Hydrochemical Characteristics and Water Quality Evaluation of Groundwater in the Luohe Formation of Binchang Mining Area, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. General Situation of the Research Area
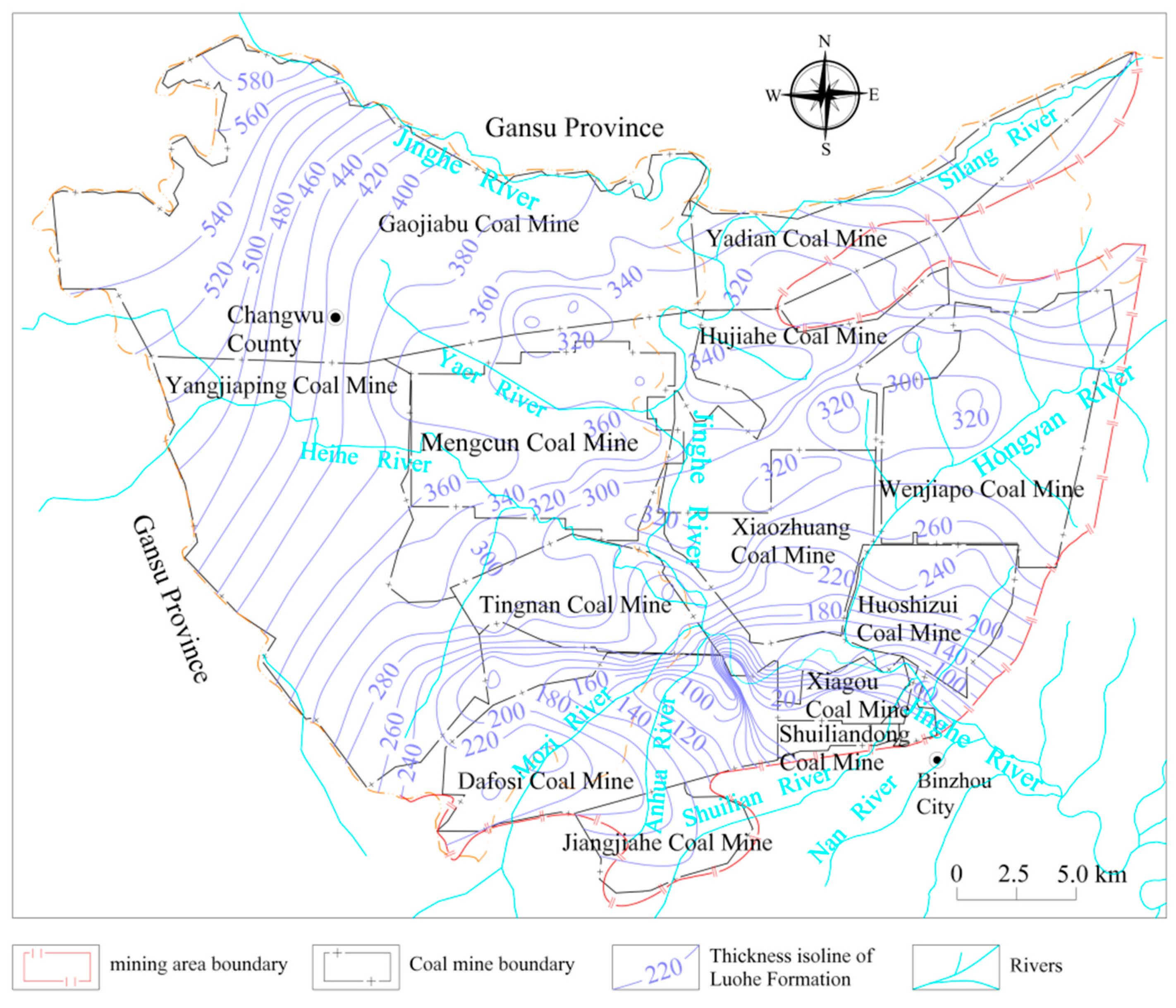
2.1. Current Situation of Coal Resources Development
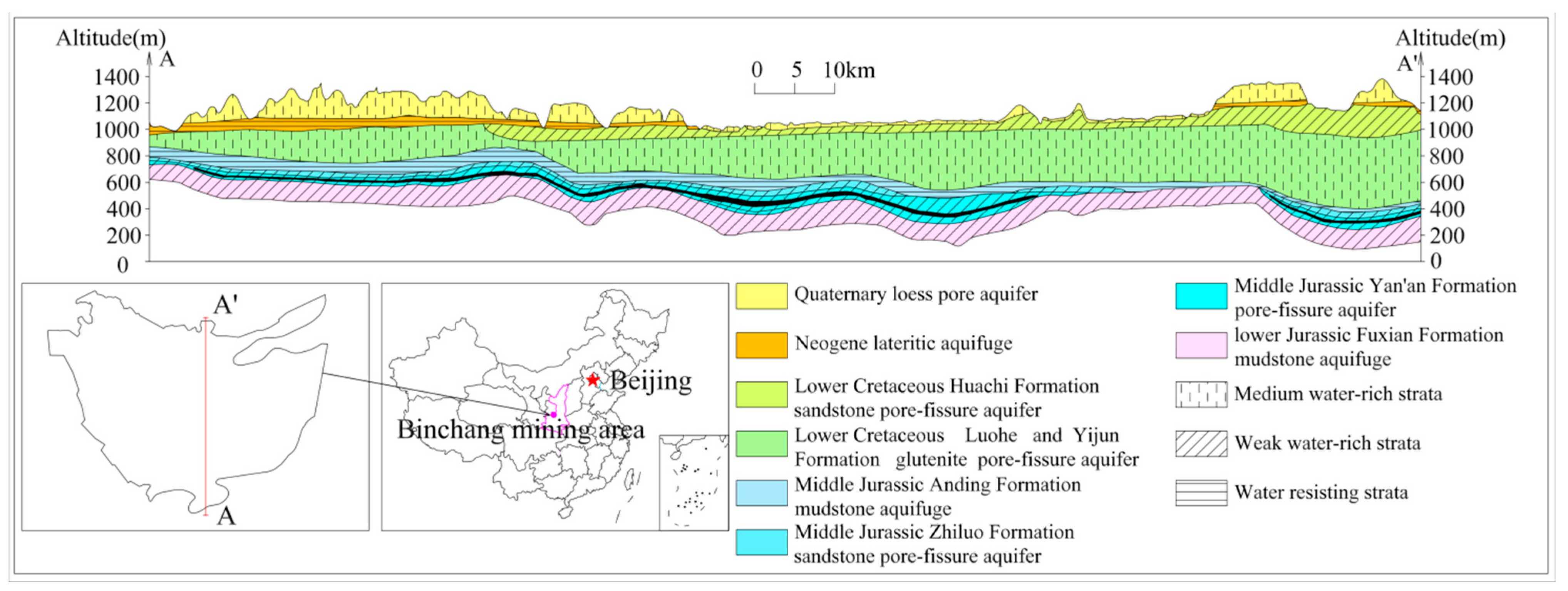
2.2. Aquifer Characteristics
2.3. Aquifer Occurrence Characteristics of Cretaceous Luohe Formation
3. Sample Collection, Testing, and Analysis
3.1. Sample Collection and Testing
3.2. Analytical Methods
3.2.1. Nemerow Index Evaluation Method
3.2.2. Fuzzy Comprehensive Evaluation Method Based on Principal Component Analysis
4. Results and Discussion
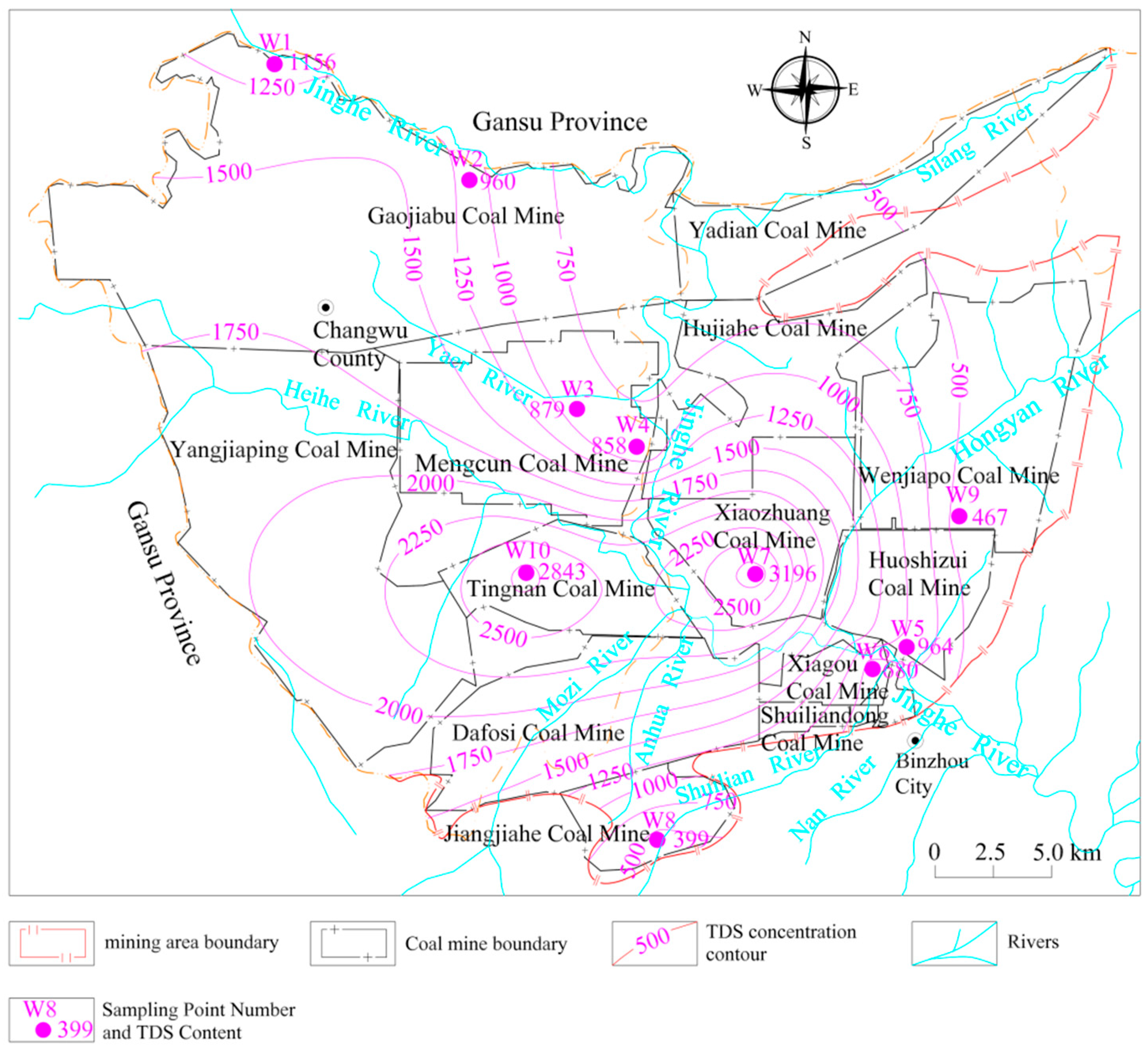
4.1. Analysis of Chemical Characteristics of Groundwater
4.1.1. Hydrochemical Characteristics of Major Ions
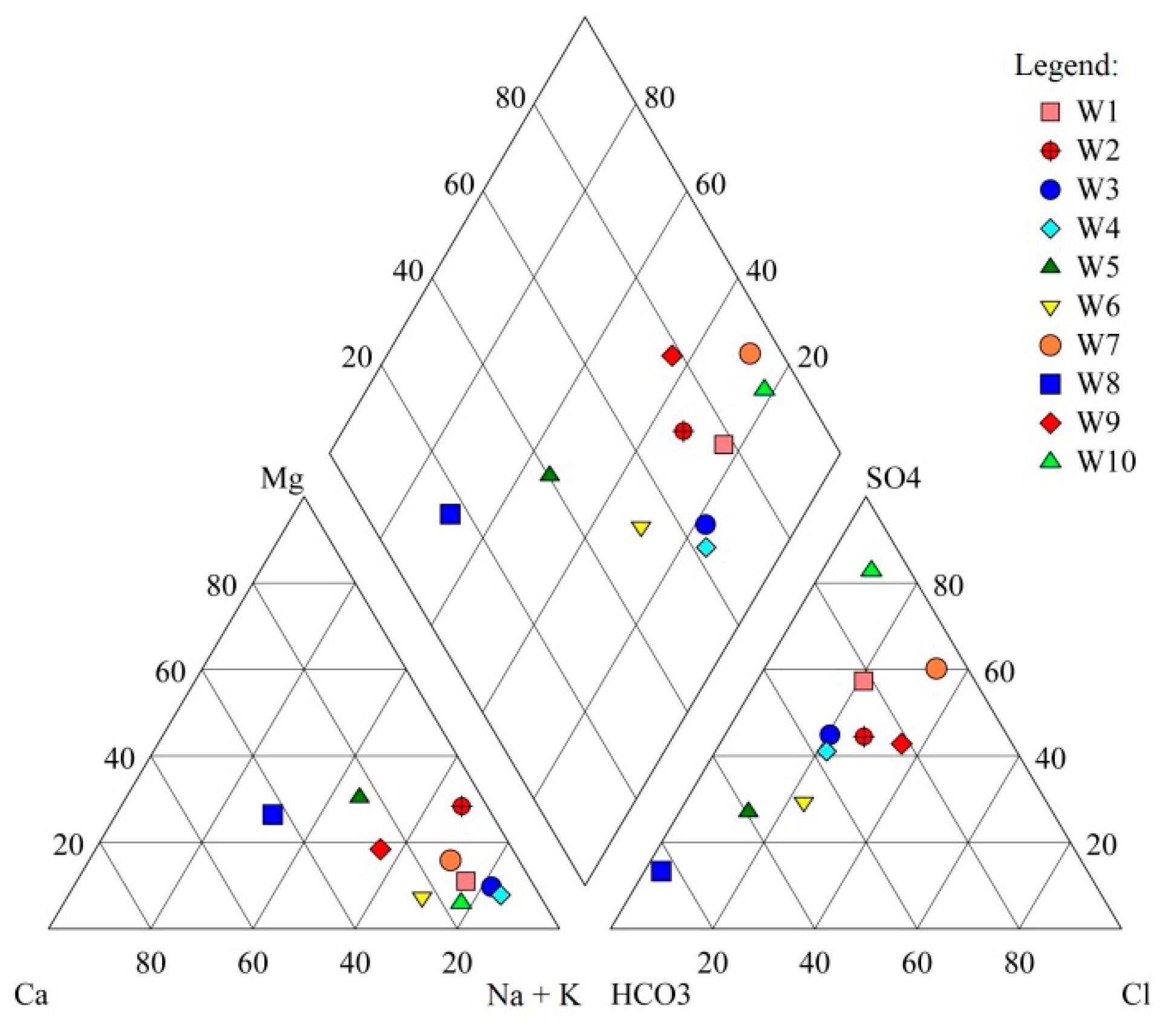
4.1.2. Chemical Types of Groundwater
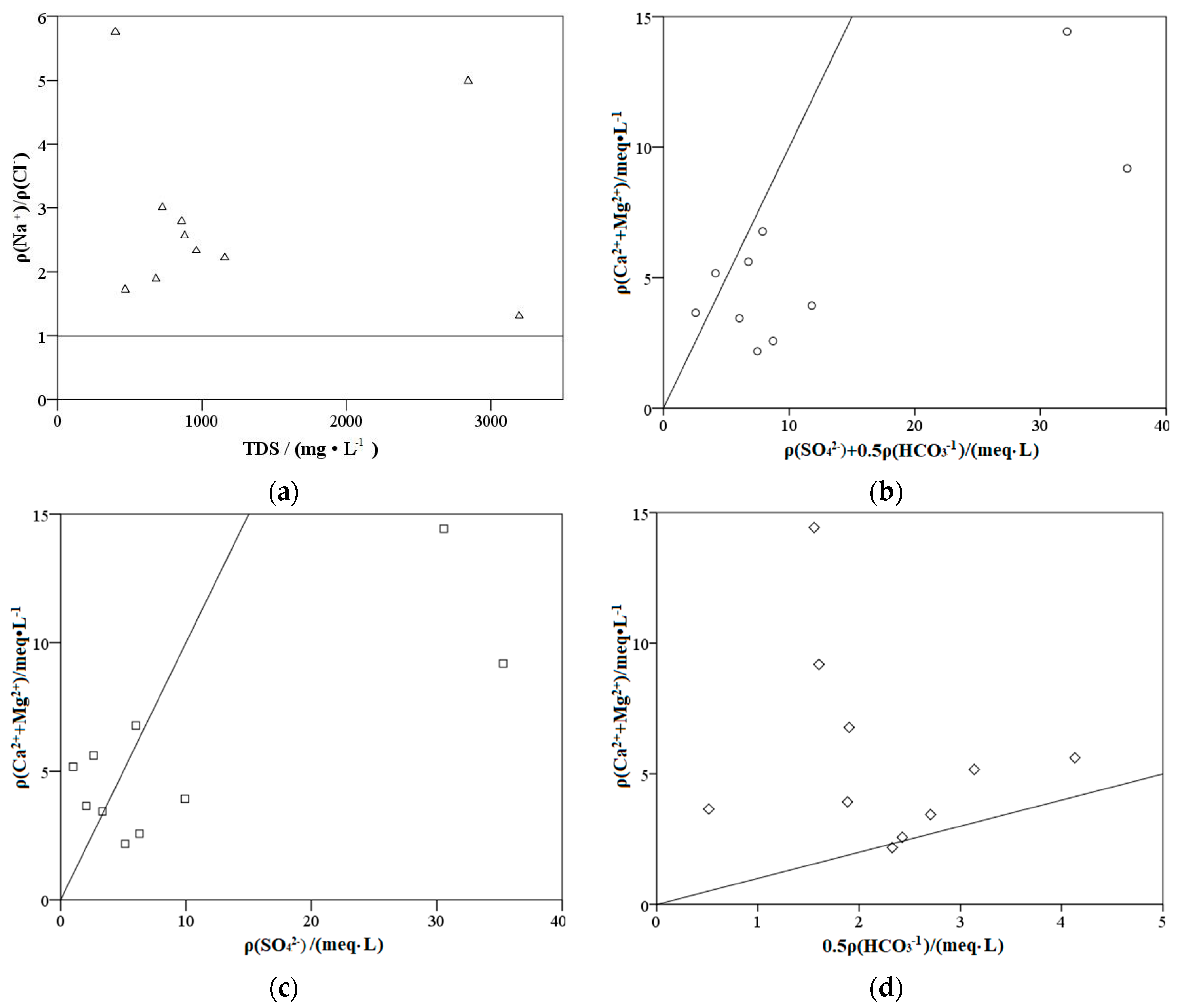
4.1.3. Ion Combination Ratio Analysis
4.2. Groundwater Quality Evaluation
4.2.1. Evaluation Results of the Nemerow Index Evaluation Method
4.2.2. Results of the Fuzzy Comprehensive Evaluation Using Principal Component Analysis
4.2.3. Comparative Analysis of Evaluation Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ouedraogo, I.; Defourny, P.; Vanclooster, M. Mapping the groundwater vulnerability for pollution at the pan African scale. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 544, 939–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazakis, N.; Voudouris, K.S. Groundwater vulnerability and pollution risk assessment of porous aquifers to nitrate: Modifying the DRASTIC method using quantitative parameters. J. Hydrol. 2015, 525, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.M. On the Water–Preserved Mining. J. China Coal Soc. 2017, 42, 27–35. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.M. Some Scientific Subjects in Water-Preserved Coal Mining. J. China Coal Soc. 2019, 44, 667–674. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.D.; Fan, L.M.; Zhang, X.T.; Zhang, H.Q.; Zhang, Y.F.; Shen, T. Driving force analysis for water and wetlands evolution at Yushenfu mining area. J. China Coal Soc. 2015, 40, 1126–1133. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.M.; Li, T.; Xiang, M.X.; He, W.Z.; Wu, B.Y.; Peng, J.; Li, Y.H.; Li, C.; Zheng, M.M.; Chen, J.P.; et al. Effect of Coal Mining on Springs in Yushenfu Mining Area of China. Geofluids 2018, 3, 3564360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Ma, X. A review on investigation of water-preserved coal mining in western China. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2018, 5, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Fan, L.M.; Xia, Y.C.; Li, C.; Chen, J.P.; Wu, B.Y.; Peng, J. Research on carrying capacity of geological environment based on the concept of coal mining under water-containing. J. China Coal Soc. 2019, 44, 830–839. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.D.; Huang, J.T.; Li, J.X.; Ning, S.X. Groundwater level threshold under the constrain of ecology security in mining area. J. China Coal Soc. 2019, 44, 675–680. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Ma, L.; Yu, Y.; Wang, S.; Xu, Y. Water-conserving mining influencing factors identification and weight determination in northwest China. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2019, 6, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.Y.; Bian, H.Y.; Peng, J.; Xiang, M.X.; Li, W.L. Hydrochemical Characteristics Analysis of Groundwater in the Western Eco-Enviroment Fragility Area. Yellow River 2019, 41, 65–69. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, R.; Wei, C.; Luo, K. Hydrogeochemical characteristics, source identification and health risks of surface water and groundwater in mining and non-mining areas of Handan, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, P.; Paul, B. Groundwater quality assessment in an industrial hotspot through interdisciplinary techniques. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cloutier, V.; Lefebvre, R.; Therrien, R.; Savard, M.M. Multivariate statistical analysis of geochemical data as indicative of the hydrogeochemical evolution of groundwater in a sedimentary rock aquifer system. J. Hydrol. 2008, 353, 294–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hao, Y.; Gao, Z.; Wang, M.; Liu, M.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S. Determining the factors controlling the chemical composition of groundwater using multivariate statistics and geochemical methods in the Xiqu coal mine, North China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Wang, R.; Li, J.F. Study on hydrochemical characteristics and formation mechanism of shallow groundwater in eastern Songnen Plain. J. Groundw. Sci. Eng. 2018, 6, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.W.; Xu, D.Q.; Yin, X.X.; Xie, W.P.; Zeng, W. Analysis on hydrochemistry and its control factors in the concealed coal mining area in North China: A case study of dominant inrush aquifers in Suxian mining area. J. China Coal Soc. 2017, 42, 996–1004. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huan, H.; Lian, X.Y.; Yang, Y.; Jia, Y.F.; Jiang, Y.H. Study on screening method for groundwater quality assessment based on Level Difference Method. Res. Environ. Sci. 2020, 33, 402–410. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.J.; Ma, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y.N.; Chen, C.Y.; Wang, H.Y.; Yu, Q.H.; Sun, C. Groundwater pollution assessment and pollution factor analysis in Songyuan City, Jilin Province. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2014, 35, 156–162. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Wu, X.; Qian, C.; Zhu, G. Hydrogeochemistry and groundwater quality assessment of high fluoride levels in the Yanchi endorheic region, northwest China. Appl. Geochem. 2018, 98, 404–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabukdhara, M.; Gupta, S.K.; Kotecha, Y.; Nema, A.K. Groundwater quality in Ghaziabad district, Uttar Pradesh, India: Multivariate and health risk assessment. Chemosphere 2017, 179, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boufekane, A.; Saighi, O. Assessing groundwater quality for irrigation using geostatistical method—Case of wadi Nil Plain (North-East Algeria). Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 8, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanoranga; Khalid, S. An assessment of groundwater quality for irrigation and drinking purposes around brick kilns in three districts of Balochistan province, Pakistan, through water quality index and multivariate statistical approaches. J. Geochem. Explor. 2019, 197, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.W.; Zhou, T.L.; Dong, J.Q.; Long, J.Y. A novel extension evaluation model of groundwater quality based on con-nection cloud model. China Environ. Sci. 2018, 38, 3035–3041. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahiya, S.; Singh, B.; Gaur, S.; Garg, V.; Kushwaha, H. Analysis of groundwater quality using fuzzy synthetic evaluation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 147, 938–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, K.N.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, H.H.; Zhou, J.W.; Wan, H.J.; Zhao, J. Hydro-chemical characteristics and quality evaluation of groundwater in Zhaoyuan city. Saf. Environ. Eng. 2018, 25, 106–111, 138. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerji, S.; Mitra, D. Geographical information system-based groundwater quality index assessment of northern part of Kolkata, India for drinking purpose. Geocarto Int. 2019, 34, 943–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Feng, P.; Jin, J.; Liu, L. Water Resources Carrying Capacity Evaluation and Diagnosis Based on Set Pair Analysis and Improved the Entropy Weight Method. Entropy 2018, 20, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Tian, C.; Fang, J.; Jin, G.; An, L. Evaluation of the environmental quality associated with near-surface groundwater characteristics in coal-mining areas based on rough set and uncertainty measure theory. Desalination Water Treat. 2019, 152, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.T.; Gui, H.R.; Zhao, H.H.; Li, J.; Guan, L.S. Temporal variability of hydro-chemical characteristics and water quality assessment of collapse pond in Zhuxianzhuang coal mining area, China. Fresenius Eviron. Bull. 2019, 28, 402–409. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.M.; Dong, S.N. Seepage law of bedrock aquifer and water–preserved mining technology in deep coal seam mining. J. China Coal Soc. 2019, 44, 804–811. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Fan, L.; Xia, Y.; Li, C.; Chen, J.; Gao, S.; Wu, B.; Peng, J.; Ji, Y. Impact of coal mining on groundwater of Luohe Formation in Binchang mining area. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2020, 8, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.F.; Hu, W.Y.; Liu, Y.F. Vertical hydrogeological characteristics of Luohe aquifer and its significance of water-preserved coal mining. J. China Coal Soc. 2019, 44, 847–856. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Liu, Y.H.; He, T.Y.; Zeng, Y.; Huang, Q.Q. Study on water chemistry and water quality evaluation of groundwater in a landfill. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 42, 221–228. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Coal Mine | Capacity (Mt/a) | Status | Coal Mine | Capacity (Mt/a) | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mengcun | 6.00 | Production | Wenjiapo | 3.20 | Production |
| Xiaozhuang | 5.00 | Production | Dafosi | 3.00 | Production |
| Hujiahe | 5.00 | Production | Huoshizui | 3.00 | Production |
| Tingnan | 5.00 | Production | Xiagou | 3.00 | Production |
| Yangjiaping | 5.00 | Construction | Shuiliandong | 1.50 | Production |
| Gaojiabu | 5.00 | Production | Jiangjiahe | 0.90 | Production |
| Yadian | 4.00 | Construction |
| Sample Date | Na+ (mg/L) | K+ (mg/L) | Ca2+ (mg/L) | Mg2+ (mg/L) | Cl− (mg/L) | SO42− (mg/L) | HCO3− (mg/L) | TDS (mg/L) | pH | CODMn (mg/L) | F− (mg/L) | NH3–N (mg/L) | NO3− (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W1 | 284.00 | 3.11 | 42.10 | 21.90 | 128.00 | 476.00 | 230.00 | 1156.00 | 8.24 | 0.64 | 0.69 | 0.06 | 0.35 |
| W2 | 306.00 | 2.60 | 20.00 | 69.30 | 131.00 | 288.00 | 232.00 | 960.00 | 8.59 | 0.82 | 0.60 | 0.02 | 0.36 |
| W3 | 262.00 | 2.62 | 23.80 | 16.60 | 102.00 | 302.00 | 296.00 | 879.00 | 8.30 | 0.42 | 0.52 | 0.07 | 0.24 |
| W4 | 270.00 | 3.02 | 21.40 | 13.30 | 96.70 | 247.00 | 284.00 | 858.00 | 8.25 | 0.45 | 0.76 | 0.09 | 1.59 |
| W5 | 170.00 | 3.48 | 79.31 | 60.99 | 46.00 | 125.60 | 350.50 | 964.00 | 7.60 | 0.58 | 0.37 | 0.02 | 341.70 |
| W6 | 177.00 | 2.40 | 52.33 | 9.92 | 93.57 | 160.20 | 330.10 | 680.00 | 7.74 | 1.13 | 0.31 | 0.02 | 15.52 |
| W7 | 792.50 | 4.92 | 131.60 | 94.21 | 606.40 | 1467.00 | 189.90 | 3196.00 | 7.76 | 0.78 | 0.41 | 0.03 | 2.55 |
| W8 | 50.40 | 1.92 | 63.78 | 23.80 | 8.75 | 48.04 | 382.70 | 399.00 | 7.70 | 0.36 | 0.50 | 0.26 | 6.72 |
| W9 | 103.50 | 1.78 | 42.52 | 18.35 | 60.13 | 97.96 | 62.90 | 467.00 | 8.06 | 0.49 | 0.45 | 0.02 | 8.00 |
| W10 | 728.00 | 6.90 | 134.10 | 29.75 | 145.90 | 1694.00 | 195.70 | 2843.00 | 7.71 | 0.77 | 1.00 | 0.55 | 2.58 |
| Max | 792.50 | 6.90 | 134.10 | 94.21 | 606.40 | 1694.00 | 382.70 | 3196.00 | 8.59 | 1.13 | 1.00 | 0.55 | 341.70 |
| Min | 50.40 | 1.78 | 20.00 | 9.92 | 8.75 | 48.04 | 62.90 | 399.00 | 7.60 | 0.36 | 0.31 | 0.02 | 0.24 |
| Mean | 314.34 | 3.28 | 61.09 | 35.81 | 141.85 | 490.58 | 255.38 | 1240.20 | 8.00 | 0.64 | 0.56 | 0.11 | 37.96 |
| Std. | 249.28 | 1.55 | 42.27 | 28.66 | 168.55 | 589.74 | 93.93 | 969.07 | 0.34 | 0.24 | 0.21 | 0.17 | 106.83 |
| Cv | 0.79 | 0.47 | 0.69 | 0.80 | 1.19 | 1.20 | 0.37 | 0.78 | 0.04 | 0.37 | 0.37 | 1.50 | 2.81 |
| I | II | III | IV | V | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fi | 0 | 1 | 3 | 6 | 10 |
| Na+ (mg/L) | Ca2+ (mg/L) | Mg2+ (mg/L) | Cl− (mg/L) | SO42− (mg/L) | TDS (mg/L) | pH | CODMn (mg/L) | F− (mg/L) | NH3–N (mg/L) | NO3− (mg/L) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | ≤100 | ≤100 | ≤10 | ≤50 | ≤50 | ≤300 | 6.5 ≤ pH ≤ 8.5 | ≤1.0 | ≤1.0 | ≤0.02 | ≤2.0 |
| II | ≤150 | ≤200 | ≤20 | ≤150 | ≤150 | ≤500 | 6.5 ≤ pH ≤ 8.5 | ≤2.0 | ≤1.0 | ≤0.10 | ≤5.0 |
| III | ≤200 | ≤400 | ≤50 | ≤250 | ≤250 | ≤1000 | 6.5 ≤ pH ≤ 8.5 | ≤3.0 | ≤1.0 | ≤0.50 | ≤20.0 |
| IV | ≤400 | ≤800 | ≤200 | ≤350 | ≤350 | ≤2000 | 5.5 ≤ pH < 6.5; 8.5 < pH ≤ 9.0 | ≤10.0 | ≤2.0 | ≤1.50 | ≤30.0 |
| V | >400 | >800 | >200 | >350 | >350 | >2000 | pH < 5.5; pH > 9.0 | >10.0 | >2.0 | >1.50 | >30.0 |
| I | II | III | IV | V | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | F < 0.80 | 0.80 ≤ F < 2.50 | 2.50 ≤ F < 4.25 | 4.25 ≤ F < 7.20 | F ≥ 7.20 |
| Component | Characteristic Value | Contribution Rate of Variance | Accumulate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5.200 | 47.273 | 47.273 |
| 2 | 2.289 | 20.813 | 68.086 |
| 3 | 1.713 | 15.576 | 83.662 |
| 4 | 0.924 | 8.401 | 92.063 |
| 5 | 0.600 | 5.452 | 97.515 |
| 6 | 0.210 | 1.907 | 99.422 |
| 7 | 0.043 | 0.391 | 99.813 |
| 8 | 0.019 | 0.176 | 99.989 |
| 9 | 0.001 | 0.011 | 100.000 |
| 10 | 4.050 × 10−17 | 3.682 × 10−16 | 100.000 |
| 11 | −2.313 × 10−16 | −2.103 × 10−15 | 100.000 |
| Index | Component | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| Na+ | 0.964 | 0.080 | 0.203 |
| Ca2+ | 0.886 | −0.131 | −0.417 |
| Mg2+ | 0.564 | −0.604 | 0.216 |
| Cl− | 0.772 | −0.369 | 0.425 |
| SO42− | 0.975 | 0.194 | 0.038 |
| TDS | 0.989 | 0.000 | 0.075 |
| pH | −0.377 | 0.301 | 0.807 |
| CODMn | 0.372 | −0.291 | 0.185 |
| F- | 0.344 | 0.857 | 0.016 |
| NH3–N | 0.479 | 0.702 | −0.474 |
| NO3− | −0.118 | −0.570 | −0.594 |
| Sample Date | Nemerow Index Evaluation Method | Principal Component Analysis-Based Fuzzy Comprehensive Evaluation Method. | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | Groundwater Quality Types | Subordination Degree | Groundwater Quality Types | |||||
| W1 | 7.329 | V | 0.110 | 0.154 | 0.206 | 0.206 | 0.323 | V |
| W2 | 4.609 | IV | 0.107 | 0.097 | 0.499 | 0.298 | 0.000 | III |
| W3 | 4.452 | IV | 0.126 | 0.166 | 0.519 | 0.189 | 0.000 | III |
| W4 | 4.398 | IV | 0.159 | 0.165 | 0.504 | 0.171 | 0.000 | III |
| W5 | 7.266 | V | 0.210 | 0.360 | 0.430 | 0.000 | 0.000 | III |
| W6 | 2.386 | II | 0.199 | 0.457 | 0.344 | 0.000 | 0.000 | II |
| W7 | 7.794 | V | 0.030 | 0.028 | 0.038 | 0.000 | 0.905 | V |
| W8 | 2.280 | II | 0.491 | 0.248 | 0.260 | 0.000 | 0.000 | I |
| W9 | 2.236 | II | 0.448 | 0.510 | 0.042 | 0.000 | 0.000 | II |
| W10 | 7.640 | V | 0.061 | 0.072 | 0.039 | 0.000 | 0.829 | V |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Sun, K.; Ma, W.; Peng, J.; Liu, R.; Chen, J.; Zhang, K.; Gao, S.; Li, C.; Zhang, P. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Water Quality Evaluation of Groundwater in the Luohe Formation of Binchang Mining Area, China. Water 2024, 16, 1913. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16131913
Wang X, Sun K, Ma W, Peng J, Liu R, Chen J, Zhang K, Gao S, Li C, Zhang P. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Water Quality Evaluation of Groundwater in the Luohe Formation of Binchang Mining Area, China. Water. 2024; 16(13):1913. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16131913
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xu, Kui Sun, Wanchao Ma, Jie Peng, Ruiping Liu, Jianping Chen, Kun Zhang, Shuai Gao, Cheng Li, and Penghua Zhang. 2024. "Hydrochemical Characteristics and Water Quality Evaluation of Groundwater in the Luohe Formation of Binchang Mining Area, China" Water 16, no. 13: 1913. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16131913
APA StyleWang, X., Sun, K., Ma, W., Peng, J., Liu, R., Chen, J., Zhang, K., Gao, S., Li, C., & Zhang, P. (2024). Hydrochemical Characteristics and Water Quality Evaluation of Groundwater in the Luohe Formation of Binchang Mining Area, China. Water, 16(13), 1913. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16131913





