Sedimentary Records of Phytoplankton Communities in Sanmen Bay in China: The Impacts of ENSO Events over the Past Two Centuries
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Phytoplankton Sample Collection
2.3. Sediment and Core Sample Collection
2.4. Pretreatment and Analysis of Sediment Samples
2.5. Sediment Chronology
2.6. Niño Index
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Phytoplankton Community Structure of the Field Survey in Sanmen Bay
3.2. Comparison of Site Survey and Biomarker Reconstruction in Sanmen Bay
3.3. Interannual Variation in Plankton Community Biomass, Reconstructed from Sediment Biomarkers
3.4. Sediment Reconstruction of Phytoplankton Response to ENSO
4. Discussion
4.1. Response of Phytoplankton Community Changes to ENSO Signals in Sanmen Bay
4.1.1. EI Niño Impact Year
4.1.2. La Niña Impact Year
4.2. Regulation of Phytoplankton by Other Physical Processes in Sanmen Bay
4.3. The Focus of Future Research
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Philander, S.G.; Fedorov, A. Is El Nino sporadic or cyclic? Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2003, 31, 579–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trenberth, K.E.; Hoar, T.J. El Nino and climate change. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1997, 24, 3057–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, S.W.; Kug, J.S.; Dewitte, B.; Kwon, M.H.; Kirtman, B.P.; Jin, F.F. El Niño in a changing climate. Nature 2009, 461, 511–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Righetti, D.; Vogt, M.; Gruber, N.; Psomas, A.; Zimmermann, N.E. Global pattern of phytoplankton diversity driven by temperature and environmental variability. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaau6253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cloern, J.E. The relative importance of light and nutrient limitation of phytoplankton growth: A simple index of coastal ecosystem sensitivity to nutrient enrichment. Aquat. Ecol. 1999, 33, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, R.T.; Chavez, F.P. Biological consequences of El Niño. Science 1983, 222, 1203–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez, F.P.; Strutton, P.G.; Friederich, C.E.; Feely, R.A.; Feldman, G.C.; Foley, D.C.; McPhaden, M.J. Biological and chemical response of the equatorial Pacific Ocean to the 1997-98 El Nino. Science 1999, 286, 2126–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrenfeld, M.J.; Randerson, J.T.; McClain, C.R.; Feldman, G.C.; Los, S.O.; Tucker, C.J.; Falkowski, P.G.; Field, C.B.; Frouin, R.; Esaias, W.E.; et al. Biospheric primary production during an ENSO transition. Science 2001, 291, 2594–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barber, R.T.; Chávez, F.P. Ocean variability in relation to living resources during the 1982–83 El Niño. Nature 1986, 319, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wang, J.; Li, F.; Yang, S.; Tan, L. Vertical distribution and indications of lipids biomarkers in the sediment core from East China Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 2016, 122, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cravo, A.; Pereira, C.; Gomes, T.; Cardoso, C.; Serafim, A.; Almeida, C.; Rocha, T.; Lopes, B.; Company, R.; Medeiros, A.; et al. A multibiomarker approach in the clam Ruditapes decussatus to assess the impact of pollution in the Ria Formosa lagoon, South Coast of Portugal. Mar. Environ. Res. 2012, 75, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishiwatari, R.; Fujino, N.; Brincat, D.; Yamamoto, S.; Takahara, H.; Shichi, K.; Krivonogov, S.K. A 35 kyr record of organic matter composition and δ13C of n-alkanes in bog sediments close to Lake Baikal: Implications for paleoenvironmental studies. Org. Geochem. 2009, 40, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, O.; Ikehara, M.; Kawamura, K.; Nakatsuka, T.; Ohnishi, K.; Wakatsuchi, M.; Narita, H.; Sakamoto, T. Reconstruction of paleoproductivity in the sea of Okhotsk over the last 30 kyr. Paleoceanography 2004, 19, PA1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schubert, C.J.; Villanueva, J.; Calvert, S.E.; Cowie, G.L.; von Rad, U.; Schulz, H.; Berner, U.; Erlenkeuser, H. Stable phytoplankton community structure in the Arabian Sea over the past 200,000 years. Nature 1998, 394, 563–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, S.M.; Volkman, J.K.; Dunstan, G.A.; LeRoi, J.-M. Sterols of 14 species of marine diatoms (bacillariophyta)1. J. Phycol. 1995, 31, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Bi, R.; Sachs, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, H.L.; Li, L.; Zhao, M.X. Lipid biomarker production by marine phytoplankton under different nutrient and temperature regimes. Org. Geochem. 2019, 131, 34–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Y.; Liu, Y.G.; Guo, L.; Rong, Z.R.; Gu, Y.Z.; Liu, Y.H. Interannual changes of sea level in the two regions of East China Sea and different responses to ENSO. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2010, 72, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Zhao, M.X.; Zhang, H.L.; Zhao, X.C.; Zhao, X.H.; Yang, Z.S.; Liu, C.L. Biomarker evidence for paleoenvironmental changes in the southern Yellow Sea over the last 8200 years. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2012, 30, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.B.; Liu, J.J.; Chen, J.F.; Chen, Q.Z.; Yan, X.J.; Xuan, J.L.; Zeng, J.N. Responses of summer phytoplankton community to drastic environmental changes in the Changjiang (Yangtze River) estuary during the past 50 years. Water Res. 2014, 54, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.L.; Li, F.; He, X.P.; He, X.L.; Wang, J.T. Lipid biomarker as indicator for assessing the input of organic matters into sediments and evaluating phytoplankton evolution in upper water of the East China Sea. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 101, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Zhang, T.; Yu, M.; Duan, S.S.; Zhang, R.P.; Huh, C.A.; Liao, W.H.; Feng, X.W. Ecosystem responses to anthropogenic and natural forcing over the last 100 years in the coastal areas of the East China Sea. Holocene 2016, 26, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lin, J.; Xu, X.P.; Liu, J.Z.; Zhou, Q.Z.; Wang, J.H. Multiple biomarkers for indicating changes of the organic matter source over the last decades in the Min-Zhe sediment zone, the East China Sea. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 139, 108917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.P.; Liu, X.; Irwin, A.J.; Laws, E.A.; Wang, L.; Chen, B.Z.; Zeng, Y.; Huang, B.Q. Warming and eutrophication combine to restructure diatoms and dinoflagellates. Water Res. 2018, 128, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.T.; Chai, F.; Xiu, P.; Xue, H.J.; Tian, J. Modeling the long-term variability of phytoplankton functional groups and primary productivity in the South China Sea. J. Oceanogr. 2013, 69, 527–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yu, R.C.; Kong, F.Z.; Wei, C.J.; Liu, Z.; Geng, H.X.; Dai, L.; Zhou, Z.X.; Zhang, Q.C.; Zhou, M.J. Distribution patterns of picosized and nanosized phytoplankton assemblages in the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea: Implications on the impacts of Kuroshio intrusion. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2019, 124, 1262–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Guo, W.; Shi, Z.; Jia, G.D.; Wei, G.J. Seasonal dynamics of particulate organic matter and its response to flooding in the Pearl River Estuary, China, revealed by stable isotope (delta C-13 and delta N-15) analyses. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2017, 122, 6835–6856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.Q.; Sun, Z.C.; Li, B.G.; Wu, X.Y.; Gong, M.; Yang, H. Distribution changes of suspended sediment concentration and its dynamic analysis in Xiangshan Bay, Zhejiang Province. Mar. Sci. Bull. 2014, 33, 694–702. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhejiang Provincial Coastal Zone and Sea Paint Resources Comprehensive Survey Report Preparation Committee. Comprehensive Survey Report on Coastal Zone and Sea Paint Resources of Zhejiang Province; Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, X.R. Research and Evaluation of Culture Ecology and Culture Capacity in Yueqing Bay and Sanmen Bay; Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 2005; pp. 129–168. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, J.J.; Gao, Y.X.; Shou, L.; Liao, Y.B.; Huang, W.; Jiang, Z.B. Seasonal variation and the factors on net-phytoplankton in Sanmen Bay. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2017, 48, 101–112. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, H.Y. Preliminary study on the phytoplankton of Jiantiao Bay of Zhejiang. J. Zhejiang Coll. Fish. 1990, 9, 126–130. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, G.H.; Chen, L.H.; Qian, J. A study on seasonal variation of phytoplankton in the sea near Sanmen nuclear power station. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 33, 36–45. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, J.N. Comprehensive Survey Report on the Ecological Environment of Key Harbors and Bays in Zhejiang Province; Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 2011; pp. 195–198. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, C.Q.; Ai, W.M.; Peng, X.; Chen, S.B.; Xie, Q.L. Diversity and seasonal variation of phytoplankton in the sea near Sanmen nuclear power station. Bull. Sci. Technol. 2015, 31, 222–228. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.Q.; Ye, R.; Wei, Y.J.; Yu, H.B.; Yang, Q.; Wang, Y.C.; Liao, Y.G. Correlation between phytoplankton community and environmental variables in Sanmen bay, East China Sea. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2017, 36, 70–86. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez-de-la-Torre, B.; Gaxiola-Castro, G.; Alvarez-Borrego, S.; Gomez-Valdes, J.; Najera-Martinez, S. Interannual variability of new production in the southern region of the California Current. Deep Sea Res. Part II 2003, 50, 2423–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittenour, T.M.; Brigham-Grette, J.; Mann, M.E. El Nino-like climate teleconnections in New England during the late Pleistocene. Science 2000, 288, 1039–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrenfeld, M.J.; O’Malley, R.T.; Siegel, D.A.; McClain, C.R.; Sarmiento, J.L.; Feldman, G.C.; Milligan, A.J.; Falkowski, P.G.; Letelier, R.M.; Boss, E.S. Climate-driven trends in contemporary ocean productivity. Nature 2006, 444, 752–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolter, K.; Timlin, M.S. El Nino/Southern Oscillation behaviour since 1871 as diagnosed in an extended multivariate ENSO index (MEI.ext). Int. J. Climatol. 2011, 31, 1074–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolton, C.T.; Lawrence, K.T.; Gibbs, S.J.; Wilson, P.A.; Cleaveland, L.C.; Herbert, T.D. Glacial–interglacial productivity changes recorded by alkenones and microfossils in late Pliocene eastern equatorial Pacific and Atlantic upwelling zones. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2010, 295, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prahl, F.G.; Muehlhausen, L.A.; Zahnle, D.L. Further evaluation of long-chain alkenones as indicators of paleoceanographic conditions. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1988, 52, 2303–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkman, J.K.; Barrerr, S.M.; Blackburn, S.I.; Sikes, E.L. Alkenones in Gephyrocapsa oceanica: Implications for studies of paleoclimate. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, H.Y.; Yu, J.Y. Contrasting eastern-Pacific and central-Pacific types of ENSO. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 615–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmeiro, F.M.; Iza, M.; Barriopedro, D.; Calvo, N.; García-Herrera, R. The complex behavior of El Niño winter 2015–2016. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 2902–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.; Ding, S.Y.; Feng, J.; Chen, S.F.; Xue, X.; Zhou, Q. Progress in the study of impacts of different types of ENSO on the East Asian monsoon and their mechanisms. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 42, 640–655. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Song, W.L.; Yuan, Y. Uncertainty analvsis of climate prediction for the 2015/2016 winter under the backaround of super El Niño event. Meteorol. Mon. 2017, 43, 1249–1258. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tian, F.; Zhang, R.H.; Wang, X. Indian Ocean warming as a potential trigger for super phytoplankton blooms in the eastern equatorial Pacific from El Niño to La Niña transitions. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 054040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Signorini, S.R.; Murtugudde, R.G.; McClain, C.R.; Christian, J.R.; Picaut, J.; Busalacchi, A.J. Biological and physical signatures in the tropical and subtropical Atlantic. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1999, 104, 18367–18382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.Y.; Xu, F.; Li, X.H.; Xia, T.Z.; Zhang, Y. Intensities and time-frequency variability of ENSO in the last 65 years. J. Trop. Meteorol. 2017, 33, 683–694. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.X.; Yu, R.C.; Zhou, M.J. Resolving the complex relationship between harmful algal blooms and environmental factors in the coastal waters adjacent to the Changjiang River estuary. Harmful Algae 2017, 62, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, Q.Y.; He, J.; Wang, H.; Ruan, Y.M.; Li, J.R. Biomarker-derived phytoplankton community for summer monsoon reconstruction in the western South China Sea over the past 450 ka. Deep Sea Res. Part II 2015, 122, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.S.; Lu, D.D.; Zhu, X.Y.; Lu, B.; Gao, A.G.; Wu, G.H. Stratigraphic record of U37K in Sanmen Bay: The effect of SST and EI Niño on life activity in macrobenthos communities. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2007, 27, 4935–4943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.C.; Hu, D.X.; Wu, L.J. Seasonal and intraseasonal variations of the surface Taiwan warm current. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2004, 22, 271–277. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, H.; Shao, D.; Wang, Y.H.; Sun, L.G. Sr/Ca profile of long-lived Tridacna gigas bivalves from South China Sea: A new high-resolution SST proxy. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2013, 112, 52–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulain, C.; Gillikin, D.P.; Thébault, J.; Munaron, J.M.; Bohn, M.; Robert, R.; Paulet, Y.-M.; Lorrain, A. An evaluation of Mg/Ca, Sr/Ca, and Ba/Ca ratios as environmental proxies in aragonite bivalve shells. Chem. Geol. 2015, 396, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corrège, T. Sea surface temperature and salinity reconstruction from coral geochemical tracers. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2006, 232, 408–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.; Capo, E.; Wessels, M.; Martin, I.; Meyer, A.; Schleheck, D.; Epp, L.S. Anthropogenic impact on the historical phytoplankton community of lake constance reconstructed by multimarker analysis of sediment-core environmental DNA. Mol. Ecol. 2021, 30, 3040–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domaizon, I.; Winegardner, A.; Capo, E.; Gauthier, J.; Gregory-Eaves, I. DNA-based methods in paleolimnology: New opportunities for investigating long-term dynamics of lacustrine biodiversity. J. Paleolimnol. 2017, 58, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.K.; Kremer, C.T.; Klausmeier, C.A.; Litchman, E. A global pattern of thermal adaptation in marine phytoplankton. Science 2012, 338, 1085–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
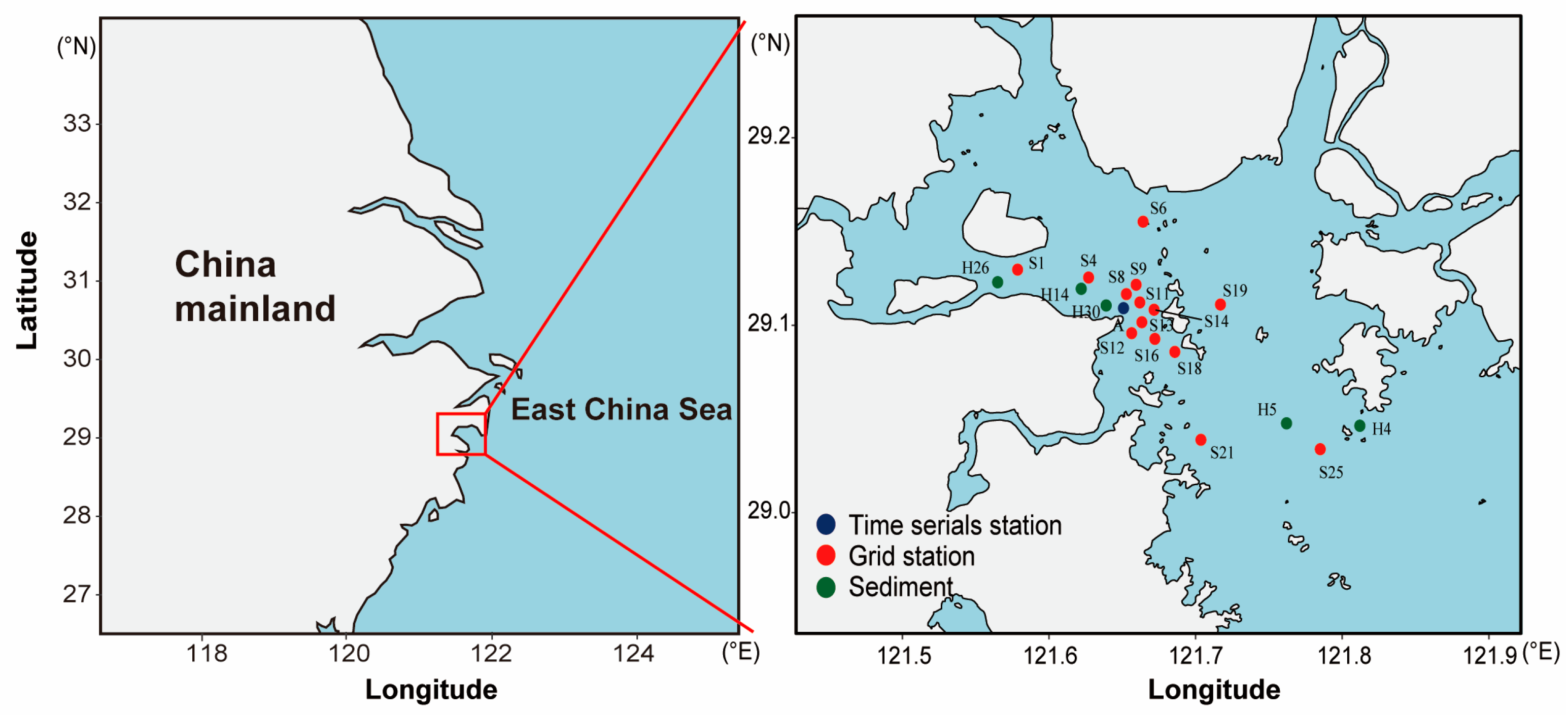
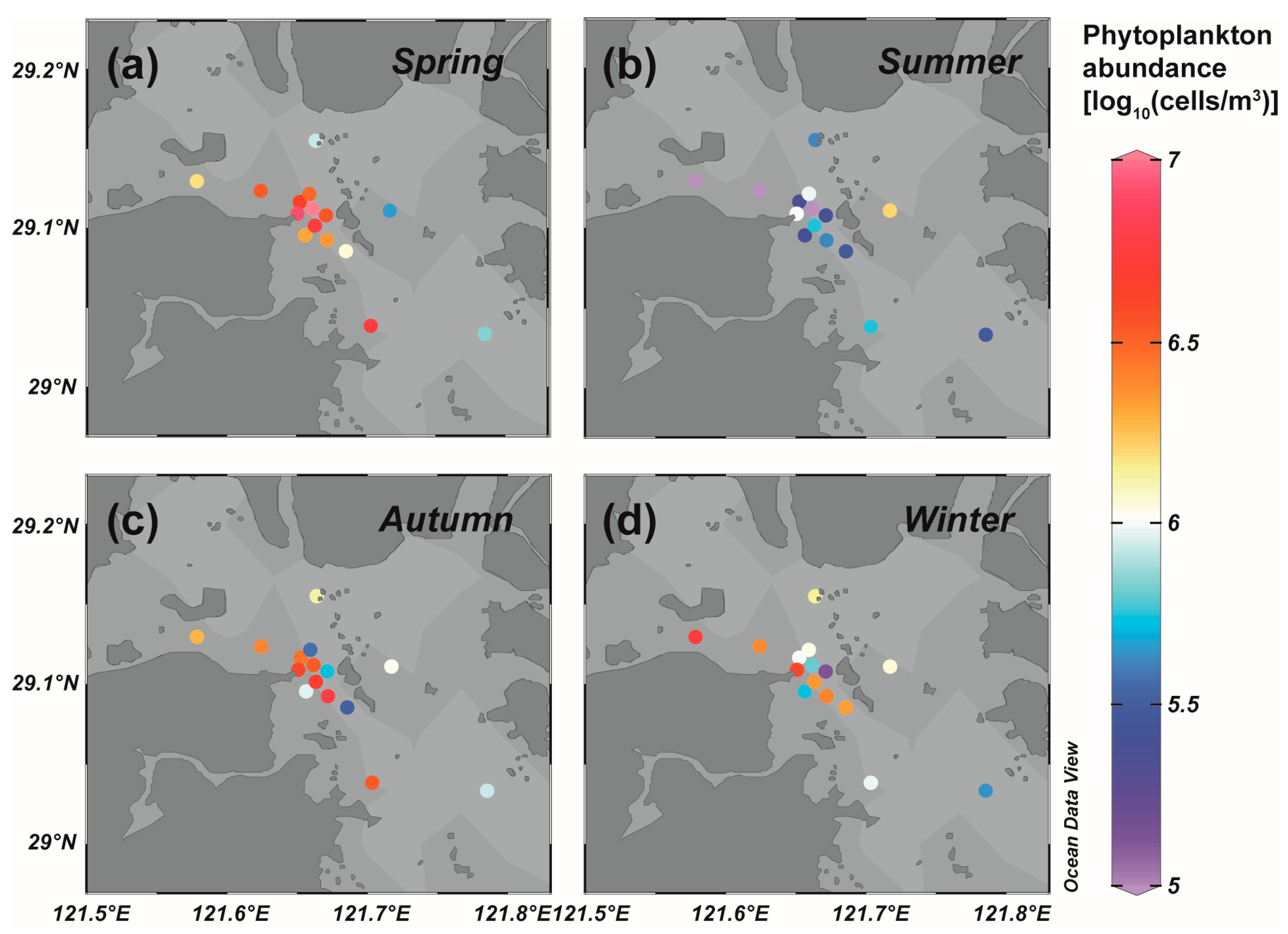
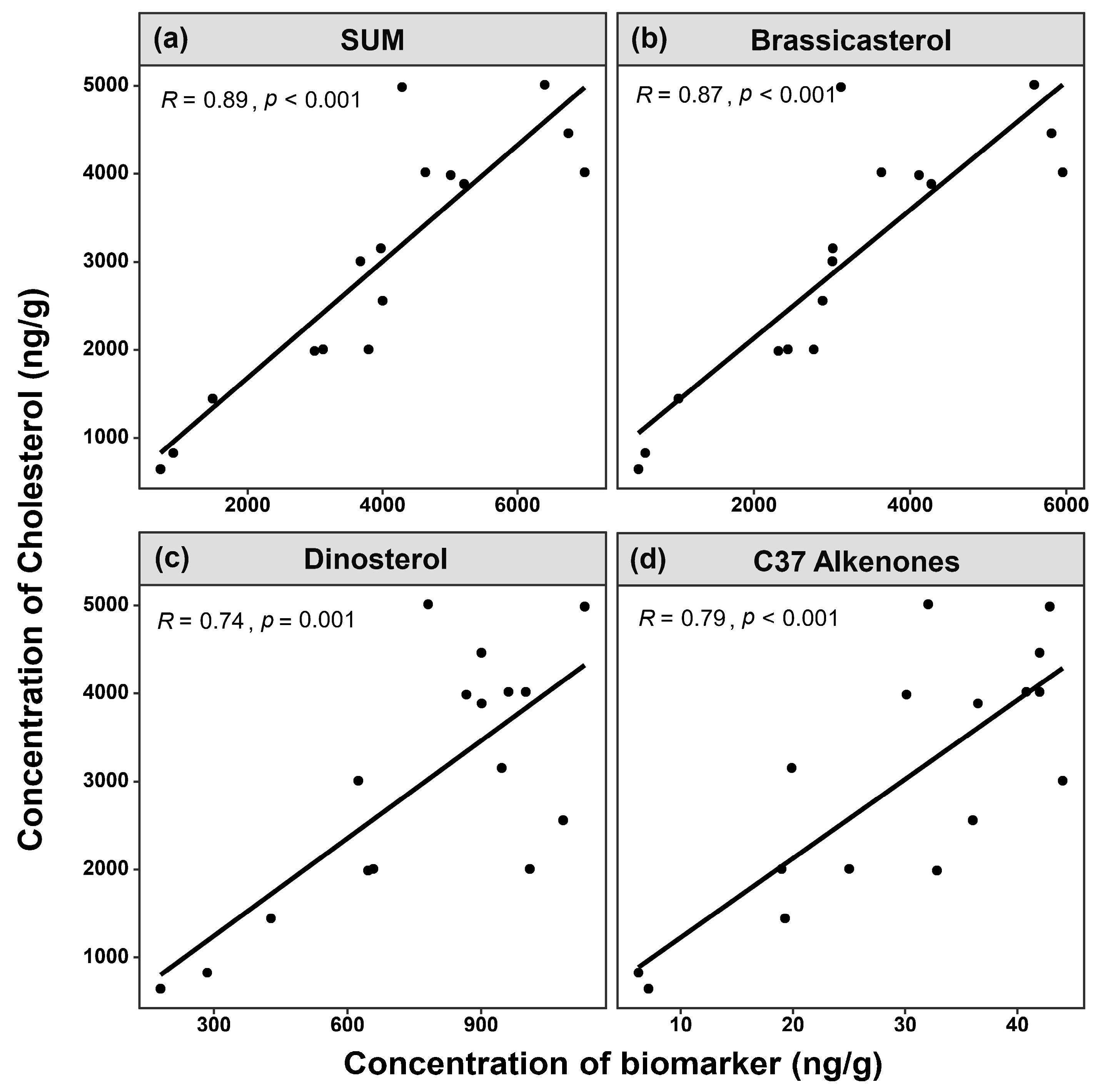

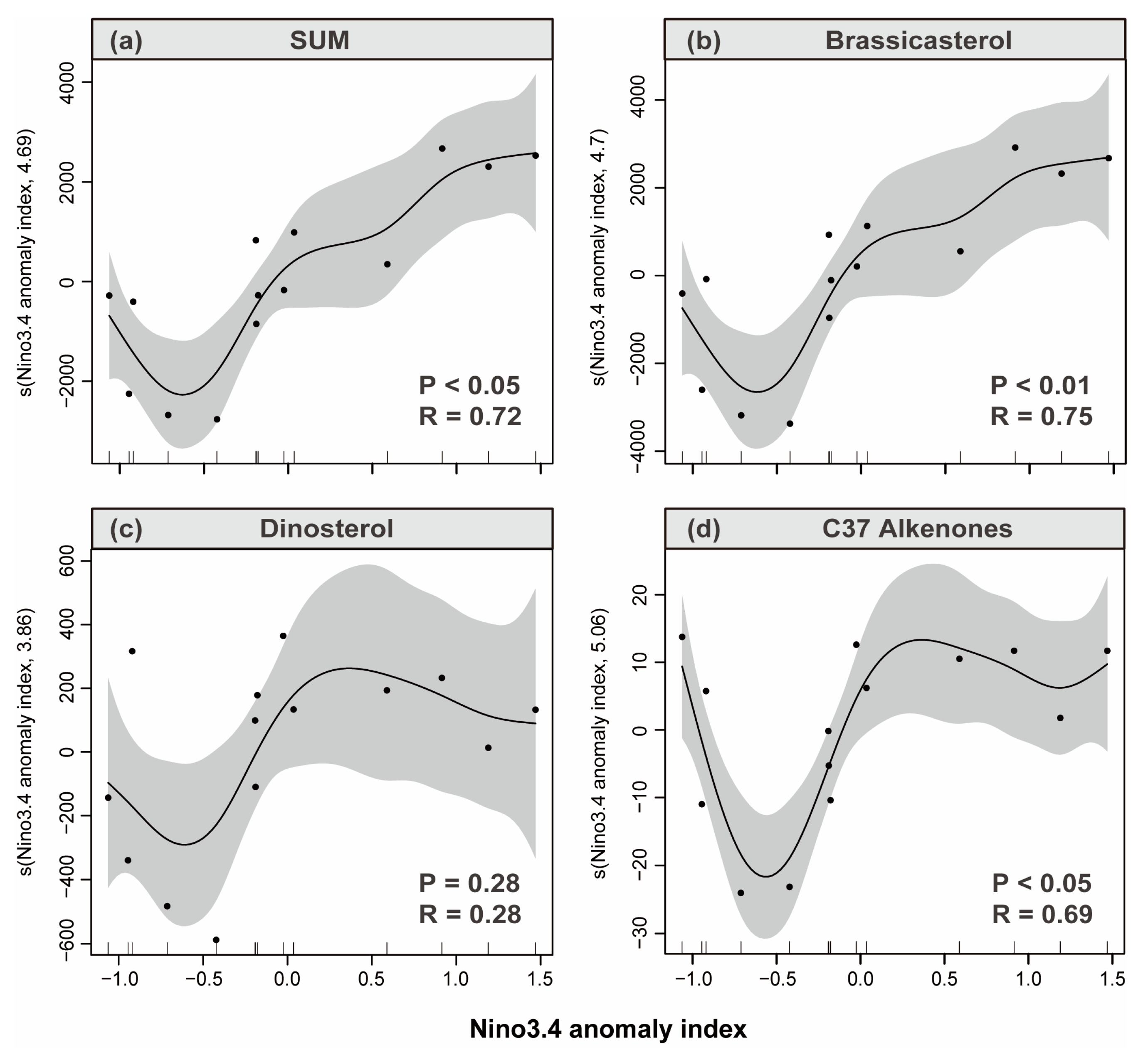
| Station | Latitude (°N) | Longitude (°E) | Type | Sample Number | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter | ||||
| S1 | 29.130 | 121.579 | Grid station | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| S4 | 29.124 | 121.625 | Grid station | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| S6 | 29.155 | 121.664 | Grid station | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| S8 | 29.117 | 121.653 | Grid station | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| S9 | 29.122 | 121.659 | Grid station | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| S11 | 29.112 | 121.662 | Grid station | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| S12 | 29.096 | 121.656 | Grid station | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| S13 | 29.102 | 121.663 | Grid station | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| S14 | 29.108 | 121.672 | Grid station | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| S16 | 29.093 | 121.672 | Grid station | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| S18 | 29.086 | 121.686 | Grid station | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| S19 | 29.111 | 121.717 | Grid station | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| S21 | 29.039 | 121.704 | Grid station | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| S25 | 29.034 | 121.785 | Grid station | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| A | 29.109 | 121.651 | Time serials station | 9 | 18 | 9 | 18 |
| Date | ENSO | Phytoplankton Abundance (Cells m−3) | Dominant Species | References | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter | ||||
| December 1981, May 1982, July 1982, October 1982 | EI Niño–EP | 3.35 × 105 | 1.04 × 106 | 3.93 × 105 | 2.34 × 108 | Coscinodiscus spp, Skeletonema spp., Ditylun brightwelli, Chaetoceros spp. | [28] |
| August 2002, November 2002, February 2003, May2003 | EI Niño–CP | 7.88 × 106 | 1.52 × 109 | 9.11 × 106 | 1.60 × 107 | Calanus sinicus, Labidocera euchaeta, Tortanus derjugini, Acartia clause, Pseudeuphausia sinica, Zonosagitta bedoti, Zonosagitta nagae | [29] |
| May 2015, August 2015, November 2015, January 2016 | EI Niño–CP–EP (mixed) | 5.31 × 105 | 5.55 × 107 | 7.81 × 106 | 5.81 × 106 | Coscinodiscus jonesianus, Thalassionema frauenfeldii, Skeletonema spp., Chaetoceros pseudocurvisetus | [30] |
| February 1985, August 1985, December 1985, February 1986 | La Niña–EP | 2.15 × 105 | 1.50 × 105 | 5.14 × 104 | 2.40 × 108 | Chaetoceros danicus, Coscinodiscus jonesianus, Coscinodiscus spinosus, Coscinodiscus asterromphalus, Skeletonema costatum | [31] |
| April 2005, July 2005, October 2005, January 2006 | Normal | 1.63 × 107 | 2.51 × 106 | 4.72 × 107 | 1.27 × 108 | Skeletonema costatum, Coscinodiscus jonesianus, Chaetoceros affinis, Melosira discigera, Ceratium furca, Planktoniella sol | [32] |
| October 2006, January 2007, April 2007, July 2007 | Normal | 1.30 × 106 | 8.30 × 106 | 1.59 × 106 | 1.44 × 106 | Coscinodiscus jonesianus, Skeletonema spp., Paralia sulcata, Tripos muelleri | [33] |
| February 2012, May 2012, August 2012, November 2012 | Normal | 2.97 × 105 | 3.72 × 106 | 1.77 × 105 | 1.43 × 105 | Skeletonema costatum, Biddulphia sinensis, Coscinodiscus oculus-iridis, Coscinodiscus jonesianus | [34] |
| May 2014, August 2014 | Normal | 2.20 × 105 | 1.88. × 106 | - | - | Coscinodiscus jonesianus, Coscinodiscus oculus-iridis, Skeletonema costatum, Nitzschia lorenziana, Coscinodiscus centralis, Ditylun brightwellii | [35] |
| Sediment Depth (cm) | Radioactive Specific Activity (dpm/g) | Year | Niño 3.4 Index (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0~0.5 | Based on sampling time | 2015 | 1.47 |
| 0~0.5 | Based on sampling time | 2005 | 0.04 |
| 0~0.5 | Based on sampling time | 2002 | 0.59 |
| 0~0.5 | Based on sampling time | 1997 | 1.19 |
| 0~0.5 | 2.95 ± 0.13 | 1995 | −0.03 |
| 11~11.5 | 3.96 ± 0.25 | 1982 | 0.92 |
| 15.0~15.5 | 2.12 ± 0.09 | 1978 | −0.18 |
| 19.0~19.5 | 2.44 ± 0.12 | 1974 | −0.95 |
| 30.0~30.5 | 3.15 ± 0.14 | 1961 | −0.19 |
| 40.0~40.5 | 2.87 ± 0.14 | 1950 | −1.06 |
| 50.0~50.5 | 1.49 ± 0.06 | 1939 | −0.19 |
| 70.0~70.5 | 2.17 ± 0.12 | 1917 | −0.42 |
| 90.0~90.5 | 1.24 ± 0.05 | 1894 | −0.92 |
| 110.0~110.5 | 1.27 ± 0.05 | 1872 | −0.71 |
| 135.0~135.5 | 1.12 ± 0.05 | 1844 | - |
| 155.0~155.5 | 1.00 ± 0.05 | 1822 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, L.; Xu, Z.; Zeng, J.; Zhu, G.; Liu, X.; Huang, B. Sedimentary Records of Phytoplankton Communities in Sanmen Bay in China: The Impacts of ENSO Events over the Past Two Centuries. Water 2023, 15, 1255. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15071255
Chen L, Xu Z, Zeng J, Zhu G, Liu X, Huang B. Sedimentary Records of Phytoplankton Communities in Sanmen Bay in China: The Impacts of ENSO Events over the Past Two Centuries. Water. 2023; 15(7):1255. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15071255
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Lihong, Zengchao Xu, Jiangning Zeng, Genhai Zhu, Xin Liu, and Bangqin Huang. 2023. "Sedimentary Records of Phytoplankton Communities in Sanmen Bay in China: The Impacts of ENSO Events over the Past Two Centuries" Water 15, no. 7: 1255. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15071255






