Artificial Intelligence Modelling to Support the Groundwater Chemistry-Dependent Selection of Groundwater Arsenic Remediation Approaches in Bangladesh
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Data Acquisition of the Source Water Chemistry
2.2. Predictor Variables
2.3. Prediction Modelling
2.4. Source Water–Remediation Efficiency Relationship
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Seondary Dataset of Source Water Chemistry
3.2. Random Forest Models
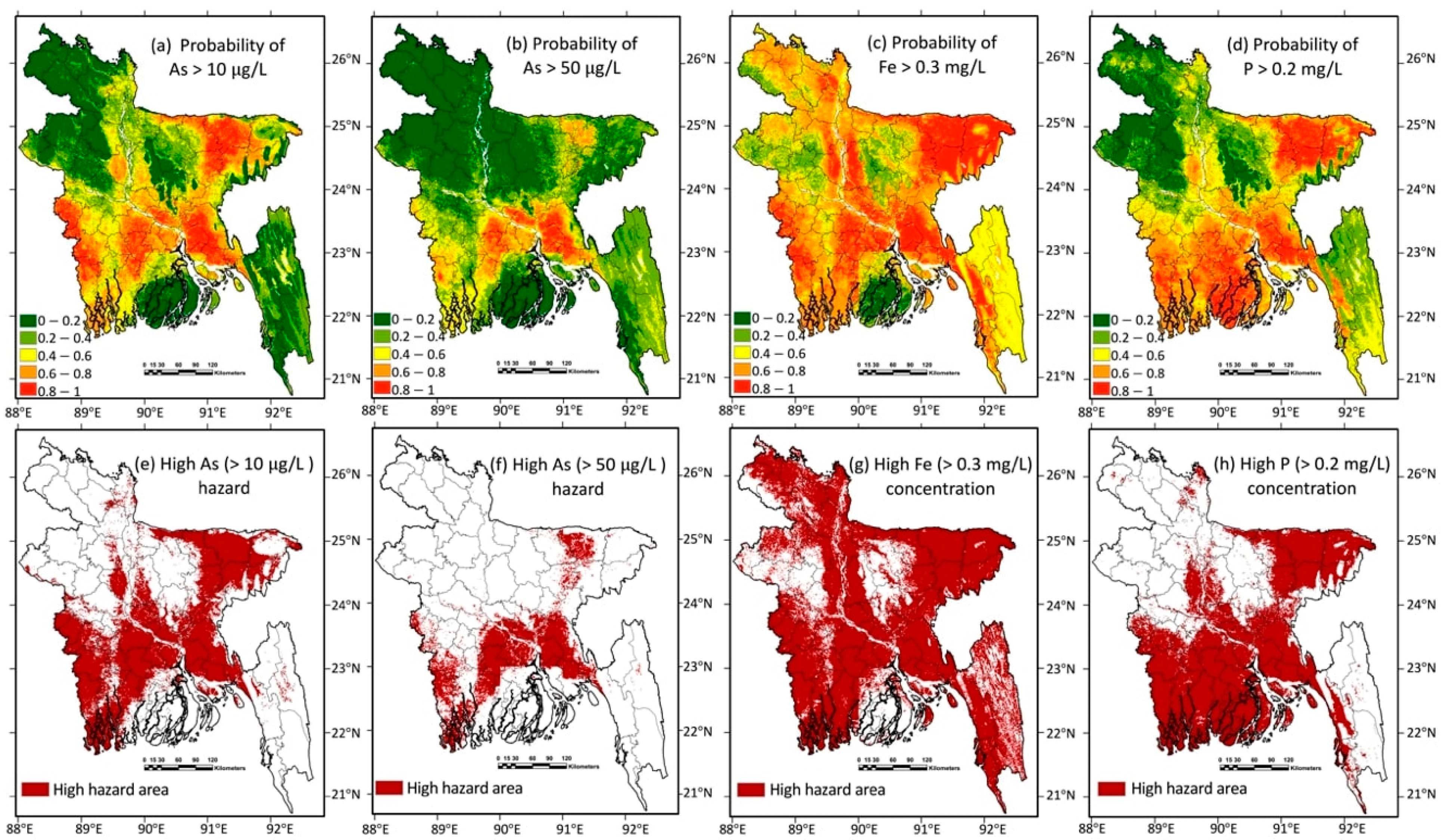
3.3. Distribution of Arsenic, Phosphorus, and Iron in Groundwater
3.4. Predicted Comparative Level of Arsenic Remediation Efficiency in Groundwater
3.5. Limitations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mishra, B.; Kumar, P.; Saraswat, C.; Chakraborty, S.; Gautam, A. Water Security in a Changing Environment: Concept, Challenges and Solutions. Water 2021, 13, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BGS; DPHE. Arsenic Contamination of Groundwater in Bangladesh; British Geological Survey: Keyworth, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- WHO; UNICEF. Arsenic Primer—Guidance on the Investigation & Mitigation of Arsenic Contamination; WHO: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Khalid, S.; Shahid, M.; Bibi, I.; Natasha; Murtaza, B.; Tariq, T.Z.; Naz, R.; Shahzad, M.; Hussain, M.M.; Niazi, N.K. Global Arsenic Contamination of Groundwater, Soil and Food Crops and Health Impacts. In Global Arsenic Hazard; Niazi, N.K., Bibi, I., Aftab, T., Eds.; Environmental Science and Engineering; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 13–33. ISBN 978-3-031-16359-3. [Google Scholar]
- Ravenscroft, P.; Brammer, H.; Richards, K.S. Arsenic Pollution: A Global Synthesis; RGS-IBG Book Series; Wiley-Blackwell: Chichester, UK; Malden, MA, USA, 2009; ISBN 978-1-4051-8602-5. [Google Scholar]
- Hug, S.J.; Leupin, O.X.; Berg, M. Bangladesh and Vietnam: Different Groundwater Compositions Require Different Approaches to Arsenic Mitigation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 6318–6323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.F.; Ahuja, S.; Alauddin, M.; Hug, S.J.; Lloyd, J.R.; Pfaff, A.; Pichler, T.; Saltikov, C.; Stute, M.; van Geen, A. Ensuring Safe Drinking Water in Bangladesh. Science 2006, 314, 1687–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IARC. Arsenic, Metals, Fibres and Dusts; IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2012; Volume 100C, ISBN 978-92-832-0135-9. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Ahsan, H. Cancer Burden from Arsenic in Drinking Water in Bangladesh. Am. J. Public Health 2004, 94, 741–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, U.K.; Biswas, B.K.; Chowdhury, T.R.; Samanta, G.; Mandal, B.K.; Basu, G.C.; Chanda, C.R.; Lodh, D.; Saha, K.C.; Mukherjee, S.K.; et al. Groundwater Arsenic Contamination in Bangladesh and West Bengal, India. Environ. Health Perspect. 2000, 108, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, P.; Majumder, C.B.; Mohanty, B. Laboratory Based Approaches for Arsenic Remediation from Contaminated Water: Recent Developments. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 137, 464–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, A.; Richards, L.A.; Bhattacharya, P. Arsenic Remediation of Drinking Water: An Overview. In Best Practice Guide on the Control of Arsenic in Drinking Water; Bhattacharya, P., Polya, D.A., Jovanovic, D., Eds.; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2017; pp. 79–98. ISBN 978-1-78040-492-9. [Google Scholar]
- Dutta, N.; Gupta, A. Development of Arsenic Removal Unit with Electrocoagulation and Activated Alumina Sorption: Field Trial at Rural West Bengal, India. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 49, 103013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Joshi, H.; Kumar, A. Remediation of Arsenic by Metal/Metal Oxide Based Nanocomposites/Nanohybrids: Contamination Scenario in Groundwater, Practical Challenges, and Future Perspectives. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2021, 50, 283–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irshad, S.; Xie, Z.; Mehmood, S.; Nawaz, A.; Ditta, A.; Mahmood, Q. Insights into Conventional and Recent Technologies for Arsenic Bioremediation: A Systematic Review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 18870–18892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Qu, J. Review on Heterogeneous Oxidation and Adsorption for Arsenic Removal from Drinking Water. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 110, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younger, P.L.; Coulton, R.H.; Froggatt, E.C. The Contribution of Science to Risk-Based Decision-Making: Lessons from the Development of Full-Scale Treatment Measures for Acidic Mine Waters at Wheal Jane, UK. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 338, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Sahu, S.; Telu, V.; Duttagupta, S.; Sarkar, S.; Bhattacharya, J.; Mukherjee, A.; Ghosal, P.S. Neural Network and Random Forest-Based Analyses of the Performance of Community Drinking Water Arsenic Treatment Plants. Water 2021, 13, 3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, L.A.; Wu, R.; Polya, D.A. Water Security in South Asia: The Potential Role of Artificial Intelligence in Supporting the Selection of Remediation Approached for Groundwater; Publisher: Denver, CO, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, K.M.; Fukuhara, T.; Hai, F.I.; Bari, Q.H.; Islam, K.M.S. Development of a Bio-Physicochemical Technique for Arsenic Removal from Groundwater. Desalination 2009, 249, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiquzzaman, M.; Azam, M.S.; Nakajima, J.; Bari, Q.H. Investigation of Arsenic Removal Performance by a Simple Iron Removal Ceramic Filter in Rural Households of Bangladesh. Desalination 2011, 265, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, L.C.; Hug, S.J.; Ruettimann, T.; Billah, M.M.; Khan, A.W.; Rahman, M.T. Arsenic Removal with Iron(II) and Iron(III) in Waters with High Silicate and Phosphate Concentrations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallier, V.; Feuillade-Cathalifaud, G.; Serpaud, B.; Bollinger, J.-C. Effect of Organic Matter on Arsenic Removal during Coagulation/Flocculation Treatment. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 342, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornejo, L.; Lienqueo, H.; Arenas, M.; Acarapi, J.; Contreras, D.; Yáñez, J.; Mansilla, H.D. In Field Arsenic Removal from Natural Water by Zero-Valent Iron Assisted by Solar Radiation. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 156, 827–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.M.; Shafiquzzaman, M.; Nakajima, J.; Bari, Q.H. Application of a Simple Arsenic Removal Filter in a Rural Area of Bangladesh. Water Supply 2012, 12, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Liu, R.; Liu, H.; Chang, F.; Lan, H.; Qu, J. Arsenic Species Transformation and Transportation in Arsenic Removal by Fe-Mn Binary Oxide–Coated Diatomite: Pilot-Scale Field Study. J. Environ. Eng. 2011, 137, 1122–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahai, N.; Lee, Y.J.; Xu, H.; Ciardelli, M.; Gaillard, J.-F. Role of Fe(II) and Phosphate in Arsenic Uptake by Coprecipitation. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2007, 71, 3193–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortun, A.; Bortun, M.; Pardini, J.; Khainakov, S.A.; García, J.R. Effect of Competitive Ions on the Arsenic Removal by Mesoporous Hydrous Zirconium Oxide from Drinking Water. Mater. Res. Bull. 2010, 45, 1628–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Klerk, R.J.; Jia, Y.; Daenzer, R.; Gomez, M.A.; Demopoulos, G.P. Continuous Circuit Coprecipitation of Arsenic(V) with Ferric Iron by Lime Neutralization: Process Parameter Effects on Arsenic Removal and Precipitate Quality. Hydrometallurgy 2012, 111–112, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senn, A.-C.; Kaegi, R.; Hug, S.J.; Hering, J.G.; Mangold, S.; Voegelin, A. Composition and Structure of Fe(III)-Precipitates Formed by Fe(II) Oxidation in Water at near-Neutral PH: Interdependent Effects of Phosphate, Silicate and Ca. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2015, 162, 220–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voegelin, A.; Kaegi, R.; Frommer, J.; Vantelon, D.; Hug, S.J. Effect of Phosphate, Silicate, and Ca on Fe(III)-Precipitates Formed in Aerated Fe(II)- and As(III)-Containing Water Studied by X-Ray Absorption Spectroscopy. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2010, 74, 164–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Mucci, A. Acid Base Reactions, Phosphate and Arsenate Complexation, and Their Competitive Adsorption at the Surface of Goethite in 0.7 M NaCl Solution. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2001, 65, 2361–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Fisher, B.; Giammar, D.E. Individual and Competitive Adsorption of Arsenate and Phosphate to a High-Surface-Area Iron Oxide-Based Sorbent. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, A.; Gustafsson, J.P.; Neidhardt, H.; Halder, D.; Kundu, A.K.; Chatterjee, D.; Berner, Z.; Bhattacharya, P. Role of Competing Ions in the Mobilization of Arsenic in Groundwater of Bengal Basin: Insight from Surface Complexation Modeling. Water Res. 2014, 55, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, B.A.; Goldberg, S. Modeling Arsenate Competitive Adsorption on Kaolinite, Montmorillonite and Illite. Clays Clay Miner. 1996, 44, 609–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youngran, J.; Fan, M.; Van Leeuwen, J.; Belczyk, J.F. Effect of Competing Solutes on Arsenic(V) Adsorption Using Iron and Aluminum Oxides. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 19, 910–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fytianos, K.; Voudrias, E.; Raikos, N. Modelling of Phosphorus Removal from Aqueous and Wastewater Samples Using Ferric Iron. Environ. Pollut. 1998, 101, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongshao, Z.; Stanforth, R. Competitive Adsorption of Phosphate and Arsenate on Goethite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 4753–4757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, S.R.; Yanful, E.K. Arsenic and Chromium Removal by Mixed Magnetite–Maghemite Nanoparticles and the Effect of Phosphate on Removal. J. Environ. Manag. 2010, 91, 2238–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.S.; Stanforth, R.; Pehkonen, S.O. Irreversible Adsorption of Methyl Arsenic, Arsenate, and Phosphate onto Goethite in Arsenic and Phosphate Binary Systems. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 317, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neidhardt, H.; Rudischer, S.; Eiche, E.; Schneider, M.; Stopelli, E.; Duyen, V.T.; Trang, P.T.K.; Viet, P.H.; Neumann, T.; Berg, M. Phosphate Immobilisation Dynamics and Interaction with Arsenic Sorption at Redox Transition Zones in Floodplain Aquifers: Insights from the Red River Delta, Vietnam. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 411, 125128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manning, B.A.; Goldberg, S. Modeling Competitive Adsorption of Arsenate with Phosphate and Molybdate on Oxide Minerals. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1996, 60, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.-S.; Park, J.-H.; Min, Y.; Lim, D.-H. Competitive Adsorption between Phosphate and Arsenic in Soil Containing Iron Sulfide: XAS Experiment and DFT Calculation Approaches. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 397, 125426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiberg, C.; Sjöstedt, C.; Eriksson, A.K.; Klysubun, W.; Gustafsson, J.P. Phosphate Competition with Arsenate on Poorly Crystalline Iron and Aluminum (Hydr)Oxide Mixtures. Chemosphere 2020, 255, 126937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niazi, N.K.; Burton, E.D. Arsenic Sorption to Nanoparticulate Mackinawite (FeS): An Examination of Phosphate Competition. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voegelin, A.; Senn, A.-C.; Kaegi, R.; Hug, S.J.; Mangold, S. Dynamic Fe-Precipitate Formation Induced by Fe(II) Oxidation in Aerated Phosphate-Containing Water. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2013, 117, 216–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, L.A.; Kumar, A.; Shankar, P.; Gaurav, A.; Ghosh, A.; Polya, D.A. Distribution and Geochemical Controls of Arsenic and Uranium in Groundwater-Derived Drinking Water in Bihar, India. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podgorski, J.; Berg, M. Global Threat of Arsenic in Groundwater. Science 2020, 368, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amini, M.; Abbaspour, K.C.; Berg, M.; Winkel, L.; Hug, S.J.; Hoehn, E.; Yang, H.; Johnson, C.A. Statistical Modeling of Global Geogenic Arsenic Contamination in Groundwater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 3669–3675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayotte, J.D.; Medalie, L.; Qi, S.L.; Backer, L.C.; Nolan, B.T. Estimating the High-Arsenic Domestic-Well Population in the Conterminous United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 12443–12454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayotte, J.D.; Montgomery, D.L.; Flanagan, S.M.; Robinson, K.W. Arsenic in Groundwater in Eastern New England: Occurrence, Controls, and Human Health Implications. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 2075–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkel, L.; Berg, M.; Amini, M.; Hug, S.J.; Annette Johnson, C. Predicting Groundwater Arsenic Contamination in Southeast Asia from Surface Parameters. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sovann, C.; Polya, D.A. Improved Groundwater Geogenic Arsenic Hazard Map for Cambodia. Environ. Chem. 2014, 11, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podgorski, J.E.; Eqani, S.A.M.A.S.; Khanam, T.; Ullah, R.; Shen, H.; Berg, M. Extensive Arsenic Contamination in High-PH Unconfined Aquifers in the Indus Valley. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1700935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.; Sarkar, S.; Chakraborty, M.; Duttagupta, S.; Bhattacharya, A.; Saha, D.; Bhattacharya, P.; Mitra, A.; Gupta, S. Occurrence, Predictors and Hazards of Elevated Groundwater Arsenic across India through Field Observations and Regional-Scale AI-Based Modeling. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 759, 143511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Xu, L.; Polya, D.A. Groundwater Arsenic-Attributable Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) Mortality Risks in India. Water 2021, 13, 2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podgorski, J.; Wu, R.; Chakravorty, B.; Polya, D.A. Groundwater Arsenic Distribution in India by Machine Learning Geospatial Modeling. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Alvareda, E.; Polya, D.; Blanco, G.; Gamazo, P. Distribution of Groundwater Arsenic in Uruguay Using Hybrid Machine Learning and Expert System Approaches. Water 2021, 13, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Yang, Q.; Zheng, Y. Machine Learning Models of Groundwater Arsenic Spatial Distribution in Bangladesh: Influence of Holocene Sediment Depositional History. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 9454–9463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Lado, L.; Sun, G.; Berg, M.; Zhang, Q.; Xue, H.; Zheng, Q.; Johnson, C.A. Groundwater Arsenic Contamination Throughout China. Science 2013, 341, 866–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretzler, A.; Lalanne, F.; Nikiema, J.; Podgorski, J.; Pfenninger, N.; Berg, M.; Schirmer, M. Groundwater Arsenic Contamination in Burkina Faso, West Africa: Predicting and Verifying Regions at Risk. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584–585, 958–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Pati, J. Assessment of Groundwater Arsenic Contamination Using Machine Learning in Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh, India. J. Water Health 2022, 20, 829–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Podgorski, J.; Berg, M.; Polya, D.A. Geostatistical Model of the Spatial Distribution of Arsenic in Groundwaters in Gujarat State, India. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 2649–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruidas, D.; Pal, S.C.; Towfiqul Islam, A.R.M.; Saha, A. Hydrogeochemical Evaluation of Groundwater Aquifers and Associated Health Hazard Risk Mapping Using Ensemble Data Driven Model in a Water Scares Plateau Region of Eastern India. Expo Health 2023, 15, 113–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, L.A.; Parashar, N.; Kumari, R.; Kumar, A.; Mondal, D.; Ghosh, A.; Polya, D.A. Household and Community Systems for Groundwater Remediation in Bihar, India: Arsenic and Inorganic Contaminant Removal, Controls and Implications for Remediation Selection. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 830, 154580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.H.; Lingas, E.O.; Rahman, M. Contamination of Drinking-Water by Arsenic in Bangladesh: A Public Health Emergency. Bull. World Health Organ. 2000, 78, 1093–1103. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, S.A.; Khan, M.A.; Faruquee, M.H.; Dutta, S.; Tani, M.; Kobayashi, M.; Shinohara, H. Arsenicosis: Nutrition and Socioeconomic Factors. J. Pre. Soc. Med. 2012, 31, 51–62. [Google Scholar]
- Flora, S.J.S. (Ed.) Handbook of Arsenic Toxicology; Academic Press: London, UK, 2015; ISBN 978-0-12-418688-0. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, S.A.; Khan, M.H.; Haque, M. Arsenic Contamination in Groundwater in Bangladesh: Implications and Challenges for Healthcare Policy. Risk Manag. Healthc. Policy 2018, 11, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UNICEF. Drinking Water Quality in Bangladesh; UNICEF: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- EPA. Drinking Water Regulations and Contaminants.; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Smedley, P.L.; Kinniburgh, D.G. A Review of the Source, Behaviour and Distribution of Arsenic in Natural Waters. Appl. Geochem. 2002, 17, 517–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, F.S.; Gault, A.G.; Boothman, C.; Polya, D.A.; Charnock, J.M.; Chatterjee, D.; Lloyd, J.R. Role of Metal-Reducing Bacteria in Arsenic Release from Bengal Delta Sediments. Nature 2004, 430, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArthur, J.M.; Banerjee, D.M.; Hudson-Edwards, K.A.; Mishra, R.; Purohit, R.; Ravenscroft, P.; Cronin, A.; Howarth, R.J.; Chatterjee, A.; Talukder, T.; et al. Natural Organic Matter in Sedimentary Basins and Its Relation to Arsenic in Anoxic Ground Water: The Example of West Bengal and Its Worldwide Implications. Appl. Geochem. 2004, 19, 1255–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlet, L.; Polya, D.A. Arsenic in Shallow, Reducing Groundwaters in Southern Asia: An Environmental Health Disaster. Elements 2006, 2, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polya, D.; Charlet, L. Rising Arsenic Risk? Nat. Geosci. 2009, 2, 383–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polya, D.A.; Middleton, D.R.S. Arsenic in Drinking Water: Sources & Human Exposure. In Best Practice Guide on the Control of Arsenic in Drinking Water; Bhattacharya, P., Polya, D.A., Jovanovic, D., Eds.; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2017; pp. 1–23. ISBN 978-1-78040-492-9. [Google Scholar]
- Polya, D.A.; Sparrenbom, C.; Datta, S.; Guo, H. Groundwater Arsenic Biogeochemistry—Key Questions and Use of Tracers to Understand Arsenic-Prone Groundwater Systems. Geosci. Front. 2019, 10, 1635–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polya, D.A.; Xu, L.; Launder, J.; Gooddy, D.C.; Ascott, M. Distribution of Arsenic Hazard in Public Water Supplies in the United Kingdom—Methods, Implications for Health Risks and Recommendations. In Environmental Arsenic in a Changing World; CRC Press: London, UK, 2019; pp. 22–25. ISBN 978-1-351-04663-3. [Google Scholar]
- Trabucco, A.; Zomer, R.J. Global Soil Water Balance Geospatial Database. CGIAR Consortium for Spatial Information, 2010. CGIAR-CSI GeoPortal. Available online: https://cgiarcsi.community/ (accessed on 22 March 2019).
- Trabucco, A.; Zomer, R.J. Global Aridity Index (Global-Aridity) and Global Potential Evapo-Transpiration (Global- PET) Geospatial Database. CGIAR Consortium for Spatial Information, 2009. CGIAR-CSI GeoPortal. Available online: https://cgiarcsi.community/ (accessed on 18 February 2019).
- Hengl, T. Global Landform and Lithology Class at 250 m Based on the USGS Global Ecosystem Map. 2018. Available online: https://zenodo.org/record/1464846 (accessed on 20 February 2021).
- Hengl, T.; Mendes de Jesus, J.; Heuvelink, G.B.M.; Ruiperez Gonzalez, M.; Kilibarda, M.; Blagotić, A.; Shangguan, W.; Wright, M.N.; Geng, X.; Bauer-Marschallinger, B.; et al. SoilGrids250m: Global Gridded Soil Information Based on Machine Learning. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, J.D.; Broxton, P.D.; Hazenberg, P.; Zeng, X.; Troch, P.A.; Niu, G.; Williams, Z.C.; Brunke, M.A.; Gochis, D. Global 1-Km Gridded Thickness of Soil, Regolith, and Sedimentary Deposit Layers; ORNL DAAC: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Li, H.; Miguez-Macho, G. Global Patterns of Groundwater Table Depth. Science 2013, 339, 940–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedl, M.A.; Sulla-Menashe, D.; Tan, B.; Schneider, A.; Ramankutty, N.; Sibley, A.; Huang, X. MODIS Collection 5 Global Land Cover: Algorithm Refinements and Characterization of New Datasets. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 168–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earth Resources Observation and Science (EROS) Center. Global 30 Arc-Second Elevation (GTOPO30). 2017. Available online: https://www.usgs.gov/centers/eros/science/usgs-eros-archive-digital-elevation-global-30-arc-second-elevation-gtopo30 (accessed on 1 October 2019).
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Lu, P.; Zheng, Z.; Tolliver, D.; Keramati, A. Accident Prediction Accuracy Assessment for Highway-Rail Grade Crossings Using Random Forest Algorithm Compared with Decision Tree. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2020, 200, 106931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wielenga, D. Identifying and Overcoming Common Data Mining Mistakes. In SAS Global Forum; SAS Institute Inc.: Cary, NC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, X.; Korfiatis, G.P.; Christodoulatos, C.; Bang, S. Treatment of Arsenic in Bangladesh Well Water Using a Household Co-Precipitation and Filtration System. Water Res. 2001, 35, 2805–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genç-Fuhrman, H.; Bregnhøj, H.; McConchie, D. Arsenate Removal from Water Using Sand–Red Mud Columns. Water Res. 2005, 39, 2944–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyrovola, K.; Nikolaidis, N.P.; Veranis, N.; Kallithrakas-Kontos, N.; Koulouridakis, P.E. Arsenic Removal from Geothermal Waters with Zero-Valent Iron—Effect of Temperature, Phosphate and Nitrate. Water Res. 2006, 40, 2375–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciardelli, M.C.; Xu, H.; Sahai, N. Role of Fe(II), Phosphate, Silicate, Sulfate, and Carbonate in Arsenic Uptake by Coprecipitation in Synthetic and Natural Groundwater. Water Res. 2008, 42, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Dong, H.; Ma, J.; Jiang, L. Removal of Arsenic from Water: Effects of Competing Anions on As(III) Removal in KMnO4–Fe(II) Process. Water Res. 2009, 43, 3891–3899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiew, H.; Sampson, M.L.; Huch, S.; Ken, S.; Bostick, B.C. Effect of Groundwater Iron and Phosphate on the Efficacy of Arsenic Removal by Iron-Amended BioSand Filters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 6295–6300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinson, C.A.; Reddy, K.J. Adsorption of Arsenic(III) and Arsenic(V) by Cupric Oxide Nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 336, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Halem, D.; Olivero, S.; de Vet, W.W.J.M.; Verberk, J.Q.J.C.; Amy, G.L.; van Dijk, J.C. Subsurface Iron and Arsenic Removal for Shallow Tube Well Drinking Water Supply in Rural Bangladesh. Water Res. 2010, 44, 5761–5769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmanan, D.; Clifford, D.A.; Samanta, G. Comparative Study of Arsenic Removal by Iron Using Electrocoagulation and Chemical Coagulation. Water Res. 2010, 44, 5641–5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitzsche, K.S.; Lan, V.M.; Trang, P.T.K.; Viet, P.H.; Berg, M.; Voegelin, A.; Planer-Friedrich, B.; Zahoransky, J.; Müller, S.-K.; Byrne, J.M.; et al. Arsenic Removal from Drinking Water by a Household Sand Filter in Vietnam—Effect of Filter Usage Practices on Arsenic Removal Efficiency and Microbiological Water Quality. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 502, 526–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annaduzzaman, M.; Rietveld, L.C.; Hoque, B.A.; van Halem, D. Sequential Fe2+ Oxidation to Mitigate the Inhibiting Effect of Phosphate and Silicate on Arsenic Removal. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2022, 17, 100749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leupin, O.X.; Hug, S.J. Oxidation and Removal of Arsenic (III) from Aerated Groundwater by Filtration through Sand and Zero-Valent Iron. Water Res. 2005, 39, 1729–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, I.; Gupta, V.K. Advances in Water Treatment by Adsorption Technology. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2661–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, R.; Richards, L.A.; Roshan, A.; Polya, D.A. Artificial Intelligence Modelling to Support the Groundwater Chemistry-Dependent Selection of Groundwater Arsenic Remediation Approaches in Bangladesh. Water 2023, 15, 3539. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203539
Wu R, Richards LA, Roshan A, Polya DA. Artificial Intelligence Modelling to Support the Groundwater Chemistry-Dependent Selection of Groundwater Arsenic Remediation Approaches in Bangladesh. Water. 2023; 15(20):3539. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203539
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Ruohan, Laura A. Richards, Ajmal Roshan, and David A. Polya. 2023. "Artificial Intelligence Modelling to Support the Groundwater Chemistry-Dependent Selection of Groundwater Arsenic Remediation Approaches in Bangladesh" Water 15, no. 20: 3539. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203539
APA StyleWu, R., Richards, L. A., Roshan, A., & Polya, D. A. (2023). Artificial Intelligence Modelling to Support the Groundwater Chemistry-Dependent Selection of Groundwater Arsenic Remediation Approaches in Bangladesh. Water, 15(20), 3539. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203539







