Evaluate the Biomass of Fenneropenaeus chinensis from the Southern Coast of Shandong Peninsula Using eDNA
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
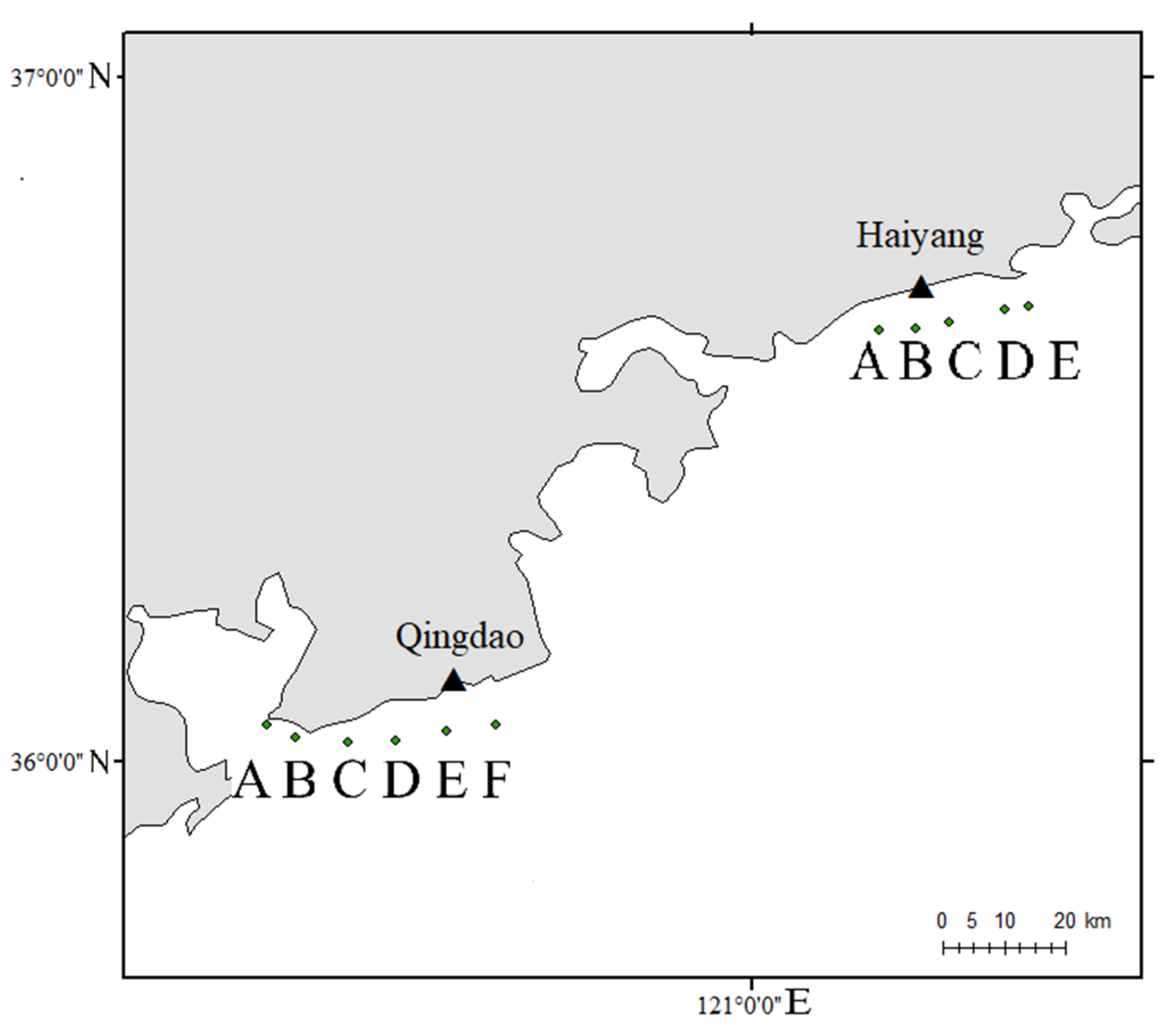
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
3. Results
3.1. eDNA Concentration of F. chinensis in Water
3.2. Estimation of the Biomass of F. chinensis in Natural Waters
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ficetola, G.F.; Miaud, C.; Pompanon, F.; Taberlet, P. Species detection using environmental DNA from water samples. Biol. Lett. 2008, 4, 423–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jerde, C.L.; Chadderton, W.L.; Mahon, A.R.; Renshaw, M.A.; Lodge, D.M. Detection of Asian carp DNA as part of a Great Lakes basin-wide surveillance program. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2013, 70, 522–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turner, C.R.; Miller, D.J.; Coyne, K.J.; Joel, C. Improved methods for capture, extraction, and quantitative assay of environmental DNA from Asian bigheaded carp (hypophthalmichthys spp.). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miya, M.; Sato, Y.; Fukunaga, T.; Sado, T.; Poulsen, J.Y.; Sato, K.; Minamoto, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Yamanaka, H.; Araki, H.; et al. MiFish, a set of universal PCR primers for metabarcoding environmental DNA from fishes: Detection of more than 230 subtropical marine species. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2015, 2, 150088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stoeckle, M.Y.; Adolf, J.; Charlop-Powers, Z. Trawl and eDNA assessment of marine fish diversity, seasonality, and relative abundance in coastal New Jersey, USA. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2021, 78, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongo, Y.; Nishijima, S.; Kanamori, Y. Fish environmental DNA in Tokyo Bay: A feasibility study on the availability of environmental DNA for fisheries. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 47, 101950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lu, G.; Zhao, L.; Du, X.; Gao, T. Assessment of fishery resources using environmental DNA: The large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) in the East China Sea. Fish. Res. 2021, 235, 105813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, M.A.; Turner, C.R. The ecology of environmental DNA and implications for conservation genetics. Conserv. Genet. 2016, 17, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adams, C.I.M.; Knapp, M.; Gemmell, N.J.; Jeunen, G.J.; Taylor, H.R. Beyond Biodiversity: Can environmental DNA (eDNA) cut it as a population genetics tool? Genes 2019, 10, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sigsgaard, E.E.; Nielsen, I.B.; Bach, S.S. Population characteristics of a large whale shark aggregation inferred from seawater environmental DNA. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2016, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, C.S.; Steel, D.; Nieukirk, S.; Klinck, H. Environmental DNA (eDNA) from the wake of whales: Droplet digital PCR for detection and species identification. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Juhel, J.-B.; Marques, V.; Polanco Fernández, A. Detection of the elusive Dwarf sperm whale (Kogia sima) using environmental DNA at Malpelo island (Eastern Pacific, Colombia). Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 2956–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldigo, B.P.; Sporn, L.A.; George, S.D.; Ball, J.A. Efficacy of environmental DNA to detect and quantify brook trout popu-lations in headwater streams of the Adirondack Mountains, New York. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2017, 146, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qian, T.; Shan, X.; Wang, W.; Jin, X. Effects of Temperature on the Timeliness of eDNA/eRNA: A Case Study of Fen-neropenaeus chinensis. Water 2022, 14, 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Shan, X.; Wang, W.; Ding, X.; Dai, F.; Lv, D.; Wu, H. Qualitative and quantitative detection using eDNA technology: A case study of Fenneropenaeus chinensis in the Bohai Sea. Aquac. Fish. 2020, 5, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejean, T.; Valentini, A.; Duparc, A.; Pellier-Cuit, S.; Pompanon, F.; Taberlet, P.; Miaud, C. Persistence of environmental DNA in freshwater ecosystems. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomsen, P.F.; Kielgast, J.; Iversen, L.L.; Møller, P.R.; Rasmussen, M.; Willerslev, E. Detection of a diverse marine fish fauna using environmental DNA from seawater samples. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klymus, K.E.; Richter, C.A.; Chapman, D.C. Quantification of eDNA shedding rates from invasive bighead carp Hy-pophthalmichthys nobilis and silver carp Hypophthalmichthys molitrix. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 183, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salter, I.; Joensen, M.; Kristiansen, R. Environmental DNA concentrations are correlated with regional biomass of Atlantic cod in oceanic waters. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, J.; Zhu, J.; Ren, S. Study on dynamic of stock recruitment relationship (SRR) of Penaeid shrimp (Penaeus chinensis) in the Bohai Sea. J. Fish. Sci. China 1996, 3, 20–26. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Y.; Qiu, S. Effects of Penaeus bohae on yield during autumn season. Chin. Fish. 1995, 10, 35–38. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Zhou, J.; Lü, Z.; Dong, J.; Liu, M.; Jin, X. Resources enhancement of Fenneropenaeus orientalis in the Bohai Sea. Prog. Fish. Sci. 2012, 33, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Zhuang, Z.; Deng, J. Stock enhancement and translocation of the shrimp Penaeus chinensis in China. Fish. Res. 2006, 80, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillotson, M.D.; Kelly, R.P.; Duda, J.J.; Hoy, M.; Kralj, J.; Quinn, T.P. Concentration of environmental DNA (eDNA) reflect spawning salmon abundance at fine spatial and temporal scales. Biol. Conserv. 2018, 220, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, T.; Allen, J.M.; Bell, D. Environmental DNA for the enumeration and management of Pacific salmon. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2019, 19, 597–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Locations in the Qingdao Sea Area | eDNA Concentration (Copies/L) | Locations in Haiyang Sea Area | eDNA Concentration (Copies/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surface layer of A | 2510.34 | Surface layer of A | 4795.98 |
| Bottom layer of A | 5966.94 | Surface layer of B | 4908.12 |
| Bottom layer of B | 1972.32 | Middle layer of B | 6297.90 |
| Bottom layer of C | 2756.46 | Bottom layer of B | 5707.80 |
| Surface layer of D | 6215.58 | Surface layer of C | 8715.00 |
| Bottom layer of D | 4512.48 | Middle layer of C | 5672.94 |
| Surface layer of E | 6937.56 | Bottom layer of C | 6105.12 |
| Bottom layer of E | 5029.92 | Surface layer of D | 8687.28 |
| Bottom layer of F | 3400.32 | Middle layer of D | 7574.38 |
| Surface layer of E | 7672.14 | ||
| Middle layer of E | 8324.40 | ||
| Bottom layer of E | 6384.42 | ||
| Mean | 4366 ± 1691 | Mean | 6737 ± 1348 |
| Number of Culture Ponds | eDNA Concentration (Copies/L) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 3,487,183 |
| 2 | 4,021,327 |
| 3 | 7,605,872 |
| 4 | 6,015,915 |
| 5 | 1,227,555 |
| 6 | 1,656,314 |
| 7 | 1,138,116 |
| 8 | 1,474,368 |
| Mean | 3.33 × 106 ± 2.28 × 106 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, S.; Lyu, D.; Qian, T.; Shan, X.; Wang, W. Evaluate the Biomass of Fenneropenaeus chinensis from the Southern Coast of Shandong Peninsula Using eDNA. Water 2023, 15, 342. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15020342
Sun S, Lyu D, Qian T, Shan X, Wang W. Evaluate the Biomass of Fenneropenaeus chinensis from the Southern Coast of Shandong Peninsula Using eDNA. Water. 2023; 15(2):342. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15020342
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Song, Ding Lyu, Tangyi Qian, Xiujuan Shan, and Weiji Wang. 2023. "Evaluate the Biomass of Fenneropenaeus chinensis from the Southern Coast of Shandong Peninsula Using eDNA" Water 15, no. 2: 342. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15020342





