The Species Diversity of the Genus Echinogorgia in Xiamen Bay and Its New Record in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
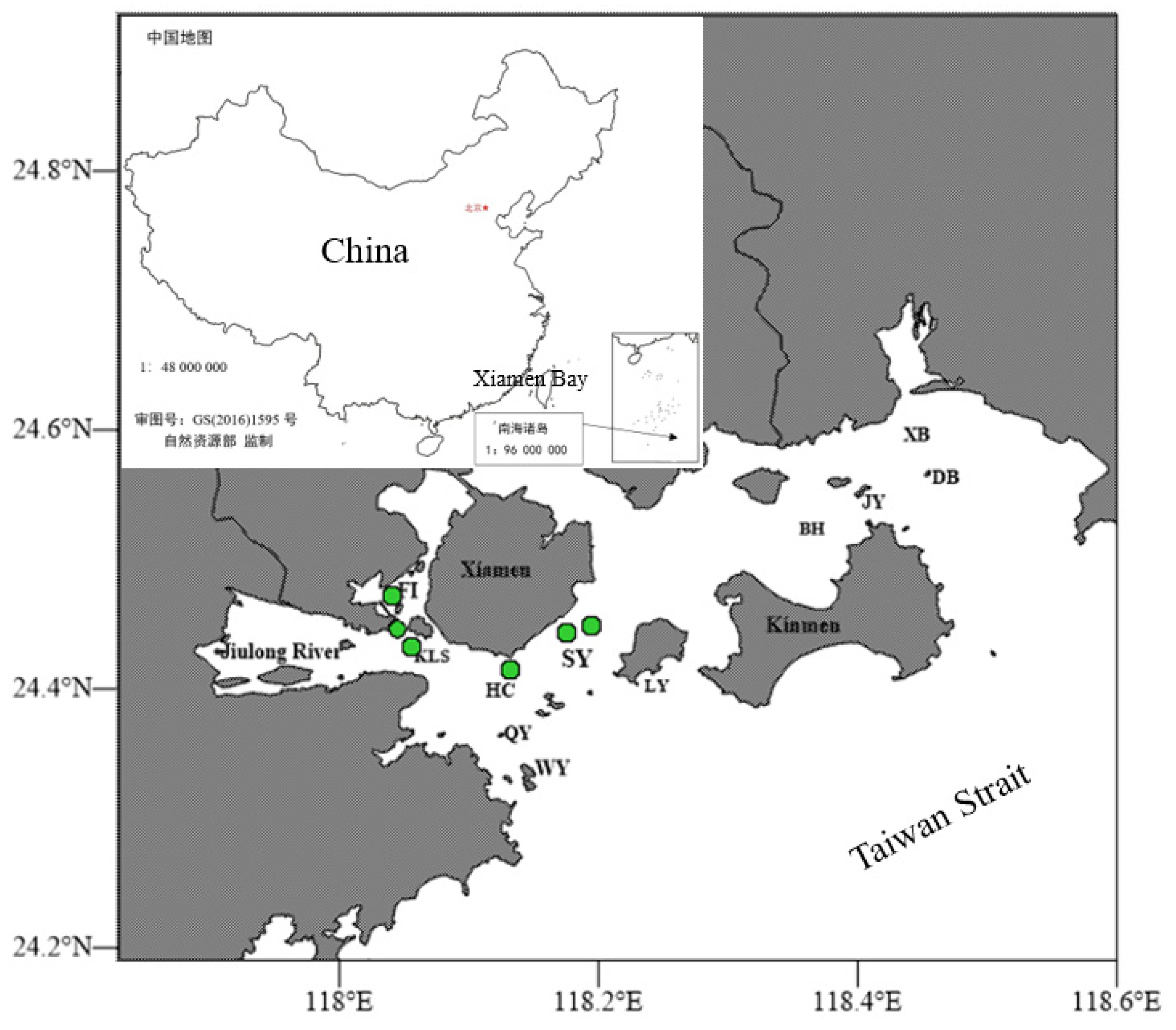
2.1. Station and Sample Collection
2.2. Material and Sample Processing
2.3. Experimental Instruments
2.4. Identification Method
2.5. Classification Basis
2.5.1. Identification Documents
2.5.2. DNA Extraction and PCR Amplification
2.5.3. Phylogenetic Analysis of Coral Samples Based on COI, mtMuts, and ITS Gene Fragments
3. Results
3.1. Systematic Approaches
3.1.1. Echinogorgia ramosa (Thomson and Henderson, 1905)

3.1.2. Echinogorgia flexilis (Thomson and Simpson, 1909)

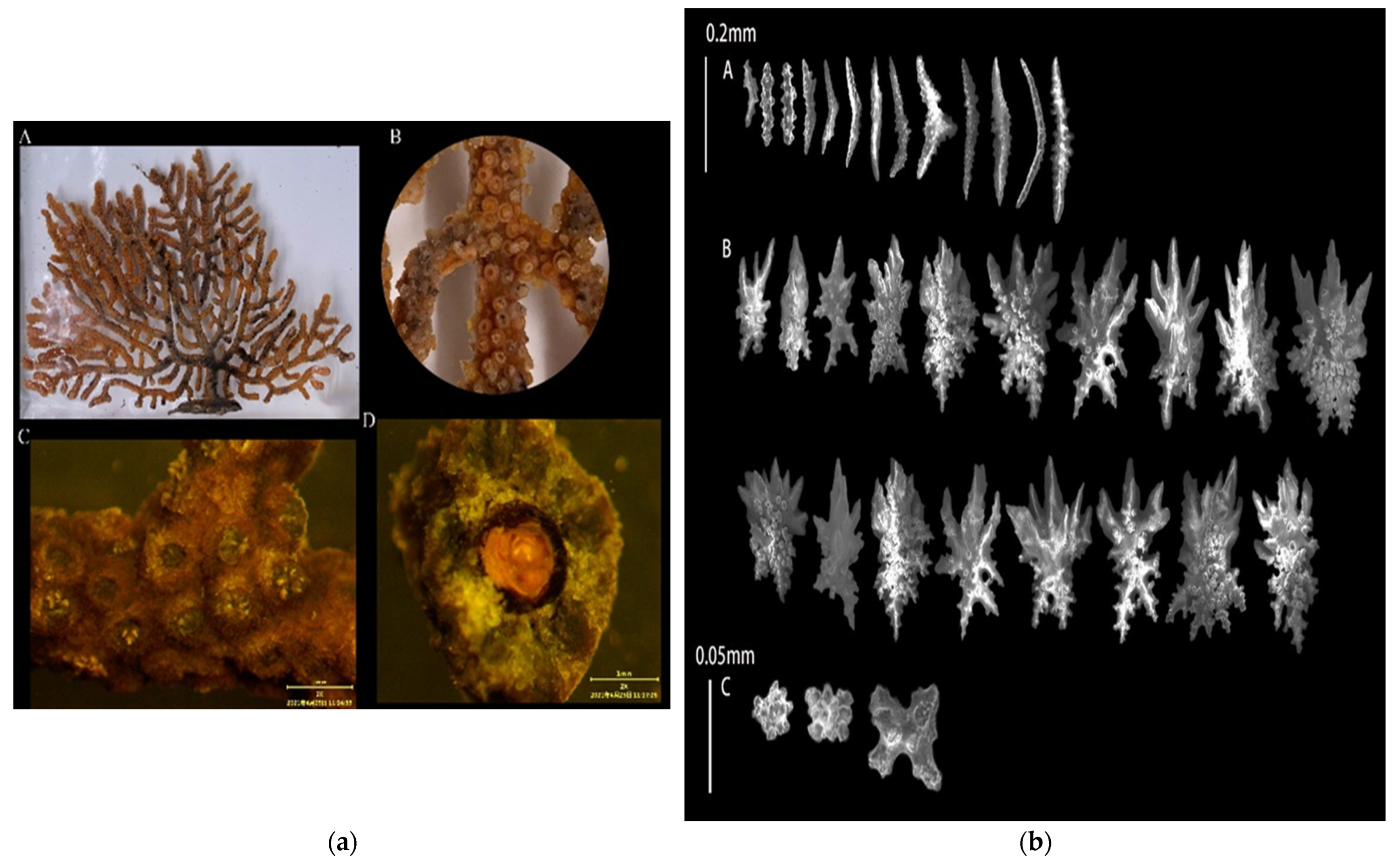
3.1.3. Echinogorgia russelli (Bayer, 1949)
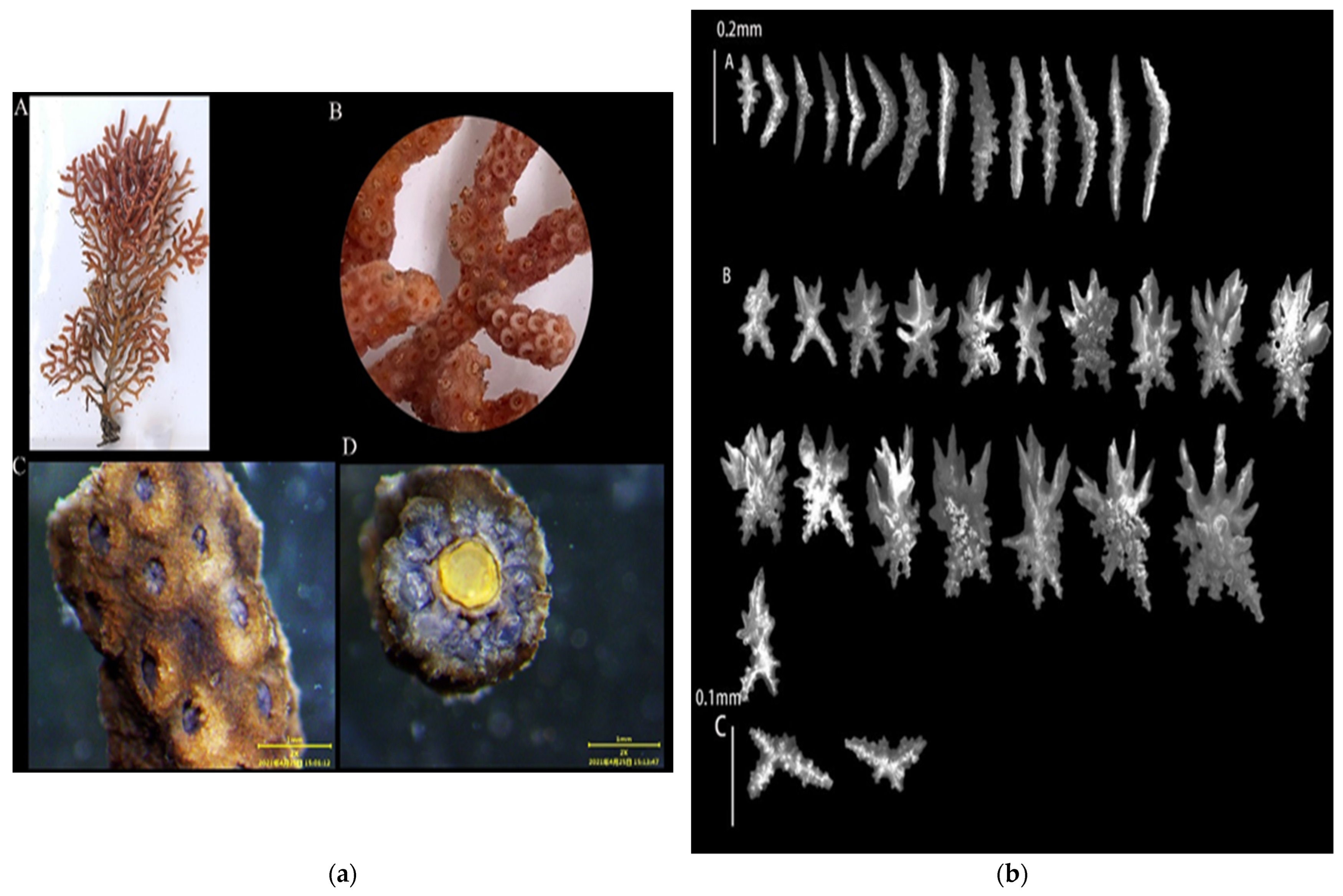
3.1.4. Echinogorgia ramulosa (Gray, 1870)
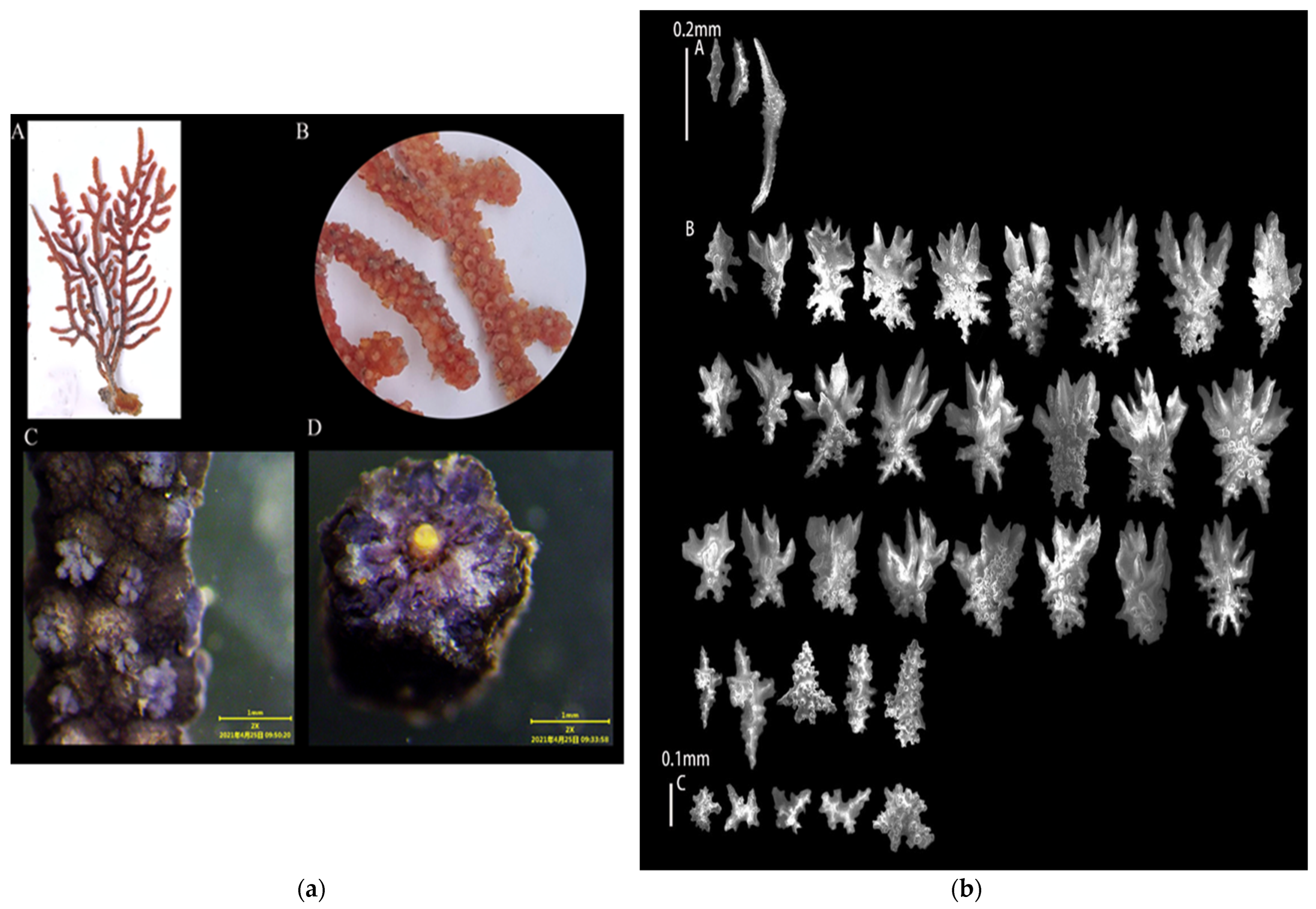
3.1.5. Echinogorgia gracillima (Kükenthal, 1917)

3.2. DNA Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Key Points for the Morphological Identification of the Genus Echinogorgia
4.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of the Genus Echinogorgia
4.3. Distribution of Species in the Genus Echinogorgia
4.4. Management Recommendations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Number | Species | GenBank Accession Number | Gene Segment |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Echinogorgia sp1 | OQ001251 | COI |
| 2 | Echinogorgia sp2 | OQ001252 | |
| 3 | Echinogorgia sp4 | OQ001253 | |
| 4 | Echinogorgia sp5 | OQ001254 | |
| 5 | Echinogorgia ramosa | OQ001255 | |
| 6 | Echinogorgia flexilis | OQ001256 | |
| 7 | Echinogorgia sp6 | OQ001257 | |
| 8 | Echinogorgia sp7 | OQ001258 | |
| 9 | Echinogorgia sp8 | OQ001259 | |
| 10 | Echinogorgia sp9 | OQ001260 | |
| 11 | Echinogorgia sp10 | OQ001261 | |
| 12 | Echinogorgia ramulosa | OQ001262 | |
| 13 | Echinogorgia gracillima | OQ001263 | |
| 14 | Echinogorgia sp. | MW401652.1 | |
| 15 | Echinomuricea sp. | KC984637.1 | |
| 16 | Echinogorgia sp1 | OQ061094 | mtMuts |
| 17 | Echinogorgia sp3 | OQ061095 | |
| 18 | Echinogorgia sp4 | OQ061096 | |
| 19 | Echinogorgia sp5 | OQ061097 | |
| 20 | Echinogorgia ramosa | OQ061098 | |
| 21 | Echinogorgia flexilis | OQ061099 | |
| 22 | Echinogorgia sp6 | OQ061100 | |
| 23 | Echinogorgia sp7 | OQ061101 | |
| 24 | Echinogorgia sp8 | OQ061102 | |
| 25 | Echinogorgia sp9 | OQ061103 | |
| 26 | Echinogorgia sp10 | OQ061104 | |
| 27 | Echinogorgia russelli | OQ061105 | |
| 28 | Echinogorgia ramulosa | OQ061106 | |
| 29 | Echinogorgia complexa | HQ694670.1 | |
| 30 | Echinogorgia complexa | HQ694668.1 | |
| 31 | Echinogorgia sp1 | OQ002388 | ITS1 |
| 32 | Echinogorgia sp2 | OQ002387 | |
| 33 | Echinogorgia sp3 | OQ002389 | |
| 34 | Echinogorgia sp8 | OQ002390 | |
| 35 | Echinogorgia russelli | OQ002405 | |
| 36 | Echinogorgia ramulosa | OQ002404 | |
| 37 | Menella indica | OP984327 | |
| 38 | Euplexaura sp2 | OQ002379 |
References
- Zhao, H.T.; Wang, L.R. The general characteristics of the coral reef ecosystem. Chin. J. Ecol. 2001, 20, 41–45. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- The Sixth Status of Corals of the World: 2020 Report. Available online: https://gcrmn.net/2020-report/ (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- Huang, H.; Zhang, C.L.; Yang, J.H.; You, F.; Lian, J.S.; Tan, Y.H. Scleractinian coral community characteristics in Zhubi reefsea area of Nansha Islands. J. Appl. Oceanogr. Taiwan Strait 2012, 31, 79–84. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Spalding, M.D.; Ravilious, C.; Green, E.P. World. Atlas of Coral Reefs; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.T.; Wang, L.R.; Yuan, J.Y. Sustainable Development of the Coral Reefs in the South China Sea Islands. Trop. Geogr. 2016, 36, 55–65. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.Y. Catalogue of Marine Life in China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2008. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.T.; Huang, H.; Jiang, L. A revised taxonomy for Chinese hermatypic corals. Biodivers. Sci. 2020, 28, 515–523. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.L.; Yang, L.; Zhao, D.B.; Ren, Y.S. Species composition and distribution of neritic Scleractinian and Gorgonian corals in coastal waters of Fujian. J. Appl. Oceanogr. 2015, 34, 209–218. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.L.; Zhao, D.B.; Ren, Y.C.; Yang, L.; Zhang, J.J.; Ji, H.D.; Luo, M.X.; Huang, J.J. Species composition and distribution of Scleractinian corals discovered in the East Fujian waters. J. Appl. Oceanogr. 2014, 33, 29–37. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.G. Species Diversity in Xiamen Bay; China Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 2006. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Li, X.B.; Lian, J.S.; Yang, J.H.; Li, Y.C.; Zou, R.L. Species diversity and distribution of Gorgonian (Cnidaria: Anthozoa: Octocoral) in Xiamen Bay and Dongshan Bay, Fujian. J. Oceanogr. Taiwan Strait 2007, 26, 92–98. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ni, Z.; Liu, J.Y.; Song, Q.Q. Study on Investigation and Taxonomy of the Scleractinian Coralin Baiha Reef; Jimei University: Xiamen, China, 2018. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.Y.; Wang, Y.P.; Yang, J.; Shi, Y.J.; Zhu, D.R. Revealing the Coral Species Diversity in Xiamen Bay: Spatial Distribution of Genus Astrogorgia (Cnidaria, Alcyonacea, Plexauridae) and Newly Recorded Species. J. Water. 2022, 14, 2417. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Liu, J.Y.; Wang, Y.P.; Shi, Y.J. Spatial distribution and new recorded species of Genus Carijoa in Xiamen Bay. J. Appl. Oceanogr. 2023, 32, 1–10. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, R.O.; Leary, R.A.; Low-Choy, S.; Brainard, R.E. Species richness on coral reefs and the pursuit of convergent global estimates. J. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, 500–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moberg, F.; Folke, C. Ecological goods and services of coral reef ecosystems. J. Ecol. Econ. 1999, 29, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, M.; Brugler, M.P.; Cartwright, P.; Collins, A.G.; Dawson, M.N.; Fautin, D.G.; France, S.C.; McFadden, C.S.; Opresko, D.M.; Rogriguez, E.; et al. The phylum Cnidaria: A review of phylogenetic patterns and diversity 300 years after Linnaeus. Zootaxa 2007, 1668, 1–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFadden, C.S.; Van Ofwegen, L.P.; Quattrini, A.M. Revisionary systematics of Octocorallia (Cnidaria: Anthozoa) guided by phylogenomics. Bull. Soc. Syst. Biol. 2022, 1, 8735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Zhao, R.; Sui, Y.Z.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Y.J.; Xu, B. Bioecological status, degradation causes and conservation suggestions of octocorals. J. Appl. Oceanogr. 2022, 1–14. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail//35.1319.p.20221206.1759.001.html (accessed on 12 March 2023).
- Esper, E.J.C. Die Pflanzenthiere in Abbildungen Nach der Natur Mit Farben Erleuchtet, Nebst Beschreibungen. In Raspischen Buchhandlung; 1791; Available online: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=267402 (accessed on 7 May 2023).
- Horton, T.; Kroh, A.; Ahyong, S.; Bailly, N.; Boury-Esnault, N.; Brandão, S.N.; Mees, J. World Register of Marine Species (WoRMS); WoRMS Editorial Board, 2018; Available online: https://www.marinespecies.org/ (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- Dai, C.F. Taxonomic morphologies and taxonomic systems of octocorallia. In A Complete Map of Corals in Taiwan: Eight Corals, 1st ed.; Li, J.H., Hu, J.Y., Eds.; Owl: Taiwan, China, 2022; pp. 1–408. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.B.; Huang, H.; Lian, J.S.; Yang, J.H.; Huang, L.M. Diversity and spatial distribution of gorgonian coral in Dongshan coastal waters in Fujian, China. J. Oceanogr. Taiwan Strait 2011, 30, 92–96. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Q.; Wei, Y.X.; Wang, C.Y.; Shao, C.L.; Li, L.; Liu, X.; Guo, Q.Q. Study on chemical constituents of Echinogorgia sassapo reticulata (Esper). Chin. J. Mar. Drugs 2010, 29, 672–681. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, R.C.; Zhang, H.; Li, P.L.; Tang, X.L.; Li, G.Q. Studies on chemical constituents of Echinogorgia flora. Chin. J. Mar. Drugs 2013, 32, 23–28. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wen, L.; Wei, Q.Q.; Cai, J.N. Advances in studies on bioactive secondary metabolites from gorgonian and microbial symbionts. Chin. J. Antibiot. 2012, 37, 641–654. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, X.Y.; Cao, F.; Wang, C.Y. Isolation, identification and bioactivities of farnesyl hydroquinone glycosides from the South China Sea gorgonian Echinogorgia rebekka. Chin. J. Mar. Drugs 2016, 35, 81–86. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xue, L.; Guan, T.W.; Yu, Y.J.; Li, P.L.; Tang, X.L.; Li, G.Q. Studies on chemical constituents of the South China Seagorgonian Echinogorgia sassapo-reticulata. Chin. J. Mar. Drugs 2014, 33, 43–47. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liao, L.; Wang, N.; Liang, Q. Three ceramides from gorgonian Echinogorgia sp. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2010, 41, 851–854. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liao, L.; Liao, X.J.; Xu, S.H. Compounds with Nitrogen in Coral Echinogorg sp. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2010, 22, 392–394. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Breedy, O.; Guzman, H.M. A revision of the genus Psammogorgia Verrill, 1868 (Cnidaria, Anthozoa, Octocorallia) in the tropical eastern Pacific Ocean. ZooKeys 2020, 961, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H. Study on the Gorgonian Morphology and 18SrDNA Molecuar Phylogeny in the South China Sea; Sun Yat-sen University: Guangzhou, China, 2005. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.B.; Huang, H.; Zhang, J.B.; Dong, Z.J.; Huang, L.M. Phylogenetic Relationships with the Gorgonian (Cndaria: Anthozoa: Octocorallia) Based on 18S rDNA Sequences. Mar. Sci. Bullet. 2006, 25, 10–19. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.J.; Liu, C.W.; Liu, L.; Liao, B.L. Phylogeny analysis of Porites link in Xuwen using its gene. Mar. Sci. 2012, 36, 56–60. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Z.Q.; Liao, B.L.; Xiao, B.H.; Yang, X.D.; Li, X.J.; Chen, Y.Y. Phylogenetic Relationships in Scleractinian from Water of Dapeng Peninsula Based on ITS Genes. J. Guangdong Ocean. Univ. 2017, 37, 8–15. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Brockman, S.A.; McFadden, C.S. The mitochondrial genome of Paraminabea aldersladei (Cnidaria: Anthozoa: Octocorallia) supports intramolecular recombination as the primary mechanism of gene rearrangement in octocoral mitochondrial genomes. Genome Biol. Evol. 2012, 4, 994–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFadden, C.S.; France, S.C.; Sánchez, J.A.; Alderslade, P. A molecular phylogenetic analysis of the Octocorallia (Cnidaria: Anthozoa) based on mitochondrial protein-coding sequences. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2006, 41, 513–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.Z.; Yang, C.J.; Wang, H.S.; Li, W.D. Preliminary identification of Aldersladum sp. in the South China Sea. J. Hainan Trop. Ocean. Univ. 2018, 25, 18–22. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y. Taxonomy and Phylogeny of the Golden Coral Family Chrysogorgiidae (Anthozoa: Alcyonacea) from Seamounts in theWestern Pacific; University of Chinese Academy of Sciences: Beijing, China, 2019. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hume, B.C.; Smith, E.G.; Ziegler, M.; Warrington, M.J.H.; Burt, A.J.; Wiedenmann, J. Sym Portal: A novel analytical frame-work and platform for coral algal symbiont next-generation sequencing ITS2 profiling. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2019, 19, 1063–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, M.; Apandi, Z.N.; Marican, H.A.; Kamphol, N.; Mubin, N.A.; Salleh, S.; Ismail, M.N. The identification of Octocorals from the northern region of straits of Malacca. Trop. Life Sci. Res. 2016, 27 (Supp. 1), 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alderslade, P.A.; Fabricius, K. Soft Corals and Sea Fans; Australian Institute of Marine Science: Cape Cleveland, Australia, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bayer, F.M. Key to the genera of Octocorallia exclusive of Pennatulacea (Coelenterata: Anthozoa), with diagnosis of new taxa. Proc. Biol. Soc. Wash. 1981, 94, 902–948. [Google Scholar]
- Cairns, S.D.; Wirshing, H.H. A phylogenetic analysis of the Primnoidae (Anthozoa: Octocorallia: Calcaxonia) with analyses of character evolution and a key to the genera and subgenera. BMC Evol. Biol. 2018, 18, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.; Lee, S.; Taylor, J. 38-Amplification and Directsequencing of Fungal Ribosomal RNA Genes for Phyogenetics; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1990; pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, C.F.; Qin, Q.X. Ecological map of Bafang Coral in Dongsha, 1st ed.; Cai, N.S., Wu, D.Y., Eds.; Marine National Park Administration: Kaohsiung, Taiwan, 2017; pp. 10–11. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Thomson, J.A.; Henderson, W.D. Report on the Alcyonaria Collected by Professor Herdman at Ceylon in 1902; Princeton University: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1905. [Google Scholar]
- Thomson, J.A.; Simpson, J.J. An account of the alcyonarians collected by the Royal Indian Marine Survey Ship ‘Investigator’ in the Indian Ocean. II. The alcyonarians of the littoral area. Trustees Indian Mus. Calcutta 1909, 1–202. [Google Scholar]
- Bayer, F.M. The Alcyonaria of Bikini and other atolls in the Marshall group. Part I Gorgonacea 1949, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Gray, J.E. XLVI.—Notes on some new genera and species of alcyonoid corals in the British Museum. J. Nat. Hist. 1870, 5, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kükenthal, W. Gorgonaria Wissenschaftliche Ergebnisse der deutschen Tiefsee-Expedition auf dem dampfer. Valdivia 1898, 1899, 1–946. [Google Scholar]
- Studer, T. Supplementary Report on the Alcyonaria Collected by HMS Challenger during the Years 1873–1876; Johnson Reprint Corporation: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1889. [Google Scholar]
- Kölliker, A. Die Bindesubstanz der Coelenteraten, Icones histologicae oder Atlas der vergleichenden Gewebslehre, II. Abt. I 1865. Available online: https://sc.panda321.com/scholar?hl=zh-cn&q=Die+Bindesubstanz+der+Coelenteraten%2C+Icones+histologicae+oder+Atlas+der+vergleichenden+Gewebslehre%2C+II.+Abt.+I+1865.++ (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- Koido, T.; Imahara, Y.; Fukami, H. High species diversity of the soft coral family Xeniidae (Octocorallia, Alcyonacea) in the temperate region of Japan revealed by morphological and molecular analyses. ZooKeys 2019, 862, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Untiedt, C.B.; Quattrini, A.M.; McFadden, C.S.; Alderslade, P.A.; Pante, E.; Burridge, C.P. Phylogenetic relationships within Chrysogorgia (Alcyonacea: Octocorallia), a morphologically diverse genus of octocoral, revealed using a target enrichment approach. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 7, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ament-Velásquez, S.L.; Breedy, O.; Cortés, J.; Guzman, H.M.; Wörheide, G.; Vargas, S. Homoplasious colony morphology and mito-nuclear phylogenetic discordance among Eastern Pacific octocorals. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2016, 98, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFadden, C.S.; Haverkort-Yeh, R.; Reynolds, A.M.; Halàsz, A.; Quattrini, A.M.; Forsman, Z.H.; Toonen, R.J. Species boundaries in the absence of morphological, ecological or geographical differentiation in the Red Sea octocoral genus Ovabunda (Alcyonacea: Xeniidae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2017, 112, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quattrini, A.M.; Georgian, S.M.; Byrnes, L.; Stevens, A.; Falco, R.; Cordes, E.E. Niche divergence by deep-sea octocorals in the genus Callogorgia across the upper continental slope of the Gulf of Mexico. Mol. Ecol. 2013, 22, 4123–4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessel, G.M.; Alderslade, P.; Bilewitch, J.P.; Schnabel, K.E.; Gardner, J.P.A. The use of integrative taxonomy in Octocorallia (Cnidaria: Anthozoa): A literature survey. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2023, 198, 677–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, C.D.; Neves, B.; Cordeiro, R.T.S.; Williams, G.C.; Cairns, S.D. Diversity and distribution of Octocorallia. In The Cnidaria, Past, Present and Future; Stefano, G., Dubinsky, Z., Eds.; Springer International: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 109–123. [Google Scholar]
- Núñez-Flores, M.; Gomez-Uchida, D.; López-González, P.J. Molecular and morphological data reveal three new species of Thouarella Gray, 1870 (Anthozoa: Octocorallia: Primnoidae) from the Southern Ocean. Mar. Biodivers. 2020, 50, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poliseno, A.; Altuna, A.; Puetz, L.C.; Mak, S.S.T.; Rios, P.; Petroni, E.; McFadden, C.S.; Sørensen, M.V.; Gilbert, M.T.P. An integrated morphological-molecular approach reveals new insights on the systematics of the octocoral Telestula humilis (Thomson, 1927) (Octocorallia: Alcyonacea: Clavulariidae). Invertebr. Syst. 2021, 35, 261–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, F.M. Octocoral research: Past, present and future. Atoll Res. Bull. 2001, 494, 79–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFadden, C.S.; Benayahu, Y.; Pante, E.; Thoma, J.N.; Nevarez, P.A.; France, S.C. Limitations of mitochondrial gene barcoding in Octocorallia. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2010, 11, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baco, A.R.; Cairns, S.D. Comparing molecular variation to morphological species designations in the deep-sea coral Narella reveals new insights into seamount coral ranges. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFadden, C.S.; Brown, A.S.; Brayton, C.; Hunt, C.B.; van Ofwegen, L.P. Application of DNA barcoding in biodiversity studies of shallow-water octocorals: Molecular proxies agree with morphological estimates of species richness in Palau. Coral Reefs 2014, 33, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFadden, C.S.; Reynolds, A.M.; Janes, M.P. DNA barcoding of xeniid soft corals (Octocorallia: Alcyonacea: Xeniidae) from Indonesia: Species richness and phylogenetic relationships. Syst. Biodivers. 2014, 12, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faircloth, B.C.; Branstetter, M.G.; White, N.D.; Brady, S.G. Target enrichment of ultraconserved elements from arthropods provides a genomic perspective on relationships among hymenoptera. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2015, 15, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, M.G.; Smith, B.T.; Glenn, T.C.; Faircloth, B.C.; Brumfield, R.T. Sequence capture versus restriction site associated DNA sequencing for shallow systematics. Syst. Biol. 2016, 65, 910–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quattrini, A.M.; Wu, T.; Soong, K.; Jeng, M.S.; Benayahu, Y.; McFadden, C.S. A next generation approach to species delimitation reveals the role of hybridization in a cryptic species complex of corals. BMC Evol. Biol. 2019, 19, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrigoni, R.; Stefani, F.; Pichon, M.; Galli, P.; Benzoni, F. Molecular phylogeny of the robust clade (Faviidae, Mussidae, Merulinidae, and Pectiniidae): An Indian Ocean perspective. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2012, 65, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Zhan, Z.; Xu, K. Morphology and phylogeny of Chrysogorgia pinniformis sp. nov. and C. varians sp. nov., two golden corals from the Caroline seamounts in the tropical Western Pacific Ocean. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2021, 39, 1767–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehoray, R.E.; Omri, S.; Maayan, Y.; Francis, C.M.; Godfray, C. Initiating a DNA Barcoding Reference Library of Stony Corals from the Gulf of Eilat (Red Sea). J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 174–184. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.N.; Liu, L.; Liu, C.W. Phylogenetic relationship in 8 species of Scleractinian coral based on COI sequences. Prog. Fish. Sci. 2012, 33, 83–88. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Yang, C.J.; Wang, P.Z.; Wang, H.S.; Xu, Y.S.; Li, W.D. Identification of the soft coral genera Sarcophyton in the coastal waters of Hainan Island. J. Appl. Oceanogr. 2019, 38, 30–41. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, B.H.; Liao, B.L.; Yang, X.D. Study of phylogenetic relationships of scleractinian from Wailingding Island based on three standard molecular markers. Reports 2017, 41, 1–8. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Haverkort-Yeh, R.D.; McFadden, C.S.; Benayahu, Y.; Berumen, M.; Halász, A.; Toonen, R.J. A taxonomic survey of Saudi Arabian Red Sea octocorals (Cnidaria: Alcyonacea). Mar. Biodivers. 2013, 43, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babcock, R.C.; Baird, A.H.; Piromvaragorn, S.; Thomson, D.P.; Willis, B.L. Identification of scleractinian coral recruits from Indo-Pacific reefs. Zool. Stud. 2003, 42, 211–226. [Google Scholar]
- McCormack, J.E.; Tsai, W.L.E.; Faircloth, B.C. Sequence capture of ultraconserved elements from bird museum specimens. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2016, 16, 1189–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruane, S.; Austin, C.C. Phylogenomics using formalin-fixed and 100+ year-old intractable natural history specimens. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2017, 17, 1003–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, H.M.; González, V.L.; Lloyd, M.; Coddington, J.; Scharff, N. Next-generation museum genomics: Phylogenetic relationships among palpimanoid spiders using sequence capture techniques (Araneae: Palpimanoidea). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2018, 127, 907–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derkarabetian, S.; Benavides, L.R.; Giribet, G. Sequence capture phylogenomics of historical ethanol-preserved museum specimens: Unlocking the rest of the vault. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2019, 19, 1531–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson, K.L.; Pentico, A.; Quattrini, A.M.; McFadden, C.S. New approaches to species delimitation and population structure of anthozoans: Two case studies of octocorals using ultraconserved elements and exons. Mol Ecol Resour. 2021, 21, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quattrini, A.M.; Faircloth, B.C.; Dueñas, L.F.; Bridge, T.C.L.; Brugler, M.R.; Calixto-Botía, I.F.; DeLeo, D.M.; Forêt, S.; Herrera, S.; Lee, S.M.Y.; et al. Universal target-enrichment baits for anthozoan (Cnidaria) phylogenomics: New approaches to long-standing problems. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2018, 18, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, K.; Morton, B. Soft corals, sea fans, gorgonians (Octocorallia: Alcyonacea) and black and wire corals (Ceriantipatharia: Antipatharia) from submarine caves in Hong Kong with a checklist of local species and a description of a new species of Paraminabea. J. Nat. Hist. 2008, 42, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellwood, D.R.; Hughes, T.P.; Folke, C.; Nyström, M. Confronting the coral reef crisis. Nature 2004, 429, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Disappearance of Coral Reefs: Causes and Consequences. Available online: https://www.gvi.ie/blog/smb-the-disappearance-of-coral-reefs-causes-and-consequences/ (accessed on 6 September 2023).
- Jones, G.P.; McCormick, M.I.; Srinivasan, M.; Eagle, J.V. Coral decline threatens fish biodiversity in marine reserves. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 8251–8253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hein, M.Y.; Vardi, T.; Shaver, E.C.; Pioch, S.; Boström-Einarsson, L.; Ahmed, M.; Grimsditch, G.; McLeod, I.M. Perspectives on the use of coral reef restoration as a strat-egy to support and improve reef ecosystem services. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 618303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bay, L.K.; Rocker, M.; Boström-Einarsson, L.; Babcock, R.; Buerger, P.; Cleves, P.; Webster, N. Reef Restoration and Adaptation Program: Intervention Technical Summary. In A Report Provided to the Australian Government by the Reef Restoration and Adaptation Program; Australian Institute of Marine Science: Townsville, Australia, 2019; p. 89. [Google Scholar]
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM). In A Research Review of Interventions to Increase the Persistence and Resilience of Coral Reefs; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [CrossRef]
- List of National Nature Reserves in China. Available online: http://www.zrbhq.com.cn/index.php?m=content&c=index&a=lists&catid=81 (accessed on 1 July 2023). (In Chinese).
- Huang, H.; Lian, J.S.; Li, Z.X.; Chen, Z.Q. Fujian Dongshan Coral Nature Reserve and Its Biodiversity; China Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 2009. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Marine Protected Areas in Coral Reef Regions Classified According to Management Effectiveness Rating. Available online: https://www.wri.org/data/marine-protected-areas-coral-reef-regions-classified-according-management-effectiveness-rating (accessed on 6 September 2023).
- Fernandes, L.; Day, J.; Lewis, A.; Slegers, S.; Kerrigan, B.; Breen, D.; Cameron, D.; Jago, B.; Hall, J.; Lowe, D.; et al. Establishing representative no-take areas in the Great Barrier Reef: Large-scale implementation of theory on marine protected areas. Conserv. Biol. 2005, 19, 1733–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coral Reef Protected Areas: A Guide for Management. Available online: https://www.coralreef.gov/ecosystem/strate.html (accessed on 6 September 2023).

| Year | Station | Longitude | Latitude |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | Shangyu Island (SY) | 118°11′19″–118°11′25″ | 24°27′12″–24°27′13″ |
| Huangcuo (HC) | 118°07′50″ | 24°25′25″ | |
| Kulangsu Island (KLS) | 118°03′14″–118°03′41″ | 24°26′23″–24°26′35″ | |
| Fire Island (FI) | 118°03′54″ | 24°29′35″ | |
| Qingyu Island (QY) | 118°05′35″–118° 07′28″ | 24° 21′45″–24°21′55″ | |
| Wuyu Island (WY) | 118° 03′54″–118° 08′35″ | 24° 20′23″–24° 29′35″ | |
| Dabai Island (DB) | 118°26′58″–118°27′40″ | 24°33′46″–24°34′9″ | |
| Xiaobai Island (XB) | 118°27′47″ | 24°33′21″ | |
| Jiaoyu Island (JY) | 118°24′14″ | 24°32′41″ | |
| Baiha Reef (BH) | 118°22′07″–118°22′17″ | 24°31′38″–24°31′55″ | |
| 2021 | Qingyu Island (QY) | 118°07′21″–118°07′50″ | 24°21′45″–24°22′11″ |
| Wuyu Island (WY) | 118°08′28″–118°08′57″ | 24°20′31″–24°20′51″ | |
| Dabai Island (DB) | 118°45′02″–118°46′06″ | 24°56′31″–24°57′51″ | |
| Xiaobai Island (XB) | 118°42′58″–118°43′38″ | 24°58′26″–24°58′96″ |
| Primers | Gene Region | Sequence (5′-3′) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| COI-LA-8398 | COI gene | F-GGA ATG GCG GGG ACA GCT TCG AGT ATG TTA ATA CGG | [44] |
| COIoct | R-ATC ATA GCA TAG ACC ATACC | ||
| AnthoCorMSH | MSH gene | F-AGG AGA ATT ATT CTA AGT ATGG | [44] |
| Mut3458R | R-TSG AGC AAA AGC CAC TCC | ||
| ITS1 | ITS gene | F-TCCGTAGGTGAACCTGCGG | [45] |
| ITS2 | R-GCTGCGTTCTTCATCGATGC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.-P.; Yang, J.; Chu, T.-J.; Liu, J.-Y. The Species Diversity of the Genus Echinogorgia in Xiamen Bay and Its New Record in China. Water 2023, 15, 3547. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203547
Wang Y-P, Yang J, Chu T-J, Liu J-Y. The Species Diversity of the Genus Echinogorgia in Xiamen Bay and Its New Record in China. Water. 2023; 15(20):3547. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203547
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yun-Pei, Jing Yang, Ta-Jen Chu, and Jia-Ying Liu. 2023. "The Species Diversity of the Genus Echinogorgia in Xiamen Bay and Its New Record in China" Water 15, no. 20: 3547. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203547





