra Species, Hydra viridissima Pallas, 1766 and Hydra oligactis Pallas, 1766. Water 2023, 15, 4228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovačević, G.; Matijević, A.; Korać, P.; Želježić, D.; Reipert, S.; Caput Mihalić, K.; Sirovina, D.; Peharec Štefanić, P.; Ivšić, M. Effects of Norflurazon and UV Radiation on Symbiotic and Free-Living Hydra. Water 2024, 16, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivšić, M.; Kovačević, G. Evaluation of algae farming using the Chlorella bioassay. Croat. J. Fish. 2018, 76, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kević, N.; Radić Brkanac, S.; Vincek, N.; Peharec Štefanić, P.; Faraguna, F.; Kovačević, G.; Kalafatić, M.; Franjević, D. Endosymbiotic green algae in European Hydra strains show quantitative difference on morphological and isoenzyme level. Symbiosis 2019, 77, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovačević, G.; Kalafatić, M.; LJubešić, N. New Observations on Green Hydra Symbiosis. Folia Biol. 2007, 55, 77–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovačević, G.; Franjević, D.; Jelenčić, B.; Kalafatić, M. Isolation and Cultivation of Endosymbiotic Algae from Green Hydra and Phylogenetic Analysis of 18S rDNA Sequences. Folia Biol. 2010, 58, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovačević, G.; Kalafatić, M.; Jelenčić, B.; Franjević, D. Endosymbiotic alga as the stronger evolutionary partner in green hydra symbiosis. J. Endocyt. Cell Res. 2010, 20, 13–15. [Google Scholar]
- Kovačević, G.; Radić, S.; Jelenčić, B.; Kalafatić, M.; Posilović, H.; Pevalek-Kozlina, B. Morphological features and isoenzyme characterization of endosymbiotic algae from green hydra. Plant Syst. Evol. 2010, 284, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovačević, G.; Sirovina, D.; Karin, M.; Bartol, V.; Vujčić, V.; Ruščić, M. The Effect of Flavonoids on Hydra—Alga Symbiosis and Implementation of the Given Experiment in Schools. Croat. J. Educ. 2018, 20, 1173–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovačević, G.; Petrinec, D.; Tramontana Ljubičić, P.; Reipert, S.; Sirovina, D.; Špoljar, M.; Peharec Štefanić, P.; Želježić, D. Formation of Microalgal Hunting Nets in Freshwater Microcosm Food Web: Microscopic Evidence. Water 2023, 15, 3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovačević, G.; Tramontana Ljubičić, P.; Petrinec, D.; Sirovina, D.; Novosel, M.; Želježić, D. How Daphnia magna Defends Itself against Predators: Mechanisms and Adaptations in a Freshwater Microcosm. Water 2024, 16, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, U.; Ozbek, S.; Engel, R.; Petri, B.; Lottspeich, F.; Holstein, T.W. NOWA, a novel protein with minicollagen Cys-rich domains involved in nematocyst formation in Hydra. J. Cell Sci. 2002, 115, 3923–3934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holstein, T. The morphogenesis of nematocytes in Hydra and Forskalia: An ultrastructural study. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 1981, 75, 276–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, G.B.; Tilney, L.G. Cytological studies of the nematocysts of Hydra. II. The stenoteles. J. Biophys. Biochem. Cytol. 1959, 5, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckmann, A.; Özbek, S. The Nematocyst: A molecular map of the Cnidarian stinging organelle. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2012, 56, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, J.A.; Hyland, C.; Steele, R.E.; Collins, E.M. Dynamics of Mouth Opening in Hydra. Biophys. J. 2016, 110, 1191–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, R.L. Intercellular attachment in the epithelium of Hydra as revealed by electron microscopy. J. Biophys. Biochem. Cytol. 1959, 6, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epp, L.; Smid, I.; Tardent, P. Synthesis of the Mesoglea by Ectoderm and Endoderm in Reassembled Hydra. J. Morphol. 1986, 189, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarras, M.P., Jr.; Deutzmann, R. Hydra and Niccolo Paganini (1782–1840)—Two peas in a pod? The molecular basis of extracel-lular matrix structure in the invertebrate, Hydra. Bioessays 2001, 23, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aufschnaiter, R.; Zamir, E.A.; Little, C.D.; Özbek, S.; Münder, S.; David, C.N.; Li, L.; Sarras, M.P., Jr.; Zhang, X. In vivo imaging of basement membrane movement: ECM patterning shapes Hydra polyps. J. Cell Sci. 2011, 124 Pt 23, 4027–4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutzmann, R.; Fowler, S.; Zhang, X.; Boone, K.; Dexter, S.; Boot-Handford, R.; Rachel, R.; Sarras, M. Molecular, biochemical and functional analysis of a novel and developmentally important fibrillar collagen (Hcol-I) in hydra. Development 2000, 127, 4669–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, L.E.; Burnett, A.L.; Haynes, J.F.; Osborne, D.G.; Spear, M.L. Histological and ultrastructural study of the muscular and nervous systems in Hydra. II. Nervous system. J. Exp. Zool. 1968, 167, 295–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupre, C.; Yuste, R. Non-overlapping neural networks in Hydra vulgaris. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, 1085–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Taralova, E.; Dupre, C.; Yuste, R. Comprehensive machine learning analysis of Hydra behavior reveals a stable basal behavioral repertoire. eLife 2018, 7, e32605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trembley, A. Mémoires Pour Servir à L’histoire d’un Genre de Polypes d’eau Douce, à Bras en Forme de Cornes; Chez Jean & Herman Verbeek: Leide, The Netherlands, 1744; p. 324. [Google Scholar]
- Naik, S.; Unni, M.; Sinha, D.; Rajput, S.S.; Reddy, P.C.; Kartvelishvily, E.; Solomonov, I.; Sagi, I.; Chatterji, A.; Patil, S.; et al. Differential tissue stiffness of body column facilitates locomotion of Hydra on solid substrates. J. Exp. Biol. 2020, 223 Pt 20, jeb232702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, R.D. Developmental Biology of Hydra. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1974, 5, 45–62. [Google Scholar]
- Galliot, B.; Chera, S. The Hydra model: Disclosing an apoptotic origin of regenerative mechanisms. Trends Cell Biol. 2010, 20, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honegger, T.G.; Schmid, V. Sexual reproduction in freshwater coelenterates: Observations on egg formation and fertilization in Hydra. Zool. Sci. 2010, 27, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Tardent, P. The differentiation of germ cells in Cnidaria. In The Origin and the Evolution of Sex; Monroy, A., Halvorson, H., Eds.; Alan Liss, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1985; pp. 163–197. [Google Scholar]
- Holstein, T.W.; Hess, M.W.; Salvenmoser, W. Preparation techniques for transmission electron microscopy of Hydra. Methods Cell Biol. 2010, 96, 285–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiltshire, K.; Boersma, M.; Meyer, B. Grazer-induced changes in the desmid Staurastrum. Hydrobiologia 2003, 491, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merle, P.L.; Sabourault, C.; Richier, S.; Allemand, D.; Furla, P. Catalase characterization and implication in bleaching of a symbiotic sea anemone. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2007, 42, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beach, M.J.; Pascoe, D. The role of Hydra vulgaris (Pallas) in assessing the toxicity of freshwater pollutants. Water Res. 1998, 32, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalafatić, M.; Kopjar, N. Response of Green Hydra to the Treatment with Different Pesticides under Laboratory Conditions. Z. Angew. Zool. 1994, 2, 213–223. [Google Scholar]
- Kalafatić, M. Regeneration and asexual reproduction of Hydra oligactis treated with different pesticides. Biologia 1997, 52, 475–480. [Google Scholar]
- Kovačević, G.; Kalafatić, M.; Ljubešić, N.; Šunjić, H. The effect of chloramphenicol on the symbiosis between alga and hydra. Biologia 2001, 56, 605–610. [Google Scholar]
- Arkhipchuk, V.V.; Blaise, C.; Malinovskaya, M.V. Use of hydra for chronic toxicity assessment of waters intended for human consumption. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 142, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachamim, T.; Sher, D. What Hydra can teach us about chemical ecology—How a simple, soft organism survives in a hostile aqueous environment. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2012, 56, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonge, C.M. Ecology and physiology of reef building corals. In Perspectives in Marine Biology; Buzzati-Traverso, A., Ed.; University California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA; Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1958; pp. 117–136. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, S.; Badhiwala, K.N.; Robinson, J.T.; Cho, W.H.; Siemann, E. Thermal plasticity of a freshwater cnidarian holobiont: Detection of transgenerational effects in asexually reproducing hosts and symbionts. ISME J. 2019, 13, 2058–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Bhattacharjee, M.; Siemann, E. Thermal tolerance in green Hydra: Identifying the roles of algal endosymbionts and hosts in a freshwater holobiont under stress. Microb. Ecol. 2019, 77, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathia, J.; Schröder, K.; Fraune, S.; Lachnit, T.; Rosenstiel, P.; Bosch, T.C.G. Symbiotic Algae of Hydra viridissima Play a Key Role in Maintaining Homeostatic Bacterial Colonization. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 869666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karntanut, W.; Pascoe, D. Effects of removing symbiotic green algae on the response of Hydra viridissima (Pallas 1776) to metals. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2005, 60, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karntanut, W.; Pascoe, D. The toxicity of copper, cadmium and zinc to four different Hydra (Cnidaria: Hydrozoa). Chemosphere 2002, 47, 1059–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovačević, G.; Kalafatić, M.; Ljubešić, N. Effects of Norflurazon on Green and Brown Hydra. Folia Biol. 2009, 57, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogg, M.C.; Galliot, B.; Tsiairis, C.D. Model systems for regeneration: Hydra. Development 2019, 146, dev177212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badhiwala, K.N.; Primack, A.S.; Juliano, C.E.; Robinson, J.T. Multiple neuronal networks coordinate Hydra mechanosensory behavior. eLife 2021, 10, e64108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gierer, A.; Bode, H.; Berking, S.; Schaller, H.; Trenkner, E.; Hansmann, G.; David, C.N.; Flick, K. Regeneration of hydra from reaggregated cells. Nat. New Biol. 1972, 239, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gierer, A. The Hydra model—A model for what? Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2012, 56, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczyk, S.; Fischer, K.; Austad, S.; Galliot, B. Hydra, a powerful model for aging studies. Invertebr. Reprod. Dev. 2015, 59, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, B.T.; Auer, K.M.; Lopez, D.A.; Shum, J.P.; Suarsana, B.; Suh, G.K.; Hedde, P.N.; Ahrar, S. Orthogonal-view microscope for the biomechanics investigations of aquatic organisms. HardwareX 2024, 18, e00533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedde, P.N.; Le, B.T.; Gomez, E.L.; Duong, L.; Steele, R.E.; Ahrar, S. SPIM-Flow: An Integrated Light Sheet and Microfluidics Platform for Hydrodynamic Studies of Hydra. Biology 2023, 12, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, B.; Gagné, F.; Blaise, C. Hydra, a model system for environmental studies. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2012, 56, 613–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeeshan, M.; Murugadas, A.; Ghaskadbi, S.; Rajendran, R.B.; Akbarsha, M.A. ROS dependent copper toxicity in Hydra-biochemical and molecular study. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 185–186, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeeshan, M.; Murugadas, A.; Ghaskadbi, S.; Ramaswamy, B.R.; Akbarsha, M.A. Ecotoxicological assessment of cobalt using Hydra model: ROS, oxidative stress, DNA damage, cell cycle arrest, and apoptosis as mechanisms of toxicity. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 224, 54–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugadas, A.; Zeeshan, M.; Thamaraiselvi, K.; Ghaskadbi, S.; Akbarsha, M.A. Hydra as a model organism to decipher the toxic effects of copper oxide nanorod: Eco-toxicogenomics approach. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cera, A.; Cesarini, G.; Spani, F.; Scalici, M. Hydra vulgaris assay as environmental assessment tool for ecotoxicology in fres-hwaters: A review. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2021, 72, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galliot, B. Hydra, a fruitful model system for 270 years. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2012, 56, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarras, M.P., Jr. Components, structure, biogenesis and function of the Hydra extracellular matrix in regeneration, pattern formation and cell differentiation. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2012, 56, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascoe, D.; Karntanut, W.; Müller, C.T. Do pharmaceuticals affect freshwater invertebrates? A study with the cnidarian Hydra vulgaris. Chemosphere 2003, 51, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinn, B.; Gagné, F.; Blaise, C. Evaluation of the acute, chronic and teratogenic effects of a mixture of eleven pharmaceuticals on the cnidarian, Hydra attenuata. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 1072–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, E.M.; Gabel, B.E.G. Application of the Hydra Assay for Rapid Detection of Developmental Hazards. J. Am. Coll. Toxicol. 1992, 1, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilby, O.K.; Newall, D.R.; Tesh, J.M. A hydra assay as a pre-screen for teratogenic potential. Food Chem. Toxic. 1986, 24, 651–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gellner, K.; Praetzel, G.; Bosch, T.C.G. Cloning and expression of a heat-inducible hsp70 gene in two species of Hydra which differ in their stress response. Eur. J. Biochem. 1992, 210, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyne, R.V.; Rippon, G.D.; Ellender, G. pH-Dependent uranium toxicity to freshwater Hydra. Sci. Total Environ. 1992, 125, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollino, C.A.; Holdway, D.A. Potential of two Hydra species as standard toxicity test animals. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1999, 43, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karntanut, W.; Pascoe, D. A comparison of methods for measuring acute toxicity to Hydra vulgaris. Chemosphere 2000, 41, 1543–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinn, B.; Gagné, F.; Blaise, C. Oxidative metabolism activity in Hydra attenuata exposed to carbamazepine. Fresen Environ. Bull. 2004, 13, 783–788. [Google Scholar]
- Pachura-Bouchet, S.; Blaise, C.; Vasseur, P. Toxicity of nonylphenol on the cnidarian Hydra attenuata and environmental risk assessment. Environ. Toxicol. 2006, 21, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugadas, A.; Mahamuni, D.; Nirmaladevi, S.D.; Thamaraiselvi, K.; Thirumurugan, R.; Akbarsha, M.A. Hydra as an alterna-tive model organism for toxicity testing: Study using the endocrine disrupting chemical Bisphenol A. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2019, 17, 680–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaise, C.; Gagne, F.; Ferard, J.F.; Eullaffroy, P. Ecotoxicity of selected nano-materials to aquatic organisms. Environ. Toxicol. 2008, 23, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchesano, V.; Ambrosone, A.; Bartelmess, J.; Strisciante, F.; Tino, A.; Echegoyen, L.; Tortiglione, C.; Giordani, S. Impact of Carbon Nano-Onions on Hydra vulgaris as a Model Organism for Nanoecotoxicology. Nanomaterials 2015, 5, 1331–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovačević, G.; Želježić, D.; Horvatin, K.; Kalafatić, M. Morphological features and comet assay of green and brown Hydra treated with aluminium. Symbiosis 2007, 44, 145–152. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, F.; Quinn, B. The effects of microplastic on freshwater Hydra attenuata feeding, morphology & reproduction. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vimalkumar, K.; Sangeetha, S.; Felix, L.; Kay, P.; Pugazhendhi, A. A systematic review on toxicity assessment of persistent emerging pollutants (EPs) and associated microplastics (MPs) in the environment using the Hydra animal model. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 256, 109320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venâncio, C.; Barbosa, C.; Lopes, I. Glyphosate and Roundup® Ready Effects in Hydra viridissima: New Data in an Old Issue. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domazet-Lošo, T.; Klimovich, A.; Anokhin, B.; Anton-Erxleben, F.; Hamm, M.J.; Lange, C.; Bosch, T.C. Naturally occurring tumours in the basal metazoan Hydra. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartl, M.; Mitterstiller, A.M.; Valovka, T.; Breuker, K.; Hobmayer, B.; Bister, K. Stem cell-specific activation of an ancestral myc protooncogene with conserved basic functions in the early metazoan Hydra. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 4051–4056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, F.D. Light-dependent herbicides: An overview. Weed Sci. 2000, 48, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korać, P.; Dotlić, S.; Matulić, M.; Zajc Petranović, M.; Dominis, M. Role of MYC in B Cell Lymphomagenesis. Genes 2017, 8, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, X.; Claeys-Bruno, M.; Andraud, J.P.; Macarie, H.; Martínez, D.E.; Robin, M.; Sergent, M.; De Jong, L. Hydra bioassay for the evaluation of chlordecone toxicity at environmental concentrations, alone or in complex mixtures with dechlorinated byproducts: Experimental observations and modeling by experimental design. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 91017–91035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziuzina, D.; Sarangapani, C.; Bourke, P. Hydra as a Model for Screening Ecotoxicological Effects of Plasma-Treated Water. Plasma Med. 2018, 8, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, E.; Kansız, S.; Doğan, M.; Topel, Ö.; Akkoyunlu, G.; Kandur, M.Y.; Turna Demir, F. Hazard Assessment of the Effects of Acute and Chronic Exposure to Permethrin, Copper Hydroxide, Acephate, and Validamycin Nanopesticides on the Physio-logy of Drosophila: Novel Insights into the Cellular Internalization and Biological Effects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatima, J.; Ara, G.; Afzal, M.; Siddique, Y.H. Hydra as a research model. Toxin Rev. 2024, 43, 157–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Želježić, D.; Kovačević, G.; Matijević, A.; Korać, P.; Caput Mihalić, K. Does the Symbiotic Relationship Between Hydra viridissima and Photoautotrophic Alga Provide an Evolutionary Advantage in Protecting DNA against Damage by the Cytotoxic or Genotoxic Mode of Action of Environmental Stressors? Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2024, 112, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, N.; Srivastava, R.; Agrawal, U.R.; Tewari, R.R. An insight into the genotoxicity assessment studies in dipterans. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2017, 773, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holstein, T.-W. The role of cnidarian developmental biology in unraveling axis formation and Wnt signaling. Dev. Biol. 2022, 487, 74–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaible, R.; Scheuerlein, A.; Dańko, M.J.; Gampe, J.; Martínez, D.E.; Vaupel, J.W. Constant mortality and fertility over age in Hydra. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 15701–15706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perros, T.; Biquet-Bisquert, A.; Meriem, Z.B.; Delarue, M.; Joseph, P.; Marcq, P.; Cochet-Escartin, O. Mechanical characterization of regenerating Hydra tissue spheres Mechanics of regenerating Hydra. Biophys. J. 2024, 123, 1792–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaskadbi, S. Hydra: A powerful biological model. Reson 2020, 25, 1197–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuhori, N.; Kitano, M.; Kimura, H. Toxic effects of bisphenol A on sexual and asexual reproduction in Hydra oligactis. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2005, 48, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, C.; Depledge, M.; Fraser, R.; Johnson, A.; Hutchison, G.; Matthiessen, P.; Murphy, R.; Owens, S.; Sumpter, J. Key actions for a sustainable chemicals policy. Environ. Int. 2020, 137, 105463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission. EU Biodiversity Strategy for 2030: Bringing Nature back into Our Lives. Directorate-General for Environment; Publications Office of the European Union: Strasbourg, France, 2021; Available online: https://data.europa.eu/doi/10.2779/677548 (accessed on 7 May 2024).
- Bosch, T.C.G.; Miller, D.J. The holobiont imperative: Perspectives from early emerging animals. In The Hydra Holobiont: A Tale of Several Symbiotic Lineages 79; Springer: Wien, Austria, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, E.; Koren, O.; Reshef, L.; Efrony, R.; Zilber-Rosoenberg, I. The role of microorganisms in coral health, disease and evolution. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zilber-Rosenberg, I.; Rosenberg, E. Role of microorganisms in the evolution of animals and plants: The hologenome theory of evolution. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 32, 723–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, R.; Margulis, L.; Berlanga, M. Symbiogenesis: The holobiont as a unit of evolution. Int. Microbiol. 2013, 16, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, E.; Zilber-Rosenberg, I. The Hologenome Concept: Human, Animal and Plant Microbiota; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; p. 178. ISBN 978-3-319-04240-4. [Google Scholar]
- Bosch, T.C.; Grasis, J.A.; Lachnit, T. Microbial ecology in Hydra: Why viruses matter. J. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, T.C.G.; Anton-Erxleben, F.; Augustin, R.; Franzenburg, S.; Fraune, S. Hydra Go Bacterial. In Beneficial Microorganisms in Multicellular Life Forms; Rosenberg, E., Gophna, U., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Bosch, T.C.G. Hydra’s Lasting Partnership with Microbes: The Key for Escaping Senescence? Microorganisms 2022, 10, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachnit, T.; Bosch, T.C.G.; Deines, P. Exposure of the Host-Associated Microbiome to Nutrient-Rich Conditions May Lead to Dysbiosis and Disease Development—An Evolutionary Perspective. mBio 2019, 10, e00355-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartl, M.; Glasauer, S.; Valovka, T.; Breuker, K.; Hobmayer, B.; Bister, K. Hydra myc2, a unique pre-bilaterian member of the myc gene family, is activated in cell proliferation and gametogenesis. Biol. Open 2014, 3, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lechable, M.; Tang, X.; Siebert, S.; Feldbacher, A.; Fernández-Quintero, M.L.; Breuker, K.; Juliano, C.E.; Liedl, K.R.; Hobmayer, B.; Hartl, M. High Intrinsic Oncogenic Potential in the Myc-Box-Deficient Hydra Myc3 Protein. Cells 2023, 12, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartl, M.; Glasauer, S.; Gufler, S.; Raffeiner, A.; Puglisi, K.; Breuker, K.; Bister, K.; Hobmayer, B. Differential regulation of myc homologs by Wnt/β-Catenin signaling in the early metazoan Hydra. FEBS J. 2019, 286, 2295–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).