Effect of Temperature on Microorganisms and Nitrogen Removal in a Multi-Stage Surface Flow Constructed Wetland
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
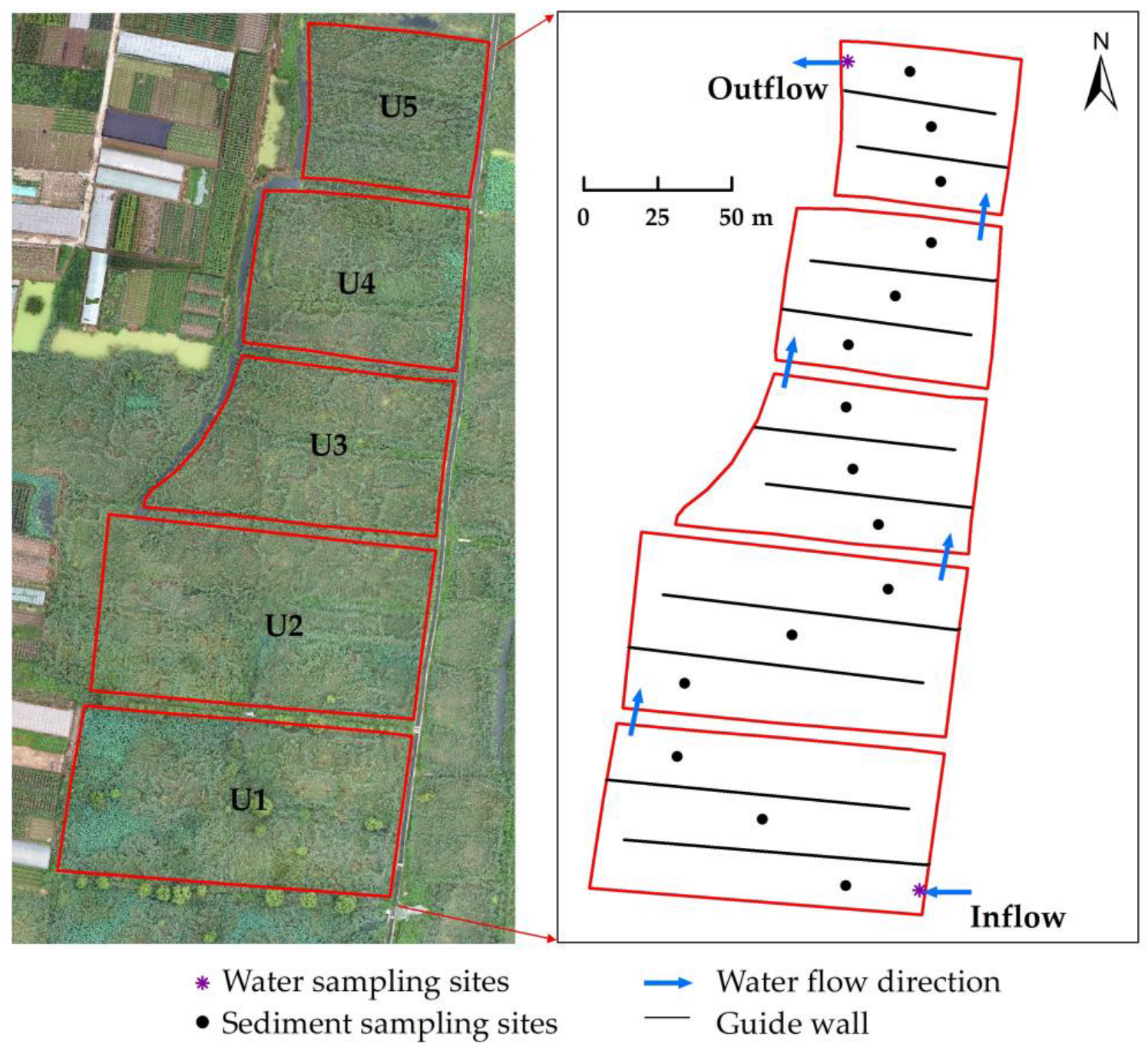
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.2.1. Water Sample Collection and Physicochemical Index Analysis
2.2.2. Microorganism Sample Collection
2.2.3. DNA Extraction, Library Construction, and Metagenomic Sequencing
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
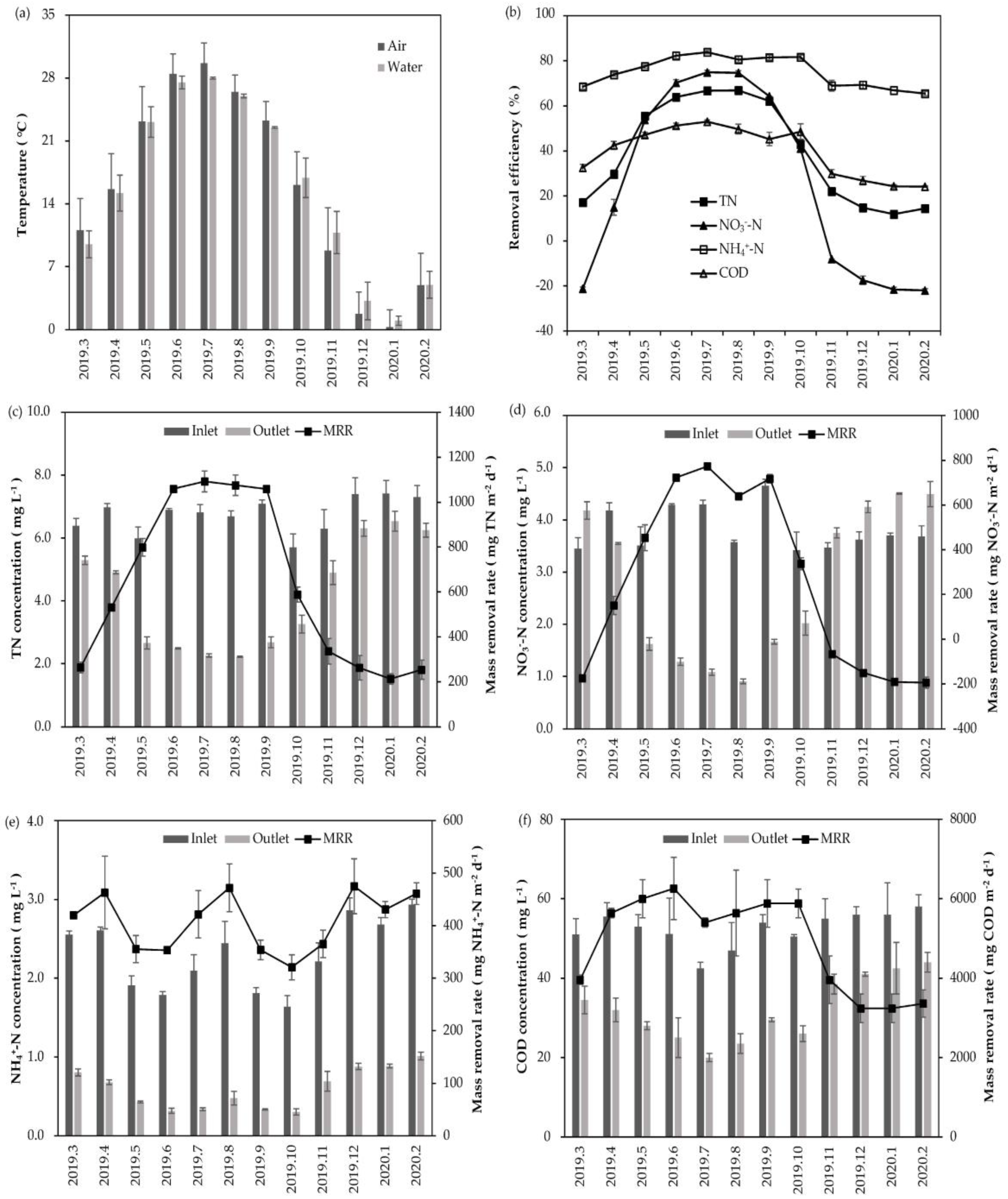
3.1. Water Purification Performance
3.2. Microbial Community Structure
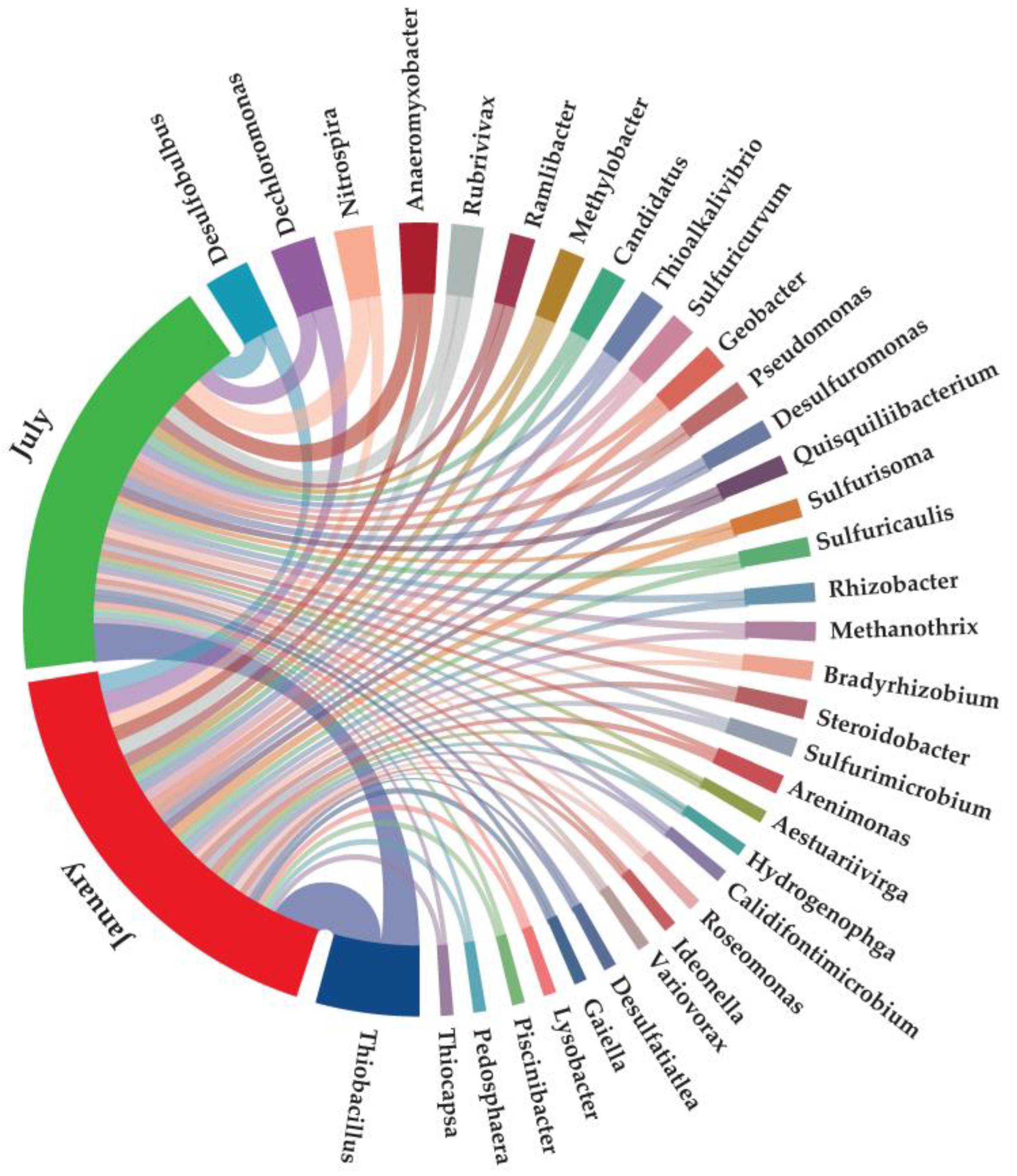
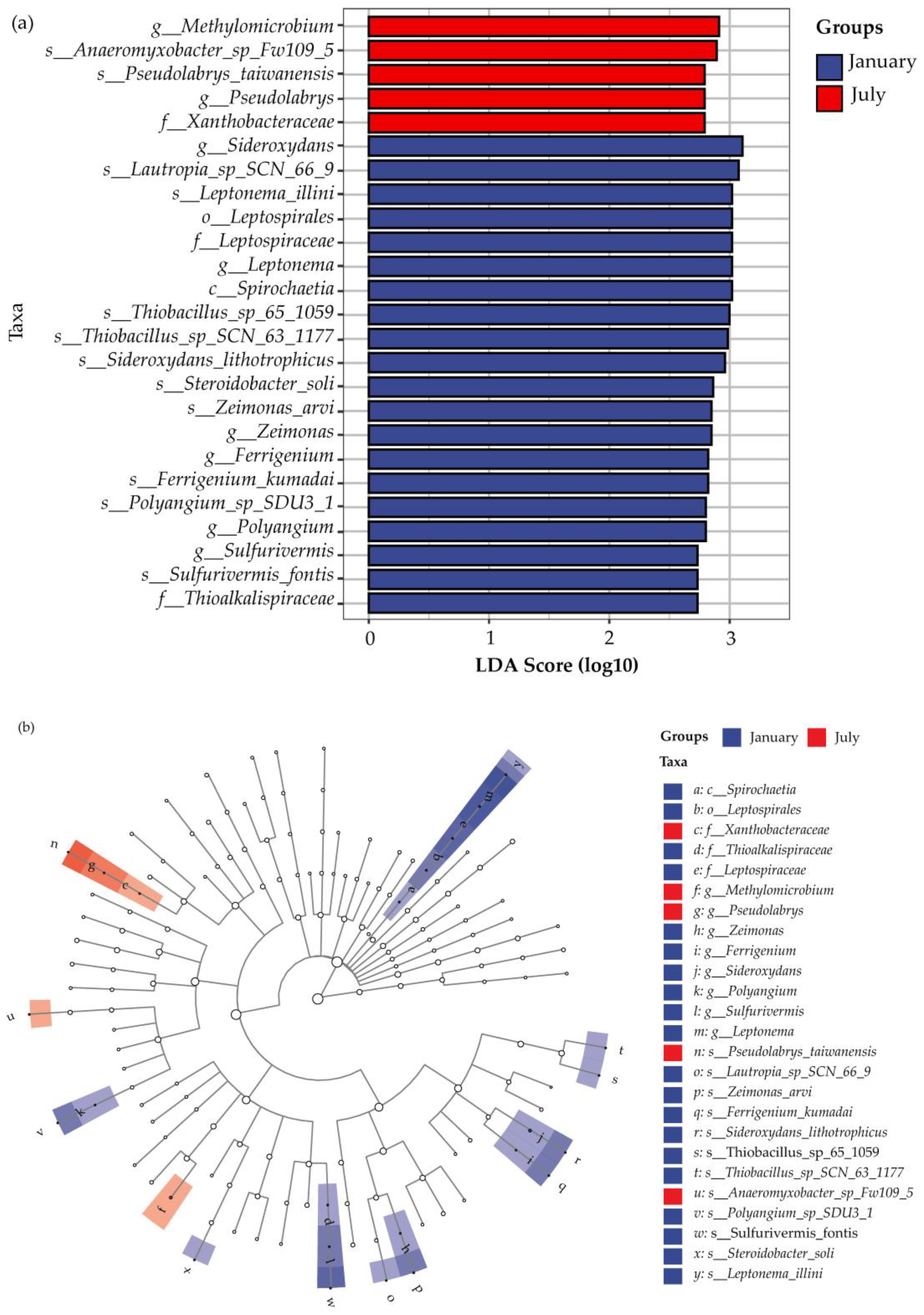
3.2.1. Dominant Microorganisms Associated with Nitrogen
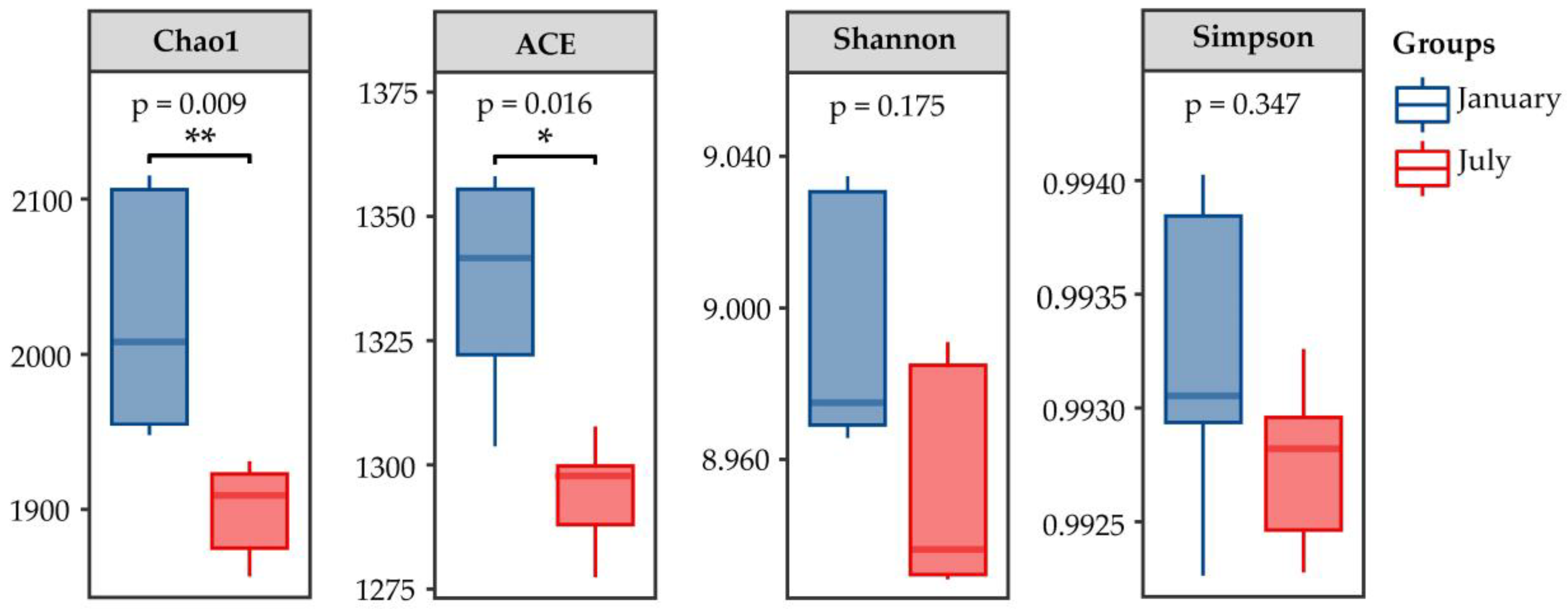
3.2.2. Microbial Community Diversity and Variation Analysis
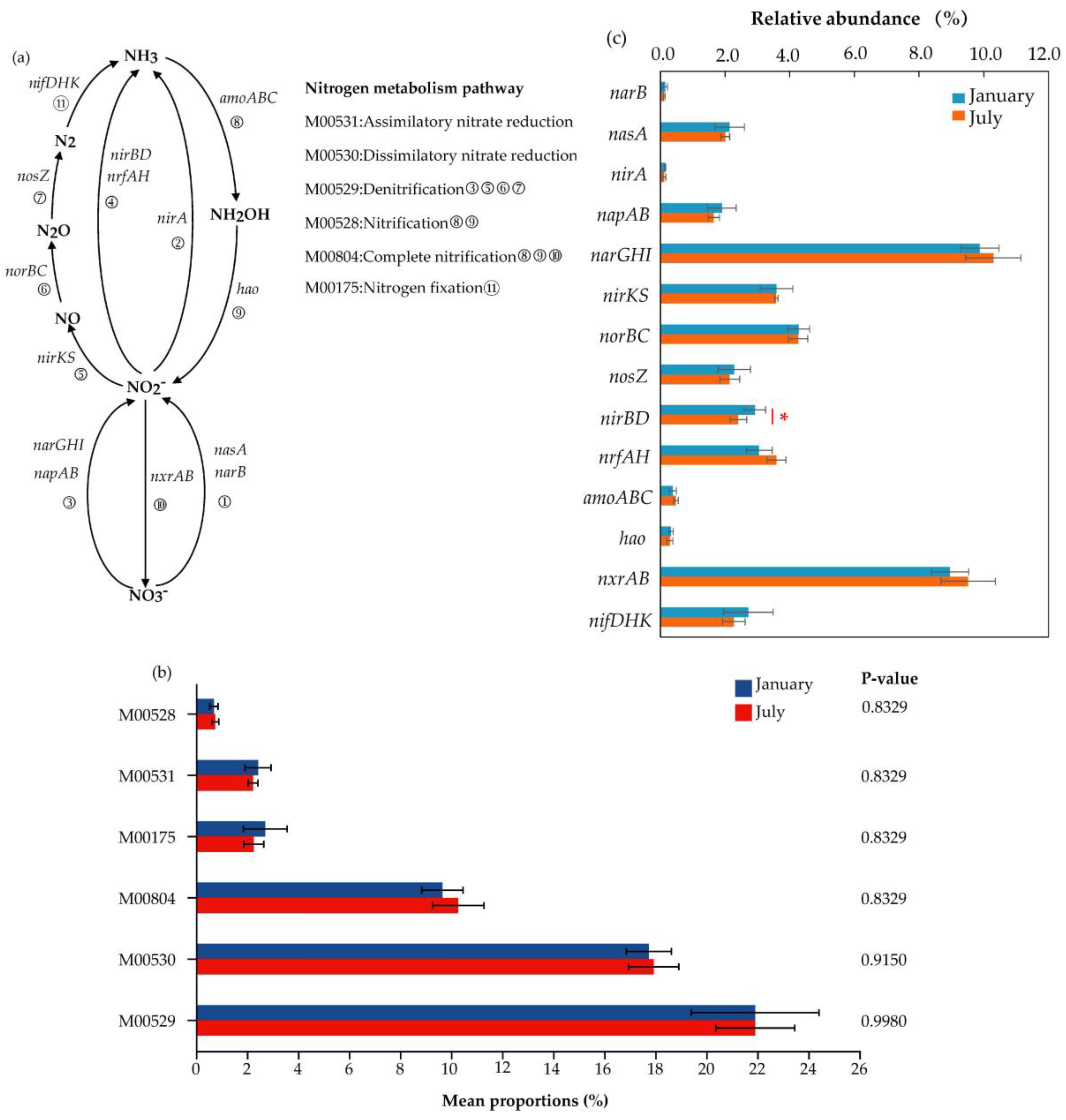
3.3. Nitrogen Metabolism Pathway and Functional Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, B.; Chen, J.; Wu, Z.; Wu, S.; Xie, S.; Liu, Y. Seasonal and spatial dynamics of denitrification rate and denitrifier community in constructed wetland treating polluted river water. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2018, 126, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ji, Z.; Pei, Y. Nutrient removal and microbial community structure in an artificial-natural coupled wetland system. Process Saf. Environ. Protect. 2021, 147, 1160–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Bao, J.; Zhao, F.; Liang, Y.; Chen, Y. New insight for purifying polluted river water using the combination of large-scale rotating biological contactors and integrated constructed wetlands in the cold season. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 324, 116433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domangue, R.J.; Mortazavi, B. Nitrate reduction pathways in the presence of excess nitrogen in a shallow eutrophic estuary. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 238, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Xiao, L.; Lu, H.; Lu, S.; Li, J.; Guo, X.; Zhao, X. Nitrogen removal from summer to winter in a field pilot-scale multistage constructed wetland-pond system. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 111, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kivaisi, A.K. The potential for constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment and reuse in developing countries: A review. Ecol. Eng. 2001, 16, 545–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, G.; Mayer, T. Natural and constructed wetlands in canada; An overview. Water Qual. Res. J. 2002, 37, 295–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorslund, J.; Jarsjo, J.; Jaramillo, F.; Jawitz, J.W.; Manzoni, S.; Basu, N.B.; Chalov, S.R.; Cohen, M.J.; Creed, I.F.; Goldenberg, R.; et al. Wetlands as large-scale nature-based solutions: Status and challenges for research, engineering and management. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 108, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Gao, J.; Guo, X.; Li, W.; Tian, X.; Zhang, R. Long-term effects and performance of two-stage baffled surface flow constructed wetland treating polluted river. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 49, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, O. Constructed wetlands revisited: Microbial diversity in the -omics era. Microb. Ecol. 2017, 73, 722–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.; Zhang, G.; Meng, F.; Zhi, R.; Zhang, P.; Zhu, Y. Nitrogen metabolism in photosynthetic bacteria wastewater treatment: A novel nitrogen transformation pathway. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 294, 122162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Li, Y.; Lv, D.; Li, Y.; Wu, J. Nitrogen and phosphorus removal performance and bacterial communities in a multi-stage surface flow constructed wetland treating rural domestic sewage. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 136235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gong, L.; Mu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, S. Characterization and co-occurrence of microbial community in epiphytic biofilms and surface sediments of wetlands with submersed macrophytes. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 715, 136950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Luo, P.; Liu, F.; Zhang, S.; Li, H.; Xiao, R.; Wu, J. Cold temperature increases nitrate accumulation in pilot-scale surface flow constructed wetlands with high rates of nitrogen removal. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 308, 107250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truu, M.; Juhanson, J.; Truu, J. Microbial biomass, activity and community composition in constructed wetlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 3958–3971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, D.Q.; Dong, J.W.; Tan, S.K. Constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment in cold climate—A review. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 57, 293–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Chu, Y.; Tan, Q.; Chen, J.; Yang, L.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Z.; He, F. Cold temperature mediated nitrate removal pathways in electrolysis-assisted constructed wetland systems under different influent c/n ratios and anode materials. Chemosphere 2022, 295, 133867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akratos, C.S.; Tsihrintzis, V.A. Effect of temperature, hrt, vegetation and porous media on removal efficiency of pilot-scale horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands. Ecol. Eng. 2007, 29, 173–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Moortel, A.M.K.; Meers, E.; De Pauw, N.; Tack, F.M.G. Effects of vegetation, season and temperature on the removal of pollutants in experimental floating treatment wetlands. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2010, 212, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ministry Of Environmental Protection of China. National Environmental Protection Standards of the People’s Republic of China (hj 636-2012): Water Quality -Determination of Alkaline Potassium Persulfate Digestion uv Spectrophotometric Method; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry Of Environmental Protection of China. National Environmental Protection Standards of the People’s Republic of China (hj 828-2017): Water Quality -Determination of the Chemical Oxygen Demand-Dichromate Method; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. Fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one fastq preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menzel, P.; Ng, K.L.; Krogh, A. Fast and sensitive taxonomic classification for metagenomics with kaiju. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, D.; Liu, C.M.; Luo, R.; Sadakane, K.; Lam, T.W. Megahit: An ultra-fast single-node solution for large and complex metagenomics assembly via succinct de bruijn graph. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1674–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steinegger, M.; Söding, J. Mmseqs2 enables sensitive protein sequence searching for the analysis of massive data sets. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 1026–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, W.; Lomsadze, A.; Borodovsky, M. Ab initio gene identification in metagenomic sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bu, D.; Luo, H.; Huo, P.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, S.; He, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Liu, J.; Guo, J.; et al. Kobas-i: Intelligent prioritization and exploratory visualization of biological functions for gene enrichment analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W317–W325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patro, R.; Duggal, G.; Love, M.I.; Irizarry, R.A.; Kingsford, C. Salmon provides fast and bias-aware quantification of transcript expression. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 417–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ye, Y.; Doak, T.G. A parsimony approach to biological pathway reconstruction/inference for genomes and metagenomes. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2009, 5, e1000465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ansola, G.; Arroyo, P.; Sáenz De Miera, L.E. Characterisation of the soil bacterial community structure and composition of natural and constructed wetlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 473–474, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Huang, J.; Dzakpasu, M.; Gao, Z.; Zhou, W.; Zhu, R.; Xiong, J. Assessment of plants radial oxygen loss for nutrients and organic matter removal in full-scale constructed wetlands treating municipal effluents. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 360, 127545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.; Rachid, C.; Pacheco, A.B.; Magalhães, V. Biotic and abiotic factors affect microcystin-lr concentrations in water/sediment interface. Microbiol. Res. 2020, 236, 126452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vipindas, P.V.; Mujeeb, R.K.M.; Jabir, T.; Thasneem, T.R.; Mohamed Hatha, A.A. Diversity of sediment bacterial communities in the south eastern arabian sea. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2020, 35, 101153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kielak, A.M.; Barreto, C.C.; Kowalchuk, G.A.; van Veen, J.A.; Kuramae, E.E. The ecology of acidobacteria: Moving beyond genes and genomes. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, X.; Li, J.; He, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, J.; Liu, C. Co-occurrence of autotrophic and heterotrophic denitrification in electrolysis assisted constructed wetland packing with coconut fiber as solid carbon source. Chemosphere 2022, 301, 134762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Duan, C.; Yu, J.; Dong, W. Transforming heterotrophic to autotrophic denitrification process: Insights into microbial community, interspecific interaction and nitrogen metabolism. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 345, 126471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Y.; Hou, T.; Li, X.; Feng, L.; Wang, Z. Metagenomic insights into comparative study of nitrogen metabolic potential and microbial community between primitive and urban river sediments. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Yang, C.; Wang, B.; He, Z.; Fu, T. Nitrogen removal performance and microbiological characteristics for the landfill leachate treatment in a three-stage vertical flow constructed wetlands system. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 28, 102728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuypers, M.M.M.; Marchant, H.K.; Kartal, B. The microbial nitrogen-cycling network. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.; Zhang, S.; Lv, X.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Han, B. Water flow and temperature drove epiphytic microbial community shift: Insight into nutrient removal in constructed wetlands from microbial assemblage and co-occurrence patterns. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 332, 125134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.J.; Dong, L.F.; Wilson, J.; Stott, A.; Osborn, A.M.; Nedwell, D.B. Seasonal variation in denitrification and dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonia process rates and corresponding key functional genes along an estuarine nitrate gradient. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.; Hu, Z.; Hou, C.; Liu, H.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Lu, S.; Zhang, J. New insights for enhancing the performance of constructed wetlands at low temperatures. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 301, 122722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Liu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wu, X.; Yang, H. Characterization of nitrification and microbial community in a shallow moss constructed wetland at cold temperatures. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 42, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Q.; Xu, W.; He, F.; Peng, F.; Zhu, X.; Xu, B.; Yu, J.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, L. Functional genera for efficient nitrogen removal under low c/n ratio influent at low temperatures in a two-stage tidal flow constructed wetland. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 804, 150142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Index | Water Temperature | p Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High | Medium | Low | |||
| Removal efficiency (%) | TN | 63.05 ± 4.27 | 36.31 ± 6.79 | 16.42 ± 3.86 | 0.000128 *** |
| NO3−-N | 67.53 ± 8.00 | 28.03 ± 13.34 | −17.63 ± 5.73 | 0.000128 *** | |
| NH4+-N | 81.19 ± 2.46 | 77.87 ± 4.00 | 67.92 ± 1.80 | 0.000516 *** | |
| COD | 49.25 ± 3.31 | 45.50 ± 4.10 | 27.45 ± 3.74 | 0.000239 *** | |
| Mass removal rate (mg m−2 d−1) | TN | 1016.79 ± 115.25 | 542.94 ± 58.09 | 267.26 ± 54.93 | 0.000127 *** |
| NO3−-N | 661.06 ± 115.63 | 244.20 ± 99.25 | −151.86 ± 51.13 | 0.000128 *** | |
| NH4+-N | 391.68 ± 58.10 | 392.40 ± 72.83 | 420.87 ± 40.19 | 0.508553 | |
| COD | 5835.84 ± 795.80 | 5760 ± 293.94 | 3573.33 ± 511.56 | 0.000393 *** | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Xu, Y.; Chai, B. Effect of Temperature on Microorganisms and Nitrogen Removal in a Multi-Stage Surface Flow Constructed Wetland. Water 2023, 15, 1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15071256
Wang H, Xu Y, Chai B. Effect of Temperature on Microorganisms and Nitrogen Removal in a Multi-Stage Surface Flow Constructed Wetland. Water. 2023; 15(7):1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15071256
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Huiyong, Yongxin Xu, and Beibei Chai. 2023. "Effect of Temperature on Microorganisms and Nitrogen Removal in a Multi-Stage Surface Flow Constructed Wetland" Water 15, no. 7: 1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15071256






