Abundance of Microplastics in Two Venus Clams (Meretrix lyrata and Paratapes undulatus) from Estuaries in Central Vietnam
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples Collection
2.2. Microplastics Extraction and Analysis
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
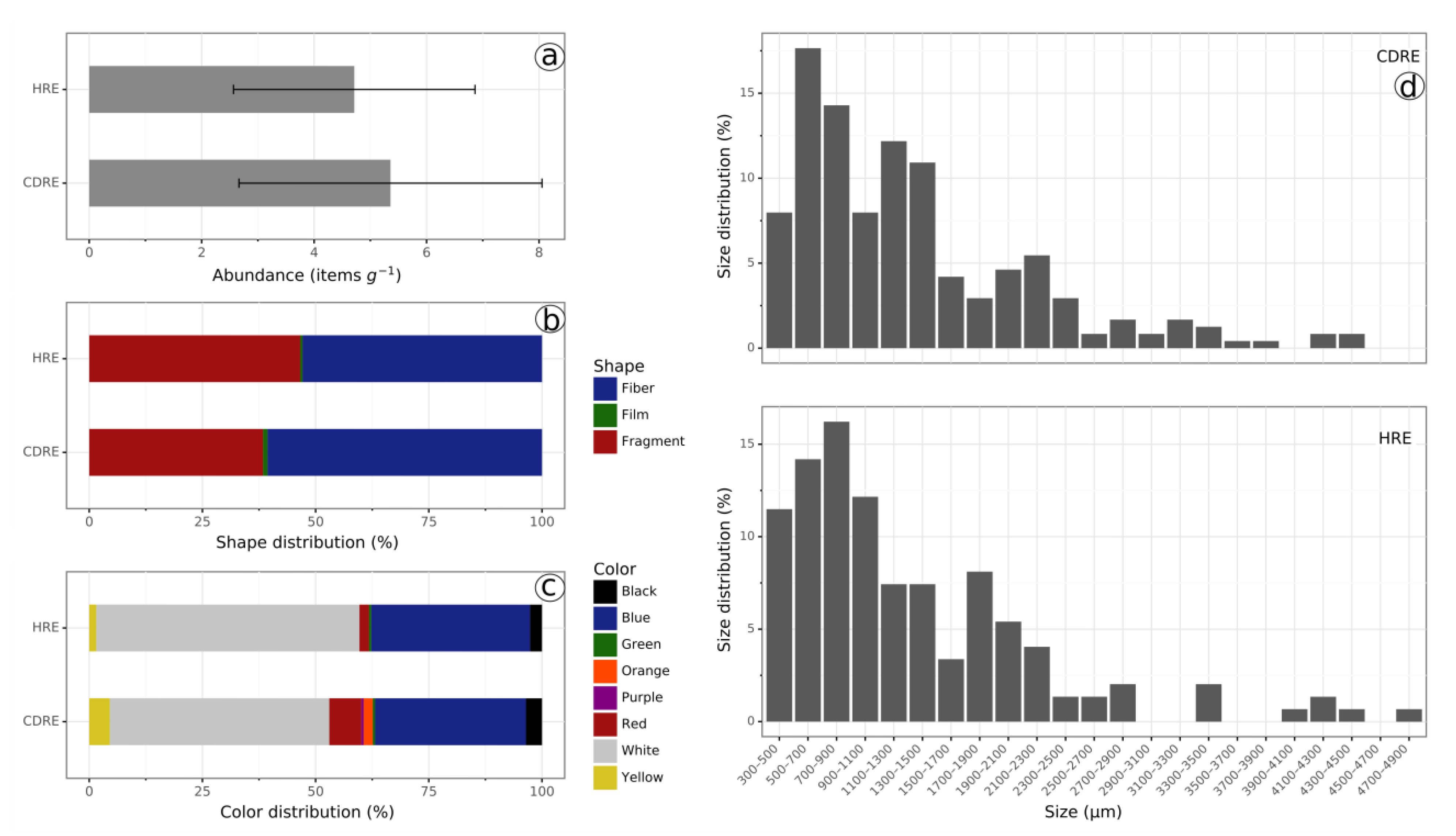
3.1. Distribution Characteristics of Microplastics in the Hard Clam Meretrix lyrata
3.2. Distribution Characteristics of Microplastics in the Undulate Venus Clam Paratapes undulatus
3.3. Distribution Characteristics of Microplastics in Estuarine Waters
4. Discussions
4.1. Microplastic Concentration in Bivalves
| Group | Species | Area | Sampling Site | Digestion Solution | MPs Concentration | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Items g−1) | (Items Individual−1) | ||||||
| Clam | Meretrix lyrata | Danang, Vietnam | Wild, Han River Estuary | KOH 10% | 4.71 ± 2.15 | 12.73 ± 4.49 | This study |
| Clam | Meretrix lyrata | Danang, Vietnam | Wild, Cu De River Estuary | KOH 10% | 5.36 ± 2.69 | 13.20 ± 7.66 | This study |
| Clam | Meretrix lyrata | Ho Chi Minh city, Vietnam | Farm, Can Gio beach sand | KOH 10% | 2.7 ± 2.4 | 3.6 ± 2.1 | [37] |
| Clam | Meretrix lyrata | Surat Thani, Thailand | Wild, Bandon Bay | H2O2 30% | 0.28 ± 0.06–0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.67 ± 0.15–0.23 ± 0.09 | [38] |
| Clam | Paratapes undulatus | Danang, Vietnam | Wild, Han River Estuary | KOH 10% | 2.17 ± 0.43 | 3.43 ± 0.98 | This study |
| Clam | Paratapes undulatus | Danang, Vietnam | Wild, Cu De River Estuary | KOH 10% | 2.38 ± 1.28 | 3.30 ± 0.94 | This study |
| Clam | Tapes philippinarum | South Korea | Market | KOH 10% | 0.34 ± 0.31 | 1.15 ± 0.74 | [24] |
| Clam | Venerupis philippinarum | British Columbia | Wild | HNO3 69–71% | 0.9 ± 0.9 | n.a. | [21] |
| Clam | Venerupis philippinarum | British Columbia | Farm | HNO3 69–71% | 1.7 ± 1.2 | n.a. | [21] |
| Mussel | Perna viridis | Thanh Hoa, Vietnam | Wild | KOH 10% | 0.29 ± 0.14 | 2.60 ± 1.14 | [39] |
| Mussel | Mytilus edulis | South Korea | Market | KOH 10% | 0.12 ± 0.11 | 0.68 ± 0.64 | [24] |
| Mussel | Mytilus edulis | Belgium | Wild | HNO3 65%: HClO4 68% (4:1 v:v) | 0.26–0.51 | n.a. | [40] |
| Mussel | Mytilus edulis | Belgium | Market | HNO3 65%: HClO4 68% (4:1 v:v) | 0.35 | n.a. | [40] |
| Mussel | Mytilus edulis | France | Wild and farm | KOH 10% | 0.23 ± 0.20 | 0.60 ± 0.56 | [20] |
| Mussel | Mytilus edulis | France | Wild | KOH 10% | 0.15 ± 0.06–0.25 ± 0.16 | 0.76 ± 0.40–0.78 ± 0.30 | [41] |
| Mussel | Mytilus edulis | Germany | Farm | HNO3 69% | 0.36 ± 0.07 | n.a. | [23] |
| Mussel | Mytilus galloprovincialis | Qingdao, China | Wild | KOH 10% | 2.0 | 0.53 | [25] |
| Mussel | Mytilus galloprovincialis | Qingdao, China | Market/farm | KOH 10% | 3.17 | 1.9 | [25] |
| Mussel | Mytilus galloprovincialis | Italy | Market | H2O2 30% | 4.4–11.4 | 3.6–12.4 | [26] |
| Mussel | Mytilus galloprovincialis | Italy | Wild | H2O2 30% | 7.2 | 3.0 | [26] |
| Oyster | Crassostrea gigas | France | Wild and farm | KOH 10% | 0.18 ± 0.16 | 2.10 ± 1.71 | [20] |
| Oyster | Crassostrea gigas | South Korea | Market | KOH 10% | 0.07 ± 0.06 | 0.77 ± 0.74 | [24] |
| Scallop | Patinopecten yessoensis | South Korea | Market | KOH 10% | 0.08 ± 0.08 | 1.21 ± 0.71 | [24] |
| Scallop | Argopecten purpuratus | Lima, Peru | Market | KOH 10% | 0.13 ± 0.03 | 2.25 ± 0.54 | [45] |
4.2. Characteristics of Microplastics in Bivalve Species
4.3. Health Risk Posed to Bivalve Consumers
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HRE | Han River Estuary |
| CDRE | Cu De River Estuary |
| PE | polyethylene |
| PP | polypropylene |
| LDPE | low-density polyethylene |
| HDPE | high-density polyethylene |
| PVC | polyvinyl chloride |
| PET | polyethylene terephthalate |
| PA | polyamide |
| PAN | polyacrylonitrile |
| PVOH | poly-ethylene vinyl alcohol copolymers |
| PDMS | polydimethylsiloxane |
| PU | polyurethane |
References
- Frias, J.P.; Nash, R. Microplastics: Finding a Consensus on the Definition. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 138, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, S. Marine Debris: Understanding, Preventing and Mitigating the Significant Adverse Impacts on Marine and Coastal Biodiversity; Secretariat of the Convention on Biological Diversity: Montreal, QC, Canda, 2016.
- Shahul Hamid, F.; Bhatti, M.S.; Anuar, N.; Anuar, N.; Mohan, P.; Periathamby, A. Worldwide Distribution and Abundance of Microplastic: How Dire Is the Situation? Waste Manag. Res. 2018, 36, 873–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jambeck, J.R.; Geyer, R.; Wilcox, C.; Siegler, T.R.; Perryman, M.; Andrady, A.; Narayan, R.; Law, K.L. Plastic Waste Inputs from Land into the Ocean. Science 2015, 347, 768–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hitchcock, J.N.; Mitrovic, S.M. Microplastic Pollution in Estuaries across a Gradient of Human Impact. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 247, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nor, N.H.M.; Obbard, J.P. Microplastics in Singapore’s Coastal Mangrove Ecosystems. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 79, 278–283. [Google Scholar]
- Bayo, J.; Rojo, D.; Olmos, S. Abundance, Morphology and Chemical Composition of Microplastics in Sand and Sediments from a Protected Coastal Area: The Mar Menor Lagoon (SE Spain). Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 1357–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falahudin, D.; Cordova, M.R.; Sun, X.; Yogaswara, D.; Wulandari, I.; Hindarti, D.; Arifin, Z. The First Occurrence, Spatial Distribution and Characteristics of Microplastic Particles in Sediments from Banten Bay, Indonesia. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 705, 135304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Cauwenberghe, L.; Vanreusel, A.; Mees, J.; Janssen, C.R. Microplastic Pollution in Deep-Sea Sediments. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 182, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, B.; Pathak, J.; Singh, P.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, A.; Kaushik, S.; Thakur, T.K. Microplastics in the Ecosystem: An Overview on Detection, Removal, Toxicity Assessment, and Control Release. Water 2022, 15, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gall, S.C.; Thompson, R.C. The Impact of Debris on Marine Life. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 92, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setälä, O.; Norkko, J.; Lehtiniemi, M. Feeding Type Affects Microplastic Ingestion in a Coastal Invertebrate Community. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 102, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, J.E.; Rosa, M.; Shumway, S.E. Capture, Ingestion, and Egestion of Microplastics by Suspension-Feeding Bivalves: A 40-Year History. Anthr. Coasts 2019, 2, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Lusher, A.L.; Rotchell, J.M.; Deudero, S.; Turra, A.; Bråte, I.L.N.; Sun, C.; Hossain, M.S.; Li, Q.; Kolandhasamy, P. Using Mussel as a Global Bioindicator of Coastal Microplastic Pollution. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 522–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Man, Y.B.; Mo, W.Y.; Man, K.Y.; Wong, M.H. Direct and Indirect Effects of Microplastics on Bivalves, with a Focus on Edible Species: A Mini-Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 50, 2109–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waser, A.M. Predation on Intertidal Mussels: Influence of Biotic Factors on the Survival of Epibenthic Bivalve Beds; Vrije Universiteit: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Smaal, A.C.; Ferreira, J.G.; Grant, J.; Petersen, J.K.; Strand, Ø. Goods and Services of Marine Bivalves; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, X.; Su, L.; Li, H.; Liang, M.; Shi, H. Assessing the Relationship between the Abundance and Properties of Microplastics in Water and in Mussels. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naji, A.; Nuri, M.; Vethaak, A.D. Microplastics Contamination in Molluscs from the Northern Part of the Persian Gulf. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuong, N.N.; Poirier, L.; Pham, Q.T.; Lagarde, F.; Zalouk-Vergnoux, A. Factors Influencing the Microplastic Contamination of Bivalves from the French Atlantic Coast: Location, Season and/or Mode of Life? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 129, 664–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, K.; Dudas, S.E. Microplastic Ingestion by Wild and Cultured Manila Clams (Venerupis philippinarum) from Baynes Sound, British Columbia. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2016, 71, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Qu, X.; Su, L.; Zhang, W.; Yang, D.; Kolandhasamy, P.; Li, D.; Shi, H. Microplastics in Mussels along the Coastal Waters of China. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 214, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Cauwenberghe, L.; Janssen, C.R. Microplastics in Bivalves Cultured for Human Consumption. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 193, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.; Shim, W.J.; Jang, M.; Han, G.M.; Hong, S.H. Abundance and Characteristics of Microplastics in Market Bivalves from South Korea. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 245, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin-Feng, D.; Jing-Xi, L.I.; Cheng-Jun, S.U.N.; Chang-Fei, H.E.; Jiang, F.; Feng-Lei, G.A.O.; Zheng, L. Separation and Identification of Microplastics in Digestive System of Bivalves. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2018, 46, 690–697. [Google Scholar]
- Renzi, M.; Guerranti, C.; Blašković, A. Microplastic Contents from Maricultured and Natural Mussels. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 131, 248–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, C.L. A Comparison of Microplastics in Farmed and Wild Shellfish near Vancouver Island and Potential Implications for Contaminant Transfer to Humans. Ph.D. Thesis, Royal Roads University, Victoria, BC, Canada, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Vietnam Association of Seafood Exporters and Producers Clam Exports in the First 8 Months of 2021 Increased by 54%. Available online: https://vasep.com.vn/san-pham-xuat-khau/hai-san-khac/xuat-nhap-khau/xuat-khau-ngheu-8-thang-dau-nam-2021-tang-54-22849.html (accessed on 27 February 2023).
- Nguyen, A.; Hai, B. Clam Export is Expected to Exceed the Range. Available online: https://thuysanvietnam.com.vn/emagazine/ngao-xuat-khau-ky-vong-vuot-tam/ (accessed on 27 February 2023).
- Strady, E.; Dang, T.H.; Dao, T.D.; Dinh, H.N.; Do, T.T.D.; Duong, T.N.; Duong, T.T.; Hoang, D.A.; Kieu-Le, T.C.; Le, T.P.Q. Baseline Assessment of Microplastic Concentrations in Marine and Freshwater Environments of a Developing Southeast Asian Country, Viet Nam. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 162, 111870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strady, E.; Kieu-Le, T.-C.; Gasperi, J.; Tassin, B. Temporal Dynamic of Anthropogenic Fibers in a Tropical River-Estuarine System. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 259, 113897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran-Nguyen, Q.A.; Nguyen, H.N.Y.; Strady, E.; Nguyen, Q.T.; Trinh-Dang, M. Characteristics of Microplastics in Shoreline Sediments from a Tropical and Urbanized Beach (Da Nang, Vietnam). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 161, 111768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T. Clam Exports Bring in More than 62 Million USD. Available online: https://haiquanonline.com.vn/xuat-khau-ngheu-mang-ve-hon-62-trieu-usd-153325.html (accessed on 27 February 2023).
- Nguyen, H.P.; Vo, S.T. Some Main Resources of Bivalve (Bivalve-Mollusca) in Marine Waters of Vietnam. Mar. Res. Anthol. Inst. Oceanogr. Nha Trang Vietnam 1996, 7, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Thiele, C.J.; Hudson, M.D.; Russell, A.E. Evaluation of Existing Methods to Extract Microplastics from Bivalve Tissue: Adapted KOH Digestion Protocol Improves Filtration at Single-Digit Pore Size. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 142, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kershaw, P.J.; Turra, A.; Galgani, F. Guidelines for the Monitoring and Assessment of Plastic Litter and Microplastics in the Ocean; GESAMP Joint Group of Experts on the Scientific Aspects of Marine Environmental Protection: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kieu-Le, T.-C.; Tran, Q.-V.; Strady, E. Anthropogenic Fibres in White Clams, Meretrix Lyrata, Cultivated Downstream a Developing Megacity, Ho Chi Minh City, Viet Nam. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 174, 113302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinfak, N.; Sompongchaiyakul, P.; Charoenpong, C.; Shi, H.; Yeemin, T.; Zhang, J. Abundance, Composition, and Fate of Microplastics in Water, Sediment, and Shellfish in the Tapi-Phumduang River System and Bandon Bay, Thailand. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 781, 146700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, P.N.; Tuan, P.Q.; Thuy, D.T.; Amiard, F. Contamination of Microplastic in Bivalve: First Evaluation in Vietnam. Sci. Earth 2019, 41, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Witte, B.; Devriese, L.; Bekaert, K.; Hoffman, S.; Vandermeersch, G.; Cooreman, K.; Robbens, J. Quality Assessment of the Blue Mussel (Mytilus edulis): Comparison between Commercial and Wild Types. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 85, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermabessiere, L.; Paul-Pont, I.; Cassone, A.-L.; Himber, C.; Receveur, J.; Jezequel, R.; El Rakwe, M.; Rinnert, E.; Rivière, G.; Lambert, C. Microplastic Contamination and Pollutant Levels in Mussels and Cockles Collected along the Channel Coasts. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 250, 807–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baechler, B.R.; Granek, E.F.; Hunter, M.V.; Conn, K.E. Microplastic Concentrations in Two Oregon Bivalve Species: Spatial, Temporal, and Species Variability. Limnol. Oceanogr. Lett. 2020, 5, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Courtene-Jones, W.; Wang, X.; Song, Z.; Wei, N.; Li, D. Elucidating the Vertical Transport of Microplastics in the Water Column: A Review of Sampling Methodologies and Distributions. Water Res. 2020, 186, 116403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.K.; Hong, S.H.; Eo, S.; Jang, M.; Han, G.M.; Isobe, A.; Shim, W.J. Horizontal and Vertical Distribution of Microplastics in Korean Coastal Waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 12188–12197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De-la-Torre, G.; Mendoza-Castilla, L.; Pilar, R. Microplastic Contamination in Market Bivalve Argopecten purpuratus from Lima, Peru. Manglar 2019, 16, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Yang, D.; Li, L.; Jabeen, K.; Shi, H. Microplastics in Commercial Bivalves from China. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 207, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-X.; Ma, L.-S.; Lin, L.; Ni, Z.-X.; Xu, X.-R.; Shi, H.-H.; Yan, Y.; Zheng, G.-M.; Rittschof, D. Microplastics in Oysters Saccostrea Cucullata along the Pearl River Estuary, China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 236, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Wang, T.; Zhu, L.; Xu, P.; Wang, X.; Gao, L.; Li, D. Analysis of Suspended Microplastics in the Changjiang Estuary: Implications for Riverine Plastic Load to the Ocean. Water Res. 2019, 161, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Niu, X.; Tang, M.; Zhang, B.-T.; Wang, G.; Yue, W.; Kong, X.; Zhu, J. Distribution of Microplastics in Surface Water of the Lower Yellow River near Estuary. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 707, 135601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathalon, A.; Hill, P. Microplastic Fibers in the Intertidal Ecosystem Surrounding Halifax Harbor, Nova Scotia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 81, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brillant, M.G.S.; MacDonald, B.A. Postingestive Selection in the Sea Scallop, Placopecten magellanicus (Gmelin): The Role of Particle Size and Density. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2000, 253, 211–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firdaus, M.; Trihadiningrum, Y.; Lestari, P. Microplastic Pollution in the Sediment of Jagir Estuary, Surabaya City, Indonesia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 150, 110790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, V.E.; Figueiredo, G.M. Microplastic in the Sediments of a Highly Eutrophic Tropical Estuary. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 146, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GSO General Statistic Office of Vietnam—Vietnam Statistical Yearbook 2021. Available online: https://www.gso.gov.vn/du-lieu-va-so-lieu-thong-ke/2022/01/infographic-dan-so-lao-dong-va-viec-lam-nam-2021/ (accessed on 28 February 2023).
- Agrotrade The First Time to Organize a Forum to Consume Clams and Oysters in the Northern Coastal Provinces. Available online: https://bnews.vn/lan-dau-to-chuc-dien-dan-tieu-thu-ngao-hau-cac-tinh-ven-bien-phia-bac/179212.html (accessed on 27 February 2023).
- Smith, M.; Love, D.C.; Rochman, C.M.; Neff, R.A. Microplastics in Seafood and the Implications for Human Health. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2018, 5, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karbalaei, S.; Hanachi, P.; Walker, T.R.; Cole, M. Occurrence, Sources, Human Health Impacts and Mitigation of Microplastic Pollution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 36046–36063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lithner, D.; Larsson, Å.; Dave, G. Environmental and Health Hazard Ranking and Assessment of Plastic Polymers Based on Chemical Composition. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 3309–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
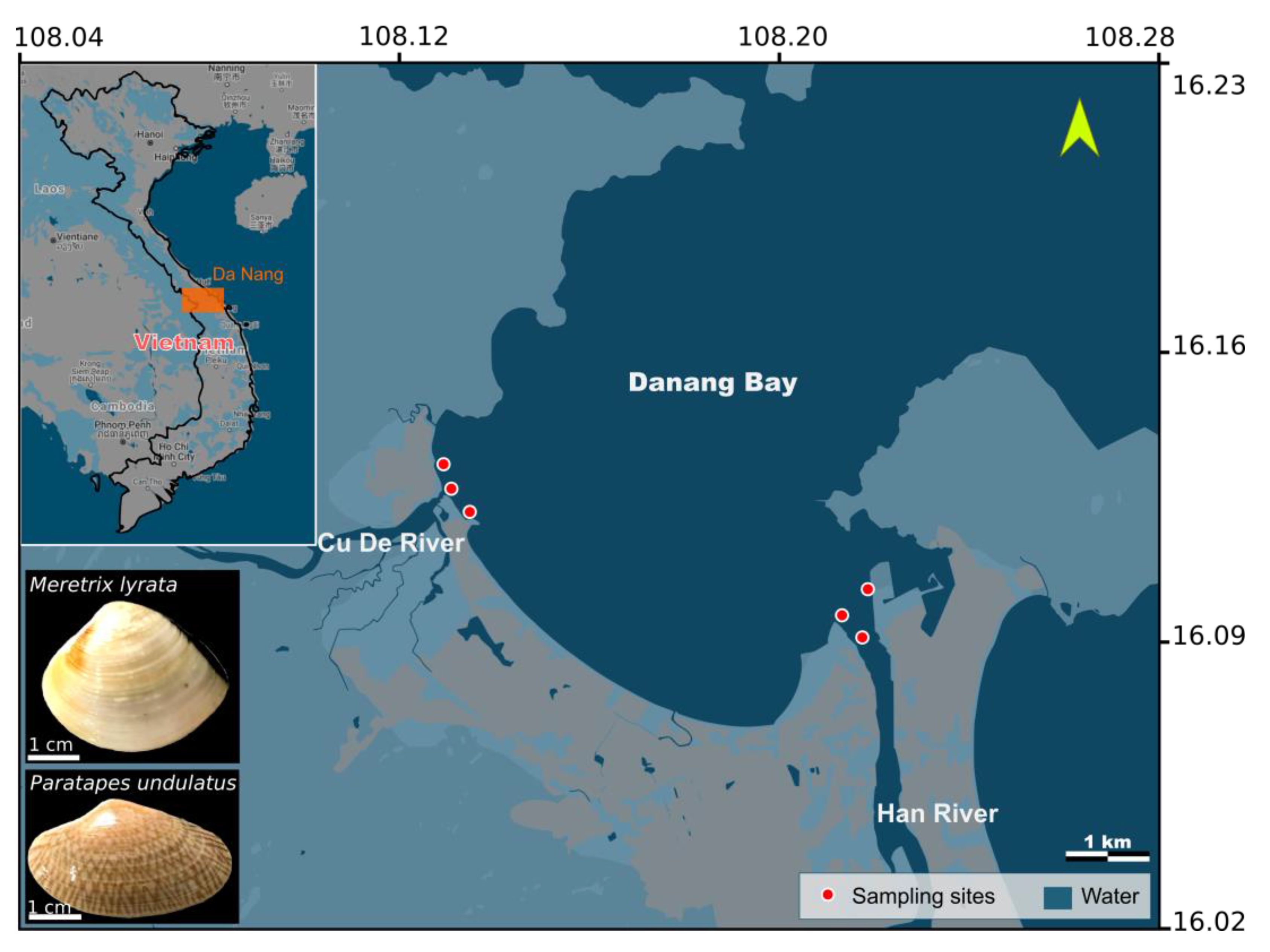


| Species | Sampling Site | Number | Shell Length (cm) | Wet Tissue Weight (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Meretrix lyrata | Han River Estuary | 15 | 3.6 ± 0.4 | 2.80 ± 1.05 |
| Cu De River Estuary | 15 | 3.8 ± 0.4 | 2.40 ± 0.73 | |
| Paratapes undulatus | Han River Estuary | 15 | 3.8 ± 0.5 | 1.56 ± 0.25 |
| Cu De River Estuary | 15 | 3.5 ± 0.7 | 1.58 ± 0.49 |
| Area | Species | Microplastic Concentration in Bivalves (Items g−1) | Bivalve Consumption (g Person−1 Year−1) | Microplastic Concentration in Consumer (Items Person−1 Year−1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vietnam | Clams (Meretrix lyrata and Paratapes undulatus) | 3.66 | 680 a | 2489 | This study |
| South Korea | Bivalves (oyster Crassostrea gigas, mussel Mytilus edulis, Manila clam Tapes philippinarum, scallop Patinopecten yessoensis) | 0.15 | 3475 a | 521 | [24] |
| China | Mussel | 2.4 | 2765 a | 6636 | [24] |
| Iran | Mollusc (A. umbonella, A. purpuratus, P. radiata) | 2.0 | 2400 b | 4800 | [19] |
| Belgium | Mollusc (M. edulis and C. gigas) | 0.42 | 26,316 b | 11,053 | [23] |
| France and Ireland | Mollusc (M. edulis and C. gigas) | 0.42 | 4307 b | 1809 | [23] |
| Canada | Mussel | 7.42 | 1133 a | 8407 | [24] |
| Italy | Mussel | 8.33 | 1437 a | 11,970 | [24] |
| UK | Mussel | 0.9 | 379 a | 341 | [24] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tran-Nguyen, Q.A.; Nguyen, T.Q.; Phan, T.L.T.; Vo, M.V.; Trinh-Dang, M. Abundance of Microplastics in Two Venus Clams (Meretrix lyrata and Paratapes undulatus) from Estuaries in Central Vietnam. Water 2023, 15, 1312. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15071312
Tran-Nguyen QA, Nguyen TQ, Phan TLT, Vo MV, Trinh-Dang M. Abundance of Microplastics in Two Venus Clams (Meretrix lyrata and Paratapes undulatus) from Estuaries in Central Vietnam. Water. 2023; 15(7):1312. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15071312
Chicago/Turabian StyleTran-Nguyen, Quynh Anh, Tuan Quy Nguyen, Thao Linh Thi Phan, Minh Van Vo, and Mau Trinh-Dang. 2023. "Abundance of Microplastics in Two Venus Clams (Meretrix lyrata and Paratapes undulatus) from Estuaries in Central Vietnam" Water 15, no. 7: 1312. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15071312
APA StyleTran-Nguyen, Q. A., Nguyen, T. Q., Phan, T. L. T., Vo, M. V., & Trinh-Dang, M. (2023). Abundance of Microplastics in Two Venus Clams (Meretrix lyrata and Paratapes undulatus) from Estuaries in Central Vietnam. Water, 15(7), 1312. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15071312







