Ecological Response of Enzyme Activities in Watershed Sediments to the Reintroduction of Antibiotics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site and Sampling
2.2. Determination of Sediment Physico-Chemical Properties and Heavy Metals
2.3. Determination of Enzyme Activity
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Result and Discussion
3.1. Response of Enzyme Activities to Antibiotic Reintroduction
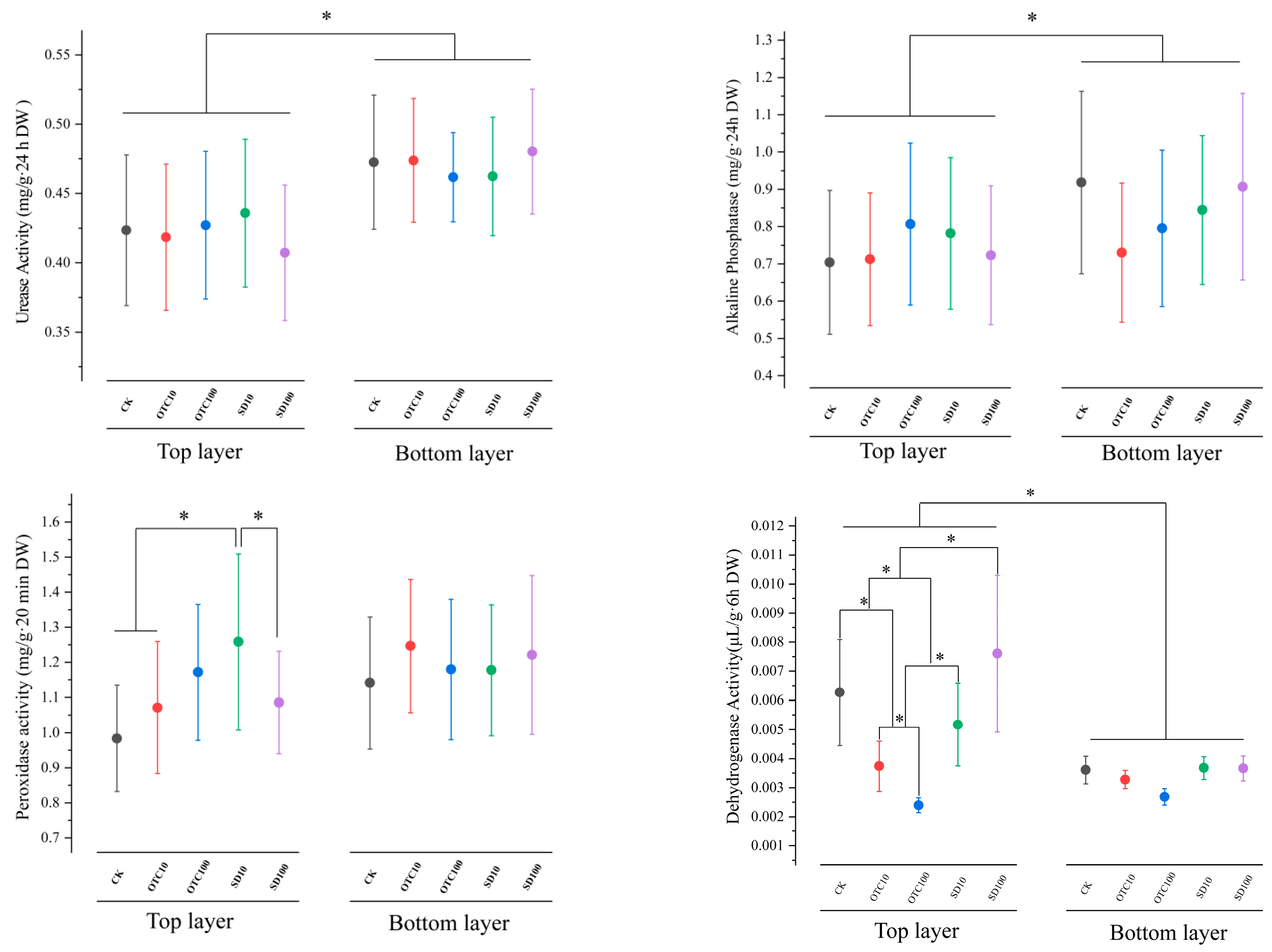
3.2. Changes in Enzyme Activities in Both the Top and Bottom Sediment Layers
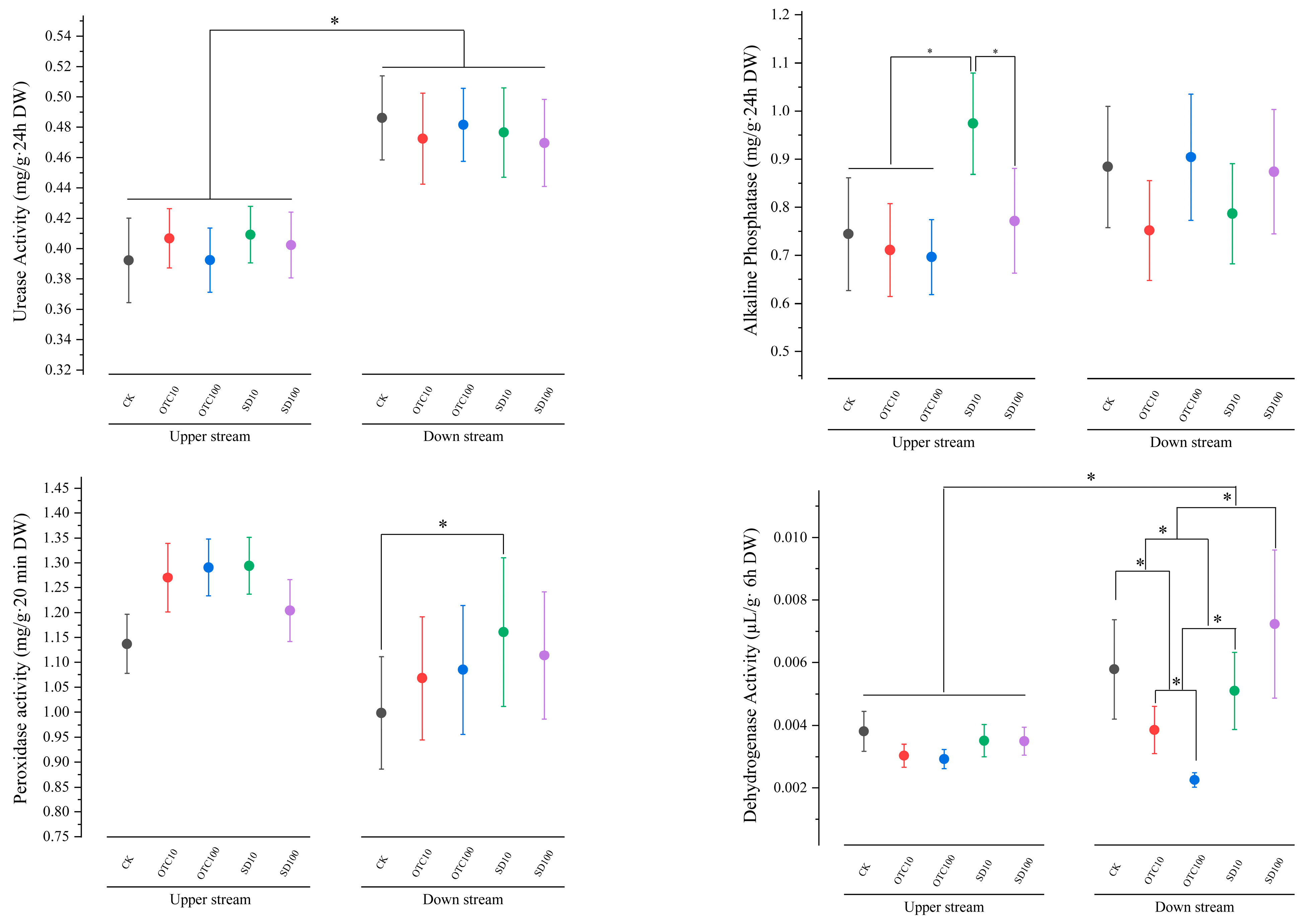
3.3. Changes in Enzyme Activities in Sediment Environments Upstream and Downstream
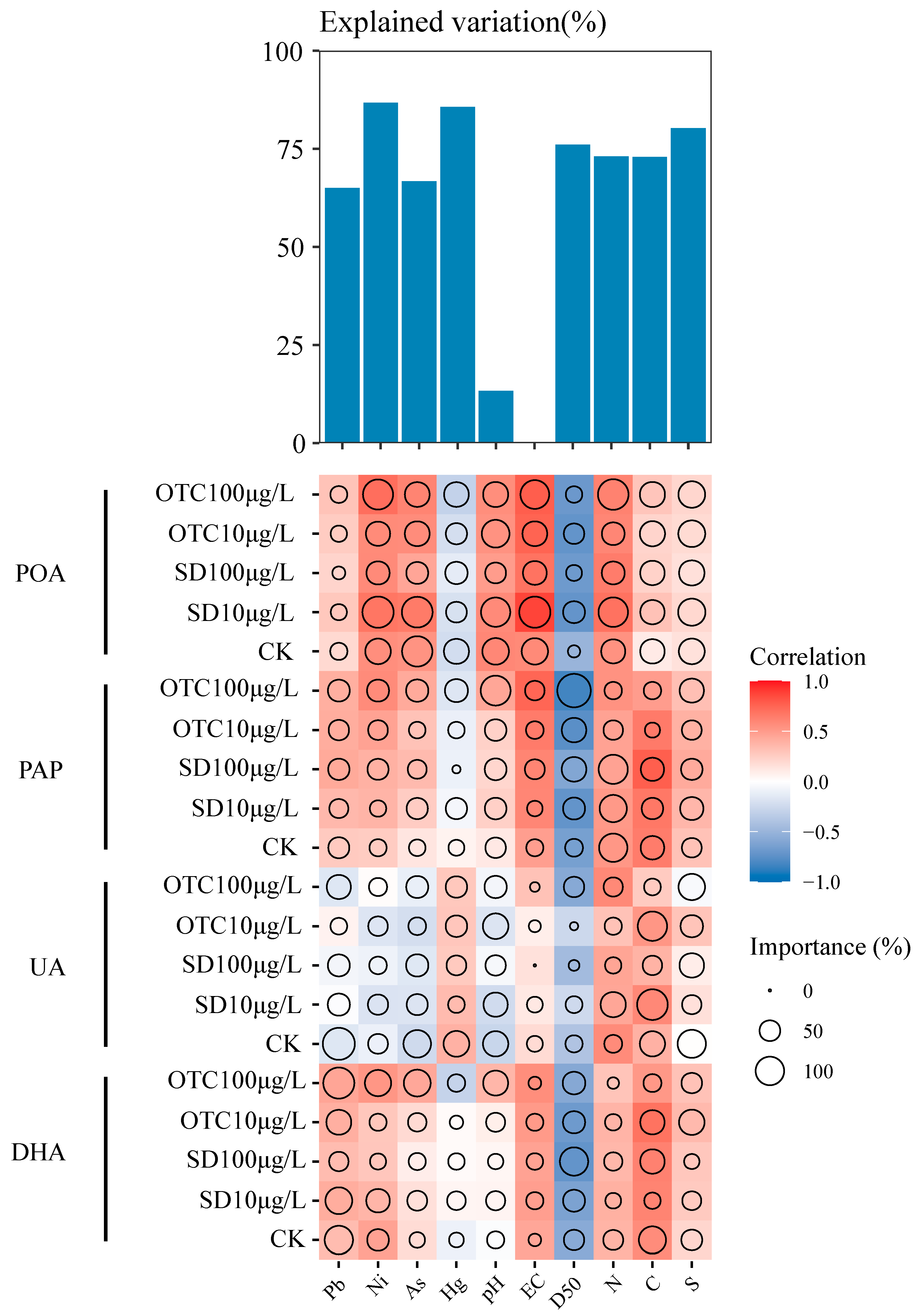
3.4. Impacts of Environmental Factors on Enzyme Activities in Watershed Environment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, K.; Yin, X.; Zhang, D.; Yan, D.; Cui, L.; Zhu, Z.; Wen, L. Distribution, sources, and ecological risk assessment of quinotone antibiotics in the surface sediments from Jiaozhou Bay wetland, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 129, 859–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, E.Y.; Van Boeckel, T.P.; Martinez, E.M.; Pant, S.; Gandra, S.; Levin, S.A.; Goossens, H.; Laxminarayan, R. Global increase and geographic convergence in antibiotic consumption between 2000 and 2015. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 3463–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zeng, S.; He, M.; Gu, A.Z. Water Disinfection Byproducts Induce Antibiotic Resistance-Role of Environmental Pollutants in Resistance Phenomena. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 3193–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, N.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, W.A.; Ma, Y.; Niu, Z. Colonization Characteristics of Bacterial Communities on Plastic Debris Influenced by Environmental Factors and Polymer Types in the Haihe Estuary of Bohai Bay, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 10763–10773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Mao, L.; Yuan, Z.; Bond, P.L.; Guo, J. Non-antibiotic pharmaceuticals promote the transmission of multidrug resistance plasmids through intra- and intergenera conjugation. ISME J. 2021, 15, 2493–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandegren, L. Low sub-minimal inhibitory concentrations of antibiotics generate new types of resistance. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2019, 11, 46–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Li, R.; Yan, Y.; Cui, L. Urbanization drives the succession of antibiotic resistome and microbiome in a river watershed. Chemosphere 2022, 301, 134707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, B.; Chen, C.; Cheng, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, B.; Li, J. Antibiotic resistance genes in Chishui River, a tributary of the Yangtze River, China: Occurrence, seasonal variation and its relationships with antibiotics, heavy metals and microbial communities. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 846, 157472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, W.; Hu, J.; Magnuson, J.T.; Greer, J.; Yang, M.; Chen, Q.; Fang, M.; Zheng, C.; Schlenk, D. Evidence linking exposure of fish primary macrophages to antibiotics activates the NF-kB pathway. Environ. Int. 2020, 138, 105624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lu, X.; Jing, Q.; Zhang, B.; Ye, J.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, Z.; Zhang, J. Spatiotemporal characterization of heavy metal and antibiotics in the Pearl River Basin and pollutants removal assessment using invasive species-derived biochars. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 454, 131409. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, R.; Zhong, Y.; Xiao, S.; Mao, H.; Li, G.; Wang, Y.; et al. Distribution and correlation between antibiotic resistance genes and host-associated markers before and after swine fever in the longjiang watershed. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 313, 120101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Fang, Y.; Zhou, D. Selective pressure of PFOA on microbial community: Enrichment of denitrifiers harboring ARGs and the transfer of ferric-electrons. Water Res. 2023, 233, 119813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Hu, J.; Chen, Y.; Xu, J.; Yang, B.; Jiang, J. Ecological response to antibiotics re-entering the aquaculture environment with possible long-term antibiotics selection based on enzyme activity in sediment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 19033–19044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Lu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xu, J.; Jiang, J. Microbial community structure and antibiotic resistance profiles in sediments with long-term aquaculture history. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 341, 118052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roose-Amsaleg, C.; Laverman, A.M. Do antibiotics have environmental side-effects? Impact of synthetic antibiotics on biogeochemical processes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 4000–4012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nannipieri, P.; Ascher-Jenull, J.; Ceccherini, M.T.; Landi, L.; Pietramellara, G.; Renella, G. Microbial diversity and soil functions. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2017, 68, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, G.; Lu, J.; Xuan, L.; Chen, J.; Xiong, J. Sediment prokaryotic assembly, methane cycling, and ammonia oxidation potentials in response to increasing antibiotic pollution at shrimp aquafarm. J. Hazard. 2022, 434, 128885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiele-Bruhn, S.; Beck, I.C. Effects of sulfonamide and tetracycline antibiotics on soil microbial activity and microbial biomass. Chemosphere 2005, 59, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Han, Y.; Yin, Y.; Pan, X.; Yu, Y. Variations in dissipation rate, microbial function and antibiotic resistance due to repeated introductions of manure containing sulfadiazine and chlortetracycline to soil. Chemosphere 2014, 96, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.F.; Qu, J.H.; Hu, Y.S. Spatial and temporal characteristics and correlation of phosphorus, pH and alkaline phosphatase at the water-sediment interface of Taihu Lake. Ecol. Environ. 2012, 21, 907–912. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Chen, L.J.; Chen, X.H.; Tan, M.L.; Duan, Z.H.; Wu, Z.J.; Li, X.J.; Fan, X.H. Response of soil enzyme activity to long-term restoration of desertified land. Catena 2015, 133, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.; Chen, J.; Qiao, X.; Tian, R.; Zhu, M. Insight into dynamics and bioavailability of antibiotics in paddy soils by in situ soil moisture sampler. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 135562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.S.; Xi, X.P.; Xu, J.H.; Xie, R.J.; Jiang, J.J. Distribution patterns of antibiotic residues in an urban river catchment. Water Environ. J. 2019, 33, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, N.; Dick, R.P. Sampling and Pretreatment of Soil before Enzyme Analysis. Methods Soil Enzymol. 2011, 9, 85–101. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, S.Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Z. Soil Enzyme and Its Research Methods; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 1986; pp. 274–297. [Google Scholar]
- Nosrati, K.; Govers, G.; Ahmadi, H.; Sharifi, F.; Amoozegar, M.A.; Merckx, R.; Vanmaercke, M. An exploratory study on the use of enzyme activities as sediment tracers: Biochemical fingerprints? Int. J. Sediment Res. 2011, 26, 136–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hou, L.; Liu, M.; Lin, X.; Li, Y.; Li, S. Primary effects of extracellular enzyme activity and microbial community on carbon and nitrogen mineralization in estuarine and tidal wetlands. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 2895–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, J.; Wang, F.; Qiu, L. Effects of biogas residues containing antibiotics on soil enzyme activity and lettuce growth. Environ. Sci. Pollut. 2019, 26, 6116–6122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yu, X.; Liu, H.; Gong, Z. The spatio-temporal distribution of alkaline phosphatase activity and phoD gene abundance and diversity in sediment of Sancha Lake. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Pan, X.; Chen, L.k.; Liu, W.; Christie, P.; Luo, Y.; Wu, L. Effects of different concentrations and application frequencies of oxytetracycline on soil enzyme activities and microbial community diversity. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2016, 76, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Singh, A.B.; Kumar, R.V.; Manna, M.C.; Bhattacharyya, R.; Rahman, M.M.; Sharma, P.; Rajput, P.S.; Misra, S. Soil enzymes and microbial elemental stoichiometry as bio-indicators of soil quality in diverse cropping systems and nutrient management practices of Indian Vertisols. Appl. Soil. Ecol. 2020, 145, 103304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, A.; Zulfiqar, A.; Arshed, M.Z.; Hussain, S.; Khan, M.T.; Zivcak, M.; Zuan, A.T.K.; Alshahrani, S.M.; Alarjani, K.M. The impact of newly synthesized sulfonamides on soil microbial population and respiration in rhizospheric soil of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0264476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Huang, X.-H.; Shen, X.-X.; Chen, H.-Q.; Li, C.; Jin, G.-Q.; Cao, J.-S.; Xue, Z.-X. Metagenomic insights into the spatiotemporal responses of antibiotic resistance genes and microbial communities in aquaculture sediments. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrena, R.; Vázquez, F.; Sánchez, A. Dehydrogenase activity as a method for monitoring the composting process. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 905–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, G.; Wu, N. A Review of Studies on Soil Enzymology. J. Trop. Subtrop. Bot. 2004, 1, 83–90. [Google Scholar]
- Widdig, M.; Schleuss, P.-M.; Biederman, L.A.; Borer, E.T.; Crawley, M.J.; Kirkman, K.P.; Seabloom, E.W.; Wragg, P.D.; Spohn, M. Microbial carbon use efficiency in grassland soils subjected to nitrogen and phosphorus additions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 146, 107815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, X.; Jin, X. Variations of alkaline phosphatase activity and P fractions in sediments of a shallow Chinese eutrophic lake (Lake Taihu). Environ. Pollut. 2007, 150, 288–294. [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair, D.C.R.; Smith, G.M.; Bruce, A.; Staines, H.J. Soil dehydrogenase activity adjacent to remedially treated timber, weathered in a physical field model. Int. Biodeter. Biodegr. 1997, 39, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keplin, B.; Broll, G. Earthworms and dehydrogenase activity of urban biotopes. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1997, 29, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiquia, S.M.; Wan, J.H.C.; Tam, N.F.Y. Dynamics of yard trimmings composting as determined by dehydrogenase activity, ATP content, arginine ammonification, and nitrification potential. Process Biochem. 2002, 37, 1057–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, M.; Hu, C.; Zhang, H. Effects of tourmaline addition on the dehydrogenase activity of Rhodopseudomonas palustris. Process Biochem. 2006, 41, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, F. Soil Enzyme Activities and Soil Fertility Dynamics. In Advances in Citrus Nutrition; Srivastava, A.K., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 143–156. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Ying, G.-G.; Tao, R.; Zhao, J.-L.; Yang, J.-F.; Zhao, L.-F. Effects of six selected antibiotics on plant growth and soil microbial and enzymatic activities. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 1636–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.Z.; Xiao, W.J.; Liu, Y.B.; Liu, J.Y.; Zhou, Y.Y. Determination of dehydrogenase activity in sediment of shallow lakes and its ecological significance. J. Lake Sci. 2009, 21, 345–350. [Google Scholar]
- Xi, X.; Wang, M.; Chen, Y.; Yu, S.; Hong, Y.; Ma, J.; Wu, Q.; Lin, Q.; Xu, X. Adaption of the microbial community to continuous exposures of multiple residual antibiotics in sediments from a salt-water aquacultural farm. J. Hazard. 2015, 290, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, X.; Li, H.; Pan, B.; You, M.; Sun, W. Interactions between antibiotics and heavy metals determine their combined toxicity to Synechocystis sp. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Zhang, Y.; An, W.; Lu, J.; Hu, J.; Yang, M. Antibiotic resistomes in drinking water sources across a large geographical scale: Multiple drivers and co-occurrence with opportunistic bacterial pathogens. Water Res. 2020, 183, 116088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xun, W.; Huang, T.; Zhao, J.; Ran, W.; Wang, B.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, R. Environmental conditions rather than microbial inoculum composition determine the bacterial composition, microbial biomass and enzymatic activity of reconstructed soil microbial communities. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 90, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.W.; Hui, L.L. Soil particle size distribution and its fractal dimension among degradation sequences of the alpine meadow in the source region of the Yangtze and Yellow River, Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. J. Appl. Ecol. 2014, 25, 679–686. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Z.Y.; Zhao, H.L. Losses of Soil Organic Carbon and Nitrogen and Their Mechanisms in the Desertification Process of Sandy Farmlands in Horqin Sandy Land. Agric. Sci. China 2003, 8, 890–897. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C.F.; Yu, R.; Wang, X.; Chuang, S.C.; Yang, H.X.; Xie, Y. Effects of Antibiotics on Soil Enzyme Activities in Different Soils. J. Ecol. Environ. 2022, 31, 2234–2241. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, M.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Fu, T.; Zeng, T.; Huang, Y.; Yang, X. Effects of Microplastics on the Mineral Elements Absorption and Accumulation in Hydroponic Rice Seedlings (Oryza sativa L.). Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2022, 108, 949–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.R.; Niu, S.F.; Zhang, W.W. Effects of soil particle size on enzyme activities and the amount of soil microorganism in rhizosphere of Caragana korshinskii in desert steppe. Acta. Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 9171–9178. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, X.W.; Du, C.; Zhou, H.; Liu, L.; Dong, X. Effects of Changing Dryland into Paddy Field on pH, Electrical Conductivity and Enzyme Activities in Black Soil. Hubei Agric. Sci. 2017, 56, 2045–2048. [Google Scholar]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xu, J.; Feng, Y.; Jiang, J. Ecological Response of Enzyme Activities in Watershed Sediments to the Reintroduction of Antibiotics. Water 2024, 16, 1393. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16101393
Lu Y, Chen Y, Xu J, Feng Y, Jiang J. Ecological Response of Enzyme Activities in Watershed Sediments to the Reintroduction of Antibiotics. Water. 2024; 16(10):1393. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16101393
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Yue, Yongshan Chen, Jinghua Xu, Ying Feng, and Jinping Jiang. 2024. "Ecological Response of Enzyme Activities in Watershed Sediments to the Reintroduction of Antibiotics" Water 16, no. 10: 1393. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16101393
APA StyleLu, Y., Chen, Y., Xu, J., Feng, Y., & Jiang, J. (2024). Ecological Response of Enzyme Activities in Watershed Sediments to the Reintroduction of Antibiotics. Water, 16(10), 1393. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16101393











