Characterization of Sub-Catchment Stream and Shallow Groundwater Nutrients and Suspended Sediment in a Mixed Land Use, Agro-Forested Watershed
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site Description
2.2. Nutrient and Suspended Sediment Data Collection
2.3. Data Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Climate during Study
3.2. Nutrient Concentrations
3.3. Suspended Sediment Characteristics
3.4. Physicochemical Variables
3.5. Principal Component Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Nutrient Concentrations, Suspended Sediment Characteristics, and Physicochemical Variables
4.2. Principle Components Analysis
4.3. Study Implications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| NO3-N (mg L−1) | ||||||||
| Site # | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 1 | 1 | |||||||
| 2 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 5 | 1 | 0.6 | 0.56 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 6 | 0.001 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.004 | 0.001 | 1 | ||
| 7 | 0.16 | 1 | 1 | 0.82 | 0.006 | 1 | 1 | |
| 8 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1 | 0.05 | 1 |
| NO2-N (mg L−1) | ||||||||
| Site # | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 1 | 1 | |||||||
| 2 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 6 | 0.95 | 0.44 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| 7 | 0.19 | 0.07 | 0.88 | 0.45 | 0.29 | 1 | 1 | |
| 8 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| NH3-N (mg L−1) | ||||||||
| Site # | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 1 | 1 | |||||||
| 2 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| 4 | 0.76 | 0.65 | 0.52 | 1 | ||||
| 5 | 0.76 | 0.65 | 0.52 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 6 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| 7 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.009 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 8 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| TN-N (mg L−1) | ||||||||
| Site # | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 1 | 1 | |||||||
| 2 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 5 | 1 | 0.7 | 0.16 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 6 | 0.6 | 1 | 1 | 0.44 | 0.005 | 1 | ||
| 7 | 0.07 | 0.65 | 1 | 0.05 | 0.001 | 1 | 1 | |
| 8 | 0.001 | 0.004 | 0.03 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.65 | 1 | 1 |
| PO43-P (mg L−1) | ||||||||
| Site # | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 1 | 1 | |||||||
| 2 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| 4 | 0.44 | 0.21 | 0.08 | 1 | ||||
| 5 | 0.003 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 6 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1 | ||
| 7 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1 | 1 | |
| 8 | 0.002 | 0.00575 | 0.02 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| TP-P (mg L−1) | ||||||||
| Site # | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 1 | 1 | |||||||
| 2 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| 4 | 1 | 0.82 | 0.88 | 1 | ||||
| 5 | 0.008 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 6 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1 | ||
| 7 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1 | 1 | |
| 8 | 0.001 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| TSS (mg L−1) | ||||||||
| Site # | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 1 | 1 | |||||||
| 2 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 6 | 0.29 | 0.7 | 0.07 | 1 | 0.17 | 1 | ||
| 7 | 1 | 1 | 0.34 | 1 | 0.76 | 1 | 1 | |
| 8 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.21 | 0.88 | 1 |
| MZ (µm) | ||||||||
| Site # | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 1 | 1 | |||||||
| 2 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 6 | 0.16 | 0.002 | 0.04 | 1 | 0.85 | 1 | ||
| 7 | 1 | 0.23 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 8 | 0.85 | 0.02 | 0.27 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| CS (m2 mL−1) | ||||||||
| Site # | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 1 | 1 | |||||||
| 2 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 3 | 1 | 0.53 | 1 | |||||
| 4 | 1 | 0.05 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.98 | 1 | |||
| 6 | 0.04 | 0.001 | 0.27 | 1 | 0.002 | 1 | ||
| 7 | 0.07 | 0.001 | 0.45 | 1 | 0.005 | 1 | 1 | |
| 8 | 0.62 | 0.001 | 1 | 1 | 0.07 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Ski | ||||||||
| Site # | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 1 | 1 | |||||||
| 2 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 5 | 1 | 0.19 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 6 | 0.38 | 1 | 0.35 | 0.02 | 0.001 | 1 | ||
| 7 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.02 | 1 | |
| 8 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.1 | 1 | 1 |
| Sand (%) | ||||||||
| Site # | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 1 | 1 | |||||||
| 2 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| 4 | 1 | 0.35 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 5 | 1 | 0.32 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 6 | 0.29 | 0.003 | 0.27 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| 7 | 1 | 0.09 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 8 | 0.25 | 0.002 | 0.23 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Silt (%) | ||||||||
| Site # | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 1 | 1 | |||||||
| 2 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 5 | 1 | 0.27 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 6 | 0.32 | 0.05 | 0.98 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| 7 | 1 | 0.62 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 8 | 0.06 | 0.007 | 0.23 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Clay (%) | ||||||||
| Site # | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 1 | 1 | |||||||
| 2 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 3 | 1 | 0.85 | 1 | |||||
| 4 | 1 | 0.05 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.49 | 1 | |||
| 6 | 0.07 | 0.001 | 0.29 | 1 | 0.006 | 1 | ||
| 7 | 0.04 | 0.001 | 0.17 | 1 | 0.001 | 1 | 1 | |
| 8 | 0.35 | 0.001 | 1 | 1 | 0.013 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Tw (°C) | ||||||||
| Site # | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 1 | 1 | |||||||
| 2 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 3 | 0.76 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| 4 | 0.002 | 0.12 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 5 | 0.001 | 0.06 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 6 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.82 | 0.44 | 1 | ||
| 7 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 1 | 1 | |
| 8 | 0.01 | 0.44 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.19 | 1 |
| DO (% saturation) | ||||||||
| Site # | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 1 | 1 | |||||||
| 2 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| 4 | 1 | 0.38 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 6 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1 | ||
| 7 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1 | 1 | |
| 8 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.04 | 0.34 | 0.009 | 1 | 0.09 | 1 |
| SPC (µs cm−1) | ||||||||
| Site # | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 1 | 1 | |||||||
| 2 | 0.27 | 1 | ||||||
| 3 | 0.7 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| 4 | 1 | 0.05 | 0.16 | 1 | ||||
| 5 | 0.7 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 6 | 0.001 | 0.009 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1 | ||
| 7 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1 | 1 | |
| 8 | 0.001 | 0.1572 | 0.05 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| pH | ||||||||
| Site # | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 1 | 1 | |||||||
| 2 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 3 | 1 | 0.48 | 1 | |||||
| 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 6 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1 | ||
| 7 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1 | 1 | |
| 8 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| NO3-N (mg L−1) | ||||||||
| Site # | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 1 | 1 | |||||||
| 2 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 3 | 0.06 | 0.001 | 1 | |||||
| 4 | 1 | 1 | 0.001 | 1 | ||||
| 5 | 1 | 1 | 0.007 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 6 | 0.005 | 0.001 | 1 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1 | ||
| 7 | 0.13 | 0.001 | 1 | 0.001 | 0.02 | 1 | 1 | |
| 8 | 1 | 0.11 | 0.82 | 0.37 | 1 | 0.12 | 1 | 1 |
| NO2-N (mg L−1) | ||||||||
| Site # | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 1 | 1 | |||||||
| 2 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 3 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1 | |||||
| 4 | 0.95 | 1 | 0.001 | 1 | ||||
| 5 | 1 | 1 | 0.001 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 6 | 0.005 | 0.001 | 1 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1 | ||
| 7 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1 | 1 | |
| 8 | 1 | 0.06 | 0.34 | 0.004 | 0.03 | 1 | 0.48 | 1 |
| NH3-N (mg L−1) | ||||||||
| Site # | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 1 | 1 | |||||||
| 2 | 0.41 | 1 | ||||||
| 3 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1 | |||||
| 4 | 0.1 | 0.001 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 5 | 1 | 0.006 | 0.06 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 6 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1 | 0.07 | 0.001 | 1 | ||
| 7 | 0.09 | 0.001 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.08 | 1 | |
| 8 | 0.65 | 0.001 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.007 | 1 | 1 |
| TN-N (mg L−1) | ||||||||
| Site # | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 1 | 1 | |||||||
| 2 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 3 | 0.006 | 0.001 | 1 | |||||
| 4 | 1 | 1 | 0.01 | 1 | ||||
| 5 | 1 | 1 | 0.001 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 6 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1 | ||
| 7 | 0.19 | 0.001 | 1 | 0.34 | 0.004 | 0.27 | 1 | |
| 8 | 1 | 0.04 | 1 | 1 | 0.17 | 0.006 | 1 | 1 |
| PO43-P (mg L−1) | ||||||||
| Site # | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 1 | 1 | |||||||
| 2 | 0.001 | 1 | ||||||
| 3 | 0.6 | 0.001 | 1 | |||||
| 4 | 0.001 | 0.03 | 0.65 | 1 | ||||
| 5 | 0.001 | 0.02 | 0.82 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 6 | 1 | 0.001 | 1 | 0.19 | 0.24 | 1 | ||
| 7 | 0.001 | 1 | 0.002 | 1 | 1 | 0.001 | 1 | |
| 8 | 0.001 | 0.24 | 0.12 | 1 | 1 | 0.02 | 1 | 1 |
| TP-P (mg L−1) | ||||||||
| Site # | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 1 | 1 | |||||||
| 2 | 0.003 | 1 | ||||||
| 3 | 0.16 | 0.001 | 1 | |||||
| 4 | 0.09 | 1 | 0.001 | 1 | ||||
| 5 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.52 | 1 | |||
| 6 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.82 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1 | ||
| 7 | 0.004 | 0.001 | 1 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1 | 1 | |
| 8 | 1 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.27 | 1 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1 |
| TSS (mg L−1) | ||||||||
| Site # | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 1 | 1 | |||||||
| 2 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 3 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1 | |||||
| 4 | 0.19 | 0.7 | 0.001 | 1 | ||||
| 5 | 1 | 1 | 0.001 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 6 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1 | ||
| 7 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1 | 1 | |
| 8 | 1 | 0.48 | 0.44 | 0.001 | 0.05 | 0.17 | 0.82 | 1 |
| MZ (µm) | ||||||||
| Site # | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 1 | 1 | |||||||
| 2 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 3 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1 | |||||
| 4 | 0.34 | 0.95 | 0.001 | 1 | ||||
| 5 | 1 | 1 | 0.13 | 0.002 | 1 | |||
| 6 | 1 | 1 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 1 | 1 | ||
| 7 | 1 | 1 | 0.001 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 8 | 0.76 | 0.27 | 0.95 | 0.001 | 1 | 1 | 0.17 | 1 |
| CS (m2 mL−1) | ||||||||
| Site # | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 1 | 1 | |||||||
| 2 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 3 | 1 | 0.04 | 1 | |||||
| 4 | 1 | 1 | 0.02 | 1 | ||||
| 5 | 0.19 | 0.001 | 1 | 0.001 | 1 | |||
| 6 | 1 | 0.26661 | 1 | 0.16 | 1 | 1 | ||
| 7 | 0.95 | 1 | 0.009 | 1 | 0.001 | 0.07 | 1 | |
| 8 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.07 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Ski | ||||||||
| Site # | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 1 | 1 | |||||||
| 2 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 3 | 0.001 | 0.12 | 1 | |||||
| 4 | 1 | 1 | 0.003 | 1 | ||||
| 5 | 1 | 1 | 0.05 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 6 | 1 | 1 | 0.02 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| 7 | 0.007 | 1 | 1 | 0.19 | 1 | 0.7 | 1 | |
| 8 | 1 | 1 | 0.13 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Sand (%) | ||||||||
| Site # | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 1 | 1 | |||||||
| 2 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 3 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1 | |||||
| 4 | 1 | 0.95 | 0.001 | 1 | ||||
| 5 | 1 | 1 | 0.09 | 0.005 | 1 | |||
| 6 | 1 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 1 | 1 | ||
| 7 | 1 | 1 | 0.001 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 8 | 0.37 | 0.52 | 0.7 | 0.001 | 1 | 1 | 0.37 | 1 |
| Silt (%) | ||||||||
| Site # | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 1 | 1 | |||||||
| 2 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 3 | 0.82 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| 4 | 0.03 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1 | ||||
| 5 | 1 | 0.7 | 0.01 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 6 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.006 | 1 | 1 | ||
| 7 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.001 | 0.04 | 1 | 1 | |
| 8 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.001 | 0.7 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Clay (%) | ||||||||
| Site # | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 1 | 1 | |||||||
| 2 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 3 | 0.11 | 0.001 | 1 | |||||
| 4 | 1 | 1 | 0.001 | 1 | ||||
| 5 | 0.52 | 0.01 | 1 | 0.001 | 1 | |||
| 6 | 1 | 1 | 0.7 | 0.37 | 1 | 1 | ||
| 7 | 1 | 1 | 0.001 | 1 | 0.006 | 1 | 1 | |
| 8 | 1 | 1 | 0.32 | 0.82 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Tw (°C) | ||||||||
| Site # | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 1 | 1 | |||||||
| 2 | 0.007 | 1 | ||||||
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| 4 | 1 | 0.02 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 5 | 1 | 0.24 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 6 | 1 | 0.08 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| 7 | 1 | 0.08 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 8 | 1 | 0.03 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| DO (% saturation) | ||||||||
| Site # | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 1 | 1 | |||||||
| 2 | 0.001 | 1 | ||||||
| 3 | 1 | 0.001 | 1 | |||||
| 4 | 1 | 0.009 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 5 | 1 | 0.03 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 6 | 0.001 | 1 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1 | ||
| 7 | 0.001 | 0.65 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1 | 1 | |
| 8 | 0.001 | 1 | 0.001 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 1 | 0.45 | 1 |
| SPC (µs cm−1) | ||||||||
| Site # | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 1 | 1 | |||||||
| 2 | 0.6 | 1 | ||||||
| 3 | 0.02 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| 4 | 1 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1 | ||||
| 5 | 1 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 6 | 0.13 | 1 | 1 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1 | ||
| 7 | 1 | 1 | 0.05 | 0.88 | 0.65 | 0.24 | 1 | |
| 8 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| pH | ||||||||
| Site # | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 1 | 1 | |||||||
| 2 | 0.007 | 1 | ||||||
| 3 | 0.006 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| 4 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1 | ||||
| 5 | 0.001 | 0.48 | 0.56 | 0.1 | 1 | |||
| 6 | 0.6 | 1 | 1 | 0.001 | 0.005 | 1 | ||
| 7 | 0.001 | 0.22428 | 0.27 | 0.32 | 1 | 0.002 | 1 | |
| 8 | 1 | 0.09901 | 0.08 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1 | 0.001 | 1 |
| Principal Component | Eigenvalue | Percentage of Variance | Cumulative Variance |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6.02 | 30.11% | 30.11% |
| 2 | 3.21 | 16.07% | 46.18% |
| 3 | 1.96 | 9.82% | 56.00% |
| 4 | 1.86 | 9.30% | 65.30% |
| 5 | 1.26 | 6.29% | 71.59% |
| 6 | 0.94 | 4.72% | 76.31% |
| 7 | 0.84 | 4.21% | 80.52% |
| 8 | 0.75 | 3.76% | 84.28% |
| 9 | 0.69 | 3.44% | 87.71% |
| 10 | 0.60 | 3.02% | 90.73% |
| 11 | 0.39 | 1.93% | 92.67% |
| 12 | 0.31 | 1.53% | 94.20% |
| 13 | 0.28 | 1.40% | 95.60% |
| 14 | 0.26 | 1.30% | 96.90% |
| 15 | 0.23 | 1.15% | 98.05% |
| 16 | 0.18 | 0.89% | 98.94% |
| 17 | 0.12 | 0.62% | 99.56% |
| 18 | 0.09 | 0.44% | 100.00% |
| 19 | 0.00 | 0.00% | 100.00% |
| 20 | 0.00 | 0.00% | 100.00% |
| Variable of Interest | Ag | For | Dev | NO3-N | NO2-N | NH3-N | TN-N | PO43-P | TP-P | TSS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ag | 1 | |||||||||
| For | −0.85 | 1 | ||||||||
| Dev | −0.7 | 0.7 | 1 | |||||||
| NO3-N | 0.05 | −0.05 | −0.03 | 1 | ||||||
| NO2-N | 0.08 | −0.1 | −0.08 | 0.25 | 1 | |||||
| NH3-N | 0.02 | −0.04 | −0.05 | 0.09 | 0.75 | 1 | ||||
| TN-N | 0.05 | −0.06 | −0.06 | 0.22 | 0.57 | 0.58 | 1 | |||
| PO43-P | 0.33 | −0.41 | −0.17 | −0.04 | −0.23 | −0.27 | −0.22 | 1 | ||
| TP-P | 0.52 | −0.53 | −0.45 | 0.17 | 0.6 | 0.63 | 0.39 | 0.21 | 1 | |
| TSS | 0.19 | −0.21 | −0.21 | 0.17 | 0.78 | 0.79 | 0.51 | −0.23 | 0.7 | 1 |
| MZ | 0.01 | −0.04 | −0.06 | −0.14 | −0.59 | −0.6 | −0.38 | 0.27 | −0.47 | −0.66 |
| CS | −0.06 | 0.14 | 0.12 | 0.01 | 0.6 | 0.66 | 0.32 | −0.34 | 0.42 | 0.66 |
| Ski | 0.02 | −0.04 | 0.02 | −0.02 | 0.48 | 0.61 | 0.19 | −0.19 | 0.4 | 0.56 |
| Sand | 0.02 | −0.03 | −0.06 | −0.1 | −0.57 | −0.58 | −0.39 | 0.28 | −0.44 | −0.63 |
| Silt | −0.02 | −0.03 | 0.03 | 0.19 | 0.23 | 0.15 | 0.28 | −0.13 | 0.12 | 0.23 |
| Clay | −0.06 | 0.11 | 0.09 | 0.03 | 0.65 | 0.68 | 0.34 | −0.35 | 0.46 | 0.71 |
| Tw | 0.01 | −0.03 | −0.02 | 0.31 | 0.1 | 0.26 | 0.09 | 0.05 | 0.15 | 0.08 |
| DO | −0.01 | 0.01 | −0.01 | 0.06 | −0.5 | −0.75 | −0.29 | 0.11 | −0.54 | −0.65 |
| SPC | −0.16 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.09 | 0.58 | 0.69 | 0.39 | −0.42 | 0.34 | 0.66 |
| pH | −0.3 | 0.3 | 0.21 | −0.02 | −0.43 | −0.58 | −0.23 | 0.02 | −0.6 | −0.63 |
| Continued… | MZ | CS | Ski | Sand | Silt | Clay | Tw | DO | SPC | pH |
| Ag | ||||||||||
| For | ||||||||||
| Dev | ||||||||||
| NO3-N | ||||||||||
| NO2-N | ||||||||||
| NH3-N | ||||||||||
| TN-N | ||||||||||
| PO43-P | ||||||||||
| TP-P | ||||||||||
| TSS | ||||||||||
| MZ | 1 | |||||||||
| CS | −0.77 | 1 | ||||||||
| Ski | −0.33 | 0.61 | 1 | |||||||
| Sand | 0.97 | −0.74 | −0.33 | 1 | ||||||
| Silt | −0.57 | 0.17 | −0.06 | −0.65 | 1 | |||||
| Clay | −0.81 | 0.96 | 0.61 | −0.76 | 0.17 | 1 | ||||
| Tw | −0.11 | −0.01 | 0.13 | −0.11 | 0.16 | 0.01 | 1 | |||
| DO | 0.55 | −0.61 | −0.61 | 0.53 | −0.12 | −0.62 | −0.21 | 1 | ||
| SPC | −0.64 | 0.69 | 0.52 | −0.63 | 0.27 | 0.7 | 0.03 | −0.62 | 1 | |
| pH | 0.52 | −0.5 | −0.5 | 0.5 | −0.18 | −0.53 | −0.22 | 0.75 | −0.53 | 1 |
References
- Carpenter, S.R.; Caraco, N.F.; Correll, D.L.; Howarth, R.W.; Sharpley, A.N.; Smith, V.H. Nonpoint Pollution of Surface Waters with Phosphorus and Nitrogen. Ecol. Appl. 1998, 8, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noe, G.B.; Cashman, M.J.; Skalak, K.; Gellis, A.; Hopkins, K.G.; Moyer, D.; Webber, J.; Benthem, A.; Maloney, K.; Brakebill, J.; et al. Sediment dynamics and implications for management: State of the science from long-term research in the Chesapeake Bay watershed, USA. WIREs Water 2020, 7, e1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syvitski, J.P.; Vörösmarty, C.J.; Kettner, A.J.; Green, P. Impact of humans on the flux of terrestrial sediment to the global coastal ocean. Science 2005, 308, 376–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, A.C.; Withers, P.J.A. Transport and delivery of suspended solids, nitrogen and phosphorus from various sources to freshwaters in the UK. J. Hydrol. 2008, 350, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilmin, L.; Mogollón, J.M.; Beusen, A.H.W.; Bouwman, A.F. Forms and subannual variability of nitrogen and phosphorus loading to global river networks over the 20th century. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2018, 163, 67–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beusen, A.H.W.; Bouwman, A.F.; Van Beek, L.P.H.; Mogollón, J.M.; Middelburg, J.J. Global riverine N and P transport to ocean increased during the 20th century despite increased retention along the aquatic continuum. Biogeosciences 2016, 13, 2441–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Green, P.A.; Vörösmarty, C.J.; Meybeck, M.; Galloway, J.N.; Peterson, B.J.; Boyer, E.W. Pre-industrial and contemporary fluxes of nitrogen through rivers: A global assessment based on typology. Biogeochemistry 2004, 68, 71–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, E.W.; Howarth, R.W.; Galloway, J.N.; Dentener, F.J.; Green, P.A.; Vörösmarty, C.J. Riverine nitrogen export from the continents to the coasts. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2006, 20, GB1S91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Howarth, R.W.; Billen, G.; Swaney, D.; Townsend, A.; Jaworski, N.; Lajtha, K.; Downing, J.A.; Elmgren, R.; Caraco, N.; Jordan, T.; et al. Regional nitrogen budgets and riverine N & P fluxes for the drainages to the North Atlantic Ocean: Natural and human influences. Biogeochemistry 1996, 35, 75–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitousek, P.M.; Aber, J.D.; Howarth, R.W.; Likens, G.E.; Matson, P.A.; Schindler, D.W.; Schlesinger, W.H.; Tilman, D.G. Human Alteration of the Global Nitrogen Cycle: Sources and Consequences. Ecol. Appl. 1997, 7, 737–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, B.J.; Wollheim, W.M.; Mulholland, P.J.; Webster, J.R.; Meyer, J.L.; Tank, J.L.; Martí, E.; Bowden, W.B.; Valett, H.M.; Hershey, A.E.; et al. Control of Nitrogen Export from Watersheds by Headwater Streams. Science 2001, 292, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward; Tockner, K. Biodiversity: Towards a unifying theme for river ecology. Freshw. Biol. 2001, 46, 807–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzadri, A.; Tonina, D.; Bellin, A.; Tank, J.L. A hydrologic model demonstrates nitrous oxide emissions depend on streambed morphology. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 5484–5491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milliman, J.D.; Meade, R.H. World-Wide Delivery of River Sediment to the Oceans. J. Geol. 1983, 91, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiger, S.J.; Hubbart, J.A. Characterizing Land Use Impacts on Channel Geomorphology and Streambed Sedimentological Characteristics. Water 2019, 11, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeiger, S.; Hubbart, J. Assessing the Difference between Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) Simulated Pre-Development and Observed Developed Loading Regimes. Hydrology 2018, 5, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borda, T.; Celi, L.; Zavattaro, L.; Sacco, D.; Barberis, E. Effect of agronomic management on risk of suspended solids and phosphorus losses from soil to waters. J. Soils Sediments 2011, 11, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, C.S.S.; Walsh, R.P.D.; Kalantari, Z.; Ferreira, A.J.D. Impact of Land-Use Changes on Spatiotemporal Suspended Sediment Dynamics within a Peri-Urban Catchment. Water 2020, 12, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beusen, A.H.W.; Dekkers, A.L.M.; Bouwman, A.F.; Ludwig, W.; Harrison, J. Estimation of global river transport of sediments and associated particulate C, N, and P. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2005, 19, GB4S05. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalmers, A.T.; Van Metre, P.C.; Callender, E. The chemical response of particle-associated contaminants in aquatic sediments to urbanization in New England, U.S.A. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2007, 91, 4–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrabadi, T.; Ruegner, H.; Sirdari, Z.Z.; Schwientek, M.; Grathwohl, P. Using total suspended solids (TSS) and turbidity as proxies for evaluation of metal transport in river water. Appl. Geochem. 2016, 68, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correll, D.L. Phosphorus: A rate limiting nutrient in surface waters. Poult. Sci. 1999, 78, 674–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruszowski, K.E.; Foster, I.D.L.; Lees, J.A.; Charlesworth, S.M. Sediment sources and transport pathways in a rural catchment, Herefordshire, UK. Hydrol. Process. 2003, 17, 2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiger, S.J.; Hubbart, J.A. Nested-Scale Nutrient Flux in a Mixed-Land-Use Urbanizing Watershed. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 1475–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilling, K.E.; Isenhart, T.M.; Palmer, J.A.; Wolter, C.F.; Spooner, J. Impacts of Land-Cover Change on Suspended Sediment Transport in Two Agricultural Watersheds1. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2011, 47, 672–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, A.O.; Quinn, J.M.; McKergow, L.A. Land use influences on suspended sediment yields and event sediment dynamics within two headwater catchments, Waikato, New Zealand. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2012, 46, 315–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Powers, S.M.; Tank, J.L.; Robertson, D.M. Control of nitrogen and phosphorus transport by reservoirs in agricultural landscapes. Biogeochemistry 2015, 124, 417–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiger, S.J.; Hubbart, J.A. Quantifying flow interval–pollutant loading relationships in a rapidly urbanizing mixed-land-use watershed of the Central USA. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajželj, B.; Richards, K.S.; Allwood, J.M.; Smith, P.; Dennis, J.S.; Curmi, E.; Gilligan, C.A. Importance of food-demand management for climate mitigation. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 924–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Dijk, M.; Morley, T.; Rau, M.L.; Saghai, Y. A meta-analysis of projected global food demand and population at risk of hunger for the period 2010–2050. Nat. Food 2021, 2, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilman, D.; Balzer, C.; Hill, J.; Befort, B.L. Global food demand and the sustainable intensification of agriculture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 20260–20264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ray, D.K.; Mueller, N.D.; West, P.C.; Foley, J.A. Yield Trends Are Insufficient to Double Global Crop Production by 2050. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kopittke, P.M.; Menzies, N.W.; Wang, P.; McKenna, B.A.; Lombi, E. Soil and the intensification of agriculture for global food security. Environ. Int. 2019, 132, 105078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kellner, E.; Hubbart, J.A. Confounded by forgotten legacies: Effectively managing watersheds in the contemporary age of unknown unknowns. Hydrol. Process. 2017, 31, 2802–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corriveau, J.; van Bochove, E.; Cluis, D. Sources of nitrite in streams of an intensively cropped watershed. Water Environ. Res. 2010, 82, 622–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.V.; Denis, J.M.; Ator, S.W.; Brakebill, J.W. Nutrients in Streams During Baseflow in Selected Environmental Settings of the Potomac River Basin. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1998, 33, 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boesch, D.F.; Brinsfield, R.B.; Magnien, R.E. Chesapeake Bay Eutrophication: Scientific Understanding, Ecosystem Restoration, and Challenges for Agriculture. J. Environ. Qual. 2001, 30, 303–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diego-Feliu, M.; Rodellas, V.; Alorda-Kleinglass, A.; Saaltink, M.; Folch, A.; Garcia-Orellana, J. Extreme precipitation events induce high fluxes of groundwater and associated nutrients to coastal ocean. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 26, 4619–4635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, W. Saturated and field-unsaturated water flow parameters: Laboratory methods. Phys. Methods 2002, 4, 802–817. Available online: https://acsess.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.2136/sssabookser5.4.c31 (accessed on 20 September 2022).
- Foster, I.D.L.; Chapman, A.S.; Hodgkinson, R.M.; Jones, A.R.; Lees, J.A.; Turner, S.E.; Scott, M. Changing suspended sediment and particulate phosphorus loads and pathways in underdrained lowland agricultural catchments; Herefordshire and Worcestershire, U.K. Hydrobiologia 2003, 494, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gootman, K.S.; Hubbart, J.A. A Comparison of Stream Water and Shallow Groundwater Suspended Sediment Concentrations in a West Virginia Mixed-Use, Agro-Forested Watershed. Land 2022, 11, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charizopoulos, N.; Zagana, E.; Psilovikos, A. Assessment of natural and anthropogenic impacts in groundwater, utilizing multivariate statistical analysis and inverse distance weighted interpolation modeling: The case of a Scopia basin (Central Greece). Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jantz, P.; Goetz, S.; Jantz, C. Urbanization and the Loss of Resource Lands in the Chesapeake Bay Watershed. Environ. Manag. 2005, 36, 808–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemp, W.M.; Boynton, W.R.; Adolf, J.E.; Boesch, D.F.; Boicourt, W.C.; Brush, G.; Cornwell, J.C.; Fisher, T.R.; Glibert, P.M.; Hagy, J.D. Eutrophication of Chesapeake Bay: Historical trends and ecological interactions. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 303, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barlow, R.A.; Brakebill, J.W.; Bratton, J.F.; Blazer, V.S.; Bohlke, J.K.; Bricker, O.P.; Colman, S.M.; Cronin, T.M.; Hupp, C.R.; Keough, J.R.; et al. The U.S. Geological Survey and the Chesapeake Bay—The Role of Science in Environmental Restoration; Circular 1220; USGS: Reston, VA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Brakebill, J.; Ator, S.; Sekellick, A. Input and predictions from a suspended-sediment SPARROW model CBSS_V2 in the Chesapeake Bay Watershed; US Geological Survey Data Release; USGS: Reston, VA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Boesch, D.F.; Greer, J. Chesapeake Futures: Choices for the 21st Century; Chesapeake Research Consortium: Edgewater, MD, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. Chesapeake Bay Total Maximum Daily Load for Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Sediment; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2010.
- Shenk, G.W.; Linker, L.C. Development and Application of the 2010 Chesapeake Bay Watershed Total Maximum Daily Load Model. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2013, 49, 1042–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Brady, D.C.; Boynton, W.R.; Ball, W.P. Long-Term Trends of Nutrients and Sediment from the Nontidal Chesapeake Watershed: An Assessment of Progress by River and Season. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2015, 51, 1534–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langland, M.; Blomquist, J.; Moyer, D.; Hyer, K. Nutrient and Suspended-Sediment Trends, Loads, and Yields and Development of an Indicator of Streamwater Quality at Nontidal Sites in the Chesapeake Bay Watershed, 1985–2010; US Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Report 2012-5093; USGS: Reston, VA, USA, 2012; 26p. [Google Scholar]
- Moyer, D.; Blomquist, J. Summary of Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Suspended-Sediment Loads and Trends Measured at the Chesapeake Bay Nontidal Network Stations for Water Years 2009–2018. United States Geological Survey Report. 2018. Available online: https://d18lev1ok5leia.cloudfront.net/chesapeakebay/documents/ii.a._ntn_load_and_trend_summary_2018.pdf (accessed on 20 September 2022).
- Zhang, Q. Synthesis of nutrient and sediment export patterns in the Chesapeake Bay watershed: Complex and non-stationary concentration-discharge relationships. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 618, 1268–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.R.; Bhatt, G.; Filoso, S.; Yactayo, G. Stream restoration performance and its contribution to the Chesapeake Bay TMDL: Challenges posed by climate change in urban areas. Estuaries Coasts 2017, 40, 1227–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renwick, W.H.; Andereck, Z.D. Reservoir sedimentation trends in Ohio, USA: Sediment delivery and response to land-use change. IAHS Publ. 2006, 306, 341. [Google Scholar]
- Zeiger, S.J.; Hubbart, J.A. A SWAT model validation of nested-scale contemporaneous stream flow, suspended sediment and nutrients from a multiple-land-use watershed of the central USA. Sci Total Environ. 2016, 572, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Ball, W.P.; Moyer, D.L. Decadal-scale export of nitrogen, phosphorus, and sediment from the Susquehanna River basin, USA: Analysis and synthesis of temporal and spatial patterns. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 563–564, 1016–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hubbart, J.A.; Kellner, E.; Zeiger, S.J. A Case-Study Application of the Experimental Watershed Study Design to Advance Adaptive Management of Contemporary Watersheds. Water 2019, 11, 2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechmann, M.; Stålnacke, P. Effect of policy-induced measures on suspended sediments and total phosphorus concentrations from three Norwegian agricultural catchments. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 344, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bainbridge, Z.T.; Brodie, J.E.; Faithful, J.W.; Sydes, D.A.; Lewis, S.E. Identifying the land-based sources of suspended sediments, nutrients and pesticides discharged to the Great Barrier Reef from the Tully-Murray Basin, Queensland, Australia. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2009, 60, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseau, A.N.; Savary, S.; Hallema, D.W.; Gumiere, S.J.; Foulon, É. Modeling the effects of agricultural BMPs on sediments, nutrients, and water quality of the Beaurivage River watershed (Quebec, Canada). Can. Water Resour. J. 2013, 38, 99–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NRAC. West Virginia Land Use Land Cover (NAIP 2016); West Virginia GIS Technical Center: Morgantown, WV, USA, 2020. Available online: http://www.mapwv.gov/ (accessed on 20 September 2022).
- Knight, H.G. Reymann Memorial Farms; West Virginia Agricultural and Forestry Experiment Station: Morgantown, WV, USA, 1925; Volume 194, Available online: https://researchrepository.wvu.edu/wv_agricultural_and_forestry_experiment_station_bulletins/194/ (accessed on 20 September 2022).
- WVU. Reymann Memorial Farms West Virginia University. Wardensville, West Virginia, USA. Available online: https://www.davis.wvu.edu/about-davis-college/farms-and-forests/reymann-memorial-farm (accessed on 20 September 2022).
- Nicholson, S.W.; Dicken, C.L.; Horton, J.D.; Labay, K.A.; Foose, M.P.; Mueller, J.A.L. Preliminary Integrated Geologic Map Databases for the United States: Kentucky, Ohio, Tennessee, and West Virginia; Open-File Report 2005-1324; USGS: Reston, VA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- NRCS. Web Site for Official Soil Series Descriptions and Series Classification. 2020. Available online: https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/resources/data-and-reports/official-soil-series-descriptions-osd (accessed on 20 September 2022).
- Gootman, K.; Kellner, E.; Hubbart, J. A Comparison and Validation of Saturated Hydraulic Conductivity Models. Water 2020, 12, 2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NOAA. Climate Data Online Search. 2020. Available online: https://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/cdo-web/search (accessed on 20 September 2022).
- Zeiger, S.J.; Hubbart, J.A. Quantifying relationships between urban land use and flow frequency of small Missouri streams. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 659, 1008–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbart, J.A. Improving Best Management Practice Decisions in Mixed Land Use and/or Municipal Watersheds: Should Approaches Be Standardized? Land 2021, 10, 1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbart, J.A.; Link, T.E.; Gravelle, J.A.; Elliot, W.J. Timber harvest impacts on water yield in the continental/maritime hydroclimatic region of the United States. For. Sci. 2007, 53, 169–180. [Google Scholar]
- Karwan, D.L.; Gravelle, J.A.; Hubbart, J.A. Effects of timber harvest on suspended sediment loads in Mica Creek, Idaho. For. Sci. 2007, 53, 181–188. [Google Scholar]
- Guzman, J.A.; Moriasi, D.N.; Gowda, P.H.; Steiner, J.L.; Starks, P.J.; Arnold, J.G.; Srinivasan, R. A model integration framework for linking SWAT and MODFLOW. Environ. Model. Softw. 2015, 73, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiger, S.; Hubbart, J. Urban Stormwater Temperature Surges: A Central US Watershed Study. Hydrology 2015, 2, 193–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbart, J.; Kellner, E.; Hooper, L.; Lupo, A.; Market, P.; Guinan, P.; Stephan, K.; Fox, N.; Svoma, B. Localized Climate and Surface Energy Flux Alterations across an Urban Gradient in the Central U.S. Energies 2014, 7, 1770–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kellner, E.; Hubbart, J.; Stephan, K.; Morrissey, E.; Freedman, Z.; Kutta, E.; Kelly, C. Characterization of sub-watershed-scale stream chemistry regimes in an Appalachian mixed-land-use watershed. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellner, E.; Hubbart, J.A. Spatiotemporal variability of suspended sediment particle size in a mixed-land-use watershed. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 615, 1164–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubbart, J.A.; Kellner, E.; Freeman, G. A case study considering the comparability of mass and volumetric suspended sediment data. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 4051–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. 2540 Solids. In Standard Methods For the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1999. Available online: https://www.standardmethods.org/doi/10.2105/SMWW.2882.030 (accessed on 20 September 2022).
- Plantz, P.E. Pigment Particle Size Using Microtrac Laser Technology; SL-AN-30 Revision A. 2009. Available online: http://www.microtrac.com (accessed on 10 February 2020).
- Plantz, P.E. Blue Laser Technology Applied to the Microtrac Unified Scatter Technique for Full-Range Particle Size Measurement. Application Note; Microtrac, Inc.: Montgomeryville, PA, USA, 2007; 8p. [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal, Y.C.; Whitmire, A.; Mikkelsen, O.A.; Pottsmith, H.C. Light scattering by random shaped particles and consequences on measuring suspended sediments by laser diffraction. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, C04023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kellner, E.; Hubbart, J. Advancing Understanding of the Surface Water Quality Regime of Contemporary Mixed-Land-Use Watersheds: An Application of the Experimental Watershed Method. Hydrology 2017, 4, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Helsel, D.R.; Hirsch, R.M.; Ryberg, K.R.; Archfield, S.A.; Gilroy, E.J. Statistical Methods in Water Resources; 4-A3; USGS: Reston, VA, USA, 2020; p. 484. [Google Scholar]
- Yazici, B.; Yolacan, S. A comparison of various tests of normality. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 2007, 77, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.C. Statistics and Data Analysis in Geology; Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2002; Available online: https://www.kgs.ku.edu/Mathgeo/Books/Stat/ClarifyEq4-81.pdf (accessed on 20 September 2022).
- Friedman, M. The use of ranks to avoid the assumption of normality implicit in the analysis of variance. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1937, 32, 675–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauke, J.; Kossowski, T. Comparison of Values of Pearson’s and Spearman’s Correlation Coefficients on the Same Sets of Data. Quaest. Geogr. 2011, 30, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lehr, C.; Pöschke, F.; Lewandowski, J.; Lischeid, G. A novel method to evaluate the effect of a stream restoration on the spatial pattern of hydraulic connection of stream and groundwater. J. Hydrol. 2015, 527, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jolliffe, I.T.; Cadima, J. Principal component analysis: A review and recent developments. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2016, 374, 20150202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petersen, F.; Hubbart, J.A.; Kellner, E.; Kutta, E. Land-use-mediated Escherichia coli concentrations in a contemporary Appalachian watershed. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutta, E.; Hubbart, J. Changing Climatic Averages and Variance: Implications for Mesophication at the Eastern Edge of North America’s Eastern Deciduous Forest. Forests 2018, 9, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kutta, E.; Hubbart, J. Climatic Trends of West Virginia: A Representative Appalachian Microcosm. Water 2019, 11, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Linting, M.; Meulman, J.J.; Groenen, P.J.; van der Koojj, A.J. Nonlinear principal components analysis: Introduction and application. Psychol Methods 2007, 12, 336–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bro, R.; Smilde, A.K. Principal component analysis. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 2812–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coulter, C.B.; Kolka, R.K.; Thompson, J.A. Water Quality in Agricultural, Urban, and Mixed Land Use Watersheds1. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2004, 40, 1593–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huizenga, A.; Bailey, R.T.; Gates, T.K. Stream-aquifer and in-stream processes affecting nitrogen along a major river and contributing tributary. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2017, 199, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murphy, J.C. Changing suspended sediment in United States rivers and streams: Linking sediment trends to changes in land use/cover, hydrology and climate. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 24, 991–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wieben, C.M.; Baker, R.J.; Nicholson, R.S. Nutrient Concentrations in Surface Water and Groundwater, and Nitrate Source Identification Using Stable Isotope Analysis, in the Barnegat Bay-Little Egg Harbor Watershed, New Jersey, 2010–2011; Scientific Investigations Report 2012-5287; USGS: Reston, VA, USA, 2013; pp. 1–44. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.; Rozemeijer, J.; Van Breukelen, B.M.; Ouboter, M.; Van Der Vlugt, C.; Broers, H.P. Groundwater impacts on surface water quality and nutrient loads in lowland polder catchments: Monitoring the greater Amsterdam area. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 487–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chinnasamy, P.; Hubbart, J.A. Stream and shallow groundwater nutrient concentrations in an Ozark forested riparian zone of the central USA. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 6577–6590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, J.J.; Scholefield, D.; Cabral, F.; Hofman, G. The effects of nutrient losses from agriculture on ground and surface water quality: The position of science in developing indicators for regulation. Environ. Sci. Policy 2004, 7, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldenberg, L.C.; Mandel, S.; Magaritz, M. Fluctuating, non-homogeneous changes of hydraulic conductivity in porous media. Q. J. Eng. Geol. Hydrogeol. 1986, 19, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florsheim, J.L.; Pellerin, B.A.; Oh, N.H.; Ohara, N.; Bachand, P.A.M.; Bachand, S.M.; Bergamaschi, B.A.; Hernes, P.J.; Kavvas, M.L. From deposition to erosion: Spatial and temporal variability of sediment sources, storage, and transport in a small agricultural watershed. Geomorphology 2011, 132, 272–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frostick, L.E.; Lucas, P.M.; Reid, I. The infiltration of fine matrices into coarse-grained alluvial sediments and its implications for stratigraphical interpretation. J. Geol. Soc. 1984, 141, 955–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duff, J.H.; Murphy, F.; Fuller, C.C.; Triska, F.J.; Harvey, J.W.; Jackman, A.P. A mini drivepoint sampler for measuring pore water solute concentrations in the hyporheic zone of sand-bottom streams. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1998, 43, 1378–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, S.; Heathwaite, L.; Binley, A.; Keenan, P. Nitrate concentration changes at the groundwater-surface water interface of a small Cumbrian river. Hydrol. Process. 2009, 23, 2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffioen, J.; Vermooten, S.; Janssen, G. Geochemical and palaeohydrological controls on the composition of shallow groundwater in the Netherlands. Appl. Geochem. 2013, 39, 129–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Mostaghimi, S.; Kang, M.S. Development and application of a modeling approach for surface water and groundwater interaction. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wainwright, J.; Turnbull, L.; Ibrahim, T.G.; Lexartza-Artza, I.; Thornton, S.F.; Brazier, R.E. Linking environmental regimes, space and time: Interpretations of structural and functional connectivity. Geomorphology 2011, 126, 387–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.-M.; Meybeck, M. Elemental mass-balance of material carried by major world rivers. Mar. Chem. 1979, 7, 173–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meybeck, M. Global analysis of river systems: From Earth system controls to Anthropocene syndromes. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2003, 358, 1935–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walling, D.E.; Owens, P.N.; Carter, J.; Leeks, G.J.L.; Lewis, S.; Meharg, A.A.; Wright, J. Storage of sediment-associated nutrients and contaminants in river channel and floodplain systems. Appl. Geochem. 2003, 18, 195–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dukes, M.D.; Evans, R.O. Impact of Agriculture on Water Quality in the North Carolina Middle Coastal Plain. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2006, 132, 250–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.N.; Scott, D.T.; Guth, C.; Hester, E.T.; Hession, W.C. Influence of Sampling Frequency on Estimation of Annual Total Phosphorus and Total Suspended Solids Loads1. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2012, 48, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinozuka, K.I.; Chiwa, M.; Tayasu, I.; Yoshimizu, C.; Otsuki, K.; Kume, A. Differences in Stream Water Nitrate Concentrations between a Nitrogen-Saturated Upland Forest and a Downstream Mixed Land Use River Basin. Hydrology 2017, 4, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Griffiths, N.A.; Tank, J.L.; Royer, T.V.; Roley, S.S.; Rosi-Marshall, E.J.; Whiles, M.R.; Beaulieu, J.J.; Johnson, L.T. Agricultural land use alters the seasonality and magnitude of stream metabolism. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2013, 58, 1513–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Brady, D.C.; Ball, W.P. Long-term seasonal trends of nitrogen, phosphorus, and suspended sediment load from the non-tidal Susquehanna River Basin to Chesapeake Bay. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 452–453, 208–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.N.; Scott, D.T.; Guth, C.; Hester, E.T.; Hession, W.C. Seasonal Variation in Floodplain Biogeochemical Processing in a Restored Headwater Stream. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 13190–13198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, R.; Pan, Z.; Jin, J.; Li, C.; Ning, S. Forewarning Model of Regional Water Resources Carrying Capacity Based on Combination Weights and Entropy Principles. Entropy 2017, 19, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petersen, F.; Hubbart, J.A. Advancing Understanding of Land Use and Physicochemical Impacts on Fecal Contamination in Mixed-Land-Use Watersheds. Water 2020, 12, 1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tripathi, M.; Singal, S.K. Use of Principal Component Analysis for parameter selection for development of a novel Water Quality Index: A case study of river Ganga India. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 96, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gootman, K.S.; Hubbart, J.A. Rainfall, runoff and shallow groundwater response in a mixed-use, agro-forested watershed of the northeast, USA. Hydrol. Process. 2021, 35, e14312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechmann, M.; Deelstra, J.; Stålnacke, P.; Eggestad, H.O.; Øygarden, L.; Pengerud, A. Monitoring catchment scale agricultural pollution in Norway: Policy instruments, implementation of mitigation methods and trends in nutrient and sediment losses. Environ. Sci. Policy 2008, 11, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chase, J.W.; Benoy, G.A.; Hann, S.W.R.; Culp, J.M. Small differences in riparian vegetation significantly reduce land use impacts on stream flow and water quality in small agricultural watersheds. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2016, 71, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noe, G.B.; Hupp, C.R. Retention of Riverine Sediment and Nutrient Loads by Coastal Plain Floodplains. Ecosystems 2009, 12, 728–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouxel, M.; Molénat, J.; Ruiz, L.; Legout, C.; Faucheux, M.; Gascuel-Odoux, C. Seasonal and spatial variation in groundwater quality along the hillslope of an agricultural research catchment (Western France). Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 831–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pionke, H.B.; Gburek, W.J.; Sharpley, A.N. Critical source area controls on water quality in an agricultural watershed located in the Chesapeake Basin. Ecol. Eng. 2000, 14, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, P.T.; Vanni, M.J.; Renwick, W.H. Assessing uncertainty in annual nitrogen, phosphorus, and suspended sediment load estimates in three agricultural streams using a 21-year dataset. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerco, C.F.; Noel, M.R.; Linker, L. Managing for water clarity in Chesapeake Bay. J. Environ. Eng. 2004, 130, 631–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, A.; Reghenzani, J.; Furnas, M.; De’ath, G.; Brodie, J.; Lewis, S. Nutrients and Suspended Sediments in the Tully River: Spatial and Temporal Trends; ACTFR Report 06/10; Australian Centre for Tropical Freshwater Research: Townsville, Australia, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Linker, L.C.; Dennis, R.; Shenk, G.W.; Batuik, R.A.; Grimm, J.; Wang, P. Computing Atmospheric Nutrient Loads to the Chesapeake Bay Watershed and Tidal Waters. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2013, 49, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
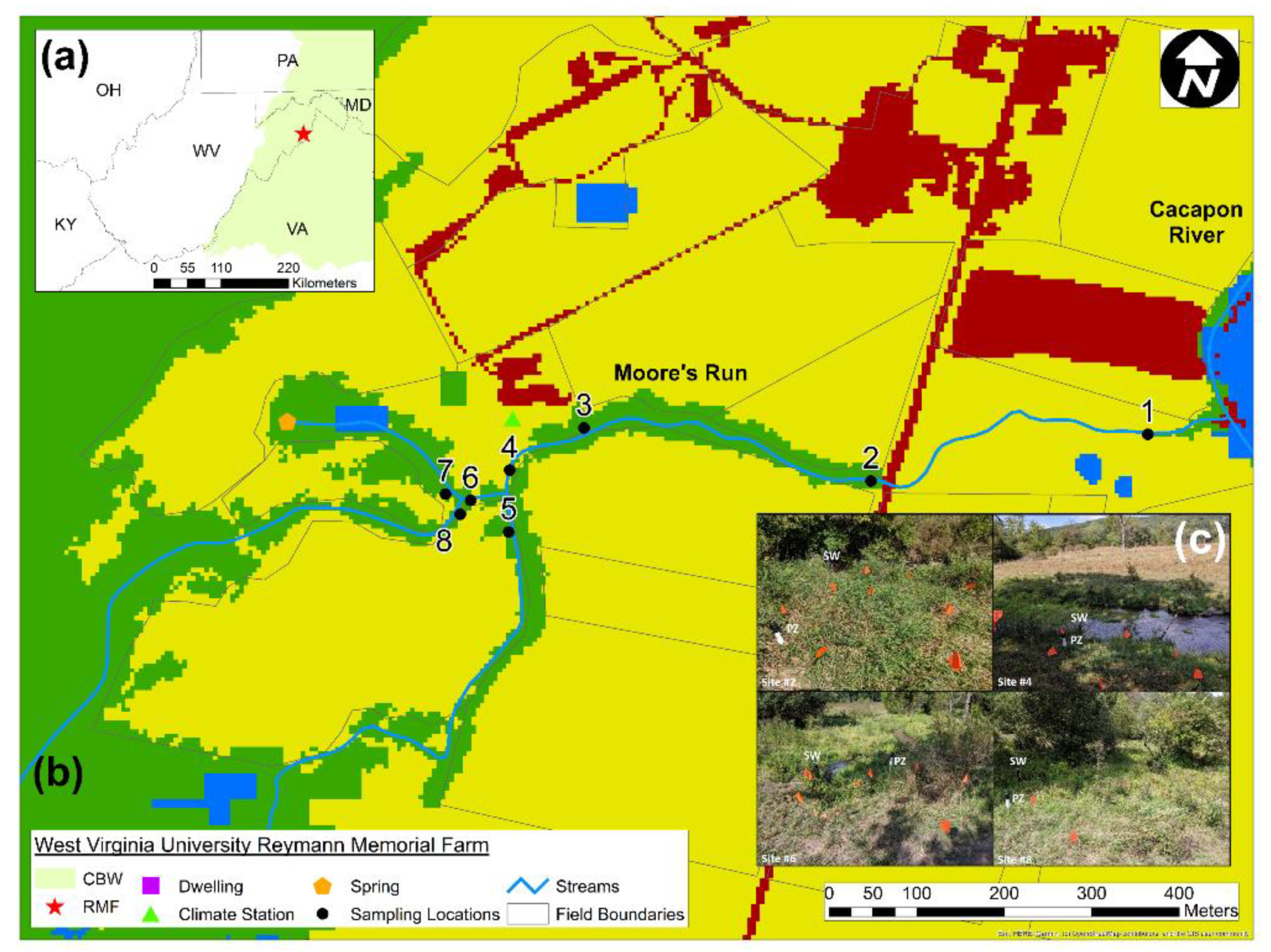

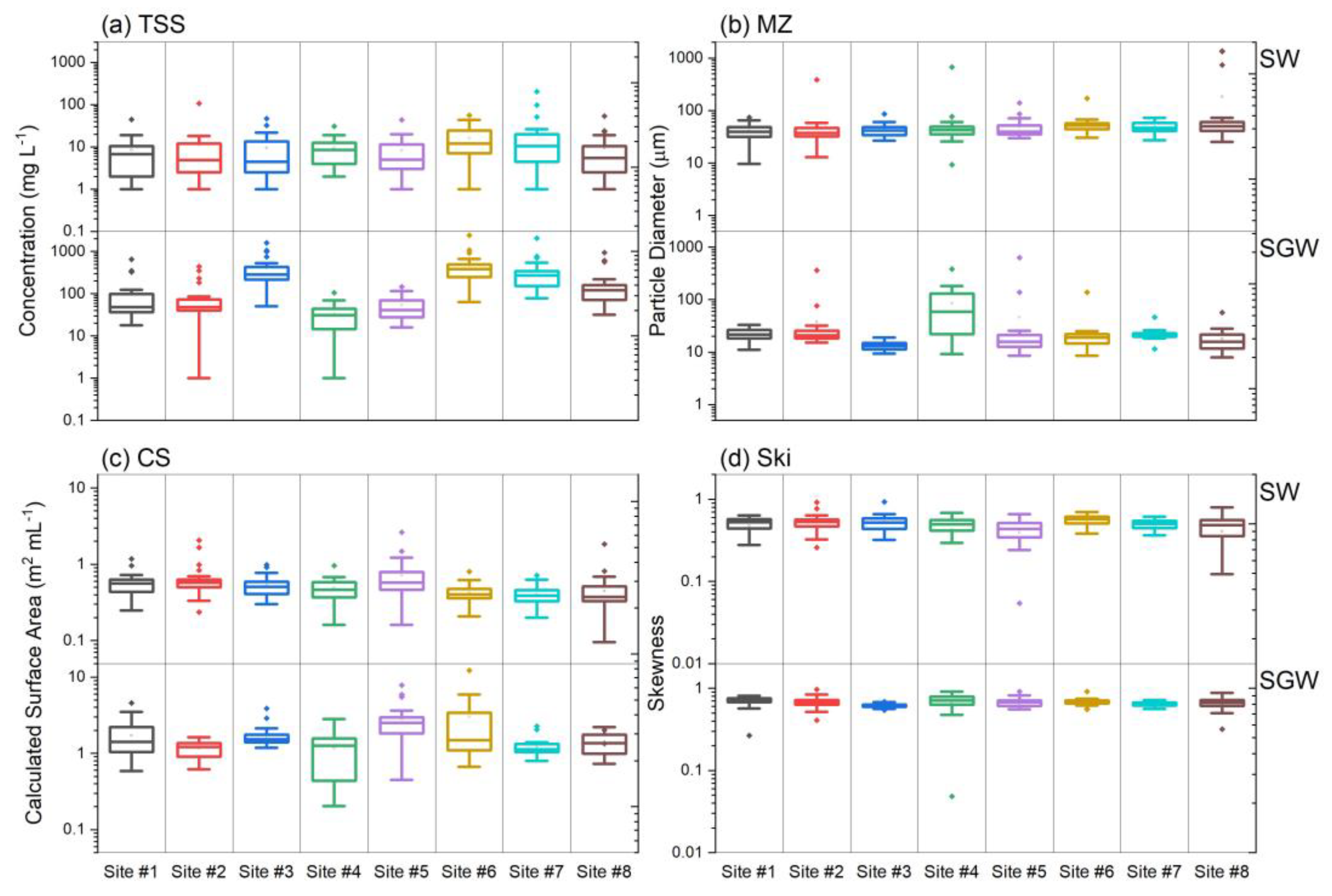

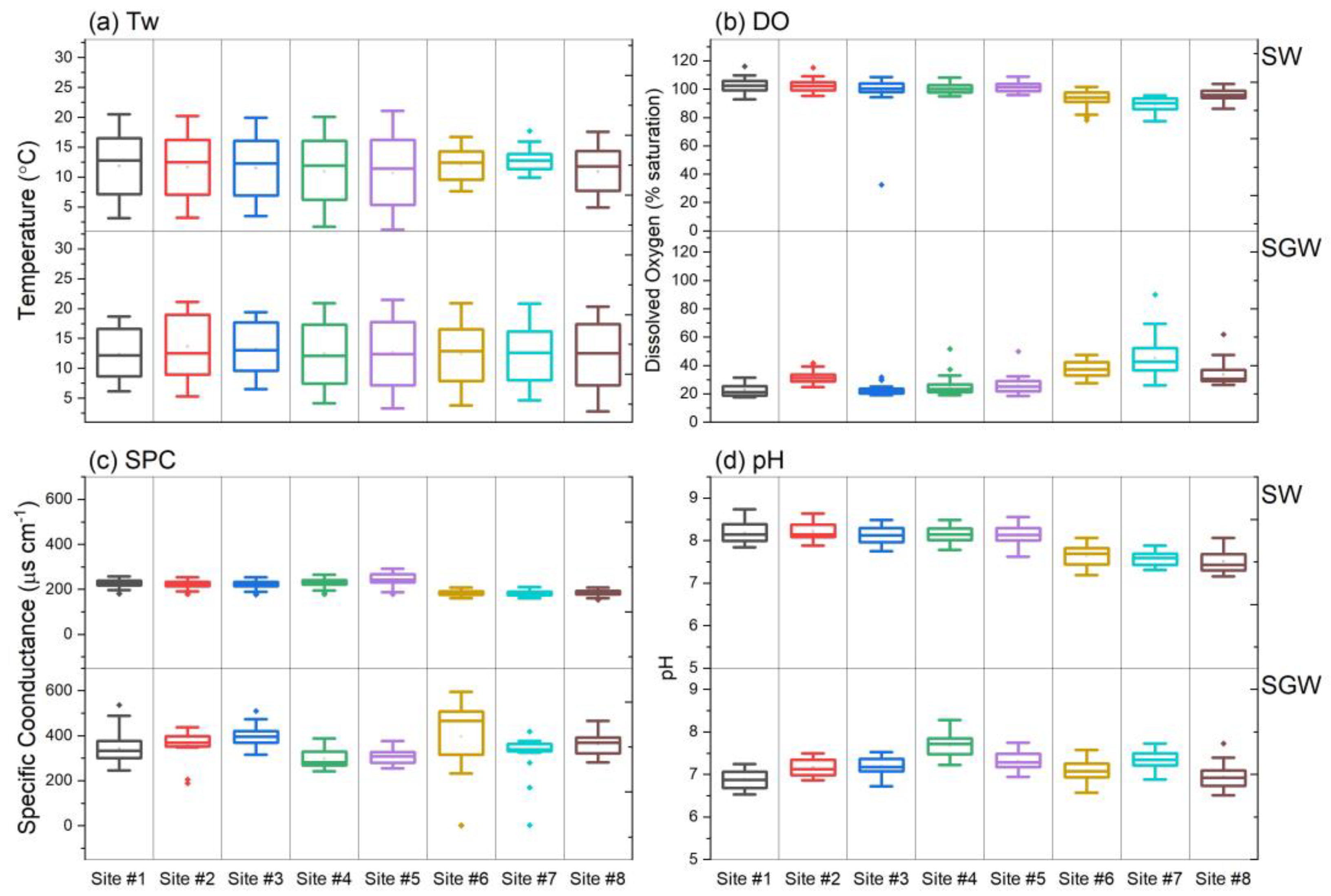

| Site | Forest (%) | Agriculture (%) | Developed (%) | Drainage Area (km2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 86.5 | 10.5 | 2.0 | 35.5 |
| 2 | 88.3 | 8.8 | 1.9 | 34.6 |
| 3 | 88.3 | 8.8 | 1.9 | 34.5 |
| 4 | 88.3 | 8.8 | 1.9 | 34.5 |
| 5 | 88.5 | 8.5 | 1.9 | 33.7 |
| 6 | 79.2 | 20.3 | 0.2 | 0.8 |
| 7 | 57.2 | 42.8 | 0.0 | <0.1 |
| 8 | 83.4 | 16.3 | 0.3 | 0.5 |
| SW | Site #1 | Site #2 | Site #3 | Site #4 |
| NO3-N | 0.34 (0.21) | 0.32 (0.19) | 0.32 (0.19) | 0.33 (0.19) |
| NO2-N | 0.03 (0.12) | 0.03 (0.12) | 0.03 (0.13) | 0.02 (0.09) |
| NH3-N | 0.02 (0.01) | 0.02 (0.01) | 0.02 (0.01) | 0.02 (0.01) |
| TN-N | 0.93 (0.29) | 0.84 (0.29) | 0.86 (0.29) | 0.99 (0.42) |
| PO43-P | 0.09 (0.06) | 0.10 (0.06) | 0.10 (0.05) | 0.07 (0.05) |
| TP-P | 0.18 (0.07) | 0.20 (0.14) | 0.18 (0.07) | 0.14 (0.06) |
| TSS | 8.46 (9.25) | 11.26 (21.31) | 9.52 (11.03) | 9.42 (6.61) |
| MZ | 41.18 (14.72) | 52.81 (71.61) | 43.05 (13.05) | 68.48 (128.47) |
| CS | 0.56 (0.20) | 0.67 (0.40) | 0.53 (0.17) | 0.49 (0.16) |
| Ski | 0.47 (0.18) | 0.53 (0.13) | 0.53 (0.12) | 0.43 (0.26) |
| Sand | 28.12 (11.65) | 28.44 (10.55) | 29.94 (8.17) | 32.06 (13.26) |
| Silt | 63.78 (9.72) | 62.72 (9.20) | 62.33 (8.11) | 61.11 (11.39) |
| Clay | 8.10 (3.83) | 8.84 (4.85) | 7.74 (3.63) | 6.83 (3.07) |
| Tw | 11.85 (5.38) | 11.64 (5.21) | 11.49 (5.06) | 10.95 (5.54) |
| DO | 102.61 (4.97) | 102.67 (4.67) | 98.30 (14.53) | 100.43 (3.27) |
| SPC | 225.74 (19.65) | 221.86 (19.51) | 222.10 (19.64) | 228.89 (21.00) |
| pH | 8.17 (0.24) | 8.21 (0.22) | 8.13 (0.21) | 8.14 (0.21) |
| SW | Site #5 | Site #6 | Site #7 | Site #8 |
| NO3-N | 0.38 (0.23) | 0.67 (2.44) | 0.23 (0.13) | 0.10 (0.09) |
| NO2-N | 0.02 (0.10) | 0.02 (0.12) | 0.02 (0.10) | 0.02 (0.10) |
| NH3-N | 0.02 (0.01) | 0.02 (0.02) | 0.02 (0.01) | 0.02 (0.03) |
| TN-N | 1.25 (0.90) | 0.88 (0.58) | 0.73 (0.43) | 0.60 (0.35) |
| PO43-P | 0.02 (0.03) | 0.29 (0.05) | 0.30 (0.03) | 0.28 (0.06) |
| TP-P | 0.06 (0.05) | 0.38 (0.11) | 0.39 (0.13) | 0.36 (0.14) |
| TSS | 8.35 (9.38) | 16.28 (13.84) | 23.50 (43.14) | 9.26 (11.39) |
| MZ | 48.67 (23.53) | 55.34 (26.09) | 49.31 (12.68) | 184.71 (383.01) |
| CS | 0.72 (0.50) | 0.43 (0.13) | 0.40 (0.12) | 0.45 (0.35) |
| Ski | 0.40 (0.25) | 0.53 (0.18) | 0.47 (0.19) | 0.41 (0.28) |
| Sand | 34.02 (13.19) | 35.58 (9.99) | 34.92 (10.64) | 40.92 (22.17) |
| Silt | 57.75 (11.96) | 58.68 (10.17) | 59.89 (10.28) | 53.03 (20.24) |
| Clay | 8.23 (3.52) | 5.74 (2.71) | 5.19 (2.63) | 6.04 (5.25) |
| Tw | 10.65 (6.22) | 11.99 (2.71) | 12.72 (1.84) | 10.95 (3.78) |
| DO | 101.25 (3.09) | 92.93 (6.42) | 89.15 (5.15) | 95.50 (5.04) |
| SPC | 244.87 (30.38) | 183.36 (12.29) | 182.68 (11.50) | 185.04 (13.15) |
| pH | 8.14 (0.23) | 7.65 (0.24) | 7.58 (0.17) | 7.52 (0.29) |
| SGW | Site #1 | Site #2 | Site #3 | Site #4 |
| NO3-N | 0.26 (0.31) | 0.12 (0.13) | 0.57 (0.58) | 0.10 (0.07) |
| NO2-N | 0.06 (0.16) | 0.04 (0.14) | 0.19 (0.34) | 0.04 (0.14) |
| NH3-N | 0.19 (0.09) | 0.10 (0.06) | 0.47 (0.24) | 0.34 (0.15) |
| TN-N | 1.27 (0.90) | 0.93 (0.48) | 2.03 (1.25) | 1.17 (0.54) |
| PO43-P | 0.23 (0.14) | 0.00 (0.01) | 0.12 (0.19) | 0.04 (0.04) |
| TP-P | 0.86 (0.74) | 0.13 (0.15) | 1.97 (0.98) | 0.25 (0.07) |
| TSS | 104.95 (144.77) | 87.48 (108.00) | 407.75 (357.51) | 32.78 (23.97) |
| MZ | 21.61 (6.07) | 37.84 (69.41) | 13.20 (2.39) | 85.88 (85.98) |
| CS | 1.71 (0.98) | 1.17 (0.29) | 1.69 (0.60) | 1.17 (0.77) |
| Ski | 0.70 (0.11) | 0.68 (0.11) | 0.61 (0.03) | 0.65 (0.25) |
| Sand | 14.48 (5.19) | 15.52 (7.08) | 6.35 (2.29) | 33.56 (21.30) |
| Silt | 63.81 (8.72) | 65.76 (7.64) | 67.15 (3.85) | 51.30 (15.49) |
| Clay | 21.72 (8.25) | 18.73 (4.26) | 26.50 (4.27) | 15.14 (10.25) |
| Tw | 12.31 (4.24) | 13.65 (5.57) | 13.14 (4.28) | 12.48 (5.45) |
| DO | 22.60 (4.27) | 31.87 (4.53) | 22.97 (3.67) | 25.28 (7.11) |
| SPC | 342.18 (69.46) | 362.75 (56.44) | 396.00 (45.26) | 296.24 (39.47) |
| pH | 6.88 (0.23) | 7.17 (0.19) | 7.18 (0.20) | 7.68 (0.27) |
| (SGW) | Site #5 | Site #6 | Site #7 | Site #8 |
| NO3-N | 0.15 (0.10) | 0.89 (1.05) | 0.52 (0.44) | 0.34 (0.47) |
| NO2-N | 0.04 (0.11) | 0.20 (0.33) | 0.18 (0.37) | 0.17 (0.57) |
| NH3-N | 0.24 (0.14) | 0.61 (0.29) | 0.33 (0.13) | 0.36 (0.35) |
| TN-N | 0.97 (0.46) | 3.02 (2.21) | 2.12 (1.52) | 1.63 (1.12) |
| PO43-P | 0.04 (0.04) | 0.34 (0.69) | 0.09 (0.35) | 0.03 (0.04) |
| TP-P | 0.58 (0.32) | 5.18 (3.18) | 3.14 (1.77) | 0.66 (0.70) |
| TSS | 53.76 (34.68) | 477.63 (482.48) | 360.18 (403.95) | 182.87 (216.46) |
| MZ | 46.60 (126.30) | 23.03 (25.08) | 22.04 (5.91) | 18.09 (10.15) |
| CS | 2.81 (1.77) | 2.98 (3.23) | 1.21 (0.34) | 1.39 (0.44) |
| Ski | 0.64 (0.20) | 0.68 (0.07) | 0.65 (0.04) | 0.66 (0.11) |
| Sand | 13.31 (12.20) | 12.78 (6.37) | 14.53 (5.28) | 10.05 (6.18) |
| Silt | 59.75 (9.82) | 63.24 (9.15) | 66.61 (5.62) | 67.11 (6.09) |
| Clay | 26.94 (9.44) | 23.98 (8.87) | 18.86 (3.84) | 22.85 (7.99) |
| Tw | 12.66 (5.95) | 12.37 (5.33) | 12.53 (4.86) | 12.45 (5.41) |
| DO | 26.00 (6.51) | 37.81 (5.93) | 45.33 (14.22) | 33.69 (7.69) |
| SPC | 304.70 (32.68) | 395.26 (177.55) | 326.27 (82.23) | 363.79 (49.04) |
| pH | 7.31 (0.22) | 7.08 (0.23) | 7.35 (0.24) | 6.95 (0.30) |
| Parameter | PC 1 | Parameter | PC 2 | Parameter | PC 3 | Parameter | PC 4 | Parameter | PC 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NH3-N | 0.34 | Ag | 0.49 | MZ | 0.46 | Silt | 0.44 | Tw | 0.65 |
| Clay | 0.31 | PO43-P | 0.21 | Sand | 0.35 | NO2-N | 0.3 | PO43-P | 0.46 |
| TSS | 0.3 | TP-P | 0.2 | TN-N | 0.28 | pH | 0.27 | NO3-N | 0.29 |
| TP-P | 0.29 | Sand | 0.16 | TSS | 0.26 | TN-N | 0.27 | Ski | 0.22 |
| SPC | 0.29 | DO | 0.16 | For | 0.23 | DO | 0.24 | For | 0.11 |
| TN-N | 0.27 | TSS | 0.14 | NH3-N | 0.23 | TSS | 0.22 | Sand | 0.1 |
| CS | 0.23 | NO2-N | 0.13 | NO2-N | 0.2 | NO3-N | 0.2 | NO2-N | 0.06 |
| Ski | 0.2 | TN-N | 0.13 | NO3-N | 0.19 | Tw | 0.18 | MZ | 0.04 |
| NO3-N | 0.17 | NO3-N | 0.1 | TP-P | 0.17 | Dev | 0.18 | Dev | 0.04 |
| Silt | 0.13 | MZ | 0.1 | Dev | 0.14 | For | 0.15 | NH3-N | −0.01 |
| NO2-N | 0.12 | Tw | 0.04 | pH | 0.12 | TP-P | 0.04 | SPC | −0.04 |
| Tw | 0.09 | NH3-N | 0.03 | SPC | 0.04 | NH3-N | 0.03 | Silt | −0.07 |
| Ag | 0.07 | pH | −0.01 | DO | 0.01 | PO43-P | −0.03 | Clay | −0.08 |
| PO43-P | 0.01 | Silt | −0.05 | CS | 0.01 | SPC | −0.13 | Ag | −0.1 |
| For | −0.06 | Ski | −0.11 | Tw | −0.03 | Ag | −0.16 | DO | −0.14 |
| Dev | −0.09 | CS | −0.16 | PO43-P | −0.04 | Sand | −0.18 | TN-N | −0.14 |
| MZ | −0.15 | SPC | −0.17 | Clay | −0.05 | Clay | −0.21 | TSS | −0.16 |
| pH | −0.28 | Clay | −0.21 | Ski | −0.1 | Ski | −0.22 | TP-P | −0.17 |
| Sand | −0.29 | Dev | −0.46 | Ag | −0.23 | MZ | −0.28 | CS | −0.18 |
| DO | −0.31 | For | −0.48 | Silt | −0.45 | CS | −0.29 | pH | −0.25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gootman, K.S.; Hubbart, J.A. Characterization of Sub-Catchment Stream and Shallow Groundwater Nutrients and Suspended Sediment in a Mixed Land Use, Agro-Forested Watershed. Water 2023, 15, 233. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15020233
Gootman KS, Hubbart JA. Characterization of Sub-Catchment Stream and Shallow Groundwater Nutrients and Suspended Sediment in a Mixed Land Use, Agro-Forested Watershed. Water. 2023; 15(2):233. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15020233
Chicago/Turabian StyleGootman, Kaylyn S., and Jason A. Hubbart. 2023. "Characterization of Sub-Catchment Stream and Shallow Groundwater Nutrients and Suspended Sediment in a Mixed Land Use, Agro-Forested Watershed" Water 15, no. 2: 233. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15020233





