Coastal Water Clarity in Shenzhen: Assessment of Observations from Sentinel-2
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Background
1.2. Status of Research
1.3. Purpose of this Study
2. Materials and Method
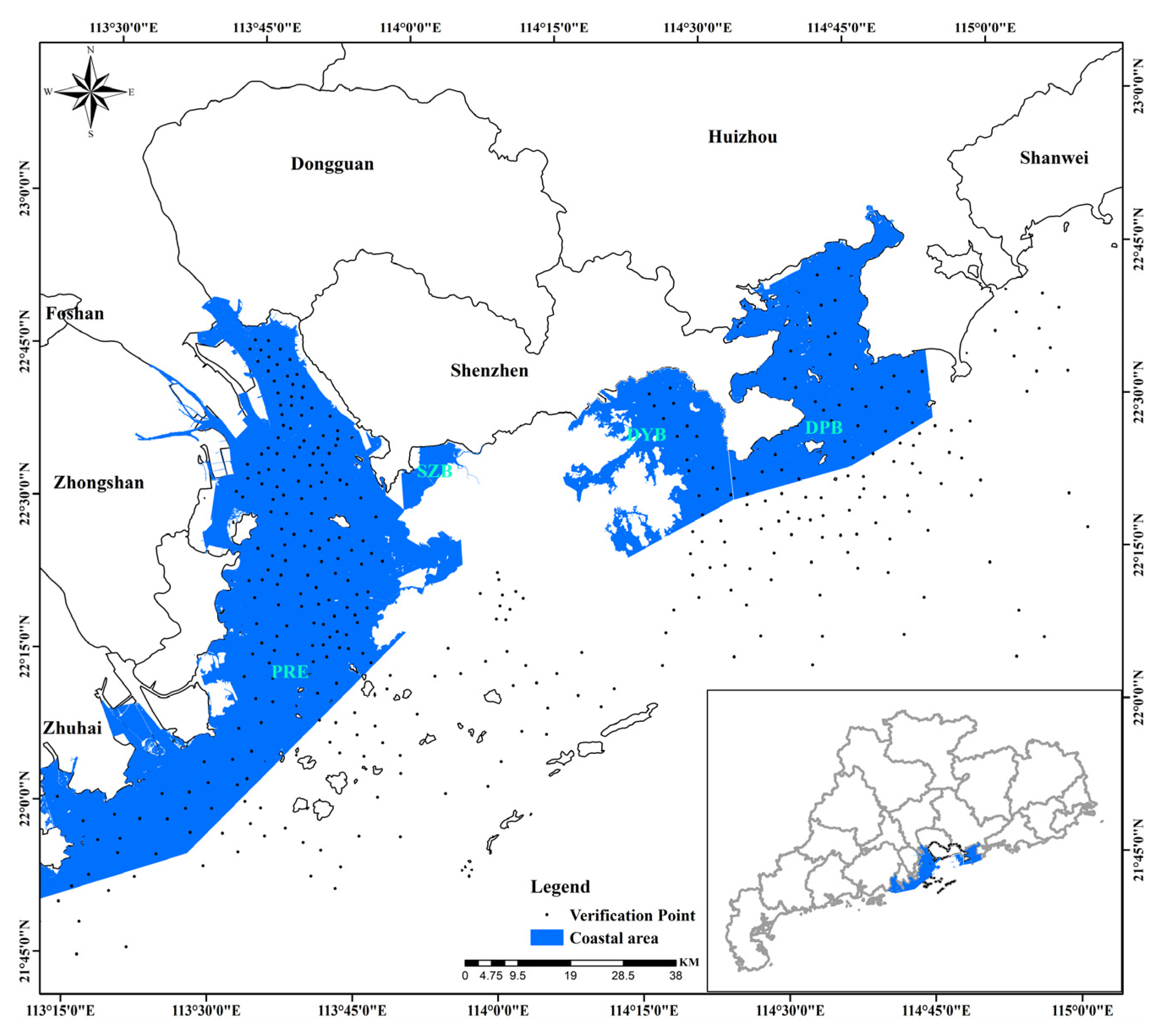
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
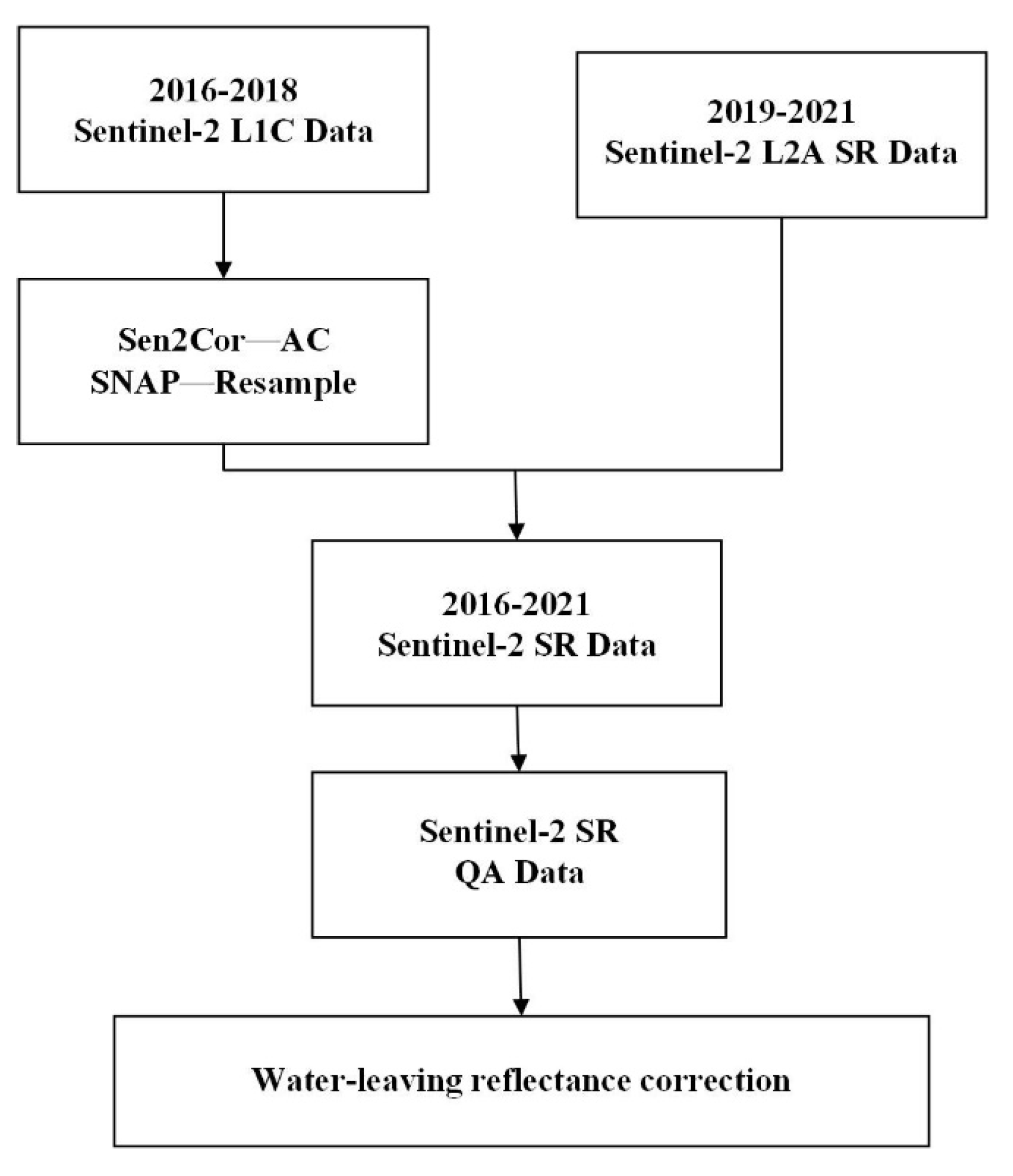
2.3. Pre-Processing
2.4. Mean Aggregation
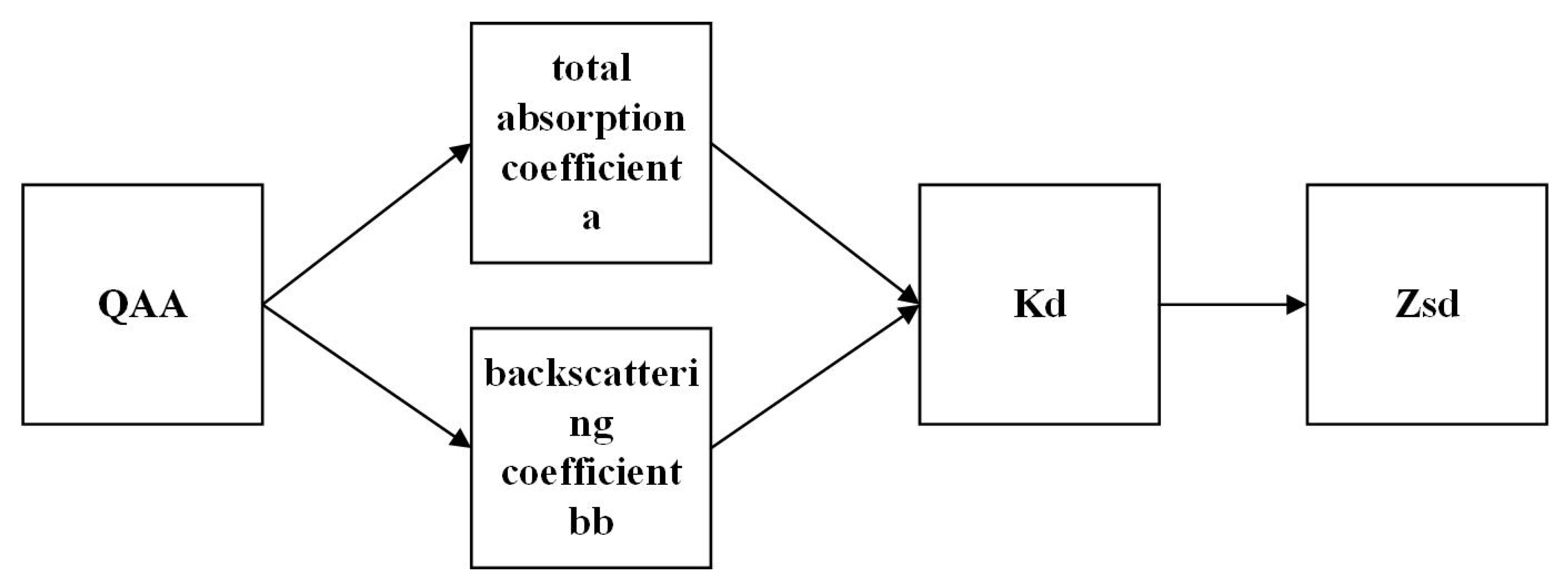
2.5. Algorithm to Retrieve Zsd
2.6. Evaluation of Zsd
3. Result
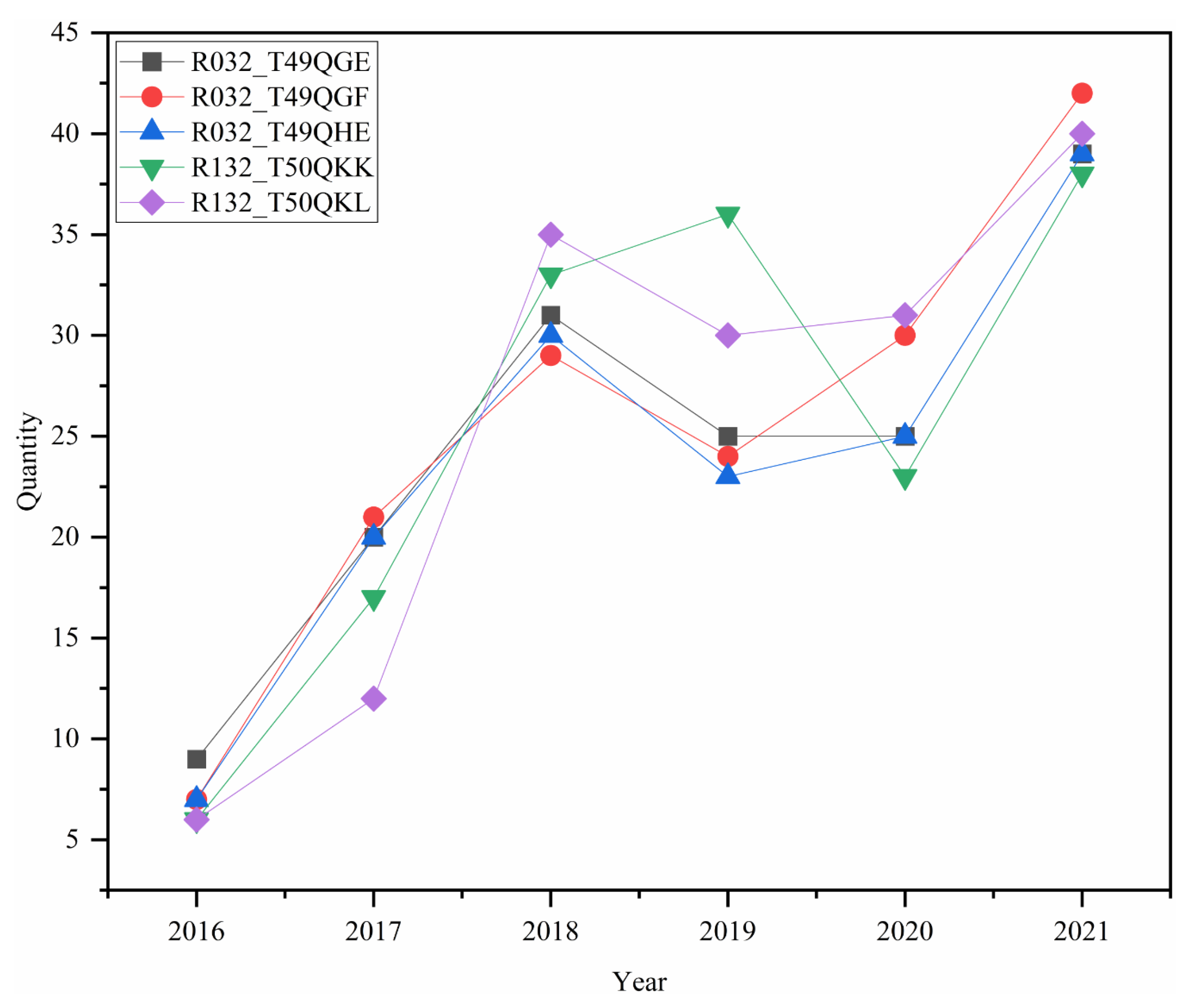
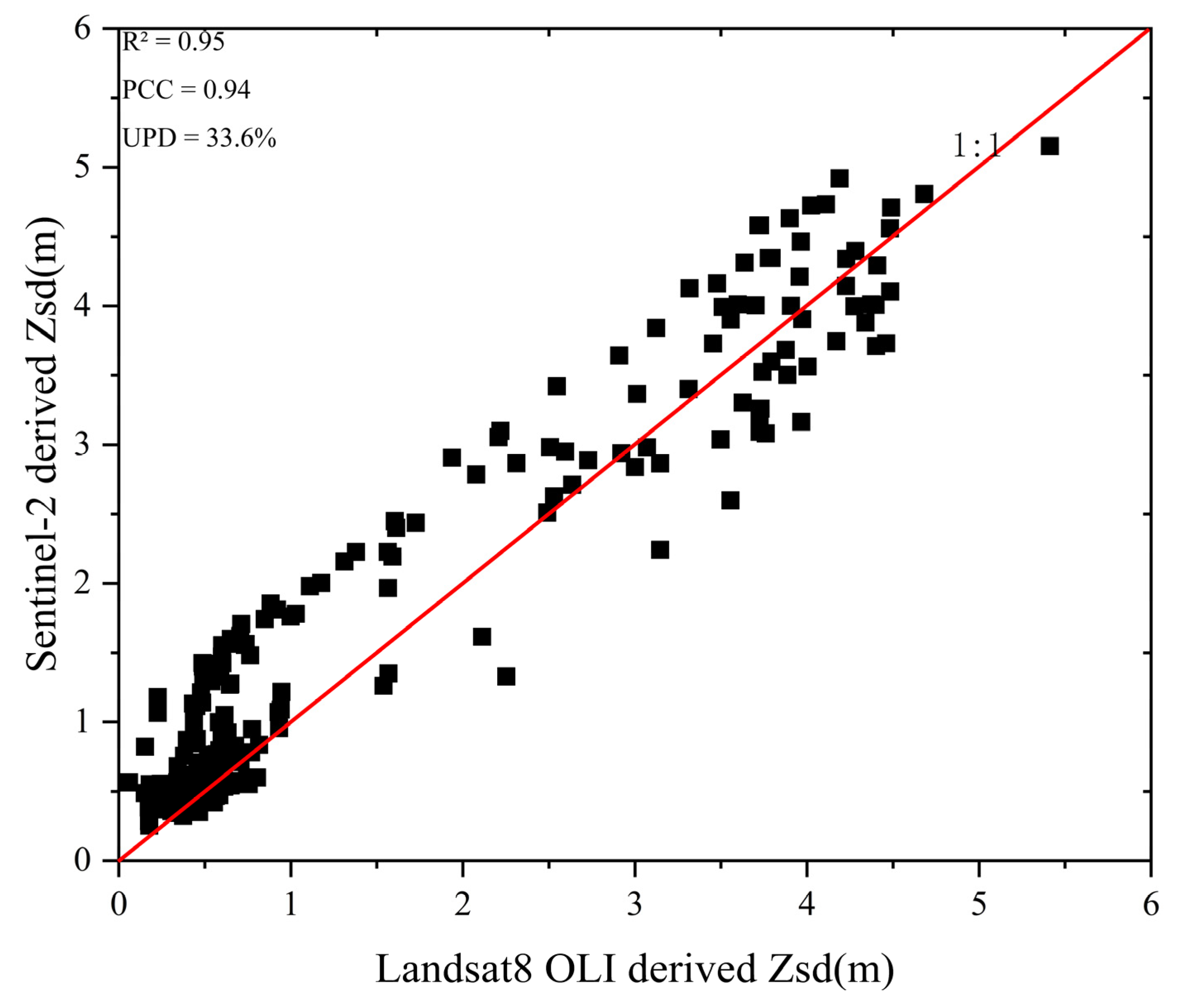
3.1. Evaluation of Model Applicability
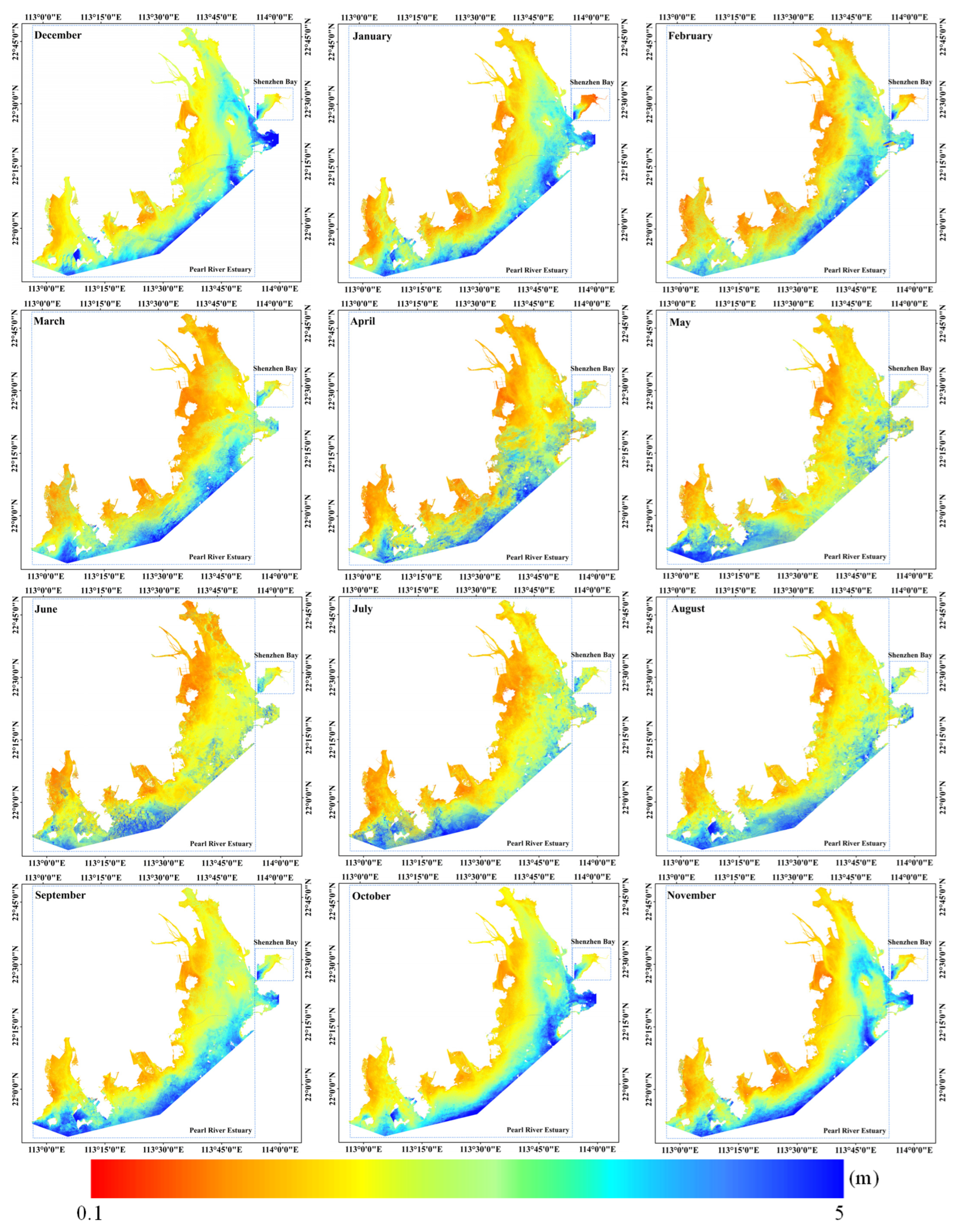
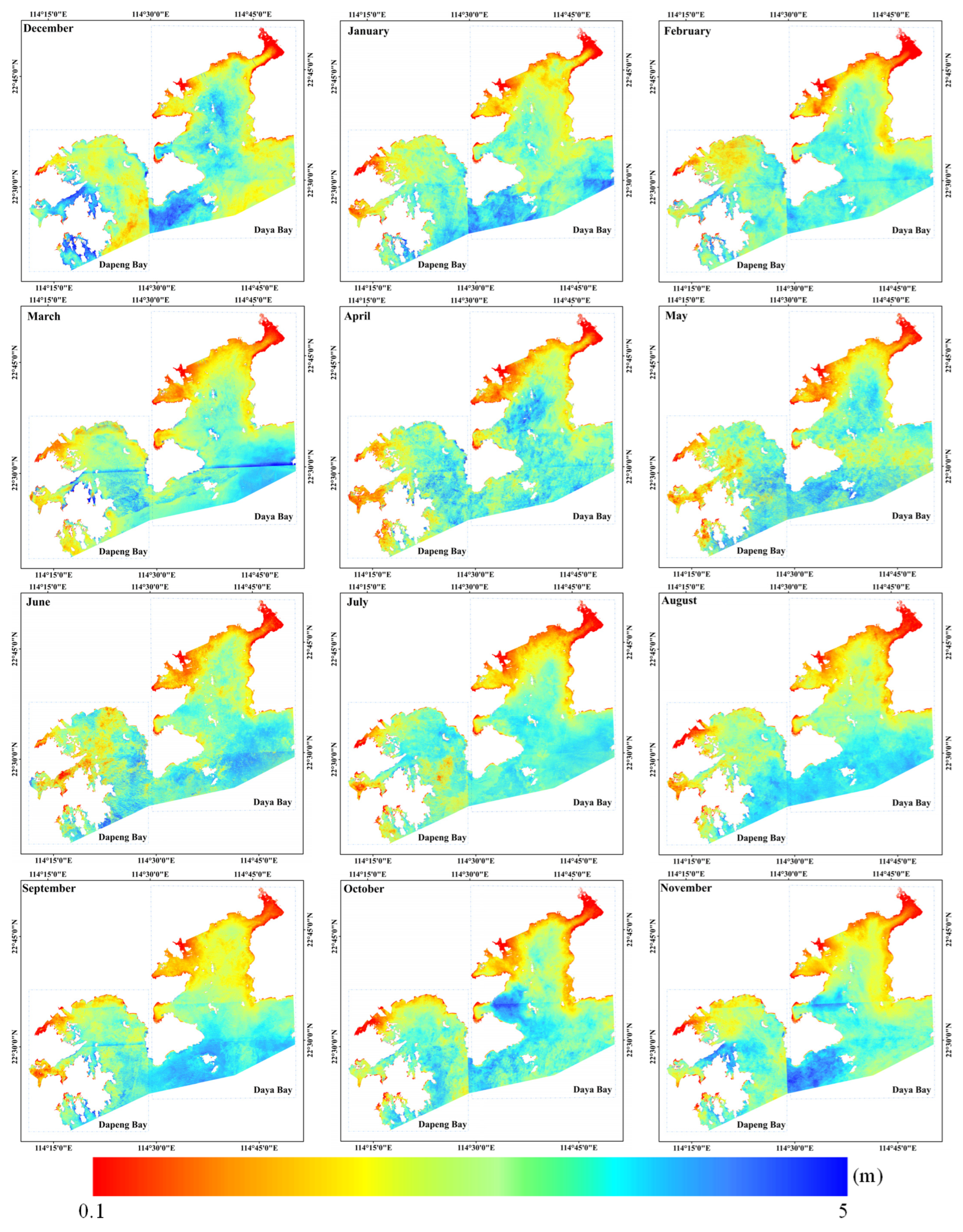
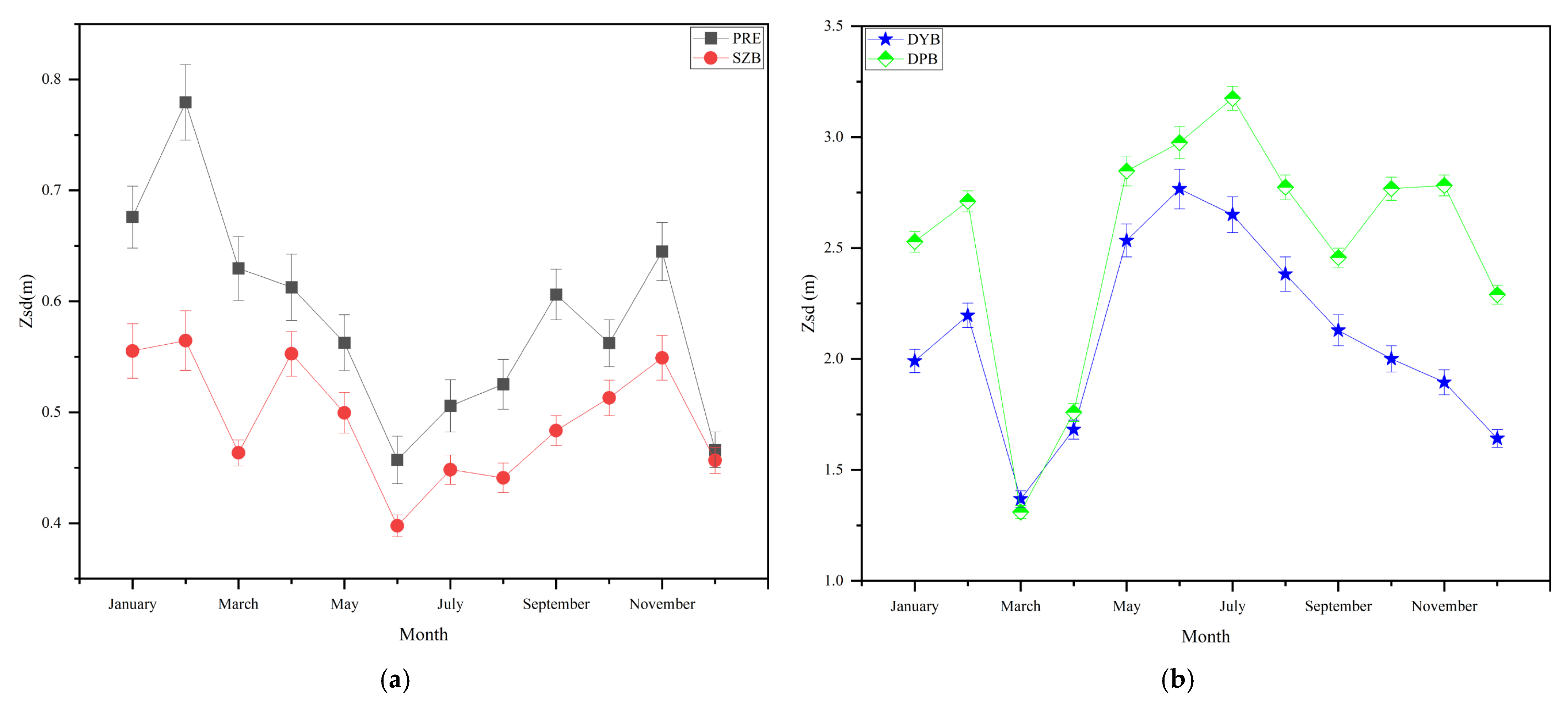
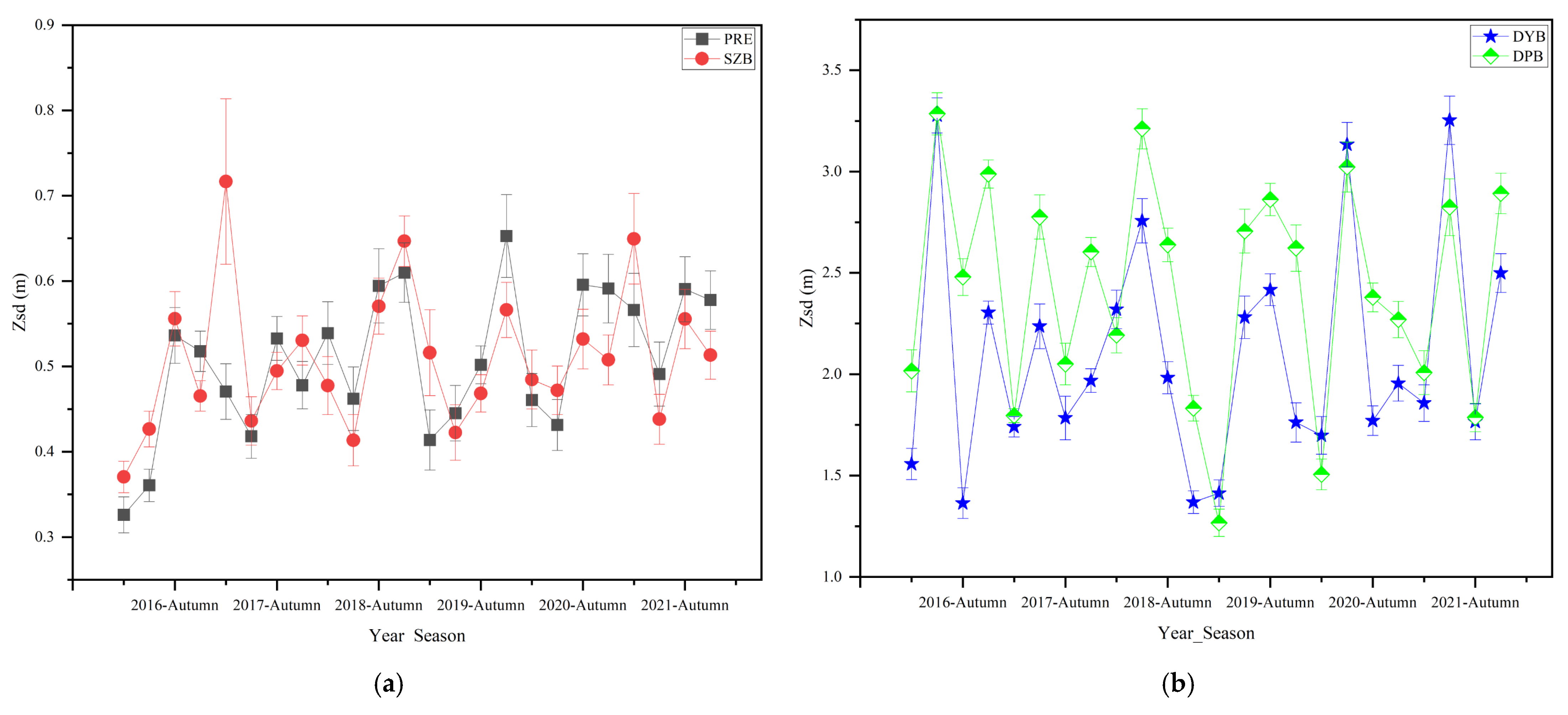
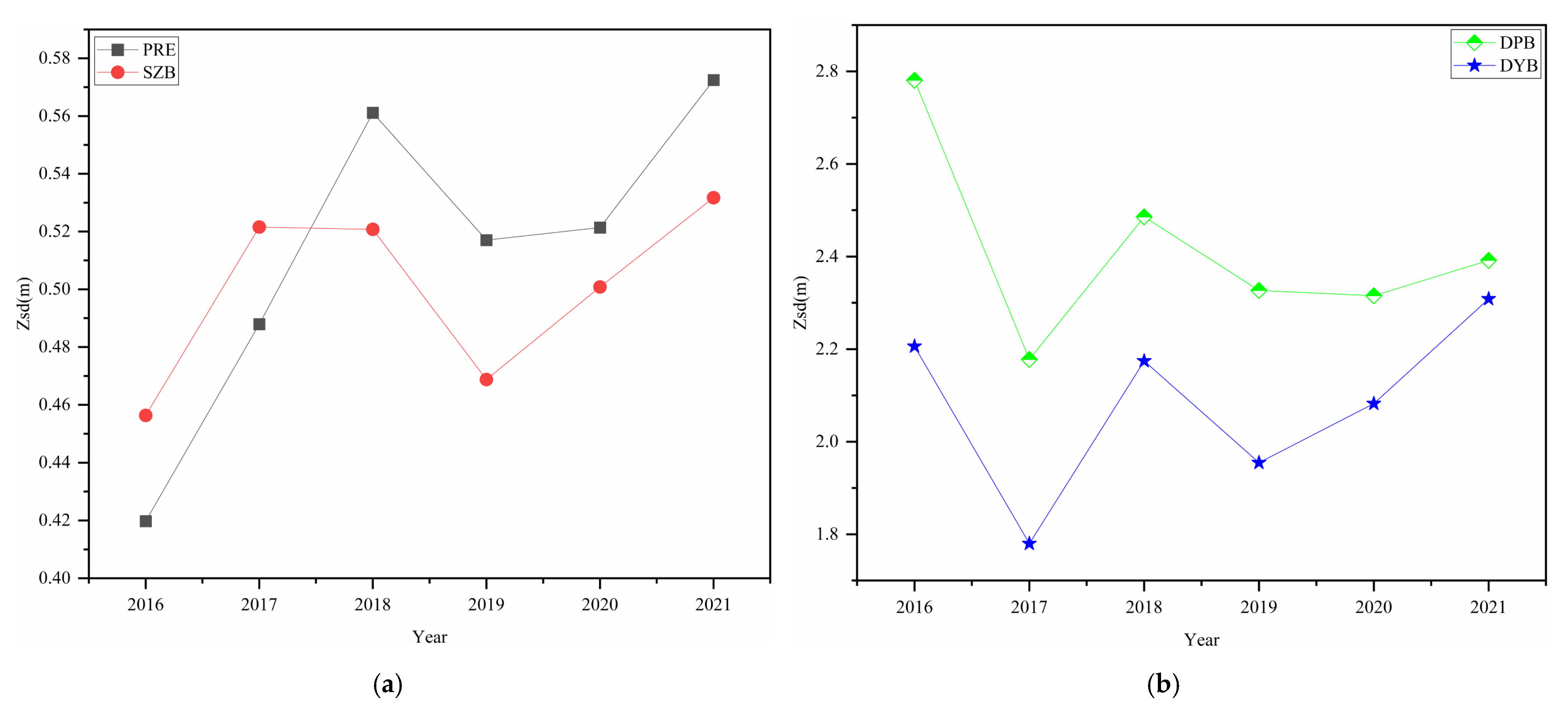
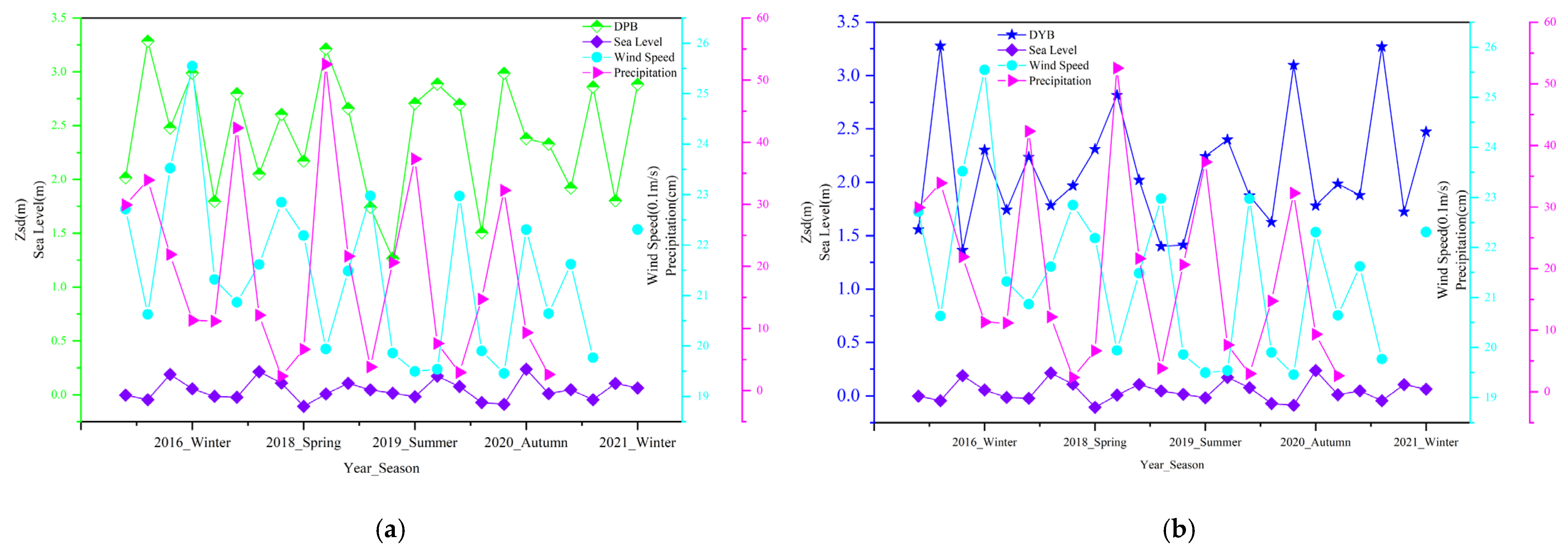
3.2. Variations in Water Clarity
4. Discussion
4.1. Uncertainties in Zsd Estimation
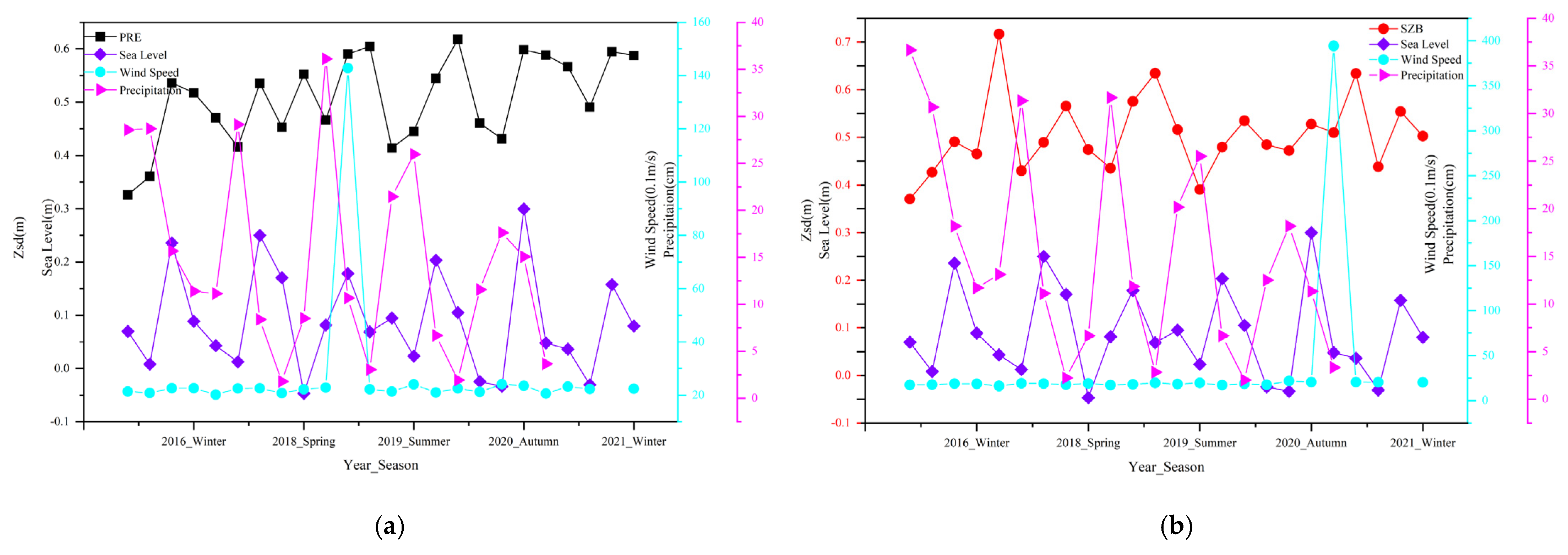
4.2. Driving Forces of Water Clarity
4.3. Implications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.; Yufei, W.; Wang, Y.; Xi, H. Investigating the Impacts of Landuse-Landcover (LULC) Change in the Pearl River Delta Region on Water Quality in the Pearl River Estuary and Hong Kong’s Coast. Remote Sens. 2009, 1, 1055–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Huang, L.; Chen, J.; Zhou, M.; Tan, Y. Water Quality and Phytoplankton Blooms in the Pearl River Estuary. In The Environment in Asia Pacific Harbours; Wolanski, E., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 139–145. ISBN 978-1-4020-3655-2. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, Y.; Shou, Y. Numerical Model Research on the Oil Spill in Channel of Anchorage Outside Pearl River Estuary. J. Coast. Res. 2020, 111, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyce, D.G.; Lewis, M.; Worm, B. Integrating Global Chlorophyll Data from 1890 to 2010. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2012, 10, 840–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capuzzo, E.; Stephens, D.; Silva, T.; Barry, J.; Forster, R. Decrease in Water Clarity of the Southern and Central North Sea during the 20th-Century. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2015, 21, 2206–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleming-Lehtinen, V.; Laamanen, M. Long-Term Changes in Secchi Depth and the Role of Phytoplankton in Explaining Light Attenuation in the Baltic Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 102–103, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippart, C.J.M.; Salama, M.S.; Kromkamp, J.C.; van der Woerd, H.J.; Zuur, A.F.; Cadée, G.C. Four Decades of Variability in Turbidity in the Western Wadden Sea as Derived from Corrected Secchi Disk Readings. J. Sea Res. 2013, 82, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, R.E. A Trophic State Index for Lakes 1. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1977, 22, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaika, M. The Water Framework Directive: A New Directive for a Changing Social, Political and Economic European Framework. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2003, 11, 299–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, S.; Lee, Z.; Shi, L.; Lin, G.; Wei, G.; Li, X. Changes in Water Clarity of the Bohai Sea: Observations from MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 186, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoitink, A.J.F.; Hoekstra, P. Observations of Suspended Sediment from ADCP and OBS Measurements in a Mud-Dominated Environment. Coast. Eng. 2005, 52, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Chen, X.; Zhang, F.; Shen, Q.; Peng, D.; Tian, L. MODIS Observations of Water Color of the Largest 10 Lakes in China between 2000 and 2012. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2016, 9, 788–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, J.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, F.; Lu, Z. MODIS-Based Radiometric Color Extraction and Classification of Inland Water With the Forel-Ule Scale: A Case Study of Lake Taihu. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 907–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, B.; Spyrakos, E.; Tyler, A.N.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, F.; Kuster, T.; Lehmann, M.K.; Wu, Y.; et al. Trophic State Assessment of Global Inland Waters Using a MODIS-Derived Forel-Ule Index. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 217, 444–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, B.; Lee, Z.; Spyrakos, E.; Feng, L.; Liu, C.; Zhao, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, L.; et al. Changes of Water Clarity in Large Lakes and Reservoirs across China Observed from Long-Term MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 247, 111949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhu, L.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Ju, J.; Qiao, B.; Ma, Q.; Wang, S. The Increasing Water Clarity of Tibetan Lakes over Last 20 Years According to MODIS Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 253, 112199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Liu, G.; Wang, Q.; Wen, Z.; Lyu, L.; Du, Y.; Sha, L.; Fang, C. Quantification of Lake Clarity in China Using Landsat OLI Imagery Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 243, 111800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nukapothula, S.; Chen, C.; Wu, J. Long-Term Distribution Patterns of Remotely Sensed Water Quality Variables in Pearl River Delta, China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 221, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Ma, C.; Ai, B.; Xu, X.; Huang, W.; Zhao, J. Assessing the Effects of the Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macau Bridge on the Total Suspended Solids in the Pearl River Estuary Based on Landsat Time Series. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2020, 125, e2020JC016202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmanson, L.G.; Brezonik, P.L.; Finlay, J.C.; Bauer, M.E. Comparison of Landsat 8 and Landsat 7 for Regional Measurements of CDOM and Water Clarity in Lakes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmanson, L.G.; Brezonik, P.L.; Bauer, M.E. Geospatial and Temporal Analysis of a 20-Year Record of Landsat-Based Water Clarity in Minnesota’s 10,000 Lakes. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2014, 50, 748–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmanson, L.G.; Bauer, M.E.; Brezonik, P.L. A 20-Year Landsat Water Clarity Census of Minnesota’s 10,000 Lakes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 4086–4097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, B. Water Clarity Changes in Lake Taihu over 36 Years Based on Landsat TM and OLI Observations. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 102, 102457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setiawan, F.; Subehi, L.; Matsushita, B. Long-Term Change of Water Clarity in Lake Limboto Derived from Landsat Data. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 789, 012035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, R.; Wang, S.; Shi, J.; Shen, W.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, F.; Li, J. Sentinel-2 MSI Observations of Water Clarity in Inland Waters across Hainan Island and Implications for SDG 6.3.2 Evaluation. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, F.; Shen, Q.; Li, J. Retrieval and Spatio-Temporal Variations Analysis of Yangtze River Water Clarity from 2017 to 2020 Based on Sentinel-2 Images. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, F.; Shen, Q.; Li, J.; Yang, F. Remote Sensing-Based Analysis of Spatial and Temporal Water Colour Variations in Baiyangdian Lake after the Establishment of the Xiong’an New Area. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Shen, Q.; Wang, Q.; Yang, F.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, F.; Yue, Y. Recognition of Water Colour Anomaly by Using Hue Angle and Sentinel 2 Image. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, X. Sentinel-2 Observation of Water Color Variations in Inland Water across Guangzhou and Shenzhen after the Establishment of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Bay Area. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 9039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, T.; Alcântara, E.; Watanabe, F.; Imai, N. Retrieval of Secchi Disk Depth from a Reservoir Using a Semi-Analytical Scheme. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 198, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ya, X.; Zhao, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, F.; Wang, S.; Yin, Z.; Shen, W. Phytoplankton Biomass Variation after Cage Aquaculture Removal from the Daheiting Reservoir, China: Observations from Satellite Data. Hydrobiologia 2022, 849, 4759–4775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Chen, S.; Ji, H.; Ke, Y.; Fu, Y. Combining Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 to Investigate Seasonal Changes of Suspended Particulate Matter off the Abandoned Distributary Mouths of Yellow River Delta. Mar. Geol. 2021, 441, 106622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.B.; Yang, S.L.; Cai, A.M. Impacts of Dams on the Sediment Flux of the Pearl River, Southern China. Catena 2008, 76, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Cui, L.; Duan, H.; Fei, T.; Liu, Y. An Approach for Developing Landsat-5 TM-Based Retrieval Models of Suspended Particulate Matter Concentration with the Assistance of MODIS. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 85, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Q.; Lou, M.; Chen, C.; Shi, P. Using in Situ and Satellite Hyperspectral Data to Estimate the Surface Suspended Sediments Concentrations in the Pearl River Estuary. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Chen, C.; Tang, S.; Tian, L.; Sun, Z.; Yang, C.; Liu, F. Remote Sensing Assessment of Sediment Variation in the Pearl River Estuary Induced by Typhoon Vicente. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2014, 17, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Cao, W.; Xu, Z.; Ye, H.; Yang, Y.; Wang, G.; Zhou, W.; Sun, Z. Estimation of Suspended Particulate Matter in Turbid Coastal Waters: Application to Hyperspectral Satellite Imagery. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 10476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Yang, C.; Tang, S.; Chen, C. The Phytoplankton Variability in the Pearl River Estuary Based on VIIRS Imagery. Cont. Shelf Res. 2020, 207, 104228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazeer, M.; Nichol, J.E. Improved Water Quality Retrieval by Identifying Optically Unique Water Classes. J. Hydrol. 2016, 541, 1119–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazeer, M.; Nichol, J. Development and Application of a Remote Sensing-Based Chlorophyll-a Concentration Prediction Model for Complex Coastal Waters of Hong Kong. J. Hydrol. 2015, 532, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chunlei, M.; Zhao, J.; Ai, B.; Sun, S.; Yang, Z. Machine Learning Based Long-Term Water Quality in the Turbid Pearl River Estuary, China. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2022, 127, e2021JC018017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Junsheng, L.; Bing, Z.; Qian, S.; Fangfang, Z.; Zhaoyi, L. A Simple Correction Method for the MODIS Surface Reflectance Product over Typical Inland Waters in China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 37, 6076–6096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.; Carder, K.L.; Arnone, R.A. Deriving Inherent Optical Properties from Water Color: A Multiband Quasi-Analytical Algorithm for Optically Deep Waters. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 5755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Z.P.; Shang, S.; Hu, C.; Du, K.; Weidemann, A.; Hou, W.; Lin, J.; Lin, G. Secchi Disk Depth: A New Theory and Mechanistic Model for Underwater Visibility. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 169, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Xiao, F.; Wang, Z.; Feng, Q.; Ban, X.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, Z. An Improved QAA-Based Method for Monitoring Water Clarity of Honghu Lake Using Landsat TM, ETM+ and OLI Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, K.H.; Ramachandra Rao, A. A Modified Mann-Kendall Trend Test for Autocorrelated Data. J. Hydrol. 1998, 204, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric Test against Trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.; Shang, S.; Qi, L.; Yan, J.; Lin, G. A Semi-Analytical Scheme to Estimate Secchi-Disk Depth from Landsat-8 Measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 177, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, L.; Xue, H.; Dong, L.; Su, J.; Heinke, G. A Model Study of the Circulation in the Pearl River Estuary (PRE) and Its Adjacent Coastal Waters: 1. Simulations and Comparison with Observations. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, B.; Liu, Z.; Shen, J.; Wu, H.; Gong, W.; Xu, H.; Wang, D. Potential Physical Impacts of Sea-Level Rise on the Pearl River Estuary, China. J. Mar. Syst. J. Eur. Assoc. Mar. Sci. Tech. 2020, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Gan, J. Controls of Seasonal Variability of Phytoplankton Blooms in the Pearl River Estuary. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2015, 117, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tong, Y.; Feng, L.; Zhao, D.; Zheng, C.; Tang, J. Satellite-Observed Decreases in Water Turbidity in the Pearl River Estuary: Potential Linkage With Sea-Level Rise. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2021, 126, e2020JC016842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syvitski, J.P.M.; Kettner, A.J.; Overeem, I.; Hutton, E.W.H.; Hannon, M.T.; Brakenridge, G.R.; Day, J.; Vörösmarty, C.; Saito, Y.; Giosan, L.; et al. Sinking Deltas Due to Human Activities. Nat. Geosci. 2009, 2, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.B.; Yang, S.; Li, M. The Sharp Decrease in Suspended Sediment Supply from China’s Rivers to the Sea: Anthropogenic and Natural Causes. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2009, 54, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Gong, W.; Cai, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, H. Dispersal of the Pearl River Plume over Continental Shelf in Summer. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017, 194, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.S.; Yang, S.L.; Lei, Y. Quantifying the Anthropogenic and Climatic Impacts on Water Discharge and Sediment Load in the Pearl River (Zhujiang), China (1954–2009). J. Hydrol. 2012, 452–453, 190–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.-L.; Yang, Q.-S.; Wu, C.-Y.; Bao, Y.; Ren, J. Changing Water and Sediment Dynamics in the Pearl River Network and Consequences on Water and Sediment Regimes in the Lingdingyang Estuary. Adv. Water Sci. 2010, 21, 69–76. [Google Scholar]
| Step | Property | Calculation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | rrs(λ) | ||
| 2 | u(λ) | ||
| 3 | Else [25] | ||
| 4 | |||
| 5 | η | ||
| 6 | |||
| 7 | |||
| 8 | |||
| P | Slope | Intercept | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PRE | 0.023 | 0.006 | 0.457 |
| SZB | 0.172 | 0.003 | 0.455 |
| DPB | 0.709 | −0.008 | 2.628 |
| DYB | 0.441 | 0.011 | 1.845 |
| PRE | SZB | DPB | DYB | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wind Speed | 0.24 | 0.01 | −0.02 | −0.39 |
| Precipitation | −0.71 | -0.64 | 0.41 | 0.47 |
| Sea Level | 0.39 | 0.13 | −0.01 | −0.42 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Zhao, L. Coastal Water Clarity in Shenzhen: Assessment of Observations from Sentinel-2. Water 2023, 15, 4102. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15234102
Zhao Y, Chen J, Li X, Li H, Zhao L. Coastal Water Clarity in Shenzhen: Assessment of Observations from Sentinel-2. Water. 2023; 15(23):4102. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15234102
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yelong, Jinsong Chen, Xiaoli Li, Hongzhong Li, and Longlong Zhao. 2023. "Coastal Water Clarity in Shenzhen: Assessment of Observations from Sentinel-2" Water 15, no. 23: 4102. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15234102
APA StyleZhao, Y., Chen, J., Li, X., Li, H., & Zhao, L. (2023). Coastal Water Clarity in Shenzhen: Assessment of Observations from Sentinel-2. Water, 15(23), 4102. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15234102











