KDE-Based Rainfall Event Separation and Characterization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Statistical Representation of Rainfall Events
2.2. Rainfall Event Characterization Using KDE Approach
2.2.1. KDE for Estimating PDFs of Rainfall Characteristics
2.2.2. Correction for Boundary Bias of KDE
2.2.3. KDE for Estimating PDFs of Rainfall Characteristics
2.2.4. Procedures of Rainfall Event Separation and Characterization Based on KDE
2.3. Study Area and Data
3. Case Study of the Rainfall Event Separation
3.1. Parameters for Rainfall Event Separation
3.2. Results and Discussion
3.2.1. Poisson Test for the Annual Number of Events θ
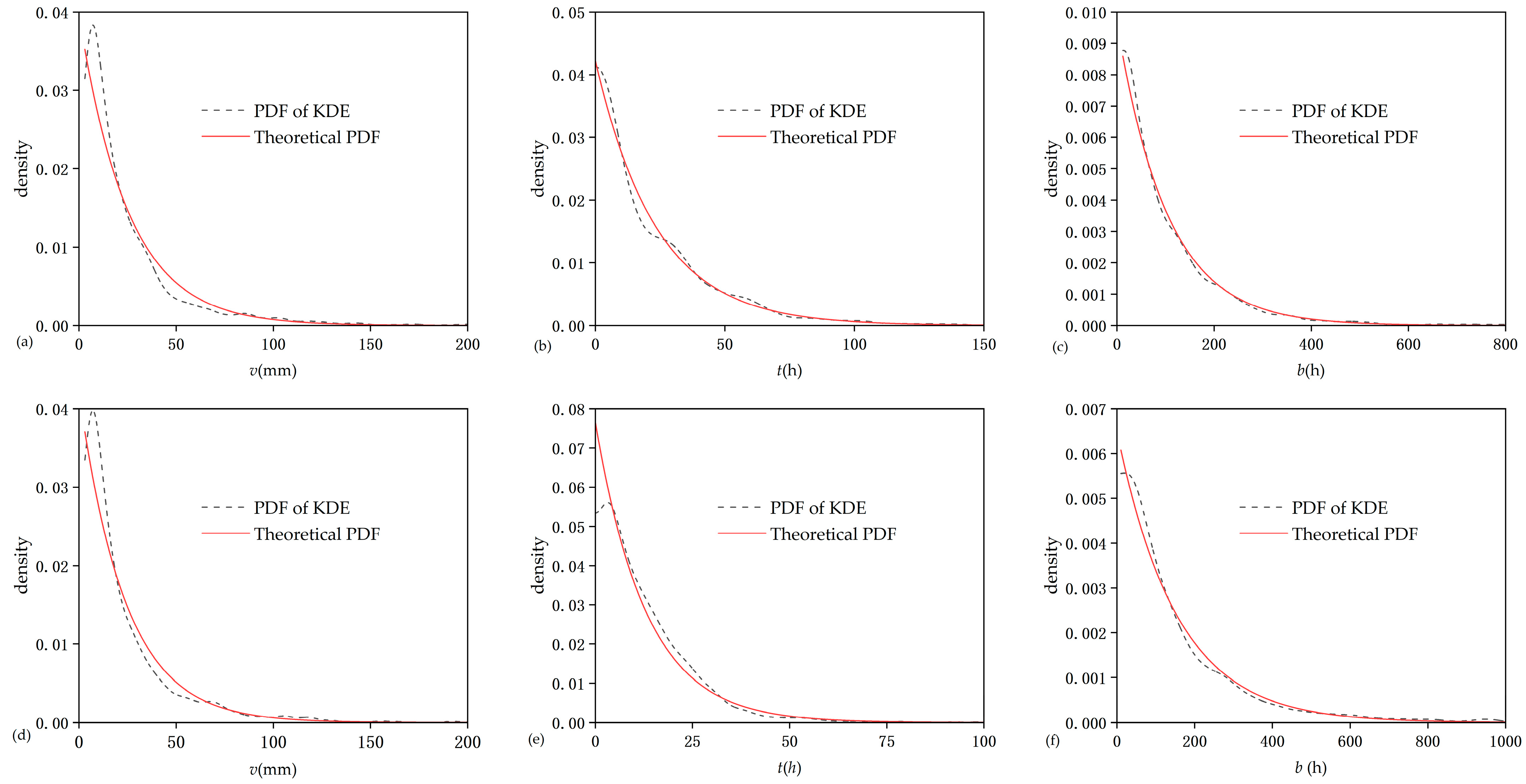
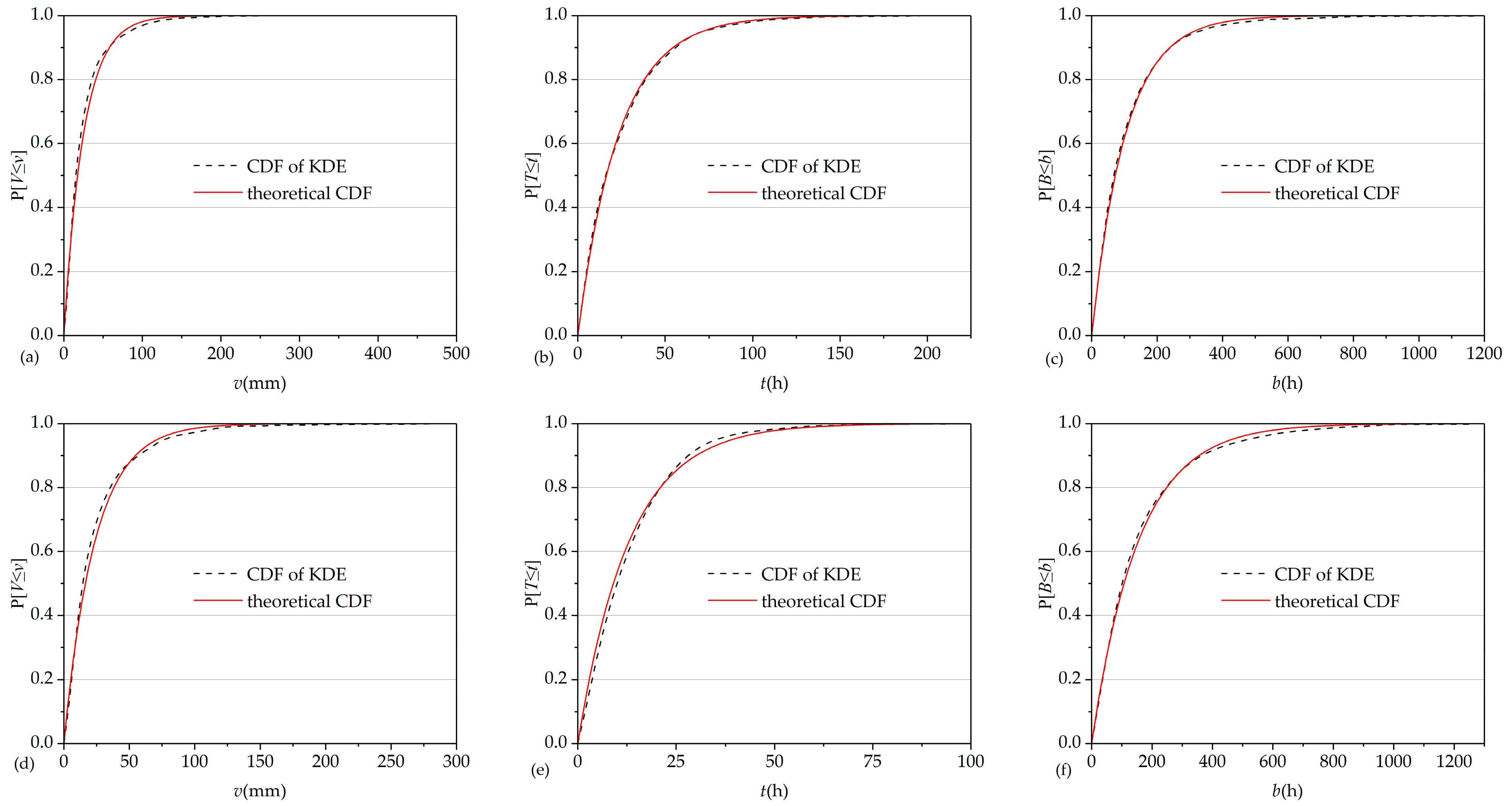
3.2.2. GOF Test of Exponentiality Using KDE
3.2.3. Optimal MIET, vt and Rainfall Event Characterization
4. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Restrepo, P.; Eagleson, P. Identification of Independent Rainstorms. J. Hydrol. 1982, 55, 303–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunkerley, D. Identifying Individual Rain Events from Pluviograph Records: A Review with Analysis of Data from an Australian Dryland Site. Hydrol. Process. 2008, 22, 5024–5036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, B.J.; Papa, F. Urban Stormwater Management Planning with Analytical Probabilistic Models, 1st ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Joo, J.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.; Jun, H.; Jo, D.J. Inter-Event Time Definition Setting Procedure for Urban Drainage Systems. Water 2013, 6, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.H.; Kim, J. Development of New Inter-Event Time Definition Technique in Urban Areas. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2018, 22, 3764–3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Adams, B. Hydrologic Analysis of Urban Catchments with Event-Based Probabilistic Models: 1. Runoff Volume. Water Resour. Res. 1998, 34, 3421–3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, M.; Turco, M.; Brunetti, G.; Piro, P. Minimum Inter-Event Time to Identify Independent Rainfall Events in Urban Catchment Scale. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 1073, 1630–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balistrocchi, M.; Grossi, G.; Bacchi, B. An Analytical Probabilistic Model of the Quality Efficiency of a Sewer Tank. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45, W12420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guo, Y. Proper Sizing of Infiltration Trenches Using Closed-Form Analytical Equations. Water Resour. Manag. 2020, 34, 3809–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, W. Design of Integrated Bioinfiltration-Detention Urban Retrofits With Design Storm and Continuous Simulation Methods. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2010, 15, 486–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Guo, Y. SWMM Simulation of the Storm Water Volume Control Performance of Permeable Pavement Systems. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2014, 20, 06014010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quader, A.; Guo, Y. Peak Discharge Estimation Using Analytical Probabilistic and Design Storm Approaches. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2006, 11, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahar, B.; Graillot, D.; Gaur, S. Storm-Water Management through Infiltration Trenches. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2012, 138, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimondi, A.; Becciu, G. Performance of Green Roofs for Rainwater Control. Water Resour. Manag. 2021, 34, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Adams, B. A Framework for Urban Storm Water Modeling and Control Analysis with Analytical Models. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42, W06419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guo, Y. An Analytical Stochastic Approach for Evaluating the Performance of Combined Sewer Overflow Tanks. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 3357–3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Guo, Y.; Wang, J. Stormwater Capture and Antecedent Moisture Characteristics of Permeable Pavements. Hydrol. Process. 2018, 32, 2708–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guo, Y. Stochastic Analysis of Storm Water Quality Control Detention Ponds. J. Hydrol. 2019, 571, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S.EPA. Methodology for Analysis of Detention Basins for Control of Urban Runoff Quality; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1986; Volume 440, pp. 5–87. [Google Scholar]
- Shamsudin, S.; Dan’azumi, S.; Aris, A.; Yusop, Z. Optimum Combination of Pond Volume and Outlet Capacity of a Stormwater Detention Pond Using Particle Swarm Optimization. Urban Water J. 2013, 11, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Huang, G.; Mai, Y.; Chen, W. Optimizing the Cost-Effectiveness of Low Impact Development (LID) Practices Using an Analytical Probabilistic Approach. Urban Water J. 2020, 17, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassini, S.; Guo, Y. Exponentiality Test Procedures for Large Samples of Rainfall Event Characteristics. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2016, 21, 04016003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojumuddin, N.; Yusof, F.; Yusop, Z. Determination of Minimum Inter-Event Time for Storm Characterization in Johor, Malaysia. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2016, 11, S687–S699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nix, S.J. Urban Stormwater Modeling and Simulation, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Balistrocchi, M.; Grossi, G.; Bacchi, B. Deriving a Practical Analytical-Probabilistic Method to Size Flood Routing Reservoirs. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 62, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacchi, B.; Balistrocchi, M.; Grossi, G. Proposal of a Semi-Probabilistic Approach for Storage Facility Design. Urban Water J. 2008, 5, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Baetz, B. Sizing of Rainwater Storage Units for Green Building Applications. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2007, 12, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopalan, B.; Lall, U.; Tarboton, D. Evaluation of Kernel Density Estimation Methods for Daily Precipitation Resampling. Stoch. Hydrol. Hydraul. 1997, 11, 523–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlides, A.; Agou, V.D.; Hristopulos, D.T. Non-parametric Kernel-based Estimation and Simulation of Precipitation Amount. J. Hydrol. 2022, 612, 127988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacoullos, T. Estimation of a Multivariate Density. Ann. Inst. Stat. Math. 1966, 18, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devroye, L. The Equivalence of Weak, Strong and Complete Convergence in L1 for Kernel Density Estimates. Ann. Stat. 1983, 11, 896–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosthaf, T.; Bárdossy, A. Regionalizing Nonparametric Models of Precipitation Amounts on Different Temporal Scales. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 2463–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, S.; Wang, D. Combined Probability Density Model for Medium Term Load Forecasting Based on Quantile Regression and Kernel Density Estimation. Energy Procedia 2019, 158, 6446–6451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Bhattacharya, B.; Xie, P.; Zevenbergen, C. Improving Flash Flood Forecasting Using a Frequentist Approach to Identify Rainfall Thresholds for Flash Flood Occurrence. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2022, 37, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Wang, M.; Ren, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Cui, H.; Xu, C.-Y. An Integrated Approach for Identification and Quantification of Ecological Drought in Rivers from an Ecological Streamflow Perspective. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 143, 109410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Jain, S.; Lee, J.H.; Chen, H.; Park, S.Y. Quantitative Vulnerability Assessment of Water Quality to Extreme Drought in a Changing Climate. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 103, 688–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eagleson, P. Dynamics of Flood Frequency. Water Resour. Res. 1972, 8, 878–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segarra, R. Reliability-Based Design of Urban Stormwater Detention Facilities with Random Carryover Storage. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2020, 146, 04019076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parzen, E. On the Estimation of Probability Density Functions and Mode. Ann. Math. Stat. 1962, 33, 1065–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botev, Z.; Grotowski, J.; Kroese, D. Kernel Density Estimation via Diffusion. Ann. Stat. 2010, 38, 2916–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marron, J.S.; Nolan, D. Canonical Kernels for Density Estimation. Stat. Probab. Lett. 1988, 7, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, B.W. Density Estimation for Statistics and Data Analysis, 1st ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Schuster, E. Incorporating Support Constraints into Nonparametric Estimators of Densities. Commun. Stat.-Theory Methods 1985, 14, 1123–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M. Simple Boundary Correction for Kernel Density Estimation. Stat. Comput. 1993, 3, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, T. Numerical Analysis, 2nd ed.; Pearson: Boston, MA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Darkwah, K.; Nortey, E.; Lotsi, A. Estimation of the Gini Coefficient for the Lognormal Distribution of Income Using the Lorenz Curve. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Karunamuni, R. Deconvolution Boundary Kernel Method in Nonparametric Density Estimation. J. Stat. Plan. Inference 2009, 139, 2269–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunnane, C. A Note on the Poisson Assumption in Partial Duration Series Models. Water Resour. Res. 1979, 15, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruise, J.; Arora, K. A Hydroclimatic Application Strategy for the Poisson Partial Duration Model. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2007, 26, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.; Drew, J.; Leemis, L. The Distribution of the Kolmogorov–Smirnov, Cramer–von Mises, and Anderson–Darling Test Statistics for Exponential Populations with Estimated Parameters. Commun. Stat.-Simulat. Comput. 2008, 37, 1396–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Guo, Y. Analyzing the Impact of Impervious Area Disconnection on Urban Runoff Control Using an Analytical Probabilistic Model. Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 33, 1753–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Gu, B.; Schlesinger, W.; Ju, X. Significant Accumulation of Nitrate in Chinese Semi-Humid Croplands. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Yue, P.; Wang, J. Effects of Evapotranspiration and Precipitation on Dryness/Wetness Changes in China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2020, 142, 1027–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yin, S.; Xie, Y.; Nearing, M.A. Minimum Inter-event Times for Rainfall in the Eastern Monsoon Region of China. Trans. ASABE 2019, 62, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

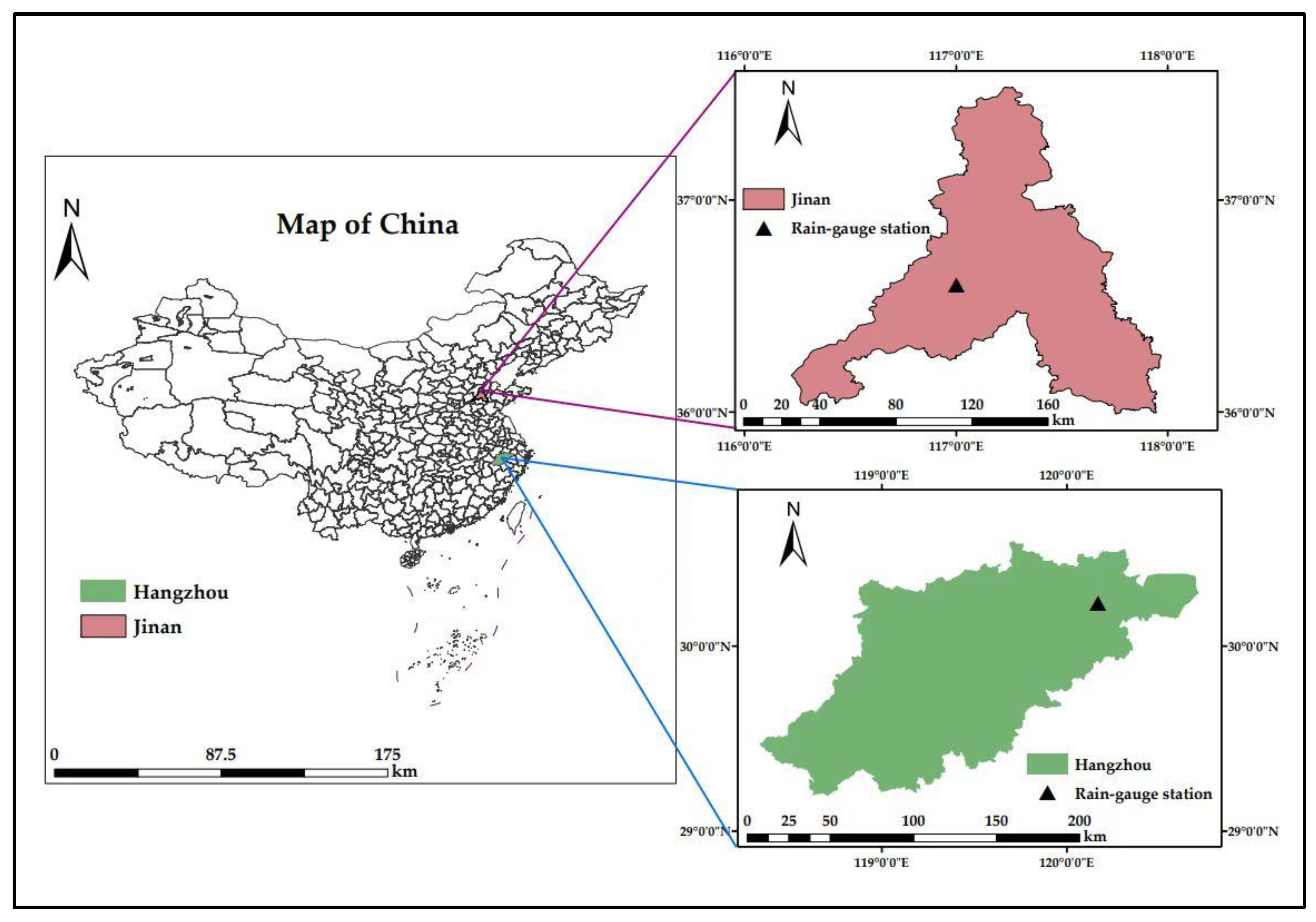

| Station | Station Number | Latitude | Longitude | Range of Years | Range of Months | Average Annual Precipitation (mm) | Climate Condition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jinan | 54,823 | N36°60′ | E117°00′ | 1959–2015 | May.–Oct. | 688.5 | Semi-humid |
| Hangzhou | 58,457 | N30°23′ | E120°17′ | 1955–2015 | Apr.–Oct. | 1510.0 | Humid |
| Hangzhou | Jinan | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIET (h) | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | MIET (h) | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | ||
| vt (mm) | vt (mm) | ||||||||||
| 0 | 5769 | 5132 | 4628 | 4172 | 0 | 2567 | 2408 | 2290 | 2180 | ||
| 1 | 3854 | 3525 | 3234 | 2955 | 1 | 1860 | 1797 | 1744 | 1692 | ||
| 2 | 3276 | 3036 | 2807 | 2590 | 2 | 1606 | 1562 | 1521 | 1490 | ||
| 3 | 2893 | 2695 | 2517 | 2333 | 3 | 1453 | 1419 | 1390 | 1360 | ||
| 4 | 2602 | 2444 | 2301 | 2147 | 4 | 1326 | 1301 | 1276 | 1248 | ||
| 5 | 2364 | 2239 | 2129 | 2000 | 5 | 1227 | 1207 | 1189 | 1164 | ||
| Hangzhou | Jinan | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIET (h)-vt (mm) | ⟨v⟩ (mm) | ⟨t⟩ (h) | ⟨b⟩ (h) | ⟨v⟩ (mm) | ⟨t⟩ (h) | ⟨b⟩ (h) |
| 6-0 | 10.48 | 8.48 | 44.66 | 13.21 | 7.48 | 87.18 |
| 6-1 | 15.49 | 11.64 | 66.70 | 18.07 | 9.49 | 117.23 |
| 6-2 | 17.95 | 12.88 | 78.69 | 20.69 | 10.32 | 135.80 |
| 6-3 | 20.00 | 13.85 | 88.60 | 22.61 | 10.84 | 148.47 |
| 6-4 | 21.84 | 14.71 | 98.92 | 24.43 | 11.28 | 161.50 |
| 6-5 | 23.58 | 15.45 | 109.51 | 26.04 | 11.66 | 174.30 |
| 8-0 | 11.78 | 10.34 | 49.41 | 14.08 | 8.40 | 92.51 |
| 8-1 | 16.96 | 14.03 | 71.63 | 18.73 | 10.45 | 120.71 |
| 8-2 | 19.45 | 15.50 | 83.33 | 21.31 | 11.35 | 138.90 |
| 8-3 | 21.60 | 16.68 | 93.32 | 23.21 | 11.93 | 151.20 |
| 8-4 | 23.45 | 17.67 | 103.35 | 24.99 | 12.40 | 163.71 |
| 8-5 | 25.19 | 18.56 | 113.41 | 26.59 | 12.83 | 176.23 |
| 10-0 | 13.06 | 12.39 | 53.87 | 14.81 | 9.27 | 96.85 |
| 10-1 | 18.51 | 16.71 | 76.75 | 19.31 | 11.42 | 123.74 |
| 10-2 | 21.10 | 18.43 | 88.46 | 21.92 | 12.44 | 141.87 |
| 10-3 | 23.24 | 19.83 | 98.04 | 23.74 | 13.05 | 154.12 |
| 10-4 | 25.09 | 20.98 | 107.67 | 25.55 | 13.51 | 166.07 |
| 10-5 | 26.76 | 21.93 | 116.89 | 27.09 | 13.97 | 177.97 |
| 12-0 | 14.49 | 14.89 | 58.62 | 15.56 | 10.26 | 101.22 |
| 12-1 | 20.29 | 20.03 | 82.27 | 19.91 | 12.51 | 126.82 |
| 12-2 | 22.94 | 22.03 | 93.90 | 22.41 | 13.56 | 144.14 |
| 12-3 | 25.19 | 23.67 | 103.53 | 24.31 | 14.23 | 156.64 |
| 12-4 | 27.06 | 25.01 | 112.91 | 26.18 | 14.73 | 169.17 |
| 12-5 | 28.72 | 26.12 | 121.73 | 27.74 | 15.26 | 180.88 |
| Hangzhou | Jinan | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIET (h)-vt (mm) | Critical Value of rp Ranges (α = 0.10) | Resulting rp | Decision | Critical Value of rp Ranges (α = 0.10) | Resulting rp | Decision |
| 6-0 | 0.72–1.32 | 1.54 | Reject | 0.71–1.33 | 1.25 | Accept |
| 6-1 | 0.72–1.32 | 1.25 | Accept | 0.71–1.33 | 0.86 | Accept |
| 6-2 | 0.72–1.32 | 1.29 | Accept | 0.71–1.33 | 0.97 | Accept |
| 6-3 | 0.72–1.32 | 1.25 | Accept | 0.71–1.33 | 1.12 | Accept |
| 6-4 | 0.72–1.32 | 1.22 | Accept | 0.71–1.33 | 1.08 | Accept |
| 6-5 | 0.72–1.32 | 1.16 | Accept | 0.71–1.33 | 1.21 | Accept |
| 8-0 | 0.72–1.32 | 1.44 | Reject | 0.71–1.33 | 1.01 | Accept |
| 8-1 | 0.72–1.32 | 1.15 | Accept | 0.71–1.33 | 0.83 | Accept |
| 8-2 | 0.72–1.32 | 1.13 | Accept | 0.71–1.33 | 0.95 | Accept |
| 8-3 | 0.72–1.32 | 1.17 | Accept | 0.71–1.33 | 1.09 | Accept |
| 8-4 | 0.72–1.32 | 1.11 | Accept | 0.71–1.33 | 1.06 | Accept |
| 8-5 | 0.72–1.32 | 1.07 | Accept | 0.71–1.33 | 1.16 | Accept |
| 10-0 | 0.72–1.32 | 1.29 | Accept | 0.71–1.33 | 0.93 | Accept |
| 10-1 | 0.72–1.32 | 1.01 | Accept | 0.71–1.33 | 0.79 | Accept |
| 10-2 | 0.72–1.32 | 0.94 | Accept | 0.71–1.33 | 0.93 | Accept |
| 10-3 | 0.72–1.32 | 0.98 | Accept | 0.71–1.33 | 1.02 | Accept |
| 10-4 | 0.72–1.32 | 0.98 | Accept | 0.71–1.33 | 0.98 | Accept |
| 10-5 | 0.72–1.32 | 0.90 | Accept | 0.71–1.33 | 1.10 | Accept |
| 12-0 | 0.72–1.32 | 1.15 | Accept | 0.71–1.33 | 0.87 | Accept |
| 12-1 | 0.72–1.32 | 0.82 | Accept | 0.71–1.33 | 0.76 | Accept |
| 12-2 | 0.72–1.32 | 0.73 | Accept | 0.71–1.33 | 0.84 | Accept |
| 12-3 | 0.72–1.32 | 0.75 | Accept | 0.71–1.33 | 0.93 | Accept |
| 12-4 | 0.72–1.32 | 0.74 | Accept | 0.71–1.33 | 0.86 | Accept |
| 12-5 | 0.72–1.32 | 0.70 | Reject | 0.71–1.33 | 0.95 | Accept |
| Rainfall Event Volume v | Rainfall Event Duration t | Rainfall Inter-Event Time b | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIET (h)- vt (mm) | K-S Statistic | Critical Value (α = 0.10) | K-S Statistic | Critical Value (α = 0.10) | K-S Statistic | Critical Value (α = 0.10) |
| 6-0 | 0.213 | 0.066 | 0.107 | 0.102 | 0.155 | 0.209 |
| 6-1 | 0.098 | 0.066 | 0.044 | 0.102 | 0.096 | 0.188 |
| 6-2 | 0.069 | 0.066 | 0.033 | 0.102 | 0.078 | 0.188 |
| 6-3 a | 0.058 | 0.066 | 0.031 | 0.102 | 0.073 | 0.174 |
| 6-4 | 0.081 | 0.066 | 0.033 | 0.101 | 0.064 | 0.174 |
| 6-5 | 0.108 | 0.066 | 0.032 | 0.102 | 0.054 | 0.174 |
| 8-0 | 0.210 | 0.066 | 0.132 | 0.100 | 0.124 | 0.209 |
| 8-1 | 0.099 | 0.066 | 0.052 | 0.100 | 0.069 | 0.188 |
| 8-2 | 0.071 | 0.066 | 0.033 | 0.100 | 0.063 | 0.186 |
| 8-3 a | 0.058 | 0.066 | 0.019 | 0.099 | 0.056 | 0.176 |
| 8-4 | 0.069 | 0.066 | 0.016 | 0.099 | 0.048 | 0.174 |
| 8-5 | 0.093 | 0.066 | 0.017 | 0.098 | 0.040 | 0.174 |
| 10-0 | 0.202 | 0.059 | 0.143 | 0.086 | 0.087 | 0.209 |
| 10-1 | 0.097 | 0.059 | 0.055 | 0.086 | 0.055 | 0.188 |
| 10-2 | 0.068 | 0.059 | 0.033 | 0.085 | 0.047 | 0.186 |
| 10-3 a | 0.056 | 0.059 | 0.017 | 0.085 | 0.040 | 0.174 |
| 10-4 | 0.060 | 0.059 | 0.013 | 0.085 | 0.031 | 0.174 |
| 10-5 | 0.084 | 0.059 | 0.017 | 0.085 | 0.026 | 0.174 |
| 12-0 | 0.198 | 0.059 | 0.151 | 0.086 | 0.076 | 0.209 |
| 12-1 | 0.092 | 0.059 | 0.062 | 0.085 | 0.037 | 0.188 |
| 12-2 | 0.063 | 0.059 | 0.038 | 0.085 | 0.027 | 0.186 |
| 12-3 a | 0.051 | 0.059 | 0.021 | 0.084 | 0.021 | 0.174 |
| 12-4 a | 0.055 | 0.059 | 0.020 | 0.084 | 0.020 | 0.174 |
| 12-5 | 0.079 | 0.059 | 0.026 | 0.084 | 0.017 | 0.174 |
| Rainfall Event Volume v | Rainfall Event Duration t | Rainfall Inter-Event Time b | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIET (h)- vt (mm) | KS Statistic | Critical Value (α = 0.10) | KS Statistic | Critical Value (α = 0.10) | KS Statistic | Critical Value (α = 0.10) |
| 6-0 | 0.179 | 0.071 | 0.049 | 0.125 | 0.056 | 0.188 |
| 6-1 | 0.089 | 0.071 | 0.042 | 0.124 | 0.025 | 0.171 |
| 6-2 a | 0.061 | 0.071 | 0.052 | 0.123 | 0.029 | 0.169 |
| 6-3 a | 0.051 | 0.071 | 0.055 | 0.123 | 0.026 | 0.169 |
| 6-4 a | 0.058 | 0.071 | 0.055 | 0.123 | 0.028 | 0.151 |
| 6-5 | 0.079 | 0.071 | 0.059 | 0.123 | 0.026 | 0.150 |
| 8-0 | 0.168 | 0.071 | 0.047 | 0.119 | 0.039 | 0.188 |
| 8-1 | 0.087 | 0.071 | 0.032 | 0.118 | 0.018 | 0.171 |
| 8-2 a | 0.061 | 0.071 | 0.043 | 0.118 | 0.027 | 0.169 |
| 8-3 a | 0.051 | 0.071 | 0.049 | 0.117 | 0.025 | 0.169 |
| 8-4 a | 0.054 | 0.071 | 0.052 | 0.117 | 0.026 | 0.155 |
| 8-5 | 0.075 | 0.071 | 0.055 | 0.117 | 0.023 | 0.150 |
| 10-0 | 0.160 | 0.071 | 0.051 | 0.118 | 0.030 | 0.188 |
| 10-1 | 0.084 | 0.071 | 0.024 | 0.118 | 0.015 | 0.171 |
| 10-2 a | 0.060 | 0.071 | 0.037 | 0.117 | 0.025 | 0.169 |
| 10-3 a | 0.049 | 0.071 | 0.044 | 0.117 | 0.023 | 0.169 |
| 10-4 a | 0.052 | 0.071 | 0.049 | 0.117 | 0.024 | 0.155 |
| 10-5 | 0.071 | 0.071 | 0.053 | 0.117 | 0.021 | 0.150 |
| 12-0 | 0.154 | 0.071 | 0.058 | 0.106 | 0.022 | 0.188 |
| 12-1 | 0.086 | 0.071 | 0.016 | 0.105 | 0.024 | 0.171 |
| 12-2 a | 0.062 | 0.071 | 0.028 | 0.105 | 0.022 | 0.169 |
| 12-3 a | 0.050 | 0.071 | 0.035 | 0.105 | 0.022 | 0.169 |
| 12-4 a | 0.048 | 0.071 | 0.041 | 0.104 | 0.023 | 0.155 |
| 12-5 a | 0.067 | 0.071 | 0.047 | 0.104 | 0.020 | 0.150 |
| Hangzhou | Jinan | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| MIET (h)-vt (mm) | Rr (%) | MIET (h)-vt (mm) | Rr (%) |
| 12-3 | 8.84 | 10-3 | 8.97 |
| 10-3 | 9.67 | 8-3 | 9.08 |
| 6-3 | 9.77 | 6-3 | 9.20 |
| 8-3 | 10.19 | 12-3 | 9.29 |
| 12-4 | 32.54 | 6-2 | 11.88 |
| 8-2 | 12.09 | ||
| 10-2 | 12.13 | ||
| 12-2 | 12.75 | ||
| 12-4 | 27.35 | ||
| 10-4 | 29.21 | ||
| 8-4 | 30.04 | ||
| 6-4 | 31.24 | ||
| 12-5 | 34.68 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, S.; Diao, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Raimondi, A.; Wang, J. KDE-Based Rainfall Event Separation and Characterization. Water 2023, 15, 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15030580
Cao S, Diao Y, Wang J, Liu Y, Raimondi A, Wang J. KDE-Based Rainfall Event Separation and Characterization. Water. 2023; 15(3):580. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15030580
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Shengle, Yijiao Diao, Jiachang Wang, Yang Liu, Anita Raimondi, and Jun Wang. 2023. "KDE-Based Rainfall Event Separation and Characterization" Water 15, no. 3: 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15030580
APA StyleCao, S., Diao, Y., Wang, J., Liu, Y., Raimondi, A., & Wang, J. (2023). KDE-Based Rainfall Event Separation and Characterization. Water, 15(3), 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15030580







