Sustainability of Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene: From Prehistoric Times to the Present Times and the Future
Abstract
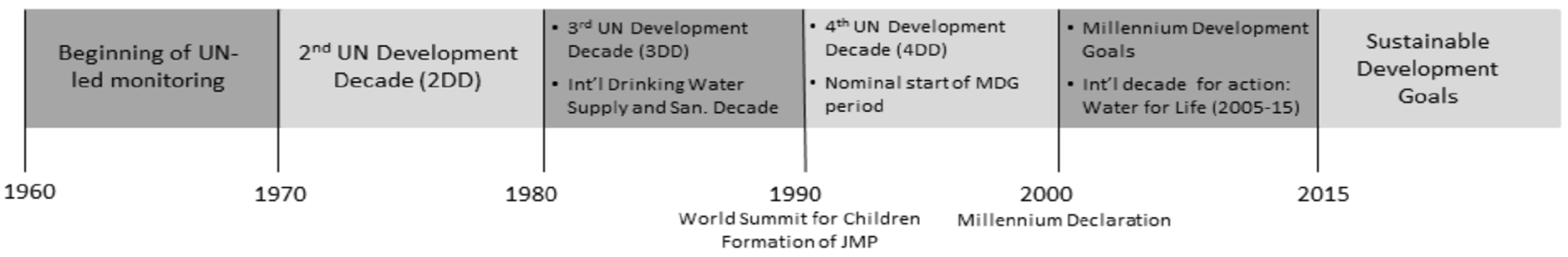
:1. Prolegomena
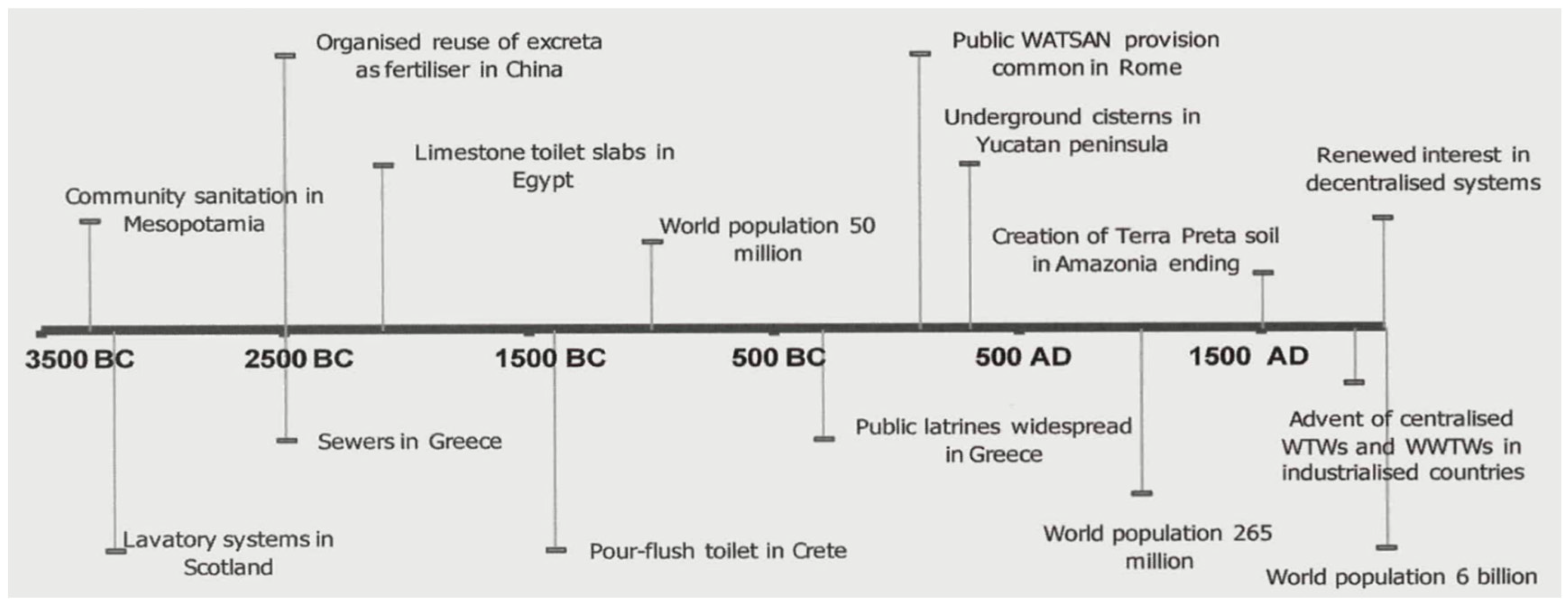
2. WASH: From Prehistoric Era to Medieval Era (ca 7600 BC–1400 AD)
2.1. Prehistoric Period (ca 7600–1100 BC)
2.1.1. Iranian and Other Prehistoric Civilizations (ca 7600–1100 BC)
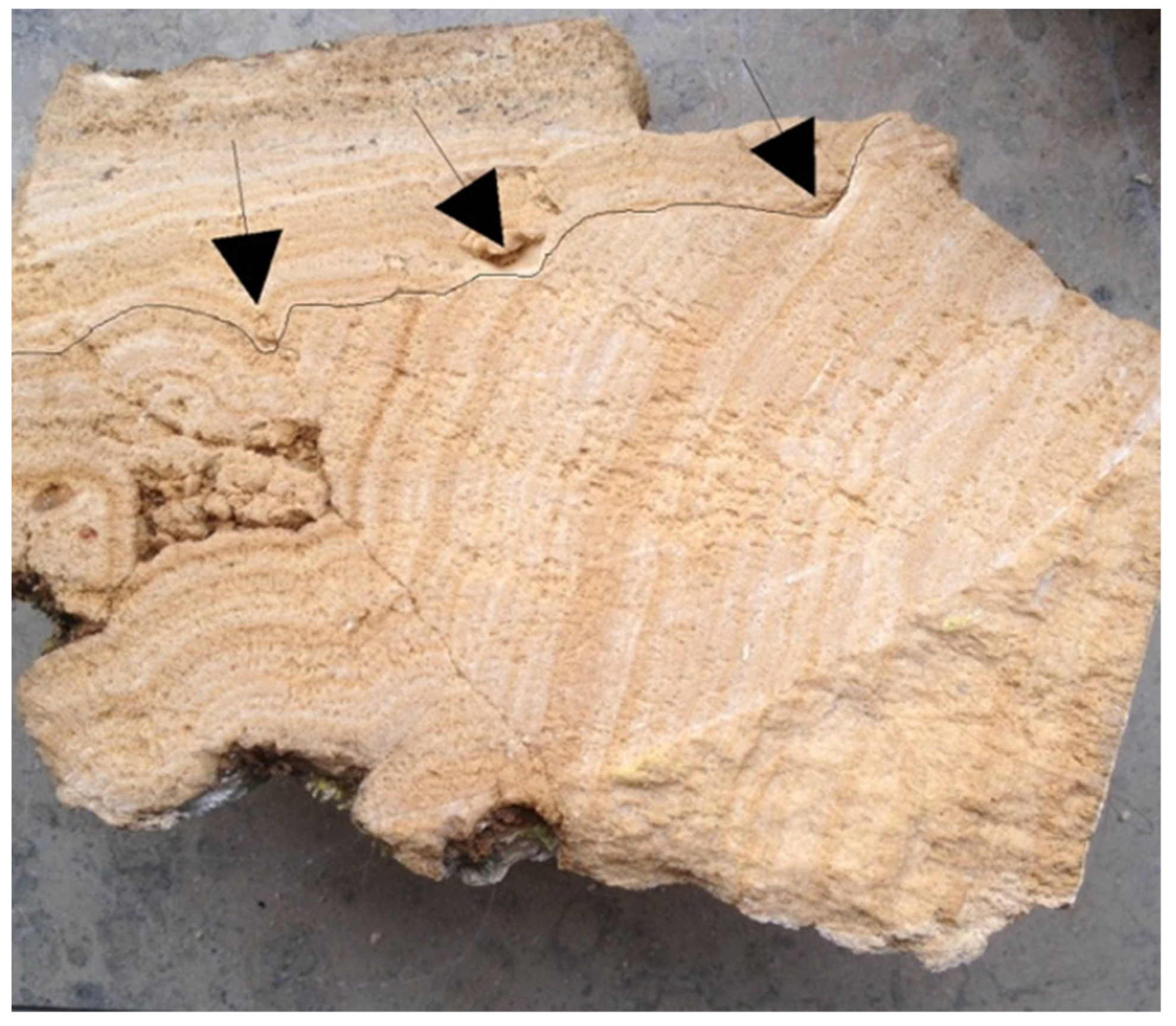
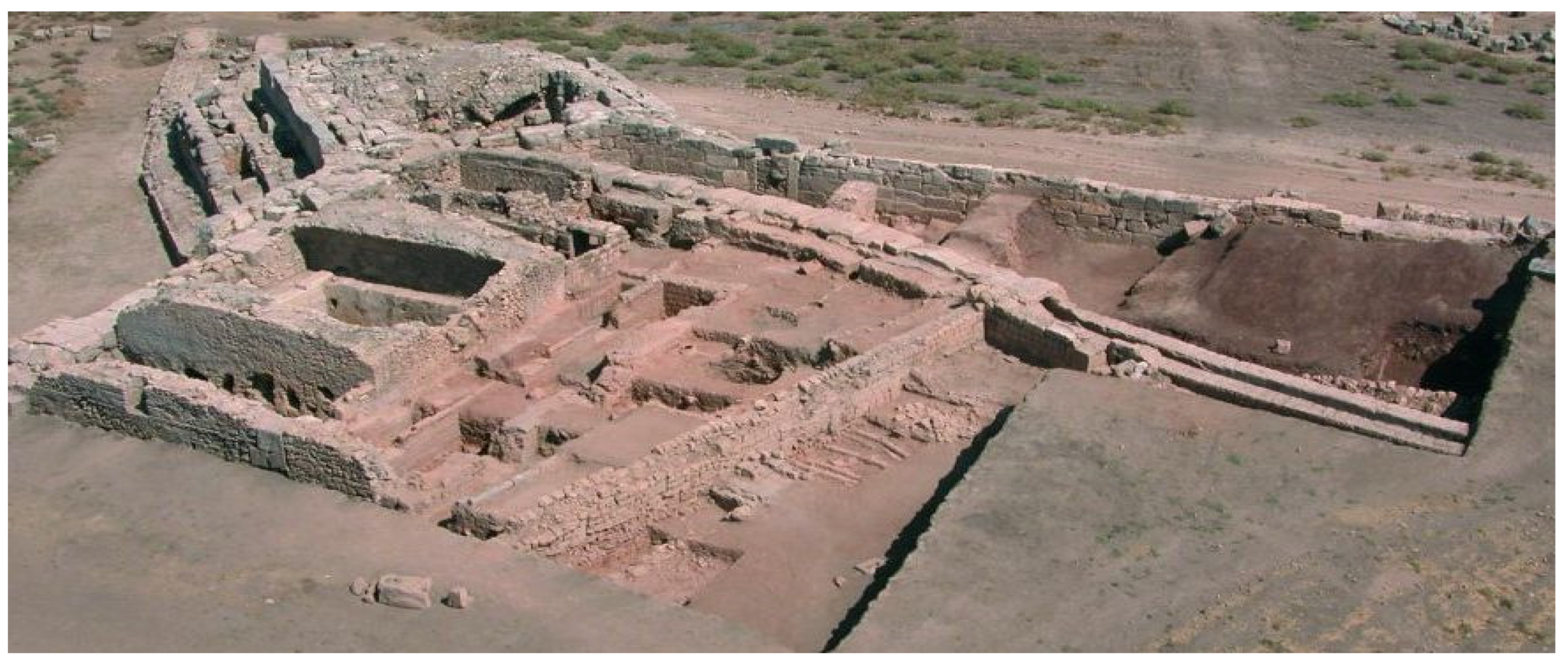
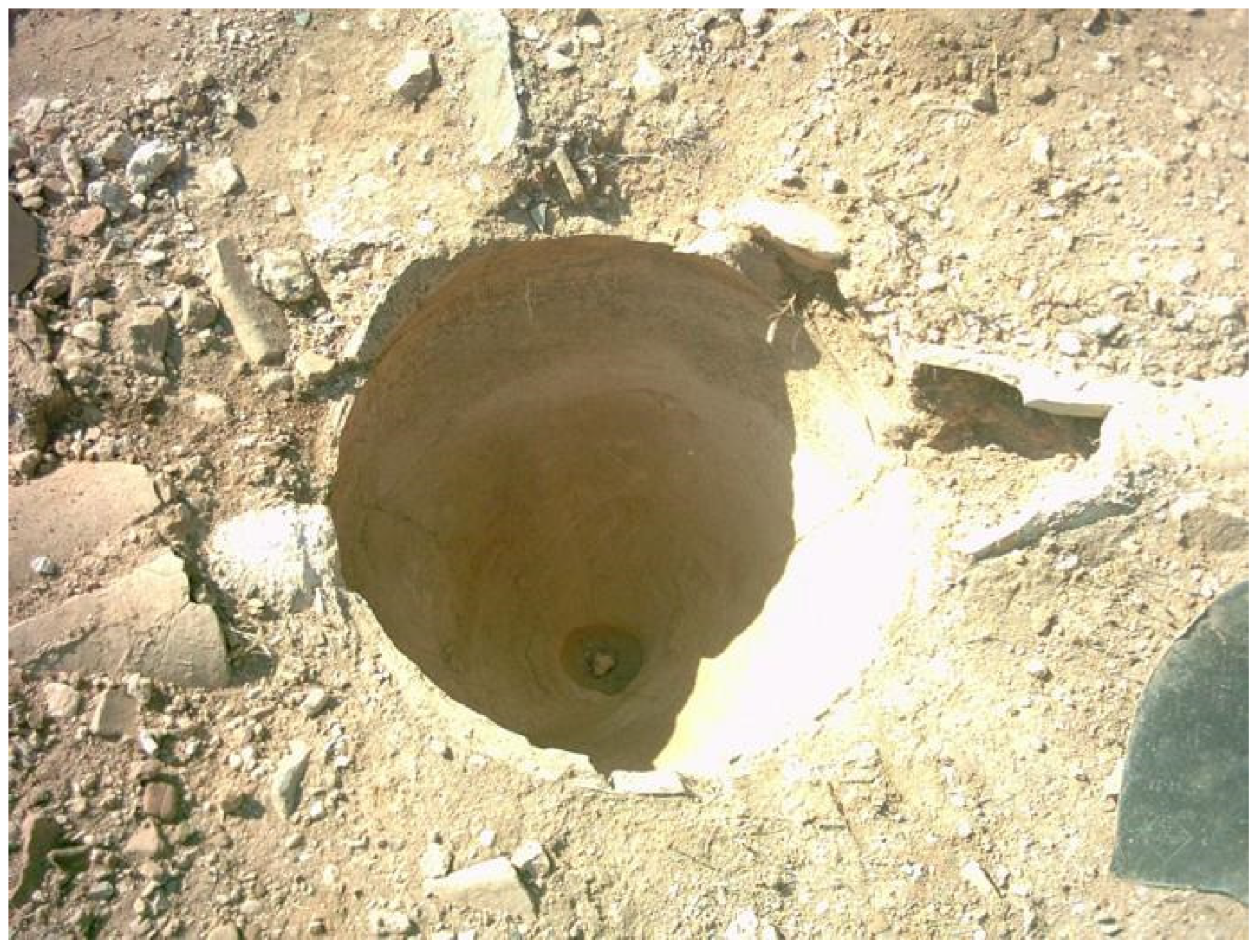
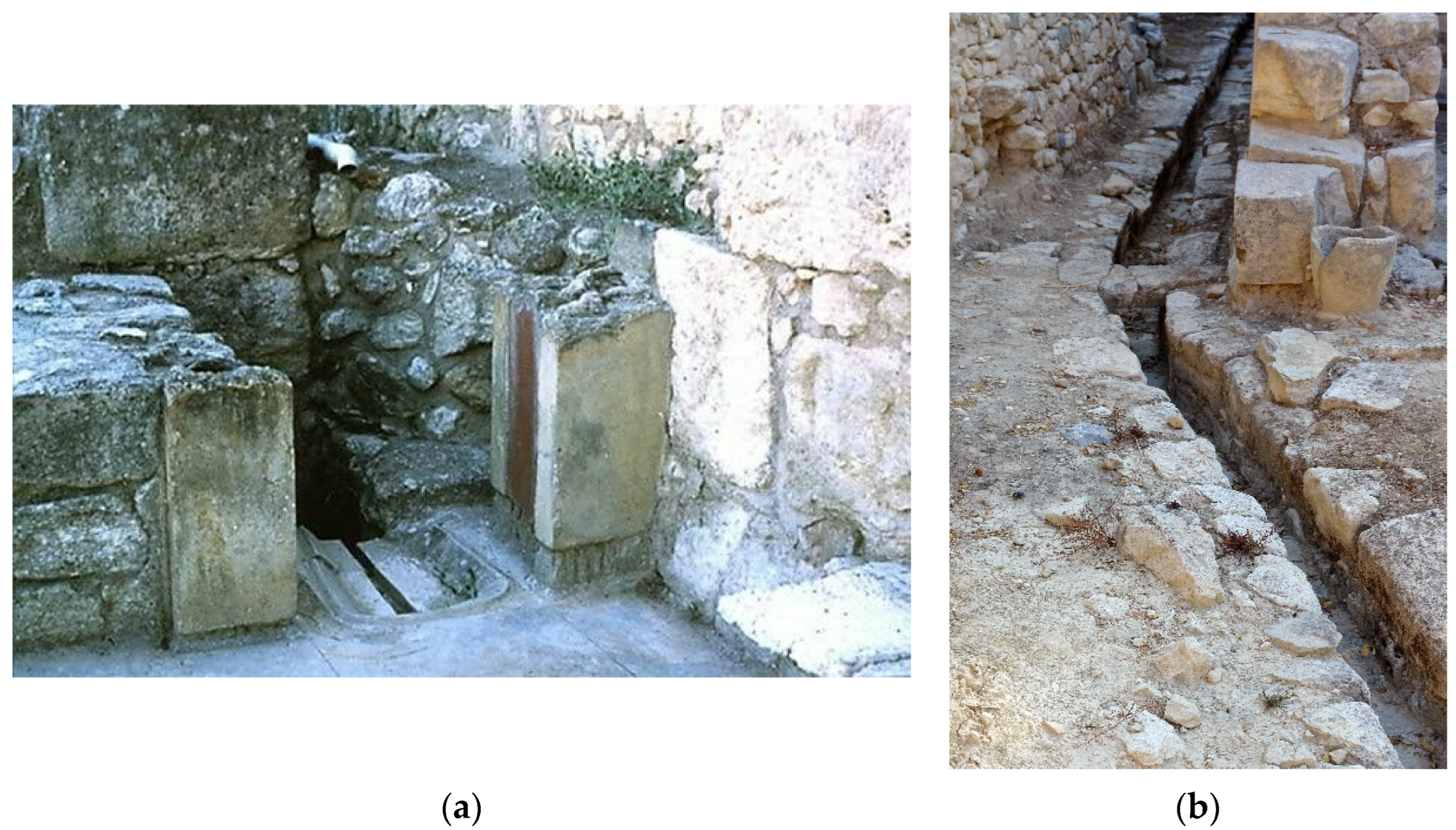
2.1.2. Minoan and Mycenaean Civilizations (ca 3200–1100 BC)
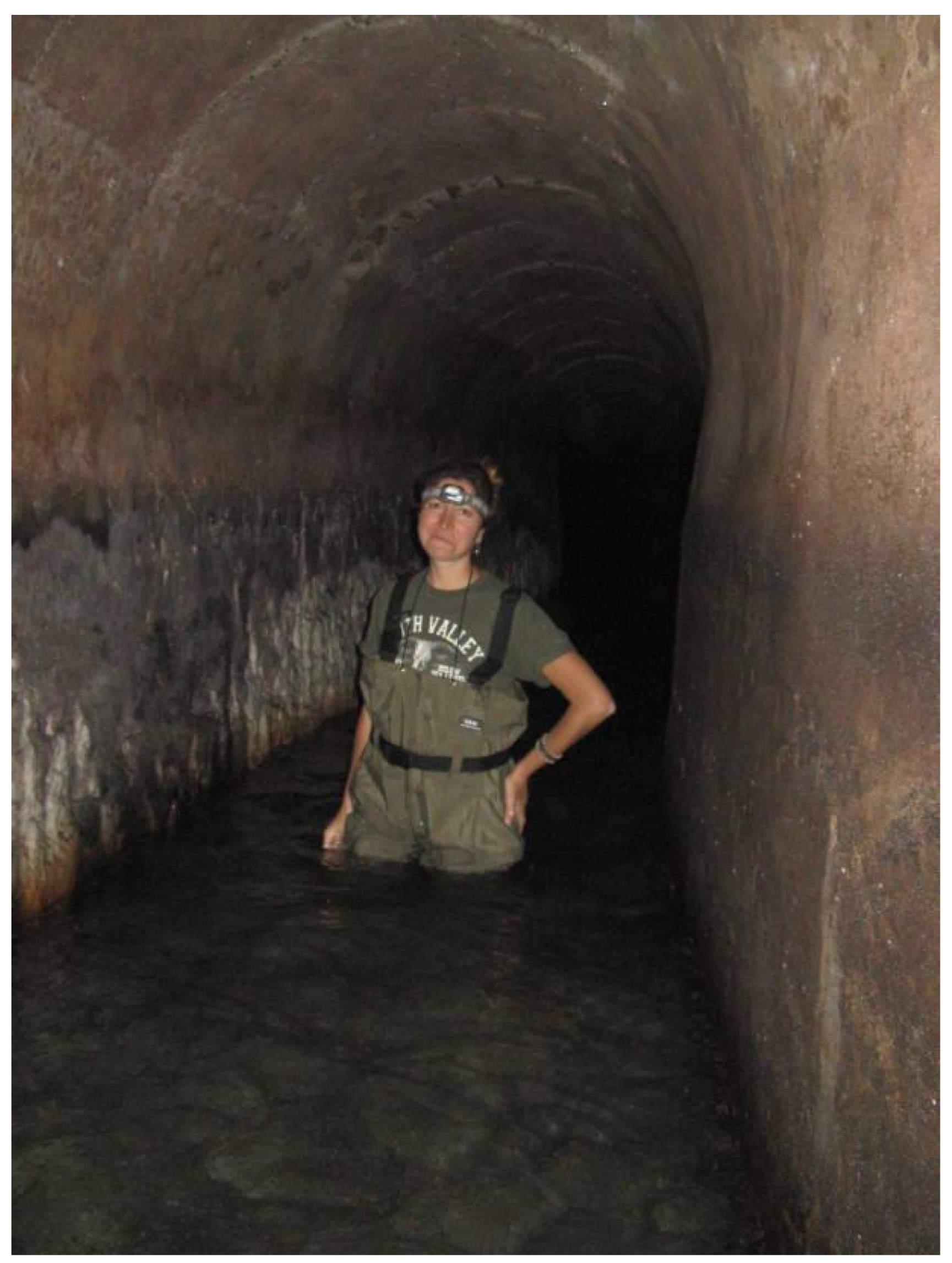
“…all the sewers were still working! It was very interesting for me to see the water in the drainages and sewers so big that a man could enter. I doubt if there are other examples of ancient sewerages working after 4 thousand years…”
Perhaps we also may be permitted to doubt whether our modern sewerage systems will still be functioning after even one thousand years.
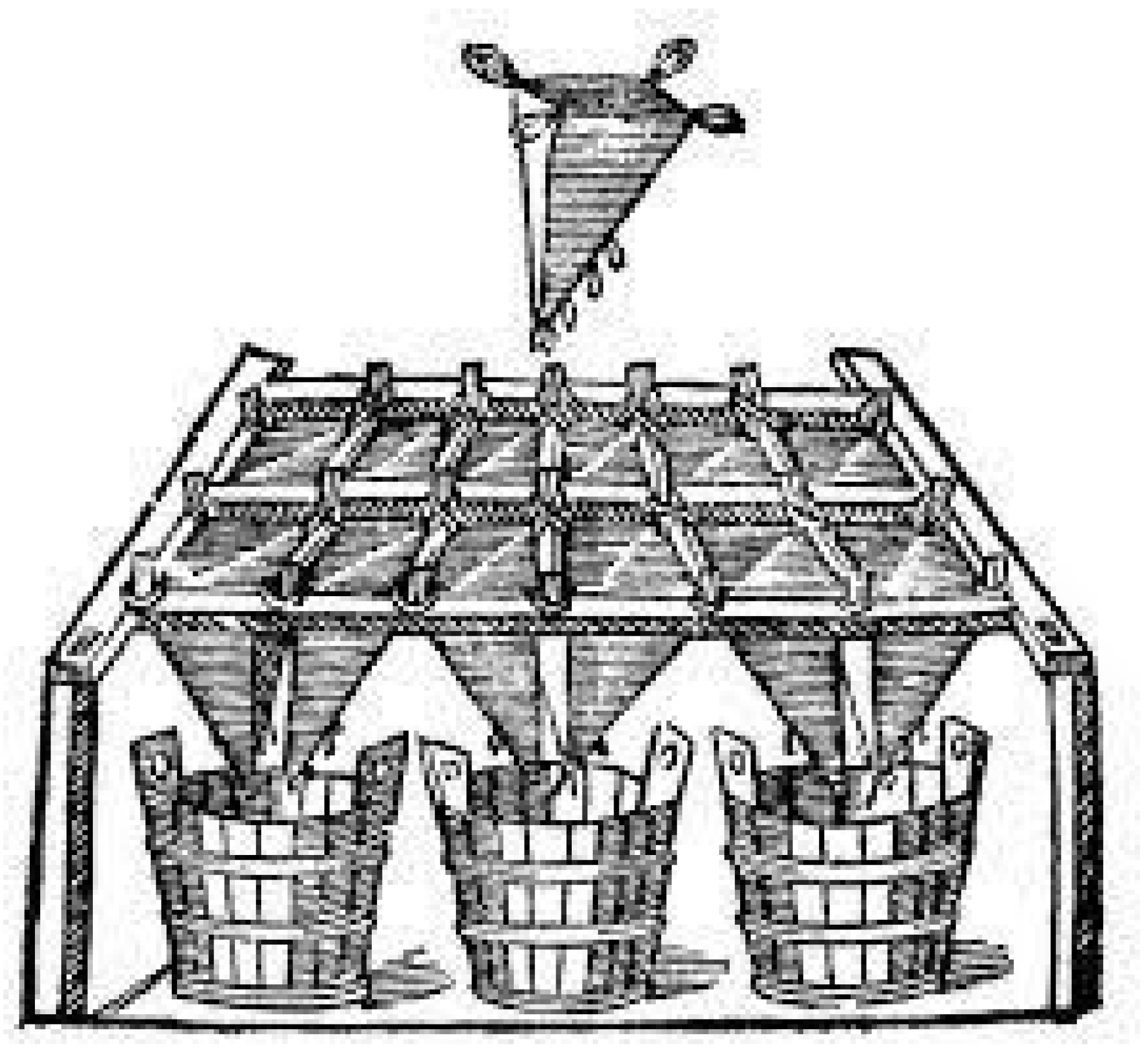
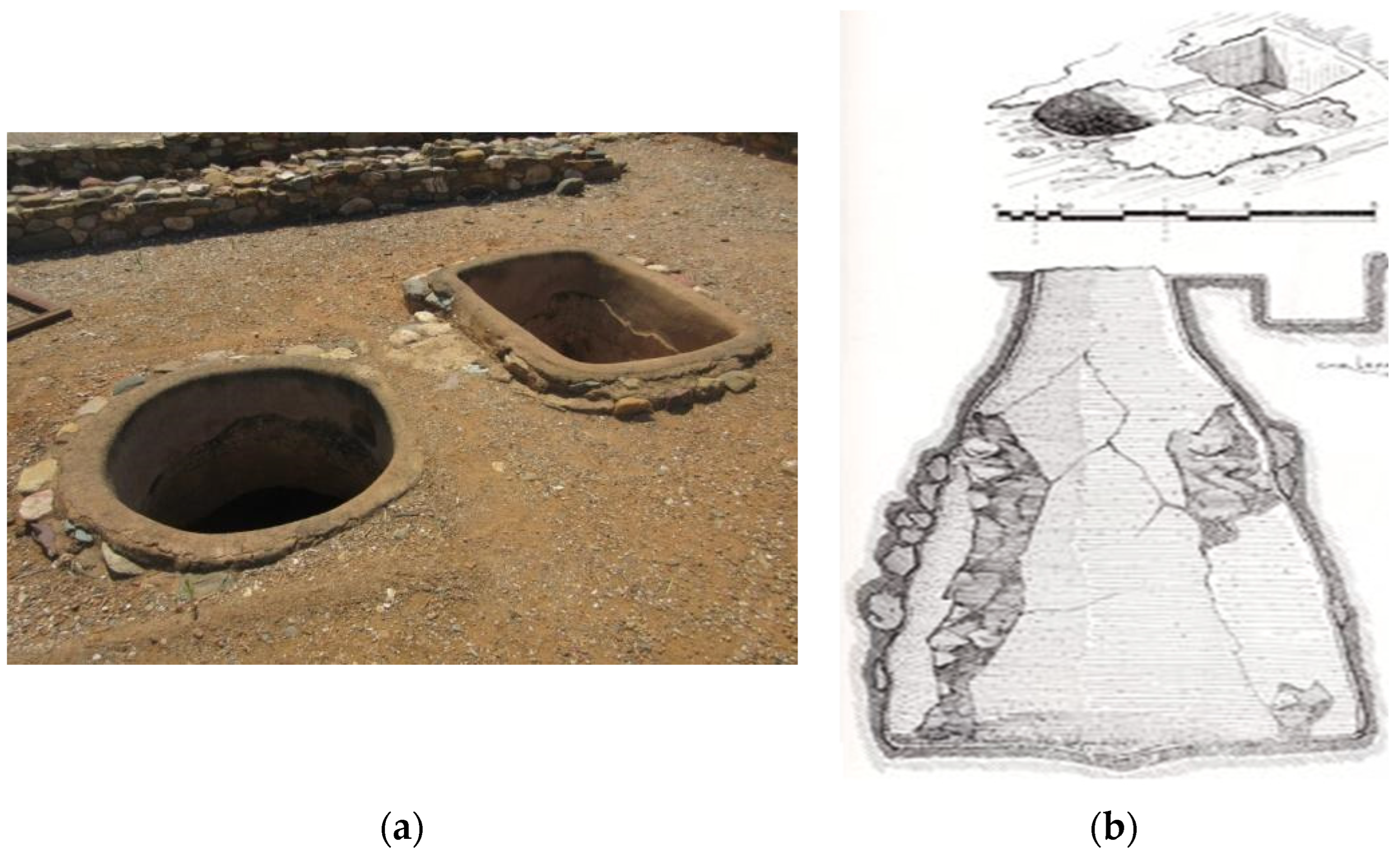
2.1.3. Indus Valley Civilizations (ca 3200–1300 BC)
2.2. Historical Times (ca 1100 BC–476 AD)
2.2.1. Iron Age (ca 1200–750 BC)
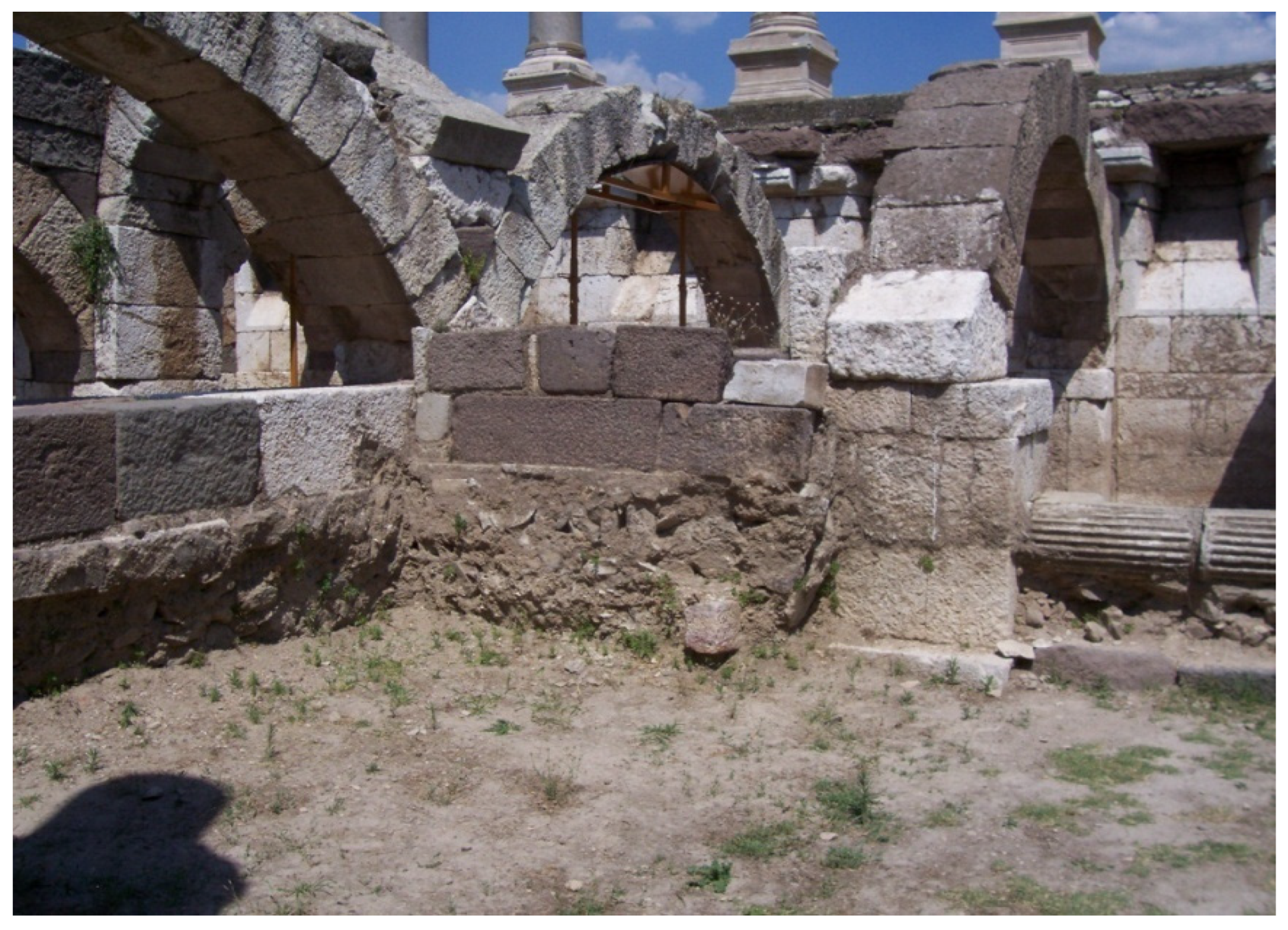
2.2.2. Archaic, Classical, and Hellenistic Periods (ca 750–31 BC)
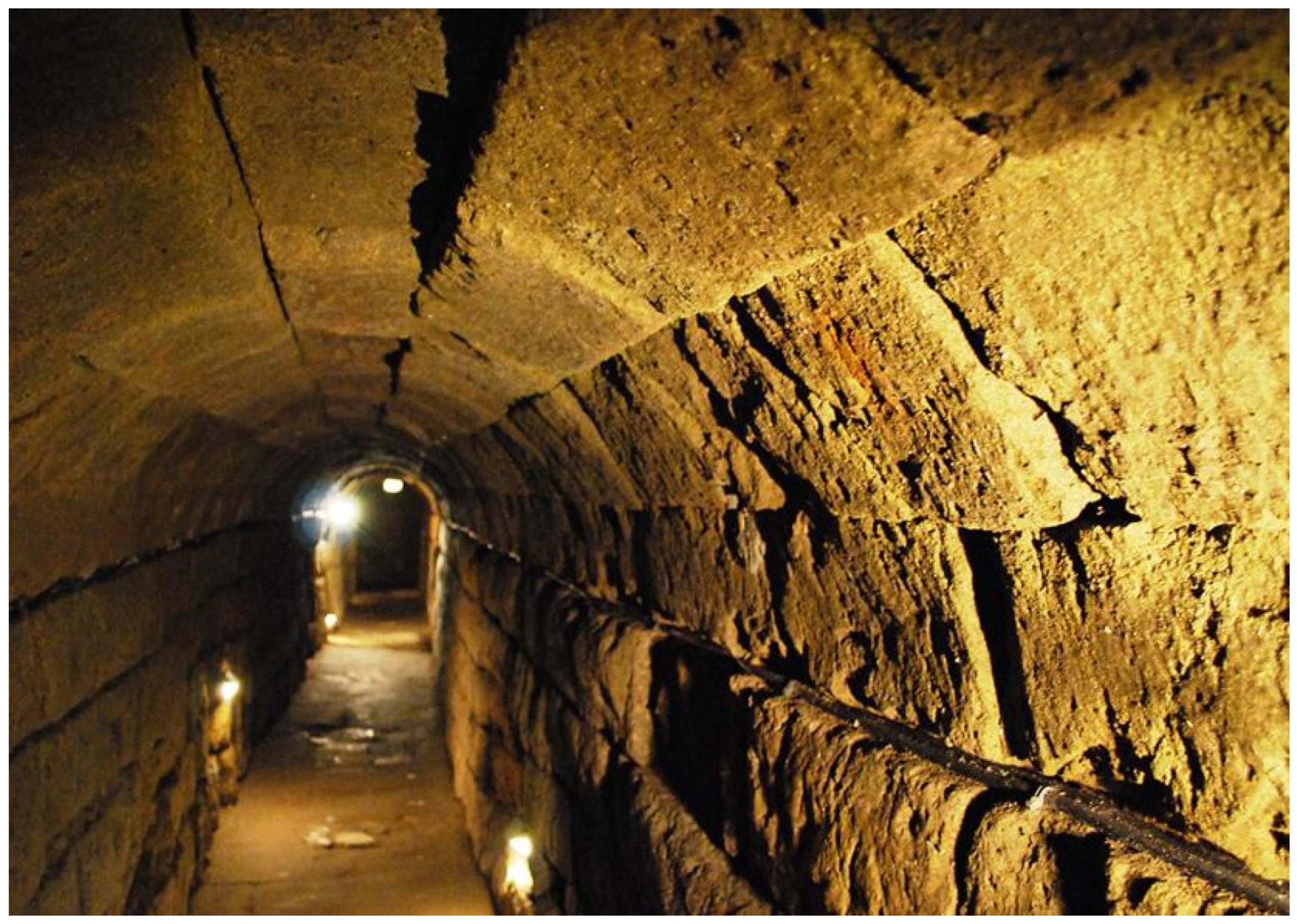
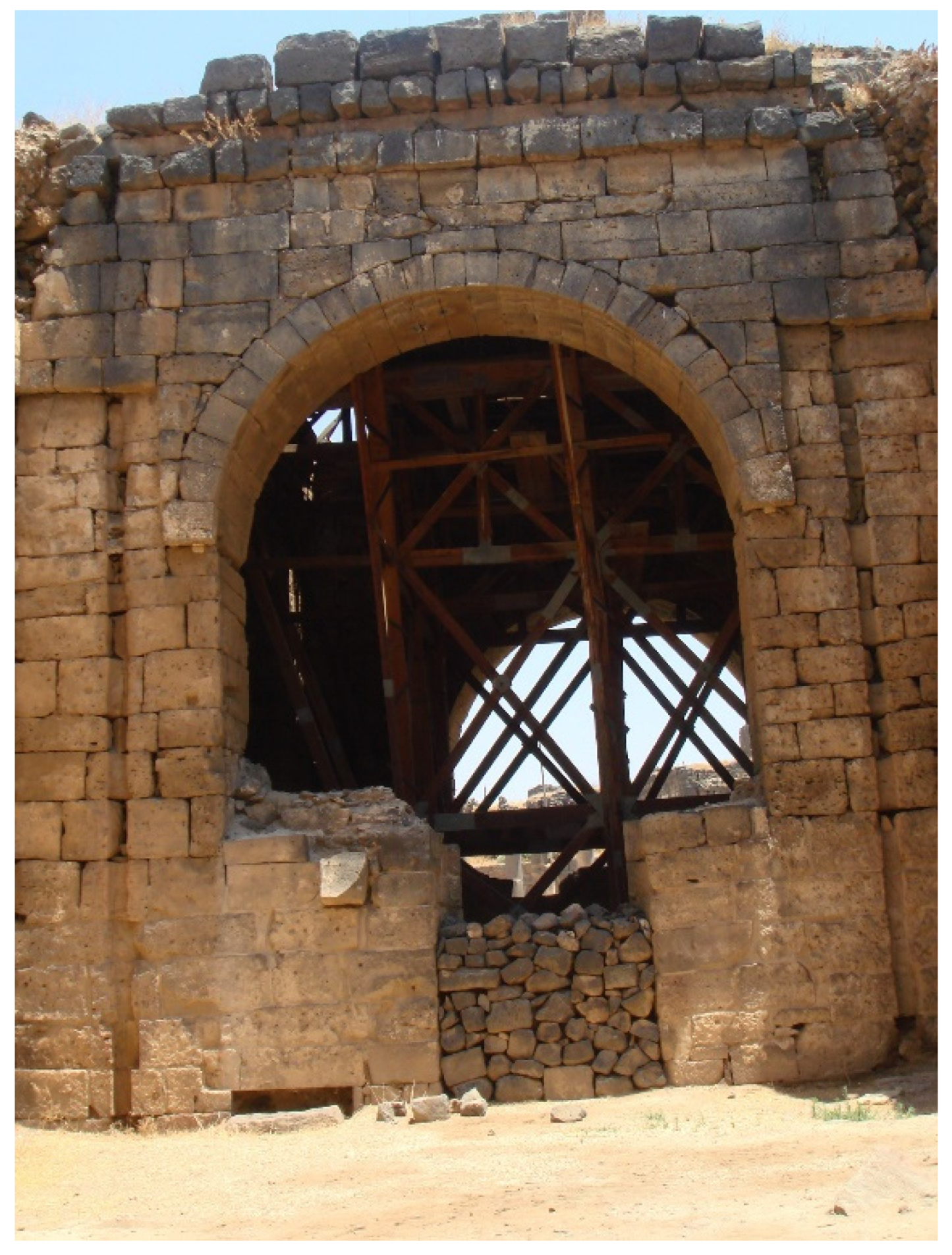
2.2.3. Roman Period (31 BC–476 AD)
2.2.4. Han China Dynasties (ca 206 BC–220 AD)
2.2.5. The Gupta Period (ca 319–467 AD)
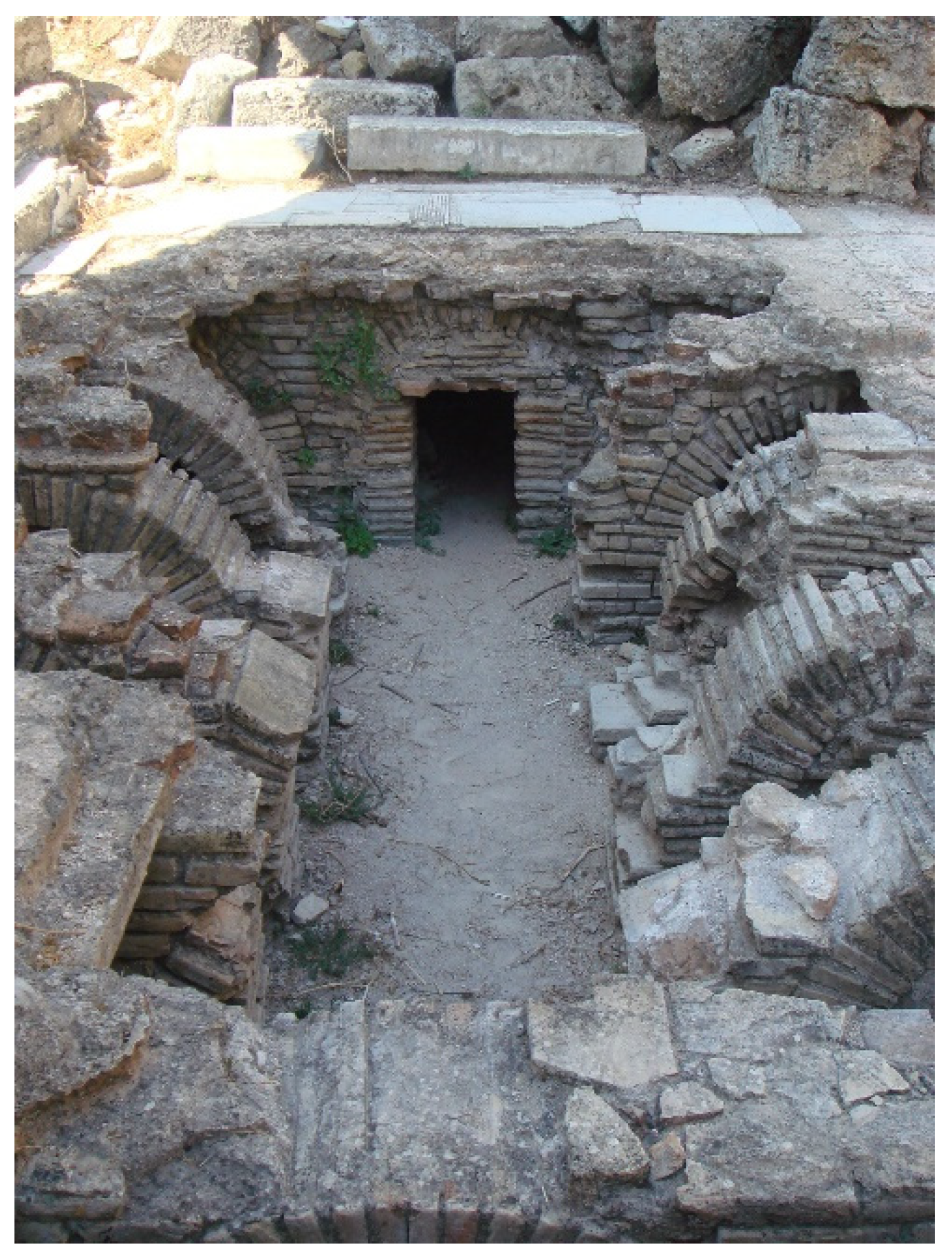
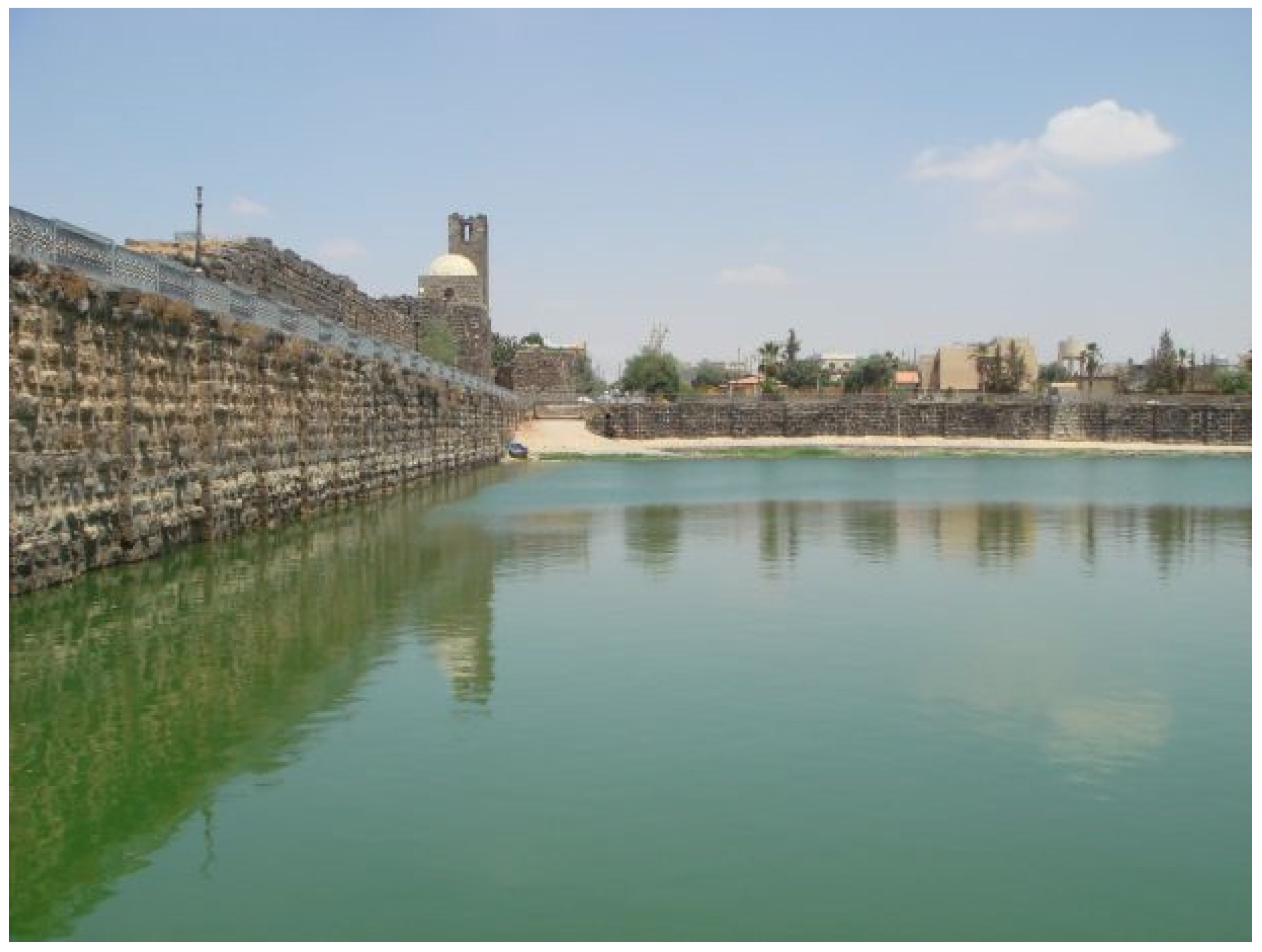
2.2.6. Byzantine Period (ca 330–1453 AD)
2.2.7. Medieval Times (ca 476–1400 AD)
2.2.8. The Mughal Empire (1526–1761 AD)
3. WASH in Early and Mid-Modern Times (ca 1400–1850 AD)
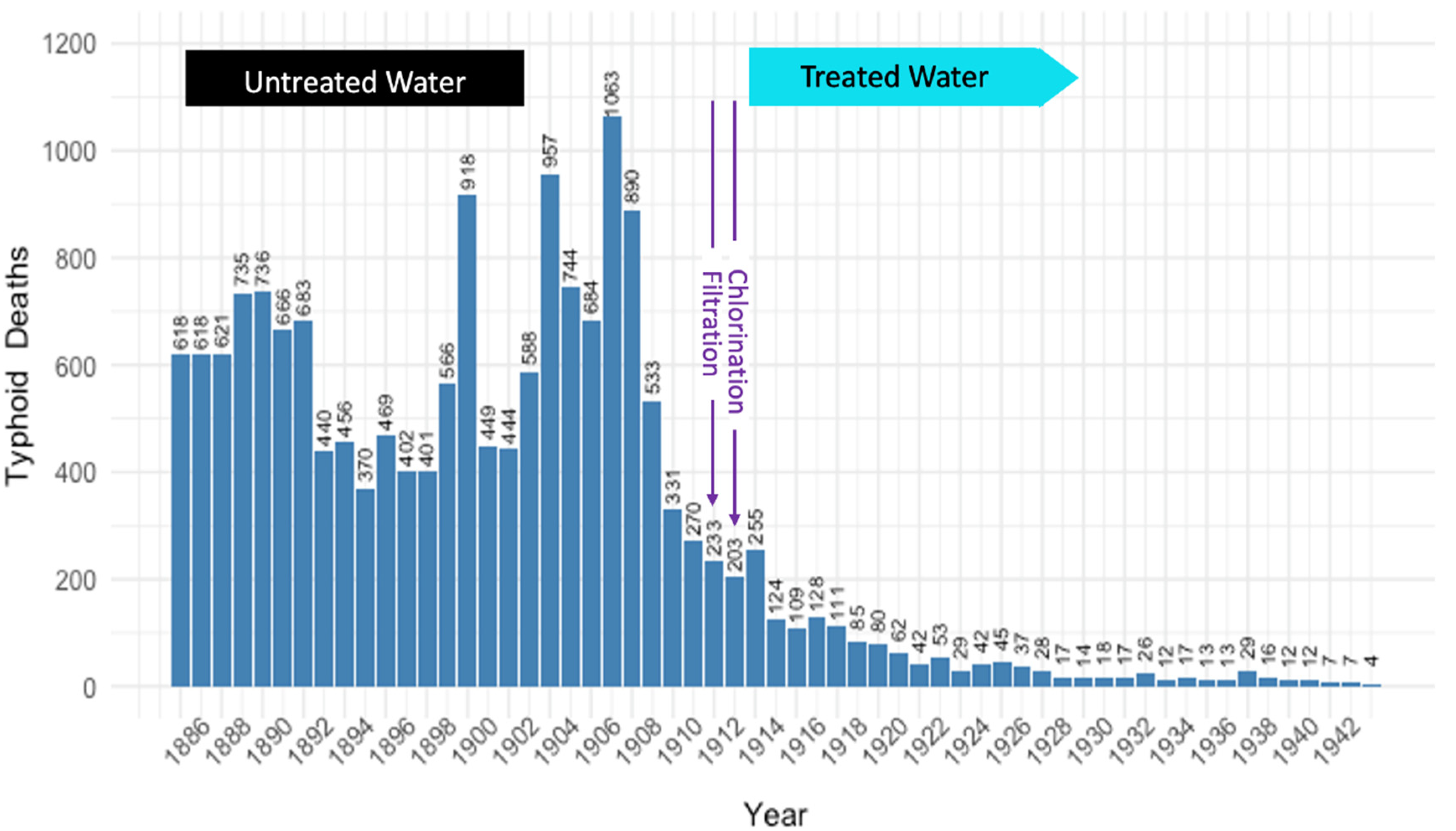
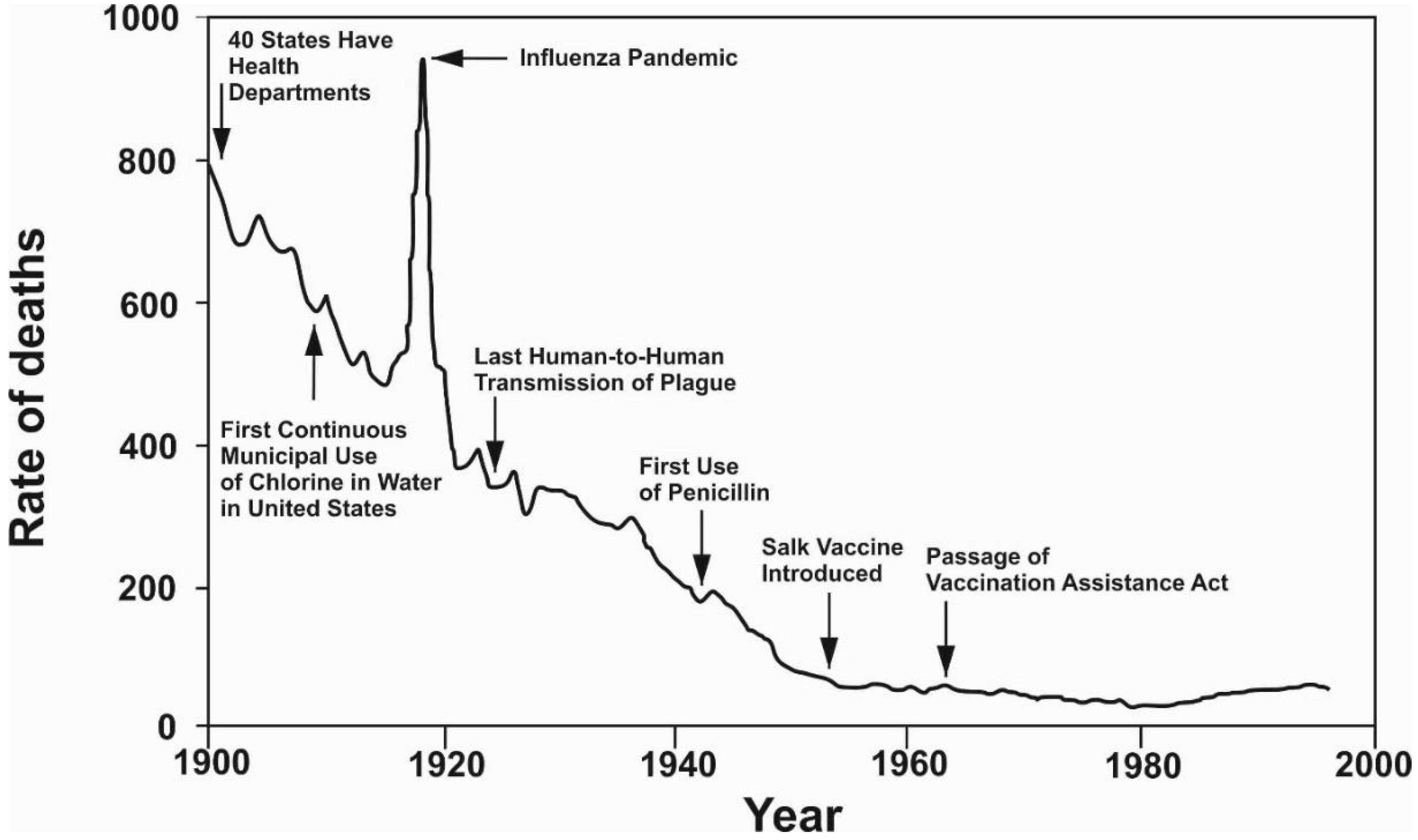
4. WASH in Contemporary Times (1850 AD–Present)
5. Emerging Trends and Possible Future Challenges of WASH Measures Development
6. Epilogue
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UN; United Nations. Sustainable Development Goals Report 2022. Goal 6: Ensure Access to Water and Sanitation for All. United Nations. 2022. Available online: https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/water-and-sanitation/ (accessed on 15 April 2023).
- WHO; UNICEF. World Health Organization. Progress on Drinking Water, Sanitation and Hygiene: 2017 Update and SDG Baselines; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; p. 21. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, P.L.; Lachan, J.P.E. Hygiene and Its Role in Health; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2008; OCLC 181862629; ISBN 978-1-60456-195-1. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenqvist, T.; Mitchell, C.; Willetts, J. A short history of how we think and talk about sanitation services and why it matters. J. Water Sanit. Hyg. Dev. 2016, 6, 298–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dopheide, D. Water, Sanitation and Hygiene in India. 2019. Available online: https://borgenproject.org/water-sanitation-and-hygiene-in-india/ (accessed on 22 March 2023).
- Khuller, A. Water Crisis in India: The World’s Largest Groundwater User. NITI (National Institutions of Transforming Indians) Aayog. 2022. Available online: https://www.teriin.org/article/water-crisis-india-worlds-largest-groundwater-user (accessed on 22 March 2023).
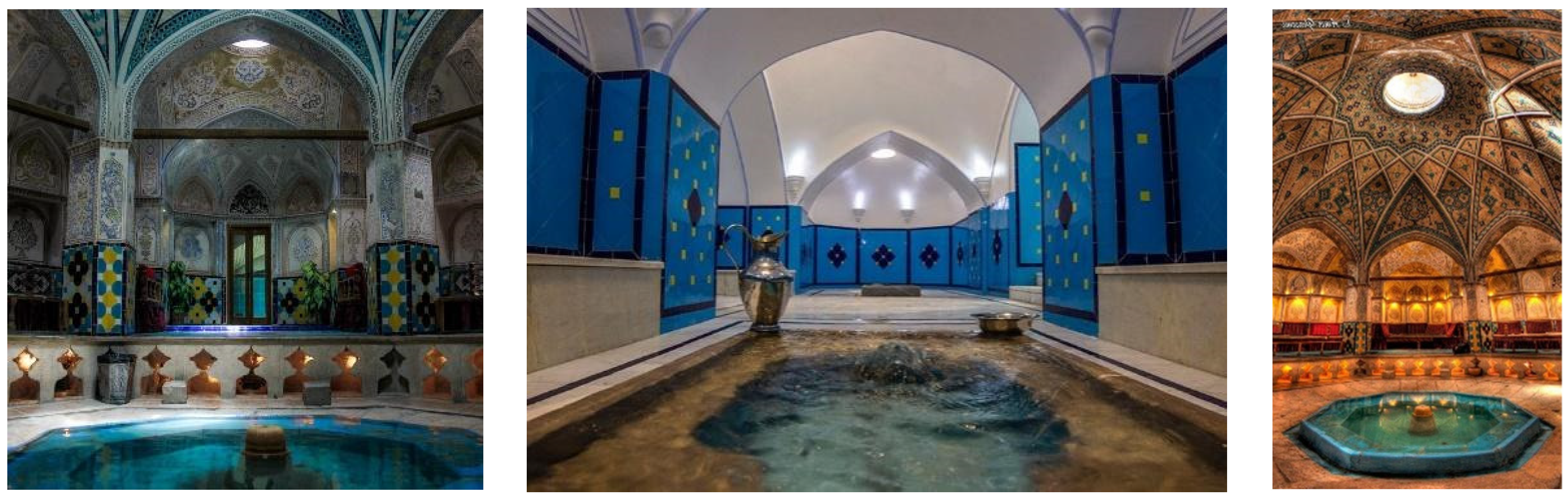
- Rezaei, M. Persian Bath in Iran—BitoTrip. 2019. Available online: https://medium.com/@77.rezai/persian-bath-in-iran-bitotrip-8b0e6ce10d58 (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- Angelakis, A.N.; Antoniou, G.P.; Yapijakis, C.; Tchobanoglous, G. History of hygiene focusing on the crucial role of water in the Hellenic Asclepieia (i.e., Ancient Hospitals). Water 2020, 12, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mays, L.W.; Angelakis, A.N. Gods and Goddesses of Water. In Evolution of Water Supply throughout Millennia; Angelakis, A.N., Mays, L.W., Koutsoyiannis, D., Mamassis, N., Eds.; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2012; Chapter 1; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Trckova-Flamee, A. Minoan Snake Goddess. Encyclopedia Mythical. 2002. Available online: http://www.pantheon.org/articles/m/minoan_snake_goddess.html/ (accessed on 25 April 2022).
- Evans, H.B. Water Distribution in Ancient Rome: The Evidence of Frontinus; University of Michigan Press: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Roeder, S.B. H Aπατηλή οικειοποίηση του παρελθόντος ενάντια στην Πατριαρχική τύφλωση. Aρχαιολογία & Τέχνες 1998, 67, 6–24. [Google Scholar]
- Angelakis, A.N.; Dercas, N.; Tzanakakis, V.A. Water Quality Focusing on the Hellenic World: From Ancient to Modern Times and the Future. Water 2022, 14, 1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mays, L.; Sklivaniotis, M.; Angelakis, A. Water for Human Consumption through History; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2012; pp. 19–42. [Google Scholar]
- Antoniou, G.P.; De Feo, G.; Fardin, F.; Tamburrino, A.; Khan, S.; Tie, F.; Reklaityte, I.; Kanetaki, E.; Zheng, X.Y.; Mays, L.W. Evolution of toilets worldwide through the millennia. Sustainability 2016, 8, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yannopoulos, S.; Yapijakis, C.; Kaiafa-Saropoulou, A.; Antoniou, G.; Angelakis, A.N. History of sanitation and hygiene technologies in the Hellenic world. J. Water Sanit. Hyg. Dev. 2017, 7, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelakis, A.; Kavoulaki, E.; Dialynas, E. Sanitation and Wastewater Technologies in Minoan Era; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald, C.F.; Driessen, J.M. The Storm Drains of the East Wing at Knossos. In L’ Habitat égéen Préhistorique; Darcque, P., Treuil, R., Eds.; Bulletin de Correspondance Hellénique, Supplément 19; Peeters Publishing: Leuven, Belgium, 1990; pp. 141–146. [Google Scholar]
- Mosso, A. Escursioni Nel Mediterraneo e Gli Scavi di Creta; Treves: Milano, Italy, 1907. [Google Scholar]
- Gray, H.F. Sewerage in Ancient and Medieval Times. Sew. Work. J. 1940, 12, 939–946. [Google Scholar]
- Civilization, I.V. World History Encyclopedia. 2020. Available online: https://www.worldhistory.org/Indus_Valley_Civilization/ (accessed on 2 February 2023).
- Singh, P.K.; Dey, P.; Jain, S.K.; Mujumdar, P.P. Hydrology and water resources management in ancient India. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 24, 4691–4707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, B. History of toilets. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Public Toilets, Hong Kong, China, 25–27 May 1995; pp. 25–27. [Google Scholar]
- Tiwary, S.K.; Saurabh, S. Archaeological Evidences of Toilet System in Ancient India. J. Multidiscip. Stud. Archaeol. 2018, 6, 764–781. [Google Scholar]
- Klingborg, P. Greek Cisterns: Water and Risk in Ancient Greece, 600–650 BC; Department of Archaeology and Ancient History, Uppsala University: Uppsala, Sweden, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lucore, S.K. Greek Baths. In A Companion to Greek Architecture; Miles, M.M., Ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 328–341. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, J.M. Bath-Tubs in Ancient Greece. Greece Rome 1959, 6, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassenhoven, M.-E. The Bath in Greece in Classical Antiquity; Series 2368; BAR Publishing: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ginouvès, R. Recherches sur le Bain dans l’Antiquité Grecque; E. de Boccard: Paris, France, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Lucore, S.K. Bathing in Hieronian Sicily. In Greek Baths and Bathing Culture: New Discoveries and Approaches; Luroce, S.K., Trümper, M., Eds.; Peeters: Walpole, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 150–179. [Google Scholar]
- Redon, B. (Ed.) Collective Baths in Egypt 2: New Discoveries and Perspectives; Études Urbaines 10; Institut Français d’Archéologie Orientale: Cairo, Egypt, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mays, L.W. A brief history of water filtration/sedimentation. Water Supply 2013, 13, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risse, G.B. Mending Bodies, Saving Souls: A History of the Hospitals; Oxford University Press, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Melfi, M. I Santuari di Asclepio in Grecia: I. 2007. Available online: https://www.torrossa.com/en/resources/an/2637758 (accessed on 15 April 2023).
- Kavvadias, P. The Sanctuary of Asclepius at Epidarus and the Treatment of the Patients; Perris Bros Press: Athens, Greece, 1900; p. 320. (In Greek) [Google Scholar]
- Christopoulou-Aletra, H.; Togia, A.; Varlami, C. The “smart” Asclepieion: A total healing environment. Arch. Hell. Med. 2010, 27, 259–263. [Google Scholar]
- Klingborg, P.; Finné, M. Modelling the freshwater supply of cisterns in ancient Greece. Water Hist. 2018, 10, 113–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grewe, K. Aquädukte: Wasser für Roms Städte; der Große Überblick-Vom Römerkanal zum Aquäduktmarmor; Regionalia Verlag: Daun, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hodge, A.T. Roman Aqueducts and Water Supply, 2nd ed.; Duckwort: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- ROMAQ. The Atlas Project of Roman Aqueducts. 2018. Available online: https://www.romaq.org/ (accessed on 14 February 2023).
- Wikander, O. Handbook of Ancient Water Technology; Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2000; ISBN 978-90-04-47382-9. Available online: https://brill.com/edcollbook/title/1327 (accessed on 14 February 2023).
- Bruun, C. Water legislation in ancient world (c. 2200BC-c AD500). In Handbook of Ancient Water Technology; Wikader, O., Ed.; Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 539–604. [Google Scholar]
- Sürmelihindi, G. Palaeo-environmental condition factor on the diffusion of ancient water technologies. In Water Management in Ancient Civilizations; Geschichts- und Kulturwissenschaften: Berlin, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Jansen, G.C.; Koloski-Ostrow, A.O.; Moormann, E.M. Roman Toilets. In Their Archaeology and Cultural History; Peeters Publishers: Leuven, Belgium, 2011; Available online: https://d1wqtxts1xzle7.cloudfront.net/33321567/Camardo_Roman_Toilets-libre.pdf?1395885877=&response-content-disposition=inline%3B+filename%3DD_Camardo_Ercolano_la_ricostruzione_dei.pdf&Expires=1681887788&Signature=DefKaMRkmo6HBctJiw6EcVzZWMeiauf4as4bK~5DClJIqtokzXzIDVw4io~I1Kj0XLRnycki3VR6u7gULA7f0xurrzOOwGNVpTAZodSna9z3kcGns5PvxWQtz5gMkp6L6n2z62QYAi7wyrTq4SqDsyiHfrkhBO1Kr9Tr9IN~Rk6HvQyWOuIhoZmWTqX5da~VS1Uny3p4AoknQMrtqcfMIu0jw3QaMcKw6XxWZ6ax1IZp~99OeeYziwcgcoP8iZsnyVgRtJiJBkHCNZJOC~mYz4wdVE2RQOWuWR--ICsuDVK4EF~raM~8qZL9vF~dUCq9Altc7VlQbfbRh1K6aHEL6Q__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAJLOHF5GGSLRBV4ZA (accessed on 15 April 2023).
- Mirsky, S. Getting to the bottom. Sci. Am. 2013, 308, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, O.F. Ancient Rome: City Planning and Administration; Routledge: Oxfordshire, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, P.D. Human parasites in the Roman World: Health consequences of conquering an empire. Parasitology 2017, 144, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanum, I. Hygiene in Ancient Romans. Imperium Romanum. 2022. Available online: https://imperiumromanum.pl/en/roman-society/hygiene-in-ancient-romans/ (accessed on 2 February 2023).
- Nielsen, I. Thermae et Balnea; Aarhus University Press: Aarhus, Denmark, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Yegül, F. Baths and Bathing in Antiquity; The Architectural History Foundation and Massachusetts Institute of Technology, the MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Schalles, H.J.; Rieche, A.; Precht, G. Die Römischen Bäder; Rheinland Verlag: Köln, Germany, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Weeks, D.M. A Dissertation Submitted in Partial Satisfaction of the Requirements for the Degree Doctor of Philosophy in Indo-European Studies; University of California: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Deming, D. The aqueducts and water supply of Ancient Rome. Ground Water 2020, 58, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omrania. Urban Water Systems: The Great Sewer of Ancient Rome. 2019. Available online: https://omrania.com/inspiration/urban-water-systems-the-great-sewer-of-ancient-rome/ (accessed on 15 March 2023).
- Geographic, N. Roman Aqueducts. 2022. Available online: https://education.nationalgeographic.org/resource/roman-aqueducts (accessed on 15 March 2023).
- Clamagirand, E.; Rais, S.; Chahed, J.; Guefrej, R.; Smaoui, L. L’aqueduc de Carthage. In La Houille Blanche. 1990. Available online: https://www.shf-lhb.org/articles/lhb/abs/1990/05/lhb1990034/lhb1990034.html (accessed on 15 April 2023).
- Ferchiou, N. Le Chant des Nymphes: Les Aqueducs et Les Temples des Eaux de Zaghouan à Carthage; Editions Nirvana: El Ghazela, Tunisia, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Vannesse, M. L’eau et l’amoenitas urbium. Étude du paysage urbain d’Antioche et d’Apamée. In Proceedings of the Les Réseaux d’eau Courante dans l’Antiquité. Réparations, Modifications, Réutilisations, Abandon, Récupération, Actes du Colloque International, Nancy, France, 20–21 November 2009; pp. 20–21. [Google Scholar]
- Sürmelihindi, G.; Passchier, C.; Crow, J.; Spötl, C.; Mertz-Kraus, R. Carbonates from the ancient world’s longest aqueduct: A testament of Byzantine water management. Geoarchaeology 2021, 36, 643–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessener, H.P.M. Roman water taps and (two) paradigms. Babesch Suppl. 2017, 4, 371–379. [Google Scholar]
- Passchier, C.; Sürmelihindi, G.; Spötl, C.; Mertz-Kraus, R.; Scholz, D. Carbonate deposits from the ancient aqueduct of Béziers, France—A high-resolution palaeoenvironmental archive for the Roman Empire. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2016, 461, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passchier, C.; Sürmelihindi, G.; Boyer, D.; Yalçın, C.; Spötl, C.; Mertz-Kraus, R. The aqueduct of Gerasa–intra-annual palaeoenvironmental data from Roman Jordan using carbonate deposits. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2021, 562, 110089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sürmelihindi, G.; Leveau, P.; Spötl, C.; Bernard, V.; Passchier, C.W. The second century CE Roman watermills of Barbegal: Unraveling the enigma of one of the oldest industrial complexes. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaar3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sürmelihindi, G.; Passchier, C. Sinter Analysis—A Tool for the Study of Ancient Aqueducts. Hist. Wasserleitungen Gestern-Heute-Morgen. Babesch Suppl. 2011, 24, 269–287. [Google Scholar]
- Passchier, C.W.; Rigal, D.; Sürmelihindi, G. Preuves du nettoyage des concrétions calcaires de l’aqueduc antique de Divonna· Cahors. In Proceedings of the Aquae Ductus, Actualité de la Recherche en France et en Espagne, Actes du Coloque International de Toulouse, Toulouse, France, 15–16 February 2013; pp. 233–241. [Google Scholar]
- Dengfeng Workstation of Henan Provincial Museum. Preliminary Excavation of Underground Water Transmission Pipeline and Storage Tank in Yangcheng of the Eastern Zhou Dynasty; Henan Cultural, Dengfeng Workstation of Henan Provincial Museum: Dengfeng, China, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Çeçen, K. Roma su Yollarının en Uzunu (The Longest Roman Water Supply Line); Ârkiye Sinai Kalkinma Bankasi: Istanbul, Turkey, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Crow, J.; Bardill, J.; Bayliss, R.; Bono, P.; Krausmüller, D. The Water Supply of Byzantine Constantinople. 2008. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/John-Oleson/publication/269544222_The_Water_Supply_of_Byzantine_Constantinople_Book_Review/links/584ae99508aecb6bd8bf9b8c/The-Water-Supply-of-Byzantine-Constantinople-Book-Review.pdf (accessed on 15 April 2023).
- Crow, J. Ruling the waters: Managing the water supply of Constantinople, AD 330–1204. Water Hist. 2012, 4, 35–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haut, B.; Viviers, D. Analysis of the water supply system of the city of Apamea, using Computational Fluid Dynamics. Hydraulic system in the north-eastern area of the city, in the Byzantine period. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2007, 34, 415–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannesse, M.; Haut, B.; Debaste, F.; Viviers, D. Analysis of three private hydraulic systems operated in Apamea during the Byzantine period. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2014, 46, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dentzer, J.-M.; Blanc, P.-M.; Fournet, T. Le développement urbain de Bosra de l’époque nabatéenne à l’époque byzantine: Bilan des recherches françaises 1981–2002. Syria 2002, 79, 75–154. [Google Scholar]
- Haut, B.; Viviers, D. Water Supply in the Middle East during Roman and Byzantine Periods; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2012; pp. 319–350. [Google Scholar]
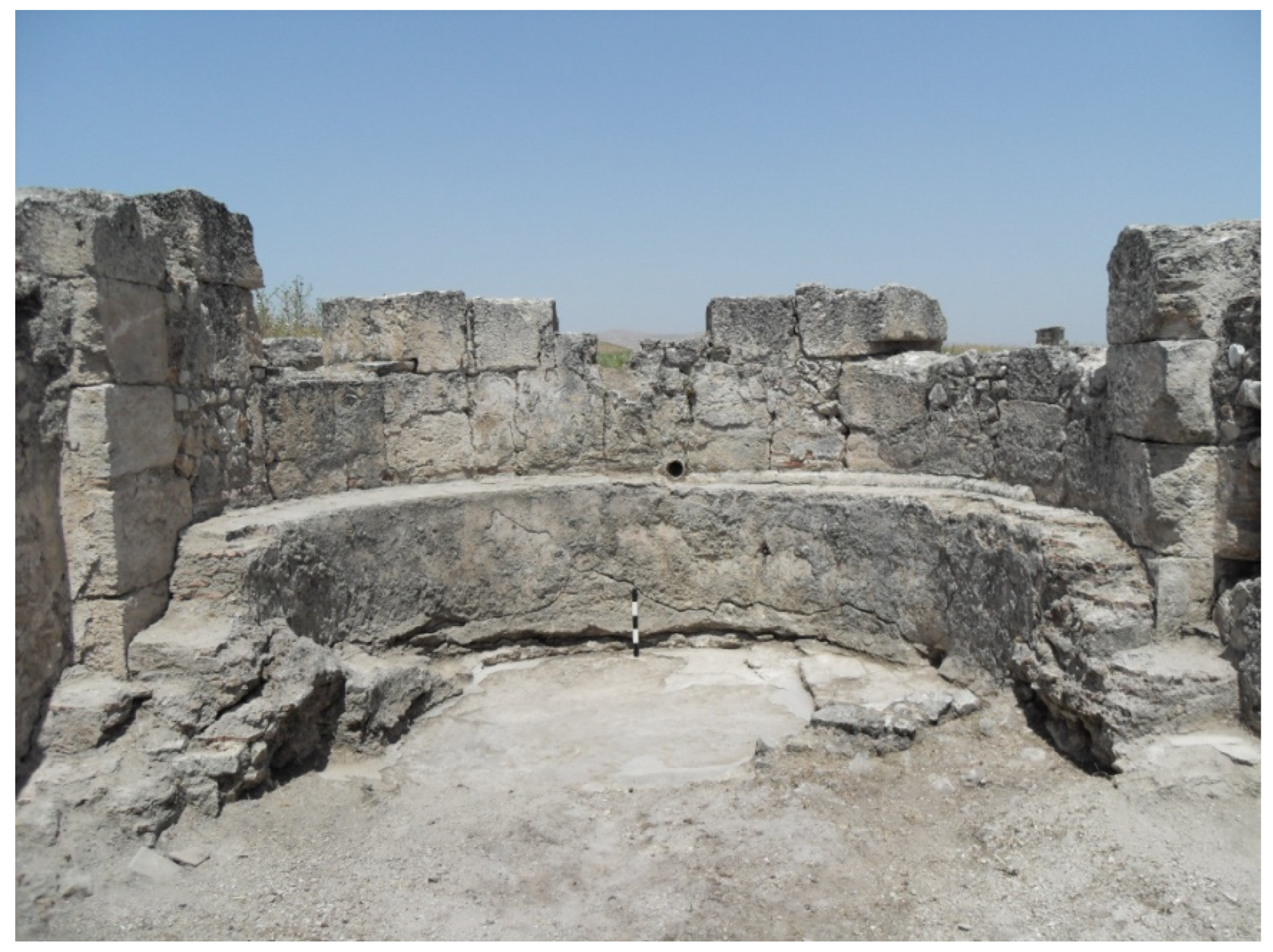
- Vekemans, O.; Haut, B. Hydraulic analysis of the water supply system of the Roman city of Perge. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2017, 16, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasoglu, H. Perge. Curr. World Archaeol. 2010, 41, 28. [Google Scholar]
- Tunçer, M. Perge Conservation Plan Report. Perge Conservation Plan Research Report; Akman Project Co.: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Viollet, P. L’hydraulique dans les Civilisations Anciennes (Hydraulics in Ancient Civilizations); Presse de l’Ecole des Ponts et Chaussées: Paris, France, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Haut, B.; Zehng, X.Y.; Mays, L.; Han, M.; Passchier, C.; Angelakis, A. Evolution of rainwater harvesting in urban areas through the millennia. In Water Heritage: Material, Conceptual Spiritual Connections; Sidestone Press: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 37–56. [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster, L.C. Early Examples of So-Called Pitched Brick Barrel Vaulting in Roman Greece and Asia Minor: A Question of Origin and Intention. In Bautechnik im Antiken und Vorantiken Kleinasien. 2009. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/235632/Early_Examples_of_So_Called_Pitched_Brick_Barrel_Vaulting_in_Roman_Greece_and_Asia_Minor_A_Question_of_Origin_and_Intention (accessed on 15 April 2023).
- Levi, E.A. The Agora of İzmir and Cultural Tourism. In Proceedings of the International Committee for Documentation of Cultural Heritage (CIPA), Antalya Symposium, Antalya, Turkey, 30 September–4 October 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Mouton, M.; Al-Dbiyat, M. Stratégies d’acquisition de l’eau et Société au Moyen-Orient Depuis l’Antiquité; Institut Français du Proche-Orient: Beirut, Lebanon, 2009; Volume 186. [Google Scholar]
- Karpozilos, A. About Lavatories, Sewers and Sewerage. In Everyday Life in Byzantium, Proceedings of the 1st International Symposium, Athens, Greece, 8–12 June 1987; Aggelidi, X., Ed.; Center of Byzantine Research: Athens, Greece, 1989; pp. 335–352. (In Greek) [Google Scholar]
- Martínez Jiménez, J. A preliminary study of the aqueduct of Reccopolis. Oxf. J. Archaeol. 2015, 34, 301–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzado, M.A.A. La vivienda en” Emerita” durante la antigüedad tardía: Propuesta de un modelo para” Hispania”. In Proceedings of the VI Reunió d’Arqueologia Cristiana Hispànica, Les Ciutats Tardoantigues d’Hispania, Cristianització I Topografia, València, Spain, 8–10 May 2003; pp. 121–152. [Google Scholar]
- Ventura, A. El Abastecimiento de Agua a la Cordoba Romana—El Acueducto de Valpuentes; Monografías 197; Universidad de Cordoba: Cordoba, Portogues, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Coates-Stephens, R. The walls and aqueducts of Rome in the Early Middle Ages, AD 500–1000. J. Rom. Stud. 1998, 88, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enzler, S. History of Water Treatment. 1998. Available online: www.lenntech.com/history-wtare-treatment.htm (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- Grewe, K. Die Wasserversorgung im Mittelalter. In Von Zabern; Ph. von Zabern: Mainz, Germany, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Parmar, A. An Insight into the Royal Mughal Toilets. S.A.M. TOURS & TRAVELS. 2022. Available online: https://www.tajwithguide.com/blog/an-insight-into-the-royal-mughal-toilets/ (accessed on 30 March 2023).
- Khator, N. The Stink from India’s Past, The Hindu. 2017. Available online: https://www.thehindu.com/opinion/open-page/the-stink-from-indias-past/article18713879.ece (accessed on 14 February 2023).
- Moayed, N. Hammam, the Second Home to Ancient Iranians. 2019. Available online: https://www.tasteiran.net/stories/10047/persian-hammam (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- Guihuan, L.; Jianmin, S. Population Change and Environmental Protection in China’s Historical Period; Metallurgical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 1991; p. 237. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, L. Dirty Old London: The Victorian Fight against Filth; Yale University Press Yale: New Haven, CT, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bartram, J.; Brocklehurst, C.; Fisher, M.B.; Luyendijk, R.; Hossain, R.; Wardlaw, T.; Gordon, B. Global monitoring of water supply and sanitation: History, methods and future challenges. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 8137–8165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSA, U. World Population Prospects: The 2012 Revision; Population Division of the Department of Economic and Social Affairs of the United Nations Secretariat: New York, NY, USA, 2013; Volume 18, pp. 620–626. [Google Scholar]
- WHO; UN. Progress on Drinking Water and Sanitation: 2014 Update; World Health Organization and United Nations Children‘s Fund: Geneva, Swizerland; New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery, M.A.; Elimelech, M. Water and sanitation in developing countries: Including health in the equation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prüss, A.; Kay, D.; Fewtrell, L.; Bartram, J. Estimating the burden of disease from water, sanitation, and hygiene at a global level. Environ. Health Perspect. 2002, 110, 537–542. [Google Scholar]
- Kramek, N.; Loh, L. The History of Philadelphia’s Water Supply and Sanitation System. Lessons in Sustainability of Developing Urban Water Systems. Master’s Thesis, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia Global Water Initiative, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
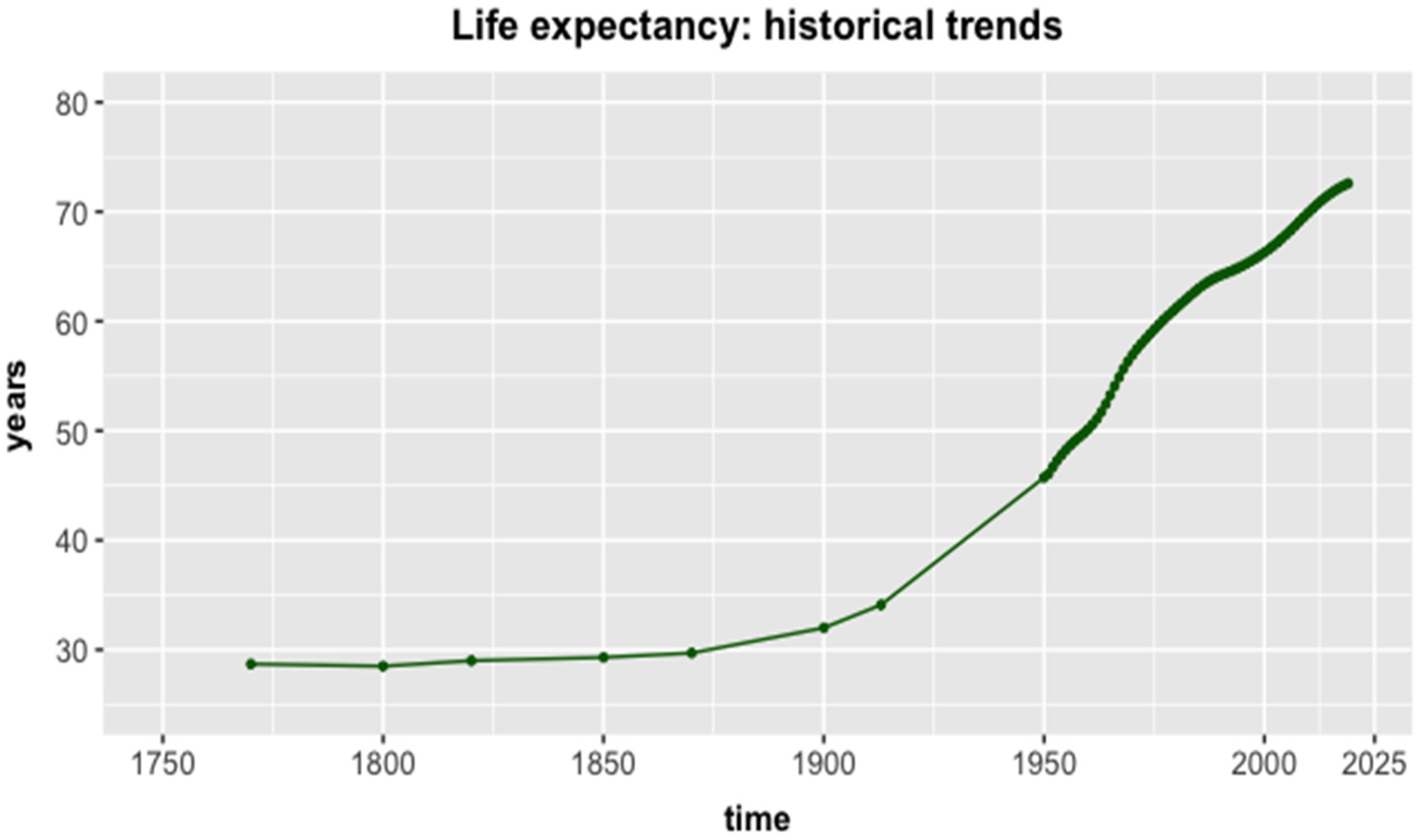
- Angelakis, A.N.; Vuorinen, H.S.; Nikolaidis, C.; Juuti, P.S.; Katko, T.S.; Juuti, R.P.; Zhang, J.; Samonis, G. Water quality and life expectancy: Parallel courses in time. Water 2021, 13, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Office for National Statistics. How Has Life Expectancy Changed over Time? 2015. Available online: https://www.ons.gov.uk/peoplepopulationandcommunity/birthsdeathsandmarriages/lifeexpectancies/articles/howhaslifeexpectancychangedovertime/2015-09-09 (accessed on 14 December 2022).
- Mishra, B.K.; Kumar, P.; Saraswat, C.; Chakraborty, S.; Gautam, A. Water security in a changing environment: Concept, challenges and solutions. Water 2021, 13, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNICEF. Water, Sanitation and Hygiene: Thematic Report; UNICEF: New Delhi, India, 2019; Available online: https://open.unicef.org/sites/transparency/files/2020-06/India-TP6-2018.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2023).
- Prevention, C.A.; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Global WASH Fast Facts. Global Water, Sanitation and Hygiene. 2022. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/healthywater/global/wash_statistics.html (accessed on 15 March 2023).
- Gelting, R.; Bliss, K.; Patrick, M.; Lockhart, G.; Handzel, T. Water, sanitation and hygiene in Haiti: Past, present, and future. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2013, 89, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Republic of Haiti: Ministry of Public Health and Population, National Directorate for Water Supply and Sanitation, 2013. National Plan for the Elimination of Cholera in Haiti, 2013–2022. Port-au-Prince: Republic of Haiti. Available online: http://new.paho.org/hq/index.php?option=com_docman&task=doc_download&gid=20326&Itemid=270&lang=eng/ (accessed on 18 March 2013).
- WHO. Drinking-Water, Sanitation and Hygiene in the WHO European Region: Highlights and Progress towards Achieving Sustainable Development Goal; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Water and Sanitation; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022; Available online: https://www.who.int/europe/news-room/fact-sheets/item/water-and-sanitation (accessed on 7 February 2023).
- Danaei, G.; Andrews, K.G.; Sudfeld, C.R.; Fink, G.; McCoy, D.C.; Peet, E.; Sania, A.; Smith Fawzi, M.C.; Ezzati, M.; Fawzi, W.W. Risk factors for childhood stunting in 137 developing countries: A comparative risk assessment analysis at global, regional, and country levels. PLoS Med. 2016, 13, e1002164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank Group. Reducing Inequalities in Water Supply, Sanitation, and Hygiene in the Era of the Sustainable Development Goals Synthesis Report of the WASH Poverty Diagnostic Initiative; OKR: 2017. Available online: https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/handle/10986/27831 (accessed on 14 February 2023).
- Donde, O.O.; Atoni, E.; Muia, A.W.; Yillia, P.T. COVID-19 pandemic: Water, sanitation and hygiene (WASH) as a critical control measure remains a major challenge in low-income countries. Water Res. 2021, 191, 116793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, A.B.; Raqib, R.; Khan, W.A.; Rahman, M.; Haque, R.; Alam, M.; Zaman, K.; Ross, A.G. Integrated Control of COVID-19 in Resource-Poor Countries; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Volume 101, pp. 98–101. [Google Scholar]
- Bond, T.; Roma, E.; Foxon, K.; Templeton, M.; Buckley, C. Ancient water and sanitation systems–applicability for the contemporary urban developing world. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 67, 935–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Jin, L.; He, T.; Chen, B.; Luo, X.; Feng, B.; Huang, W.; Li, J.; Fu, P.; Li, X. Bacteria and Antibiotic Resistance Genes (ARGs) in PM2.5 from China: Implications for Human Exposure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 963–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arditsoglou, A.; Voutsa, D. Partitioning of endocrine disrupting compounds in inland waters and wastewaters discharged into the coastal area of Thessaloniki, Northern Greece. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2010, 17, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, L.; Manaia, C.; Merlin, C.; Schwartz, T.; Dagot, C.; Ploy, M.C.; Michael, I.; Fatta-Kassinos, D. Urban wastewater treatment plants as hotspots for antibiotic resistant bacteria and genes spread into the environment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 447, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarzenbach, R.P.; Egli, T.; Hofstetter, T.B.; Von Gunten, U.; Wehrli, B. Global water pollution and human health. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2010, 35, 109–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazda, M.; Kumirska, J.; Stepnowski, P.; Mulkiewicz, E. Antibiotic resistance genes identified in wastewater treatment plant systems—A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 697, 134023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatis, N.K.; Konstantinou, I.K. Occurrence and removal of emerging pharmaceutical, personal care compounds and caffeine tracer in municipal sewage treatment plant in Western Greece. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2013, 48, 800–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabri, N.A.; Schmitt, H.; Van der Zaan, B.; Gerritsen, H.W.; Zuidema, T.; Rijnaarts, H.H.M.; Langenhoff, A.A.M. Prevalence of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in a wastewater effluent-receiving river in the Netherlands. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 8, 102245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, L.J.; Chefetz, B.; Abdeen, Z.; Boxall, A.B.A. Emerging investigator series: Towards a framework for establishing the impacts of pharmaceuticals in wastewater irrigation systems on agro-ecosystems and human health. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2019, 21, 605–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aburto, J.M.; Schöley, J.; Kashnitsky, I.; Zhang, L.; Rahal, C.; Missov, T.I.; Mills, M.C.; Dowd, J.B.; Kashyap, R. Quantifying impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic through life-expectancy losses: A population-level study of 29 countries. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2022, 51, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.J.; Loaiza, J.R.; Takyar, A.; Gilman, R.H. COVID-19 in Latin America: Novel transmission dynamics for a global pandemic? PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisson, S.; Engels, D.; Gordon, B.A.; Medlicott, K.O.; Neira, M.P.; Montresor, A.; Solomon, A.W.; Velleman, Y. Water, sanitation and hygiene for accelerating and sustaining progress on neglected tropical diseases: A new Global Strategy 2015–2020. Int. Health 2016, 8, i19–i21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prüss-Ustün, A.; Bartram, J.; Clasen, T.; Colford Jr, J.M.; Cumming, O.; Curtis, V.; Bonjour, S.; Dangour, A.D.; De France, J.; Fewtrell, L. Burden of disease from inadequate water, sanitation and hygiene in low-and middle-income settings: A retrospective analysis of data from 145 countries. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2014, 19, 894–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Horby, P.W.; Hayden, F.G.; Gao, G.F. A novel coronavirus outbreak of global health concern. Lancet 2020, 395, 470–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauza, V.; Sclar, G.D.; Bisoyi, A.; Majorin, F.; Ghugey, A.; Clasen, T. Water, sanitation, and hygiene practices and challenges during the COVID-19 pandemic: A cross-sectional study in rural Odisha, India. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2021, 104, 2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, D.; Verma, S.; Verma, P.; Mahanty, B.; Dutta, K.; Daverey, A.; Arunachalam, K. SARS-CoV-2 in wastewater: Challenges for developing countries. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2021, 231, 113634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, G.; Bartram, J.; Brocklehurst, C.; Colford, J.M., Jr.; Costa, F.; Cunliffe, D.; Dreibelbis, R.; Eisenberg, J.N.S.; Evans, B.; Girones, R. COVID-19: Urgent actions, critical reflections and future relevance of ‘WaSH’: Lessons for the current and future pandemics. J. Water Health 2020, 18, 613–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, A.; Kunwar, B.M.; Meierhofer, R. Water, sanitation, hygiene practices, health and nutritional status among children before and during the COVID-19 pandemic: Longitudinal evidence from remote areas of Dailekh and Achham districts in Nepal. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, R.; Bain, R.; Cumming, O. Correction: A long way to go-Estimates of combined water, sanitation and hygiene coverage for 25 sub-Saharan African countries. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. World Health Organization. Progress on Household Drinking Water, Sanitation and Hygiene 2000–2017: Special Focus on Inequalities; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Water, Sanitation, Hygiene, and Waste Management for the COVID-19 Virus: Interim Guidance, 19 March 2020; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zar, H.J.; Dawa, J.; Fischer, G.B.; Castro-Rodriguez, J.A. Challenges of COVID-19 in children in low-and middle-income countries. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2020, 35, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, A.; Schindler, C.; Odermatt, P.; Gerold, J.; Erismann, S.; Sharma, S.; Koju, R.; Utzinger, J.; Cissé, G. Nutritional and health status of children 15 months after integrated school garden, nutrition, and water, sanitation and hygiene interventions: A cluster-randomised controlled trial in Nepal. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desye, B. COVID-19 pandemic and water, sanitation, and hygiene: Impacts, challenges, and mitigation strategies. Environ. Health Insights 2021, 15, 11786302211029447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamboj, S.; Gupta, N.; Bandral, J.D.; Gandotra, G.; Anjum, N. Food safety and hygiene: A review. Int. J. Chem. Stud. 2020, 8, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havas, K.; Salman, M. Food security: Its components and challenges. Int. J. Food Saf. Nutr. Public Health 2011, 4, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giné-Garriga, R.; Delepiere, A.; Ward, R.; Alvarez-Sala, J.; Alvarez-Murillo, I.; Mariezcurrena, V.; Sandberg, H.G.; Saikia, P.; Avello, P.; Thakar, K. COVID-19 water, sanitation, and hygiene response: Review of measures and initiatives adopted by governments, regulators, utilities, and other stakeholders in 84 countries. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 795, 148789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EC-COM; European Commission. Proposal for a Regulation of the European Parliament and of the Council on on Minimum Requirements for Water Reuse (337 Final). 2018. Available online: Ec.europa.eu/environment/water/reuse.htm (accessed on 15 March 2023).
- EC-COM; European Commission. Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament, the Council and the European Economic and Social Committee, European Union Strategic Approach to Pharmaceuticals in the Environment (COM(2019) 128 Final); European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- EC-COM; European Commission. Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament, the Council, the European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions, Chemicals Strategy for Sustainability Towards a Toxic-Free Environment (COM(2020) 667 Final); European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- EC-COM; European Commission. Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament, the Council, the European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions, Pathway to a Healthy Planet for All EU Action Plan: ‘Towards Zero Pollution for Air, Water and Soil’ (COM/2021/400 Final); European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- EC-COM; European Commission. From the Commission to the European Parliament, the Council, the European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions on the Implementation of the Circular Economy Action Plan (190 Final). 2019. Available online: ec.europa.eu/environment/circular-economy/index_en.htm (accessed on 15 March 2023).
- EC-COM. European Commision. Proposal for a Directive of the European Parliament and of the Council Concerning Urban Wastewater Treatment (Recast) (COM(2022) 541 Final; European Commision: Brussels, Belgium, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- EC-COM. Regulation (EC) No 852/2004 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 29 April 2004 on the Hygiene of Foodstuffs; European Commision: Brussels, Belgium, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Johannessen, Å.; Rosemarin, A.; Thomalla, F.; Swartling, Å.G.; Stenström, T.A.; Vulturius, G. Strategies for building resilience to hazards in water, sanitation and hygiene (WASH) systems: The role of public private partnerships. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2014, 10, 102–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Schuyler House, R.; Peri, R. Public-private partnerships (PPPs) in water and sanitation in India: Lessons from China. Water Policy 2016, 18, 153–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cissé, G. Food-borne and water-borne diseases under climate change in low- and middle-income countries: Further efforts needed for reducing environmental health exposure risks. Acta Trop. 2019, 194, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutton, G.; Chase, C. Water Supply, Sanitation, and Hygiene. In Injury Prevention and Environmental Health. 2017. Available online: https://wwwncbi.53yu.com/books/NBK525207/ (accessed on 15 April 2023).
- Nhamo, G.; Nhemachena, C.; Nhamo, S. Is 2030 too soon for Africa to achieve the water and sanitation sustainable development goal? Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 669, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez, A.; Mtango, F.F.; Cairncross, S. What role for local government in sanitation promotion? Lessons from Tanzania. Water Policy 2014, 16, 1104–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinpourtehrani, M.; Gajendran, T.; Maund, K.; Sing, M. Preconditions, processes and structures: Interorganisational collaboration in the provision of post-disaster water, sanitation and hygiene (WASH) services. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2022, 80, 103177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momberg, D.J.; Voth-Gaeddert, L.E.; Richter, L.M.; Norris, S.A.; Said-Mohamed, R. Rethinking water, sanitation, and hygiene for human growth and development. Glob. Public Health 2022, 17, 3815–3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumwenda, S. Challenges to Hygiene Improvement in Developing Countries; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]


















Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Angelakis, A.N.; Capodaglio, A.G.; Passchier, C.W.; Valipour, M.; Krasilnikoff, J.; Tzanakakis, V.A.; Sürmelihindi, G.; Baba, A.; Kumar, R.; Haut, B.; et al. Sustainability of Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene: From Prehistoric Times to the Present Times and the Future. Water 2023, 15, 1614. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081614
Angelakis AN, Capodaglio AG, Passchier CW, Valipour M, Krasilnikoff J, Tzanakakis VA, Sürmelihindi G, Baba A, Kumar R, Haut B, et al. Sustainability of Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene: From Prehistoric Times to the Present Times and the Future. Water. 2023; 15(8):1614. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081614
Chicago/Turabian StyleAngelakis, Andreas N., Andrea G. Capodaglio, Cees W. Passchier, Mohammad Valipour, Jens Krasilnikoff, Vasileios A. Tzanakakis, Gül Sürmelihindi, Alper Baba, Rohitashw Kumar, Benoît Haut, and et al. 2023. "Sustainability of Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene: From Prehistoric Times to the Present Times and the Future" Water 15, no. 8: 1614. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081614





