Study on the Spatiotemporal Distribution Characteristics of Meiofauna in Baiyangdian Lake and Its Influencing Factors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sites
2.2. Environmental Parameters
2.3. Meiofauna Analyses
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
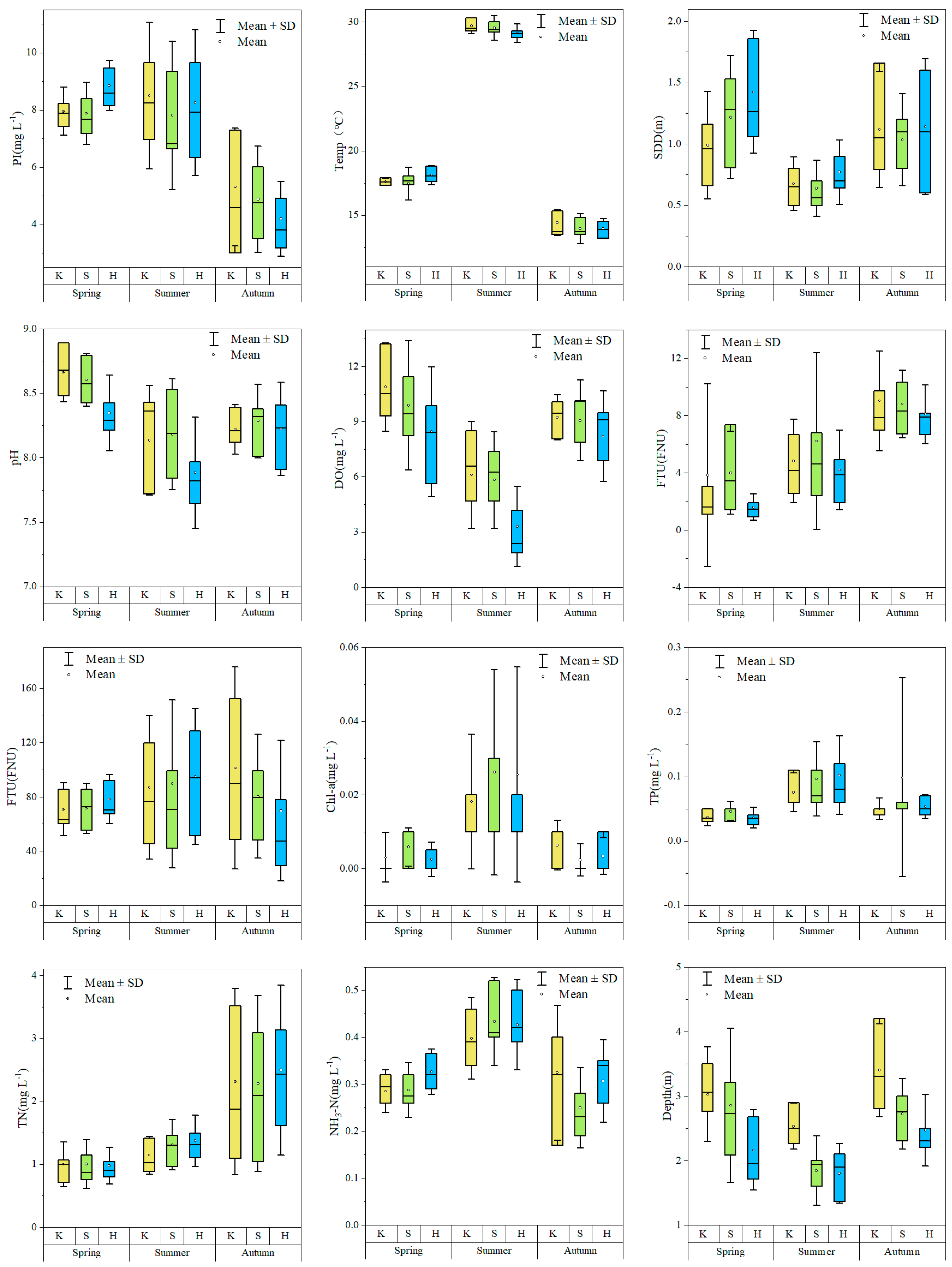
3.1. Physical and Chemical Parameters of the Water Body
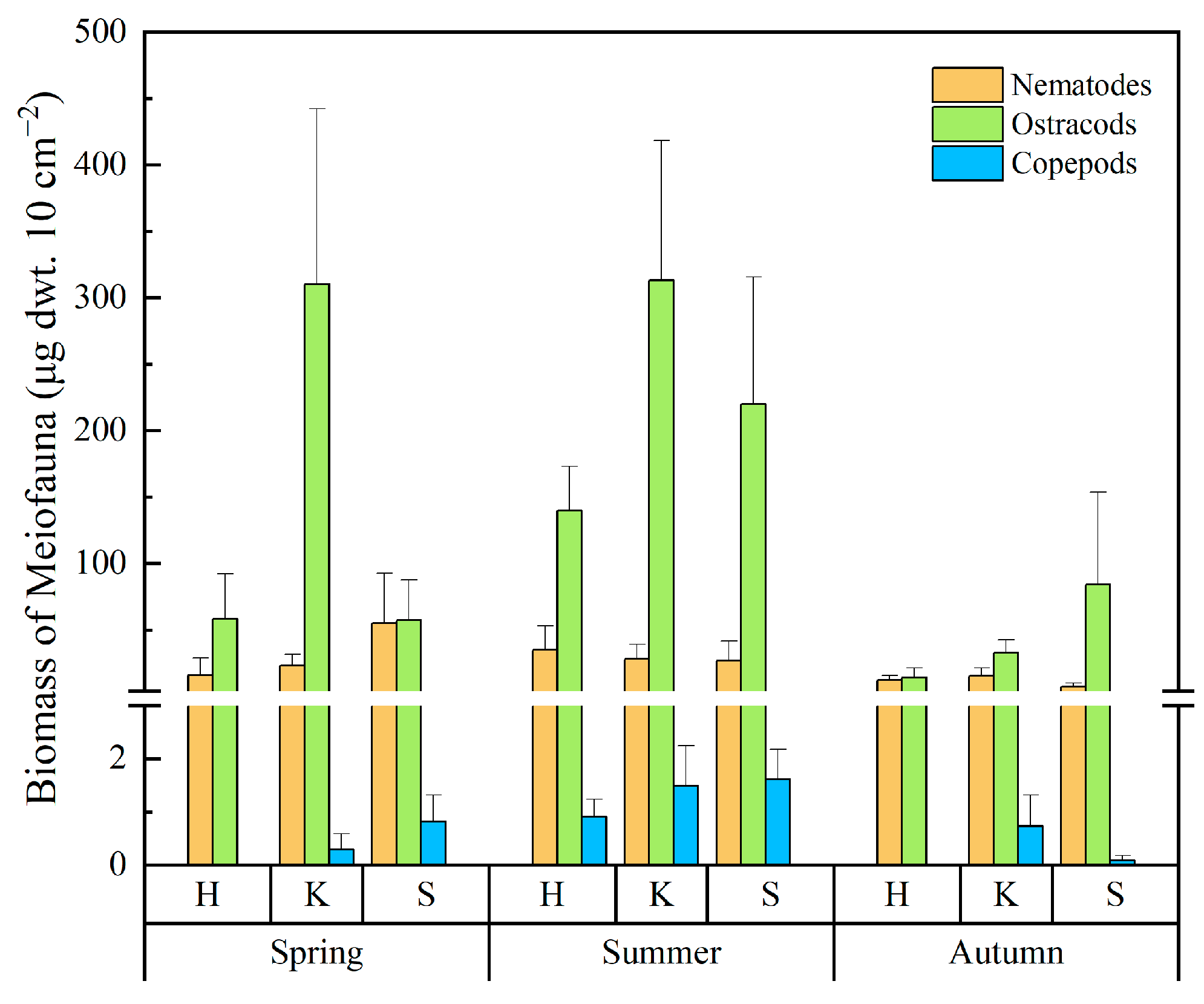
3.2. Distribution of the Meiofaunal Assemblages
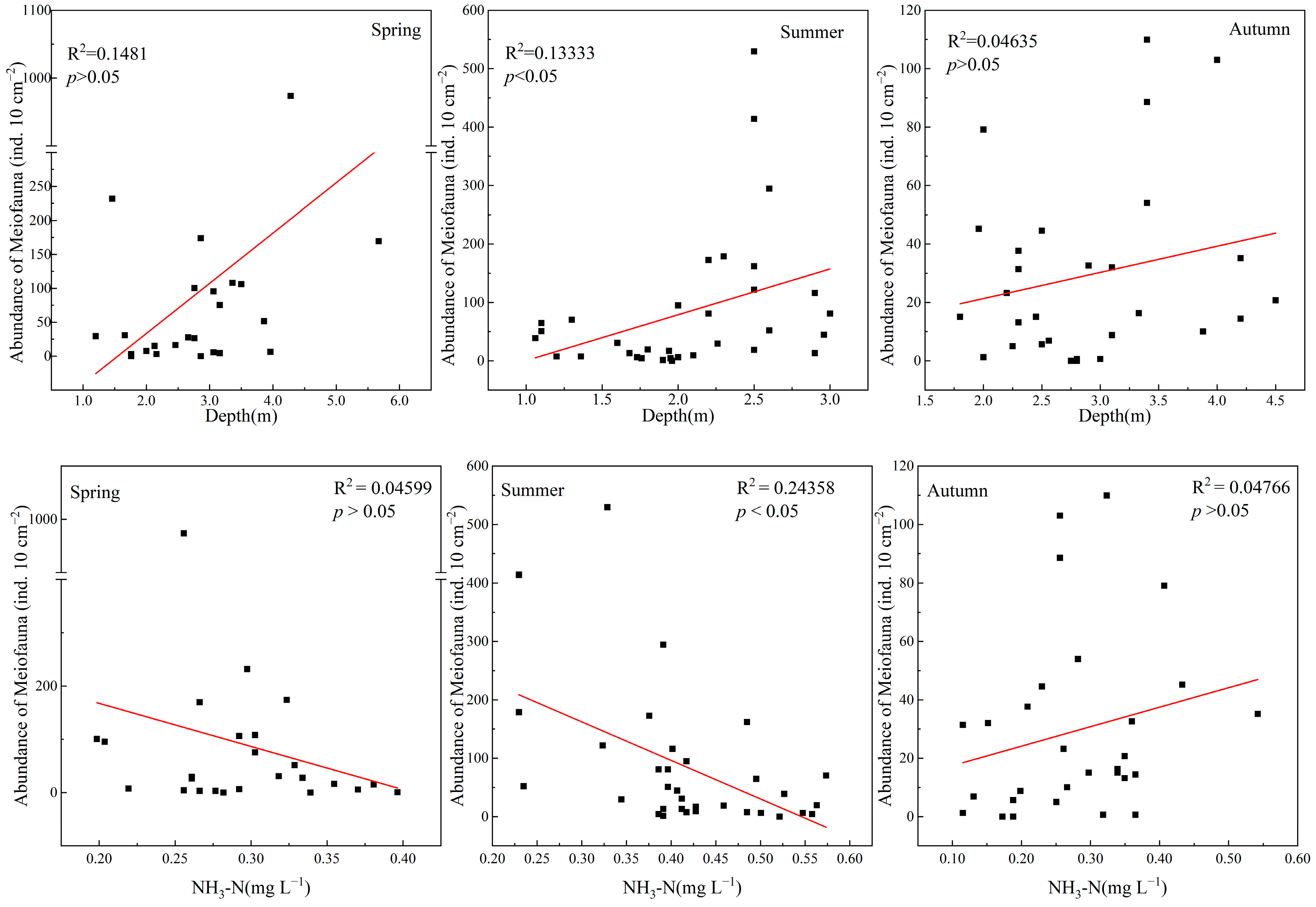
3.3. Relationships between Meiofauna and Physicochemical Parameters
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatiotemporal Distribution of Meiofauna in Baiyangdian Lake
4.2. The Characteristics of the Meiofauna Community and Their Relationships with Environmental Factors
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Rundle, S.D.; Robertson, A.L.; Schmid-Araya, J.M. Freshwater Meiofauna: Biology and Ecology; Backhuys Publishers: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Moens, T.; Beninger, P.G. Meiofauna: An inconspicuous but important player in mudflat ecology. In Mudflat Ecology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 91–147. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, A.D.; Jacoby, C.A. Biological indicators of marine environmental health: Meiofauna—A neglected benthic component? Environ. Monit. Assess. 1999, 54, 47–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridall, A.; Ingels, J. Suitability of free-living marine nematodes as bioindicators: Status and future considerations. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 685327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itaoka, M.; Tamai, K. Effect of eutrophication on the structure of meiobenthic communities in Hiroshima Bay. Benthos Res. 1993, 1993, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi-Dinan, A.; Schroeder, F.; Peters, L.; Majdi, N.; Traunspurger, W. The effect of trophic state and depth on periphytic nematode communities in lakes. Limnologica 2014, 44, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristau, K.; Spann, N.; Traunspurger, W. Species and trait compositions of freshwater nematodes as indicative descriptors of lake eutrophication. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 53, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höckelmann, C.; Moens, T.; Jüttner, F. Odor compounds from cyanobacterial biofilms acting as attractants and repellents for free-living nematodes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2004, 49, 1809–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudes, A.; Sabater, S.; Vilalta, E.; Muñoz, I. The nematode community in cyanobacterial biofilms in the river Llobregat, Spain. Nematology 2006, 8, 909–919. [Google Scholar]
- Ristau, K.; Traunspurger, W. Relation between nematode communities and trophic state in southern Swedish lakes. Hydrobiologia 2011, 663, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.H.; Liang, Y.L.; Sun, X.D. Newly recorded species of free-living nematodes from china (Chromadorida Enoplida & Araeolaimida). Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 1997, 21, 312–321, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.H.; Liang, Y.L. A comparative study of benthic nematodes in two Chinese lakes with contrasting sources of primary production. Hdrobiologia 1999, 411, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.H.; Fu, C.Z.; Liang, Y.L.; Chen, J.K. Distribution of the meiofauna community in a eutrophic shallow lake of China. Arch. Hydrobiol. 2004, 159, 555–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wu, X.Q.; Wang, X.Y.; Qi, G.L.; Cheng, B. Studies on the Meiofauna community in Dongchang Lake of Liaocheng. J. Liaocheng Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2008, 21, 68–72+78, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.J.; Huang, Y. Studies on the Meiofauna Community in Weishan Lake. J. Liaocheng Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2009, 22, 51–54, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yan, F.G. Community Characteristics and Ecological Role of Meiofaunan in Shallow Lakes; Institute of Hydrobiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences: Wuhan, China, 2012; (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yan, F.G.; Wang, H.J.; Wang, H.Z.; Zhang, T.L.; Li, W. Community characteristics of Meiofaunan in an algae-dominated shallow lakes, with discussion on the ecological role. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2010, 34, 634–638, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schratzberger, M.; Ingels, J. Meiofauna matters: The roles of meiofauna in benthic ecosystems. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2018, 502, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strayer, D.L. The benthic micrometazoans of Mirror lake. New Hampshire. Arch. Hydrobiol. Suppl. 1985, 72, 287–426. [Google Scholar]
- Tinson, S.; Laybourn-Parry, J. The distribution and abundance of benthic cyclopoid copepods in Esthwaite Water, Cumbria. Hydrobiologia 1986, 131, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traunspurger, W. Distribution of benthic nematodes in the littoral of an oligotrophic lake (Konigssee, National Park Berchtesgaden, FRG). Arch. Hydrobiol. 1996, 135, 393–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traunspurger, W. Distribution of benthic nematodes in the littoriprofundal and profundal of an oligotrophic lake (Konigssee, National Park Berchtesgaden, FRG). Arch. Hydrobiol. 1996, 135, 557–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergtold, M.; Traunspurger, W. The benthic community in the profundal of Lake Brunnsee: Seasonal and spatial patterns. Arch. Hydrobiol. 2004, 160, 527–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michiels, I.C.; Traunspurger, W. A three years study of seasonal dynamics of a zoobenthos community in a eutrophic lake. Nematology 2004, 6, 655–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michiels, I.C.; Traunspurger, W. Seasonal variation of biodiversity and assemblage structure in freshwater nematodes. Arch. Hydrobiol. 2005, 163, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, F.; Traunspurger, W.; Pettersson, K.; Peters, L. Temporal changes in periphytic meiofauna in lakes of different trophic states. J. Limnol. 2012, 71, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, F.; Peters, L.; Traunspurger, W. Temporal variations in epilithic nematode assemblages in lakes of different productivities. Fundam. Appl. Limnol. 2012, 181, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurashov, E.A. The role of meiobenthos in lake ecosystems. Aquat. Ecol. 2022, 36, 447–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristau, K.; Faupel, M.; Traunspurger, W. The effects of nutrient enrichment on a freshwater meiofaunal assemblage. Freshw. Biol. 2012, 57, 824–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, C.; Ouyang, Z.; Xu, W.; Bai, Y.; Zhou, W. Impacts of human activities on the hydrology of Baiyangdian Lake, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 62, 1343–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.Q.; Li, H.C.; Liao, C.Y.; Deng, J.Z.; Sun, H.M.; Yan, M.X.; Wang, H.W. Investigation of benthic invertebrates and analysis of water environment in Baiyangdian Lake. Hebei Fish. 2019, 308, 40–44+50, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.G.; Zhao, D.D.; Ye, B. Eeological aributes, restorlion, and prteeion of the Baivangdian in Xiong’an New Area. Aela Eeologica Sin. 2019, 39, 3019–3025, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Wang, F.; Wu, D.; Kong, F.Q.; Wang, Q. The community structure of macrobenthos and its response to environmental factors in Baiyangdian Lake. Hebei Fish. 2023, 12, 33–40, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semprucci, F.; Losi, V.; Moreno, M. A review of Italian research on free-living marine nematodes and the future perspectives on their use as Ecological Indicators (EcoInds). Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2015, 16, 352–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The State Environmental Protection Administration. The Water and Wastewater Monitoring Analysis Method Editorial Board. Water and Wastewater Monitoring Analysis Method, 4th ed.; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2002; pp. 38–47. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.C.; Liu, X.Q.; Zhang, J.H. Evaluate method and classification standard on lake eutrophication. Environ. Monit. China 2002, 5, 47–49, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q. Traceable Model of Water Quality and the Control Countermeasures of Eutrophication in Shihou Lake; China University of Geosciences Beijing: Beijing, China, 2012; (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.Q.; Zhang, Z.N.; Mu, F.H. Large-scale Patterns of Meiofaunal Abundance in the Bohai Sea. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2002, 22, 1463–1469. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.K. Study on the Biodiversity and Taxonomy of Free-Living Marine Nematodes in the Xiamen Island, China; Jimei University: Xiamen, China, 2012; (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Somerfield, P.J.; Warwick, R.M. Meiofauna in Marine Pollution Monitoring Programmes: A Laboratory Manual; Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Food, Directorate of Fisheries Research Technical Series: London, UK, 1996.
- Juario, J.V. Nematode species composition and seasonal fluctuation of a sublittoral meiofauna community in the German Bight. Veröff. Inst. Meeresforsch. Bremerh. 1975, 15, 283–337. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.N.; Zhou, H.; Yu, Z.Z.; Han, J. Abundance and biomass of the benthic in the northern soft-bottom of the Jiaozhou Bay. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2001, 32, 139–147, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.B. Studies on Community Structure and Biodiversity of Meiofauna in Taiping Bay, Qingdao, China; Ocean University of China: Qingdao, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.; Liu, Q.H.; Zhang, Z.N.; Liu, X.S. Response of free-living marine nematodes to the southern Yellow Sea cold water mass. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 105, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widbom, B. Determination of average individual dry weights and ash-free dry weights in different sieve fractions of marine meiofauna. Mar. Biol. 1984, 84, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.H.; Liu, X.S. Taxa composition and distribution patterns of meiofauna in the intertidal zones of Shandong Peninsula. J. Liaocheng Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2021, 34, 100–110, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Danovaro, R.; Gambi, C.; Lampadariou, N.; Tselepides, A. Deep-sea nematode biodiversity in the Mediterranean basin: Testing for longitudinal, bathymetric and energetic gradients. Ecography 2008, 31, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Hoogen, J.; Geisen, S.; Routh, D.; Ferris, H.; Traunspurger, W.; Wardle, D.A.; De Goede, R.G.M.; Adams, B.J.; Ahmad, W.; Andriuzzi, W.S.; et al. Soil nematode abundance and functional group composition at a global scale. Nature 2019, 572, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strayer, D.; Likens, G.E. An energy budget for the zoobenthos of Mirror Lake, New Hampshire. Ecology 1986, 67, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traunspurger, W. The biology and ecology of lotic nematodes. Freshw. Biol. 2000, 44, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traunspurger, W. Nematoda. In Encyclopedia of Inland Waters; Likens, G.E., Ed.; Academic: London, UK; Boston, MA, USA, 2009; pp. 372–383. [Google Scholar]
- Traunspurger, W.; Michiels, I.C.; Abebe, E. Composition and distribution of free-living freshwater nematodes: Global and local perspectives. In Freshwater Nematodes: Ecology and Taxonomy; Eyualem Abebe, A., Andràssy, I., Traunspurger, W., Eds.; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2006; pp. 46–76. [Google Scholar]
- Giere, O. Meiobenthology. The Microscopic Motile Fauna of Aquatic Sediments; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; 527p. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.H. Studies of Freshwater and Soil Nematodes of China; Institute of Hydrobiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences: Wuhan, China, 1999; (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wieser, W. Benthic studies in Buzzards Bay II. The Meiofauna 1. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1960, 5, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traunspurger, W.; Wilden, B.; Majdi, N. An overview of meiofaunal and nematode distribution patterns in lake ecosystems differing in their trophic state. Hydrobiologia 2020, 847, 2665–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, L.; Traunspurger, W. Species distribution of free-living nematodes and other meiofauna in littoral periphyton communities of lakes. Nematology 2005, 7, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiel, H.J. Benthos in Upwelling Regions. Upwelling Ecosystems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1978; pp. 124–138. [Google Scholar]
- Josefson, A.B.; Widbom, B. Differential response of benthic macrofauna and meiofauna to hypoxia in the Gullmar Fjord basin. Mar. Biol. 1988, 100, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, C.C. Freshwater Meiofauna: Biology and Ecology. Q. Rev. Biol. 2002, 77, 469. [Google Scholar]
- Kreuzinger-Janik, B.; Schroeder, F.; Majdi, N.; Traunspurger, W. Depth-Related Effects on a Meiofaunal Community Dwelling in the Periphyton of a Mesotrophic Lake. PLoS ONE. 2018, 10, e0137793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abebe, E.; Mees, J.; Coomans, A. Nematode communities of Lake Tana and other inland water bodies of Ethiopia. Hydrobiologia 2001, 462, 41–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michiels, C.I.; Traunspurger, W. Benthic community patterns and the composition of feeding types and reproductive modes in freshwater nematodes. Nematology 2005, 7, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.S.; Xu, M.; Zhang, J.H.; Mou, G.; Liu, D.; Li, X. Abundance and biomass of deep-sea meiofauna in the northern South China Sea. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2014, 33, 52–59. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, L.Z.; Fu, S.J.; Yang, J.; Zhou, X.P. Distribution of meiofaunal abundance in relation to environmental factors in Beibu Gulf, South China Sea. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2012, 31, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlyuk, O.N.; Trebukhova, J.A. Meiobenthos in Nha Trang Bay of the South China Sea (Vietnam). Ocean Sci. J. 2006, 41, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
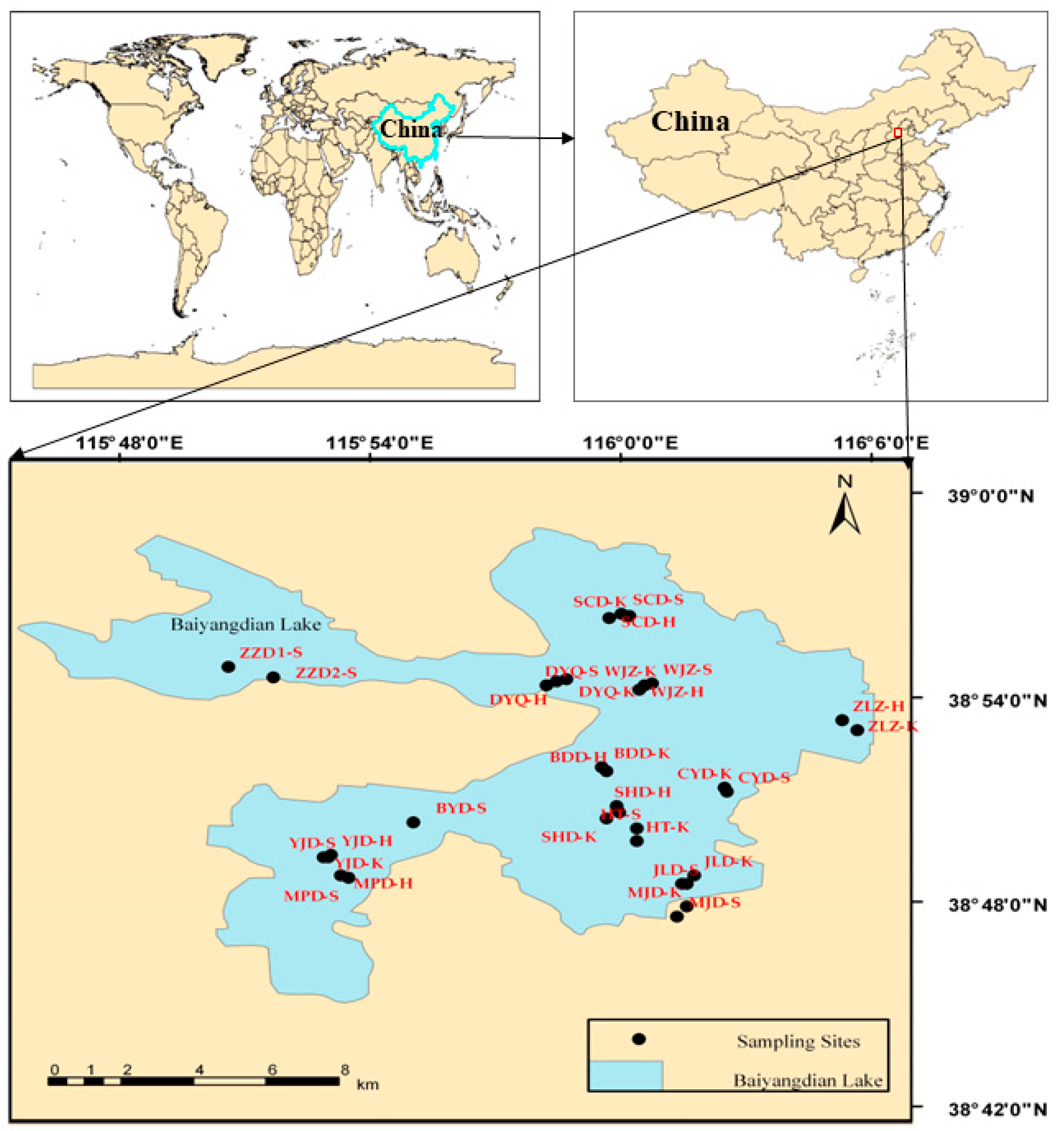


| Sampling Site Name | Longitude (°) | Latitude (°) | Habitat Type | Abbreviations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mapengdian | 115.886 | 38.814 | Aquatic plant-dominant areas | MPD-S |
| Mapengdian | 115.883 | 38.815 | Trench areas | MPD-H |
| Yangjiaodian | 115.876 | 38.824 | Pelagic areas | YJD-K |
| Yangjiaodian | 115.878 | 38.824 | Aquatic plant-dominant areas | YJD-S |
| Yangjiaodian | 115.879 | 38.825 | Trench areas | YJD-H |
| Baiyangdian | 115.912 | 38.841 | Aquatic plant-dominant areas | BYD-S |
| Houtang | 116.001 | 38.838 | Aquatic plant-dominant areas | HT-S |
| Houtang | 116.001 | 38.832 | Pelagic areas | HT-K |
| Julongdian | 116.019 | 38.811 | Trench areas | JLD-H |
| Julongdian | 116.021 | 38.811 | Aquatic plant-dominant areas | JLD-S |
| Julongdian | 116.024 | 38.815 | Pelagic areas | JLD-K |
| Mengjiadian | 116.021 | 38.8 | Pelagic areas | MJD-K |
| Mengjiadian | 116.017 | 38.795 | Aquatic plant-dominant areas | MJD-S |
| Badadian | 115.989 | 38.866 | Trench areas | BDD-H |
| Badadian | 115.987 | 38.868 | Pelagic areas | BDD-K |
| Shihoudian | 115.989 | 38.843 | Pelagic areas | SHD-K |
| Shihoudian | 115.994 | 38.846 | Aquatic plant-dominant areas | SHD-S |
| Shihoudian | 115.993 | 38.849 | Trench areas | SHD-H |
| Dayaquan | 115.969 | 38.91 | Trench areas | DYQ-H |
| Dayaquan | 115.973 | 38.911 | Pelagic areas | DYQ-K |
| Dayaquan | 115.965 | 38.908 | Aquatic plant-dominant areas | DYQ-S |
| Zaolinzhuang | 116.089 | 38.886 | Pelagic areas | ZLZ-K |
| Zaolinzhuang | 116.083 | 38.891 | Trench areas | ZLZ-H |
| Chiyudian | 116.036 | 38.858 | Pelagic areas | CYD-K |
| Chiyudian | 116.037 | 38.856 | Aquatic plant-dominant areas | CYD-L |
| Shaochedian | 115.99 | 38.941 | Trench areas | SCD-H |
| Shaochedian | 115.998 | 38.942 | Pelagic areas | SCD-K |
| Shaochedian | 115.995 | 38.943 | Aquatic plant-dominant areas | SCD-S |
| Wangjiazhai | 116.002 | 38.906 | Trench areas | WJZ-H |
| Wangjiazhai | 116.004 | 38.908 | Pelagic areas | WJZ-K |
| Wangjiazhai | 116.007 | 38.909 | Aquatic plant-dominant areas | WJZ-S |
| Zaozhadian1 | 115.838 | 38.917 | Aquatic plant-dominant areas | ZZD1-S |
| Zaozhadian2 | 115.856 | 38.912 | Aquatic plant-dominant areas | ZZD2-S |
| Category | Oligotrophic | Mesotrophic | Lightly Eutrophic | Moderately Eutrophic | Severely Eutrophic | Extremely Eutrophic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TLI | <30 | 30 ≤ TLI ≤ 50 | 50 < TLI ≤ 60 | 60 < TLI ≤ 70 | 70 < TLI ≤ 80 | TLI > 80 |
| Group | Individual Dry Weight (μg) |
|---|---|
| Nematodes | 0.40 |
| Ostracods | 26.00 |
| Copepods | 1.86 |
| Group | Item | Spring | Summer | Autumn |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nematodes | Abundance (ind. 10 cm−2) | 84.95 ± 39.19 | 74.01 ± 20.44 | 27.25 ± 5.81 |
| Relative proportion of abundance (%) | 93.86 | 88.56 | 92.91 | |
| Biomass (dwt. 10 cm−2) | 33.98 ± 15.68 | 29.60 ± 8.18 | 0.11 ± 2.32 | |
| Relative proportion of biomass (%) | 19.65 | 11.38 | 0.21 | |
| Ostracods | Abundance (ind. 10 cm−2) | 5.32 ± 1.90 | 8.81 ± 2.01 | 1.95 ± 1.20 |
| Relative proportion of abundance (%) | 5.89 | 10.55 | 6.65 | |
| Biomass (dwt. 10 cm−2) | 138.49 ± 49.30 | 229.14 ± 52.23 | 50.69 ± 31.27 | |
| Relative proportion of biomass (%) | 80.10 | 88.09 | 99.78 | |
| Copepods | Abundance (ind. 10 cm−2) | 0.23 ± 0.12 | 0.74 ± 0.18 | 0.13 ± 0.09 |
| Relative proportion of abundance (%) | 0.25 | 0.89 | 0.44 | |
| Biomass (dwt. 10 cm−2) | 0.42 ± 0.22 | 1.38 ± 0.34 | 0.24 ± 0.17 | |
| Relative proportion of biomass (%) | 0.24 | 0.53 | 0.00 |
| Environmental Factor | Season | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spring | Summer | Autumn | ||||||||||
| Nematodes | Ostracods | Copepods | Total | Nematodes | Ostracods | Copepods | Total | Nematodes | Ostracods | Copepods | Total | |
| Depth | 0.371 | 0.243 | 0.033 | 0.384 | 0.349 * | 0.302 | −0.293 | 0.365 * | 0.231 | −0.113 | 0.387 * | 0.215 |
| Temp | 0.140 | −0.006 | −0.519 ** | 0.107 | 0.099 | 0.284 | −0.053 | 0.123 | 0.217 | 0.127 | −0.015 | 0.245 |
| SDD | −0.351 | 0.230 | 0.175 | −0.348 | 0.173 | 0.083 | −0.009 | 0.176 | −0.118 | −0.282 | 0.264 | −0.174 |
| pH | 0.236 | 0.096 | 0.305 | 0.248 | 0.114 | 0.215 | −0.225 | 0.129 | 0.057 | 0.075 | −0.019 | 0.072 |
| DO | 0.218 | 0.104 | 0.063 | 0.224 | 0.288 | 0.367 * | −0.257 | 0.312 | 0.140 | 0.107 | −0.049 | 0.163 |
| FNU | 0.184 | −0.232 | −0.050 | 0.181 | −0.012 | −0.142 | −0.045 | −0.025 | 0.087 | 0.272 | 0.682 ** | 0.155 |
| TPHs | 0.040 | −0.151 | 0.060 | 0.054 | −0.309 | −0.283 | −0.294 | −0.329 | 0.088 | −0.112 | −0.046 | 0.064 |
| Chl-a | −0.071 | −0.159 | 0.118 | −0.072 | −0.177 | −0.074 | −0.221 | −0.181 | 0.261 | −0.076 | −0.164 | 0.245 |
| TP | 0.160 | −0.299 | 0.280 | 0.160 | −0.162 | −0.320 | −0.182 | −0.189 | 0.134 | 0.005 | −0.014 | 0.136 |
| TN | −0.254 | 0.268 | 0.622 ** | −0.219 | −0.067 | −0.182 | −0.220 | −0.085 | −0.233 | 0.136 | 0.083 | −0.205 |
| NH3-N | −0.206 | −0.131 | −0.274 | −0.206 | −0.482 ** | −0.282 | 0.126 | −0.494 ** | 0.248 | −0.155 | 0.051 | 0.218 |
| CODMn | −0.287 | −0.174 | −0.395 | −0.289 | −0.216 | 0.072 | −0.160 | −0.204 | 0.147 | −0.105 | −0.041 | 0.126 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, Y.; Mu, J.; Pan, Z.; Ma, F.; Liu, J.; Dong, H.; Zhang, W.; Wang, L. Study on the Spatiotemporal Distribution Characteristics of Meiofauna in Baiyangdian Lake and Its Influencing Factors. Water 2024, 16, 1959. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16141959
Cao Y, Mu J, Pan Z, Ma F, Liu J, Dong H, Zhang W, Wang L. Study on the Spatiotemporal Distribution Characteristics of Meiofauna in Baiyangdian Lake and Its Influencing Factors. Water. 2024; 16(14):1959. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16141959
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Yingkun, Jiandong Mu, Zhe Pan, Futang Ma, Jianxia Liu, Haojun Dong, Wei Zhang, and Liqing Wang. 2024. "Study on the Spatiotemporal Distribution Characteristics of Meiofauna in Baiyangdian Lake and Its Influencing Factors" Water 16, no. 14: 1959. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16141959
APA StyleCao, Y., Mu, J., Pan, Z., Ma, F., Liu, J., Dong, H., Zhang, W., & Wang, L. (2024). Study on the Spatiotemporal Distribution Characteristics of Meiofauna in Baiyangdian Lake and Its Influencing Factors. Water, 16(14), 1959. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16141959










