Abstract
Constructed wetlands (CWs) primarily achieve efficient wastewater purification through synergistic interactions among substrates, plants, and microorganisms. Serving as the structural foundation of the entire wetland system, substrates not only provide a growth medium for plants, but also serve as adhesive carriers for microorganisms and habitats for animal activities. Research on substrates has attracted considerable attention; however, in practical engineering applications, the selection of substrates often depend on personal experience, which may lead to significant gaps in the effectiveness of wetland systems in treating different characteristic contaminants. Therefore, it is of great significance to investigate the influence of substrates on the removal of contaminants in sewage and identify substrate materials with good physical and chemical properties to optimize the design and operation of CWs-based sewage-treatment systems and improve their purification efficiency. In this review, bibliometric analysis was conducted to using the Web of Science database and VOSviewer_1.6.20 software to assess the progress of research on CWs. This article provides a comprehensive overview of substrate types and characteristics based on recent research advancements in the field. Additionally, it discusses removal methods and the influence of factors related to conventional contaminants (COD, nitrogen, and phosphorus), heavy metals (HMs), fluorinated compounds, pharmaceuticals, personal care products (PPCPs), and microplastics. A thorough evaluation was conducted on the economic costs of various substrates and their ability to remove major contaminants from water bodies, providing a reference for the further development of wetland technology.
1. Introduction
CWs are ecosystems built by artificial simulation of natural processes, usually relying on the synergistic interaction of substrates, plants, and microorganisms to enhance wastewater purification through physical, chemical, and biological processes [1,2]. The physical effects primarily encompass filtration and retention, which heavily rely on collaboration between the substrate layer and plants to effectively intercept and adsorb contaminants [3]. The chemical reactions involved in this study encompass adsorption, chemical precipitation, redox reactions, and ion exchange. These processes are primarily governed by the substrate’s chemical properties [4]. Biological reactions include plant metabolism and the growth activities of various microorganisms. Microorganisms are attached to the substrate and plant roots. Various microorganisms remove contaminants through the processes of absorption, metabolism, and transformation [5]. Biological reactions are the most important step in the removal of contaminants in CWs [6].
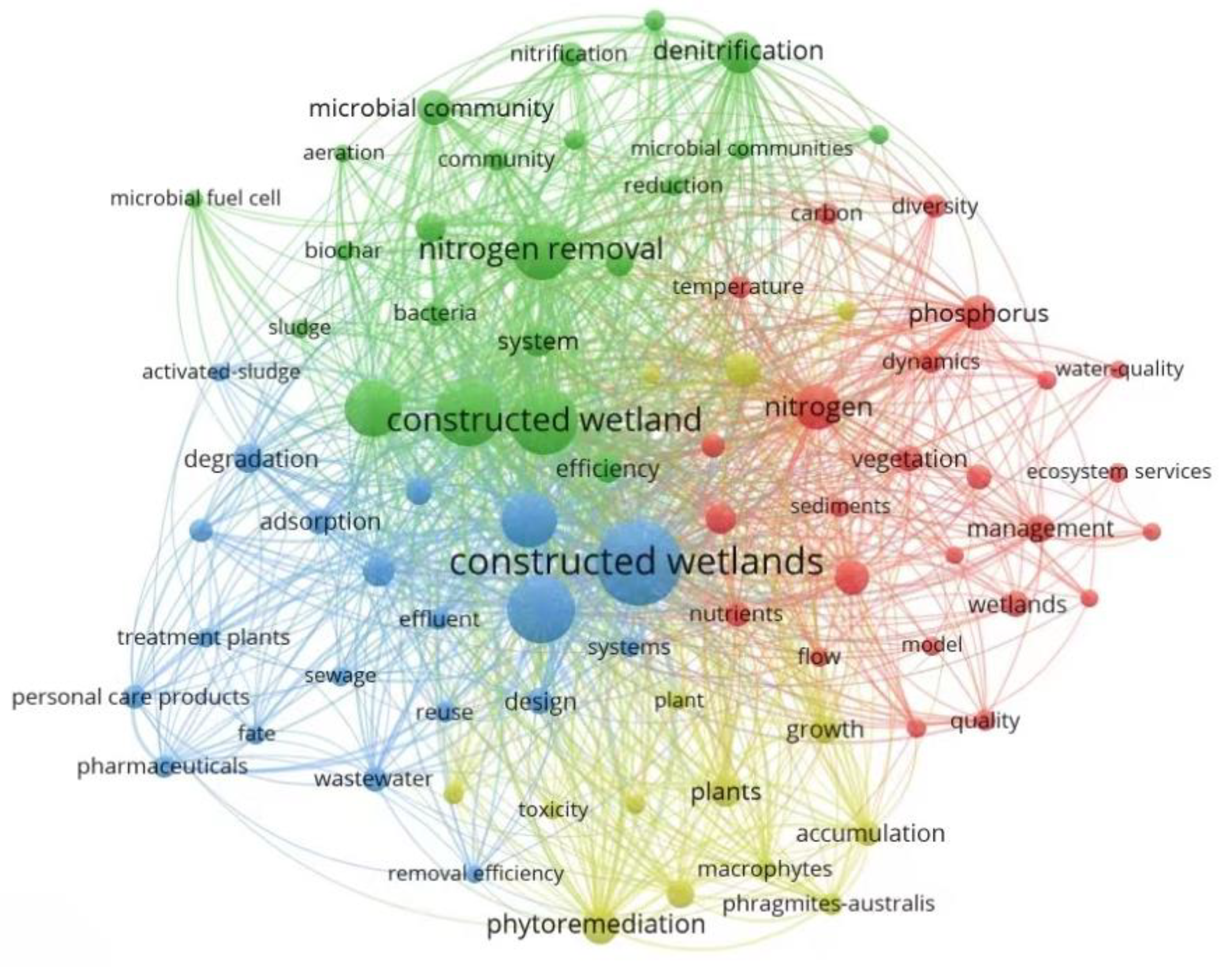
The findings of various studies have demonstrated that CWs possess the capability to effectively reduce the concentration of contaminants in domestic sewage. Moreover, CWs have also exhibited their potential in treating industrial wastewater [7], mine effluents [8], municipal effluents [9], hospital wastewater [10], agricultural wastewater [11], etc. By the end of 2023, more than 11,000 articles about CWs had been published on Web of Science. In order to better understand the current development status of CWs, “constructed wetland” was used in a keyword search of the literature from the last five years (2019–2023). After screening, a total of 5140 publications meeting the requirements were selected. The VOSviewer program was used for analysis, and the minimum frequency of occurrence was set to 100. A total of 81 keywords were included in the visualization. The outcomes of the analysis on highlighted words are presented in Figure 1. The figure exhibits four distinct color clusters, namely red, yellow, blue, and green. Words in the red cluster are mainly related to the removal of nitrogen and phosphorus, such as nitrogen, phosphorus and nutrient. Words in the yellow cluster are closely related to plants, such as phytoremediation, macrophytes, and plants. Words in the blue cluster are closely related to the direction of future research on CWs, such as personal-care products, pharmaceuticals and fate. The green cluster mainly relates to the mechanism of the removal of contaminants, such as denitrification and nitrification.
Figure 1.
Visualization of keywords in the 2019–2023 CW research.
Table 1 shows the keywords with the highest frequency in CWs. It can be seen that the current research on CWs is still focused on traditional wastewater treatment, especially the removal of nitrogen and phosphorus contaminants (sort 5, 8 and 12). However, the increasingly intricate composition of contaminants in wastewater and the growing public demand for high water quality, particularly with regards to the emergence of various EPs, present novel challenges to CWs [12]. Studies have shown that the traditional substrate (soil, gravel, sand) mainly plays a supporting role for plants, but its effect on the removal of contaminants is often unsatisfactory [13]. Therefore, in the design of substrate for CWs, reasonable configurations should be selected to improve the efficiency of treatment of contaminants.

Table 1.
2019–2023 CWs keywords prominence results table.
The substrates form the structural framework of the entire wetland, serving as a fundamental substrate for plant growth, an attachment surface for microorganisms, and a habitat for animal activities [14,15]. The physical properties of the substrate (particle size, porosity, specific surface area, and redox potential) will determine the effectiveness of treatment by CWs. For example, a substrate with increased specific surface area and porosity can facilitate biofilm formation and attachment and enhance microorganism–contaminant interactions at multiple contact points. According to the China Technical Specification of Constructed Wetlands for Wastewater Treatment (HJ 2005–2010) (MEPC, 2010), the selection of substrate should meet the following requirements: (i) good mechanical strength, high specific surface area and high stability; (ii) appropriate size in accordance with local sampling; (iii) when the content of nitrogen and phosphorus in the treated sewage is high, a functional substrate should be used to improve removal; (iv) for vertical subsurface flow (VSSF) CWs, the porosity of the substrates should be between 35–40%. Although research on substrates has attracted considerable attention, in practical engineering applications, the selection of substrate often relies on personal experience, which may lead to significant gaps in the effectiveness of wetland systems in treating different characteristic contaminants. Therefore, it is crucial to investigate the influence of substrate on the removal of contaminants in sewage and identify substrate materials with good physical and chemical properties to optimize the design and operation of CW-based sewage-treatment systems and improve their purification efficiency. This article summarizes the types and characteristics of substrates in CWs based on recent research achievements in the field of wetlands. It further discusses the removal mechanisms associated with substrates and the influence of factors specific to conventional contaminants (COD, nitrogen, and phosphorus), HMs, fluorinated compounds, PPCPs, and microplastics. A comprehensive evaluation was conducted on the economic costs of various substrates and their ability to remove major contaminants from water bodies, providing a reference for the further development of wetlands technology.
2. Typical/New Substrates for CWs
According to the source of the materials, the substrates of CWs can be divided into natural substrates, by-products and artificial synthetic substrates. Table 2 lists the representative substrates used in CWs at present. The physical and chemical properties of different substrates exhibit significant variations, thereby resulting in diverse impacts on CWs [16]. Consequently, during the operation of CWs, it is crucial to select appropriate substrates or combinations thereof based on the specific contaminant-removal requirements, as this may enhance the overall performance of CW systems.
2.1. Natural Substrates
The most common natural substrates in CWs are gravel, sand, volcanics and zeolite. In general, natural substrates are made from natural mineral materials and have the advantages of high strength, a wide range of sources, and low price. However, the permeability coefficient and specific surface area tend to be low, resulting in poor performance in contaminant removal. Therefore, the natural substrates are often used as a supporting part of the filter bed to reduce the design cost of CWs [17]. There are also studies comparing natural substrates with different substrates in order to find a material that is good at removing particular contaminants. The study conducted by Huo et al. [18] involved the construction of four CWs utilizing different substrates (gravel, biochar, zeolite, and pyrite). The results indicate that the CWs with gravel as a substrate exhibited the least efficient nitrogen removal. Microbiological analysis revealed a low abundance of nitrifying and denitrifying microorganisms in the gravel-based CW system.
2.2. By-Products
2.2.1. Agricultural By-Products
The term “agricultural by-products” refers to the waste generated during agricultural production, which mainly includes various crop residues, livestock manure, and processing by-products. In 2023, China’s grain output reached 695 million tons, which will undoubtedly produce a large number of agricultural by-products. China has emerged as the leading country in terms of agricultural by-products, displacing up to four billion tons of waste annually. However, improper utilization of these by-products can pose significant environmental risks [19]. Currently, it is increasingly common to use agricultural by-products as the substrate of CWs, which not only uses this resource, but also reduces the cost of CWs and improves their effectiveness in treatment [20,21].
2.2.2. Industrial By-Products
Industrial by-products are mainly substances that are inevitably generated during the production of target products in industrial processes. At present, the global production of industrial by-products can reach billions of tons per year [22]. The inadequate treatment of industrial by-products may lead to severe environmental issues if it is not addressed promptly. Consequently, the exploration of resource utilization for industrial by-products has emerged as a prominent research focus. Common industrial by-products used in CWs include fly ash, steel slag, iron filings, and construction solid waste. Some by-products have good physical and chemical properties, high porosity, and high specific surface area. Due to differences in the raw materials and treatment processes, different industrial by-products show significantly different performance in treating contaminants. Furthermore, it is important to note that industrial by-products may contain a substantial amount of toxic and hazardous substances, thereby posing potential environmental risks [23]. In practical applications, it is advisable to prioritize the use of harmless materials. When selecting by-products or other materials that may potentially impact the environment, appropriate modifications should be implemented to ensure their harmlessness [24,25].
2.3. Artificial Synthetic Substrates
Artificial synthetic substrates are new materials formed by calcination, carbonization, and modification, either individually or in combination with various materials. The common substrates in CWs include activated carbon, biochar, ceramsite, and modified materials. The physical and chemical properties of these materials are stability and high porosity. However, due to the influence of the preparation process and raw materials, they exhibit different levels pf performance in treating different contaminants. In addition, artificial synthetic substrates also have the problem of high cost, which have raised serious obstacles to their promotion and use. At present, the use of artificial synthetic substrates is still mainly a subject of laboratory research. Developing a low-cost and high-efficiency filler has become a hot topic for research [26,27].

Table 2.
Classification of representative CWs substrates.
Table 2.
Classification of representative CWs substrates.
| Category | Substrate | Bases | Sources | Characteristic | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural substrate | Gravel | SiO2 and Al2O3 | Rock or mineral detritus | ① Low cost ② Poor removal of contaminants | [28] |
| Natural substrate | Sand | SiO2 | Tiny stone particles | ① Availability and low cost ② Easily clog CWs | [29] |
| Natural substrate | Volcanics | SiO2, Fe2O3, CaO and Al2O3 | Cooling magma after a volcanic eruption | ① High porosity and specific surface area ② Poor contaminant removal | [30] |
| Natural substrate | Zeolite | SiO2 and Al2O3 | Mainly derived from alkaline groundwater and volcanic rocks | ① High ion exchange, low cost, can be regenerated ② Low adsorption rate, easy to be affected by the environment | [31,32] |
| By-product | Fly ash | Fe2O3, Al2O3, SiO2 and CaO | Waste from burning coal | ① Large specific surface area, good adsorption performance ② Can easily cause secondary pollution in the environment | [33] |
| By-product | Steel slag | CaO, SiO2 and Fe2O3 | From electric furnaces and refining furnaces during steelmaking | ① High phosphorus-removal performance ② Strong alkalinity, which makes it difficult for microorganisms and plants to survive | [34] |
| By-product | Construction solid waste | - | Waste generated during demolition, construction and maintenance in the construction industry | ① Low cost, high availability ② Poor reusability | [35] |
| By-product | Sludge | Organics, SiO2 and Al2O3 | Waste from drinking water treatment | ① Low cost, high capacity for P and HMs adsorption, easy to obtain ② Very sensitive to the environment, might leach toxic substances | [14] |
| By-product | Iron scraps | Fe | Waste from steel mills and machinery-processing plants | ① Low cost, large specific surface area | [36,37] |
| By-product | Woodchip | Cellulose, hemicellulose, lignin | Waste from wood processing | ① Low cost, excellent N removal ② May cause secondary pollution | [38] |
| By-product | Crushed glass | Na2SiO3, CaO and SiO2 | Waste from glass production and use | ① Wide range of sources, reusable, provides space for microbes to attach | [39] |
| Artificial synthetic substrate | Ceramsite | SiO2, Al2O3 and CaO | Made by roasting raw materials | ① Good adsorption performance, high strength ② High energy consumption | [40] |
| Artificial synthetic substrate | Activated carbon | Porous carbon | Made by carbonization of raw materials | ① Moderate adsorption effect ② High cost | [41] |
| Artificial synthetic substrate | Biochar | Porous carbon | Made by biomass pyrolysis | ① Excellent contaminant adsorption, stable ② Difficulty in preparation | [42] |
| Artificial synthetic substrate | Modified substrates | - | Further processing of materials | ① Excellent contaminant adsorption ② High cost and high energy cost | [43] |
3. Functions of Substrates Removal of Contaminants
3.1. Substrates Removes Conventional Contaminants
3.1.1. Organic
The removal of organic matter in CWs mainly primarily relies on biodegradation by microorganisms [44]. As the site of microorganism metabolism, the substrates play an important role in the growth of microorganisms. In addition, the substrate can directly remove contaminants through adsorption and retention, which heavily rely on collaboration between the substrate layer and plants [26].
The physicochemical properties of the substrates exert a significant influence on the removal of organic compounds, with porosity being identified as one of the pivotal factors. Several studies have demonstrated that during continuous operation of CWs, there is an observed increase in insoluble organic matter, leading to a gradual reduction in substrate porosity and potentially resulting in clogging [45]. Since the wetland system mainly relies on microbial oxidative decomposition, anaerobic digestion, and other life activities to purify organic matter, clogging can result in extensive anoxia within the CWs as a whole. This condition diminishes the metabolic capacity of microorganisms and consequently lowers the efficiency of organic-matter removal.
In order to increase the removal of organic matter, substrates with high porosity such as zeolite and ceramsite can be selected. Wang et al. [46] utilized sewage sludge as a raw material to prepare new ceramic particles. A VSSF-CW was constructed with this new type of ceramic particle as the substrate. The COD-removal rate reached more than 70%, while the effluent quality reached the IV water standard. The high degradation rate of COD may be attributed to the substantial specific surface area and porosity of the novel ceramic particles, which facilitate enhanced contact between microorganisms adhered to the substrate surface and organic matter. Wang et al. [47] modified corn-straw biochar by alkali treatment. The results demonstrated that the specific surface area and porosity of the modified biochar were higher than they were before modification and that the effectiveness of treatment of other contaminants was also significantly improved.
3.1.2. Nitrogen
Nitrogen removal in CWs mainly depends on the processes of ammonification, nitrification, and denitrification by microorganisms. Organic nitrogen is first converted into NH4+-N through ammonification, which is followed by aerobic transformation into NO2−-N and NO3−-N by nitrifying bacteria. Finally, denitrifying bacteria convert NO3−-N into N2 under anaerobic conditions, so as to achieve nitrogen purification. The selection of carbon-rich fillers such as biochar, straw, and wood chips can improve the nitrogen-removal effect. Wang et al. [48] utilized corn stalks to prepare activated carbon for urban tailwater treatment, and this material exhibited an impressive nitrogen-removal efficiency, exceeding 85% in urban tailwater treatment. They concluded that using carbon-rich materials as the substrate of CWs can augment the content of organic matter and the C/N ratio, thus promoting the denitrification reaction. Furthermore, in addition to supplementation of carbon sources, the limitation on denitrification caused by low C/N in wetland influent can also be solved by oxygenation reduction reactions induced by inorganic reductive fillers. Common materials include nano zero-valent iron (NZVI) [49], pyrite [50], and sulfur [51]. According to the reaction mechanism of reduction, these materials can serve as electron donors for NO3−-N to achieve nitrogen removal in a process referred to as autotrophic denitrification [37]. Chu et al. [52] established eight sets of VSSF-CWs supplemented with pyrite. The results showed that the denitrification capacity of the pyrite-addition device was improved and that the TN removal rate was more than 27.05% higher compared to that in the control group. DO content also has an important impact on wetland systems. Insufficient DO content hampers the process of nitrification, thereby impeding subsequent denitrification and resulting in limited nitrogen-removal efficiency [53]. Some researchers have found that selecting substrates with higher porosity can not only enhance microbial attachment, but also help increase the DO content [17]. Zhou et al. [54] studied a new type of CWs that use biochar as the substrate. The high porosity of biochar promotes efficient oxygen diffusion within CWs, thereby enhancing nitrogen-removal performance and resulting in a TN-removal rate of 39%. In addition, apart from direct nitrogen removal via physical adsorption, the substrate can also remove NH3-N through ion-exchange pathways. Zeolite is a common material with high ion-exchange capacity. The zeolite lattice is composed of SiO4 and AlO4 tetrahedra, wherein the presence of aluminum imparts a negative charge to the framework. To maintain electrical neutrality, cations are required for charge balancing [55]. These cations (generally Na+ and K+.) are easily exchanged with NH4+ to remove ammonia nitrogen ions. Alshameri et al. [56] modified Yemeni zeolite by alkali treatment to allow it to adsorb ammonia nitrogen. The results showed that the removal of ammonia nitrogen by zeolite mainly depended on ion exchange, and the rate of removal of nitrogen by modified zeolite was as high as 99%.
3.1.3. Phosphorus
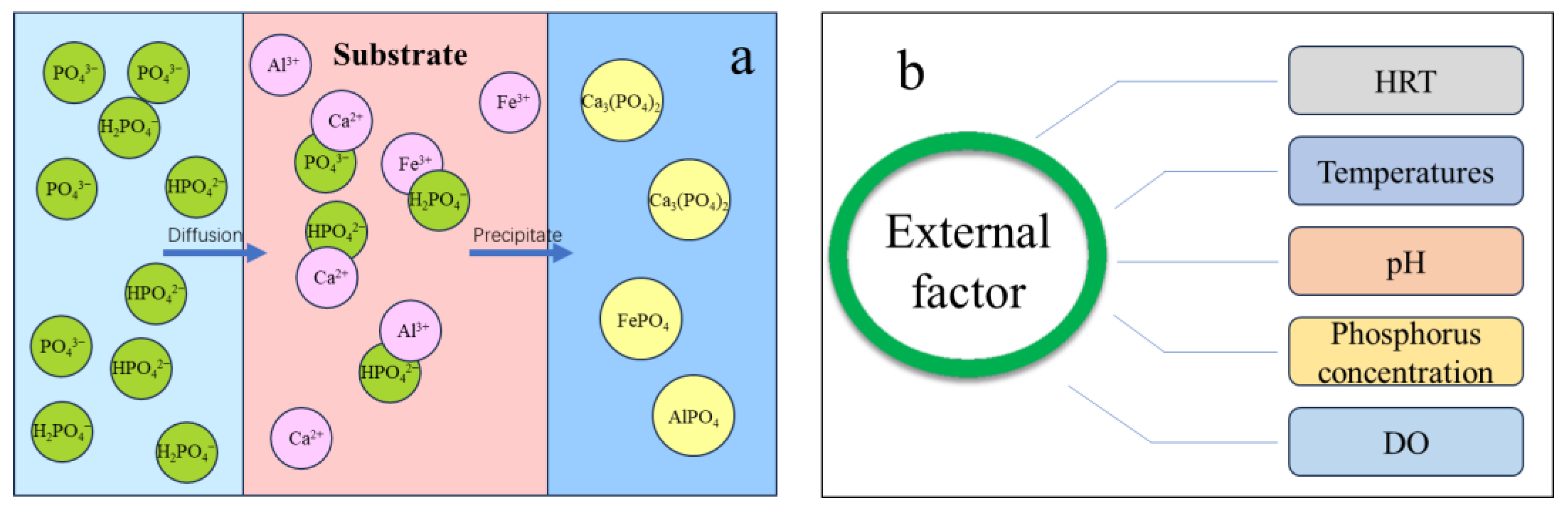
The removal of phosphorus in CWs mainly depends on microbial fixation, plant absorption, soil increment, and substrate adsorption [30,57,58]. Research has shown that the substrate can remove 36.2–87.5% of the phosphorus present in the water [59]. Phosphorus adsorption by the substrate encompasses physical adsorption and chemical precipitation processes, with chemical precipitation playing a significant role [35]. Phosphorus removal by chemical precipitation is mainly a process in which some substrates rich in Ca, Fe, and Al can combine with phosphate to form an insoluble phosphate precipitate (Figure 2a). The efficiency of chemical phosphorus removal is pH-dependent due to the existence of phosphate in various forms at different pH levels. When the sewage environment is weakly acidic or neutral, the predominant inorganic phosphate groups are HPO42− and H2PO4−. Conversely, in a weakly basic or alkaline environment, the main inorganic phosphate groups are HPO42− and PO43−. Research has demonstrated that metal ions exhibit varying phosphorus-removal efficiencies at different pH levels. Within the pH range of 4.5–7.21, Fe-Al-based phosphorus removal dominates, with a maximum phosphorus removal capacity of 17.88–21.63 mg/g. On the other hand, when the pH ranges from 5.42 to 9.83, Ca becomes the primary method for phosphorus removal, with an effective capacity ranging from 20.85 to 21.43 mg/g [60]. The selection of Ca, Al, and Fe-rich substrate materials will increase the phosphorus-adsorption capacity. The presence of metal ions in certain by-products and artificial synthetic materials makes them suitable as substrates for phosphorus removal. Jiang et al. [61] compared the phosphate-removal properties of quartz sand, anthracite, shale, and ceramics. The results showed that the anthracite and bio-ceramics had better removal effects on TP, at 85.87 and 81.44 mg/kg, respectively. The shale and quartz sand had weaker removal properties, at 59.65 and 55.98 mg/kg, respectively. The substrate can also be modified to improve phosphorus removal. Guaya et al. [62] modified zeolite by adding hydrated alumina oxide (HAlO) and showed that the adsorption properties of zeolite increased from 0.7 mg/g to 7.0 mg/g. The modification does not have a significant impact on the substrate’s original chemical properties. Stocker et al. [63] modified zeolite with Ca and showed through joint experiments with NH3-N and PO43− that the modified zeolite did not have a significant impact on the removal of ammonia nitrogen but did remove phosphate. The purification efficiency of CWs with regard to phosphorus is not only affected by the physical properties of the substrate itself but is also related to external factors such as HRT, temperature, pH, phosphorus concentration, and DO (Figure 2b). The use of a suitable operation mode is the key to achieving efficient phosphorus removal in CWs. Moreover, it is crucial to acknowledge that phosphorus removal in CWs can be achieved only through the harvesting of plants or the removal of saturated substrates. Failure to replace the substrate promptly will result in the release of previously adsorbed phosphorus back into the water body.
Figure 2.
(a) Mechanism of chemical precipitation; (b) Influence of external factors on phosphorus removal by the substrate.
3.2. HMs Removal
Due to economic development and the acceleration of industrialization, the emission of HMs has soared. However, it is currently observed that numerous countries, particularly developing countries, exhibit deficiencies in their wastewater treatment. This inadequacy may result in the direct discharge of substantial quantities of HMs into natural water bodies without any form of treatment, thereby posing a considerable threat to human health [64,65]. In recent decades, there has been growing interest in the use of CWs to remove HMs. The methods of HMs removal by CW mainly include sedimentation, adsorption, chemical precipitation, ion exchange, flocculation, microbial interaction, and plant absorption [66,67]. Insoluble HMs in water can be removed by sedimentation and retention, while ion exchange and chemical precipitation can effectively transform soluble HMs into insoluble or insoluble compounds [68]. The mechanism of HMs ion exchange is analogous to that of NH3-N ion-exchange removal. However, it should be noted that the performance of fillers for the removal of different ions varies due to disparities in ionic charge, water solubility, pKH, and ionic strength [69]. Lee et al. [70] explored adsorption by different modified biochars of Cd, Pb, and Zn. The results showed that the adsorption capacity followed the order Pb2+ > Cd2+ > Zn2+. This can be attributed to the smaller hydration radius and relatively lower pKH value of Pb2+, which facilitates its easier adsorption. Moreover, chemical precipitation is also an important way to remove HMs. Tang et al. [71] prepared iron-manganese oxide-modified biochar (FM-BC) for the adsorption of Pb (II) in sewage. The results revealed that the removal of Pb (II) mainly depended on the co-precipitation and complexation of Fe and Mn. Common methods of HM removal by precipitation also include hydroxide precipitation, sulfide precipitation, and carbonate precipitation [68]. Due to the complexity of contaminant-removal mechanisms in CWs, the substrate often serves multiple roles in the removal of HMs. In order to improve the effectiveness of HMs removal from wastewater, Kong et al. [27] prepared a Fe-Al bimetallic oxide modified zeolite to remove Cr (VI) from wastewater. When the initial concentration of Cr (VI) is 20 mg/L, the removal rate can reach 84.96% due to the oxidation–reduction reaction and co-precipitation between Cr (VI) and Fe-Al.
3.3. Fluoride Compounds Removal
Fluorine, a naturally occurring element, readily forms fluoride through chemical bonding with other elements, serving as a vital constituent for the development of teeth and bones. However, excessive exposure to fluoride can lead to dental fluorosis and even skeletal deformities [72,73]. CWs mainly rely on adsorption and coprecipitation of substrate to remove F−. Yao et al. [74] used limestone as the substrate to increase the calcium content in wetlands. XRD showed that the formation of CaF2, Ca5(PO4)3, and Ca3(PO4)2 precipitates mainly depended on adsorption and co-precipitation. It is worth noting that the researchers found that the fluoride-removal effect of CWs with limestone as the substrate was not significantly different from that of the control group. This suggests that calcium-based wetlands do not show improved fluoride-removal performance. A special organic fluoride named perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) have received extensive attention due to their toxicity and capacity for bioaccumulation [75]. CWs, synergistically with microorganisms, plants and substrates, may be able to promote their removal from water bodies. Ma et al. [76] added iron mineral to VSSF-CWs to remove perfluorooctane sulfonic acid (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) from water. The results showed that the dosage of iron mineral increased the concentration of microorganisms capable of removing PFAS (e.g., Burkholderia and Pseudomonas). Compared with the control group, the effluent PFOS and PFOA contents decreased by 35.0% and 36.8%.
3.4. PPCPs Removal
PPCPs come from various drugs, disinfectants, fragrances, and cosmetics [77]. Upon entering the aquatic environment, these substances can potentially diminish the survival rate of aquatic organisms. More importantly, their accumulation in such organisms poses a significant risk to human health through consumption [78]. Unfortunately, current wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) mainly focus on the removal of conventional contaminants, often neglecting the elimination of PPCPs. As a result, some PPCPs manage to survive in traditional WWTPs and are subsequently discharged into natural water bodies [79]. CWs are considered an effective way to deal with PPCPs due to their low cost and environmental friendliness, especially as a method for removing antibiotics and antibiotic-resistance genes (ARGs). Chen et al. [80] established four CWs based on zeolite, resulting in impressive removal efficiencies of 87.4% for antibiotics and 87.8% for ARGs. The study revealed that microbial degradation emerged as the predominant factor, followed by substrate adsorption and plant absorption. Liu et al. [81] used zeolite as the substrate to remove sulfamethoxazole (SMX) and ofloxacin (OFLO). They found that the mechanism of removal of SMX and OFLO by zeolite was actually an adsorption–degradation process. When the zeolite comes into contact with the antibiotic, it rapidly undergoes adsorption onto the surface of the zeolite, which is followed by biodegradation facilitated by microorganisms attached to the zeolite. Subsequently, the excess adsorption sites on the zeolite surface will continue to adsorb antibiotics, reducing the concentration of antibiotics. Use of a suitable adsorbent can improve the removal of PPCPs. Rodriguez et al. [82] explored the use of powdered activated carbon in combination with ultrafiltration to remove five PPCPs (1-H-benzotriazole, DEET, chlorophene, 3-methylindole, and nortriptyline-HCl) and found that adsorbents can significantly promote the removal of compounds with poor hydrophobicity. Pore size plays an important role in removing PPCPs, and powdered activated carbon with high microporosity can better adsorb PPCP and organic matter.
3.5. Microplastics Removal
Microplastics are plastic particles with a diameter of less than 5 mm. The emission of microplastics not only leads to ecological pollution, but also inflicts irreversible harm upon the health of aquatic organisms [83,84]. Microplastics can be removed by adsorption, filtration, sedimentation, flocculation, and biodegradation [85]. CWs have been reported as a good new way to remove microplastics [86]. The mechanism of removal of microplastics by CWs mainly relies on physical retention. The substrate, serving as the carrier within CWs, plays an important role in the removal of microplastics. In addition, the substrate can also be used to remove microplastics by adsorption and chemical precipitation. Chen et al. [87] studied the removal of microplastics by CWs, and the results showed that most microplastics were removed through the substrate layer of 0–20 cm at the water inlet. Selecting a substrate with a larger pore size could enable the microplastics to be transported farther and improve the removal of microplastics. In addition, since microplastics generally carry a negative charge, cations can be used to capture and remove them. Shen et al. [88] used cationic surfactants to modify an aluminosilicate filter medium, and the capture rate of microplastics reached more than 96%, much higher than that of the rapid sand filter (63%). The utilization of CWs for the removal of microplastics has emerged as a prominent area of research; however, due to an incomplete understanding of the underlying removal mechanisms, current experimental investigations on microplastic removal using CWs are primarily conducted within laboratory settings.
3.6. Chapter Summary
The above content summarizes the role of CW substrates in the removal of various contaminants. Generally speaking, substrates can directly participate in the removal of contaminants through filtration and interception, adsorption, chemical precision, redox reactions, and ion exchange. Additionally, they serve as the foundation for CWs by facilitating the growth and reproduction of microorganisms and plants. Therefore, selecting the appropriate substrate is crucial for wetlands. Table 3 summarizes 14 representative substrate materials and evaluates their ability to purify water, providing a reference for the selection of high-quality substrates.

Table 3.
The removal effect of different substrates on contaminants.
4. Problems and Prospects
4.1. Clogging
At present, the clogging problem has become a key factor restricting the long-term operation of CWs. The main causes of substrate clogging include deposition of various solids, precipitation, and microbial and plant growth [89]. Substrate clogging decreases the permeability coefficient and porosity of the substrate, which reduces the treatment performance and service life of CWs [29]. Choosing the right substrate can effectively reduce clogging. Wang et al. [90] used NaCl as a tracer to test the changes in electrical conductivity (EC) of nine substrates (quartz sand, zeolite, coarse sand, gravel, two types of biochar, and three types of ceramsite). The findings suggest that zeolite has minimal impact on the electrical conductivity (EC) of wastewater, whereas the utilization of artificial synthetic substrates like sludge biochar can significantly elevate EC levels in water, thereby increasing the susceptibility of wetlands to clogging. In addition, the adsorption capacity of the substrate is limited [91]. With increased substrate adsorption, the degree of clogging of CWs will continue to rise. Furthermore, once the adsorption reaches saturation, contaminants will escape from the adsorbent and enter the water body [92]. Therefore, the substrate needs to be replaced before it becomes clogged.
4.2. Substrate Selection and Collocation
Currently, problem of pollution associated with sewage has become increasingly complex, and relying solely on a single substrate often makes it difficult to completely remove contaminants. Developing substrates with different contaminant-removal characteristics and combining them can achieve better contaminant removal through the synergistic effect between substrate layers. Composite substrates can extend the life cycle and improve the removal of emerging pollutants. Xu et al. investigated the synergistic effect of a mixed substrate comprising manganese ore and activated alumina on enhancing the efficiency of contaminant removal. The combined approach demonstrated remarkable performance, achieving 89.4% COD removal and 98.1% TP removal. Under different types of flow direction, the optimal layout of substrates is significantly different [16]. In free water-surface-flow (FWS) CWs, the major function of substrates is to support the plants. The hydraulic permeability of substrates should be the focus in the design of vertical subsurface (VSSF) CWs. In recent research, a VSSF–horizontal subsurface flow (HSSF)-FWS hybrid system was constructed to treat domestic wastewater and showed better treatment efficiency [93,94,95]. In hybrid CWs, various substrates were applied at different stages to obtain better treatment efficiency.
However, there is currently no standardized approach for selecting the substrate type and determining the optimal mixing ratio of CWs, while the removal mechanism remains a subject of ongoing research. It is certain that the combination of substrates has become an important method by which to improve the treatment performance of contaminants and improve the service life of wetlands [96].
4.3. Combining CW Technology with Other Processes
CWs are widely used due to their advantages of cost effectiveness and ease of maintenance and management. However, major parts of the wetland do not have access to sufficient electron donors, especially oxygen, which leads to inefficient contaminant removal [97]. Combining CWs with other technologies can help ameliorate the lack of electron donors and thus improve contaminant removal. Technologies commonly combined with CWs include photocatalysis [98], microbial fuel cells (MFC) [99], membrane bioreactors (MBR) [100], etc. However, due to differences in water quality and the types and quantities of contaminants in different regions, there is still no scientific theoretical basis and standard for the research on the combination of different CWs with other technologies, which limits the promotion and application of such systems. Exploring the operating mechanism of composite systems and selecting combinations with good processing effects and strong adaptability can improve the overall processing capacity of the wetland and reduce the land area required.
5. Conclusions
This article reviews the research achievements in the field of wetlands in recent years, categorizes and summarizes the types of substrates, and elaborates on the removal methods and the influence of contaminant-related factors (conventional contaminants and EPs) in CWs. The physical properties of various substrates were comprehensively evaluated, along with their efficacy in contaminant removal, providing valuable insights for the further advancement of CWs. In summary, through a literature review of substrates, it can be concluded that:
- CWs have been widely used in wastewater treatment. At present, there are more than 11,000 articles related to CWs in the Web of Science database. The term “constructed wetland” was used as the key word to search the database. In the past five years (2019–2023), a total of 5140 relevant publications were found after deduplication. Afterwards, VOSviewer software was used to visually analyze these 5140 articles, and the results show that the current research on CWs is still mainly focused on the removal of traditional contaminants (e.g., nitrogen and phosphorus).
- According to the source of the substrates, they can be divided into natural substrates, by-products (agricultural by-products and industrial by-products) and artificially synthesized substrates. Different substrates exhibit significant disparities in performance. This paper systematically summarizes the characteristics of different substrates and their ability to remove various contaminants in CWs. For the purposes of practical engineering, this paper provides important reference information for the selection and configuration of substrates.
- CWs rely on the synergistic interaction of plants, microorganisms, and substrate to purify contaminants. Among them, the substrate plays an important role in CWs. It not only can help microbial proliferation and plant growth, but also directly participate in removing contaminants through filtration and interception, adsorption, chemical precision, redox reactions, and ion exchange.
- With the continuous improvement in requirements for contaminant removal, EPs have received extensive attention. At present, CWs have been proved to be an effective way to remove EPs. In the future, the mechanism of their removal from CWs should be studied systematically.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.W., L.M. and J.W.; validation, L.W., X.Z. and C.L. (Changqing Liu); formal analysis, X.Z.; investigation, C.L. (Cang Li) and C.J.; resources, Y.J.; data curation, M.X.; writing—original draft preparation, L.W., J.W. and C.L. (Cang Li); writing—review and editing, Y.J. and M.X.; visualization, L.M.; supervision, Y.X.; project administration, C.L. (Cang Li) and Y.X.; funding acquisition, C.L. (Changqing Liu), C.J. and M.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by Zhangcun River Water Purification Plant Ecological Water Supplement Ecological Health Risk Assessment Technology Research and Development Project (20205541). The Qingdao Science and Technology Demonstration Project for Benefiting the People (No. 23-2-7-zdfn-2-nsh), Taishan Scholar Foundation of Shandong Province (No. tsqn201909126) and the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2021YFC3201004) are also acknowledged.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors Liyan Wang, Leihui Ma, Junke Wang, Xia Zhao and Yushu Jing were employed by the company Qingdao Zhangcun River Water Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Sandoval-Herazo, L.C.; Alvarado-Lassman, A.A.; Marín-Muñiz, J.L.; Méndez-Contreras, J.M.; Zamora-Castro, S.A. Effects of the Use of Ornamental Plants and Different Substrates in the Removal of Wastewater Pollutants through Microcosms of Constructed Wetlands. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Yang, Q.; Wei, G.; Cheung, S.G.; Shin, P.K.; Wong, Y.S.; Li, Z.; Chen, Z.; Tam, N.F.Y. Changes of substrate microbial biomass and community composition in a constructed mangrove wetland for municipal wastewater treatment during 10-years operation. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 155, 111095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, J.J.; Xu, S.G.; Zhang, Y.M.; Han, C.W. Molybdenum (VI) removal by using constructed wetlands with different filter media and plants. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 67, 1859–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Xu, W.; Wang, H.; Zhao, D.; Ding, H. Nitrogen and Phosphorus Removal Efficiency and Denitrification Kinetics of Different Substrates in Constructed Wetland. Water 2022, 14, 1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Guo, Q.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Wei, Q.; Chen, L.; Liao, L. Enhancing Nitrogen and Phosphorus Removal by Applying Effective Microorganisms to Constructed Wetlands. Water 2020, 12, 2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negi, D.; Verma, S.; Singh, S.; Daverey, A.; Lin, J.-G. Nitrogen removal via anammox process in constructed wetland—A comprehensive review. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 437, 135434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehzadi, M.; Afzal, M.; Khan, M.U.; Islam, E.; Mobin, A.; Anwar, S.; Khan, Q.M. Enhanced degradation of textile effluent in constructed wetland system using Typha domingensis and textile effluent-degrading endophytic bacteria. Water Res. 2014, 58, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türker, O.C.; Böcük, H.; Yakar, A. The phytoremediation ability of a polyculture constructed wetland to treat boron from mine effluent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 252–253, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.-L.; Nakano, K.; Taniguchi, T.; Nomura, M.; Nishimura, O. Estrogen removal from treated municipal effluent in small-scale constructed wetland with different depth. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 2945–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsubih, M.; El Morabet, R.; Khan, R.A.; Khan, N.A.; Khan, A.R.; Khan, S.; Mubarak, N.M.; Dehghani, M.H.; Singh, L. Field performance investigation for constructed wetland clubbed with tubesettler for hospital wastewater treatment. J. Water Process. Eng. 2022, 49, 103147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, D.; Dong, J.; Tan, S.K. Application of constructed wetlands for treating agricultural runoff and agro-industrial wastewater: A review. Hydrobiologia 2017, 805, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilachi, I.C.; Asiminicesei, D.M.; Fertu, D.I.; Gavrilescu, M. Occurrence and Fate of Emerging Pollutants in Water Environment and Options for Their Removal. Water 2021, 13, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Huang, J.; Huang, M.; Chen, M.; Wang, M. Application of basalt fiber in vertical flow constructed wetland for different pollution loads wastewater: Performance, substrate enzyme activity and microorganism community. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 318, 124229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, T.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, J.; Ji, B.; García, A.P.; Núñez, A.E. Developing a novel lightweight substrate for constructed treatment wetland: The idea and the reality. J. Water Process. Eng. 2024, 57, 104587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Z.; Wang, S.; Ye, J.F.; Xu, Z.X.; Jin, W. A practical method for the restoration of clogged rural vertical subsurface flow constructed wetlands for domestic wastewater treatment using earthworm. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 63, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Z.; Tang, W.; Pei, Y. Constructed wetland substrates: A review on development, function mechanisms, and application in contaminants removal. Chemosphere 2021, 286, 131564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Fan, J.; Zhang, J.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Liang, S.; Lv, J.; Lu, S.; Wu, W.; Wu, S. Intensified organics and nitrogen removal in the intermittent-aerated constructed wetland using a novel sludge-ceramsite as substrate. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 210, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, J.Y.; Hu, X.J.; Cheng, S.Y.; Xie, H.J.; Hu, Z.; Wu, H.M.; Liang, S. Effects and mechanisms of constructed wetlands with different substrates on N2O emission in wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 19045–19053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehrah, D.; Reddy, M.; Novak, J.; Bansode, R.; Schimmel, K.; Yu, J.; Watts, D.; Ahmedna, M. Production and characterization of biochars from agricultural by-products for use in soil quality enhancement. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2014, 108, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, T.; Muntaha, S.; Rashid, M.; Sun, G.; Hasnat, A. Industrial wastewater treatment in constructed wetlands packed with construction materials and agricultural by-products. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 189, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandhini, K.; Karthikeyan, J. Influence of Industrial and Agricultural by-Products as Cementitious Blends in Self-Compacting Concrete—A Review. Silicon 2021, 14, 2431–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liang, S.; Hu, J.; Hou, H.; Quan, J.; Li, X.; Duan, H.; Yuan, S.; Yang, J. Environmentally sound management of industrial solid waste: A paradigm of proposed bi-tetrahedron. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 198, 107212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanlioglu, F. A multi-objective mathematical model for the industrial hazardous waste location-routing problem. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2013, 226, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, A.; Kumar, S.; Srivastava, A.; Pratap, B. Performance of recycled aggregate concrete using copper slag as fine aggregate. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 82, 108364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Chen, X.; Li, W.; Yu, Y.; Yan, K. Environmental assessment, management and utilization of red mud in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 84, 606–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zhang, X.; Tang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Xie, S.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, Y. Selection and optimization of the substrate in constructed wetland: A review. J. Water Process. Eng. 2022, 49, 103140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Tang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, S. Removal of Cr(VI) from wastewater by artificial zeolite spheres loaded with nano Fe–Al bimetallic oxide in constructed wetland. Chemosphere 2020, 257, 127224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Y.; Wang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Dzakpasu, M.; Zhao, Y.; Xiong, J. Functions of slags and gravels as substrates in large-scale demonstration constructed wetland systems for polluted river water treatment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 12982–12991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, H.; Hu, N.; Wang, Q.H.; Chen, Y.C.; Huang, L. How to select substrate for alleviating clogging in the subsurface flow constructed wetland? Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 828, 154529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Dong, J.; Liu, L.; Zhu, G.; Liu, C. Screening of phosphate-removing substrates for use in constructed wetlands treating swine wastewater. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 54, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuomo, M.; König, R.; Zanardini, E.; Di Guardo, A.; Bianchi, G.; Ortona, A.; Principi, P. Using zeolite filters to reduce activated carbon use in micropollutant removal from wastewater. J. Water Process. Eng. 2023, 56, 104298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velarde, L.; Nabavi, M.S.; Escalera, E.; Antti, M.-L.; Akhtar, F. Adsorption of heavy metals on natural zeolites: A review. Chemosphere 2023, 328, 138508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, P.; Zhou, L.; Wang, W.; Li, N.; Zhang, F. Performance and mechanisms of fly ash for graphene oxide removal from aqueous solution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 29, 3773–3783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zou, Y.; Yu, X.; Ding, S.; Yan, J.; Min, Y. Vegetated Steel Slag Substrate Constructed Wetlands can Achieve High Efficiency Simultaneous Nitrogen and Phosphorus Removal. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 947783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.M.; Liu, C.; Guo, X.C. Enhanced P, N and C removal from domestic wastewater using constructed wetland employing construction solid waste (CSW) as main substrate. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 66, 1022–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Dong, L.; Guo, Z.; Hu, Z.; Dai, P.; Zhang, J.; Wu, H. Highly efficient phosphorous removal in constructed wetland with iron scrap: Insights into the microbial removal mechanism. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 347, 119076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, S.; Li, D.; Yang, X.; Xing, W.; Li, J.; Zhang, Q. Iron [Fe(0)]-rich substrate based on iron–carbon micro–electrolysis for phosphorus adsorption in aqueous solutions. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 1486–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carstensen, M.V.; Larsen, S.E.; Kjærgaard, C.; Hoffmann, C.C. Reducing adverse side effects by seasonally lowering nitrate removal in subsurface flow constructed wetlands. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 240, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaves-Barquero, L.G.; Humeniuk, B.W.; Luong, K.H.; Cicek, N.; Wong, C.S.; Hanson, M.L. Crushed recycled glass as a substrate for constructed wetland wastewater treatment: A case study of its potential to facilitate pharmaceutical removal. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 52306–52318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Q.; Han, Q.; Luo, H.; He, T.; Xue, F.; Ye, Z.; Chen, C.; Huang, S. Ceramsite Facilitated Microbial Degradation of Pollutants in Domestic Wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vispo, C.; Geronimo, F.K.; Jeon, M.; Kim, L.-H. Performance Evaluation of Various Filter Media for Multi-Functional Purposes to Urban Constructed Wetlands. Sustainability 2023, 16, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Ann, T.-W.; Lee, S.-M. Use of biochar to enhance constructed wetland performance in wastewater reclamation. Environ. Eng. Res. 2016, 21, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, Y.; Zhou, X.; Li, Z.; Uddin, S.M.N.; Bai, X. Comparative research on phosphorus removal by pilot-scale vertical flow constructed wetlands using steel slag and modified steel slag as substrates. Water Sci. Technol. 2015, 71, 996–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Yan, B.; Xu, Y.; Guan, J.; Liu, S. Removal of nitrogen and COD in horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands under different influent C/N ratios. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 63, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Cui, L. Removal of COD from synthetic wastewater in vertical flow constructed wetland. Water Environ. Res. 2019, 91, 1661–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Xu, H.; Liu, C.; Shen, Z.; Hu, K. Preparation of Ceramsite Based on Waterworks Sludge and Its Application as Matrix in Constructed Wetlands. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.X.; Wang, X.Y.; Teng, H.W.; Xu, J.L.; Sheng, L.X. Purification mechanism of city tail water by constructed wetland substrate with NaOH-modified corn straw biochar. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 238, 113597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Xu, J.; Sheng, L.; Teng, H. Study on treatment of city tail water by constructed wetland with corn straw biochar substrate. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 28, 102855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.L.; Wang, J.R.; Hou, W.H.; Cui, Y.Q.; Yu, L.H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S. Influence of modified biochar supported sulfidation of nano-zero-valent-iron (S-nZVI/BC) on nitrate removal and greenhouse gas emission in constructed wetland. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 125, 568–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, X.-H.; Wang, H.-C.; Li, Z.-L.; Liang, B.; Sun, Y.-L.; Cheng, H.-Y.; Lu, S.-Y.; Wang, A.-J. Pyrite coupled with steel slag to enhance simultaneous nitrogen and phosphorus removal in constructed wetlands. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 470, 143944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Lin, X.; Xu, J.; Ren, J.; Sun, D.; Gu, Y.; Huang, J. Enhanced Nitrogen Removal of Steel Rolling Wastewater by Constructed Wetland Combined with Sulfur Autotrophic Denitrification. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Liu, W.; Tan, Q.; Yang, L.; Chen, J.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Z.; He, F. Vertical-flow constructed wetland based on pyrite intensification: Mixotrophic denitrification performance and mechanism. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 347, 126710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Song, X.; Li, F.; Ji, X.; Hou, M. Intensified nitrogen removal in constructed wetlands by novel spray aeration system and different influent COD/N ratios. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 306, 123008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Liang, C.; Jia, L.; Feng, L.; Wang, R.; Wu, H. An innovative biochar-amended substrate vertical flow constructed wetland for low C/N wastewater treatment: Impact of influent strengths. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 844–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inglezakis, V.J. The concept of “capacity” in zeolite ion-exchange systems. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 281, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshameri, A.; Ibrahim, A.; Assabri, A.M.; Lei, X.; Wang, H.; Yan, C. The investigation into the ammonium removal performance of Yemeni natural zeolite: Modification, ion exchange mechanism, and thermodynamics. Powder Technol. 2014, 258, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.Q.; Huang, S.L.; Scholz, M. Comparison of phosphorus removal between vertical subsurface flow constructed wetlands with different substrates. Water Environ. J. 2009, 23, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubaszek, A. Nitrogen and Phosphorus Accumulation in Horizontal Subsurface Flow Constructed Wetland. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.; Ngo, H.; Guo, W.; Vu, N.; Tran, T.; Nguyen, T.; Nguyen, X.; Nguyen, V.; Pham, T. Hybrid use of coal slag and calcined ferralsol as wetland substrate for improving phosphorus removal from wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 428, 132124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Wang, Z.; Yang, W.; Wu, Q.; Yang, H.; Xue, X. Effects of pH on phosphorus removal capacities of basic oxygen furnace slag. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 89, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Jia, L.; Zhang, B.; He, Y.; Kirumba, G. Comparison of quartz sand, anthracite, shale and biological ceramsite for adsorptive removal of phosphorus from aqueous solution. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guaya, D.; Valderrama, C.; Farran, A.; Armijos, C.; Cortina, J.L. Simultaneous phosphate and ammonium removal from aqueous solution by a hydrated aluminum oxide modified natural zeolite. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 271, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, K.; Ellersdorfer, M. Phosphate Fixation and P Mineralogy on Natural and Ca-Modified Zeolites During Simultaneous Nutrient Removal. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2022, 233, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaimee, M.Z.A.; Sarjadi, M.S.; Rahman, L. Heavy Metals Removal from Water by Efficient Adsorbents. Water 2021, 13, 2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.V.; Nguyen, B.T. Heavy metal pollution in surface water bodies in provincial Khanh Hoa, Vietnam: Pollution and human health risk assessment, source quantification, and implications for sustainable management and development. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 343, 123216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bavandpour, F.; Zou, Y.; He, Y.; Saeed, T.; Sun, Y.; Sun, G. Removal of dissolved metals in wetland columns filled with shell grits and plant biomass. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 331, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafeznezami, S.; Kim, J.-L.; Redman, J. Evaluating Removal Efficiency of Heavy Metals in Constructed Wetlands. J. Environ. Eng. 2012, 138, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šíma, J.; Svoboda, L.; Pomijová, Z. Removal of Selected Metals from Wastewater Using a Constructed Wetland. Chem. Biodivers. 2016, 13, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehmani, Y.; Mohammed, B.B.; Oukhrib, R.; Dehbi, A.; Lamhasni, T.; Brahmi, Y.; El-Kordy, A.; Franco, D.S.; Georgin, J.; Lima, E.C.; et al. Adsorption of various inorganic and organic pollutants by natural and synthetic zeolites: A critical review. Arab. J. Chem. 2024, 17, 105474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-S.; Shin, H.-S. Competitive adsorption of heavy metals onto modified biochars: Comparison of biochar properties and modification methods. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 299, 113651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.-F.; Zhou, H.; Tan, W.-T.; Huang, J.-G.; Zeng, P.; Gu, J.-F.; Liao, B.-H. Adsorption Characteristics and Mechanisms of Fe-Mn Oxide Modified Biochar for Pb(II) in Wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otal, E.H.; Kim, M.L.; Dietrich, S.; Takada, R.; Nakaya, S.; Kimura, M. Open-Source Portable Device for the Determination of Fluoride in Drinking Water. ACS Sensors 2021, 6, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Styburski, D.; Baranowska-Bosiacka, I.; Goschorska, M.; Chlubek, D.; Gutowska, I. Beer as a Rich Source of Fluoride Delivered into the Body. Biol. Trace Element Res. 2016, 177, 404–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, D.D.; Hu, X.J.; Shen, X.T.; Xie, H.J.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Liang, S. Can calcium-based constructed wetlands improve fluoride removal performance? Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 450, 138314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickard, B.P.; Overchuk, M.; Tulino, J.; Tan, X.; Ligler, F.S.; Bae-Jump, V.L.; Fenton, S.E.; Rizvi, I. Exposure to select PFAS and PFAS mixtures alters response to platinum-based chemotherapy in endometrial cancer cell lines. Environ. Health 2023, 22, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Kang, Y.; Li, M.; Dong, J.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, J.; Guo, Z. Enhancement of perfluorooctanoic acid and perfluorooctane sulphonic acid removal in constructed wetland using iron mineral: Performance and mechanisms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 447, 130819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srain, H.S.; Beazley, K.F.; Walker, T.R. Pharmaceuticals and personal care products and their sublethal and lethal effects in aquatic organisms. Environ. Rev. 2021, 29, 142–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilroy, E.A.M.; Klinck, J.S.; Campbell, S.D.; McInnis, R.; Gillis, P.L.; de Solla, S.R. Toxicity and bioconcentration of the pharmaceuticals moxifloxacin, rosuvastatin, and drospirenone to the unionid mussel Lampsilis siliquoidea. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 487, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krogh, J.; Lyons, S.; Lowe, C.J. Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products in Municipal Wastewater and the Marine Receiving Environment Near Victoria Canada. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Deng, W.-J.; Liu, Y.-S.; Hu, L.-X.; He, L.-Y.; Zhao, J.-L.; Wang, T.-T.; Ying, G.-G. Fate and removal of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in hybrid constructed wetlands. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 894–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Lu, S.; Zhao, B.; Wang, Z.; Xi, B.; Guo, W. Adsorption and biodegradation of sulfamethoxazole and ofloxacin on zeolite: Influence of particle diameter and redox potential. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 384, 123346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, E.; Campinas, M.; Acero, J.L.; Rosa, M.J. Investigating PPCP Removal from Wastewater by Powdered Activated Carbon/Ultrafiltration. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, H. Adsorption of antibiotics on microplastics. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Ge, J.; Yu, X. Bioavailability and toxicity of microplastics to fish species: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 189, 109913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, R.; Hamid, A.K.; Krebsbach, S.A.; He, J.; Wang, D. Critical review of microplastics removal from the environment. Chemosphere 2022, 293, 133557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.F.; Jin, R.X.; Chen, Y.H.; Zhang, J.H.; Tao, S.Y.; Liu, S.W.; Shen, M.C. Constructed wetlands as neglected fixed source of microplastics and antibiotic resistance genes in natural water bodies? Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 902, 166474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Li, T.; Hu, H.; Ao, H.; Xiong, X.; Shi, H.; Wu, C. Transport and fate of microplastics in constructed wetlands: A microcosm study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 415, 125615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, M.; Hu, T.; Huang, W.; Song, B.; Zeng, G.; Zhang, Y. Removal of microplastics from wastewater with aluminosilicate filter media and their surfactant-modified products: Performance, mechanism and utilization. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 421, 129918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, S.T.; de Matos, A.T.; de Matos, M.P.; Saraiva, C.B.; Teixeira, D.L. Influence of the substrate type and position of plant species on clogging and the hydrodynamics of constructed wetland systems. J. Water Process. Eng. 2019, 31, 100871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Sun, J.; Xu, J.; Sheng, L. Study on clogging mechanisms of constructed wetlands from the perspective of wastewater electrical conductivity change under different substrate conditions. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 292, 112813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Gu, T.; Yi, W.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Y. The release mechanism of heavy metals from lab-scale vertical flow constructed wetlands treating road runoff. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 16588–16595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ury, E.A.; Arrumugam, P.; Herbert, E.R.; Badiou, P.; Page, B.; Basu, N.B. Source or sink? Meta-analysis reveals diverging controls of phosphorus retention and release in restored and constructed wetlands. Environ. Res. Lett. 2023, 18, 083002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávila, C.; Bayona, J.M.; Martín, I.; Salas, J.J.; García, J. Emerging organic contaminant removal in a full-scale hybrid constructed wetland system for wastewater treatment and reuse. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 80, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jehawi, O.H.; Abdullah, S.R.S.; Kurniawan, S.B.; Ismail, N.; Idris, M.; Al Sbani, N.H.; Muhamad, M.H.; Abu Hasan, H. Performance of pilot Hybrid Reed Bed constructed wetland with aeration system on nutrient removal for domestic wastewater treatment. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 19, 100891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.K.; Rausa, K.; Rani, A.; Mukherjee, S.; Kumar, M. Biopurification of dairy farm wastewater through hybrid constructed wetland system: Groundwater quality and health implications. Environ. Res. 2021, 200, 111426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Xu, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, X. Study of the effect of pyrite and alkali-modified rice husk substrates on enhancing nitrogen and phosphorus removals in constructed wetlands. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 54234–54249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Srivastava, P.; Patil, S.A.; Yadav, A.K. A comprehensive review on emerging constructed wetland coupled microbial fuel cell technology: Potential applications and challenges. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 320, 124376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.-C.; Wang, Y.-H.; Lu, Y.-C. Treatment of polluted water for reclamation using photocatalysis and constructed wetlands. Catal. Today 2011, 175, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, F.; Lin, Y.; Sun, L.; Guo, X.; Yang, S.; He, J. Enhanced Swine Wastewater Treatment by Constructed Wetland—Microbial Fuel Cell Systems. Water 2022, 14, 3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, E.-R.; Liang, W.; He, F.; Cheng, S.-P.; Wu, Z.-B. Performance of the combined SMBR–IVCW system for wastewater treatment. Desalination 2010, 250, 781–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).