Rapid Formation and Performance of Aerobic Granular Sludge Driven by a Sodium Alginate Nucleus under Different Organic Loading Rates and C/N Ratios
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of the Sodium Alginate Nucleus (SAN)
2.2. Batch Experiment
2.3. Seed Sludge and Wastewater Characteristics
2.4. Analysis Methods
3. Results and Discussion
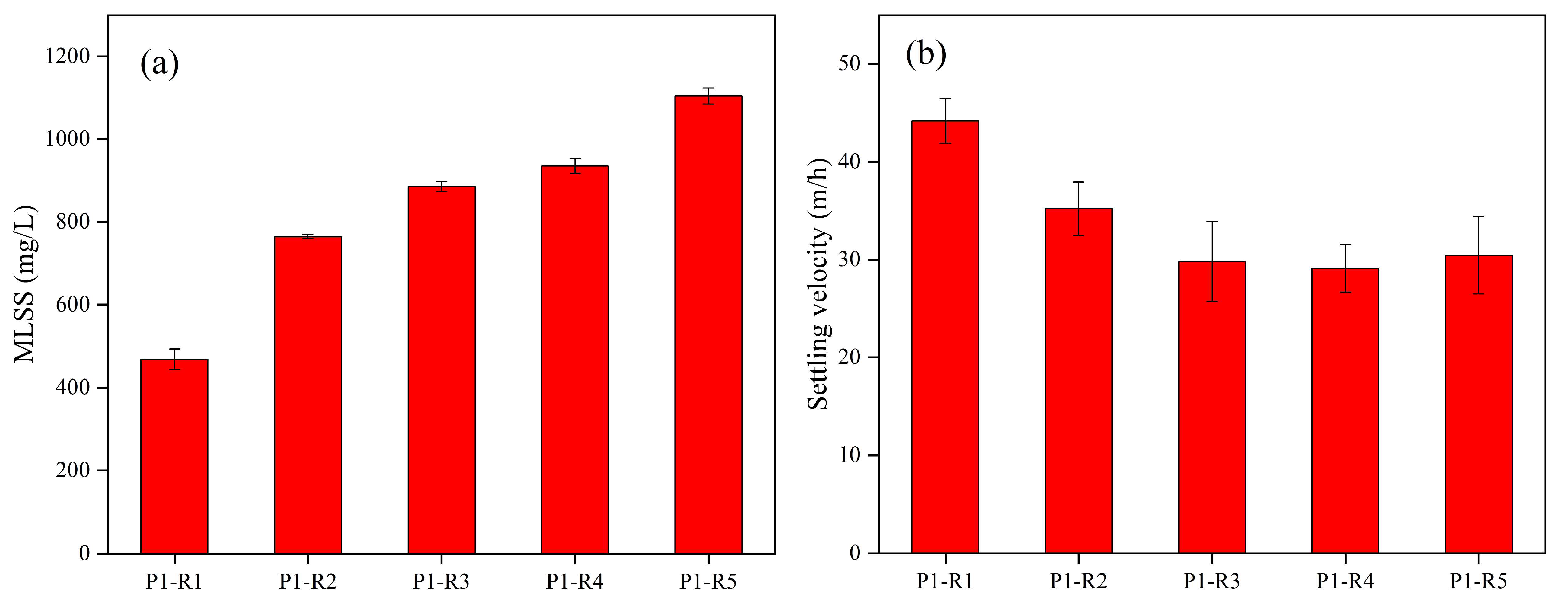
3.1. The Effect of Different OLRs on AGS
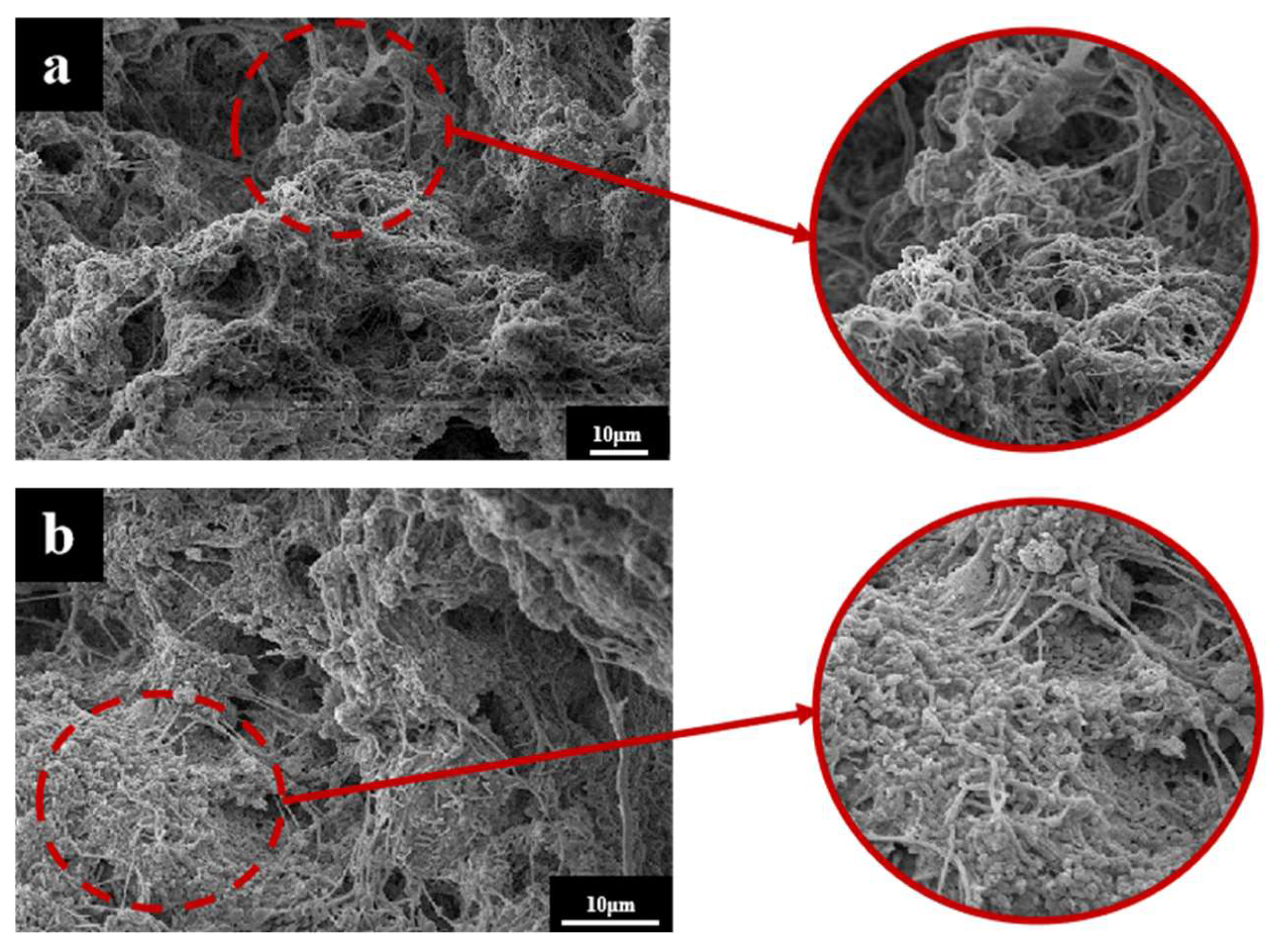
3.1.1. Morphological Changes in AGS under Different OLRs
3.1.2. Physicochemical Properties of AGS under Different OLRs
3.1.3. Overall Performances during the Granulation Period under Different OLRs
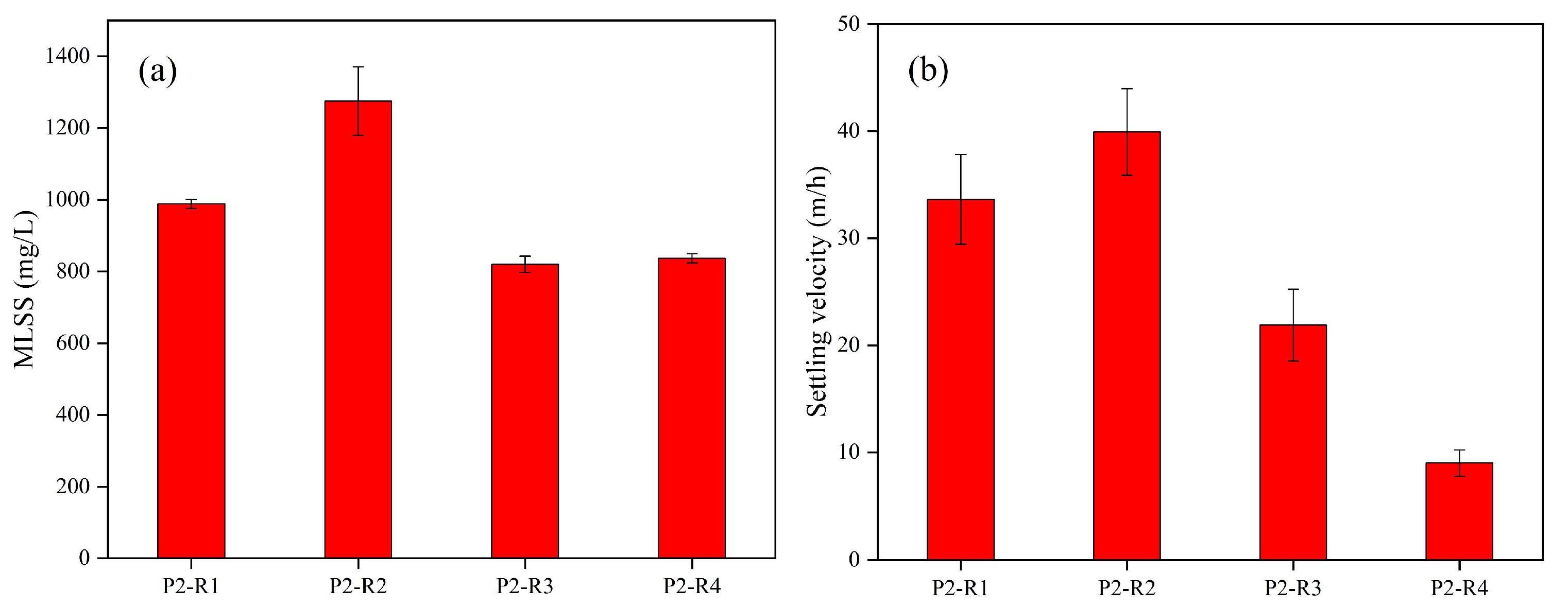
3.2. The Effect of Different C/N Ratios on AGS
3.2.1. Morphological Changes in AGS under Different C/N Ratios
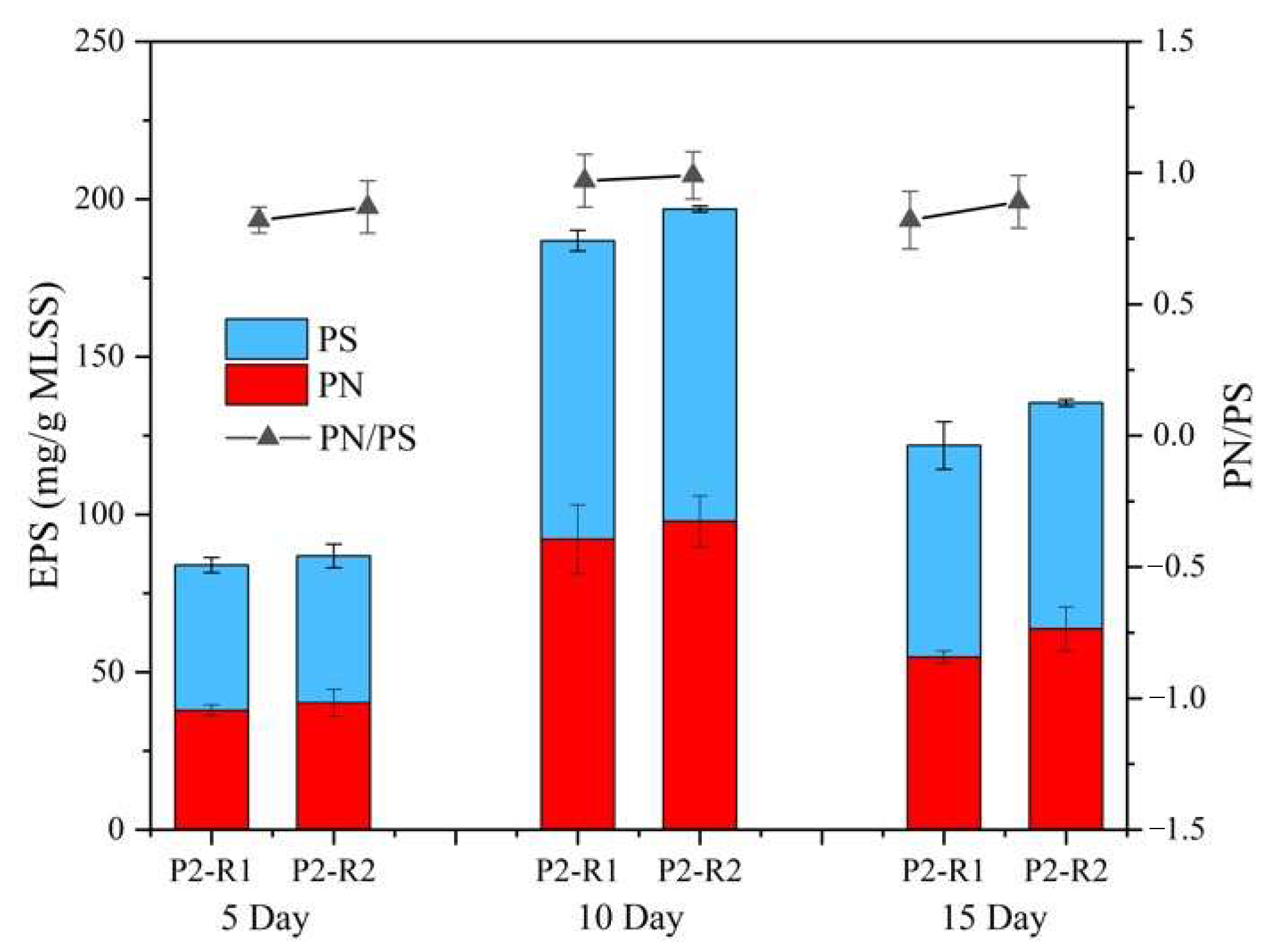
3.2.2. Physicochemical Properties of AGS under Different C/N Ratios
3.2.3. Overall Performances during the Granulation Period under Different C/N Ratios
3.3. Recyclability Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hussain, S.; Ferrentino, R.; Khan, K.; Ali, Z.; Yousuf, M.; Andreottola, G. Rapid startup of aerobic granular sludge: Recent advances and future challenges. Results Eng. 2024, 22, 102035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Li, J.; Qu, X.; Ma, H. Advances in continuous flow aerobic granular sludge: A review. Process Saf. Environ. 2022, 163, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iorhemen, O.T.; Liu, Y. Effect of feeding strategy and organic loading rate on the formation and stability of aerobic granular sludge. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 39, 101709–101719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarvajith, M.; Nandini, D.; Nancharaiah, Y.V. Comparative evaluation of activated sludge and aerobic granular sludge for biological treatment of real domestic wastewater with oxytetracycline dosing. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera, P.; Casero-Díaz, T.; Castro-Barros, C.M.; Méndez, R.; Val del Río, A.; Mosquera-Corral, A. Features of aerobic granular sludge formation treating fluctuating industrial saline wastewater at pilot scale. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 296, 113135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.; Gan, C.; Chen, R.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, S.; Chen, Y. Characteristics of aerobic granular sludge and factors that influence its stability: A mini review. Water 2021, 13, 2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, D.; Yang, R.; Wang, J.; Duan, Y.; Gao, M.; Wang, J.; Zhang, A.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z. Changes and stage disparity of aerobic sludge granulation with increasing organic load rate under low organotrophic conditions. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 450, 141937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Costa, R.; Ghobril, C.; Perrin, R.; Sanson, N. Adsorption of sodium alginate on calcium carbonate microparticles: Effect of molar mass and composition. Colloids Surface A 2024, 682, 132782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Guo, C.; Hao, J.; Zhao, Z.; Long, H.; Li, M. Adsorption of heavy metal ions by sodium alginate based adsorbent—A review and new perspectives. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 4423–4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díez-García, I.; Lemma, M.R.D.C.; Barud, H.S.; Eceiza, A.; Tercjak, A. Hydrogels based on waterborne poly(urethane-urea)s by physically cross-linking with sodium alginate and calcium chloride. Carbohyd. Polym. 2020, 250, 116940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wan, Y.S.; Zheng, Y.L.; Lee, X.Q.; Liu, T.Z.; Yu, Z.B.; Huang, J.; Ok, Y.S.; Chen, J.J.; Gao, B. Alginate-based composites for environmental applications: A critical review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 318–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Covarrubias, S.A.; De-Bashan, L.E.; Moreno, M.; Bashan, Y. Alginate beads provide a beneficial physical barrier against native microorganisms in wastewater treated with immobilized bacteria and microalgae. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 93, 2669–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Chen, R.; Wu, Q.; Ren, B.; Li, C. Addition of sodium alginate as a nucleus shortens granulation of aerobic sludge. Environ. Sci.-Water Res. Technol. 2022, 8, 2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moy, B.Y.; Tay, J.H.; Toh, S.K.; Liu, Y.; Tay, S.T. High organic loading influences the physical characteristics of aerobic sludge granules. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 34, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corsino, S.F.; Trapani, D.D.; Torregrossa, M.; Viviani, G. Aerobic granular sludge treating high strength citrus wastewater: Analysis of pH and organic loading rate effect on kinetics, performance and stability. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 214, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Li, Z.; Wan, C.; Zhang, Y. Filamentous aerobic granular sludge: A critical review on its cause, impact, control and reuse. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adav, S.S.; Lee, D.J.; Lai, J.Y. Potential cause of aerobic granular sludge breakdown at high organic loading rates. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 1601–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.M.; Yu, H.Q.; Liu, S.J.; Liu, X.Z. Formation and instability of aerobic granules under high organic loading conditions. Chemosphere 2006, 63, 1791–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Yu, Z.; Dong, J.; Wang, Z.; Ma, K. Stability of aerobic granular sludge under condition of low influent C/N ratio: Correlation of sludge property and functional microorganism. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 270, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Guo, W.; Liang, D.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Li, P.; Wu, Y.; Bian, X.; Ding, F. Rapid start-up and advanced nutrient removal of simultaneous nitrification, endogenous denitrification and phosphorus removal aerobic granular sequence batch reactor for treating low C/N domestic wastewater. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Antwi, P.; Deng, K.; Wang, C.; Buelna, G. Nitrogen removal from low COD/TN ratio manure-free piggery wastewater within an upflow microaerobic sludge reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 198, 884–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Hao, T.; Wei, L.; Mackey, H.R.; Lin, Z.; Chen, G.H. Impact of influent COD/N ratio on disintegration of aerobic granular sludge. Water Res. 2014, 62, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarv Aj Ith, M.; Reddy, G.; Nancharaiah, Y.V. Aerobic granular sludge for high-strength ammonium wastewater treatment: Effect of COD/N ratios, long-term stability and nitrogen removal pathways. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 306, 123150–123160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Xue, T.; Li, B.; Dai, X.; Peng, Y. Treating low carbon/nitrogen (C/N) wastewater in simultaneous nitrification-endogenous denitrification and phosphorous removal (SNDPR) systems by strengthening anaerobic intracellular carbon storage. Water Res. 2015, 77, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derlon, N.; Wagner, J.; da Costa, R.H.R.; Morgenroth, E. Formation of aerobic granules for the treatment of real and low-strength municipal wastewater using a sequencing batch reactor operated at constant volume. Water Res. 2016, 105, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Peng, Y.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, S.; Liu, C.; Zhang, L. A novel two-stage aerobic granular sludge system for simultaneous nutrient removal from municipal wastewater with low C/N ratios. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 462, 142318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Deng, K.; Li, J.; Liu, M.; Meng, J. Nitrogen removal and bacterial mechanism in a hybrid anoxic/oxic baffled reactor affected by shortening HRT in treating manure-free piggery wastewater. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2021, 163, 105284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Li, J.; Fan, Y.; Li, J.; Meng, J. Performance and nitrogen removal mechanism in a novel aerobic-microaerobic combined process treating manure-free piggery wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 345, 126494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H. The Two-Stage Anaerobic Digestion—Subsurface Flow Wetland Process for the Courtyard Sewage Treatment in South Hilly Area; Chinese Research Academy of Environmental Sciences: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sajjad, M.; Kim, K.S. Studies on the interactions of Ca2+ and Mg2+ with EPS and their role in determining the physicochemical characteristics of granular sludges in SBR system. Process Biochem. 2015, 50, 966–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Qiu, J.; Xiang, R.; Yu, H.; Xu, X.; Zhu, L. Organic loading rate (OLR) regulation for enhancement of aerobic sludge granulation: Role of key microorganism and their function. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 653, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Ye, L.; Ren, H.; Zhang, X. Microbial community structure and function in aerobic granular sludge. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 3967–3979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Yu, W.; Zhang, C. Granulation process and mechanism of aerobic granular sludge under salt stress in a sequencing batch reactor. Tecnol. Cienc. Agua 2019, 10, 156–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, M.; Val del Río, A.; Campos, J.L.; Méndez, R.; Mosquera-Corral, A. Filamentous bacteria existence in aerobic granular reactors. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2015, 38, 841–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, B.; Xuan, X.; Yang, C.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, J. Stability of aerobic granular sludge in a pilot scale sequencing batch reactor enhanced by granular particle size control. Chemosphere 2019, 225, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, B.; Yang, C.Z.; Pu, W.H.; Yang, J.K.; Liu, F.B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, K. Tolerance to organic loading rate by aerobic granular sludge in a cyclic aerobic granular reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 182, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Show, K.Y.; Lee, D.J.; Tay, J.H. Aerobic Granulation: Advances and Challenges. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 167, 1622–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Yu, P.; Li, Q.; Ren, H.; Liu, B.; Ye, L.; Zhang, X.-X. Transformation of anaerobic granules into aerobic granules and the succession of bacterial community. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 7703–7713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Shen, L.; Chen, F. DO diffusion profile in aerobic granule and its microbiological implications. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2008, 43, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verawaty, M.; Tait, S.; Pijuan, M.; Yuan, Z.; Bond, P.L. Breakage and growth towards a stable aerobic granule size during the treatment of wastewater. Water Res. 2013, 47, 5338–5349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Lv, M.; Dai, X.; Yu, Y.; Qi, H.; Xu, X. Role and significance of extracellular polymeric substances on the property of aerobic granule. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 107, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Fang, F.; Yan, P.; Liu, Z. Effect of different forms and components of EPS on sludge aggregation during granulation process of aerobic granular sludge. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 135116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Huang, X.; Fang, F.; Guo, J.; Yan, P. Effect of EPS and its forms of aerobic granular sludge on sludge aggregation performance during granulation process based on XDLVO theory. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 795, 148682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seviour, T.; Yuan, Z.; Loosdrecht, M.; Lin, Y. Aerobic sludge granulation: A tale of two polysaccharides? Water Res. 2012, 46, 4803–4813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wei, D.; Xu, W.; Feng, R.; Wei, Q. Nitrogen removal in a combined aerobic granular sludge and solid-phase biological denitrification system: System evaluation and community structure. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 288, 121504–121511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassin, J.P.; Kleerebezem, R.; Dezotti, M.; Van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Measuring biomass specific ammonium, nitrite and phosphate uptake rates in aerobic granular sludge. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 1161–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassin, J.P.; Tavares, D.C.; Borges, R.C.; Dezotti, M. Development of aerobic granular sludge under tropical climate conditions: The key role of inoculum adaptation under reduced sludge washout for stable granulation. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 230, 168–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coma, M.; Verawaty, M.; Pijuan, M.; Yuan, Z.; Bond, P.L. Enhancing aerobic granulation for biological nutrient removal from domestic wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 103, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, X.; Qin, J. Rapid start-up of partial nitritation in aerobic granular sludge bioreactor and the analysis of bacterial community dynamics. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2019, 42, 1973–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mlinar, S.; Weig, A.R.; Freitag, R. Influence of NH3 and NH4+ on anaerobic digestion and microbial population structure at increasing total ammonia nitrogen concentrations. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 361, 127638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.H.; Zhang, Z.M.; Zhao, H.; Yu, H.T.; Alvarez, P.; Xu, X.Y.; Zhu, L. Optimizing granules size distribution for aerobic granular sludge stability: Effect of a novel funnel-shaped internals on hydraulic shear stress. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 216, 562–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gül, G.A.; Ferhan, Ç. Production of protein- and carbohydrate-EPS in activated sludge reactors operated at different carbon to nitrogen ratios. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2016, 91, 522–531. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhou, S.; Fan, J.; Chen, Y. Large-scale (500 kg N/day) two-stage partial nitritation/anammox (PN/A) process for liquid-ammonia mercerization wastewater treatment: Rapid start-up and long-term operational performance. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 326, 116404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, G.; Zhu, Y.; Saeed, T.; Zhang, G.; Lu, X. Nitrogen removal and microbial community profiles in six wetland columns receiving high ammonia load. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 203, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Chen, L.; Zhang, S.; Chen, R.; Wang, H. Hydrodynamic shear force shaped the microbial community and function in the aerobic granular sequencing batch reactors for low carbon to nitrogen (C/N) municipal wastewater treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 271, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| Ingredients | Concentration (mg/L) | |
|---|---|---|
| P1 | P2 | |
| C6H12O6 | 600–4800 | 1000 |
| NH4Cl | 250 | 154–385 |
| KH2PO4 | 50 | 50 |
| NaHCO3 | 750 | 450–1150 |
| CaCl2 | 111 | 111 |
| MgSO4 | 260 | 260 |
| EDTA | 21 | 21 |
| Yeast | 100 | 100 |
| ZnSO4∙7H2O | 0.12 | 0.12 |
| H3BO3 | 0.11 | 0.11 |
| CuSO4∙5H2O | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| MnCl2∙4H2O | 0.12 | 0.12 |
| CoCl2 | 0.17 | 0.17 |
| H8MoN2O4 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| FeSO4∙7H2O | 0.16 | 0.16 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gan, C.; Cheng, Q.; Chen, R.; Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, C.; Xu, S.; Chen, Y. Rapid Formation and Performance of Aerobic Granular Sludge Driven by a Sodium Alginate Nucleus under Different Organic Loading Rates and C/N Ratios. Water 2024, 16, 1336. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16101336
Gan C, Cheng Q, Chen R, Chen X, Chen Y, Wu Y, Li C, Xu S, Chen Y. Rapid Formation and Performance of Aerobic Granular Sludge Driven by a Sodium Alginate Nucleus under Different Organic Loading Rates and C/N Ratios. Water. 2024; 16(10):1336. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16101336
Chicago/Turabian StyleGan, Chunjuan, Qiming Cheng, Renyu Chen, Xi Chen, Ying Chen, Yizhou Wu, Cong Li, Shanchuan Xu, and Yao Chen. 2024. "Rapid Formation and Performance of Aerobic Granular Sludge Driven by a Sodium Alginate Nucleus under Different Organic Loading Rates and C/N Ratios" Water 16, no. 10: 1336. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16101336
APA StyleGan, C., Cheng, Q., Chen, R., Chen, X., Chen, Y., Wu, Y., Li, C., Xu, S., & Chen, Y. (2024). Rapid Formation and Performance of Aerobic Granular Sludge Driven by a Sodium Alginate Nucleus under Different Organic Loading Rates and C/N Ratios. Water, 16(10), 1336. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16101336








