Migration Movements of Accidentally Spilled Oil in Environmental Waters: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Kinematics and Dynamics Characterizing of the Free-Rising Motion of Oil Droplets
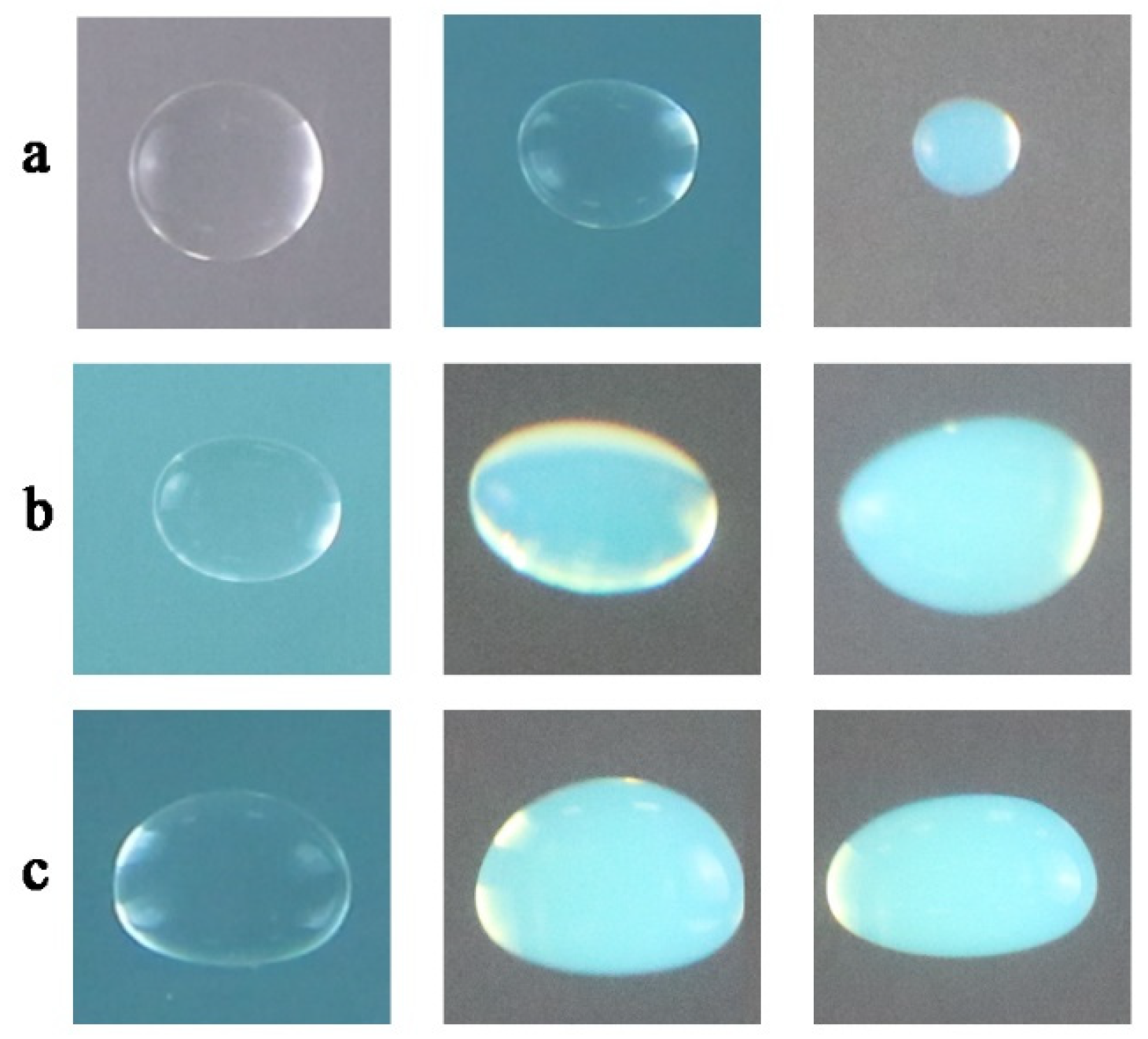
2.1. The Shape and Trajectory of Oil Droplets
2.2. The Terminal Velocity of Oil Droplets
2.3. The Determination of Drag Coefficient CD in Oil Droplets Motion
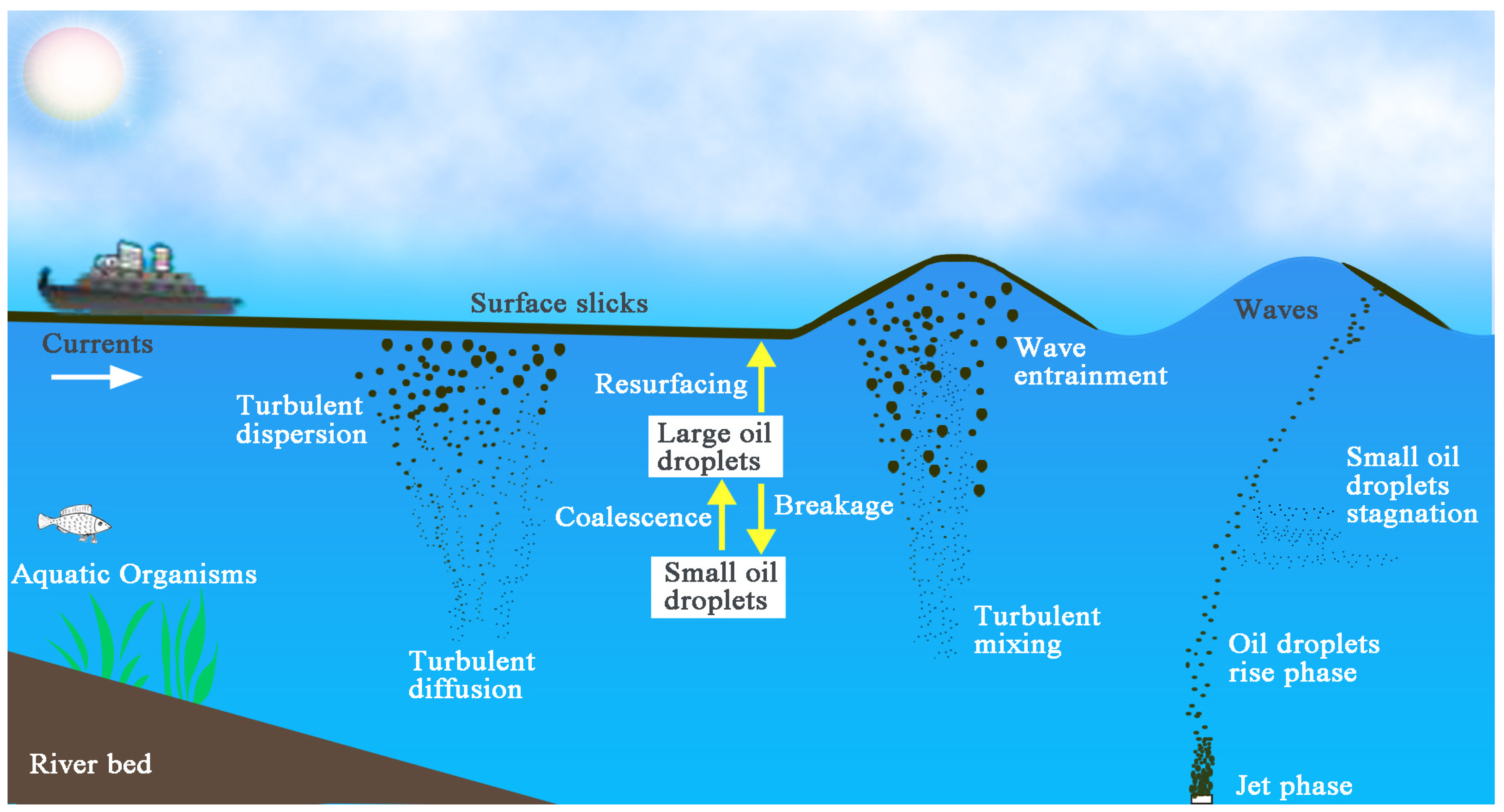
3. Migration and Transformation Characteristics of Oil in Inland Riverine Environment
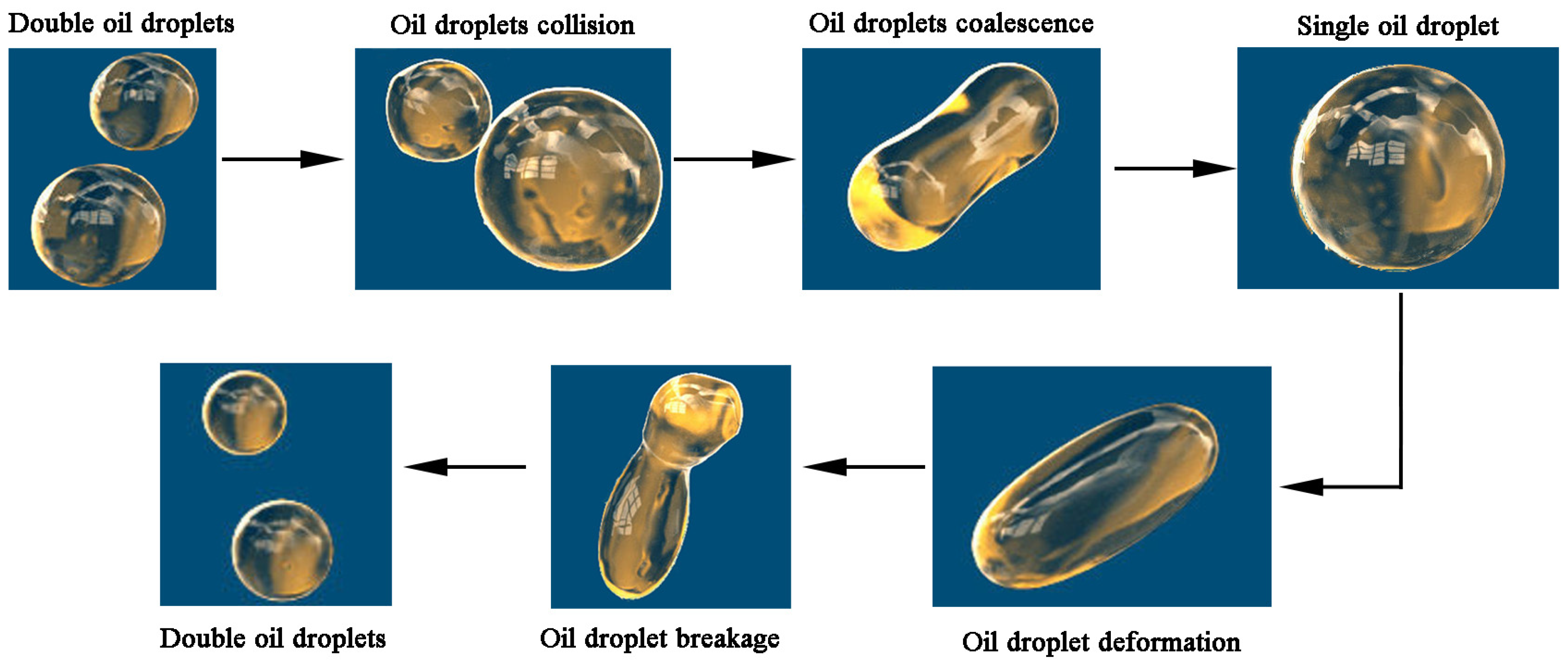
3.1. Behavior of Oil Droplets Collision, Coalescence or Breakage
3.2. Vertical Diffusion Characteristics of Oil
4. Migration and Transformation Characteristics of Oil in Oceanic Environment
4.1. Oil Droplet Size Distribution
4.2. Vertical Mixing Characteristics of Oil
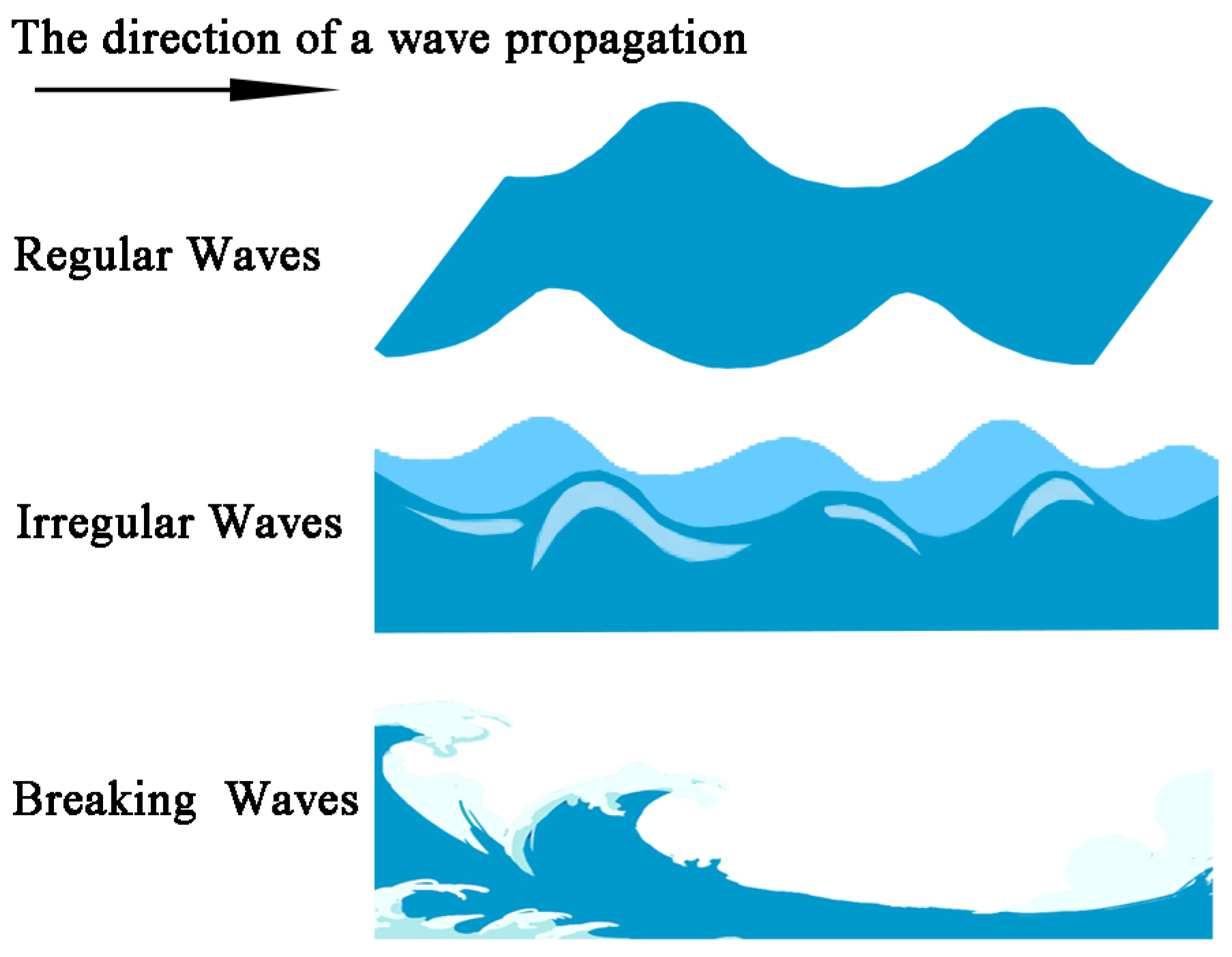
4.3. Diffusion Characteristics of Oil under the Combined Action of Waves and Current
5. Conclusions and Perspectives
- The related research on the free rising motion of a single oil droplet began earlier, and the research results are also more numerous. Early researchers, due to research conditions and other reasons for the limitations, have obtained results that are generally lower in precision. With the continuous refinement of related theories and equipment, more researchers choose to start from the subtle factors affecting the movement of oil droplets (e.g., the concentration and type of surface-active pollutants, different droplet shapes produced by different nozzle types, etc.), in order to obtain more accurate theoretical results and quantitative relationships. However, theoretical or experimental studies ultimately serve for engineering applications. Future research should focus more on the optimization of relevant parameters in engineering applications, mainly considering the following two points. (1) In capturing the range of relevant physical properties according to the possible types of oil spills, through theoretical analysis and experimental research, a more comprehensive set of models applicable to oil droplets can be integrated by adopting the method of re-proposing or amending the original correlation equation. (2) Surface-active pollutants are bound to exist in environmental waters but are difficult to quantify, and optimization results of relevant parameters within a certain error range or fluctuable range can be obtained based on the average situation under different water conditions.
- At present, the research on the migration and transformation characteristics of oil spills in the ocean environment is mainly divided into two categories: experimental research and numerical simulation. Although experimental research can precisely control the influence factors, the final results are more idealized. Numerical simulation reveals the actual situation more realistically, but its accuracy depends on the hydrodynamic conditions of the provided waters and the accuracy of the relevant parameters. Therefore, on the one hand, future experimental studies should be based on the existing research, through the gradual coupling of more hydrodynamic conditions (e.g., the combination of wave, current, etc.) in order to obtain results closer to the actual water environment. On the other hand, numerical simulation should be combined with experimental research, and the results of the two can be the prerequisite for and verify each other.
- The amount of accidental oil spills occurring in inland rivers is relatively small but more frequent, many studies on the migration and transformation process of oil spills in inland rivers are currently in a state of blankness, and a large number of relevant studies are urgently needed in the future. Initially, the research can be carried out with reference to the relevant research in the ocean environment. Firstly, the particle size distribution characteristics of oil droplets under different flow conditions are the basis for further research. Secondly, the vertical water depth of the river is much lower than that of the ocean, which makes it more important to determine the vertical dispersion characteristics of the oil spill compared to the marine environment. Finally, the interaction between oil spills and sediment, although not considered in this review, is also a focus for future research.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Latin letters | |
| a | Radius, m |
| amax | Radius of cross-sectional, m |
| d | Equivalent diameter of droplets, m |
| U | Instantaneous velocity of droplets, m/s |
| UT | Terminal velocity of droplets, m/s |
| UHS | Terminal velocity of a hard sphere, m/s |
| CD | Drag coefficient |
| CDs | Standard drag coefficient |
| Greek letters | |
| κ | |
| μ | Dynamic viscosity, N·s/m2 |
| ρ | Density, kg/m3 |
| γ | |
| ∆ρ | , kg/m3 |
| σ | Oil–water interfacial tension, N/m |
| dimensionless numbers | |
| Re | |
| Eo | |
| Mo | |
| Oh | |
| We | |
| Subscripts | |
| c | Continuous phase |
| d | Dispersed phase, droplet |
References
- Suleman, S.; Ennin, G.K.; Iledare, O.O. An empirical review of petroleum revenue management and distribution after a decade of oil production and export in Ghana. Extr. Ind. Soc. 2023, 13, 101228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobling, A.; Jamasb, T. Price Volatility and Demand for Oil: A Comparative Analysis of Developed and Developing Countries; Cambridge Working Paper in Economics 1512; Energy Policy Research Group: Cambridge, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- OEUK. Economic Report 2022; OEUK: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Long, S.M.; Holdway, D.A. Acute toxicity of crude and dispersed oil to Octopus pallidus (Hoyle, 1885) hatchlings. Water Res. 2002, 36, 2769–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nissanka, I.D.; Yapa, P.D. Calculation of oil droplet size distribution in ocean oil spills: A review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 135, 723–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Z.; An, C.; Yue, R.; Bi, H.; Zhao, S. Assessment of the infiltration of water-in-oil emulsion into soil after spill incidents. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 896, 165325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Callies, U. A probabilistic model of decision making regarding the use of chemical dispersants to combat oil spills in the German Bight. Water Res. 2020, 169, 115196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruckberger, M.C.; Morgan, M.J.; Bastow, T.P.; Walsh, T.; Prommer, H.; Mukhopadhyay, A.; Kaksonen, A.H.; Davis, G.B.; Puzon, G.J. Investigation into the microbial communities and associated crude oil-contamination along a Gulf War impacted groundwater system in Kuwait. Water Res. 2020, 170, 115314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClenachan, G.; Turner, R.E. Disturbance legacies and shifting trajectories: Marsh soil strength and shoreline erosion a decade after the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 322, 121151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohal, M.; Barrera, N.; Escobar-Briones, E.; Brooks, G.; Hollander, D.; Larson, R.; Montagna, P.A.; Pryor, M.; Romero, I.C.; Schwing, P. How quickly will the offshore ecosystem recover from the 2010 Deepwater Horizon oil spill? Lessons learned from the 1979 Ixtoc-1 oil well blowout. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarlett, A.G.; Nelson, R.K.; Gagnon, M.M.; Holman, A.I.; Reddy, C.M.; Sutton, P.A.; Grice, K. MV Wakashio grounding incident in Mauritius 2020: The world’s first major spillage of Very Low Sulfur Fuel Oil. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 171, 112917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeinstra-Helfrich, M.; Koops, W.; Murk, A.J. How oil properties and layer thickness determine the entrainment of spilled surface oil. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 110, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Ma, J.; Lai, Q.; Shui, J.; Li, W. Environmental Impact Assessment of a Wharf Oil Spill Emergency on a River Water Source. Water 2023, 15, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naggea, J.; Miller, R. A comparative case study of multistakeholder responses following oil spills in Pointe d’Esny, Mauritius, and Huntington Beach, California. Ecol. Soc. 2023, 28, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soussi, A.; Bersani, C.; Sacile, R.; Bouchta, D.; Amarti, A.E.; Seghiouer, H.; Nachite, D.; Miys, J.A. An oil spill trajectory model: Validation in the Mediterranean Sea. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Symposium on Systems Engineering (ISSE), Edinburgh, UK, 1–3 October 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Olascoaga, M.J.; Beron-Vera, F.J. Exploring the use of Transition Path Theory in building an oil spill prediction scheme. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 9, 1041005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Yapa, P.D. Buoyant Velocity of Spherical and Nonspherical Bubbles/Droplets. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2000, 126, 852–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delvigne, G.A.L.; Sweeney, C.E. Natural dispersion of oil. Oil Chem. Pollut. 1988, 4, 281–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keramea, P.; Spanoudaki, K.; Zodiatis, G.; Gikas, G.; Sylaios, G. Oil Spill Modeling: A Critical Review on Current Trends, Perspectives, and Challenges. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, O.; Reed, M.; Bodsberg, N.R. Natural dispersion revisited. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 93, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagheeby, M.; Kolahdoozan, M. Numerical modeling of two-phase fluid flow and oil slick transport in estuarine water. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 7, 771–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Meng, L.; Shen, T.; Zhang, J.; Bao, M.; Sun, P. The formation process and responsive impacts of single oil droplet in submerged process. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 124, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelbaliyev, G.I. Drag coefficients of variously shaped solid particles, drops, and bubbles. Theor. Found. Chem. Eng. 2011, 45, 248–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clift, R.; Grace, J.R.; Weber, M.E. Bubbles, Drops, and Particles; Dover Publication: New York, NY, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Kvočka, D.; Žagar, D.; Banovec, P. A Review of River Oil Spill Modeling. Water 2021, 13, 1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Zhao, X.; Cai, Z.; O’Reilly, S.E.; Hao, X.; Zhao, D. A review of oil, dispersed oil and sediment interactions in the aquatic environment: Influence on the fate, transport and remediation of oil spills. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 79, 16–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Lucas, D. A literature review on mechanisms and models for the coalescence process of fluid particles. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2010, 65, 2851–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.J.; Wang, D.F.; Cai, Z.Q.; Li, Z.P.; Huang, X.B.; Gao, Z.M.; Derksen, J.J.; Komrakova, A.E. Deformation and breakup of single drop in laminar and transitional jet flows. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 386, 121812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.M.; Rao, L.; Bao, Y.Y.; Cai, Z.Q. Hydrodynamics and Deformation of Single Drop Rising in Newtonian Fluids. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 2015, 48, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myint, W.; Hosokawa, S.; Tomiyama, A. Terminal Velocity of Single Drops in Stagnant Liquids. J. Fluid Sci. Technol. 2006, 1, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegener, M.; Kraume, M.; Paschedag, A.R. Terminal and transient drop rise velocity of single toluene droplets in water. AIChE J. 2010, 56, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.K.; Biswas, M.N. Separation of oil-water mixture in tank. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2010, 190, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.; Reddy, R.K.; Valsaraj, K.T.; Nandakumar, K.; Pandey, S.; Wu, C. Influence of unsteady mass transfer on dynamics of rising and sinking droplet in water: Experimental and CFD study. AIChE J. 2015, 61, 342–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haberman, W.L.; Morton, R.K. An Experimental Investigation of the Drag and Shape of Air Bubbles Rising in Various Liquids; DEFENSE TECHNICAL INFORMATION CENTER: Virginia, VA, USA, 1953. [Google Scholar]
- Wairegi, T.; Grace, J.R. The behaviour of large drops in immiscible liquids. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 1976, 3, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myint, W.; Hosokawa, S.; Tomiyama, A. Shapes of Single Drops Rising Through Stagnant Liquids. J. Fluid Sci. Technol. 2007, 2, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegener, M.; Paul, N.; Kraume, M. Fluid dynamics and mass transfer at single droplets in liquid/liquid systems. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2014, 71, 475–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorsen, G.; Stordalen, R.M.; Terjesen, S.G. On the terminal velocity of circulating and oscillating liquid drops. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1968, 23, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmathy, T.Z. Velocity of large drops and bubbles in media of infinite or restricted extent. AIChE J. 1960, 6, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licht, W.; Narasimhamurty, G.S.R. Rate of fall of single liquid droplets. AIChE J. 1955, 1, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.; Luo, K.; Fan, J. Detailed numerical simulation of unsteady drag coefficient of deformable droplet. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 308, 619–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.Q. A deformable liquid drop falling through a quiescent gas at terminal velocity. J. Fluid Mech. 2010, 658, 438–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, T.D.; Acrivos, A. On the deformation and drag of a falling viscous drop at low Reynolds number. J. Fluid Mech. 1964, 18, 466–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.-w.; Zhou, H.-j.; Shao, D.-d.; Niu, X.-j. Experimental study of non-uniform bubbles in a plume. J. Hydrodyn. 2022, 34, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASCE Task Committee on Modeling of Oil Spills. State-of-the-art review of modeling transport and fate of oil spills. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1996, 122, 594–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalman, H.; Matana, E. Terminal velocity and drag coefficient for spherical particles. Powder Technol. 2022, 396, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; You, J.; Zhao, H. An experimental investigation of underwater spread of oil spill in a shear flow. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 116, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Jia, Y.; Wang, L.; Cao, Y. Drag coefficient fluctuation prediction of a single bubble rising in water. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 316, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klee, A.J.; Treybal, R.E. Rate of rise or fall of liquid drops. AIChE J. 1956, 2, 444–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, J.T.; Rideal, E.K. Interfacial Phenomena; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1961; Volume 39. [Google Scholar]
- Aravamudan, K.; Raj, P.; Ostlund, J.; Newman, E.; Tucker, W. Break-up of Oil on Rough Seas-Simplified Models and Step-by-Step Calculations; Little (Arthur D) Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Röhrs, J.; Dagestad, K.-F.; Asbjørnsen, H.; Nordam, T.; Skancke, J.; Jones, C.E.; Brekke, C. The effect of vertical mixing on the horizontal drift of oil spills. Ocean Sci. 2018, 14, 1581–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, J.R.; Wairegi, T.; Nguyen, T.H. Shapes and Velocities of Single Drops and Bubbles Moving Freely Through Immiscible Liquids. Chem.Eng.Res.Des 1976, 54, 167–173. [Google Scholar]
- Kelbaliyev, G.; Ceylan, K. Development of New Empirical Equations for Estimation of Drag Coefficient, Shape Deformation, and Rising Velocity of Gas Bubbles or Liquid Drops. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2007, 194, 1623–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ervik, Å.; Bjørklund, E. The transition in settling velocity of surfactant-covered droplets from the Stokes to the Hadamard–Rybczynski solution. Eur. J. Mech. B-Fluid. 2017, 66, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savic, P. Circulation and Distortion of Liquid Drops Falling through a Viscous Medium, Tech.Rep.MT-22; National Research Council of Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1953. [Google Scholar]
- Bond, W.N. LXXXII.Bubbles and drops and Stokes’ law. Lond. Edinb. Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 1927, 4, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, W.N.; Newton, D.A. LXXXII.Bubbles, drops, and Stokes’ law. (Paper 2). Lond. Edinb. Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 1928, 5, 794–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oellrich, L.; Schmidt-Traub, H.; Brauer, H. Theoretische Berechnung des Stofftransports in der Umgebung einer Einzelblase. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1973, 28, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserman, M.L.; Slattery, J.C. Creeping flow past a fluid globule when a trace of surfactant is present. AIChE J. 1969, 15, 533–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levich, V.G. Physieochemical Hydrodynamics; Prentice-Hall, Inc.: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Helenbrook, B.T.; Edwards, C.F. Quasi-steady deformation and drag of uncontaminated liquid drops. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2002, 28, 1631–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, J.B.; Nandakumar, K.; Patwardhan, A.W.; Nayak, A.K.; Pareek, V.; Gumulya, M.; Wu, C.; Minocha, N.; Pal, E.; Kumar, M.; et al. Computational fluid dynamics. In Advances of Computational Fluid Dynamics in Nuclear Reactor Design and Safety Assessment; Woodhead Publishing: Shaston, UK, 2018; pp. 21–238. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Spaulding, M.L.; French-McCay, D. An algorithm for modeling entrainment and naturally and chemically dispersed oil droplet size distribution under surface breaking wave conditions. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 119, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeinstra-Helfrich, M.; Koops, W.; Murk, A.J. Predicting the consequence of natural and chemical dispersion for oil slick size over time. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2017, 122, 7312–7324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Kinter, R.C. The fall of single liquid drops through water. AIChE J. 1955, 1, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, A.J. Shear diffusion and the spread of oil in the surface layers of the North Sea. Dtsch. Hydrogr. Z. 1986, 39, 113–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.J.; Wang, Y.X. A numerical oil spill model based on a hybrid method. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, J.; Wang, H. The impact of different vertical diffusion schemes in a three-dimensional oil spill model in the Bohai Sea. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2013, 30, 1569–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, J.R.; Wairegi, T.; Brophy, J. Break-up of drops and bubbles in stagnant media. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 1978, 56, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissanka, I.D.; Yapa, P.D. Oil slicks on water surface: Breakup, coalescence, and droplet formation under breaking waves. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 114, 480–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, N.; Kraume, M.; Schön, S.; von Klitzing, R. Transport processes at single droplets in micellar liquid/liquid systems. AIChE J. 2015, 61, 1092–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turton, R.; Levenspiel, O. A short note on the drag correlation for spheres. Powder Technol. 1986, 47, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceylan, K.; Altunbaş, A.; Kelbaliyev, G. A new model for estimation of drag force in the flow of Newtonian fluids around rigid or deformable particles. Powder Technol. 2001, 119, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, F.; Boufadel, M.C.; Geng, X.; Gao, F.; Zhao, L.; King, T.; Lee, K. Oil Droplets Transport Under a Deep-Water Plunging Breaker: Impact of Droplet Inertia. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2018, 123, 9082–9100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivkind, V.Y.; Ryskin, G.M. Flow structure in motion of a spherical drop in a fluid medium at intermediate Reynolds numbers. Fluid Dyn. 1976, 11, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamielec, A.E.; Storey, S.H.; Whitehead, J.M. Viscous flow around fluid spheres at intermediate reynolds numbers (II). Can. J. Chem. Eng. 1963, 41, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaba, H.; Sato, K. Fundamental Study of Latent Cold Heat Energy Storage by Means of Oil Droplets at Low Freezing Point. Numerical Calculation of Motion and Solidification Characteristics of Oil Droplets Ascending in a Cold Water Solution due to Buoyancy. JSME Int. J. Ser. B 1998, 41, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Feng, Z.-G.; Michaelides, E.E. Drag Coefficients of Viscous Spheres at Intermediate and High Reynolds Numbers. J. Fluids Eng. 2001, 123, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saboni, A.; Alexandrova, S. Numerical study of the drag on a fluid sphere. AIChE J. 2002, 48, 2992–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodi, W.; Fueyo, N. Engineering Turbulence Modelling and Experiments 5, Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium on Engineering Turbulence Modelling and Measurements; Mallorca, Spain, 16–18 September 2002; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, P.; Tong, S.; Wang, Y.; Xu, G. Modelling the oil spill transport in inland waterways based on experimental study. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 284, 117473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.-j.; Yang, Y.-p.; Jia, M.-l.; Zhu, Y.-d.; Wang, J.-j. Relationship between adjustment of low water level and utilization of water depth in Shashi Reach in middle Yangtze River. Water Sci. Eng. 2022, 15, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Liu, S.; Sun, S.; Xia, X. Unexpected low CO2 emission from highly disturbed urban inland waters. Environ. Res. 2023, 235, 116689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Cerqueira, R.F.L.; Perissinotto, R.M.; Verde, W.M.; Biazussi, J.L.; de Castro, M.S.; Bannwart, A.C. Development and assessment of a particle tracking velocimetry (PTV) measurement technique for the experimental investigation of oil drops behaviour in dispersed oil–water two-phase flow within a centrifugal pump impeller. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2023, 159, 104302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.-x.; Cheng, X.-s.; Zhou, Z.-c.; Gao, Q.; Shao, X.-m. An experimental study on the velocity fluctuations generated by the flow past fixed spheres. J. Hydrodyn. 2022, 34, 214–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Kim, S.; Ishii, M.; Beus, S.G. One-group interfacial area transport in vertical bubbly flow. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1998, 41, 1103–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, M.J.; Blanch, H.W. Bubble coalescence and break-up in air-sparged bubble columns. AIChE J. 1990, 36, 1485–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.; Han, L.; Luo, H.a. A novel multiscale theoretical model for droplet coalescence induced by turbulence in the framework of entire energy spectrum. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2018, 176, 377–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.; Han, L.; Luo, H.a. A novel multiscale theoretical model for droplet coalescence in turbulent dispersions. Int. J. Comput. Methods Exp. Meas. 2017, 6, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedlander, S.K.; Marlow, W.H. Smoke, Dust and Haze: Fundamentals of Aerosol Behavior. Phys. Today 1977, 30, 58–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesters, A.K. The modelling of coalescence processes in fluid-liquid dispersions: A review of current understanding. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 1991, 69, 259–270. [Google Scholar]
- Orvalho, S.; Stanovsky, P.; Ruzicka, M.C. Bubble coalescence in electrolytes: Effect of bubble approach velocity. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 406, 125926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanada, T.; Sato, A.; Shirota, M.; Watanabe, M. Motion and coalescence of a pair of bubbles rising side by side. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2009, 64, 2659–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavehpour, H.P. Coalescence of Drops. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2015, 47, 245–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, F.; Taweel, A.M.A. Turbulently flowing liquid–liquid dispersions. Part I: Drop breakage and coalescence. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 166, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Fu, T.; Zhu, C.; Ma, Y.; Li, H.Z. Breakup dynamics for high-viscosity droplet formation in a flow-focusing device: Symmetrical and asymmetrical ruptures. AIChE J. 2016, 62, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Gao, Z.; Buffo, A.; Podgorska, W.; Marchisio, D.L. Droplet breakage and coalescence in liquid–liquid dispersions: Comparison of different kernels with EQMOM and QMOM. AIChE J. 2016, 63, 2293–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rijn, L.C. Unified View of Sediment Transport by Currents and Waves. II: Suspended Transport. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2007, 133, 668–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.-f.; Xu, H.; Chen, Z.; Wu, D.-w.; Zhang, S.-z. Experimental study on suspended sediment concentration and its vertical distribution under spilling breaking wave actions in silty coast. China Ocean Eng. 2011, 25, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imanian, H.; Kolahdoozan, M.; Zarrati, A.R. Vertical Dispersion Process of Oil Spills. In Proceedings of the 2011 2nd International Conference on Innovative Computing and Communication and 2011 Asia-Pacific Conference on Information Technology and Ocean Engineering (CICC-ITOE 2011), Macau, China, 5–6 March 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Coleman, N.L. Flume Studies of the Sediment Transfer Coefficient. Water Resour. Res. 1970, 6, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, W.H.; Cellino, M. Suspension flows in open channels; experimental study. J. Hydraul. Res. 2002, 40, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobson, H.E. Vertical Mass Transfer in Open Channel Flow; U.S. Geological Survey: Liston, VA, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, A.G. Distribution of suspended sediment in a natural stream. Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1942, 23, 678–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikora, V.I.; Goring, D.G. Fluctuations of Suspended Sediment Concentration and Turbulent Sediment Fluxes in an Open-Channel Flow. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2002, 128, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billingham, J.; King, A.C. Wave Motion; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Zhan, C.S.; Lee, K. Formation and Vertical Mixing of Oil Droplets Resulting from Oil Slick Under Breaking Waves—A Modeling Study. Environ. Forensics 2009, 10, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsa, R.; Kolahdoozan, M.; Moghaddam, M.R.A. Vertical oil dispersion profile under non-breaking regular waves. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2016, 16, 833–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, F.; Geng, X.; Robinson, B.; King, T.; Lee, K.; Boufadel, M.C. Oil Droplet Dispersion under a Deep-Water Plunging Breaker: Experimental Measurement and Numerical Modeling. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, P.P.K.; Griffiths, R.A. The Survival of Oil Slicks on the Ocean as a Function of Sea State Limit1. Int. Oil Spill Conf. Proc. 1979, 1979, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Boufadel, M.C.; Lee, K.; King, T.; Loney, N.; Geng, X. Evolution of bubble size distribution from gas blowout in shallow water. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2016, 121, 1573–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Ya, Z.; Wang, Z.; Sun, B.; Fu, H.; Bénédicte, M.-C.J. Study on the Effects of Waves and Dispersant on the Submergence of Spilled Oil. Water Resour. 2020, 47, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhan, C.S.; Lee, K.; Li, Z.K.; Boufadel, M. Modeling Oil Droplet Formation and Evolution under Breaking Waves. Energy Sources Part A: Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2009, 31, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, P.P.K. Theoretical Study to Determine the Sea State Limit for the Survival of Oil Slicks on the Ocean; Final Report; DEFENSE TECHNICAL INFORMATION CENTER: Virginia, VA, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Aravamudan, K.S.; Raj, P.K.; Marsh, G. Simplified Models To Predict the Breakup of Oil on Rough Seas. Int. Oil Spill Conf. Proc. 1981, 1981, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinze, J.O. Fundamentals of the hydrodynamic mechanism of splitting in dispersion processes. AIChE J. 1955, 1, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Torlapati, J.; Boufadel, M.C.; King, T.; Robinson, B.; Lee, K. VDROP: A comprehensive model for droplet formation of oils and gases in liquids-Incorporation of the interfacial tension and droplet viscosity. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 253, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissanka, I.D.; Yapa, P.D. Calculation of oil droplet size distribution in an underwater oil well blowout. J. Hydraul. Res. 2016, 54, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delvigne, G.A.L. Natural Dispersion of Oil by Different Sources of Turbulence. Int. Oil Spill Conf. Proc. 1993, 1993, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, M.; Johansen, Ø.; Leirvik, F.; Brørs, B.; Moldestad, M.Ø. Numerical Algorithm to Compute the Effects of Breaking Waves on Surface Oil Spilled at Sea; SINTEF Institute for Materials and Chemistry: Trondheim, Norway, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lefebvre, A.H.; McDonell, V.G. Atomization and Sprays; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Lee, K.; Kepkey, P.E.; Mikkelsen, O.; Pottsmith, C. Monitoring Dispersed Oil Droplet Size Distribution at the Gulf of Mexico Deepwater Horizon Spill Site. Int. Oil Spill Conf. Proc. 2011, 2011, abs377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lee, K.; King, T.; Boufadel, M.C.; Venosa, A.D. Effects of temperature and wave conditions on chemical dispersion efficacy of heavy fuel oil in an experimental flow-through wave tank. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 1550–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lee, K.; King, T.; Boufadel, M.C.; Venosa, A.D. Evaluating Chemical Dispersant Efficacy in an Experimental Wave Tank: 2—Significant Factors Determining In Situ Oil Droplet Size Distribution. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2009, 26, 1407–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lee, K.; King, T.; Kepkay, P.; Boufadel, M.C.; Venosa, A.D. Evaluating Chemical Dispersant Efficacy in an Experimental Wave Tank: 1, Dispersant Effectiveness as a Function of Energy Dissipation Rate. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2009, 26, 1139–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Spaulding, M.; French McCay, D.; Crowley, D.; Payne, J.R. Development of a unified oil droplet size distribution model with application to surface breaking waves and subsea blowout releases considering dispersant effects. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 114, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Miller, J.; Wang, J.; Koley, S.S.; Katz, J. Size Distribution and Dispersion of Droplets Generated by Impingement of Breaking Waves on Oil Slicks. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2017, 122, 7938–7957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, Ø. Development and verification of deep-water blowout models. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2003, 47, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Masutani, S.M. Laminar to Turbulent Flow Liquid-liquid Jet Instability And Breakup. In Proceedings of the International Offshore and Polar Engineering Conference (ISOPE-2003), Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–30 May 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Johansen, Ø.; Rye, H.; Cooper, C. DeepSpill––Field Study of a Simulated Oil and Gas Blowout in Deep Water. Spill Sci. Technol. Bull. 2003, 8, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Shaffer, F.; Robinson, B.; King, T.; D’Ambrose, C.; Pan, Z.; Gao, F.; Miller, R.S.; Conmy, R.N.; Boufadel, M.C. Underwater oil jet: Hydrodynamics and droplet size distribution. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 299, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandvik, P.J.; Johansen, O.; Leirvik, F.; Farooq, U.; Daling, P.S. Droplet breakup in subsurface oil releases--part 1: Experimental study of droplet breakup and effectiveness of dispersant injection. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 73, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansen, Ø.; Brandvik, P.J.; Farooq, U. Droplet breakup in subsea oil releases--part 2: Predictions of droplet size distributions with and without injection of chemical dispersants. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 73, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandara, U.C.; Yapa, P.D. Bubble Sizes, Breakup, and Coalescence in Deepwater Gas/Oil Plumes. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2011, 137, 729–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Boufadel, M.C.; Socolofsky, S.A.; Adams, E.; King, T.; Lee, K. Evolution of droplets in subsea oil and gas blowouts: Development and validation of the numerical model VDROP-J. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 83, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.; Boufadel, M.C.; Ozgokmen, T.; King, T.; Lee, K.; Lu, Y.; Zhao, L. Oil droplets transport due to irregular waves: Development of large-scale spreading coefficients. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 104, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkalich, P.; Chan, E.S. Vertical mixing of oil droplets by breaking waves. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2002, 44, 1219–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lee, K.; King, T.; Boufadel, M.C.; Venosa, A.D. Evaluating crude oil chemical dispersion efficacy in a flow-through wave tank under regular non-breaking wave and breaking wave conditions. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Lee, K.; King, T.; Boufadel, M.C.; Venosa, A.D. Assessment of chemical dispersant effectiveness in a wave tank under regular non-breaking and breaking wave conditions. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2008, 56, 903–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsa, R.; Kolahdoozan, M.; Alavi Moghaddam, M.R. Mid-depth oil concentration due to vertical oil dispersion in a regular wave field. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2015, 16, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, K. The mixing processes in a tidal estuary. Int. J. Air Water Pollut. 1963, 7, 343–356. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, W.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xu, T.; Ren, X.; Cao, F.; Wang, S. Development and application of an oil spill model with wave-current interactions in coastal areas. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 84, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youssef, M.M. The Behavior of the Near Ocean Surface under the Combined Action of Waves and Currents in Shallow Water; University of Rhode Island: Kingston, RI, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Lonin, S.A. Lagrangian Model for Oil Spill Diffusion at Sea. Spill Sci. Technol. Bull. 1999, 5, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; You, J.; Zhao, H. Underwater spreading and surface drifting of oil spilled from a submarine pipeline under the combined action of wave and current. Appl. Ocean Res. 2017, 64, 217–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rijn, L.C.; Havinga, F.J. Transport of Fine Sands by Currents and Waves. II. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean Eng. 1995, 121, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenstra, K.J.H.; Pluis, S.R.P.M.; Ridderinkhof, W.; Ruessink, G.; van der Vegt, M. Cyclic channel-shoal dynamics at the Ameland inlet: The impact on waves, tides, and sediment transport. Ocean Dyn. 2019, 69, 409–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.E.; Brown, R.S.; Hodson, P.V. The bioavailability of oil droplets trapped in river gravel by hyporheic flows. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 269, 116110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Time, Proposer | Expression | Applicable Situation | Eq. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1850, Stokes | (1) | |||
| 1911, Hadamard and Rybczynski | (2) | |||
| * 1913, Boussinesq [24] | (3) | |||
| 1956, Klee and Treybal [49] | Critical diameter d: | (4a) | ||
| (4b) | ||||
| * 1961, Devies and Rideal [24,50] | where: | Presence of surface contaminants; | (5) | |
| 1968, Thorsen et al. [38] | (6) | |||
| 1982, Aravamudan et al. [51]; 2018, Röhrs et al. [52] | Critical diameter : | (7a) | ||
| (7b) | ||||
| * 1978, Grace et al. [53]; 1978, Clift et al. [24]; 2000, Zheng and Yapa [17] | (In this formula, Re has a separate correlation, see 1978, Clift et al.) | Spherical (small size range) | (8a) | |
where | Ellipsoidal (intermediate size range) | Critical diameter d (For the values of and , see Zheng and Yapa in 2000) | (8b) | |
| Spherical-cap (large size range), | (8c) | |||
| 2007, Kelbaliyev and Ceylan [54] | where | (9) | ||
| 1976, Grace et al. [53]; 1978, Clift et al. [24]; 2010, Wegener and Kraume [31] | where | used the formula proposed by Clift et al. in 1978 | (10) | |
| * 2017, Ervik and Bjørklund [55] | Denotes the drop radius normalized by the critical radius as | (11a) | ||
| (11b) | ||||
| Time, Proposer | Expression | Scope of Application/Conditions | Eq. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1850, Stokes | (12) | ||||
| 1911, Hadamard and Rybczynski; 1962, Levich [61] | (13) | ||||
| 1935, Schiller and Naumann; 2018, Cui et al. [75] | (14a) | ||||
| (14b) | |||||
| 1964, Taylor and Acrivos [43] | (15) | ||||
| 1976, Rivkind and Ryskin [76] | (16) | ||||
| 1978, Clift et al. [24]; 1963, Hamielec et al. [77] | (17a) | ||||
( and are functions of ; see 1978, Clift et al. for details) | (17b) | ||||
| (17c) | |||||
| (17d) | |||||
| 1998, Inaba and Sato [78] | (18a) | ||||
| (18b) | |||||
| 2001, Ceylan et al. [74] | of which: | (19) | |||
| 2001, Feng and Michaelides [79] | (20) | ||||
| 2002, Saboni and Alexandrova [80] | (21) | ||||
| 2002, Rodi and Fueyo [81]; 2011, Kelbaliyev [23] | (22a) | ||||
| (22b) | |||||
| (22c) | |||||
| (22d) | |||||
| 2006, Myint et al. [30] | −0.9, , , | clean systems | (23a) | ||
| fully contaminated systems | (23b) | ||||
| 2007, Kelbaliyev and Ceylan [54] | (24a) | ||||
| (24b) | |||||
| 2010, Feng [42] | (25) | ||||
| 2017, Shao et al. [41] | the unsteady parameter A: | where: | (26a) | ||
where: | (26b) | ||||
| 2019, Joshi et al. [63] | (27a) | ||||
| (27b) | |||||
| (27c) | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, A.; Han, L.; Wang, C.; Zhao, J. Migration Movements of Accidentally Spilled Oil in Environmental Waters: A Review. Water 2023, 15, 4092. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15234092
Jiang A, Han L, Wang C, Zhao J. Migration Movements of Accidentally Spilled Oil in Environmental Waters: A Review. Water. 2023; 15(23):4092. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15234092
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Anqi, Longxi Han, Chenfang Wang, and Jinjing Zhao. 2023. "Migration Movements of Accidentally Spilled Oil in Environmental Waters: A Review" Water 15, no. 23: 4092. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15234092
APA StyleJiang, A., Han, L., Wang, C., & Zhao, J. (2023). Migration Movements of Accidentally Spilled Oil in Environmental Waters: A Review. Water, 15(23), 4092. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15234092






