Assessment of the Spatial Variations of Mercury and Methylmercury in the Sediment of a Lake and Its Inflow River Estuaries
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sediment Sample Collection
2.2. Analysis Methods
2.3. Quality Assurance and Control
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Basic Physicochemical Properties of Sediment
3.2. Contents of THg and MMHg in Sediment
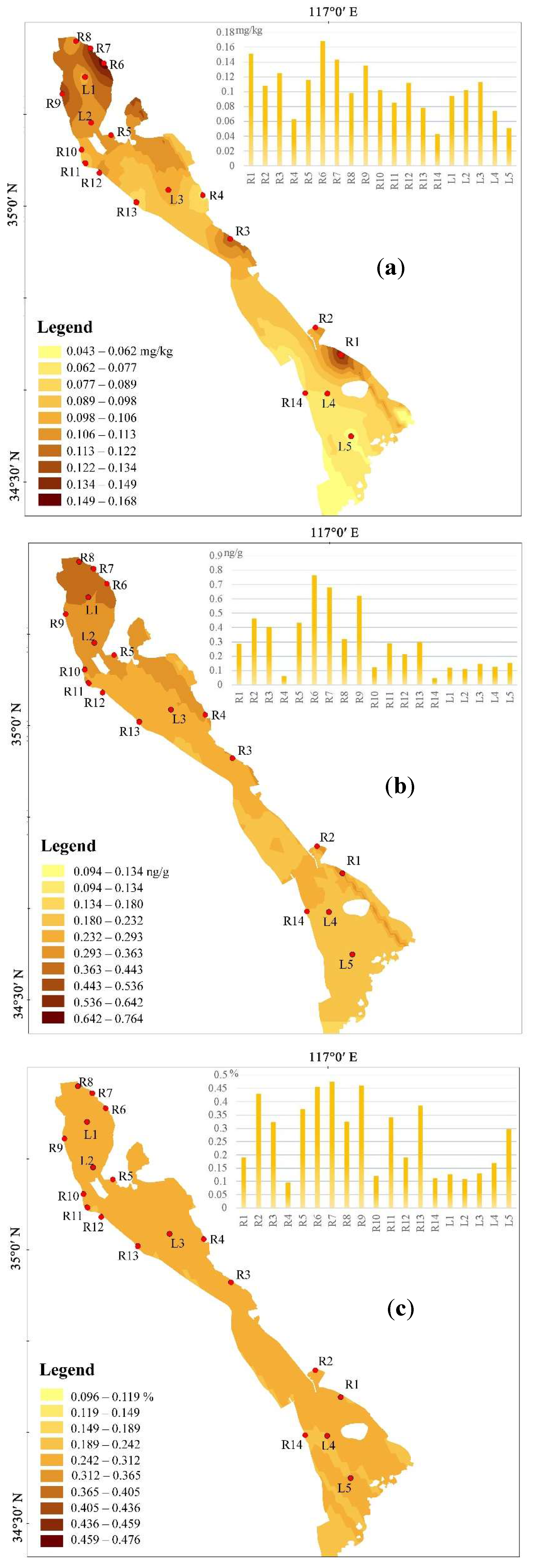
3.3. Spatial Distribution of THg and MMHg in Sediment
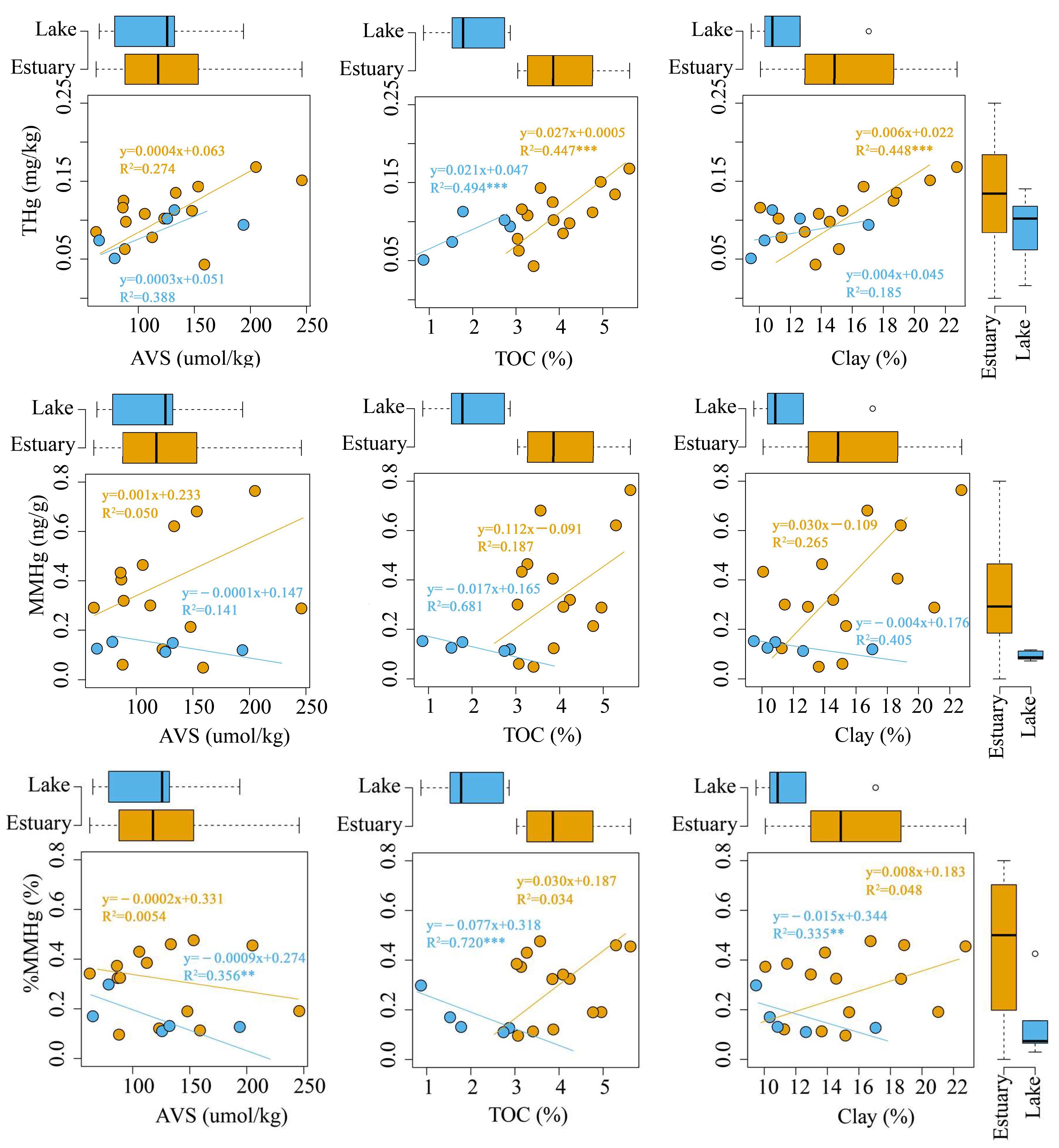
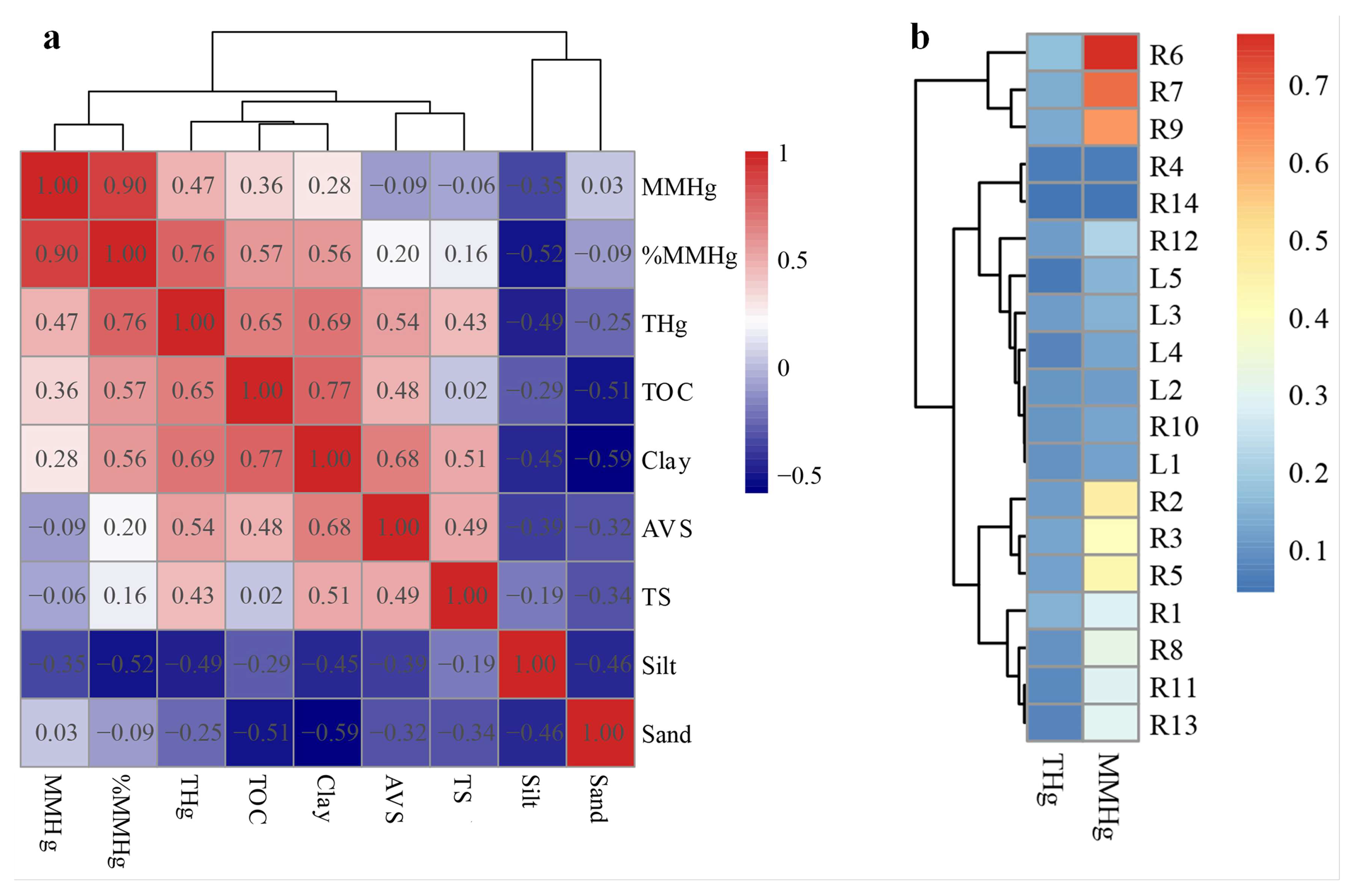
3.4. Relationship between THg and MMHg and Mineral Phases
3.5. Potential Source Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, S.; Jia, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, B. Total mercury and monomethylmercury in water, sediments, and hydrophytes from the rivers, estuary, and bay along the Bohai Sea coast, northeastern China. Appl. Geochem. 2009, 24, 1702–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Vogt, R.; Larssen, T. Environmental mercury in China: A review. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 2431–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C. Global distribution and environmental drivers of methylmercury production in sediments. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 407, 124700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Yang, Y.; Peng, R.; Huang, L. Distribution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Mercury in Soil around Some Coal-Fired Power Plant of Inner Mongolia. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2015, 9, 6135–6140. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Xiao, W.; Xu, Y.; Sun, X.; Wang, X. Spatial-temporal characteristics of mercury and methylmercury in marine sediment under the combined influences of river input and coastal currents. Chemosphere 2021, 274, 129728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.; Xu, Y.; Yan, Y.; Xiao, W.; Liu, M.; Cheng, M.; He, W.; Xu, F.; Wang, X. Mercury and methylmercury in China’s lake sediments and first estimation of mercury burial fluxes. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 770, 145338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.N.; Jiao, W.T.; Xiao, R.B.; Chen, W.P.; Chang, A.C. Soil pollution and site remediation policies in China: A review. Environ. Rev. 2015, 23, 150318143344008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haris, H.; Aris, A.Z.; bin Mokhtar, M. Mercury and methylmercury distribution in the intertidal surface sediment of a heavily anthrophogenically impacted saltwater-mangrove-sediment interplay zone. Chemosphere 2017, 166, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperfeld, M.; Diekert, G.; Studenik, S. Community dynamics in a nitrate-reducing microbial consortium cultivated with p-alkylated vs. non-p-alkylated aromatic compounds. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2018, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, C.; Ma, X.; Yang, L.; Ding, S. Evaluating the mercury distribution and release risks in sediments using high-resolution technology in Nansi Lake, China. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 3466–3478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, G.J.; Davidson, P.W.; Cox, C.; Shamlaye, C.F.; Palumbo, D.; Cernichiari, E.; Sloane-Reeves, J.; Wilding, G.E.; Kost, J.; Huang, L.S.; et al. Prenatal methylmercury exposure from ocean fish consumption in the Seychelles child development study. Lancet 2003, 361, 1686–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Yan, H.; Zhang, L.; Sun, G.; Li, P.; Feng, X. Mercury contents in rice and potential health risks across China. Environ. Int. 2019, 126, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.-L.; Liu, Y.-R.; Guan, W.-Y.; Zhong, H.; Qu, X.-M.; Zhang, T. Understanding mercury methylation in the changing environment: Recent advances in assessing microbial methylators and mercury bioavailability. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 714, 136827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Q.; Zhu, X.-M.; Wang, Q.; Fu, H.-H.; Hao, Y.-Q.; He, J.; Yang, Z.-L. Effects of Microbial Activities on Mercury Methylation in Farmland near Mercury Mining Area. Huan Jing Ke Xue Huanjing Kexue 2017, 38, 3020–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paranjape, A.R.; Hall, B.D. Recent advances in the study of mercury methylation in aquatic systems. Facets 2017, 2, 85–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Du, H.; Wang, D. Mercury methylation by anaerobic microorganisms: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 1893–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Obraztsova, A.; Pretto, P.; Deheyn, D.D.; Gieskes, J.; Tebo, B.M. Sulfide and iron control on mercury speciation in anoxic estuarine sediment slurries. Mar. Chem. 2008, 111, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollweg, T.A.; Gilmour, C.C.; Mason, R.P. Methylmercury production in sediments of Chesapeake Bay and the mid-Atlantic continental margin. Mar. Chem. 2009, 114, 86–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Ma, F.; Yao, X.; Shao, K.; Yang, L. Multi-spectroscopic investigation on the spatial distribution and copper binding ability of sediment dissolved organic matter in Nansi Lake, China. J. Hydrol. 2020, 591, 125289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Kim, M.-K.; Yi, S.-M.; Zoh, K.-D. Distributions of total mercury and methylmercury in surface sediments and fishes in Lake Shihwa, Korea. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 1059–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Dai, J.; Chen, G.; Jiang, F. Role of Sulfur Biogeochemical Cycle in Mercury Methylation in Estuarine Sediments: A Review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 423, 126964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Yin, D.; Rui, W. Research Progress on Mercury Methylation in Sediments. Asian J. Ecotoxicol. 2014, 5, 819–831. Available online: http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-STDL201405003.htm (accessed on 3 June 2022).
- Shi, T.; Cao, X.; Wang, S.; Dong, C.; Wang, R.; Liu, C.; Ren, Z. Distribution of Total Mercury and Methylmercury in the Sediment of the Nansi Lake, China. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2012, 21, 2722–2729. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Shen, W.; Ma, Z. Estimation of Mercury Emission from Coal Combustion in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 2711–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.P.; Li, A.C.; Xu, K.H.; Velozzi, D.M.; Yang, Z.S.; Milliman, J.D.; Demaster, D.J. Sedimentary features of the Yangtze River-derived along-shelf clinoform deposit in the East China Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 2006, 26, 2141–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, R.; Zhang, C.; Yin, D.; Yang, S.; Huang, X. Geochemical controls on the distribution of mercury and methylmercury in sediments of the coastal East China Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 667, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoit, J.M.; Gilmour, C.C.; Mason, R.P.; Riedel, G.S.; Riedel, G.F. Behavior of mercury in the Patuxent River estuary. Biogeochemistry 1998, 40, 249–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.C.; Pan, D.W.; Han, H.T.; Hu, X.P. Distribution and contamination assessment of arsenic and mercury in surface sediments from the intertidal zone of Yantai Sishili Bay, China. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2018, 24, 2024–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.-H.; Lien, C.-Y. Different Mercury Species Partitioning and Distribution in the Water and Sediment of a Eutrophic Estuary in Northern Taiwan. Water 2021, 13, 2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Ordiales, E.; Covelli, S.; Braidotti, G.; Petranich, E.; Pavoni, E.; Acquavita, A.; Loredo, J. Mercury and arsenic mobility in resuspended contaminated estuarine sediments (Asturias, Spain): A laboratory-based study. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 744, 140870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-F.; Ju, Y.-R.; Lin, G.-T.; Chen, C.-W.; Dong, C.-D. Methylmercury in Industrial Harbor Sediments in Taiwan: First Observations on its Occurrence, Distribution, and Measurement. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baeyens, W.; Leermakers, M. Elemental mercury concentrations and formation rates in the Scheldt estuary and the North Sea. Mar. Chem. 1998, 60, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Yan, W.; Wand, W.; Gu, S.; Chen, Z. Pollution of heavy metals in the Pearl River Estuary and its assessment of potential ecological risk. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2002, 21, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.; Liu, G.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y. Distribution, bioavailability and contamination assessment of mercury and arsenic in the surface sediments from the Yellow River Estuary, China. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2020, 27, 274–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolfhus, K.R.; Sakamoto, H.E.; Cleckner, L.B.; Stoor, R.W.; Babiarz, C.L.; Back, R.C.; Manolopoulos, H.; Hurley, J.P. Distribution and Fluxes of Total and Methylmercury in Lake Superior. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, M.; Li, B.; Xing, D.; Wang, X.; Wei, C.; Jia, Y. Comparison of mercury speciation and distribution in the water column and sediments between the algal type zone and the macrophytic type zone in a hypereutrophic lake (Dianchi Lake) in Southwestern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 417, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, D.F.; Moreira, R.A.; Sanches NA, O.; do Vale, C.A.; Daam, M.A.; Gorni, G.R.; Bastos, W.R. Dynamics of (total and methyl) mercury in sediment, fish, and crocodiles in an Amazonian Lake and risk assessment of fish consumption to the local population. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; DFan Ming, L.; Yuan, T.; Yue, P.; Liao, H. Source identification, geochemical normalization and influence factors of heavy metals in Yangtze River Estuary sediment. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 241, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopikrishna, V.G.; Kannan, V.M.; Binish, M.B.; Shu Kk Ur, M.A.; Mohan, M. Mercury in the sediments of freshwater lakes in Ny-lesund, Arctic. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmour, C.C.; Elias, D.A.; Kucken, A.M.; Brown, S.D.; Palumbo, A.V.; Schadt, C.W.; Wall, J.D. Sulfate-Reducing Bacterium Desulfovibrio desulfuricans ND132 as a Model for Understanding Bacterial Mercury Methylation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 3938–3951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parkpoin, P.; Thongra-Ar, W.; Delaune, R.D.; Jugsujinda, A. Adsorption and desorption of mercury by Bangpakong River sediments as influenced by salinities. Environ. Lett. 2001, 36, 623–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kainz, M.; Lucotte, M.; Parrish, C.C. Relationships between Organic Matter Composition and Methyl Mercury Content of Offshore and Carbon-Rich Littoral Sediments in an Oligotrophic Lake. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2003, 60, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirlean, N.; Andrus, V.E.; Baisch, P. Mercury pollution sources in sediments of Patos Lagoon Estuary, Southern Brazil. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2003, 46, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanei, H.; Goodarzi, F. Relationship between organic matter and mercury in recent lake sediment: The physical–geochemical aspects. Appl. Geochem. 2006, 21, 1900–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, P.; Vudamala, K.; Coulibaly, M.; Ramteke, D.; Chennuri, K.; Lean, D. Reduction of mercury (II) by humic substances—Influence of pH, salinity of aquatic system. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 10529–10538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Feng, Q.; Algeo, T.J.; Liu, J.; Zhou, C.; Wei, W.; Liu, J.; Them, T.R., II; Gill, B.C.; Chen, J. Sedimentary host phases of mercury (Hg) and implications for use of Hg as a volcanic proxy. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2020, 543, 116333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravichandran, M. Interactions between mercury and dissolved organic matter—A review. Chemosphere 2004, 55, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, D.; Lei, P.; Lan, W.; Li, T.; Pan, K. Litterfall-derived organic matter enhances mercury methylation in mangrove sediments of South China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 765, 142763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, J.E.; Hines, M.E. Biogeochemical mercury methylation influenced by reservoir eutrophication, Salmon Falls Creek Reservoir, Idaho, USA. Chem. Geol. 2009, 258, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, J.K.; Harmon, S.M.; Fu, T.T.; Gladden, J.B. Mercury removal, methylmercury formation, and sulfate-reducing bacteria profiles in wetland mesocosms. Chemosphere 2002, 46, 859–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesário, R.; Hintelmann, H.; O’Driscoll, N.J.; Monteiro, C.E.; Caetano, M.; Nogueira, M.; Canário, J. Biogeochemical Cycle of Mercury and Methylmercury in Two Highly Contaminated Areas of Tagus Estuary (Portugal). Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, J.K.; Kostka, J.E.; Frischer, M.E.; Saunders, F.M. Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria Methylate Mercury at Variable Rates in Pure Culture and in Marine Sediments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 2430–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Jiang, T.; Huang, R.; Wang, D.; Zhang, J.; Qian, S.; Yin, D. A simulation study of inorganic sulfur cycling in the water level fluctuation zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China and the implications for mercury methylation. Chemosphere 2017, 166, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravo, A.G.; Bouchet, S.; Tolu, J.; Björn, E.; Mateos-Rivera, A.; Bertilsson, S. Molecular Composition of Organic Matter Controls Methylmercury Formation in Boreal Lakes. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Regnell, O.; Watras, C.J. Microbial Mercury Methylation in Aquatic Environments: A Critical Review of Published Field and Laboratory Studies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 4–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavoie, R.A.; Amyot, M.; Lapierre, J. Global Meta-Analysis on the Relationship Between Mercury and Dissolved Organic Carbon in Freshwater Environments. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2019, 124, 1508–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ethier, A.L.M.; Scheuhammer, A.M.; Blais, J.M.; Paterson, A.M.; Mierle, G.; Ingram, R.; Lean, D.R.S. Mercury empirical relationships in sediments from three Ontario lakes. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 2087–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickard, D.; Morse, J.W. Acid volatile sulfide (AVS). Mar. Chem. 2005, 97, 141–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Li, Z.; Shao, B.; Zhang, Y.; He, W.; Lu, Y.; Gusvitskii, K.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; et al. Impact of dissolved organic matter and environmental factors on methylmercury concentrations across aquatic ecosystems inferred from a global dataset. Chemosphere 2022, 294, 133713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLaune, R.D.; Jugsujinda, A.; Devai, I.; Patrick, W.H.J. Relationship of sediment redox conditions to methyl mercury in surface sediment of Louisiana Lakes. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2004, 39, 1925–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmour, C.C.; Henry, E.A.; Mitchell, R. Sulfate stimulation of mercury methylation in freshwater sediments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1992, 26, 2281–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Mangal, V.; Rennie, M.D.; Tong, H.; Simpson, M.J.; Mitchell, C.P.J. Mercury Methylation and Methylmercury Demethylation in Boreal Lake Sediment with Legacy Sulphate Pollution. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2022, 24, 932–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Site | Lake | THg | MMHg | %MMHg | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg/kg | ng/g | % | |||
| Estuary | Dagu Estuary, China | 0.036 | - | - | [28] |
| Danshuei River Estuary, China | 0.379 | - | - | [29] | |
| Asturias Estuary, Spain | 0.52 | - | - | [30] | |
| Kaohsiung Estuary, China | 0.149 | 0.31 | - | [31] | |
| Scheldt Estuary, Belgium | 0.18 | - | - | [32] | |
| Pearl River Estuary, China | 0.354 | - | - | [33] | |
| Lake | Yellow River, China | 0.015 | - | [34] | |
| Superior Lake, Canada | 0.088 | 0.21 | - | [35] | |
| Dianchi, China | 0.18 | 1.2 | - | [36] | |
| Amazonian Lake | 0.12 | 2 | 1.7 | [37] | |
| Chao Lake, China | 0.096 | - | - | [38] | |
| Tai Lake, China | 0.097 | - | - | [39] | |
| Daxingkai Lake, China | 1.66 | 1.66 | - | [6] | |
| Xiaoxingkai Lake, China | - | 0.78 | - | [6] | |
| Arctic freshwater lakes | 22.23 | 0.41 | - | [38] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xin, S.; Wang, B.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, S. Assessment of the Spatial Variations of Mercury and Methylmercury in the Sediment of a Lake and Its Inflow River Estuaries. Water 2023, 15, 1494. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081494
Xin S, Wang B, Yuan Y, Wang S. Assessment of the Spatial Variations of Mercury and Methylmercury in the Sediment of a Lake and Its Inflow River Estuaries. Water. 2023; 15(8):1494. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081494
Chicago/Turabian StyleXin, Shuhan, Bingbing Wang, Yin Yuan, and Shiliang Wang. 2023. "Assessment of the Spatial Variations of Mercury and Methylmercury in the Sediment of a Lake and Its Inflow River Estuaries" Water 15, no. 8: 1494. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081494
APA StyleXin, S., Wang, B., Yuan, Y., & Wang, S. (2023). Assessment of the Spatial Variations of Mercury and Methylmercury in the Sediment of a Lake and Its Inflow River Estuaries. Water, 15(8), 1494. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081494






