The Geochemical and Environmental Characteristics of Trace Metals in Coastal Sediment Discharge off the Mailiao Industrial Zone of Central Western Taiwan
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Analytical Methods
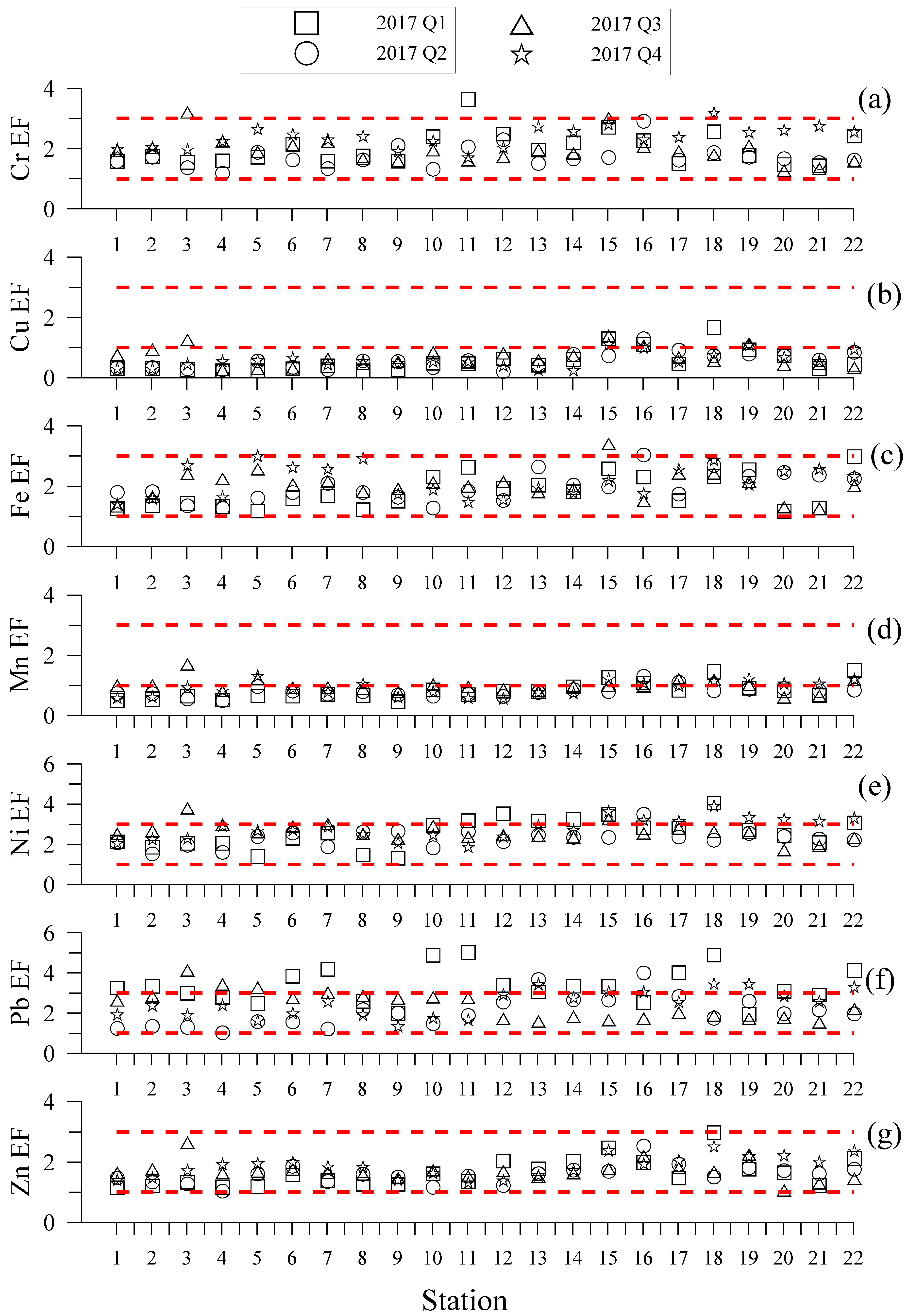
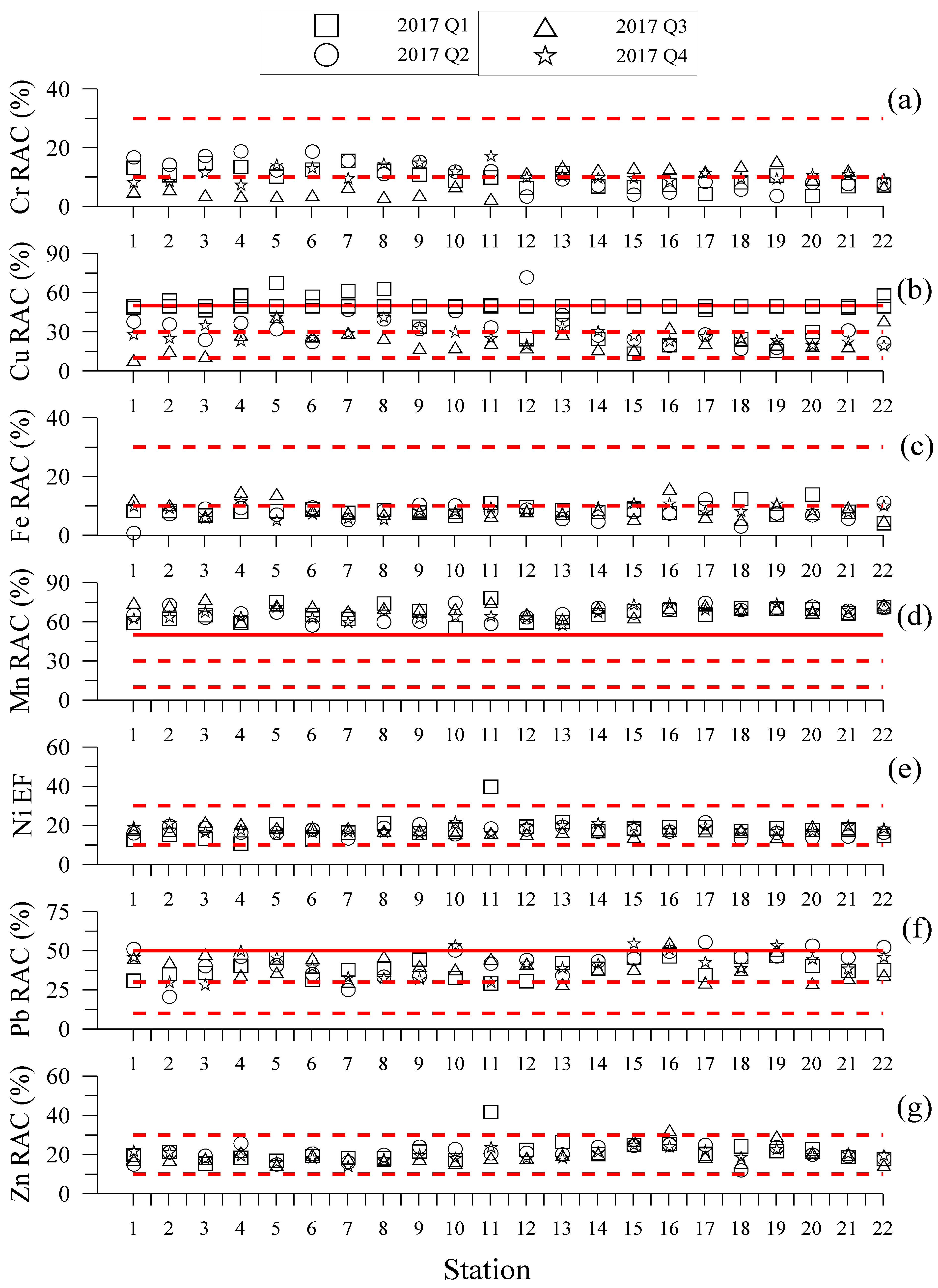
2.3. Trace Metals Contamination Assessment
3. Results
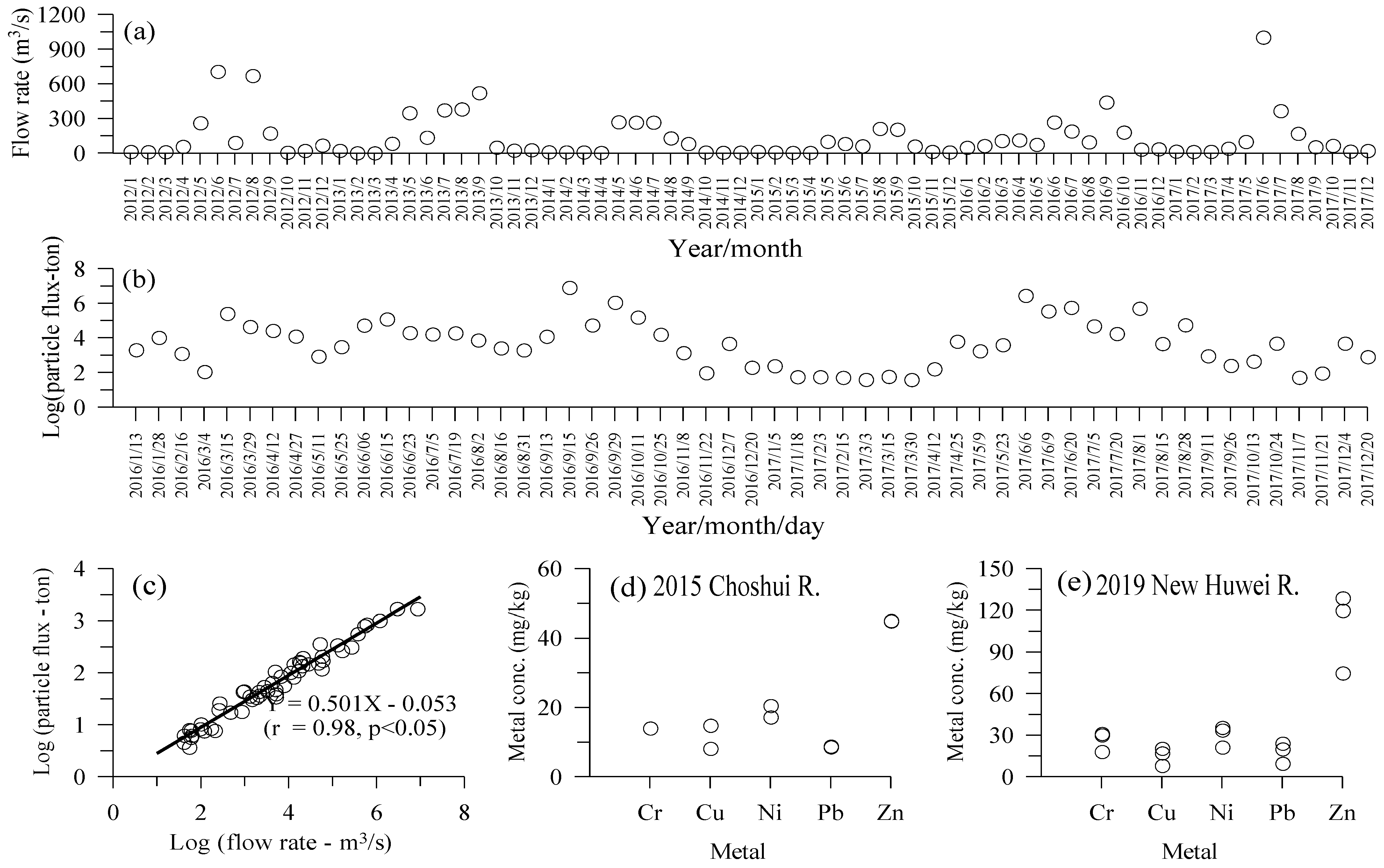
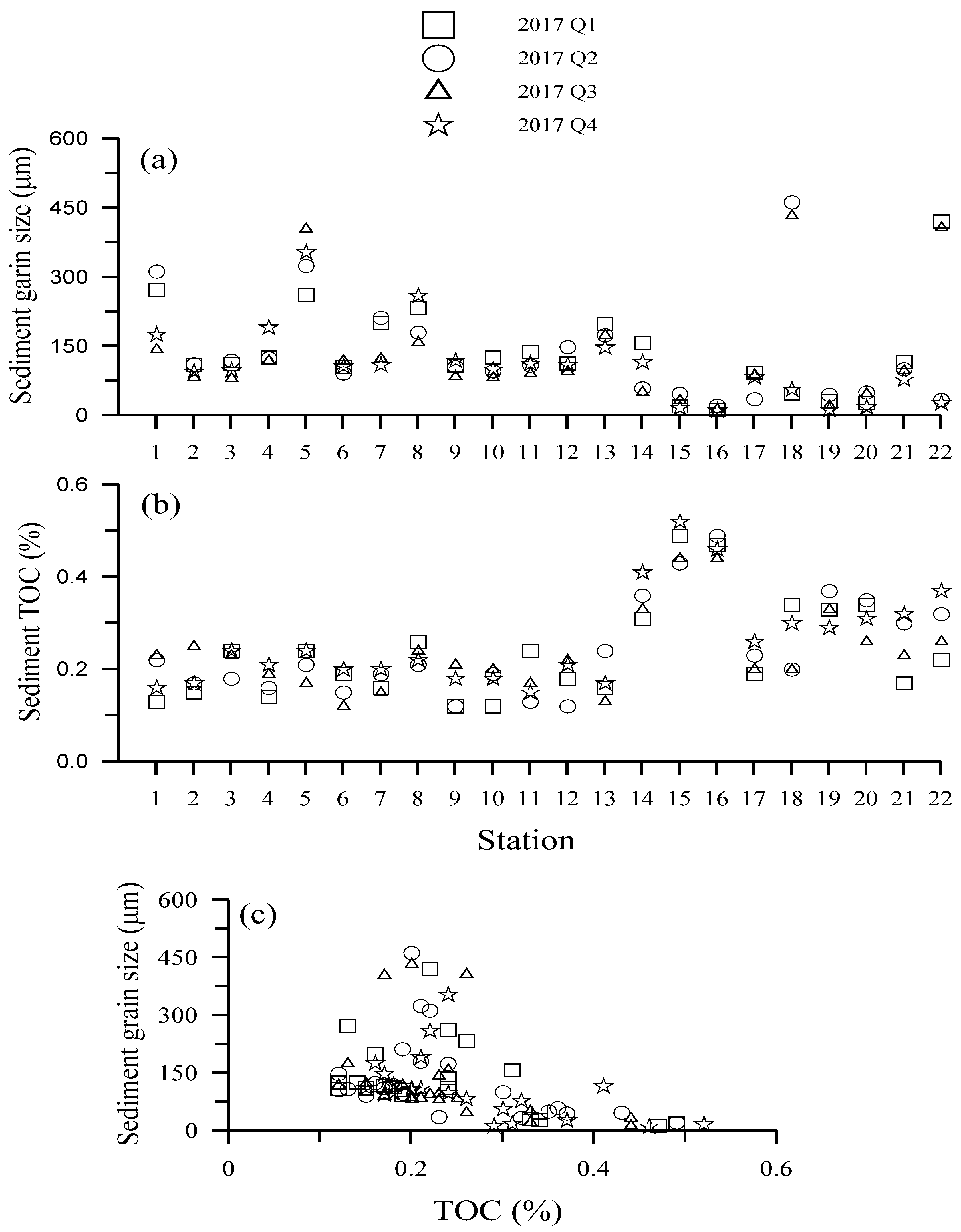
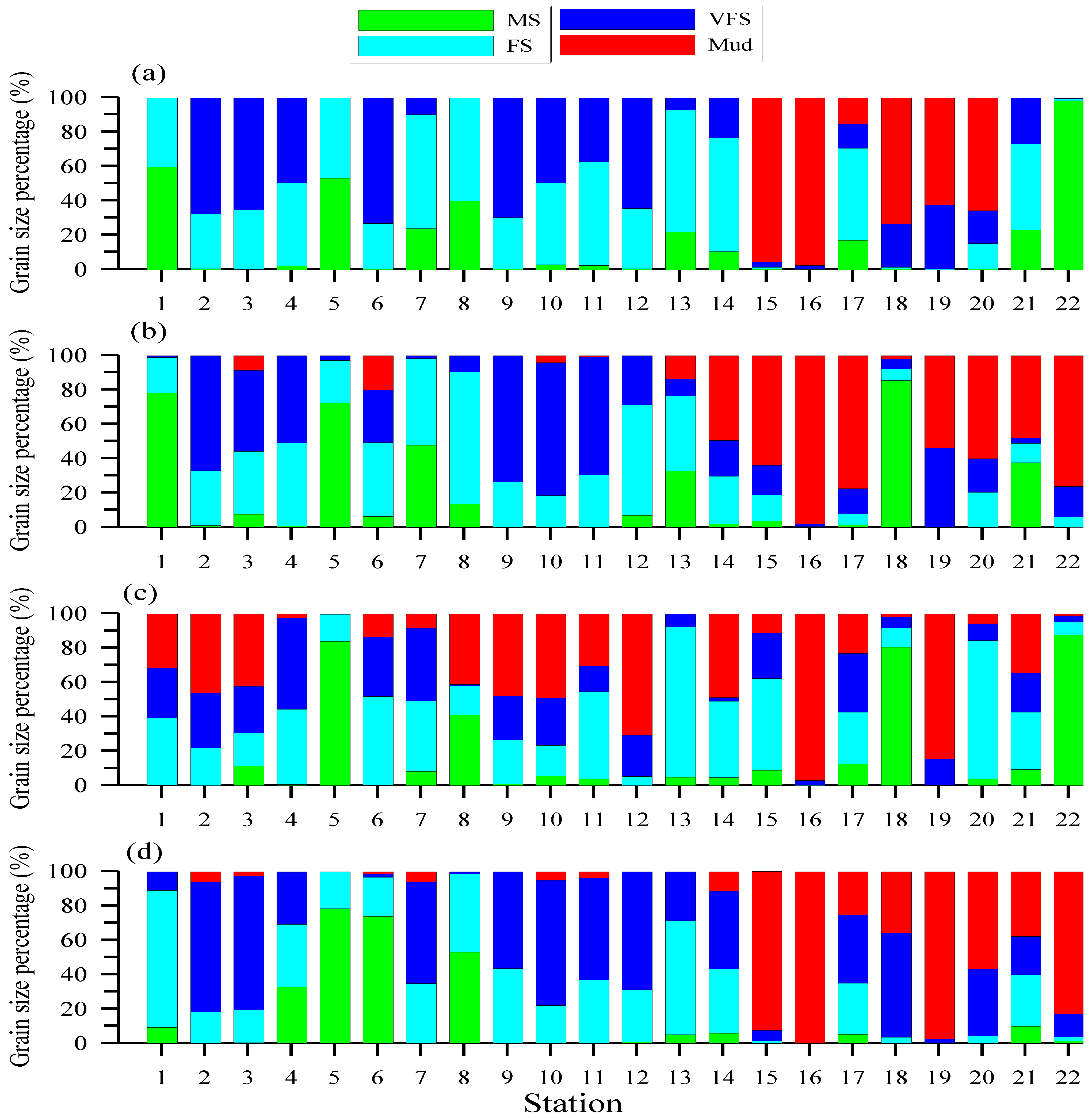
3.1. Grain Size (GS) and TOC
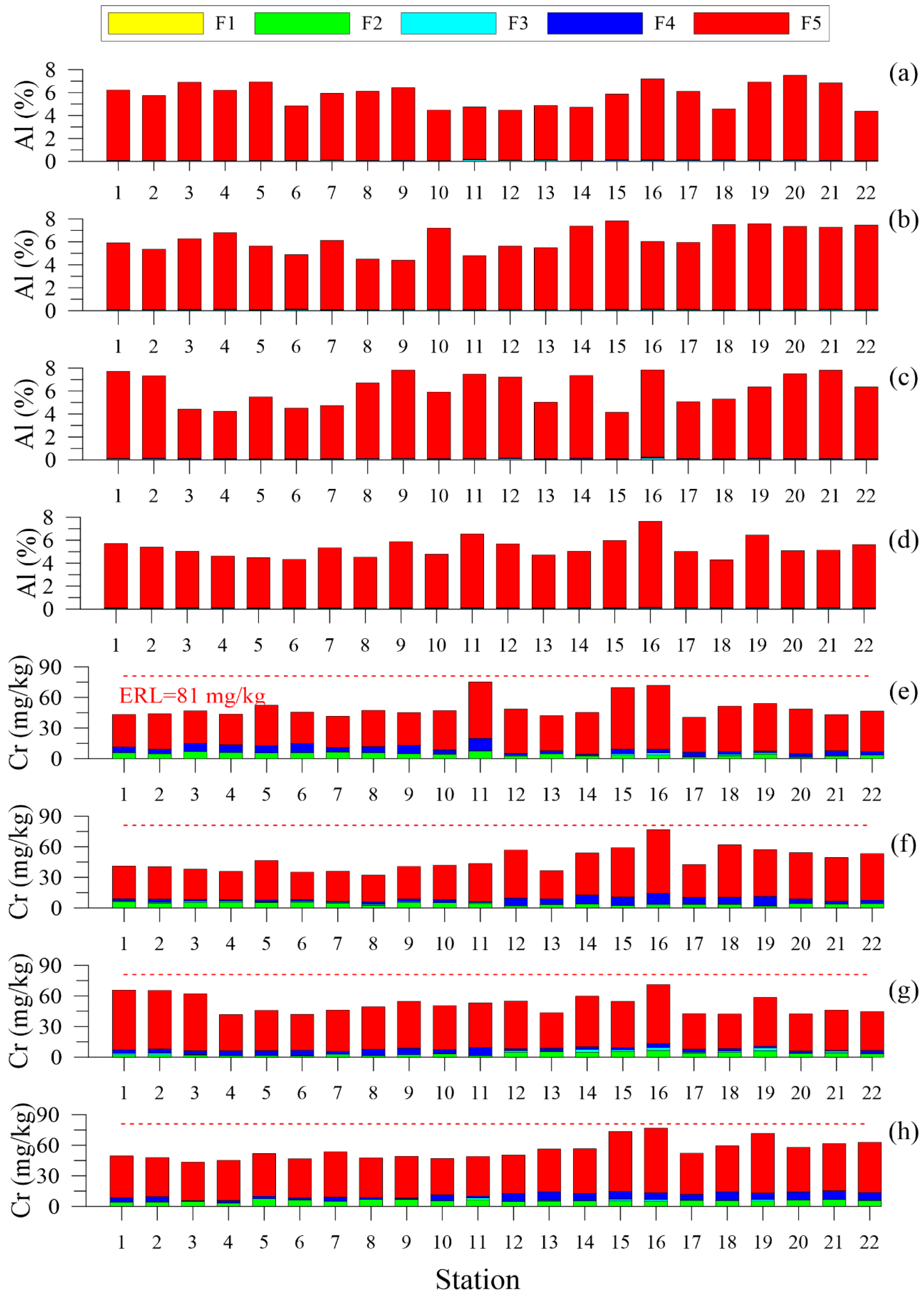
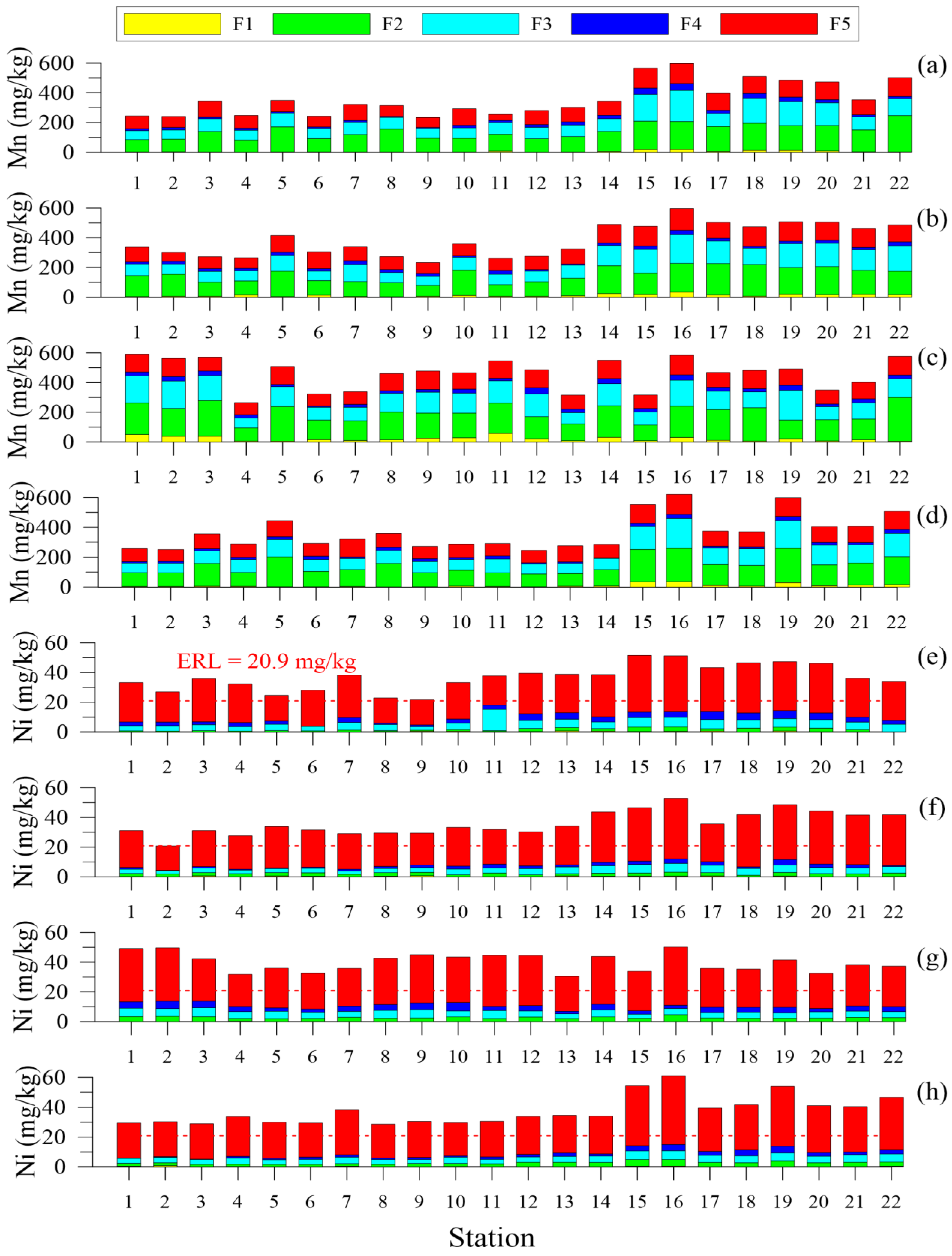
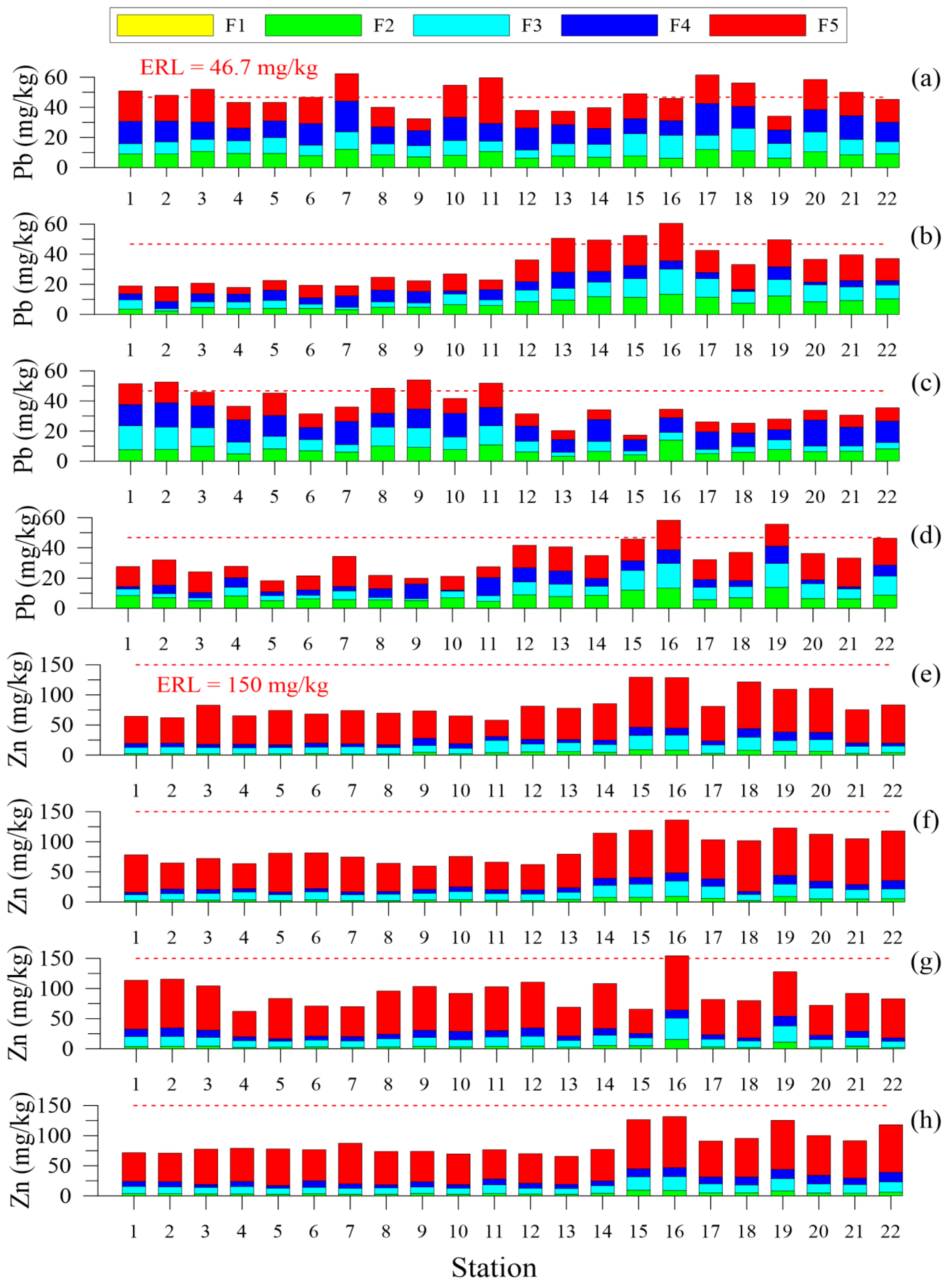
3.2. Trace Metals
3.3. Trace Metals Contamination Assessment
4. Discussion
4.1. Grain Size and TOC
4.2. Trace Metals
4.2.1. Metals Total Concentrations
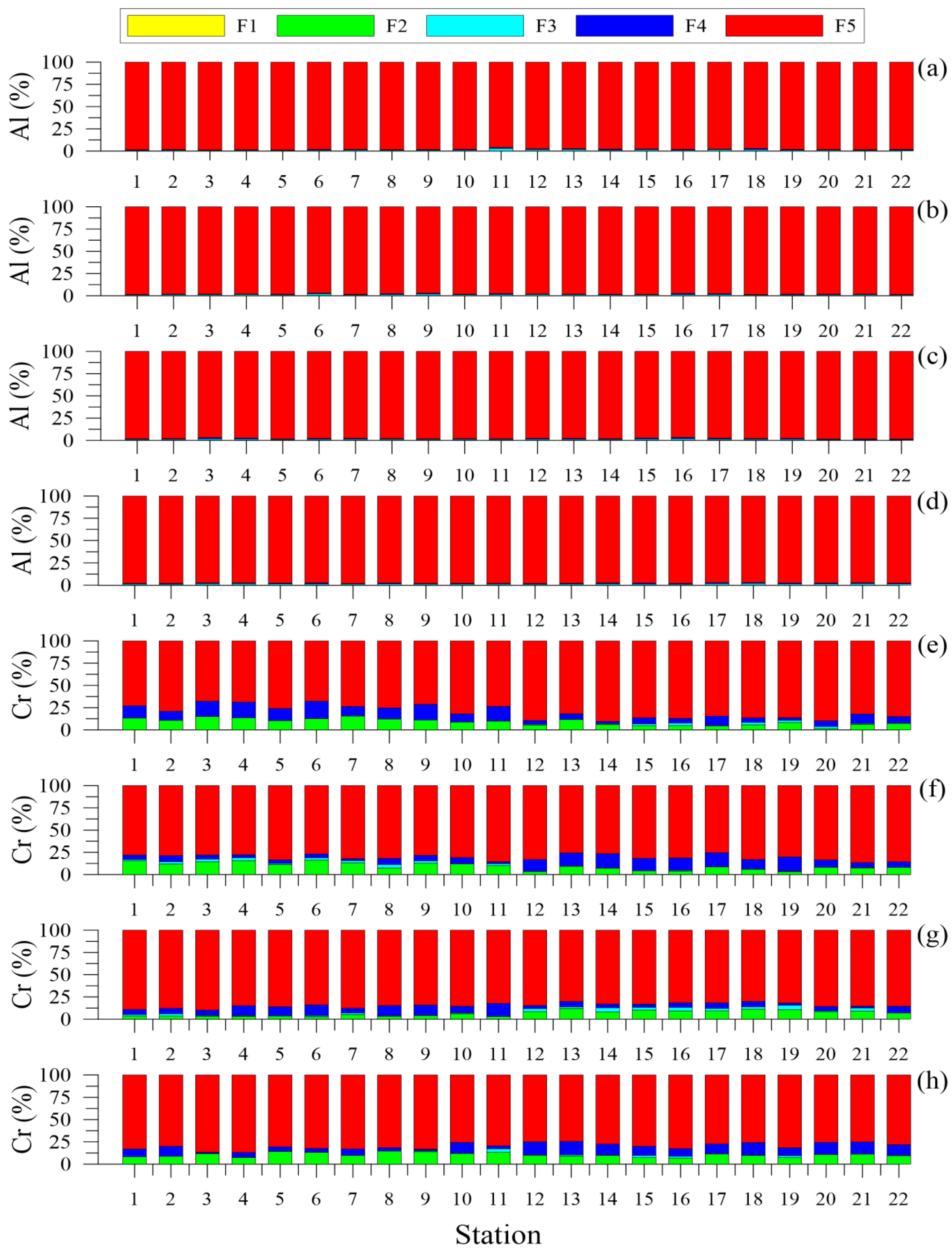
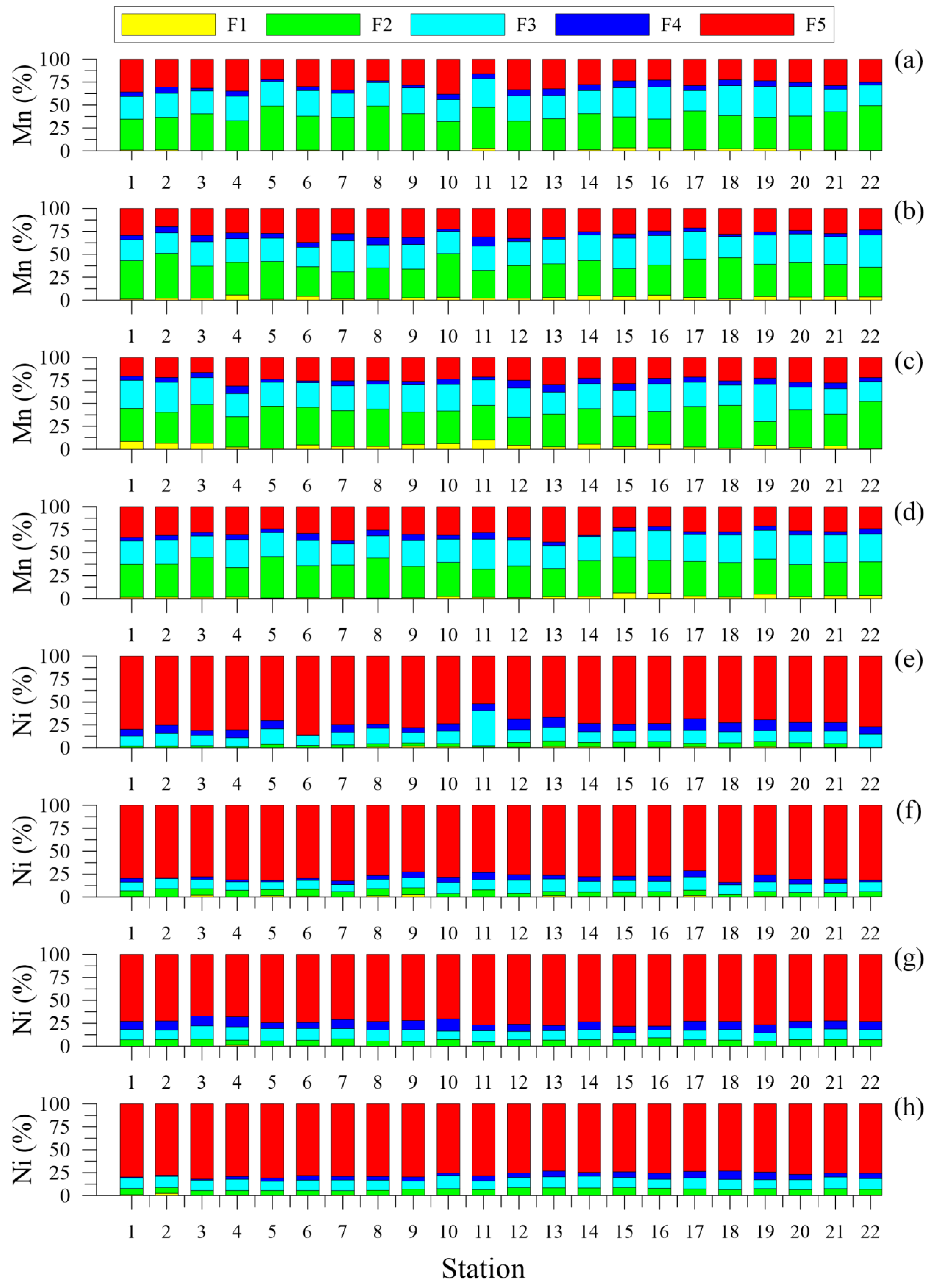
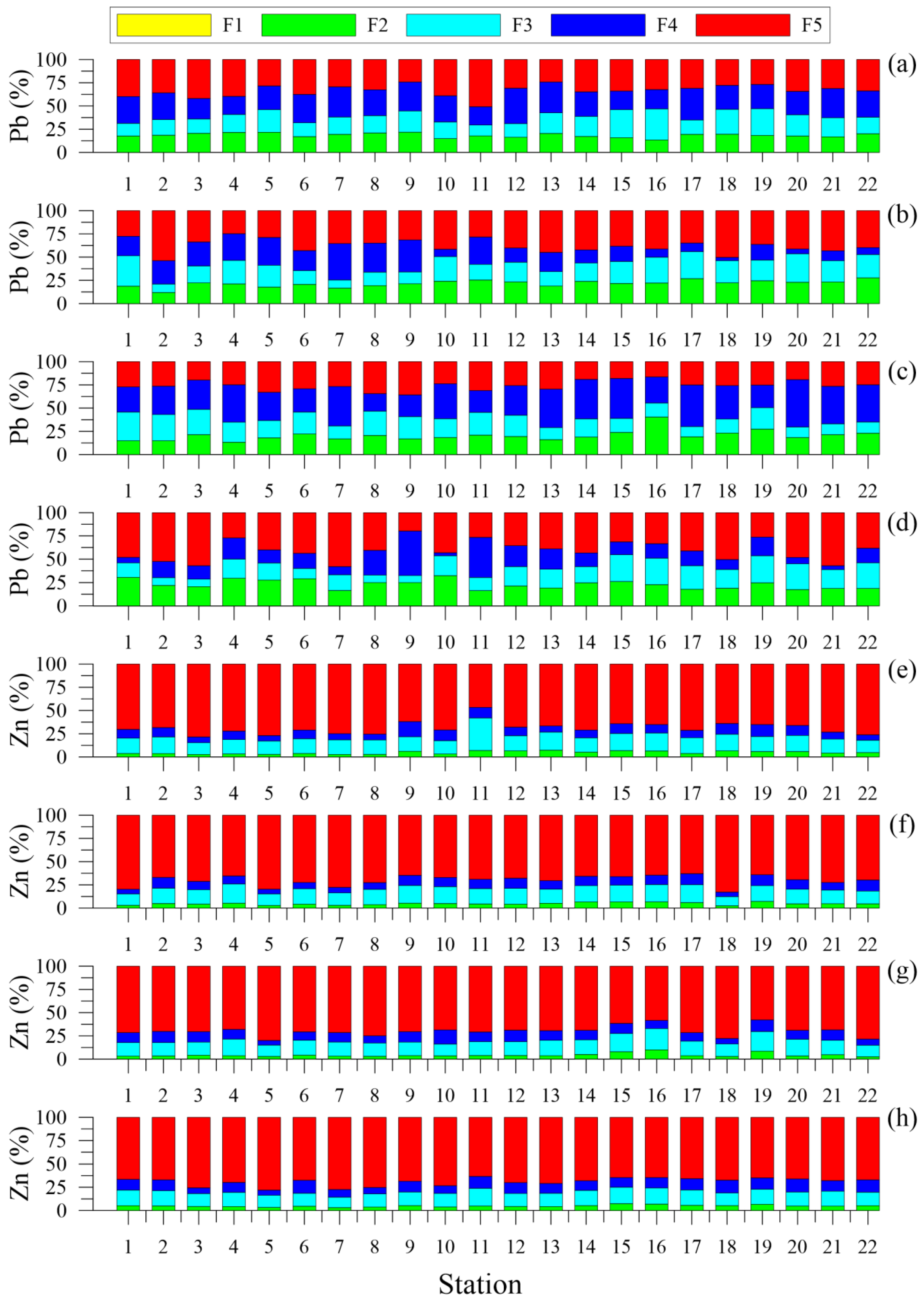
4.2.2. Trace Metals Speciation
- Fe, Ni, and Zn: F5 > F3 > F4 > F2 > F1
- Cr: F5 > F2 > F4 > F3 > F1
- Cu: F5 > F4 > F3 > F2 > F1
- Mn: F2 > F3 > F5 > F4 > F1
- Pb: F5 > F4 > F2 > F3 > F1
4.2.3. Trace Metals Contamination Assessment
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, J.P.; Liu, C.S.; Xu, K.H.; Milliman, J.D.; Chiu, J.K.; Kao, S.J.; Lin, S.W. Flux and fate of small mountainous rivers derived sediments into the Taiwan Strait. Mar. Geol. 2008, 256, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, S.J.; Milliman, J.D. Water and sediment discharge from small mountainous rivers, Taiwan: The role of lithology, episodic events, and human activities. J. Geol. 2008, 116, 431–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Water Resources Bureau. Hydrological Year Book of Taiwan, Ministry of Economic Affairs, Republic of China 2016. Available online: https://gweb.wra.gov.tw/wrhygis (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- Liou, S.M.; Lo, S.L.; Wang, S.H. A Generalized Water Quality Index for Taiwan. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2004, 96, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.Y.; Fang, T.H.; Wu, C.H.; Lee, H.J. Interplay between Asian Monsoon and Tides Affects the Plume Dispersal of the New Hu-Wei River off the Coast of Midwest Taiwan. Water 2022, 14, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, E.R.; Macdonald, D.D.; Smith, S.; Calder, F.D. Incidence of adverse biological effects within ranges of chemical concentrations in marine and estuarine sediments. Environ. Manag. 1995, 19, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neff, J.M. Bioaccumulation in Marine Organisms: Effect of Contaminants from Oil Well Produced Water; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Bjerregaard, P.; Anderson, C.B.I.; Anderson, O. Ecotoxicology of Metals-Sources, Transport and Effects on the Ecosystem. In Handbook on the Toxicology of Metals; Nordberg, G.F., Fowler, B.A., Nordberg, M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Chapter 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luoma, S.N. Processes Affecting Metal Concentrations in Estuarine and Coastal Marine Sediments. In Heavy Metals in the Marine Environment; Furness, R.W., Rainbow, P.S., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1990; pp. 51–66. [Google Scholar]
- Loring, D.H.; Rantala, R.T.T. Manual for the geochemical analyses of marine sediments and suspended particulate matter. Earth Sci. Rev. 1992, 32, 235–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacon, J.; Davidson, C. Is there a future for sequential chemical extraction. Analyst 2008, 133, 25–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessier, A.; Campbell, P.G.C.; Bisson, M. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Anal. Chem. 1979, 51, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, S.Y. Tidal modulation of estuarine plumes. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1990, 20, 1115–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.T.; Chao, S.Y.; Fan, K.L. Wind modulation of small-scale plumes from Yin-Yang bay. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 1994, 5, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, I.; Nishikawa, M.; Tanimura, T.; Quan, H. Change in size distribution and chemical composition of kosa (Asian dust) aerosol during long-range transport. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 4253–4263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, H.; Chian, W.S.; Kao, S.J.; Liu, J.T.; Liu, K.K.; Liu, P.L.F. Sediment Dynamics Observed in the Jhoushuei River and Adjacent Coastal Zone in Taiwan Strait. Oceanography 2011, 24, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, T.H.; Hong, E. Mechanisms Influencing the Spatial Distribution of Trace Metals in Surficial Sediments off the South-Western Taiwan. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1999, 38, 1026–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folk, R.L. Petrologie of Sedimentary Rocks; Hemphll Publishing Company: Austin, TX, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Kumkrong, P.; Mercier, P.H.J.; Gedara, I.P.; Mihai, O.; Tyo, D.D.; Cindy, J.; Kingston, D.M.; Mester, Z. Determination of 27 metals in HISS-1, MESS-4 and PACS-3 marine sediment certified reference materials by the BCR sequential extraction. Talanta 2021, 221, 121543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kryc, K.A.; Murray, R.W.; Murray, D.W. Elemental fractionation of Si, Al, Ti, Fe, Ca, Mn, P and Ba in five marine sedimentary reference materials: Results from sequential extractions. Anal. Chim. Acta 2003, 487, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, E.R.; Macdonald, D.D.; Severn, C.G.; Hong, C.B. Classifying probabilities of acute toxicity in marine sediments with emprically derived sediment quality guildlines. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2000, 19, 2598–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, G.A., Jr. Sediment quality criteria in use around the world. Limnology 2002, 3, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, G.F. Determination of sediment metal background concentrations and enrichment in marine environment—A critical review. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 580, 813–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, G. Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. Geojournal 1969, 2, 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- Zoller, W.H.; Gladney, E.S.; Duce, R.A. Atmospheric Concentrations and Sources of Trace Metals at the South Pole. Science 1974, 183, 198–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahim, G.M.S.; Parker, R.J. Assessment of heavy metal enrichment factors and the degree of contamination in marine sediments from Tamaki Estuary, Auckland, New Zealand. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 136, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhuang, W.; Chen, C.T.A.; Zhang, Y. Sediment quality of the SW coastal Laizhou Bay, Bohai Sea, China: A comprehensive assessment based on the analysis of heavy metals. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.H.; Huang, Z.T.; Chang, F.W. The geochemical and environmental characteristics of trace metals in surface sediments of the river estuarine mouths around the Taiwan Island and the Taiwan Strait. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 182, 113967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumm, W.; Morgan, J.J. Aquatic Chemistry, 3rd ed.; Wiley-Interscience Publication: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Milliman, J.D.; Kao, S.J. Hyperpycnal discharge of fluvial sediment to the ocean: Impact of Super-Typhoon Herb (1996) on Taiwanese Rivers. J. Geol. 2005, 113, 503–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milliman, J.D.; Lin, S.W.; Kao, S.J.; Liu, J.P.; Liu, C.S.; Chiu, J.K.; Lin, Y.C. Short-term changes in seafloor character due to flood-derived hyperpycnal discharge: Typhoon Mindulle, Taiwan, July 2004. Geology 2007, 35, 779–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, X.; Zhou, F.; Chen, F.; Lao, Q.; Zhu, Q.; Meng, Y.; Chen, C. Spatial and seasonal variations of sedimentary organic matter in a subtropical bay: Implication for human interventions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, J.; Han, Y.; Tan, J.; Abarike, G.A.; Song, Z. The characteristics of organic carbon in the offshore sediments surrounding the Leizhou Peninsula, China. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 648338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, L.; Gomoiu, M.T.; Boiceno, L.; Vasiliu, D. Total organic carbon (TOC) of the surface layer sediments covering the seafloor of the Romanian Black Sea coast. GeoEcoMarina 2012, 12, 121–132. [Google Scholar]
- Birch, G.F. Indicators of Anthropogenic Change and Biological Risk in Coastal Aquatic Environments. In Treaties on Estuarine and Coastal Science, Geochemistry of Estuaries and Coasts; Shimmield, G., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 4, Chapter 9. [Google Scholar]
- Sakai, H.; Kojima, Y.; Saito, K. Distribution of heavy metals in water and sieved sediment in the Toyohira River. Water Res. 1986, 20, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubb, J.M.; Rudd, T.; Lester, J.N. Distribution of heavy metals in the River Yare and its associated broads III. Lead and zinc. Sci. Total Environ. 1990, 102, 189–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.H.; Wang, C.W. Distribution of Geochemical Species of P, Fe and Mn in Surface Sediments in the Eutrophic Estuary, Northern Taiwan. Water 2021, 13, 3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.H.; Li, J.Y.; Feng, H.M.; Chen, H.Y. Distribution and contamination of trace metals in surface sediments of the East China Sea. Mar. Environ. Res. 2009, 68, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, T.H.; Lien, C.Y. Mini review of trace metal contamination status in East China Sea sediment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 152, 110874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pejman, A.; Bidhendi, G.N.; Ardestani, M.; Saeedi, M.; Baghvand, A. Fractionation of heavy metals in sediments and assessment of their availability risk: A case study in the northwestern of Persian Gulf. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 114, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.B.; Meng, K. Risk assessment of toxic metals in marine sediments from the Arctic Ocean using a modified BCR sequential extraction procedure. Environ. Sci. Health A 2018, 53, 278–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Zheng, K.; Qin, Z.; Wang, Y. Spatial distribution and risk assessment of metal(loid) in marine sediments in the Arctic Ocean and Bering Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 179, 113729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnick, R.L.; Gao, S. Composition of the Continental Crust. In Treatise on Geochemistry; Holland, H.D., Turekian, K.K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; Volume 3, pp. 1–64. [Google Scholar]
- Koshikawa, M.K.; Takamatsu, T.; Takada, J.; Zhu, M.; Xu, B.; Chen, Z.; Murakami, S.; Xu, K.; Watanabe, M. Distribution of dissolved and particulate elements in the Yangtze estuary in 2007–2002: Background data before the closure of the Three Gorges Dam. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2007, 71, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Li, J.; Bi, N.; Wang, H.; Yang, J.; Wei, H.; Zhao, J.; Li, G.; Yin, X.; Liu, M.; et al. Seasonal variability and flux of particulate trace elements from the Yellow River: Impacts of the anthropogenic flood event. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 91, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyler, P.T.; Boaventura, G.R. Distribution and partition of trace metals in the Amazon basin. Hydrol. Process. 2003, 17, 1345–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupre, B.; Gaillardet, J.; Rousseau, D.; Allegre, C.J. Major and trace elements of river-borne material: The Congo Basin. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1996, 60, 1301–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ip, C.C.M.; Li, X.D.; Zhang, G.; Wai, O.W.H.; Li, Y.S. Trace metal distribution in sediments of the Pearl River Estuary and the surrounding coastal area, South China. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 147, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, L.; Song, J.; Yuan, H.; Li, X.; Li, N. Spatial-temporal distribution and environmental risk of arsenic in sediments of the East China Sea. Chem. Geol. 2013, 340, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Pan, S.; Sun, Z.; Ma, R.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S. Heavy metal spatial variability and historical changes in the Yangtze River estuary and North Jiangsu tidal flat. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 98, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhou, F.; Lui, H.K.; Lou, J.Y.; Chen, C.T.A.; Zhuang, W. Trace metals in surface sediments of the Taiwan Strait: Geochemical characteristics and environmental indication. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 10494–10503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, R.; Men, C.; Xu, F.; Guo, L.; Shen, Z. Spatial-temporal distribution and risk assessment of mercury in different fractions in surface sediments from the Yangtze River estuary. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 124, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.G.; Lin, Q.; Yu, Z.L.; Wang, X.N.; Ke, C.L.; Ning, J.J. Speciation and risk of heavy metals in sediments and human health implications of heavy metals in edible nekton in Beibu Gulf, China: A case study of Qinzhou Bay. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 101, 852–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, J.P.; Kinaev, I.; Goonetilleke, A.; Ayoko, G.A. Comparison of partial extraction reagents for assessing potential bioavailability of heavy metals in sediments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 106, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosado, D.; Usero, J.; Morillo, J. Ability of 3 extraction methods (BCR, Tessier and Protease K) to estimate bioavailable metals in sediments from Huelva estuary (Southwestern Spain). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 102, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgay, F.; Abollino, O.; Buoso, S.; Costa, E.; Giacomino, A.; La Gioia, C.; Garofalo, S.F.; Pecoraro, G.; Malandrino, M. Geochemical characterization of a marine sediment core from the Joides Basin, Ross Sea, Antarctica. Mar. Geol. 2020, 428, 106286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougheriet, A.; Ouddane, B.; Fischer, J.C.; Wartel, M.; Leman, G. Variability of dissolved Mn and Zn in the Seine estuary and chemical speciation of these metals in suspended matter. Water Res. 1992, 26, 1359–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougheriet, A.; Wartel, M.; Cordier, C.; Douez, C.; Deram, L.; Martin, E.; Ouddane, B.; Chamley, H.; Recourt, P. Chemical speciation of some particulate elements in the English Channel, and impact of human activities on the magnetic behavior of suspended matter. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1994, 28, 541–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shen, Z.; Wai, O.W.H.; Li, Y.S. Chemical forms of Pb, Zn and Cu in the sediment profiles of the Pearl River Estuary. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2001, 42, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, H.M. Heavy metal distribution in sediments and ecological risk assessment: The role of diagenetic processes in reducing metal toxicity in bottom sediments. Environ. Pollut. 1997, 97, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norwood, W.P.; Borgmann, U.; Dixon, D.G. Chronic toxicity of arsenic, cobalt, chromium and manganese to Hyalella Azteca in relation to exposure and bioaccumulation. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 147, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, A.; Lofts, S.; Merrington, G.; Brown, B.; Stubblefield, W.; Harlow, K. Development of biotic models for chronic manganese toxicity to fish, invertebrate, and algae. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2011, 30, 2407–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twining, B.S.; Baines, S.B. The trace metal composition of marine phytoplankton. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2012, 5, 191–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eklund, B.; Kautsky, L. Review on toxicity testing with marine macroalgae and the need for method standardization-exemplified with copper and phenol. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2003, 46, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruland, K.W.; Lohan, M.C. Controls of Trace Metals in Seawater. In Treaties on Geochemistry: The Ocean and Marine Geochemistry; Holland, H.D., Turekian, K.K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; Volume 6. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.J.; Liu, F.; Yan, Y.; Wang, W.X. Spatial variation and subcellular binding of metals in oysters from a large estuary in China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 70, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Wang, Q.; Wu, H.; Tan, Q.; Wang, W.X. A metabolomics study on the biological effects of metal pollutions in oyster Crassostrea sikamea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 102, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, N.; Wang, W.X. Variations of trace metals in two estuarine environments with contrasting pollution histories. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 485–486, 604–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.H.; Dai, S.Y. Green oysters occurring in an industrial harbor in Central Taiwan. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 124, 1006–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Zhao, Z.; Dai, M. Tracing the recently increasing anthropogenic Pb inputs into the East China Sea shelf sediments using Pb isotopic analysis. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 79, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanenta, P.; Duursma, E.K.; Merks, A.G.A.; Rutzel, H.; Nurnberg, H.W. Distribution of Cd, Pb and Cu between the dissolved and particulate phase in the eastern Scheldt and western Scheldt estuaries. Sci. Total Environ. 1986, 53, 41–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhou, F.; Chen, C.T.A.; Xing, Q. Trace metals in the suspended particulate matter of the Yellow River (Huanghe) Estuary: Concentrations, potential mobility, contamination assessment and the fluxes into the Bohai Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 2015, 104, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlik-Skowrongska, B. Correlations between toxic Pb effects and production of Pb-induced thio peptides in the microalga Stichococcus bacillaris. Environ. Pollut. 2002, 119, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebenezer, V.; Ki, J.S. Evaluation of the sub-lethal toxicity of Cu, Pb, bisphenol A and polychlorinated biphenyl to the marine dinoflagellate Cochlodinium polykrikoides. Algae 2012, 27, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carfagna, S.; Lanza, N.; Salbitani, G.; Basile, A.; Sorbo, S.; Vona, V. Physical and morphological responses of lead or cadmium exposed Chlorella sorokiniana 211-8K (Chlorophyceae). SpringerPlus 2013, 2, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.W.; Choi, H.; Hwang, U.K.; Kang, J.C.; Kang, Y.J.; Kim, K.; Kim, J.H. Toxic effects of lead exposure on bioaccumulation, oxidative stress, neurotoxicity, and immune responses in fish: A review. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 68, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Species Element | F1 Exchangeable | F2 Carbonate | F3 Fe-Mn Oxides | F4 Organic | F5 Residue | Total Conc. | Certified Values | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al | <0.001 | <0.003 | 0.044 ± 0.001 | 0.061 ± 0.001 | 5.78. ± 0.02 | 5.89 ± 0.04 | 8.59 ± 0.23 | 68.6 ± 0.25 |
| Cr | <DL | <DL | 3.99 ± 0.22 | 6.81 ± 0.36 | 75.3 ± 1.29 | 86.1 ± 1.88 | 105 ± 4 | 81.9 ± 1.79 |
| Cu | 1.33 ± 0.19 | 1.01 ± 0.05 | 1.58 ± 0.12 | 8.90 ± 0.42 | 18.13 ± 0.07 | 30.96 ± 0.52 | 33.9 ± 1.6 | 91.3 ± 1.5 |
| Fe | <DL | 0.042 ± 0.000 | 0.698 ± 0.007 | 0.068 ± 0.012 | 3.029 ± 0.044 | 3.837 ± 0.049 | 4.34 ± 0.11 | 88.4 ± 1.1 |
| Mn | 42.22 ± 0.67 | 66.41 ± 1.50 | 78.48 ± 2.13 | 13.44 ± 0.57 | 105.8 ± 0.69 | 306.4 ± 1.42 | 324 ± 12 | 94.6 ± 1.4 |
| Ni | 0.27 ± 0.10 | 2.99 ± 0.35 | 10.78 ± 0.94 | 5.32 ± 0.10 | 32.28 ± 0.02 | 51.65 ± 1.31 | 46.9 ± 2.2 | 110.1 ± 2.8 |
| Pb | <DL | 3.81 ± 0.31 | 4.47 ± 0.16 | <DL | 13.42 ± 0.57 | 21.69 ± 0.10 | 21.1 ± 0.7 | 102.8 ± 0.5 |
| Zn | 2.26 ± 0.08 | 14.47 ± 0.67 | 42.75 ± 0.97 | 13.07 ± 0.58 | 101.57 ± 0.14 | 174.12 ± 1.00 | 159 ± 8 | 109.5 ± 0.6 |
| Al | Cr | Cu | Fe | Mn | Ni | Pb | Zn | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total conc. | 4.13~7.84 | 32.3~76.7 | 3.75~26.6 | 3.18~8.85 | 234~622 | 20.8~61.2 | 17.4~62.3 | 58.0~154 |
| Fraction 1 (%) | <0.01 | <0.1 | <0.1~0.43 | <0.1 | 0.3~10.5 | <0.1~2.6 | <0.1 | <0.1 |
| Fraction 2 (%) | 0.04~0.31 | 1.4~16.3 | 2.1~15.0 | 0.23~2.34 | 25.8~51.3 | 0.3~9.3 | 11.9~40.5 | 2.5~10.0 |
| Fraction 3 (%) | 0.78~2.86 | <0.1~5.0 | 1.0~57.2 | 0.57~14.3 | 21.3~40.6 | 7.8~37.9 | 7.2~33.3 | 9.7~35.1 |
| Fraction 4 (%) | 0.42~1.32 | 1.7~19.5 | 1.3~55.3 | 0.2~1.99 | 1.2~10.1 | 0.8~13.2 | 3.3~51.0 | 4.9~16.2 |
| Fraction 5 (%) | 95.9~98.7 | 67.7~90.3 | 17.7~68.0 | 83.1~98.6 | 16.0~38.4 | 52.0~86.0 | 16.4~58.0 | 46.7~82.7 |
| Enrichment factor | 1.21~3.65 | 0.23~1.69 | 1.19~3.43 | 0.49~1.73 | 1.35~4.09 | 1.06~5.06 | 1.06~3.00 | |
| Igeo | −0.70~0.55 | −3.32~−0.49 | −0.72~0.75 | −1.95~−0.53 | −0.53~1.03 | −0.79~1.05 | −0.88~0.54 | |
| Risk assessment code | 2.9~19.0 | 9.1~72.2 | 1.0~16.2 | 56.0~78.6 | 11.1~40.2 | 21.0~55.9 | 12.3~42.1 |
| TOC | Al | Cr | Cu | Fe | Mn | Ni | Pb | Zn | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sampled time 6 Jan. 2017 | |||||||||
| GS | −0.46 | −0.30 | −0.36 | −0.63 | −0.31 | −0.29 | −0.55 | −0.11 | −0.54 |
| TOC | 0.24 | 0.71 | 0.86 | 0.65 | 0.85 | 0.70 | 0.02 | 0.88 | |
| Al | 0.06 | 0.21 | 0.12 | 0.24 | 0.08 | −0.003 | 0.26 | ||
| Cr | 0.58 | 0.68 | 0.47 | 0.46 | 0.09 | 0.48 | |||
| Cu | 0.71 | 0.85 | 0.84 | 0.10 | 0.95 | ||||
| Fe | 0.72 | 0.66 | −0.09 | 0.66 | |||||
| Mn | 0.76 | 0.12 | 0.92 | ||||||
| Ni | 0.30 | 0.80 | |||||||
| Pb | 0.00 | ||||||||
| Sampled time 14 April 2017 | |||||||||
| GS | −0.41 | −0.12 | −0.13 | −0.31 | −0.03 | −0.22 | −0.28 | −0.40 | −0.34 |
| TOC | 0.60 | 0.71 | 0.85 | 0.76 | 0.86 | 0.89 | 0.82 | 0.92 | |
| Al | 0.52 | 0.60 | 0.71 | 0.67 | 0.64 | 0.46 | 0.68 | ||
| Cr | 0.79 | 0.72 | 0.77 | 0.83 | 0.72 | 0.77 | |||
| Cu | 0.79 | 0.93 | 0.91 | 0.77 | 0.94 | ||||
| Fe | 0.82 | 0.83 | 0.70 | 0.85 | |||||
| Mn | 0.89 | 0.76 | 0.96 | ||||||
| Ni | 0.83 | 0.94 | |||||||
| Pb | 0.80 | ||||||||
| Sampled time 13 July 2017 | |||||||||
| GS | −0.37 | −0.21 | −0.46 | −0.57 | 0.07 | 0.14 | −0.31 | 0.00 | −0.34 |
| TOC | 0.26 | 0.59 | 0.69 | 0.31 | 0.26 | 0.34 | −0.23 | 0.49 | |
| Al | 0.47 | 0.46 | 0.31 | 0.55 | 0.69 | 0.45 | 0.66 | ||
| Cr | 0.90 | 0.29 | 0.66 | 0.86 | 0.39 | 0.86 | |||
| Cu | 0.33 | 0.53 | 0.75 | 0.08 | 0.82 | ||||
| Fe | 0.47 | 0.42 | 0.17 | 0.36 | |||||
| Mn | 0.80 | 0.52 | 0.76 | ||||||
| Ni | 0.63 | 0.89 | |||||||
| Pb | 0.37 | ||||||||
| Sampled time 17 Nov. 2017 | |||||||||
| GS | −0.50 | −0.49 | −0.59 | −0.57 | −0.21 | −0.41 | −0.67 | −0.68 | −0.64 |
| TOC | 0.34 | 0.81 | 0.67 | 0.48 | 0.75 | 0.79 | 0.63 | 0.80 | |
| Al | 0.58 | 0.67 | 0.10 | 0.48 | 0.60 | 0.62 | 0.56 | ||
| Cr | 0.83 | 0.48 | 0.85 | 0.95 | 0.86 | 0.90 | |||
| Cu | 0.52 | 0.91 | 0.88 | 0.70 | 0.93 | ||||
| Fe | 0.73 | 0.50 | 0.26 | 0.62 | |||||
| Mn | 0.87 | 0.67 | 0.93 | ||||||
| Ni | 0.89 | 0.96 | |||||||
| Pb | 0.78 | ||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, T.-H.; Chang, J.-R. The Geochemical and Environmental Characteristics of Trace Metals in Coastal Sediment Discharge off the Mailiao Industrial Zone of Central Western Taiwan. Water 2023, 15, 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15020250
Fang T-H, Chang J-R. The Geochemical and Environmental Characteristics of Trace Metals in Coastal Sediment Discharge off the Mailiao Industrial Zone of Central Western Taiwan. Water. 2023; 15(2):250. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15020250
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Tien-Hsi, and Jie-Ren Chang. 2023. "The Geochemical and Environmental Characteristics of Trace Metals in Coastal Sediment Discharge off the Mailiao Industrial Zone of Central Western Taiwan" Water 15, no. 2: 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15020250





