Abstract
Wastewater-based epidemiology (WBE) evaluates the health status, environmental exposure, and lifestyle habits of community inhabitants through the investigation of chemical or biological markers present in urban wastewater systems. This approach is frequently employed in discerning drug abuse, disease prevalence, and the presence of environmental contaminants. To comprehend the current state and developmental trajectories in WBE research, the current study utilizes the source literature of the Web of Science Core Collection (WOSCC) database. Implementing the Bibliometrix toolkit in R language and employing CiteSpace and VOSviewer for bibliometric analysis, this investigative pursuit effectuates an all-encompassing evaluation of the WBE literature, traversing a substantial time span of 16 years, encompassing 2008 through 2023. The results of this bibliometric analysis illuminate annual propensities and disciplinary distribution related to WBE research, while discerning the most impactful and prolific contributors, including authors, institutions, countries, and scholarly journals. The onset of the COVID-19 pandemic has engendered the expedited progression of WBE, leading to a substantial escalation in research endeavors in the past three years. By meticulously evaluating highly-cited publications, co-occurrence network of keywords, and keyword burst analysis, it is concluded that the research hotspots in this field focus on the monitoring of illicit drugs, psychoactive substances, and viruses in sewage. Subsequent investigations possess the capacity to propel the advancement of emerging methodologies for biomarker identification and analytical techniques. By concurrently integrating big data technologies (including artificial intelligence and cloud computing) with epidemiological and clinical data sets, a more expansive, precise, and efficacious rendition of WBE research can be realized.
1. Introduction
The concept of “wastewater-based epidemiology (WBE)” was first proposed by Christian G. Daughton, an environmental scientist at the National Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in 2001. This scientific method aims to explore the health status, environmental factors, and lifestyle habits of a population through the analysis of biomarkers (e.g., drug metabolites, pathogens, etc.) present in urban sewage systems [1]. WBE constitutes an indirect, non-invasive surveillance approach capable of providing real-time, dynamic data reflecting the health conditions and environmental exposure levels experienced by community inhabitants [2]. Considered a powerful and cost-efficient tool, WBE facilitates the investigation of population-level chemical consumption, pathogen infections, and overall health conditions. Initially implemented for investigating psychoactive substance abuse, WBE has since progressed to include evaluations of the consumption of legal drugs [3], pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) [4], and industrial chemicals [5]. Moreover, this approach enables the analysis of temporal and spatial consumption trends within a study area, facilitating further exploration of consumption patterns or epidemiological circumstances, which subsequently broadens the applicability of WBE. In recent years, WBE has garnered increasing significance in the realms of public health and environmental protection. During the COVID-19 pandemic, WBE demonstrated successful application in virus surveillance and transmission risk assessments, thus further substantiating its invaluable role in community health monitoring [6].
Presently, the majority of WBE research reviews concentrate on the application of WBE in the investigation of illicit drugs, chemical pollutants, and viruses, or the detection technology for WBE biomarkers. For example, Huizer et al. employed WBE methodology and performed a data analysis on a global scale, evaluating the illicit drug consumption situation across diverse regions [7]. Boogaerts et al. scrutinized the utilization of WBE as an alternative technique for drug monitoring in countries exhibiting suboptimal records of drug usage [8]. Meanwhile, Rahman et al. assessed the design and working principles of nanobiosensors, and their progressive application in biomarker detection [8], while Sims et al. reviewed the analysis of infectious disease dissemination and drug resistance in wastewater based on WBE, enabling comprehensive real-time surveillance of emerging outbreaks [9]. Nonetheless, a discernible scarcity exists in the current literature pertaining to employing bibliometric approaches for the analysis of WBE research advancements via knowledge mapping.
Bibliometrics revolves around the quantitative analysis and statistical evaluation of the quantitative attributes and evolutionary principles of scientific literature. This methodology entails examining distribution structures, quantitative features, and patterns of change in the literature corpus, enabling the assessment of research status and development trajectories in a particular discipline, field, or topic through qualitative and quantitative investigations [10]. Recently, the bibliometric method has found extensive applications in environmental DNA technology implementation in aquatic ecosystem monitoring [11], the application of artificial intelligence in wastewater treatment [12], and the application of thin-film diffusive gradient technology in the environmental field [13]. To date, there remains a conspicuous absence of systematic discussions addressing the research status and development trends related to WBE.
To gain a comprehensive understanding of the research landscape in the field of WBE, this study utilizes the Web of Science Core Collection (WOSCC) database as the primary data source and conducts a bibliometric systematic analysis of the research literature related to WBE. The R language-based Bibliometrix toolkit was employed to collate literature data from 2008 to 2023, and in-depth analyses of publication trends, journal distribution, high citation paper analysis, international scientific research collaboration networks, and keyword co-occurrence analysis were performed. VOSviewer and CiteSpace software were used to visualize and analyze the data to fully understand the discipline dynamics and application status in the research field of WBE, reveal the research hotspots, and accurately locate the existing challenges, to provide reference for further research in the field in the future.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources and Retrieval Strategies
This study’s literature data retrieval predominantly relies on the WOSCC database, which serves as the world’s most extensive comprehensive academic information resource encompassing a multitude of disciplines. The WOSCC database, with its robust search capabilities and abundant bibliometric information, facilitates the swift and precise acquisition of valuable scientific insights reflecting development trends, latest advances, and current challenges in the selected field [14]. The search field was set to the subject, employing keywords such as “wastewater-based epidemiology” or “sewage epidemiology”. The search was conducted on 17 April 2024, with the literature types restricted to original research papers and reviews, excluding conferences, data, letters, news, revisions, editorial materials, and books. A manual review of titles, abstracts, keywords, and research directions for each article was conducted, eliminating irrelevant publications to yield a total of 990 retrieved literature items. The data were downloaded and stored as plain text files (.txt format). Given the presence of singular or plural keywords, synonyms or near-synonyms, and abbreviations, keywords were consolidated to ensure the generation of meaningful and accurate keyword frequency statistics, along with consistent cluster analysis outcomes.
2.2. Data Analysis and Visualization
In this study, the Bibliometrix package (version 3.1.4) [15] was employed to conduct statistical analyses on the gathered WBE research articles. Comparative assessments were carried out regarding publication years, quantities, countries, authors, journals, and keyword frequencies. Scimago Graphica, a visualization tool, was utilized to display the influence and collaboration among countries involved in the publications. VOSviewer (version 1.6.15) [16] was used to analyze the co-occurrence network of keywords in the WBE research field. CiteSpace (version 6.2.R7) [17] was used to analyze the keyword burst in the field of WBE, thereby vividly representing the comprehensive research orientation, hotspots, and frontier directions of WBE research at each historical stage. The flow chart of this bibliometric analysis is shown in Figure 1.
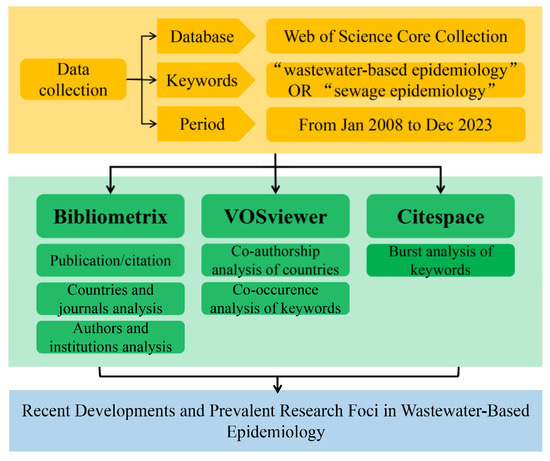
Figure 1.
Flow chart of the bibliometric analysis.
3. Results
3.1. Trend of Published Articles
The number of publications reflects the attention of researchers to research hotspots in this field and indicates the development degree and speed of research in related fields [10]. Between 2008 and 2023, the WOSCC database contains 990 WBE-related articles. Figure 2 illustrates the number and citation frequency of publications related to WBE research. Throughout this period, WBE research manifests an overall ascending trajectory. From 2008 to 2019, the number of published articles in the field of WBE research remains relatively modest, with a cumulative total of 168 papers, averaging 14 publications per annum. At this stage, the field of WBE research is in its nascent development. However, during the three-year timeframe from 2021 to 2023, the publication output in WBE research experienced explosive growth. A total of 736 papers were published, amassing 74.34% of the entire publication count, with an annual average of over 245 publications during this period, thus exhibiting a rapid expansion trend. This surge in publication volume since 2021 indicates a heightened focus on WBE research, as the cumulative annual publication count and citation frequency display a stable, upward progression. Consequently, this field has garnered considerable attention from the research community.
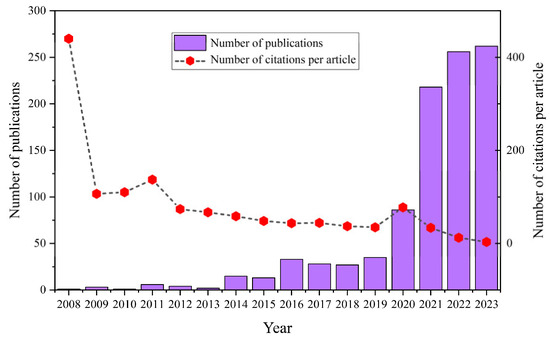
Figure 2.
The annual number of publications related to WBE during the period of 2008–2023.
3.2. Subject Distribution and Published Journals
The subject distribution data of the WOSCC database offers insights into the number and proportion of academic fields encompassed within this research engine, facilitating an understanding of each subject’s degree of activity in the global research landscape and scholars’ focus on specific fields [18]. Publications pertaining to WBE span across 55 disciplines, with the top 10 fields in terms of publication volume illustrated in Figure 3. Among these, the three disciplines with the largest output are Environmental Sciences, Engineering Environmental, and Water Resources, accounting for 42.67%, 12.48%, and 10.77%, respectively. Furthermore, WBE research also intersects with Public, Environmental & Occupational Health, Microbiology, Analytical Chemistry, Biochemical Research Methods, Virology, and Pharmacology & Pharmacy. WBE research holds the potential to furnish vital information for public health and environmental protection while enabling timely detection and response to potential health risks and outbreaks. This interdisciplinary domain fosters close collaboration with clinical medicine, pharmacy, statistics, and other fields to enhance the pertinence and efficacy of research endeavors.
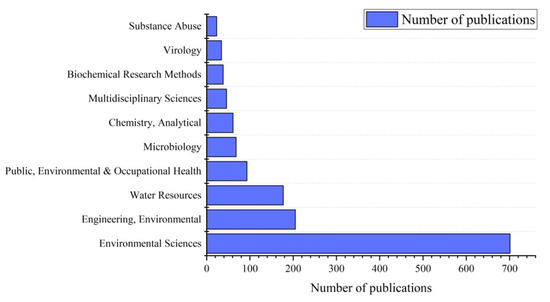
Figure 3.
The top 10 categories related to WBE research from 2008–2023.
Analyzing the number of published journals in a research field can help researchers accurately grasp the core journals in the research field [19]. Upon analysis of the sample data, the dispersion of articles in this field was found to encompass 166 journals. Figure 4 enumerates the top 10 journals in the WBE research field, collectively accounting for 58.38% of the global publication count. Among these top ten journals, Science of The Total Environment holds the highest number of articles (307), contributing to 31.01% of the total, while Water Research follows in second place as a primary source journal, with 86 published papers. It is noteworthy that Environment International published a comparatively smaller number of articles (27), representing only 2.73% of the global aggregate; however, its average citation frequency (48.78) ranks the highest among the top 10 journals. Articles appearing in highly-cited journals in the research field are extensively utilized by fellow scholars, signifying their academic authority and contribution to this field. Environment International’s impact factor is ranked third (IF2023 = 11.8). Although the Journal of Hazardous Materials contributed only 23 papers, constituting merely 2.32% of the total publications, its impact factor emerges as the highest at 13.6.
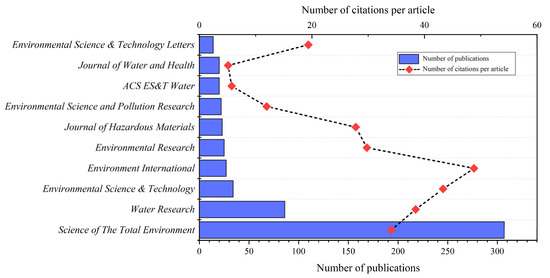
Figure 4.
The top 10 journals in the number of publications related to WBE during the period of 2008–2023.
3.3. Main Publishing Countries
Figure 5 delineates the top 10 countries contributing to the field of WBE research. Excluding China and Japan, the remaining eight countries among the top 10 contributors from 2008 to 2023 are primarily situated in European and North American regions, suggesting that WBE research is principally concentrated in developed countries and areas within Europe and North America. The USA demonstrates the most prominent contribution to this research field, with a total of 218 published articles, accounting for 22.02% of the aggregate article count, primarily due to its pioneering role in initiating WBE research. Subsequently, Australia (110 articles, 11.11%) and China (93 articles, 9.39%) emerge as the next leading contributors. The USA, displaying both a high article count and elevated citation frequency per article, is recognized as a country of vigorous development momentum in the WBE research field. Though Italy and Belgium contributed a comparatively modest number of publications, with 41 and 24 articles respectively, the high citation frequency per article denotes substantial influence from these countries in the WBE research sphere.
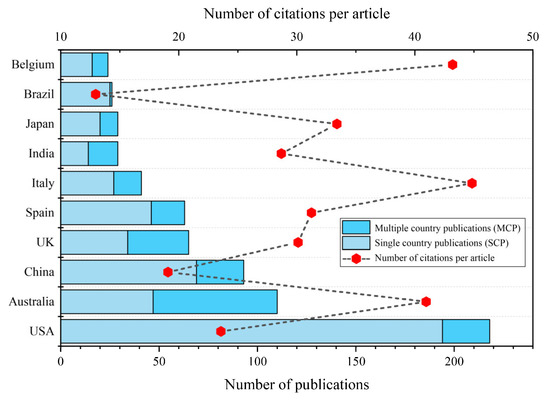
Figure 5.
The top 10 countries in the number of publications related to WBE during the period of 2008–2023.
Attributable to variations in the research foundations and scientific resources across different countries, distinctive characteristics of cooperative networks emerge at the national level. In the present investigation, it was discerned that 80 countries contributed to the publications in this field. VOSviewer was employed to analyze the visual representation of international scientific research collaborations in WBE-related research, while Scimago Graphica software facilitated the construction of international cooperation networks. The larger the node in the national collaboration network graph, the greater the number of published articles (with larger keyword nodes signifying a higher frequency of occurrence). The connections between nodes represent the robustness of cooperative relationships between nations, where thicker lines indicate closer collaboration. As illustrated in Figure 6, numerous countries partake in WBE research and exhibit a certain degree of collaboration, thereby forming a relatively stable cooperative network that encompasses three principal research clusters in America, Europe, and Asia. By fostering international cooperation, countries can collectively address challenges within the WBE research field, concurrently sharing resources and technologies to further stimulate the advancement of WBE investigations.
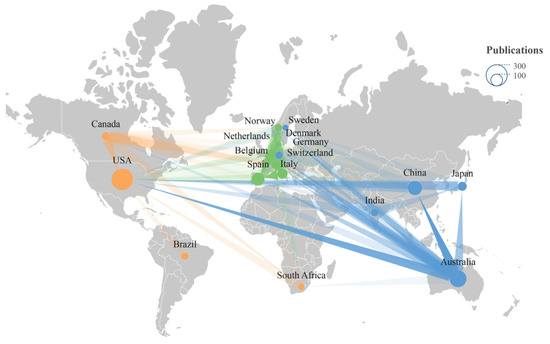
Figure 6.
Collaborative network of major countries for publications related to WBE during the period of 2008–2023.
3.4. Main Publishing Institutions and Authors
Assessing the research contributors of publishing institutions and authors enables a swift understanding of prevailing trends in the field. A total of 1499 institutions published WBE-related publications from 2008 to 2023. Table 1 enumerates the top 10 institutions in terms of publication volume in WBE research. With 118 publications, the University of Queensland stands as the preeminent institution in the field, holding an internationally leading position. The top three institutions, which consist of the University of Queensland, the University of Bath (51 papers, 5.15%), and the University of Antwerp (48 papers, 4.85%), have collectively published 217 articles. The seven remaining research entities collectively generated a total of 194 publications in this field. Evaluating the average citations per article, despite the relatively modest number of papers authored by Hokkaido University and the Norwegian Institute for Water Research (27 and 22, respectively), these two research institutions demonstrate considerable influence. Their crucial contributions have significantly impacted the evolution of WBE research and have garnered extensive recognition in the academic community.

Table 1.
The top 10 institutions in the number of publications related to WBE during the period of 2008–2023.
Globally, more than 5059 scholars have contributed to the field of WBE research. The foremost 10 authors are enumerated in Table 2, comprising five researchers from Australia, two from Italy, two from Belgium, and one from the UK. Authors hailing from the University of Queensland in Australia claim the top three positions based on publication count; notably, Mueller JF maintains the first rank, boasting 65 publications and exhibiting absolute dominance in total citation frequency (3603), thereby manifesting substantial advantage and influence in the WBE field. Thomas KV and Thai PK occupy the second and third places with 59 and 51 papers, respectively. Despite publishing a relatively fewer number of papers (30), Zuccato E from Istituto di Ricerche Farmacologiche Mario Negri in Italy possesses the highest average citation per article (60.63). It is noteworthy that Ettore Zuccato, along with his colleagues, pioneered the concept of WBE in 2001, exemplifying not only his considerable academic impact in the WBE research community, but also the quality of his published articles.

Table 2.
The top 10 authors in the number of publications related to WBE during the period of 2008–2023.
3.5. Highly Cited Papers
Pursuant to the citation frequency analysis of the literature, highly cited publications can embody the quality of the literature and its foundational status in the research field. The examination and analysis of the specific content of highly cited articles can further aid in refining research hotspots and directing the development trajectory of a discipline [20]. An analysis was conducted for the top ten cited WBE research articles from 2008 to 2023, as indexed in the WOSCC database (Table 3). Among these, eight publications focused on the utilization of WBE for SARS-CoV-2 surveillance, primarily addressing the early detection of epidemic onset, tracking the progress of the outbreak, and evaluating the extent of infection.

Table 3.
Higher cited publications related to WBE during the period of 2008–2023.
SARS-CoV-2 RNA can be identified in the stool samples of infected individuals. Upon entering the sewer system via feces, the virus is subsequently conveyed into wastewater, surviving for durations ranging from a few hours to several days. The specific timeframe may be influenced by environmental factors such as temperature, pH, and the presence of other biological particles in sewage. For instance, in conditions exhibiting lower temperatures and higher pH, the virus may exhibit increased stability in wastewater, prolonging its survival period [21]. Owing to the extended incubation period of SARS-CoV-2 in the human body, early incubation stages reveal low viral nucleic acid detection positivity rates, increasing the likelihood of false-negative results. Consequently, RNA from SARS-CoV-2’s genetic material can be discerned in sewage before the clinical confirmation of cases [22]. This finding suggests that WBE can function as an exceptionally sensitive early warning instrument. By performing quantitative analyses on viral RNA present in sewage samples, viral transmission can be detected among asymptomatic infected individuals, mild cases, and untested patients, thereby facilitating early warnings for virus outbreaks and informing the development of public health policies aimed at curbing viral spread. Ultimately, this approach contributes to mitigating the impact of pandemics on global health systems and economies.
Moreover, by continuously monitoring the viral concentration in sewage samples over a specified period, the transmission trend of the virus in a particular area can be estimated. Currently, researchers typically employ the transmission index (Rt) to characterize the transmission dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 and assess the efficacy of preventive and control measures. However, accurate measurement of Rt still largely depends on extensive RNA testing and epidemiological inquiries. Should testing fail to keep pace with the virus’s spread, the implementation of adequate containment measures may be hindered, potentially exacerbating outbreak dissemination. Nevertheless, the WBE methodology possesses certain advantages in monitoring and providing early warnings for viral transmission, particularly when virus detection capacity is limited and the incidence of infection remains low. Numerous studies have demonstrated that monitoring viral RNA in sewage can preemptively predict a rising trend in infection cases (typically around 3–7 days in advance), thereby serving an early warning function. For example, Wurtzer et al., through the 16 months of monitoring and analysis under the OBEPINE project, discovered a strong correlation between the WBE index and incidence rates, with growth trends in the latter possibly predicted, on average, by an advanced duration of 3 days [23]. This finding offers compelling evidence supporting the use of WBE to represent the dynamic shifts in COVID-19 transmission. It is influenced by various factors, including but not limited to population density, social activities, government response measures, and virus mutations. Some mutating virus strains may exhibit increased infectivity [24]. By sequencing and analyzing the viral genetic material within sewage samples, virus variants can be promptly detected, thereby assisting evaluations of vaccine effectiveness, diagnosis, and treatment, as well as the impact of variations on viral transmissibility. Fontenele et al. conducted a single nucleotide variation (SNV) analysis of SARS-CoV-2 sequence data in sewage and observed a greater number of SARS-CoV-2 lineages circulating in sewage compared to clinical sources [25]. This finding may facilitate assessments of the repercussions of variations on vaccine and diagnostic efficacy, in addition to the virus’s transmissibility.
Simultaneously, viral RNA detection data from sewage samples can serve as an essential supplementary indicator that, in conjunction with epidemiological models and demographic data, aids in predicting the size of the infected population in an entire community. A substantial body of research demonstrates a high correlation between viral RNA indices in sewage and other epidemiological data, such as new cases, hospital admissions, and infection rates. For instance, Kuhn et al. estimated the number of infected cases based on the concentration of SARS-CoV-2 in wastewater, achieving 81–92% accuracy when compared to reported cases [26]. Nonetheless, considerable uncertainty persists regarding individual fecal virus shedding rates and viral decay rates within sewage pipes, leading to significant fluctuations in SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid content detected in sewage across different regions. Furthermore, large sewage flow volumes and uncertain dilution ratios introduce unpredictable deviations in sample collection and detection accuracy, complicating the representation of an accurate viral load. Detection samples are affected by various factors, including environmental factors, sampling methods, and analytical techniques, necessitating enhancement of sewage detection sensitivity. Consequently, current detection methods for SARS-CoV-2 require improvement to elevate detection accuracy and sensitivity levels. The concentration and detection rate of SARS-CoV-2 in primary sludge surpass those in corresponding wastewater, and primary sludge monitoring may exhibit heightened sensitivity compared to wastewater [27]. Moreover, the precise relationship between virus concentration and the number of infected individuals warrants further investigation. Continuing method optimization and integration with other epidemiological research approaches will facilitate advancements in prediction accuracy.
3.6. Main Research Hotspots
3.6.1. Keyword Co-Occurrence Analysis
Keywords are highly refined and generalized in an article and often represent research hotspots in a certain field. Keyword co-occurrence analysis can reveal the research hotspots in the field of WBE research by studying the keywords with high frequency and important centrality in the literature and displaying them in the form of visual maps [28]. In this study, keywords were extracted from the sample data, cleaned, and consolidated, followed by the utilization of VOSviewer software for cluster analysis. Subsequently, 134 keywords with a frequency exceeding 10 were selected, resulting in the construction of the keyword co-occurrence network depicted in Figure 7. This network primarily forms three distinct clusters (Cluster I, Cluster II, and Cluster III).
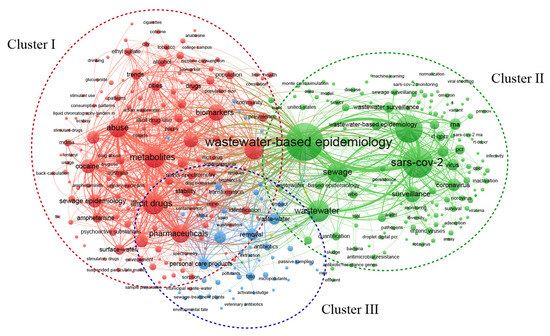
Figure 7.
Co-occurrence map of keywords.
Cluster I (red cluster): The primary keywords in this cluster include “illicit drugs”, “psychoactive substances”, “metabolites”, “abuse”, “consumption”, “biomarkers”, “cocaine”, “solid-phase extraction”, and “LC-MS/MS”. These keywords indicate that the predominant research hotspots in this cluster pertain to the epidemiology of illicit drugs and psychoactive substances. WBE was initially employed to monitor illicit drug intake and psychoactive substance usage. Zuccato et al. pioneered its application in 2005 by monitoring cocaine concentrations in wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) samples from Milan and Como, Italy, to investigate urban cocaine abuse [29]. Since then, this method has been adopted internationally to monitor various illicit drugs and psychoactive substances, encompassing cocaine, cannabis, morphine, heroin, methadone, codeine, amphetamine, methamphetamine, ketamine, and others. In addition to conventional drugs, some emerging designer drugs, such as methcathinone, synthetic cannabinoids, methylphenidate, tramadol, zolpidem, oxazepam, and oxycodone, also serve as subjects of sewage epidemiological investigations. Concurrently, WBE has facilitated inquiries into the consumption of tobacco, alcohol, and other drugs, providing novel insights difficult to obtain through traditional survey methods [30,31]. Compared to social epidemiological surveys (including crime statistics, medical records, drug production, and attack rates), WBE offers the advantage of yielding objective, continuous, and real-time data, while also reflecting public health information in smaller regions, such as communities. Consequently, numerous countries worldwide have conducted correlating studies to unveil the prevalence of psychoactive substances and illicit drugs in their respective regions. In 2010, the European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction established the Sewage Analysis CORe group-Europe (SCORE) to create a WBE monitoring network for illicit drug usage across Europe via standardized sewage sampling, preservation, and testing.
WBE, when applied to the monitoring of illicit drugs and psychoactive substances, encompasses various aspects such as analytical target selection, sample collection, and preservation, sample pretreatment and detection, and drug consumption estimation. Biomarkers (drug metabolites) constitute crucial components in WBE research, as they enter the sewage system alongside sewage sources like human excreta, and domestic and industrial wastewater. They reflect multiple facets of regional population information, including living habits, health statuses, and environmental exposure factors. The appropriate selection of drug metabolites should consider factors such as correlation, stability, specificity, representativeness, and detectability [32]. In sewage, drug metabolites may undergo degradation or transformation due to environmental conditions. As such, ensuring the stability of biomarkers during sampling, transportation, and storage is crucial in obtaining reliable experimental data. Owing to the presence of numerous impurities such as organic matter, particulate matter, and microorganisms in sewage samples, pretreatment methods (e.g., solid-phase extraction, and filter membrane concentration) are essential for optimizing the detection of drug metabolites. Considering the low concentration of specific drug metabolites present in sewage, detection sensitivity is crucial. Therefore, more sensitive and accurate detection methods or technologies, such as liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS), are required for the qualitative or quantitative analysis of drug metabolites, ensuring high detection efficiency and low detection limits. Drug consumption estimation is founded on the acquired drug metabolite concentration data, coupled with information regarding the number of individuals serviced by the WWTPs and sewage flow rates. This approach enables the calculation of drug usage within a corresponding area. However, various factors impact drug metabolite concentration data. Population structure differences and traditional habits across geographical regions, in addition to population movements, may pose challenges for population estimation, potentially resulting in errors in WBE population estimation. Consequently, identifying more suitable demographic methods is necessary to establish a foundation for reasonable drug consumption estimations.
Cluster II (green cluster): The principal keywords in this cluster include “COVID-19”, “SARS-CoV-2”, “surveillance”, “RT-qPCR”, “infection”, “pandemic”, and “enteric viruses”, among others. This cluster primarily investigates the WBE of viruses, with a particular emphasis on SARS-CoV-2. Compared to conventional clinical tests and diagnostic methods, sewage epidemiological surveillance presents numerous advantages, such as relatively convenient, low-cost sampling processes that do not rely on traditional case reporting. Detecting the viral load in sewage enables researchers to promptly identify the risk of virus transmission and infection, facilitating a faster and more accurate understanding of viral spread among the population. In addition to SARS-CoV-2, WBE has been successfully applied to monitor various viruses, including the Zika Virus [33], human adenovirus F41 [34], norovirus [35], arbovirus [36], and other viruses. The rapid development of modern molecular biology technology has led to the widespread adoption of polymerase chain reaction (PCR), enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), and high-throughput sequencing (NGS) in virus research, providing technical support for the application of WBE in virus detection. By employing gene sequencing technology, researchers can conduct genetic analyses of viruses in sewage samples, yielding crucial information for traceability research. Furthermore, viral gene analysis in sewage enables researchers to evaluate viral variations and establish a foundation for virus control strategies. This research approach can assist health authorities in evaluating vaccine strategy effectiveness and updating antiviral treatment regimens as needed. Currently, numerous countries and regions worldwide have undertaken WBE projects to monitor and predict viral spread, furnishing data support for public health policy development. Despite substantial advancements in the investigation of viruses within the domain of WBE, there remain challenges, including the enhancement of detection method accuracy and sensitivity, as well as the improvement of data interpretation and model predictions.
Cluster III (blue cluster): The primary keywords in this cluster include “pharmaceuticals”, “personal care products”, “antibiotics”, “liquid chromatography”, “transformation”, and “degradation”, signifying that this cluster primarily concentrates on the application of WBE to environmental pollutants. The implementation of WBE pertains to the monitoring, assessment, and early warning of pollutants. To date, WBE has successfully detected various environmental pollutants, such as pesticides [37], antibiotics [38], antibiotic resistance genes [39], hormones [40], and so on. By utilizing qualitative (e.g., liquid chromatography, gas chromatography) and quantitative analysis methods (e.g., mass spectrometry, RT-qPCR), researchers can monitor waterborne environmental pollutant distribution and concentration, collect real-time data, and track pollutant spatial distribution and temporal trends, thereby establishing a foundation for pollution early warning. This approach also aids in revealing the connection between environmental pollutant spatial distribution and temporal change trends and socio-economic activities. For instance, Zhang et al. monitored antibiotic content in sewage using WBE and compared their results with pre-2013 data, uncovering a positive correlation between consumption and socio-economic factors such as housing prices and population density [41]. Moreover, by monitoring environmental pollutants in sewage and identifying and tracking pollution sources, researchers can elucidate the long-term environmental impact of pollutants, the interaction between soil, water, and organisms, and accurately assess pollution status and risk levels [42]. Employing multidisciplinary methods such as toxicology and ecology, ecological risk assessment of environmental pollutants in sewage from a biological perspective can analyze the harm they pose to ecosystems and organisms. Furthermore, the findings of WBE research can then be leveraged to guide and optimize various sewage treatment technologies, enhance treatment outcomes, and mitigate the environmental burden of sewage discharge.
3.6.2. Burst Analysis
Keyword burst denotes a significant increase in keyword frequency over a brief period, indicating heightened attention to these keywords during that time. This phenomenon can showcase shifts in research hotspots across different periods and predict potential development trends and frontier research [43]. In this study, CiteSpace visualization software was utilized to identify bursts of keywords in the literature from 2008 to 2023, ultimately selecting a set of 15 primary burst keywords with a duration of over two years. As depicted in Figure 8, 15 burst keywords have surfaced throughout the past decade. Among these, “pharmaceuticals”, “abuse”, “illicit drugs”, and “cocaine” emerged before 2020 with substantial burst, suggesting that researchers primarily focused on drug epidemiology, particularly that of illicit drugs. Post-2020, keywords with high burst include “trends”, “population”, and “survival”. The outbreak of COVID-19 has promoted the extensive application of WBE globally. Researchers in various countries have utilized WBE methods to enhance surveillance, prevention, and control of virus transmission, as well as to provide support for governments in formulating targeted policies. WBE plays a critical role in the prevention and control of COVID-19, ranging from virus detection to the evaluation of SARS-CoV-2 vaccination effectiveness.
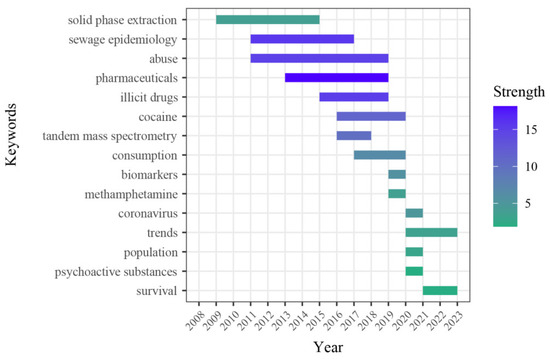
Figure 8.
Keywords with the strongest citation bursts.
4. Discussion
4.1. Emerging Analysis and Detection Techniques for Biomarkers
As an emerging tool for environmental and public health surveillance, WBE plays an important role in multiple application fields, such as illicit drug use surveillance, infectious disease surveillance, environmental pollutant assessment, etc. Despite substantial progress in biomarker monitoring, WBE still encounters numerous challenges and issues. Achieving precise and efficient separation and detection of biomarkers in actual sewage samples, marked by intricate components and diverse pollutants, continues to be a critical aspect. Currently, the predominant methodologies employed in WBE for gene detection include PCR and NGS technologies, etc., but PCR can only target a specific gene or several target genes, and it is difficult to detect a large number of gene sequences at the same time. Moreover, PCR may be interfered with by other substances derived from the sewage sample, resulting in false positive or false negative results [44]. NGS can determine the entire genome or multiple genomes at once and is suitable for the detection of multiple pathogens in complex samples. However, compared with PCR, NGS has a higher cost in data processing, analysis, and storage; a huge amount of data generated by NGS requires professional bioinformatics tools and software for processing and analysis. Additionally, NGS necessitates the utilization of high-caliber nucleic acid specimens. Consequently, sewer-derived samples may mandate the execution of sophisticated purification procedures to ensure optimal performance in subsequent analysis [45]. The aforementioned methodologies, viz. PCR and NGS, prove insufficient in satisfying contemporary demands for elevated sensitivity and specificity, augmented throughput, expeditious and uncomplicated sample processing, and enhanced reliability and accuracy in WBE detection. In recent years, advancements such as automatic sewage samplers, real-time online monitoring technology, microfluidic chip technology, and sensor network technology have made biomarker detection in practical scenarios faster and more convenient. An automated workflow based on a simplified approach, like the one developed by Banadaki et al., takes a mere 40 min from raw wastewater to purified RNA, which is significantly faster than traditional WBE methods. With a total analysis cost of USD 6.50 per sample/replicate, this approach considerably reduces assay complexity, and compared to manual methods, enhances detection accuracy [46]. Alvarez-Serna et al. proposed a label-free and portable field-effect transistor (FET)-based sensor capable of detecting the N and ORF1ab genes of the SARS-CoV-2 genome. Integrating a reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP) reaction as a low-cost molecular test with high specificity, this sensor offers a novel method for identifying the N and ORF1ab genes within the SARS-CoV-2 genome. The detection limit for the SARS-CoV-2 genome in actual wastewater samples was 0.31 × 10−3 ng/μL [47]. As science and technology continue to advance, more efficient and accurate automated detection techniques are anticipated to emerge, catering to the demands of sewage epidemiological research.
Secondly, given that biomarker concentrations in sewage are frequently low, detection methods necessitate high accuracy and sensitivity. Advances in analytical techniques and detection methodologies have contributed to the enhancement of biomarker sensitivity and specificity, especially with the advent of high-resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS) technologies, such as Fourier Transform Ion Cyclotron Resonance Mass Spectrometry (FT-ICR MS) and Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry (Orbitrap MS), which exhibit significant advantages in high-resolution and high-sensitivity detection. For instance, Campos-Manas et al. utilized ultra-high-pressure liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry to measure 11 human-specific biomarkers, including triazines, urea herbicides, insecticides, and organophosphorus substances, in municipal wastewater at trace levels (ng L−1). This approach demonstrates strong applicability for assessing human pesticide exposure [48]. Bade et al. utilized α-pyrrolidino-2-phenylacetophenone (α-D2PV) as a case study, and developed a high-throughput workflow based on a human liver S9 fraction in vitro metabolism assay. Through the utilization of liquid chromatography-high-resolution mass spectrometry, four metabolites were identified, thereby offering valuable insights into the intricate metabolic pathways of chemical compounds, enhancing detection capabilities, and potentially expanding applications in WBE [49].
The detection and analysis methods of biomarkers are evolving towards multi-dimensional and high-information approaches. The integration of multi-omics technologies (e.g., proteomics and metabolomics) can yield more comprehensive biomarker information. As an illustration, proteomics can elucidate organism adaptation strategies in response to environmental stress and unveil the effects of environmental pollution on ecosystems. Additionally, it can detect and identify pathogens (such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites) in sewage and explore potential protein biomarkers indicative of environmental pollution or health risks. Sanchez-Jimenez et al. were the first to apply proteomics to novel biomarkers in wastewater using high-resolution mass spectrometry [50]. With the ongoing development in fields like biological science and analytical chemistry, more advanced sewage epidemiological biomarker detection techniques are anticipated to become widespread. These techniques will not only enhance detection efficiency but also broaden the application scope of WBE.
4.2. Applications of Big Data and Artificial Intelligence
Big data and machine learning technology exhibit considerable potential for application in WBE, furnishing robust support for the analysis and interpretation of extensive multi-level biomarker data. WBE research involves vast quantities of environmental and biological data, encompassing spatio-temporal information, biomarker concentrations, and climatic factors. Data mining techniques can uncover meaningful patterns and trends from these large datasets, aiding in the elucidation of intricate relationships between biomarkers and environmental, biological, and social factors. Machine learning algorithms, including cluster analysis, principal component analysis, and time series, can be implemented to reduce data dimensionality and extract features, thereby assisting researchers in identifying key variables and rules [51]. For instance, Lai et al. proposed a time series-based machine learning strategy capable of extracting deeper knowledge and insights from time-structured WBE data, incorporating relevant temporal variables such as minimum ambient temperature and water temperature. This approach enhances the predictive ability for the number of COVID-19 cases per week [52].
Machine learning techniques (e.g., regression analysis, neural networks, random forests, support vector machines) offer advantages in constructing predictive models. In WBE research, monitoring and analyzing sewage volume bear significant relevance for assessing the distribution of pollutants, pathogens, and community structure. However, acquiring sewage volume data generally presents challenges. Utilizing machine learning models, researchers can establish a predictive model of sewage volume and analyze existing data to project future sewage volume trends. For instance, Kanneganti et al. employed a random forest model to train a series of variables (e.g., feces-related indicators, weather data, regional demographic data) for predicting sewer pipe flow rate, achieving an accuracy of 91.7% and significantly promoting WBE application [53]. Furthermore, machine learning methods can be used to assist risk assessment and enable researchers to comprehend the potential impacts of different pollution sources on the environment and human health. For example, Salem et al. developed a simulation optimization framework based on machine learning to discern the pollution characteristics of multiple simultaneous injection sources within a sewer system, which can be applied to the identification of sewer system pollution sources [54]. Zamarreno et al. developed a dynamic artificial neural network (DANN) to predict COVID-19 hospital admissions in Valladolid (Spain). The results of this assessment demonstrated a remarkable alignment with the data recorded and disclosed by the regional health authorities, exhibiting a compatibility of 95% and 93% for respective cases [55].
In conclusion, the application of big data and machine learning techniques in the realm of WBE is continually expanding and is now an essential tool for analyzing biomarker data and uncovering environmental and biological relationships. In the future, with the further cross-integration of disciplines such as bioinformatics, geographic information systems, data science, and environmental science, big data and machine learning will present both additional opportunities and challenges for WBE research.
4.3. Policy and Public Health Practice
Through the analysis of biomarker fluctuations in sewage, a more profound comprehension of shifts in human activities, disease transmission, and environmental stress can be attained, providing data-backed support for decision-making by policymakers and health officials. However, due to regional and systematic differences, directly comparing and generalizing sewage epidemiological data is challenging. Consequently, establishing common standards and methods is essential for enhancing data comparability and universality.
Concurrently, through the comprehensive integration of epidemiological data and clinical monitoring data from medical institutions into the analysis of drug metabolites and other biomarkers, a thorough understanding of drug dependence, abuse, and their impact on public health can be achieved, thereby laying the groundwork for intervention measures. Investigating the association between environmental pollutants and diseases can deepen our understanding of the relationships between environmental factors, living factors, and diseases, and support the examination of and intervention in environment-related diseases. Furthermore, it can identify disease prevalence trends, such as long-term fluctuations in chronic diseases like diabetes and cardiovascular diseases, assisting policymakers in adjusting public health strategies. Assessing intervention effectiveness can inform more targeted policy and public health planning within the health sector. Finally, strengthening cooperation with various departments (e.g., health bureaus and other government entities) and interdisciplinary participants (such as toxicologists) is required to facilitate the application and improvement of WBE monitoring.
5. Conclusions
In this study, the Bibliometrix toolkit in R programming language, in conjunction with VOSviewer and CiteSpace software, has been employed to analyze and visualize the WBE-related publications in the WOSCC database, spanning from 2008 to 2023. Through a comprehensive analysis encompassing publication trends, research contributors, research hotspots, and the progression and developmental trajectories of topics, the subsequent conclusions have been reached:
- (1)
- The emergence of the COVID-19 pandemic has significantly catalyzed the advancement of WBE. An expeditious augmentation in the number of research publications pertaining to WBE has been observed, particularly in the last three years. The USA has consistently exhibited a preeminent research capacity globally. The three institutions contributing the highest number of publications include the University of Queensland, the University of Bath, and the University of Antwerp. The top-tier journals in this field are Science of The Total Environment, Water Research, and Environmental Science & Technology. Notably, Mueller JF, Thomas KV, and Thai PK from the University of Queensland were major contributors to the realm of WBE research.
- (2)
- The analysis of research status and hotspots in the WBE field, based on highly co-cited literature, keyword co-occurrence, and burst keywords, reveals that the core focus of WBE research encompasses the surveillance of illicit drugs, psychoactive substances, and viruses. Future research should prioritize the development of emerging biomarker detection and analysis techniques to facilitate real-time updates and early warnings of sewage epidemiological data. Concurrently, integrating big data technology (e.g., artificial intelligence and cloud computing) could assist researchers in enhancing the efficiency, accuracy, and practicality of their investigations. Upon establishing unified research standards and methodologies, the integration of epidemiological data with clinical surveillance data from medical institutions may provide a more comprehensive foundation for public health research and decision-making.
- (3)
- Distinct literature databases exhibit varying coverage across disciplines and fields. In this study, the WOSCC database was solely employed, and the search terms were only for part of the subject (i.e., title, abstract, keywords, etc.), potentially overlooking contributions from certain fields and consequently yielding incomplete research outcomes. Future endeavors could encompass the utilization of databases such as PubMed, Scopus, Google Scholar, and Dimensions to broaden the search purview and furnish more comprehensive data substantiation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.S.; software, M.B.; writing—original draft preparation, F.Y., F.J. and W.J.; writing—review and editing, Z.L., C.F. and Y.L.; visualization, F.Y., J.L. and W.J.; supervision, Y.L. and Z.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This project was jointly supported by Compilation Service for the Implementation Plan of the Pilot Project on Regional Reclaimed Water Recycling Utilization in Lvliang City (CRAES2023-1156) and the Special Project for the Construction of the Chenzhou National Sustainable Development Agenda Innovation Demonstration Zone (2021 sfQ26).
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Daughton, C.G. Illicit Drugs in Municipal Sewage. Pharmaceuticals and Care Products in the Environment; ACS Symposium Series; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2001; pp. 348–364. [Google Scholar]
- Gagliano, E.; Biondi, D.; Roccaro, P. Wastewater-based epidemiology approach: The learning lessons from COVID-19 pandemic and the development of novel guidelines for future pandemics. Chemosphere 2023, 313, 137361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boogaerts, T.; Jurgelaitiene, L.; Dumitrascu, C.; Kasprzyk-Hordern, B.; Kannan, A.; Been, F.; Emke, E.; de Voogt, P.; Covaci, A.; van Nuijs, A.L. Application of wastewater-based epidemiology to investigate stimulant drug, alcohol and tobacco use in Lithuanian communities. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 777, 145914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, J.; Duan, L.; Wang, B.; Dong, Q.; Liu, Y.; Chen, C.; Huang, J.; Yu, G. In-sewer stability assessment of 140 pharmaceuticals, personal care products, pesticides and their metabolites: Implications for wastewater-based epidemiology biomarker screening. Environ. Int. 2024, 184, 108465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Mariño, I.; Rodil, R.; Barrio, I.; Cela, R.; Quintana, J.B. Wastewater-based epidemiology as a new tool for estimating population exposure to phthalate plasticizers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 3902–3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, W.; Angel, N.; Edson, J.; Bibby, K.; Bivins, A.; O’Brien, J.W.; Choi, P.M.; Kitajima, M.; Simpson, S.L.; Li, J. First confirmed detection of SARS-CoV-2 in untreated wastewater in Australia: A proof of concept for the wastewater surveillance of COVID-19 in the community. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huizer, M.; Ter Laak, T.L.; de Voogt, P.; van Wezel, A.P. Wastewater-based epidemiology for illicit drugs: A critical review on global data. Water Res. 2021, 207, 117789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, A.; Kang, S.; Wang, W.; Garg, A.; Maile-Moskowitz, A.; Vikesland, P.J. Nanobiotechnology enabled approaches for wastewater based epidemiology. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 143, 116400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sims, N.; Kasprzyk-Hordern, B. Future perspectives of wastewater-based epidemiology: Monitoring infectious disease spread and resistance to the community level. Environ. Int. 2020, 139, 105689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Yang, M.; Xie, D.; Ni, J.; Meng, J.; Wang, Q.; Gao, M.; Wu, C. Research trend analysis of composting based on Web of Science database. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2021, 28, 59528–59541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Yoshitake, K.; Watabe, S.; Asakawa, S. Environmental DNA study on aquatic ecosystem monitoring and management: Recent advances and prospects. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 323, 116310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Dai, T.; Qiao, Z.; Sun, P.; Hao, J.; Yang, Y. Application of artificial intelligence to wastewater treatment: A bibliometric analysis and systematic review of technology, economy, management, and wastewater reuse. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 133, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.J.; Guan, D.X.; Li, X.Y.; Hao, Y.L.; Teng, H.H.; Yang, J.F.; Xu, Y.Y.; Li, G. Analysis of studies on environmental measurements using diffusive gradients in thin-films (DGT) from 1994 to 2020. J. Soils Sediments 2022, 22, 1069–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Wei, Y.; Ji, N. Global trends of waste-to-energy (WtE) technologies in carbon neutral perspective: Bibliometric analysis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 270, 115913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aria, M.; Cuccurullo, C. bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. J. Informetr. 2017, 11, 959–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eck, N.; Waltman, L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C. CiteSpace II: Detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2006, 57, 359–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Rollins, J.; Yan, E. Web of Science use in published research and review papers 1997–2017: A selective, dynamic, cross-domain, content-based analysis. Scientometrics 2018, 115, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Xu, D.; Ding, C.; Lu, W.; Wang, M.; Yan, W.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y. Comparative analysis of domestic and foreign coal mine safety supervision modes based on knowledge map. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 89535–89547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, J.; Tan, L.; Yao, J.; Zheng, Y.; Shen, Q.; Tan, X. The impact of land use on stream macroinvertebrates: A bibliometric analysis for 2010–2021. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Q.; Liu, M.; Qi, F.; Gong, S.; Zhou, S.; Zhan, S.; Bao, L. Sensitivity of SARS-CoV-2 to different temperatures. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 3, 316–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Xu, X.; Zheng, X.; Ding, J.; Li, S.; Chui, H.K.; Wong, T.K.; Poon, L.L.; Zhang, T. Use of sewage surveillance for COVID-19 to guide public health response: A case study in Hong Kong. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 821, 153250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurtzer, S.; Waldman, P.; Levert, M.; Cluzel, N.; Almayrac, J.; Charpentier, C.; Masnada, S.; Gillon-Ritz, M.; Mouchel, J.; Maday, Y. SARS-CoV-2 genome quantification in wastewaters at regional and city scale allows precise monitoring of the whole outbreaks dynamics and variants spreading in the population. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 810, 152213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.H.; Wen, T.H. Assessing the impact of emergency measures in varied population density areas during a large dengue outbreak. Heliyon 2024, 10, E27931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontenele, R.S.; Kraberger, S.; Hadfield, J.; Driver, E.M.; Bowes, D.; Holland, L.A.; Faleye, T.O.; Adhikari, S.; Kumar, R.; Inchausti, R. High-throughput sequencing of SARS-CoV-2 in wastewater provides insights into circulating variants. Water Res. 2021, 205, 117710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, K.G.; Jarshaw, J.; Jeffries, E.; Adesigbin, K.; Maytubby, P.; Dundas, N.; Miller, A.C.; Rhodes, E.; Stevenson, B.; Vogel, J. Predicting COVID-19 cases in diverse population groups using SARS-CoV-2 wastewater monitoring across Oklahoma City. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 812, 151431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, K.E.; Loeb, S.K.; Wolfe, M.K.; Catoe, D.; Sinnott-Armstrong, N.; Kim, S.; Yamahara, K.M.; Sassoubre, L.M.; Mendoza Grijalva, L.M.; Roldan-Hernandez, L. SARS-CoV-2 RNA in wastewater settled solids is associated with COVID-19 cases in a large urban sewershed. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 488–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Feng, C. Mapping the knowledge domain of the evolution of emergy theory: A bibliometric approach. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 28, 43114–43142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuccato, E.; Chiabrando, C.; Castiglioni, S.; Calamari, D.; Bagnati, R.; Schiarea, S.; Fanelli, R. Cocaine in surface waters: A new evidence-based tool to monitor community drug abuse. Environ. Health 2005, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarei, S.; Salimi, Y.; Repo, E.; Daglioglu, N.; Safaei, Z.; Güzel, E.; Asadi, A. A global systematic review and meta-analysis on illicit drug consumption rate through wastewater-based epidemiology. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 36037–36051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, M.; Picó, Y. Wastewater-based epidemiology: Current status and future prospects. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2019, 9, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracia-Lor, E.; Castiglioni, S.; Bade, R.; Been, F.; Castrignanò, E.; Covaci, A.; González-Mariño, I.; Hapeshi, E.; Kasprzyk-Hordern, B.; Kinyua, J. Measuring biomarkers in wastewater as a new source of epidemiological information: Current state and future perspectives. Environ. Int. 2017, 99, 131–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Bibby, K. A Model-Based Framework to Assess the Feasibility of Monitoring Zika Virus with Wastewater-Based Epidemiology. ACS EST Water 2023, 3, 1071–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyne, M.I.; Allen, D.M.; Levickas, A.; Allingham, P.; Lock, J.; Fitzgerald, A.; McSparron, C.; Nejad, B.F.; McKinley, J.; Lee, A. Detection of human adenovirus F41 in wastewater and its relationship to clinical cases of acute hepatitis of unknown aetiology. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markt, R.; Stillebacher, F.; Nägele, F.; Kammerer, A.; Peer, N.; Payr, M.; Scheffknecht, C.; Dria, S.; Draxl-Weiskopf, S.; Mayr, M. Expanding the pathogen panel in wastewater epidemiology to influenza and norovirus. Viruses 2023, 15, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfe, M.K.; Paulos, A.H.; Zulli, A.; Duong, D.; Shelden, B.; White, B.J.; Boehm, A.B. Wastewater detection of emerging arbovirus infections: Case study of Dengue in the United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2023, 11, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousis, N.I.; Gracia-Lor, E.; Hernández, F.; Poretti, F.; Santos, M.M.; Zuccato, E.; Castiglioni, S. Wastewater-based epidemiology as a novel tool to evaluate human exposure to pesticides: Triazines and organophosphates as case studies. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 793, 148618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Wang, Z.; Huang, H.; Wang, T.; Zhou, Z.; Bai, Y.; Du, P.; Li, X. Estimating antibiotics use in major cities in China through wastewater-based epidemiology. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 826, 154116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javvadi, Y.; Mohan, S.V. Understanding the distribution of antibiotic resistance genes in an urban community using wastewater-based epidemiological approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 868, 161419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driver, E.M.; Gushgari, A.J.; Steele, J.C.; Bowes, D.A.; Halden, R.U. Assessing population-level stress through glucocorticoid hormone monitoring in wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 155961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Duan, L.; Wang, B.; Du, Y.; Cagnetta, G.; Huang, J.; Blaney, L.; Yu, G. Wastewater-based epidemiology in Beijing, China: Prevalence of antibiotic use in flu season and association of pharmaceuticals and personal care products with socioeconomic characteristics. Environ. Int. 2019, 125, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qodah, Z.; Dweiri, R.; Khader, M.; Al-Sabbagh, S.; Al-Shannag, M.; Qasrawi, S.; Al-Halawani, M. Processing and characterization of magnetic composites of activated carbon, fly ash, and beach sand as adsorbents for Cr (VI) removal. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2023, 7, 100333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Sun, Y.; Luo, Z.; Li, X.; Wen, Y.; Shi, Y.; Wu, X.; Huang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, C. Application and development of zero-valent iron (ZVI)-based materials for environmental remediation: A scientometric and visualization analysis. Environ. Res. 2023, 241, 117659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tozaki, T.; Ohnuma, A.; Iwai, S.; Kikuchi, M.; Ishige, T.; Kakoi, H.; Hirota, K.; Kusano, K.; Nagata, S. Robustness of digital PCR and real-time PCR in transgene detection for gene-doping control. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 7133–7139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Puchol, S.; Rusiñol, M.; Fernández-Cassi, X.; Timoneda, N.; Itarte, M.; Andrés, C.; Antón, A.; Abril, J.F.; Girones, R.; Bofill-Mas, S. Characterisation of the sewage virome: Comparison of NGS tools and occurrence of significant pathogens. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banadaki, M.D.; Torabi, S.; Strike, W.D.; Noble, A.; Keck, J.W.; Berry, S.M. Improving wastewater-based epidemiology performance through streamlined automation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Serna, B.E.; Ramírez-Chavarría, R.G.; Castillo-Villanueva, E.; Carrillo-Reyes, J.; Ramírez-Zamora, R.M.; Buitrón, G.; Alvarez-Icaza, L. Label-free and portable field-effect sensor for monitoring RT-LAMP products to detect SARS-CoV-2 in wastewater. Talanta 2023, 253, 124060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos-Mañas, M.; Fabregat-Safont, D.; Hernández, F.; de Rijke, E.; de Voogt, P.; van Wezel, A.; Bijlsma, L. Analytical research of pesticide biomarkers in wastewater with application to study spatial differences in human exposure. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bade, R.; Huchthausen, J.; Huber, C.; Dewapriya, P.; Tscharke, B.J.; Verhagen, R.; Puljevic, C.; Escher, B.I.; O’Brien, J.W. Improving Wastewater-Based Epidemiology for New Psychoactive Substance Surveillance by Combining a High-Throughput In Vitro Metabolism Assay and LC− HRMS Metabolite Identification. Water Res. 2024, 253, 121297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Jiménez, E.; Abian, J.; Ginebreda, A.; Barceló, D.; Carrascal, M. Shotgun proteomics to characterize wastewater proteins. MethodsX 2023, 11, 102403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashayeri, M.; Abbasabadi, N.; Heidarinejad, M.; Stephens, B. Predicting intraurban PM2. 5 concentrations using enhanced machine learning approaches and incorporating human activity patterns. Environ. Res. 2021, 196, 110423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, M.; Cao, Y.; Wulff, S.S.; Robinson, T.J.; McGuire, A.; Bisha, B. A time series based machine learning strategy for wastewater-based forecasting and nowcasting of COVID-19 dynamics. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 897, 165105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanneganti, D.; Reinersman, L.E.; Holm, R.H.; Smith, T. Estimating sewage flow rate in Jefferson County, Kentucky, using machine learning for wastewater-based epidemiology applications. Water Supply 2022, 22, 8434–8439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, A.K.; Abokifa, A.A. Machine Learning–Based Source Identification in Sewer Networks. J. Water Res. Plan. Man. 2023, 149, 04023034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamarreño, J.M.; Torres-Franco, A.F.; Gonçalves, J.; Muñoz, R.; Rodríguez, E.; Eiros, J.M.; García-Encina, P. Wastewater-based epidemiology for COVID-19 using dynamic artificial neural networks. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 917, 170367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).