Abstract
Groundwater-dependent cultivation is imperative to meet the ever-increasing food demands in Egypt. To explore the Moghra aquifer’s potential, where a large-scale rural community is being established, a finite element groundwater flow (i.e., FEFLOW®) model was invoked. The developed model was calibrated against the observed water levels. GRACE-based groundwater storage was incorporated into the tuning procedure of the developed model. Eight abstraction rates from 1000 wells, changing from 800 to 1500 m3/day/well, were simulated for a 100-year test period. The maximum resulting drawdown values, respectively, ranged from 59 to 112 m equating to about 20–40% of the aquifer’s saturated thickness. The implications of the climate change from gradual sea level rise and an increase in crop consumptive water use were investigated. Extending seawater invasion into the aquifer caused a slight increase in the piezometric levels within a narrow strip along the seaside. Applying a chronologically increasing withdrawal rate to meet the projected increment in crop water requirements raised the maximum resulting drawdown by about 7.5%. The sustainable exploitation regime was defined as a time-increasing withdrawal rate adequate to reclaim 85,715 acres (34,688 ha). The recommended development scheme is compatible with the withdrawal rationing rule, aiming to maintain that the resulting drawdown does not exceed one meter a year.
1. Introduction
Globally, water and food shortage problems have aggravated during the last few decades. Intensifying groundwater withdrawal has taken place to satisfy freshwater demands for domestic purposes [1]. The malpractice of uncontrolled pumping is further exacerbated to meet increasing agricultural water requirements [2]. Even fossil (non-renewable) aquifers are highly exploited, particularly in semiarid and arid countries [3]. Overdraft resulting in aquifer depletion is an emerging issue owing to the development of such non-renewable aquifers [4]. Thus, it is widely urged to rationalize pumping and judiciously use non-renewable aquifers [5]. However, achieving sustainable management of such resources is a key challenge, particularly in regions plagued with water scarcity. Egypt is within an arid climate region featuring extinct precipitation, high temperatures, and elevated humidity, which leads to an increased rate of evapotranspiration [6,7]. Due to climate change (CC) and the damming construction at the Nile River upstream, Egypt would be unable to draw as much as its water quota [8,9]. Accordingly, Egypt shall witness an imminent challenge for the agriculture sector to cater to the demands of the exponentially growing human population [10]. Rural development is therefore crucial in Egypt to meet the growing food needs [11,12]. Accordingly, the government has initiated an ambitious rural development strategy through a mega groundwater-dependent cultivation project [13].
A mega reclamation project is now being implemented in Egypt under the framework of moving towards horizontal expansion in barren lands distanced from the Nile River [14]. Thus, desert fossil aquifers have become the sole source of freshwater [11,15]. Currently, groundwater withdrawal is well underway in the newly cultivated areas, mainly for irrigation purposes [16]. The pumping of groundwater is projected to increase year in and year out [17]. A concentrated number of wells that are not spatially distributed over wide areas, are being established [18]. Mismanagement or lack of pumping management, with its consequent overconsumption of the underground reserve, restricts groundwater availability. It, therefore, endangers the exploited aquifer through depletion and water quality degradation. Additionally, the severe decline in groundwater level might result in adverse consequences, including land subsidence, diminished surface vegetation, etc. [19]. Deficient replenishment of arid-region aquifer systems poses additional intricacy in their management. Attainment of a sustainable yield from an aquifer is, therefore, a major constraint for groundwater-beholden agribusiness [20]. Thus, a management approach should be set to maintain the aquifer storage in terms of quantity and quality aspects.
Groundwater flow models are increasingly recognized as a supportive utility for a sustainable groundwater management approach [21]. Groundwater models provide an approximate solution for the partial differential equation that visualizes water flow through a porous medium [22]. Modelling is, therefore, an essential tool for assessing an aquifer’s potentiality and exemplifying its stages under pumping stresses [23]. Several numerical simulation codes have been programmed based on finite difference and finite element approaches [24]. MODFLOW is the most commonly used finite difference-based code used in the field of groundwater modelling. The Finite Element subsurface FLOW (FEFLOW®) is a relatively new 3D groundwater simulation code [25]. However, it has become one of the simulators widely utilized for groundwater flow and transport problems. FEFLOW has a substantial geometrizing skill over alternative finite-difference models (e.g., MODFLOW) [26]. Many studies have employed the FEFLOW for assessing trade-offs among potential water pumping policies and accounting for the drivers that have resulted in aquifer depletion and deteriorating water quality [27,28,29,30].
The recently drilled wells into the Moghra aquifer (Egypt) may be a clear-cut cause for water table drawdown and quality degradation. Thus, groundwater managers urged defining the sustainable management scheme of the aquifer. Herein, a hydrogeological investigation of the subsurface Moghra aquifer system is provided through the robust development of a 3D conceptual numerical model. The groundwater flow mechanism of the Moghra aquifer and its behaviour under stressful pumping conditions were thoroughly simulated utilizing the FEFLOW® numerical model. The main goal is to provide an exploitation approach that sustains groundwater in the target development area. CC, the resulting SLR, and increases in crop water requirements were considered. The developed hydrologic model could provide additive support for decision-makers to maintain the sustainability of ongoing agribusiness activities.
2. Study Area
The availability of a huge amount of stored water, convenient climatic conditions, and favourable soil texture render the Moghra desert one of the most promising reclamation plots in Egypt [14,15]. Accordingly, the Moghra desert was incorporated into a mega-rural development project. Previously, the study area of the Moghra desert was almost barren, with no land cover feature that may hinder such proposed large-scale cultivation activities [14]. It is located within the Marmarican Homoclinal plateau, which covers the uninhabited desert region between the Mediterranean Sea and the Qattara depression. It is in an arid climate region featuring long, hot summers and short, warm, rainless winters. It occupies a non-perennial area of 150,000 acres (60,702 ha), extending between latitude 28°11′ and 31°38′ N and between longitude 28°14′ and 31°22′ E, as shown in Figure 1. It includes the proposed cultivation swaths suggested within the national strategic plan, where the fossil groundwater reserves would be the main water source. The wells field is located 75 km away from the Mediterranean shoreline and away from the coastal area that is highly susceptible to seawater intrusion [31]. It includes two conspicuous features, namely, the Qattara depression to the west and the Moghra swamp (locally called Moghra Lake), which is located at 38 m below the mean sea level (MSL), as shown in Figure 1. Recently, the region has been subject to significant land use changes since 2015, when intense agribusiness activities of the national rural development project were initiated. The cultivation project is well underway in the area. As deduced by the analysis of Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) satellite mission-derived groundwater storage (GWS), the GWS within the development area is currently overexploited, a fact that bears adverse impacts on the whole aquifer extent [32]. The Moghra aquifer is the main water-bearing formation, covering the majority of the study area [33]. The Moghra aquifer occupies a surface area of approximately 5 million hectares (ha), stretching between the Qattara depression to the west and the Nile River to the east and between the El-Fayoum depression to the south and the Mediterranean Sea to the north [34].
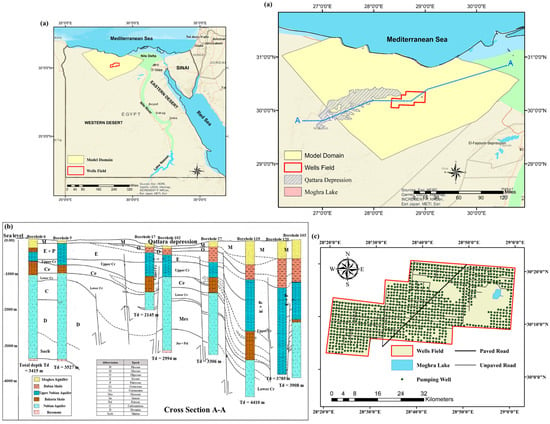
Figure 1.
(a) Location and main features of the study area, (b) geological cross-section of the Moghra aquifer (adapted with permission from Ref. [35]. 2024, Elsevier), and (c) spatial distribution of the production wells within the development area.
The Moghra Formation is a well-identified geological unit composed of sand and sandstone that belongs to the Lower Miocene epoch [36]. The deposition is intercalated by clay and siltstone that increase in the northward direction [37]. The depth of the aquifer ranges from 0 to 500 m, underlain by Oligocene Dabaa shale and Eocene Baharia shale, as shown in Figure 1b [34]. The aquifer is almost phreatic, but it seems confined within the narrow strip adjacent to the Nile delta aquifer [38]. Paleo (fossil) groundwater constitutes the main bulk of the aquifer storage [17]. However, the aquifer may be recharged by lateral seepage from the adjacent Nile Delta aquifer (Pleistocene formation) and the Nile River in the east [39]. The groundwater level varies from about −50 m at the Qattara depression in the west to −10 m in the eastern portions close to the Nile Delta. The main groundwater flow is from the north and northeast towards the Qattara depression in the southwest [36].
An area of 142,716 ha (about 352,659 acres) to the east of the Qattara depression was dedicated as a wells field within the reclamation project, as shown in Figure 1a. Installing the production wells was initiated by the end of 2015 with an ambitious plan to cultivate 135,000 acres (about 54,633 ha) [39]. Pumping and replacement experiments conducted on some existing pumping and test wells within the development area indicated high potentiality in terms of groundwater storage and productivity [37]. Moderate conductivity in a range between 5 and 25 m/d along with high storativity in a range between 0.1 and 0.001 were reported [40]. The transmissivity values range between 550 and 3500 m2/d [31].
3. Conceptual Model Development
The conceptual model is the digital 3D hydro-geologic representation of the physical groundwater system that is organized in a computerized format. FEFLOW (version 7.5) numerical software is adopted for model compilation and development. FEFLOW is favourable for aquifers with complex geological structures [41]. FEFLOW facilitates local mesh refinements along the model domain borders; hence, the boundary conditions (BCs) are precisely defined. Further, the ability of mesh refinements within the area of interest (e.g., the wells fields) helps to avoid the creation of excessive element numbers [42]. Herein, the conceptual model assumes that the aquifer system comprises an unconfined, one-layered formation. A hydraulic connection with the underlying Nubian Sandstone Aquifer (NSA) through an aquitard was suggested [17]. However, the vertical leakage remains poorly defined. The exchange is hereby negligible due to a lack of precise data to quantify water exchange by the interlayer vertical flow.
3.1. Digital Hydro-Geologic Framework Model
To describe the modelled system geometry, ArcGIS was used to prepare the input files in a format accepted by FEFLOW. ArcGIS is vital to ensure all input parameters are properly projected into Zone 35 N of the Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) coordinate system. Figure 1 shows the map that denotes the computational domain and embedded stress area (i.e., the wells field). The modelled system covers a total area of about 6 M ha, and it is 445 km in length and 224 km wide at its longest and widest parts, respectively, as shown in Figure 1. The location of the installed and proposed pumping wells was retrieved from the Egyptian Countryside Development Company (ECDC’s website at http://elreefelmasry.com; accessed on 1 May 2023). During the first stage of the reclamation project, from 2016 to 2019, 450 wells were drilled [17]. As a development expansion, 550 wells are proposed to be added [43]. Worth mentioning is that the wells field was found within the most favourable areas for such a cultivation project according to environmental and economic criteria [14].
3.2. Hydro-Geologic Boundary Conditions
The accurate denotation of hydrogeologic conditions along the outer boundaries of the conceptual model area is essential. The BCs control fluid flows into or out of the modelled system during steady-state and time-dependent (transient state) simulations [44]. All boundaries were selected far enough from the effect of pumping wells to be regarded as constant head boundaries, as shown in Figure 2. Along the outer border of the modelled area, the first kind (Dirichlet) BC that specifies a time-constant or time-varying head value is applied. The northern and northeastern BCs were chosen to be natural boundaries (i.e., water bodies). The Mediterranean Sea completely controls the head along the northern boundary. The water level of 0.0 m was initially assigned as the head value for northern BC. A wide main canal, locally called the “El-Nubariya” canal, appears on the right side of the studied area and extends for 127 km in length. It starts as a tributary of the “El-Rayah El-Beheiry” at the “Pollin” barrage area and cuts through the sandy soil, reaching the Mediterranean Sea. Its water levels are controlled by a few hydraulic structures (e.g., regulators) and temporally change according to the releasing discharges, with an average water level of 9.03 m at its mouth [45]. Accordingly, it acts as an influent stream and is considered a source for groundwater recharge. Dirichlet BC of head linearly change from 0.0 to 9.03 m was assumed along the line striking at almost N-E direction, as shown in Figure 2. Along other borders, no natural BC or fault (water divide) exists close to the boundary. Instead, head contour lines that represent the aquifer’s water levels before initializing the development project were used [33]. The head values at each intersection of the model borders with the contour lines were assigned. Then, the interactive linear 1D interpolation tool was used to interpolate hydraulic head values along the BCs, as shown in Figure 2. Pumping wells were set as nodal BCs (i.e., the fourth kind of BC) within the development area, based on the wells map that depicts the original locations of pumping wells. Several pumping rates were assigned through a linked attribute table containing the pumping rate, radius, and screen’s top and bottom elevation of each well. The well’s diameter (outer/inner) was 420/280 mm (16.5/11″). The penetration depth reaches a maximum of 140 m into the Moghra geological formation. The screen depth was an average of 30 m.
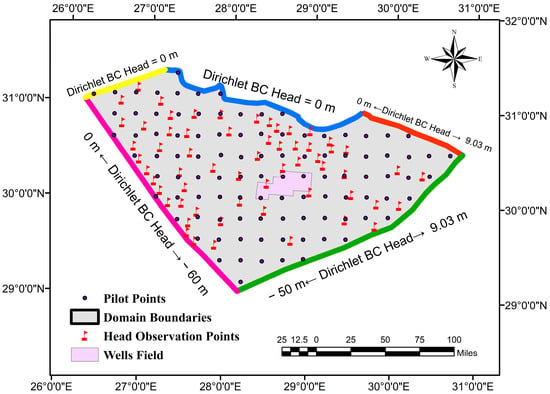
Figure 2.
Applied boundary conditions for the modelled domain and distribution of observation heads and pilot points to define the aquifer’s anisotropic conductivities.
Episodic recharge that may result from infrequent, low-intensity precipitation events in such arid climates was neglected [46,47]. Additionally, the water table throughout the aquifer extent is below the extinction depth of 0.5 m to include evaporation [48]. Thus, no evaporation of groundwater from such bare, sandy soil occurs.
3.3. Domain Discretization
Obtaining a proper spatial discretization of the model domain into well-shaped prisms that have no distorted elements reduces simulation difficulties and the risk of instabilities [42,49]. So much attention was paid to discretizing the finite element mesh of the computational model domain. The available element types allow the selection of either quadrilateral or triangular elements, where the fluid flow is calculated over each element node [41]. The triangulation algorithm was selected to discretize the model domain into 2D-triangle meshes. This mesh generation algorithm is favourable for such a complex model domain, allowing a minimum angle to be determined for all accommodated complex configurations of finite elements [29]. Local mesh refinements with a maximum element size along the domain margins and within the area of production wells were carried out. Mesh smoothing was typically applied to generate better mesh quality. “The denser the mesh, the better the numerical accuracy, and the higher the computational effort” [41]. Satisfactory element numbers and geometrical criteria optimized with computational time have been obtained after many trials. Figure 3 depicts the super-element mesh that represents the basic structure of the model domain. The mesh area averaged 4.56 km2, but with element concentration and refinements along the domain borders and throughout the wells field, as shown in Figure 3. The mesh configuration led to 13,064 elements and 7004 nodes on each slice (surface). Then, this mesh has been expanded in depth according to the lithology information, resulting in six-node finite elements.
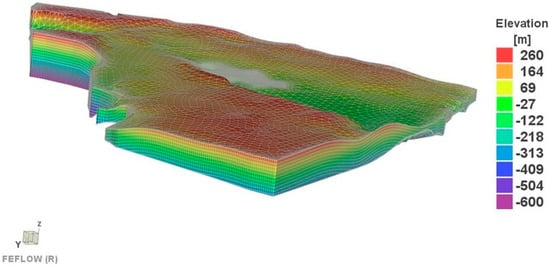
Figure 3.
Configured unstructured meshes along with a 3D view of the constructed groundwater flow model (depth is scaled up by 30 times).
3.4. Subsurface Stratigraphy
The conceptualized hydrogeological system has a simplistic physiographic feature. It is vertically composed of one main Miocene formation resting on Oligocene basaltic sheets that create thick impervious base strata, as shown in Figure 1b [50]. The topography of the model domain was retrieved using the Digital Elevation Model (DEM) processed from the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) data. The ground surface elevation within the model domain ranges from −111 m below MSL to 269 m above MSL, as shown in Figure 3. Two data sources were employed to locate the depth down to the impervious shale base and construct the geological stratification of the modelled area: (1) fifty-four groundwater exploration wells were excavated by the Egyptian Ministry of Water Resources and Irrigation (MWRI) to locate groundwater supplies in the Western Desert of Egypt [51], and (2) forty-two deep boreholes were drilled by the national oil companies to explore for fossil fuels in the Western Desert [52]. The subsurface lithologic elevation information of the wells was utilized in combination with surface geologic data for the expansion of the modelled grid into three dimensions (3D). Akima’s bivariate data regionalization method, along with the linear interpolation technique, was applied to assigning the elevation to a group of adjacent nodes. The aquifer’s total depth ranges from 302 to 824 m. The aquifer was then discretized into a few sublayers of varied depths with an average of 50 m. A 3D view of the constructed model domain, composed of 12 slices and 11 layers, is shown in Figure 3. A total of 143,704 elements and 84,048 nodes, which cover an area of about 5.9 × 104 km2 and a volume of 2.4 × 104 km3, were created. The flexible, unstructured discretization and local grid refinements appropriately fulfil the irregular geometry and topography of the model domain without nesting. Figure A1 in Appendix A depicts the super-element mesh that represents the basic structure of the model domain.
3.5. Hydrogeological and Pumping Data
Following the 3D mesh expansion, the properties of the depositing formation and pumping conditions were set up. The development progress in the Moghra region has been divided into three successive stages. The ECDC is technically and administratively supervising the project [43]. The first stage was initiated in early 2016 by drilling 450 pumping wells; each well is about 1 km away from the others. According to the wells’ pumping test analysis, the clear separation distance between the adjacent wells is sufficient to prevent pumping interference. The pre-development static water levels within the installed wells field ranged from −35 to −49 m, and the depth down to the water level was about 55 m. A drip irrigation system, as a high-efficiency distribution technique, is adopted, and the average water duty is 14 m3/acre/day (≈34.6 m3/hectare/day). The developed lands in the first stage were distributed to small investors and young people [43]. Further, 550 wells are being established during the following phases, as shown in Figure 1c. The groundwater salinity (as measured by TDS measurements) reaches up to 8000 mg/L, rating it as brackish water. Thus, only salt-tolerant crops such as canola, barley, quinoa, olive, and jojoba are cultivated in the project area. Through a field survey report with the investors and farmers in the study area, a close picture of overall groundwater pumping was obtained. The pumping pattern for each well was difficult to retrieve due to irregular monitoring frequencies of pumped water. The pumping hydrograph shows a seasonal pattern that peaks in summers while troughs occur in winters. Solar energy, as a renewable energy resource, is used to pump water. The sunshine limits the well’s daily operation time to eight hours and restricts the maximum pumping rate to 120 m3/h.
The hydraulic parameters were compiled from diverse literature, field surveys, and recently executed pumping and recovery analysis tests. A wide range of hydrogeological parameters for the extended Moghra aquifer were reported in the literature [13]. In general, the values of hydraulic parameters are higher in the central portion of the model domain, where the wells field is. The horizontal hydraulic conductivity (Kx) of the entire Moghra aquifer ranges between 0.2 and 100 m/d. The transmissivity values vary from 760 m2/d to 7600 m2/d. The vertical conductivity (Kz) was found to be 10% of the horizontal conductivity (Kx). In such an unconfined aquifer, the specific yield “Sy” is used to represent the aquifer’s storativity (S). Ten pumping tests that have been conducted in the Moghra aquifer demonstrated a relatively narrow range of specific storage (Ss) values varying from 5 × 10−4 to 1 × 10−4 m−1 with the majority ranging around 13 × 10−5 m−1 [37]. While the specific yield (Sy) varied from 0.005 to 0.13 [37]. The average storativity is about 0.15. The spatial distribution and the actual values of the initially assigned parameters were reviewed during the calibration process.
4. Numerical Model Set-Up
A saturated stratum, where Darcy’s Law is applicable, was configured. By default, the whole model domain was initially kept as unconstrained heads. The upper slice was defined as the free surface of a movable slice. The simulation was initiated in a steady state and then run under transient conditions.
4.1. Steady-State Simulation
Accurate simulation of a flow problem through an aquifer requires achieving a reliable steady state. Up until late 2015, before initializing the rural development project, the Moghra aquifer was almost untapped. Water levels within the aquifer system were near equilibrium, and the effect of wide-distributed private tube wells was negligible.
4.1.1. Model Calibration
The calibration is imperative to ensure a reliable simulation result by adjusting the input hydrogeological parameters [53]. The steady-state calibration was executed as a fully implicit simulation in which the pre-development water heads (by the year 2015) were used as a target condition. The system is regarded as steady when the overall balance for the entire domain is achieved. Due to the importance of the conductivity and the model’s high sensitivity to its alteration, anisotropic conductivity was adopted, in which the conductivity is calibrated along the X, Y, and Z axes. Given their swiftness and ease, non-linear parameter estimation techniques (PEST) are now commonly used for the proper identification of adjustment parameters. FePEST® is the graphical user interface for the development of the FEFLOW model with the PEST utilities. In FePEST, two spatial characterization techniques (i.e., pilot points and constant zones) are used to represent heterogeneities of hydraulic properties within the modelled hydrogeological basin [26]. The pilot points approach was applied in this study as it provides an improved heterogeneity representation of the system. A uniform distribution of 101 pilot points was generated throughout the model domain, as shown in Figure 2. Exaggeration in the number of pilot points would require extensive modelling times and could result in over-parameterization and large variations in the parameter values over small distances [26]. Herein, the Moghra model was calibrated by adjusting conductivity values such that simulated groundwater tables matched the observed hydraulic heads. Kx was bounded between 0.1 and 200 m/day (minimum and maximum limits), according to prior information given in the literature. Ky and Kz values were tied to changes in Kx by applying an initial relationship: Kx = Ky = 10 Kz. The calibration fit was assumed when a divergence of less than 1 m (about 10% of the difference between the maximum and minimum water levels) was achieved between the computed and observed heads.
The model’s results were assessed by comparing simulated heads against observed heads at 60 points scattered throughout the model domain, as shown in Figure 2. The observed heads ranged from 0 to −80 m. The model demonstrated a normalized root mean square error (NRMSE) of 1.8% (1.6 m) and a correlation factor (r) of 0.9973. Figure 4 shows a scatter plot depicting the comparison conducted between the monitored water levels and the simulated results. The value of the obtained root mean square error (RMSE) was 1.94 m. The conductivities were largely consistent with values reported in the literature, varying between a maximum of 2.4 × 10−3 m/s and a minimum of 1.2 × 10−6 m/s. Model simulations thereby replicated flow patterns in terms of hydraulic gradients and flow directions. The estimated hydraulic head throughout the model domain under the steady-state condition is shown in Figure 5. Using the particle tracking technique, streamlines of regional groundwater flow were visualized, as shown in Figure A2 in Appendix A. The flow’s main direction is from the north and northeast towards the south and then radially south-westward.
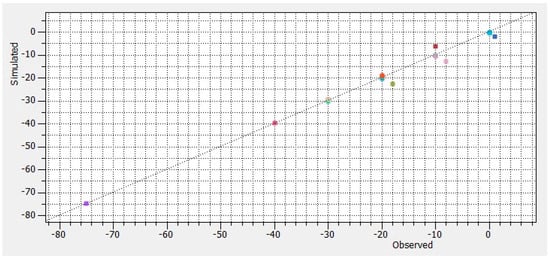
Figure 4.
Comparison between observed and simulated water levels for steady-state calibration.
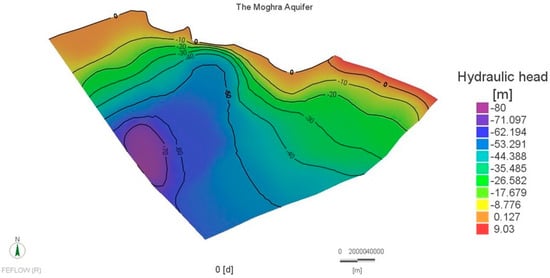
Figure 5.
Steady state simulated hydraulic heads for the year 2015 over the modelled domain.
4.1.2. Model Sensitivity
It is essential to analyse the uncertainty and sensitivity related to the input hydrologic parameters. The sensitivity analysis identifies uncertainties in input parameters for the model. Additionally, this analysis addresses an overall understanding of the modelled system and enhances the calibration procedures [54]. In this context, FePEST, through the “SENSAN” utility, enables estimating sensitivities for a set of input parameters. The model’s sensitivity was examined by multiplying calibrated conductivities throughout the model’s interior nodes by factors of 3.0, 2.5, 2.0, 1.5, 1.2, 0.8, 0.4, and 0.2.
Table 1 summarizes the sensitivity analysis to changes in K of the steady-state model. The model is reasonably sensitive to alterations in hydraulic conductivity, referring to its importance in model adjustment. A change of 20% in conductivity values resulted in an average sensitivity value of 0.22. Applying a constant change factor for both longitudinal and transverse conductivities throughout the model domain maintained the general groundwater flow direction. But a high-water budget imbalance was indicated when applying higher and lower conductivity values.

Table 1.
Percentage of groundwater head variations versus the changes in hydraulic conductivity.
4.2. Time-Dependent Simulation
4.2.1. Transient Calibration Using Pumping Test Data
Adjusting the input properties under transient state conditions was performed by employing data from continuous pumping experiments conducted on 39 recently installed production wells [37]. The pumping analysis test is transient data commonly utilized for calibration of the groundwater flow model in cases of insufficient temporal variation in pumping records and water level [55]. The storativity was adjusted to fit the observed drawdown in response to pumping. As shown in Figure 6, the computed drawdown matches well with those observed during the pumping tests.
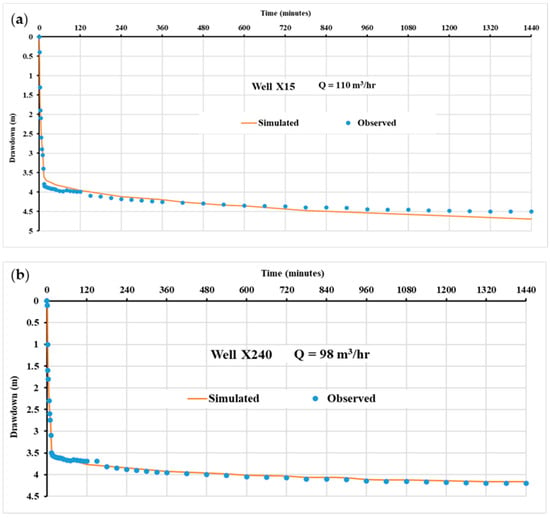
Figure 6.
Transient calibration using (a) 24 h pumping test data of Well X15 @ (longitude 28.48° and latitude 30.12°) and (b) 48 h pumping test data of Well X136 @ (longitude 28.56° and latitude 30.27°).
4.2.2. Transient Verification Using GRACE-Retrieved Data
Motivated by the observed capacity of the GRACE mission for tracking changes in GWS, this study explores the use of GRACE-derived GWS changes for the transient verification of the developed model [56]. GRACE-based GWS alterations were incorporated in the tuning procedure of groundwater flow models to overcome insufficient in situ measurements [57,58]. GRACE was also employed to estimate groundwater storage coefficients, including the storativity or specific yield (Sy), as appropriate [59,60]. The time series that represents the change in terrestrial water storage (ΔTWS) was extracted from the recently released gridded GRACE dataset provided by the three processing centres (i.e., GRACE’s science data centres) [32]. This dataset consists of a temporal monthly TWS anomaly, a mass deviation from the baseline, which is expressed in terms of equivalent water height (EWH) and posted on a 1° grid resolution (PODAAC website at https://grace.jpl.nasa.gov/data/get-data/monthly-mass-grids-land; accessed on 1 March 2023). Within such a semiarid area with no perennial surface waters, groundwater, and soil moisture (SM) account for all inferred alterations in the TWS. Therefore, ΔGWS was estimated by subtracting the SM’s contribution from GRACE-derived TWS [61]. The SM was estimated based on the outputs of the land surface model (GLDAS-NOAH) [62]. During the verification period (2016–2021), the water table had undergone an average decline of 0.96 m within the wells field. Minor alterations in groundwater tables were observed in the rest of the model domain.
The temporal pattern of GRACE-inferred GWS has been incorporated as an additional regularization dataset for verification of the developed model. The FEFLOW software allows the control of the simulation time via an integration scheme [41], while the simulation results can be depicted according to the recorded output time steps. An automatic time control scheme using the Adams-Bashforth/backward trapezoid (AB/TR) predictor-corrector scheme was adopted [30]. Using the “Period Budget” utility, the developed model can capture the inflows and outflows quantity during a simulation period, and thereby the corresponding storage loss/gain is estimated. The simulated annual mean storage anomaly from 2016 to 2021 was obtained as 16.27 Mm3 (about 0.276 cm EWH), which is close to the GRACE-derived GWS anomaly (0.26 cm/year), as shown in Figure 7.
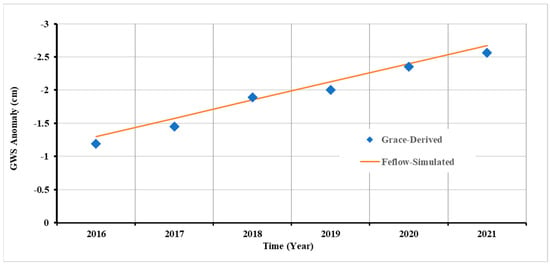
Figure 7.
Comparison of GRACE-derived and simulated GWS changes from 2016 to 2021 over the model domain.
4.3. Management Schemes
The calibrated model was run afterwards for a 100-year test period as a predictive simulation. Estimated water levels during the steady-state simulation were regarded as the initial conditions for the transient simulation. The BCs and the material properties (e.g., hydraulic conductivity and storativity) were kept unchanged. The added input to the model was the pumping wells. To investigate the CC implications, time-varying boundary-condition data were applied.
The adjusted model was employed to mimic the aquifer’s behaviour under variant exploitation strategies. The traditional safe yield concept, meant to mean discharge equals recharge, does not apply to such a non-renewable aquifer [63]. The pumping-induced loss in aquifers’ storage is not offset, and the resulting drawdown is inevitable. However, a rationing restriction is to be set to ensure the long-term water supply and, thereby, the sustainability of the dependent cultivation activities [37]. For the Moghra aquifer, the abstraction-regulating rule states the drawdown after 100 years should not exceed a third of the saturation depth. Hereby, the maximum allowable drawdown rate is one meter each year.
Sustainable management should consider CC and the resulting SLR. The Moghra model is employed to investigate the combined implications of SLR, and the water duty increment due to global warming. The Representative Concentration Pathways (RCPs) are a suite of scenarios addressed in the Fifth Assessment Report (AR5) that was released by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) to project future climatic conditions [64]. RCP 85 is the CC worst-case scenario that involves a global average temperature increase of about 4.3 °C by this century’s end [65]. The corresponding average SLR is projected in a range of 53 to 98 cm [66]. However, due to the distinct features of the Mediterranean Sea as a semienclosed basin connected with the ocean through the narrow Gibraltar Strait, its local level change will not exceed 0.5 m [67,68].
Crop consumptive use is often referenced to the evapotranspiration (ET) that can be estimated using different theoretical approaches (e.g., the Blaney–Criddle formula). Global warming causes an increase in crop water requirements that differ regionally. Regional climate models (RCMs) are therefore employed to project climate conditions on a regional scale and thus provide accurate estimates over general circulation models (GCMs) [7]. The outputs of “MPI-ESM-LR/RCA4, GCM/RCM” ensemble simulations, provided through the CORDEX project (CORDEX website at https://esg-dn1.nsc.liu.se/projects/esgf-liu/; accessed on 1 January 2024) were used to project the increase in potential evapotranspiration (PET) over the wells field [69]. Figure 8 shows the projected percentage change in PET during the upcoming 100 years. The average annual increase in PET is 0.0058 mm, which implies an annual increase in water duty by 0.019 m3/acre/day (≈0.047 m3/hectare/day).
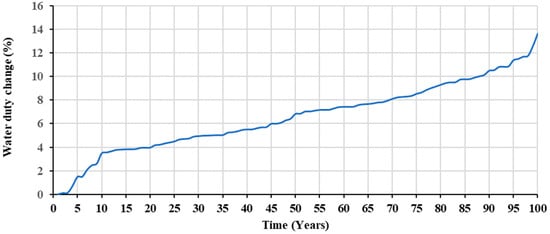
Figure 8.
Percentage increment in crop water consumptive use under the climate change worst-case scenario.
5. Results and Discussions
5.1. Pumping Scenarios
Invoking the calibrated model, a set of alternative pumping policies was designed and reliably tested to identify the optimal water resources management scheme. Eight pumping regimes ranging from 0.8 to 1.5 Mm3/day were simulated. The continuous pumping has resulted in decreasing groundwater levels throughout the model domain. The maximum drawdown was observed within the wells field. Table 2 summarizes the resulting drawdown breakthrough under the applied pumping policies during a 100-year test period.

Table 2.
Maximum drawdown (m) for different pumping rates along a 100-year test period.
According to the obtained results, it is concluded that the optimum management pathway is to pump a total water quantity of 1.3 Mm3/day through 1000 wells (i.e., Pumping Scheme No. 6). Considering a daily water duty of 14 m3/acre (34.6 m3/ha), the cultivated areas would reach up to 92,857 acres (37,578 ha). The resulting drawdown is up to about 96.49 m, which is compatible with the MWRI’s regulations stating that the drawdown threshold should not exceed 1.0 m in a year, as shown in Table 2. Figure 9 shows the simulated hydraulic head and drawdown under this pumping regime after 100 years. Appendix B showcases detailed information on the recommended pumping scheme to be adopted in the Moghra region. Figure A3 depicts the maximum drawdown resulting through a 100-year test period from different investigated pumping rates, where the optimum one is marked. Figure A4 depicts the rate budget analysis of the groundwater system under this pumping scheme during the simulation period. The net storage was estimated as the difference between captured and released storage, which showed an average storage loss of 1.31 Mm3/day. Figure A5 depicts the resulting drawdown every ten years on a cross-sectional view (Section A-A, Figure 1b) of the model domain.
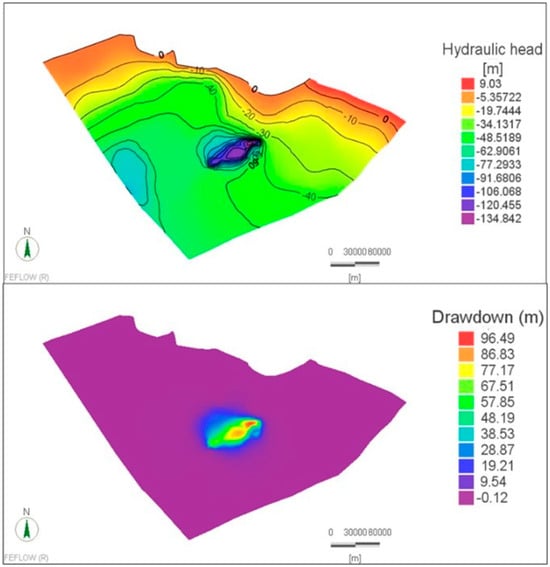
Figure 9.
Simulated hydraulic heads (Up) and drawdowns (Down) for the recommended pumping scheme (1.3 Mm3/day) after 100 years.
5.2. Climate Change Impacts
As mentioned, the maximum pumping rate is 1.3 Mm3/day through 1000 wells, which is sufficient to irrigate about 92,850 acres (about 37,575 ha) with an average water duty of 14 m3/acres/day, as shown in Table 2. However, CC would impose significant pressure on the aquifer to meet the anticipated increase in crop consumptive water use. To avoid the loss of a portion of the reclaimed areas in the future, a time-increasing abstraction rate should be applied. Accordingly, the developed model was utilized to investigate the combined effect of SLR and the increase in crop-consumptive water use. A time series representing a linear rise by 0.5 m in sea level during the upcoming 100 years was assigned for the northern BC along the Mediterranean Sea. Additionally, the daily pumping rate to maintain the cultivated area was defined as a time series considering the increase in PET under the worst-case CC scenario (i.e., RCP 85), as shown in Figure 8.
Figure 10 shows the resulting heads and drawdown after a 100-year simulation period under a constant pumping rate of 1300 m3/day/well, considering a gradual SLR of up to 0.5 m after 100 years. The water levels within a narrow strip along the seaside were marginally raised, but they were not altered over the rest of the model domain. The low effect of SLR on water levels is attributed to the vast area of the model domain. Accordingly, the resulting drawdown within the wells field was almost unaffected, as shown in Figure 10. On the contrary, the resulting drawdown from assigning a time-increased withdrawal rate was 103.7 m, as shown in Figure 10, compared to 96.5 m when applying a fixed pumping rate of 1300 m3/day/well. The simulation affirmed the exceeding of this management scenario under CC implications for the maximum rationalizing limit of drawdown. The combined effect of SLR and pumping increases in all management scenarios on the modelled domain is shown in Table 3. The exploitation scheme No. 5, which involves cultivating 85,714 acres, may be more consistent with the drawdown rationalizing limit. The resulting drawdown by the end of the simulation period under the combined effect of global warming and the resulting SLR is shown in Figure 11. The resulting drawdown is 95.4 m by the simulation period’s end. This value is compatible with the MWRI’s regulations, which state that the maximum annual drawdown should not exceed 1.0 m. Appendix C showcases more information about the implications of a variant pumping scheme considering climate change impacts. Figure A6 depicts the maximum drawdown resulting through a 100-year test period from different investigated pumping rates, where the optimum one is marked. Figure A7 depicts the average rate budget analysis of the groundwater system over 100 years of applying time-increasing abstraction rates under the combined effects of climate change. The net storage was estimated as the difference between captured and released storage, which showed an average storage loss of 1.362 Mm3/day.
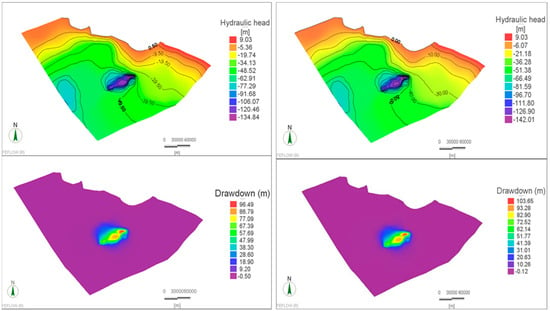
Figure 10.
Simulated hydraulic heads (Up) and drawdown (Down) after 100 years under a constant pumping rate of 1.3 m3/day/well considering (Right) a sea level rise of 0.5 m and (Left) an increase in crop water requirements.

Table 3.
Maximum drawdown (m) along a 100-year test period under a chronologically increasing abstraction rate corresponding to climate change implications on crop water requirements.
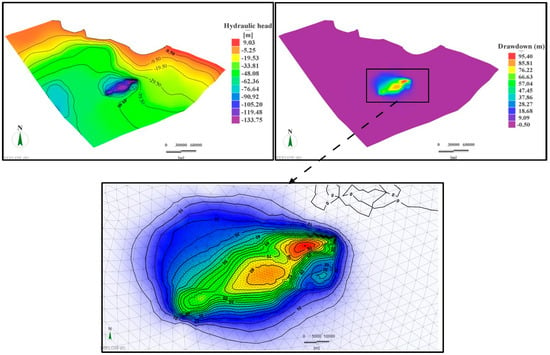
Figure 11.
Simulated hydraulic heads (Left) and drawdowns (Right) after 100 years of applying the recommended development regime under the combined effects of climate change.
6. Conclusions
To cope with the rising food shortage issue in Egypt, there is a crucial need to expand cultivation swaths outside of the overpopulated Nile Delta and Valley. Thus, a groundwater-dependent reclamation project was advocated to reclaim the barren desert areas. The allocated aquifers for the proposed cultivation activities are almost non-renewable systems. Nevertheless, there is still substantial room for exploitation of this water resource, provided its pumping is regulated by principles of wisdom and rationality. Herein, a groundwater flow model was generated using the FEFLOW software to explore the Moghra aquifer’s potential for extensive rural development. A simulation of reality is performed by representing the aquifer’s boundary conditions, hydrogeological parameters, and groundwater extraction rates. The developed model was calibrated against the observed water levels in the archive and continuous pumping experiments. Simulated losses in groundwater storage (GWS) from 2016 to 2021 were compatible with the GRACE-derived GWS anomaly. Subsequently, the calibrated model was utilized to produce the groundwater equipotential surface and hydraulic head gradient under the influence of changing abstraction regimes. The persistently high abstraction rates play a significant role in lowering groundwater heads within the development area. To provide an integrated management approach, this study has also investigated the effects of global warming. SLR would increase the extent of saltwater encroachment into the aquifer, causing a slight increase in the piezometric levels within the coastal plain. It, therefore, has no effect on the heads within the well field. The projected increase in crop water requirement was estimated for climate change’s worst-case scenario (i.e., RCP 85). The corresponding temporal-increasing abstraction rate to irrigate the cultivation area without any reduction was assigned. The maximum pumping regime that coincides with the regulation rule that was set by the MWRI for the next 100 years has been concluded. There is a potential for sustainable exploitation of this water resource to irrigate a total area of 85,715 acres (34,687 ha). The resulting drawdown is expected to reach 95.4 m.
This study addressed the first modelling of the Moghra aquifer using a finite-element-based code. The developed model can be invoked by decision-makers to beneficially use its outcomes to define sustainable management approaches. It is suggested to upgrade the model to evaluate the degree to which the production wells would intrude saltwater into the aquifer system.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.S., B.A.Z. and A.M.A.; methodology, A.S., A.M.N. and A.M.A.; software, A.S. and A.M.A.; validation, A.S. and A.M.A.; formal analysis, A.M.A. and K.P.-U.; investigation, A.S., A.M.A. and K.P.-U.; resources, K.P.-U. and A.M.A.; data curation, A.S.; writing—original draft preparation, A.S.; writing—review and editing, A.S., A.M.A. and K.P.-U.; visualization, A.S. and A.M.A.; supervision, B.A.Z. and A.M.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Financial support received from the Science, Technology & Innovation Funding Authority STDF-Egypt (Grant number: 46278) has facilitated this collaborative research as a part of a project titled “Optimal Exploitation Strategies for Sustainable Utilization of Fossil Groundwater Reserves in Egypt”.
Data Availability Statement
Research data are available from the corresponding author on request.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the STDF-Egypt for the financial support received under the framework of a project (ID#46278). The authors are beholden to the Egyptian Countryside Development Company ECDC’s officials for providing in situ observation, reports, surveys, and hosting during the field campaign. Thanks must go to the DHI group for providing technical support for the FEFLOW software. All authors acknowledge the reviewers’ time and efforts to revise and improve the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors state no conflicts of interest that could influence the study reported in this paper. The funders had no role in the design of this study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Appendix A. Model Development and Calibration
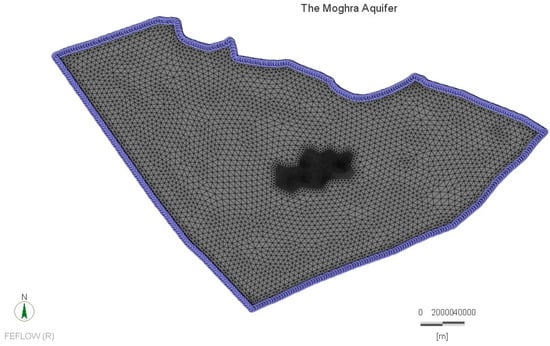
Figure A1.
Configured mesh and boundary conditions of the modelled domain.
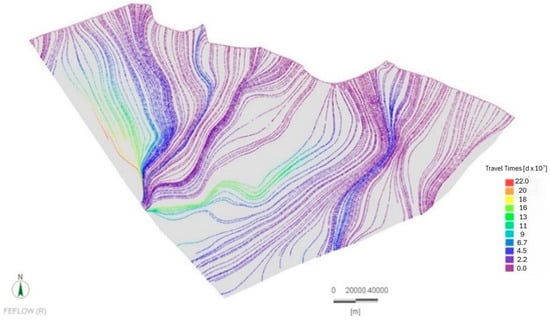
Figure A2.
Visualization of paths and travel times of virtual particles released at the domain’s boundaries.
Appendix B. Optimum Pumping Scheme without Considering Climate Change Impact
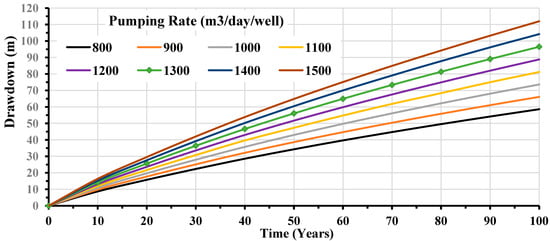
Figure A3.
Predicted maximum drawdown resulting from different pumping rates through a 100-year test period.
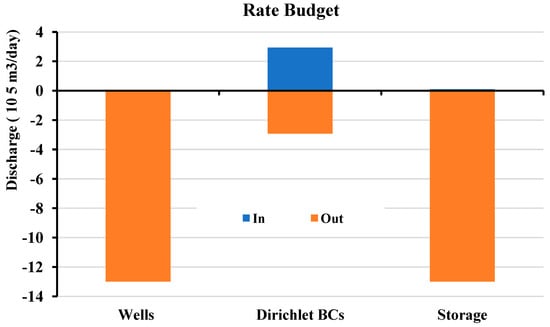
Figure A4.
Components of the groundwater budget analysis (+) for inflow and (−) for outflow for the recommended pumping scheme (1.3 Mm3/day) after 100 years.
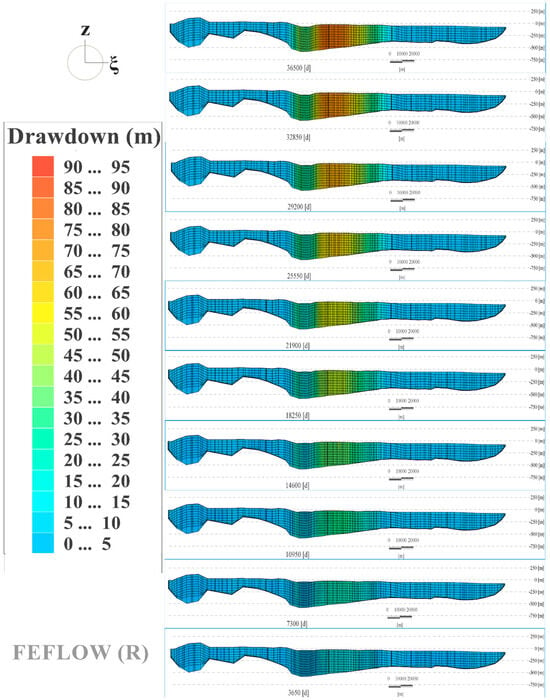
Figure A5.
Cross-section (A-A) view showing the resulting drawdown from the recommended pumping scheme (1.3 Mm3/day) (depth is scaled up by 30 times).
Appendix C. Optimum Pumping Scheme Considering Climate Change Impact
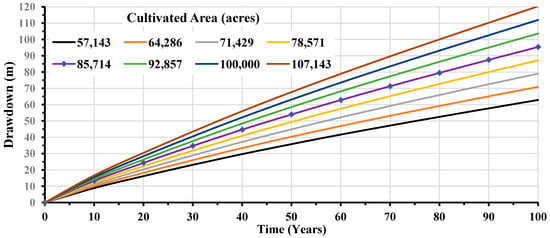
Figure A6.
Maximum drawdown resulting from time-increasing abstraction rates through a 100-year test period.
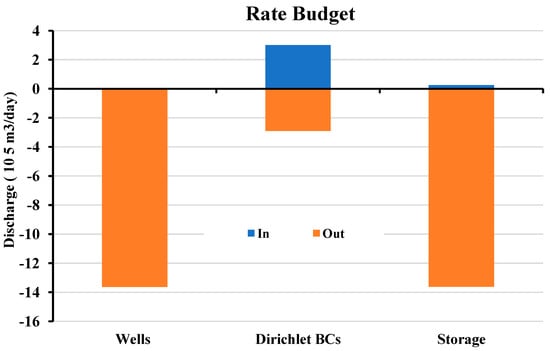
Figure A7.
Components of the groundwater budget analysis (+) for inflow and (−) for outflow after 100 years of applying the recommended development regime (a growing pumping rate initiated by 1.3 m3/day/well) under the combined effects of climate change.
References
- Frappart, F.; Ramillien, G. Monitoring groundwater storage changes using the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) satellite mission: A review. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Closas, A.; Rap, E. Solar-based groundwater pumping for irrigation: Sustainability, policies, and limitations. Energy Policy 2017, 104, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio-Aliaga, Á.; Sánchez-Lozano, J.M.; García-Cascales, M.S.; Benhamou, M.; Molina-García, A. GIS based solar resource analysis for irrigation purposes: Rural areas comparison under groundwater scarcity conditions. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2016, 156, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zektser, S.; Loáiciga, H.A.; Wolf, J.T. Environmental impacts of groundwater overdraft: Selected case studies in the southwestern United States. Environ. Geol. 2005, 47, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khater, A.R.; Water, N. Intensive groundwater use in Middle East and North Africa. In Intensive Use of Groundwater: Challenges and Opportunities; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; pp. 355–386. [Google Scholar]
- Gado, T.A.; El-Hagrsy, R.M.; Rashwan, I.M.H. Spatial and temporal rainfall changes in Egypt. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 28228–28242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gado, T.A.; Mohameden, M.B.; Rashwan, I.M.H. Bias correction of regional climate model simulations for the impact assessment of the climate change in Egypt. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 20200–20220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrag, A.A. The hydraulic and hydrochemical impacts of the Nile system on the groundwater in upper Egypt. Assuit Univ. Bull. Environ. Resour 2005, 8, 87–102. [Google Scholar]
- Aziz, S.A.; Zelenáková, M.; Mésároš, P.; Purcz, P.; Abd-Elhamid, H. Assessing the Potential Impacts of the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam on Water Resources and Soil Salinity in the Nile Delta, Egypt. Sustainability 2019, 11, 7050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, M.Y.; Al-Zahrani, K.H.; Baig, M.B.; Straquadine, G.S.; Aldosari, F. Threats and challenges to sustainable agriculture and rural development in Egypt: Implications for agricultural extension. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2011, 21, 581–588. [Google Scholar]
- Aly, M.M.; Elhamid, A.M.I.A.; Abu-Bakr, H.A.-A.; Shalby, A.; Fayad, S.A.K. Integrated Management and Environmental Impact Assessment of Sustainable Groundwater-Dependent Development in Toshka District, Egypt. Water 2023, 15, 2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, M.M.; Sakr, S.A.; Fayad, S.A.K. Evaluation of the impact of Lake Nasser on the groundwater system in Toshka under future development scenarios, Western Desert, Egypt. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Agha, D.E.; Molle, F.; Metwally, M.I.; Emara, S.R.; Shalby, A.; Armanuos, A.M.; Negm, A.; Gado, T.A. Review: Toward sustainable management of groundwater in the deserts of Egypt. Hydrogeol. J. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalby, A.; Emara, S.R.; Metwally, M.I.; Negm, A.M.; Gado, T.A.; Armanuos, A.M. Geospatial model for allocating favorable plots for groundwater-dependent cultivation activities in Egypt. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Sp. Sci. 2023, 26, 777–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, E.; Riad, P.; Elbeih, S.; Hagras, M.; Hassan, A.A. Multi criteria analysis for groundwater management using solar energy in Moghra Oasis, Egypt. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Sp. Sci. 2019, 22, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmenshawy, M.R.; Shalaby, S.M.; Elshinnawy, A.I.; Gado, T.A. Groundwater desalination for agricultural purposes using reverse osmosis and nanofiltration technologies: Case study wadi El-natrun, Egypt. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 180, 669–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomaa, S.M.; Hassan, T.M.; Helal, E. Assessment of seawater intrusion under different pumping scenarios in Moghra aquifer, Egypt. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 781, 146710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmansy, Y.; Mohamed, M.S.; Hassan, A.A.; Riad, P. Sustainable Agricultural Groundwater Management for New Reclaimed Areas in Farafra Oasis, Western Desert of Egypt. Int. J. Eng. Adv. Technol. 2020, 9, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A. Groundwater resources management through the applications of simulation modeling: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 499, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alley, W.M.; Leake, S.A. The Journey from Safe Yield to Sustainability. Ground Water 2004, 42, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janipella, R.; Pujari, P.R. Review on Groundwater Flow and Solute Transport Modelling in India: Recent Advances and Future Directions. J. Geol. Soc. India 2022, 98, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibaj, M.; Javadi, A.A.; Akrami, M.; Ke, K.Y.; Farmani, R.; Tan, Y.C.; Chen, A.S. Modelling seawater intrusion in the Pingtung coastal aquifer in Taiwan, under the influence of sea-level rise and changing abstraction regime. Hydrogeol. J. 2020, 28, 2085–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, W. A review of regional groundwater flow modeling. Geosci. Front. 2011, 2, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strack, O.D.L. Finite differences and finite elements. In Analytical Groundwater Mechanics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2017; Volume 7, pp. 403–422. ISBN 9781316563144. [Google Scholar]
- Koukidou, I.; Panagopoulos, A. Application of Feflow for the Simulation of Groundwater Flow at the Tirnavos (Central Greece). Bull. Geol. Soc. Greece 2010, 43, 1747–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenas, M.C.; Pescador, J.P.; Garzón, L.D.D.; Saavedra, E.Y.; Obando, P.F.A. Hydrogeological modeling in tropical regions via feflow. Earth Sci. Res. J. 2020, 24, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufour, R.; Aguirre, C.; Sanchez, M.; Maqueda, A.; Zwinger, J.; Renz, A.; Cho, J.; Evans, D. Pit Dewatering Optimisation of a 3D Feflow Unstructured Groundwater Model at Geologically Complex Antamina Mine Site in Peru; Australian Centre for Geomechanics: Perth, Australia, 2020; pp. 1329–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Normi Idris, A.; Zaharin Aris, A.; Sheikhy Narany, T.; Praveena Mangala, S.; Suratman, S.; Tawnie, I.; Khairul Nizar Shamsuddin, M.; Sefie, A. Simulation of Saltwater Intrusion in Coastal Aquifer of Kg. Salang, Tioman Island, Pahang, Malaysia. MATEC Web Conf. 2017, 103, 4024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, J.; Liu, N.; Miao, Y.; Lin, X.; Tan, H.; Liu, F. Numerical simulation and pollution prediction of karst groundwater in water-conducting faults distribution area. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 585, 012097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sefelnasr, A.; Sherif, M. Impacts of Seawater Rise on Seawater Intrusion in the Nile Delta Aquifer, Egypt. Groundwater 2014, 52, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emara, S.R.; Armanuos, A.M.; Shalby, A. Groundwater for Sustainable Development Appraisal seawater intrusion vulnerability for the Moghra coastal aquifer, Egypt—Application of the GALDIT index, sensitivity analysis, and hydro-chemical indicators. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 25, 101166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalby, A.; Emara, S.R.; Metwally, M.I.; Armanuos, A.M.; El-Agha, D.E.; Negm, A.M.; Gado, T.A. Satellite-based Estimates of Groundwater Depletion over Egypt. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 105, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Mogith, S.; Ibrahim, S.; Hafiez, R. Groundwater Potentials and Characteristics of El-Moghra Aquifer in the Vicinity of Qattara Depression. Egypt. J. Desert Res. 2013, 63, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Chen, Y.; Khalil, M.M. Isotopic composition of groundwater resources in arid environments. J. Hydrol. 2022, 609, 127773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, E.; Riad, P.; Elbeih, S.F.; Hassan, A.A.; Hagras, M. Sustainable groundwater management in arid regions considering climate change impacts in Moghra region, Egypt. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 11, 100385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousf, A.F.; El Fakharany, M.A.; Abu Risha, U.A.; Afifi, M.M.; Al Sayyad, M.A. Contributions to the geology of the New Valley area, Western Desert, Egypt. J. Basic Environ. Sci. 2018, 5, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- el-Aziz Abu-Bakr, H.A.; Abdelmoniem, M. Groundwater potentiality delineation in Moghra, Egypt. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2023, 102337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morad, N.A.; Masoud, M.H.; Abdel Moghith, S.M. Hydrologic factors controlling groundwater salinity in northwestern coastal zone, Egypt. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 123, 1567–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, T.; Moghazy, N.H.; Elasbah, R.; Elkiki, M.; Eltarabily, M.G. Sustainable agricultural development under different climate change scenarios for El Moghra region, Western Desert of Egypt. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 26, 14957–14979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Osta, M.; Masoud, M.; Alqarawy, A.; Badran, O. Utilizing of aquifer hydraulic parameters to assess the groundwater sustainability in the new reclamation area of Moghra Oasis: Western Desert—Egypt. Appl. Water Sci. 2023, 13, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diersch, H.J.G. FEFLOW: Finite Element Modeling of Flow, Mass and Heat Transport in Porous and Fractured Media; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; ISBN 9783642387395. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Chen, S.; Qin, H.; Jiao, J.J. Modeling the spatial and seasonal variations of groundwater head in an urbanized area under low impact development. Water 2018, 10, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ECDC “Egyptian Countryside Development Company” EGDC “Egyptian Countryside Development Company”. Available online: http://elreefelmasry.com (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- Sarwar, A.; Eggers, H. Development of a conjunctive use model to evaluate alternative management options for surface and groundwater resources. Hydrogeol. J. 2006, 14, 1676–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobeih, M.M.; El-Arabi, N.E.; Helal, E.E.D.Y.; Awad, B.S. Management of water resources to control groundwater levels in the southern area of the western Nile delta, Egypt. Water Sci. 2017, 31, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gado, T.A.; Shalaby, B.A.; Guo, Y.; Rashwan, I.M.H. Assessment of Satellite-Based Precipitation Estimates over Egypt. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2024, 29, 05023027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, B.F.; Behrangi, A.; Famiglietti, J.S. Precipitation intensity effects on groundwater recharge in the southwestern United States. Water 2016, 8, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.; Nachabe, M.; Ross, M. Extinction depth and evapotranspiration from ground water under selected land covers. Ground Water 2007, 45, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campoli, D.; Crestaz, E.; Fehervari, M.; Patata, L.; Scipioni, P. 3D density-dependent groundwater modeling in assessing optimisation of a pumping strategy within a chemical plant. Water Resour. Manag. III 2005, 80, 131–141. [Google Scholar]
- Wassef, R.; Schüttrumpf, H. Impact of sea-level rise on groundwater salinity at the development area western delta, Egypt. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2016, 2–3, 85–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Azeem, H.; El-Didy, S.; Eizeldin, M.; Helmi, A. Hydrogeological Evaluation of Massive Salty Lagoons, (Case Study: Qattara Depression). Al-Azhar Univ. Civ. Eng. Res. Mag. 2017, 39, 277–291. [Google Scholar]
- El Shazly, E.M.; Abdel Hady, M.A.; El Ghawaby, M.A.; Khawasik, S.M.; El Shazly, M.M. Landsat satellite imagery of the Qattara Depression area, Egypt. Acta Astronaut. 1978, 5, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moharram, S.H.; Gad, M.I.; Saafan, T.A.; Allah, S.K. Optimal groundwater management using Genetic Algorithm in El-Farafra Oasis, Western Desert, Egypt. Water Resour. Manag. 2012, 26, 927–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Muqdadi, S.W.H.; Abo, R.; Khattab, M.O.; Abdulhussein, F.M. Groundwater flow-modeling and sensitivity analysis in a hyper arid region. Water 2020, 12, 2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, M.; Yan, E.; Sturchio, N.; Wagdy, A.; Abdel Gelil, K.; Becker, R.; Manocha, N.; Milewski, A. Natural discharge: A key to sustainable utilization of fossil groundwater. J. Hydrol. 2007, 335, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, O.B.; Tabari, M.M.R.; Fallah-Mehdipour, E.; Mariño, M.A. Groundwater Model Calibration by Meta-Heuristic Algorithms. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 2515–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Jiao, J.J. Calibration of a large-scale groundwater flow model using GRACE data: A case study in the Qaidam Basin, China. Hydrogeol. J. 2015, 23, 1305–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, A.Y.; Green, R.; Swenson, S.; Rodell, M. Toward calibration of regional groundwater models using GRACE data. J. Hydrol. 2012, 422–423, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, M.H.; Famiglietti, J.S.; Yeh, P.J.F.; Syed, T.H. Improving parameter estimation and water table depth simulation in a land surface model using GRACE water storage and estimated base flow data. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, A.Y.; Green, R.; Rodell, M.; Swenson, S. Inferring aquifer storage parameters using satellite and in situ measurements: Estimation under uncertainty. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richey, A.S.; Thomas, B.F.; Lo, M.H.; Reager, J.T.; Famiglietti, J.S.; Voss, K.; Swenson, S.; Rodell, M. Quantifying renewable groundwater stress with GRACE. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 5217–5237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodell, M.; Chen, J.; Kato, H.; Famiglietti, J.S.; Nigro, J.; Wilson, C.R. Estimating groundwater storage changes in the Mississippi River basin (USA) using GRACE. Hydrogeol. J. 2007, 15, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bierkens, M.F.P.; Wada, Y. Non-renewable groundwater use and groundwater depletion: A review. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalby, A.; Elshemy, M.; Zeidan, B.A. Assessment of climate change impacts on water quality parameters of Lake Burullus, Egypt. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 27, 32157–32178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, R.; Babiker, M.; Brinkman, S.; Calvo, E.; Carter, T.; Edmonds, J.; Elgizouli, I.; Emori, S.; Erda, L.; Hibbard, K.; et al. Towards New Scenarios for Analysis of Emissions, Climate Change, Impacts and Response Strategies. In Proceedings of the IPCC Expert Meeting Report, Noordwijkerhout, The Netherlands, 19–21 September 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Gregory, J. Projections of Sea Level Rise; Climate Research: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Shaltout, M.; Tonbol, K.; Omstedt, A. Sea-level change and projected future flooding along the Egyptian Mediterranean coast. Oceanologia 2015, 57, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalby, A.; Elshemy, M.; Zeidan, B.A. Modeling of climate change impacts on Lake Burullus, coastal lagoon (Egypt). Int. J. Sediment Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhawaga, A.; Zeidan, B.; Elshemy, M. Climate change impacts on water security elements of Kafr El-Sheikh governorate, Egypt. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 259, 107217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).