Rapid Removal of Cr(VI) from Wastewater by Surface Ionized Iron-Based MOF: Ion Branching and Domain-Limiting Effects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Preparation
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Adsorbent Preparation
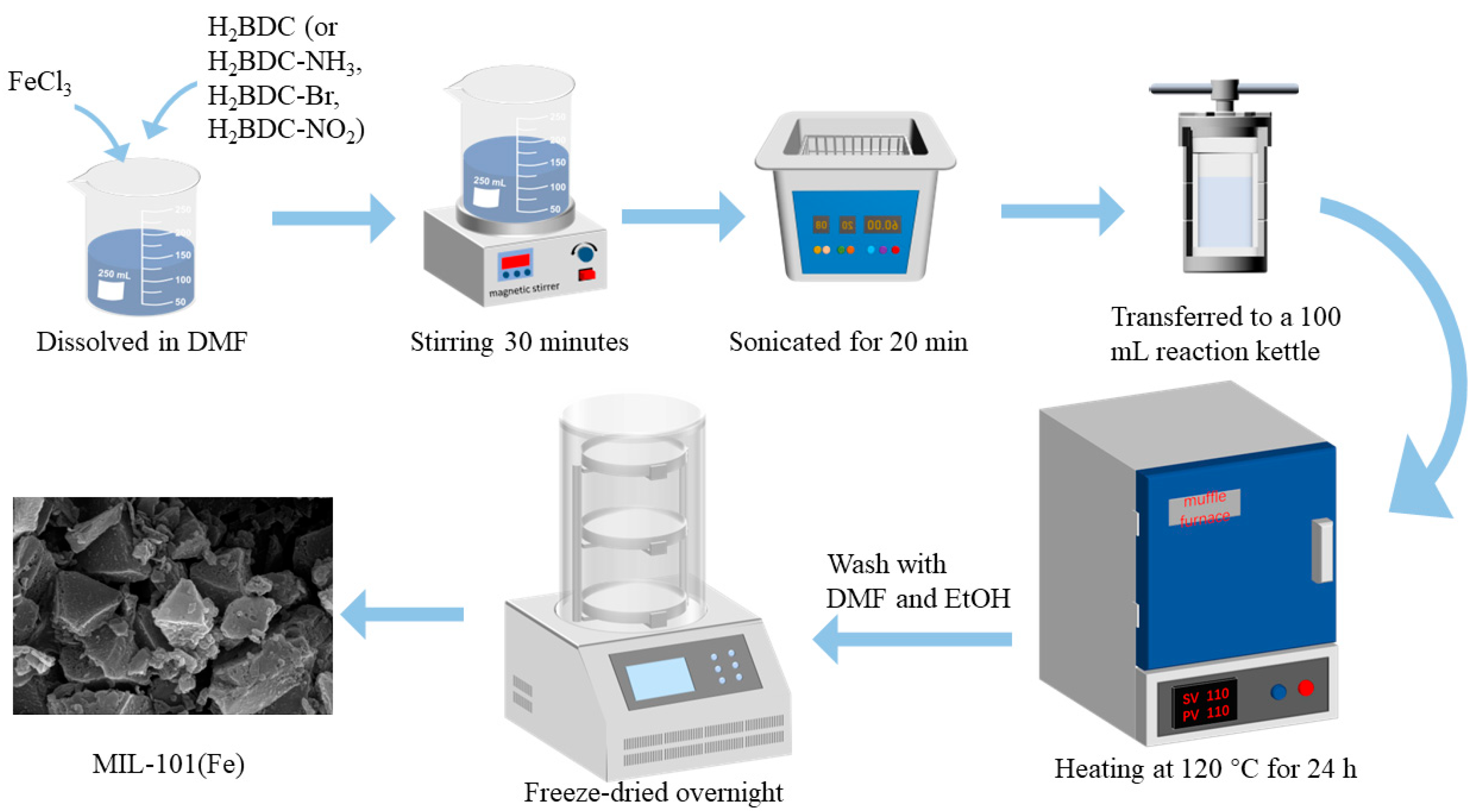
2.2.1. MIL-101 Preparation
2.2.2. Group Modification
2.2.3. CNT@MIL-101 Preparation
2.3. Reaction Conditions and Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
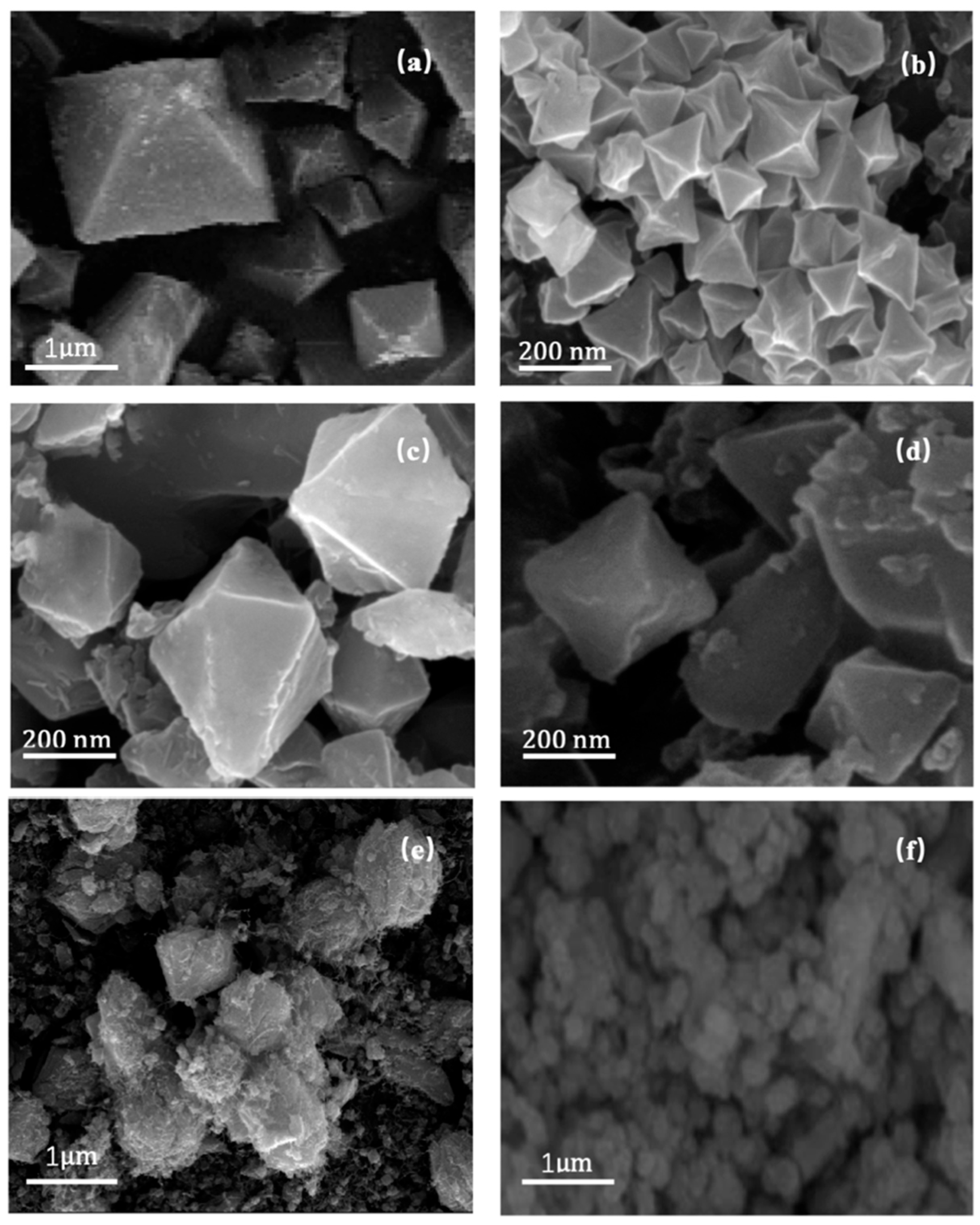
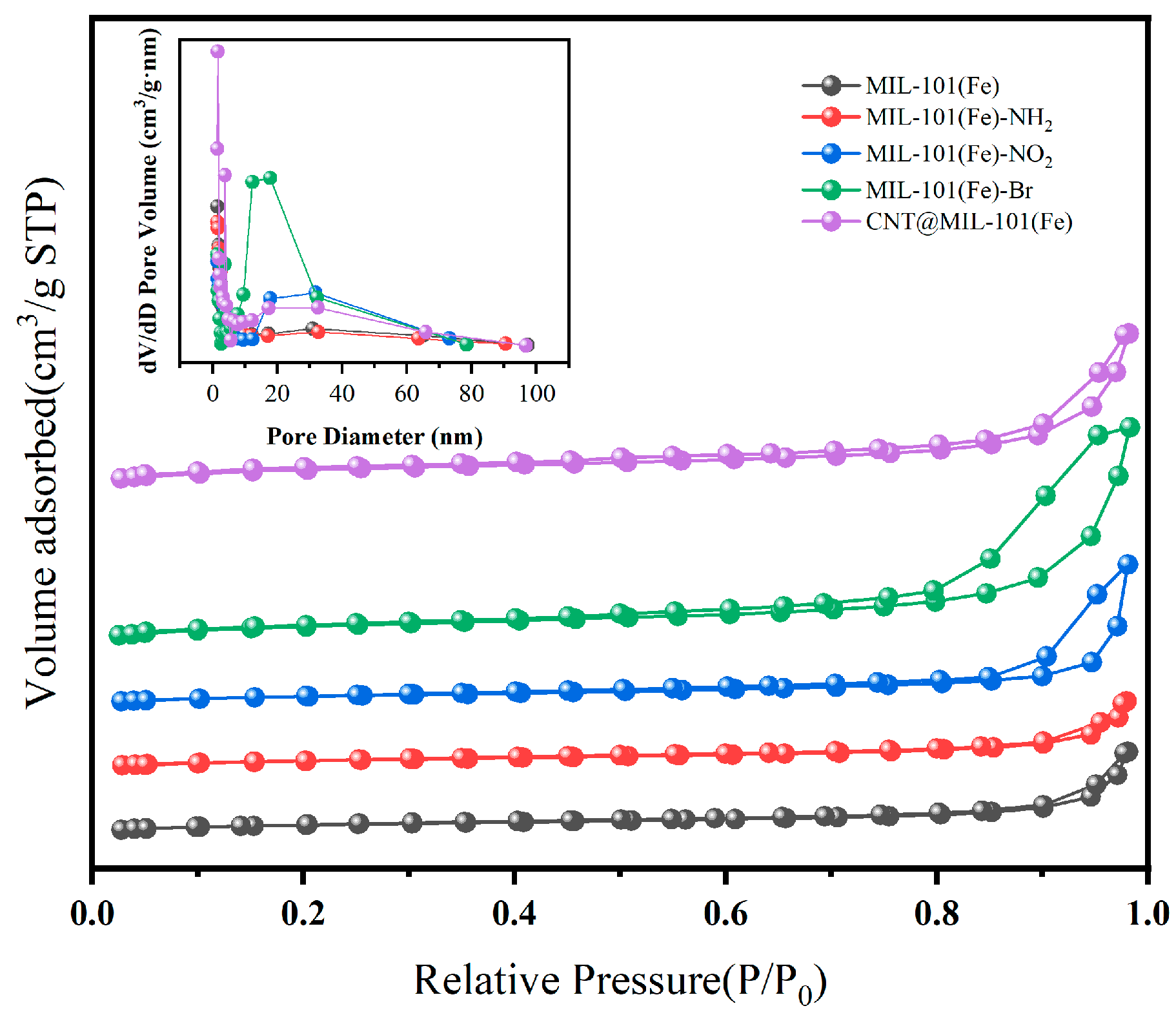
3.1. Characterization
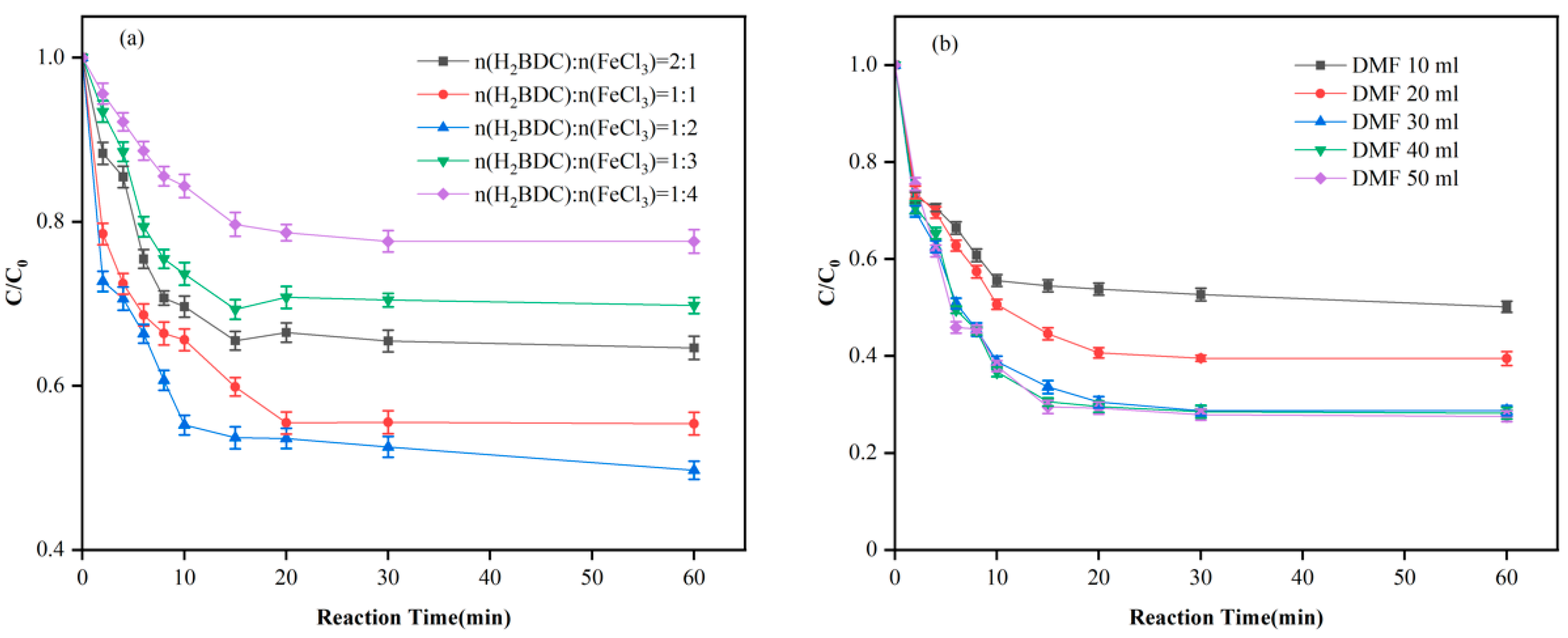
3.2. MIL-101 Preparation, Modulation, and Modification
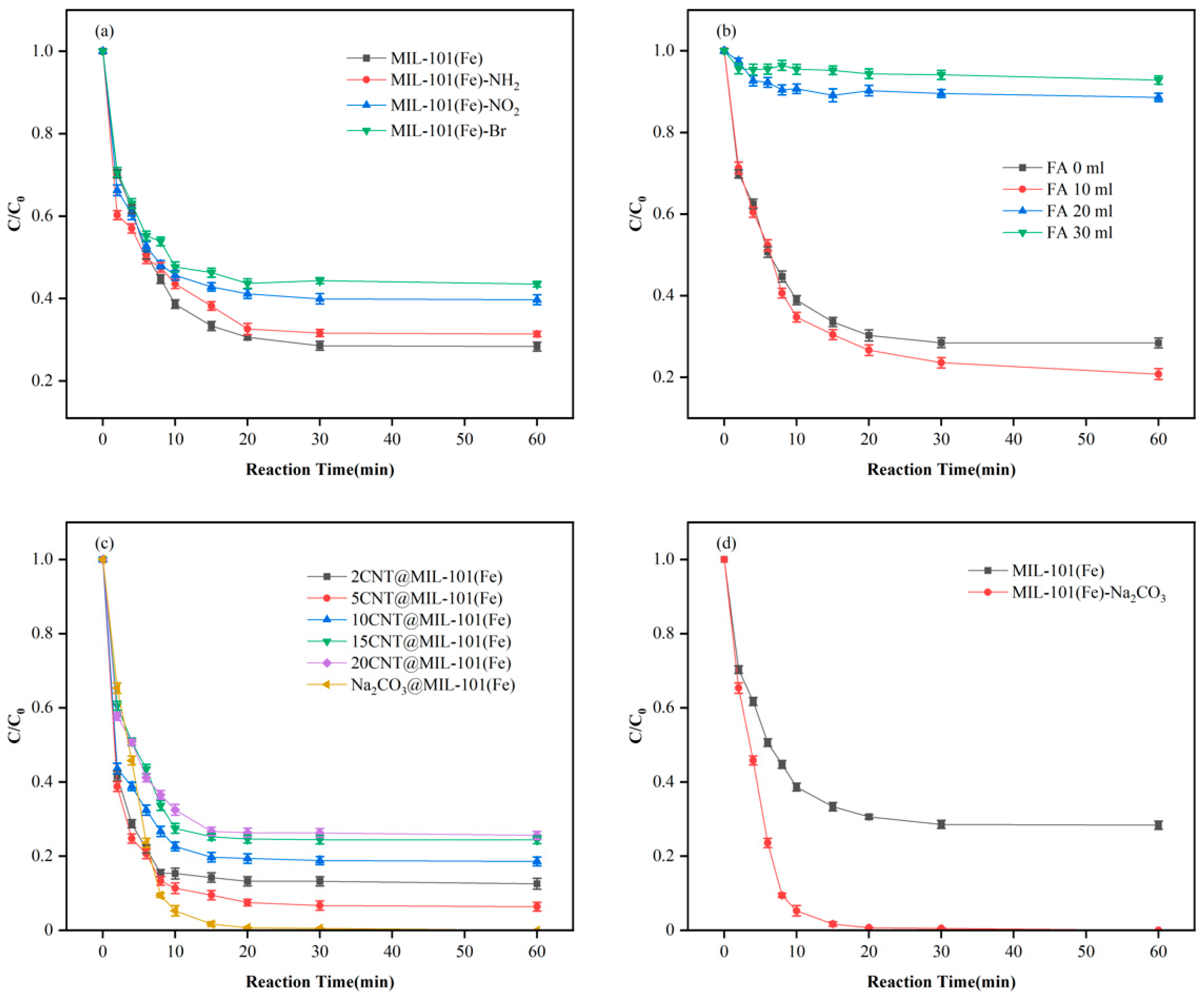
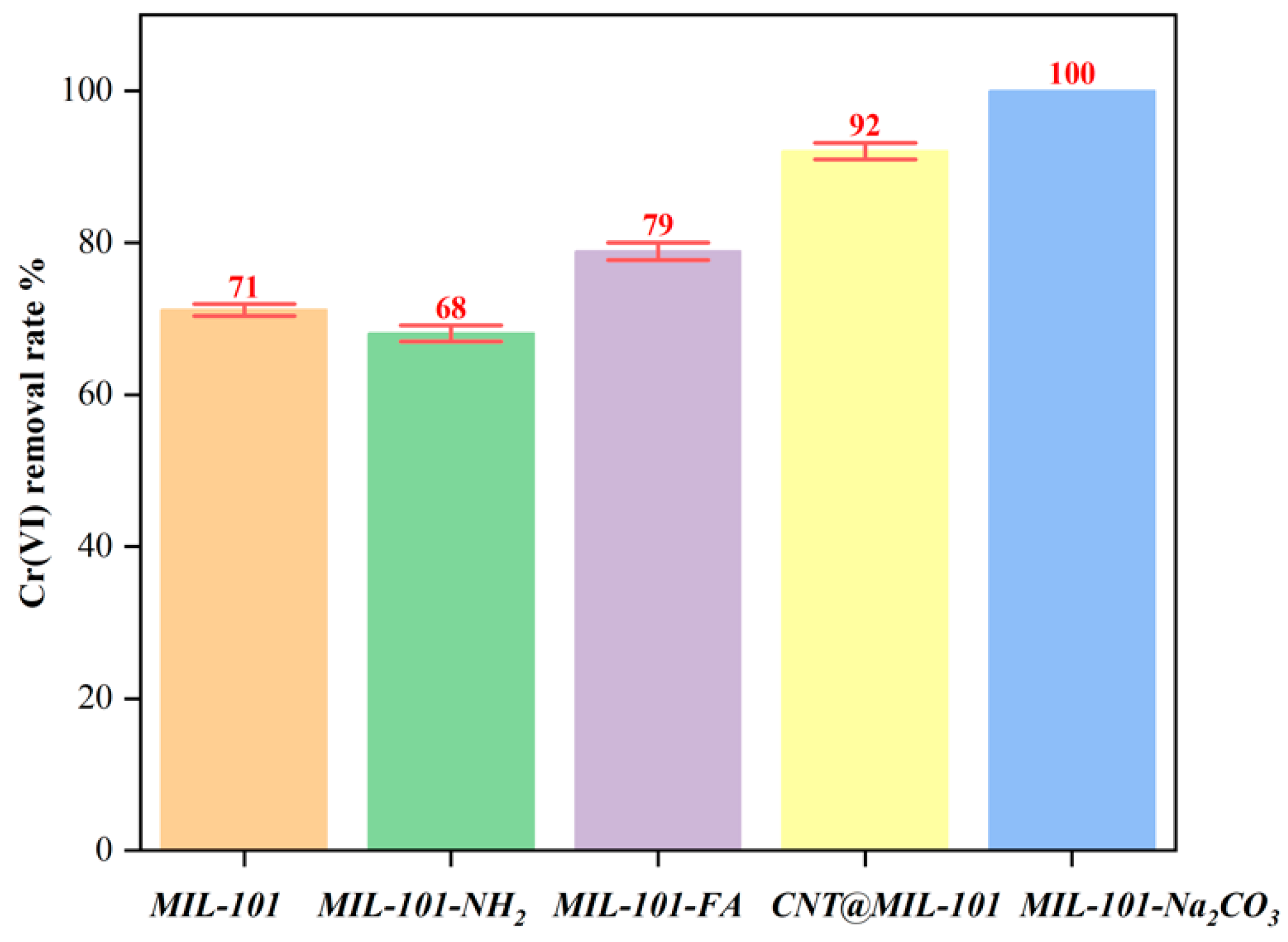
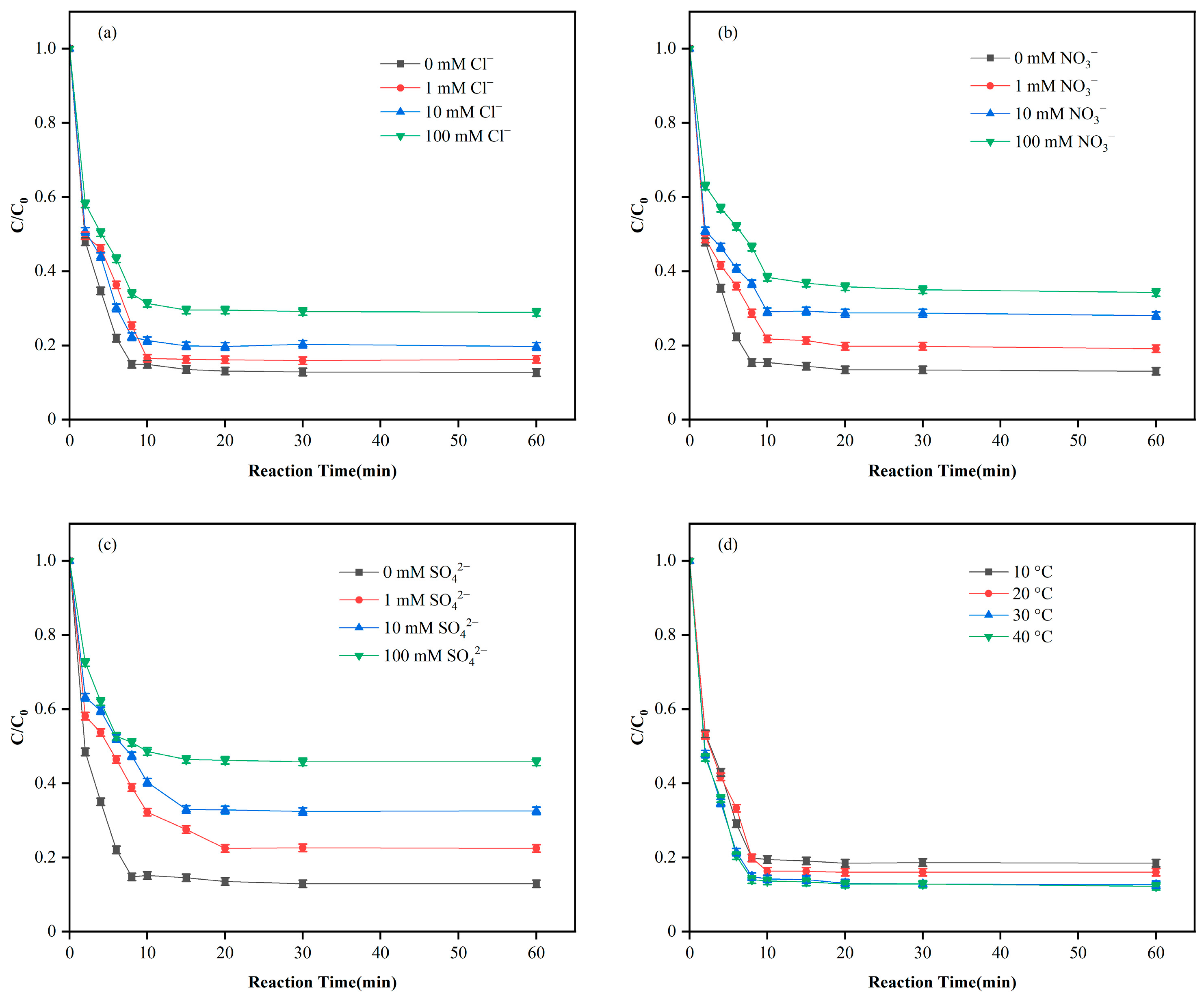
3.3. Adsorption Performance Study
3.4. Adsorption Kinetics and Isotherms
3.5. Thermodynamics and Recycling
3.6. Mechanistic Analysis
4. Conclusions
- While the modified MIL-101(Fe)–Na2CO3 material has good prospects, its stability needs to be improved, and the preparation method needs to be improved in future work to find a simpler and more economical experimental preparation method.
- Future work could explore different alloy materials to replace the single metal, reducing the cost of preparing the f materials while providing improved adsorption performance.
- Other carrier materials could be explored in order to find the most effective carrier and further optimize the removal of Cr(VI).
- The significant advantages of metal–organic frameworks can be utilized to broaden the modification methods and improve the adsorption capacity for a variety of heavy metals.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- John, B.C.; Viswambaram, V.A.; Raj, S.S.; Mankunipoyil, S.A. Adsorptive removal of Cr (VI) using mesoporous iron-aluminum oxyhydroxide-polyvinyl alcohol self-supporting film: Kinetics, optimization studies and mechanism. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 34, 105315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheth, Y.; Dharaskar, S.; Khalid, M.; Walvekar, R. Investigating chromium Cr(VI) removal using imidazolium based ionic liquid-chitosan composite adsorptive film. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 347, 118317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawal Usman, U.; Kumar Allam, B.; Bahadur Singh, N.; Banerjee, S. Adsorptive removal of Cr(VI) from wastewater by hexagonal boron nitride-magnetite nanocomposites: Kinetics, mechanism and LCA analysis. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 354, 118833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Gui, Q.; Zhang, A.; Shi, S.; Chen, X. Polyvinylamine-grafted polypropylene membranes for adsorptive removal of Cr(VI) from water. React. Funct. Polym. 2022, 170, 105108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchayanukun, P.; Muncharoen, S. Chitosan coated magnetite nanoparticle as a working electrode for determination of Cr(VI) using square wave adsorptive cathodic stripping voltammetry. Talanta 2020, 217, 121027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharya, R.; Lenka, A.; Parida, K. Magnetite modified amino group based polymer nanocomposites towards efficient adsorptive detoxification of aqueous Cr (VI): A review. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 337, 116487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Kaim Billah, R.; Shekhawat, A.; Mansouri, S.; Majdoubi, H.; Agunaou, M.; Soufiane, A.; Jugade, R. Adsorptive removal of Cr(VI) by Chitosan-SiO2-TiO2 nanocomposite. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2022, 18, 100695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korde, S.; Tandekar, S.; Jeyaseelan, C.; Saravanan, D.; Jugade, R. Mesoporous magnetic Chitosan-Zirconia-Iron oxide nanocomposite for adsorptive removal of Cr(VI) ions. Mater. Lett. 2022, 311, 131513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omer, A.M.; Abd El-Monaem, E.M.; Abd El-Latif, M.M.; El-Subruiti, G.M.; Eltaweil, A.S. Facile fabrication of novel magnetic ZIF-67 MOF@aminated chitosan composite beads for the adsorptive removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 265, 118084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doagoo, F.; Peyravi, M.; Khalili, S. Photo-degradation and discoloration of nitrogen substituted ZnO via multilayer adsorptive membrane for Cr(VI) removal. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Liu, C.; Chen, K. Removal of Cr(VI) species from water with a newly-designed adsorptive treatment train. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 234, 116041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.P.; Liu, S.Y.; Huang, C.; Li, X.X.; Chen, L.; Li, L.; Zhu, J. Effect of amylose/amylopectin ratio of esterified starch-based films on inhibition of plasticizer migration during microwave heating. Food Control 2017, 82, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, L.; Jun, B.-M.; Jang, M.; Park, C.M.; Muñoz-Senmache, J.C.; Hernández-Maldonado, A.J.; Heyden, A.; Yu, M.; Yoon, Y. Removal of contaminants of emerging concern by metal-organic framework nanoadsorbents: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 369, 928–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amenaghawon, A.N.; Anyalewechi, C.L.; Osazuwa, O.U.; Elimian, E.A.; Eshiemogie, S.O.; Oyefolu, P.K.; Kusuma, H.S. A comprehensive review of recent advances in the synthesis and application of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) for the adsorptive sequestration of pollutants from wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 311, 123246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Kosari, M.; Jing, M.; He, C. Microwave-assisted synthesis of bimetallic NiCo-MOF-74 with enhanced open metal site for efficient CO2 capture. Environ. Funct. Mater. 2023, 1, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.-P.; Pan, M.-M.; Jiang, M.; Yu, X.; Xu, L. Facile synthesis of self-assembled three-dimensional flower-like Cu-MOF and its pyrolytic derivative Cu-N-C450 for diverse applications. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, B.; Kamboj, A.; Virender; Singh, K.; Priyanka; Singh, G.; Pombeiro, A.J.L.; Ren, P. Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) materials for pesticides, heavy metals, and drugs removal: Environmental safety. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 310, 123175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Liu, C.; Shen, P.; Liu, Z.; Hu, J.; Shi, F. Facile synthesis of HPW@MOF-199 embedded in SBA-15 functionalized with -COOH groups as a steady catalyst for the esterification reaction. Fuel 2023, 340, 127563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagajyothi, P.C.; Ramaraghavulu, R.; Pavani, K.; Shim, J. Catalytic reduction of methylene blue and rhodamine B using Ce-MOF-derived CeO2 catalyst. Mater. Lett. 2023, 336, 133837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Xing, Y.; Li, C.; Li, T.; Liu, D.; Ernawati, L.; Sunarso, J.; Meng, X. Achieving high-efficiency and broad bandwidth with low filler loading for hierarchical Fe3O4/Co-MOF absorbers. Mater. Res. Bull. 2023, 161, 112171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorgani, L.; Mohammadi, M.; Darzi, G.N.; Raoof, J.B. Electrochemical aptasensor based on bimetallic CuZr-MOF for ultrasensitive detection of miR-21. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 378, 133194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash Tripathy, S.; Acharya, R.; Das, M.; Acharya, R.; Parida, K. Adsorptive remediation of Cr (VI) from aqueous solution using cobalt ferrite: Kinetics and isotherm studies. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 30, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, S.; Ehsani, M.H.; Aghazadeh, M. Direct electrosynthesis of Ni-, Co-, and Ni,Co-MOF onto porous support for high-performance supercapacitors. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 940, 168885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Ge, K.; Wang, J.; Cui, H.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Y. Photocatalytic reduction of CO2 by two-dimensional Zn-MOF-NH2/Cu heterojunctions. Catal. Commun. 2023, 175, 106613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cychosz, K.A.; Matzger, A.J. Water Stability of Microporous Coordination Polymers and the Adsorption of Pharmaceuticals from Water. Langmuir 2010, 26, 17198–17202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, A.; Achari, A.; Eswaramoorthy, M.; Maji, T.K. MOF-aminoclay composites for superior CO2 capture, separation and enhanced catalytic activity in chemical fixation of CO2. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 11378–11381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.H.; Xu, Q.; Jiang, H.L. Metal-organic frameworks meet metal nanoparticles: Synergistic effect for enhanced catalysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 4774–4808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monforte, F.; Falsaperna, M.; Pellegrino, A.L.; Bongiorno, C.; Motta, A.; Mannino, G.; Condorelli, G.G. Direct Growth on Si(100) of Isolated Octahedral Mil-101(Fe) Crystals for the Separation of Aromatic Vapors. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 28836–28845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Yang, M.; Yang, M.; Wang, J.J.; Dong, W.J.; Wang, G. Heterogeneous Fe-MIL-101 catalysts for efficient one-pot four-component coupling synthesis of highly substituted pyrroles. New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 4919–4923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; You, Y.; Hu, X.; Lu, D.; Wen, Q.; Yu, G.; Wang, W.; Xu, T. Preparation of amino-modified carbon quantum dots-ZnO/cellulose nanofiber multifunctional hydrogel: Enhanced adsorption synergistic photoreduction and reversible fluorescence response visual recognition of Cr(VI). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 254, 128068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Dong, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Jia, Q.; Shan, S.; Zhang, Y. A novel magnetic MIL-101(Fe)/TiO2 composite for photo degradation of tetracycline under solar light. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 361, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, D.Y.; Hu, H.; Gao, N.Y.; Ye, J.S.; Ou, H.S. Fabrication of carbon nanotube functionalized MIL-101(Fe) for enhanced visible-light photocatalysis of ciprofloxacin in aqueous solution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 498, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.W.; Lu, Y.F.; Hai, G.T.; Dong, W.J.; Li, R.J.; Liu, J.H.; Wang, G. Bidentate carboxylate linked TiO2 with NH2-MIL-101(Fe) photocatalyst: A conjugation effect platform for high photocatalytic activity under visible light irradiation. Sci. Bull. 2020, 65, 658–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Zhang, H.X.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.J.; Zhuang, L.; Ou, H.S. Enhanced photocatalysis degradation of organophosphorus flame retardant using MIL-101(Fe)/persulfate: Effect of irradiation wavelength and real water matrixes. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 368, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.P.; Liu, Y.P.; Ben Hammouda, S.; Doshi, B.; Guijarro, N.; Min, X.B.; Tang, C.J.; Sillanpaa, M.; Sivula, K.; Wang, S.B. MIL-101(Fe)/g-C3N4 for enhanced visible-light-driven photocatalysis toward simultaneous reduction of Cr(VI) and oxidation of bisphenol A in aqueous media. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 272, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, L.J.; Liu, Y.Q.; Zeng, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.Z. Removal of Berberine from Wastewater by MIL-101(Fe): Performance and Mechanism. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 27962–27971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, P.; Fang, C.; Jiang, R. Phosphate recovery from animal manure wastewater by struvite crystallization and CO2 degasification reactor. Ecol. Chem. Eng. S-Chem. I Inz. Ekol. S 2014, 21, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boontongto, T.; Burakham, R. Evaluation of metal-organic framework NH2-MIL-101(Fe) as an efficient sorbent for dispersive micro-solid phase extraction of phenolic pollutants in environmental water samples. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.L.; Zhang, N.; Chen, D.N.; Ma, D.; Liu, G.G.; Zou, X.G.; Chen, Y.P.; Shu, R.J.; Song, Q.Y.; Lv, W.Y. Facile synthesis of acid-modified UiO-66 to enhance the removal of Cr (VI) from aqueous solutions. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 682, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksimchuk, N.V.; Zalomaeva, O.V.; Skobelev, I.Y.; Kovalenko, K.A.; Fedin, V.P.; Kholdeeva, O.A. Metal-organic frameworks of the MIL-101 family as heterogeneous single-site catalysts. Proc. R. Soc. A-Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2012, 468, 2017–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Jin, W.; Hu, Q.; Zhao, Y. Adsorption behavior of arsenicals on MIL-101(Fe): The role of arsenic chemical structures. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 554, 692–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Li, J.-J.; Wang, C.-C. Adsorptive removal of Cr(VI) from simulated wastewater in MOF BUC-17 ultrafine powder. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 102909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.C.; Ren, X.; Wang, P.; Chang, C. The state of the art review on photocatalytic Cr(VI) reduction over MOFs-based photocatalysts: From batch experiment to continuous operation. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 134949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karbassiyazdi, E.; Kasula, M.; Modak, S.; Pala, J.; Kalantari, M.; Altaee, A.; Esfahani, M.R.; Razmjou, A. A juxtaposed review on adsorptive removal of PFAS by metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) with carbon-based materials, ion exchange resins, and polymer adsorbents. Chemosphere 2023, 311, 136933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qasem, K.M.A.; Khan, S.; Chinnam, S.; Saleh, H.A.M.; Mantasha, I.; Zeeshan, M.; Manea, Y.K.; Shahid, M. Sustainable fabrication of Co-MOF@CNT nano-composite for efficient adsorption and removal of organic dyes and selective sensing of Cr(VI) in aqueous phase. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 291, 126748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Sun, H.; Liu, W.; Yang, W.; Lin, A. Study on removal effect of Cr(VI) and surface reaction mechanisms by bimetallic system in aqueous solution. Environ. Technol. 2020, 41, 1867–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikhaylov, V.I.; Maslennikova, T.P.; Ugolkov, V.L.; Krivoshapkin, P.V. Hydrothermal synthesis, characterization and sorption properties of Al/Fe oxide-oxyhydroxide composite powders. Adv. Powder Technol. 2016, 27, 756–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokati Poursani, A.; Nilchi, A.; Hassani, A.H.; Shariat, M.; Nouri, J. A novel method for synthesis of nano-γ-Al2O3: Study of adsorption behavior of chromium, nickel, cadmium and lead ions. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 2003–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Yu, J.; Jaroniec, M. Template-free synthesis of hierarchical spindle-like γ-Al2O3 materials and their adsorption affinity towards organic and inorganic pollutants in water. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 4587–4594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Jin-Song, Z.; Yan, Z.; Ting-Lin, H.; Qiu-Xun, T. Adsorption of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution by activated alumina and activated carbon. J. Xi’an Univ. Archit. Technol. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2011, 43, 864–868. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, J.; Deng, K.; Cai, W.; Yu, J.; Liu, X.; Zhou, J. Effect of structure-directing agents on facile hydrothermal preparation of hierarchical γ-Al2O3 and their adsorption performance toward Cr(VI) and CO2. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 401, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y. Adsorptive removal of Cr (VI) by Fe-modified activated carbon prepared from Trapa natans husk. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 162, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


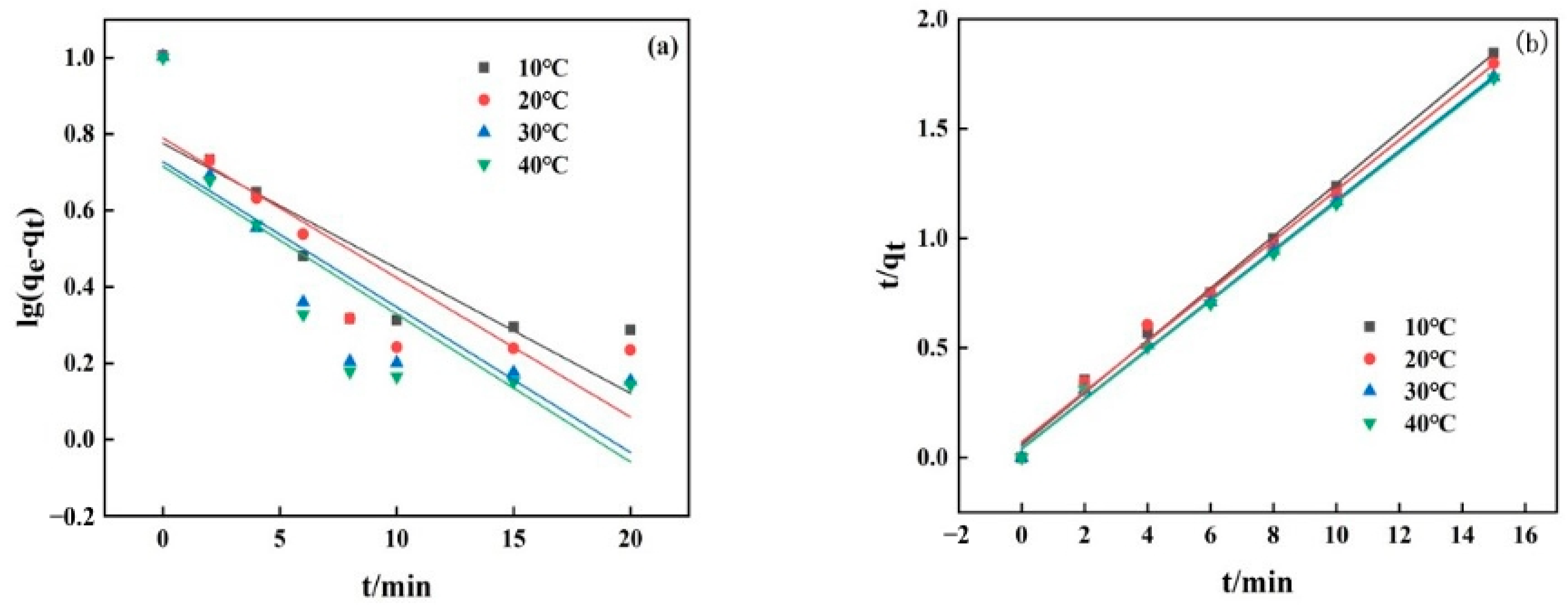


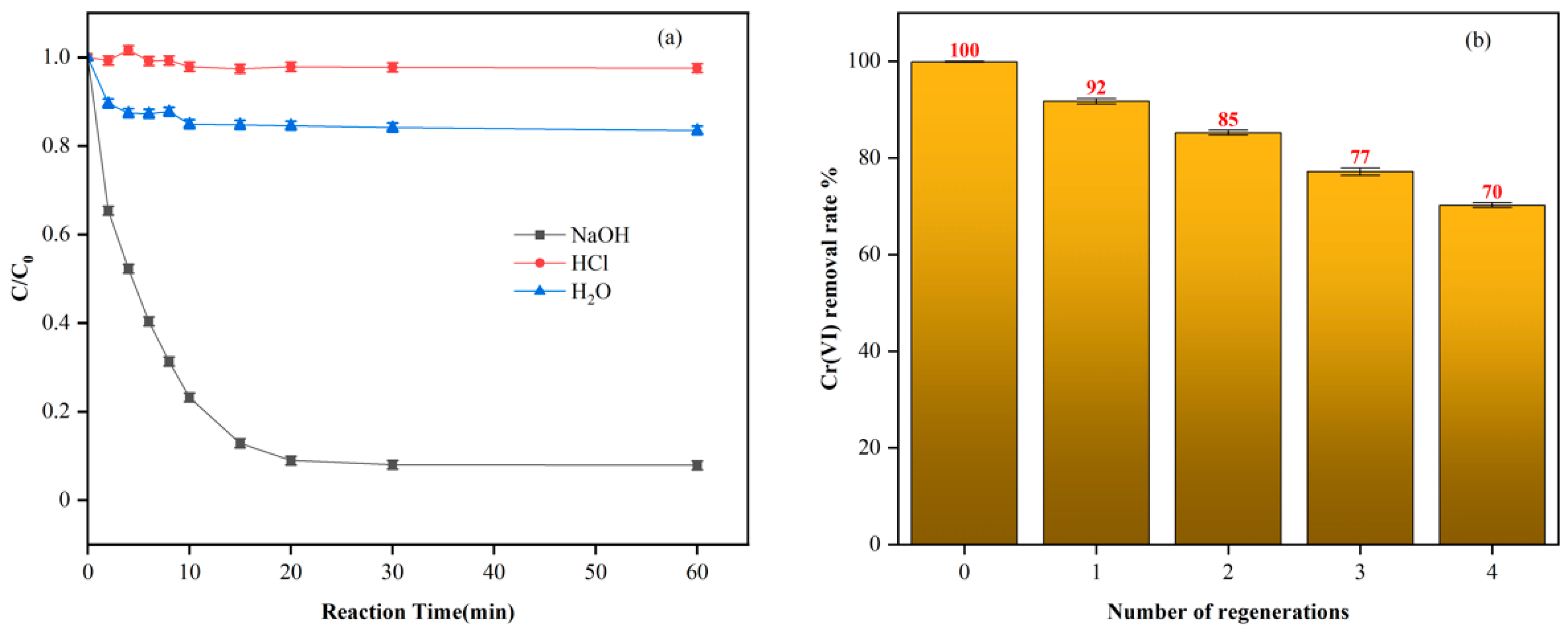
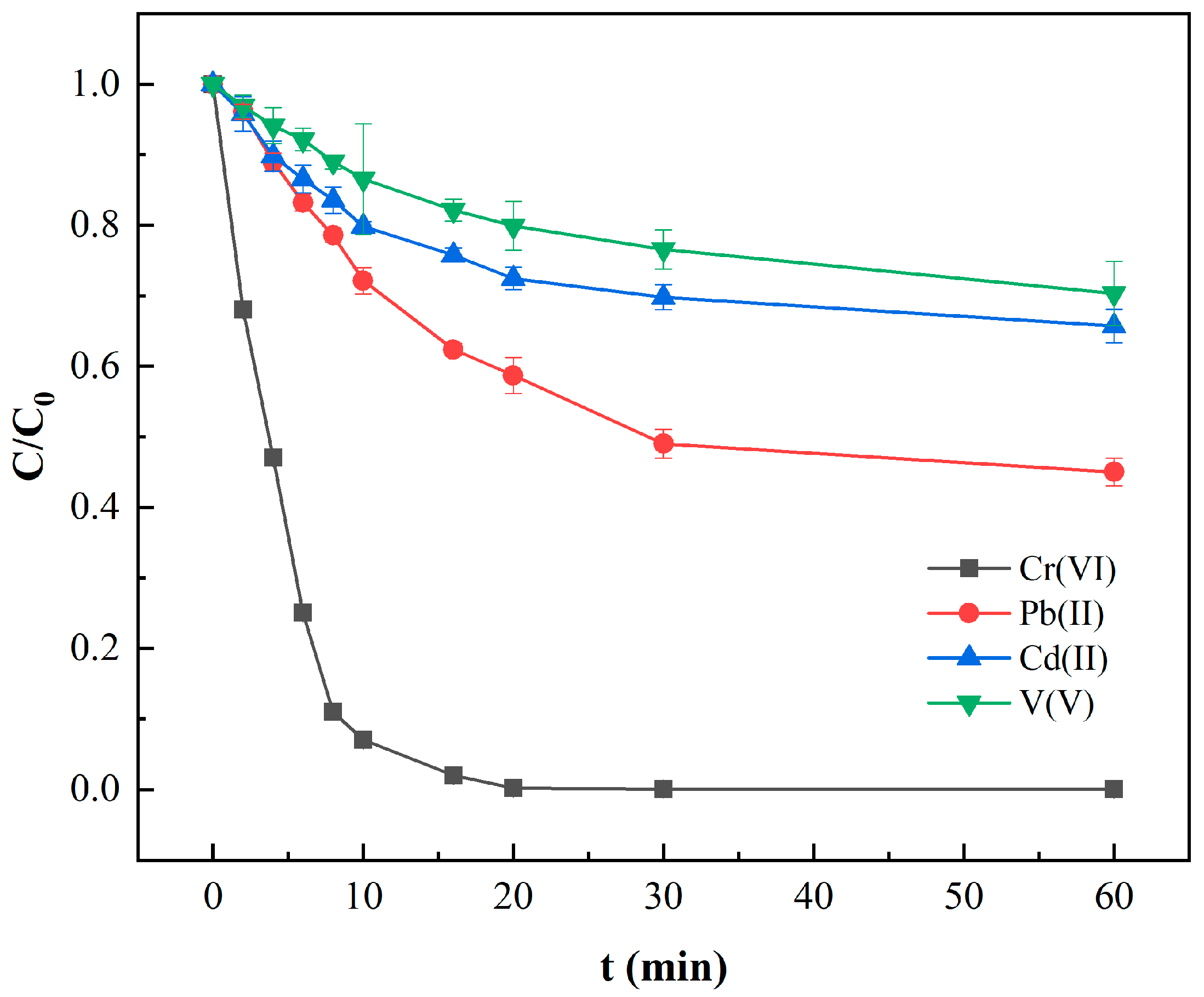
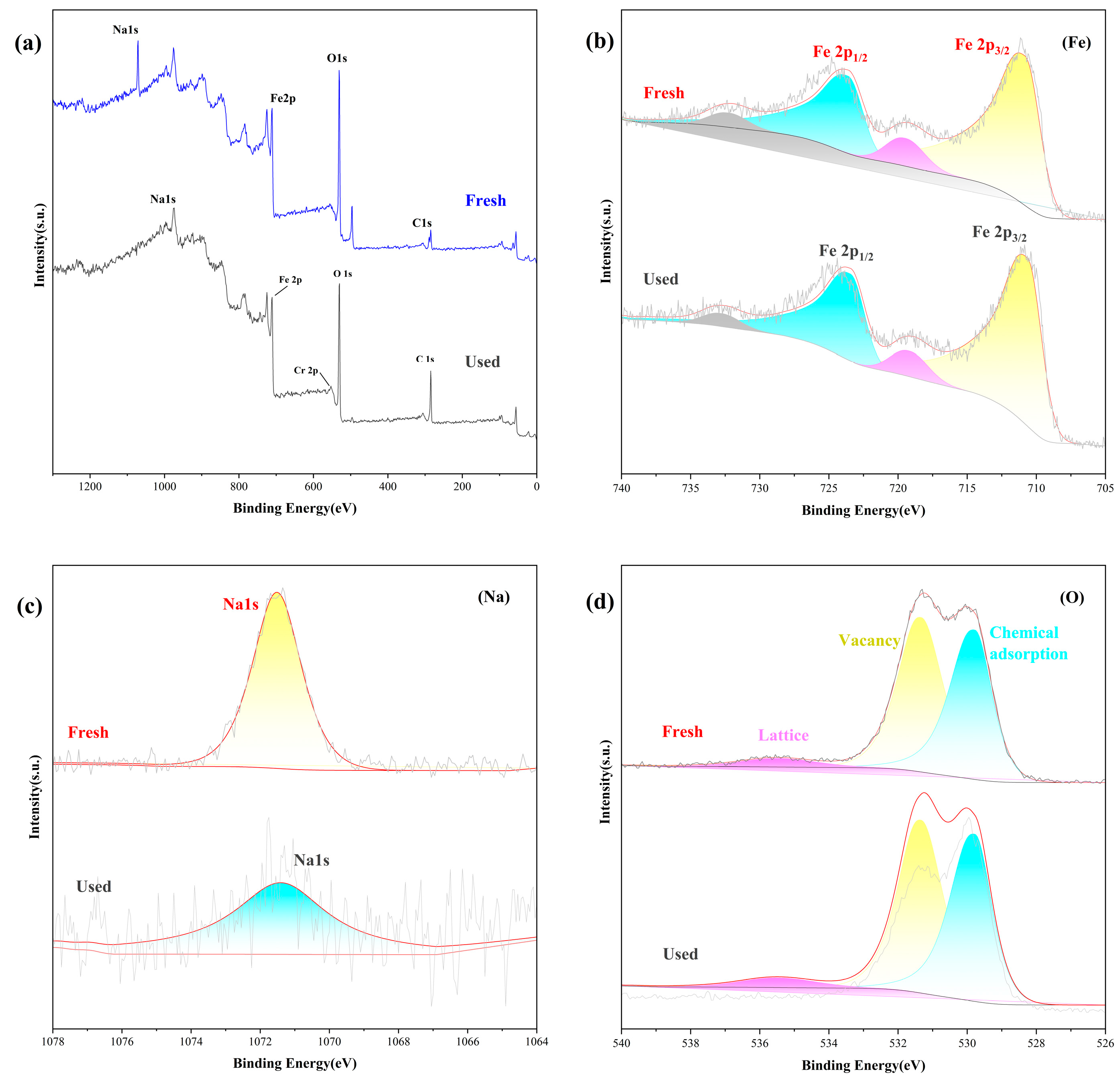
| T (°C) | Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 | qe | R2 | K2 | q2 | R2 | |
| 10 °C | 0.075 | 5.97 | 0.697 | 0.0245 | 8.42 | 0.996 |
| 20 °C | 0.084 | 6.15 | 0.745 | 0.0186 | 8.71 | 0.993 |
| 30 °C | 0.088 | 5.34 | 0.694 | 0.0309 | 8.84 | 0.998 |
| 40 °C | 0.089 | 5.19 | 0.677 | 0.0325 | 8.89 | 0.998 |
| Adsorbent | Experimental Conditions | Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) | References | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C0 (mg Cr/L) | Dose (g/L) | Time (h) | |||
| MIL-101(Fe)-Na2CO3 | 10 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 18.76 | This study |
| α-Fe2O3/γ-Al2O3 | 5 | 1.0 | 1 | 3.83 | [47] |
| Nano-γ-Al2O3 adsorbent | 20 | 4.0 | 4 | 13.3 | [48] |
| γ-Al2O3 | 90 | 0.8 | 6 | 6.70 | [49] |
| Activated alumina | 10 | 10.0 | - | 7.44 | [50] |
| Sphere-like γ-Al2O3 | 30 | 1.6 | 4 | 5.70 | [51] |
| Fe-modified T. natans | 20 | 1.5 | 8 | 11.83 | [52] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Chen, J.; Yang, Q. Rapid Removal of Cr(VI) from Wastewater by Surface Ionized Iron-Based MOF: Ion Branching and Domain-Limiting Effects. Water 2024, 16, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16010025
Wang C, Chen J, Yang Q. Rapid Removal of Cr(VI) from Wastewater by Surface Ionized Iron-Based MOF: Ion Branching and Domain-Limiting Effects. Water. 2024; 16(1):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16010025
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Chen, Jiakun Chen, and Qi Yang. 2024. "Rapid Removal of Cr(VI) from Wastewater by Surface Ionized Iron-Based MOF: Ion Branching and Domain-Limiting Effects" Water 16, no. 1: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16010025
APA StyleWang, C., Chen, J., & Yang, Q. (2024). Rapid Removal of Cr(VI) from Wastewater by Surface Ionized Iron-Based MOF: Ion Branching and Domain-Limiting Effects. Water, 16(1), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16010025









