Spatial–Temporal Distribution and Interrelationship of Sulfur and Iron Compounds in Seabed Sediments: A Case Study in the Closed Section of Mikawa Bay, Japan
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
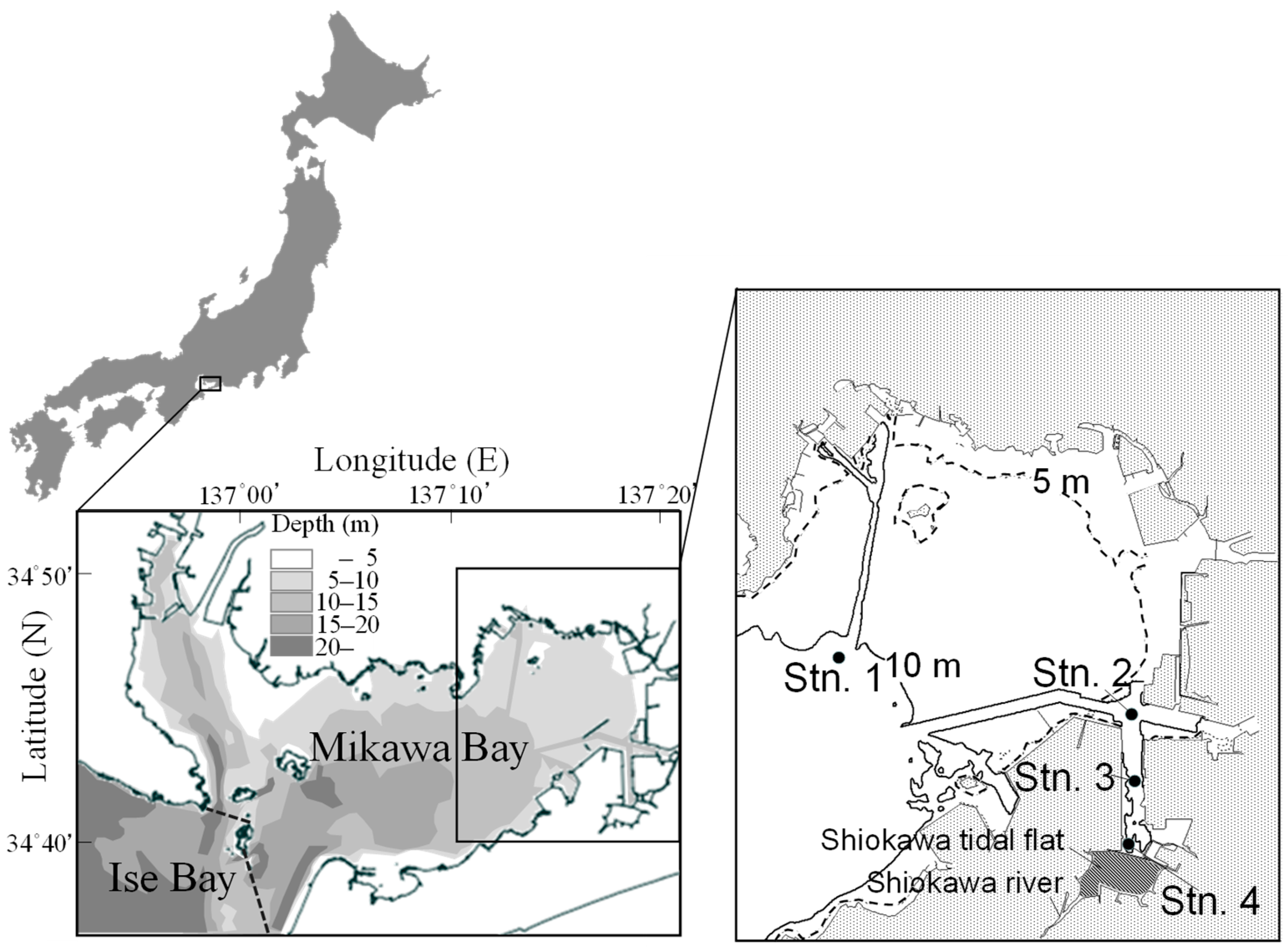
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Field Observations and Sampling
2.3. Chemical Analysis of Sediment Samples
3. Results
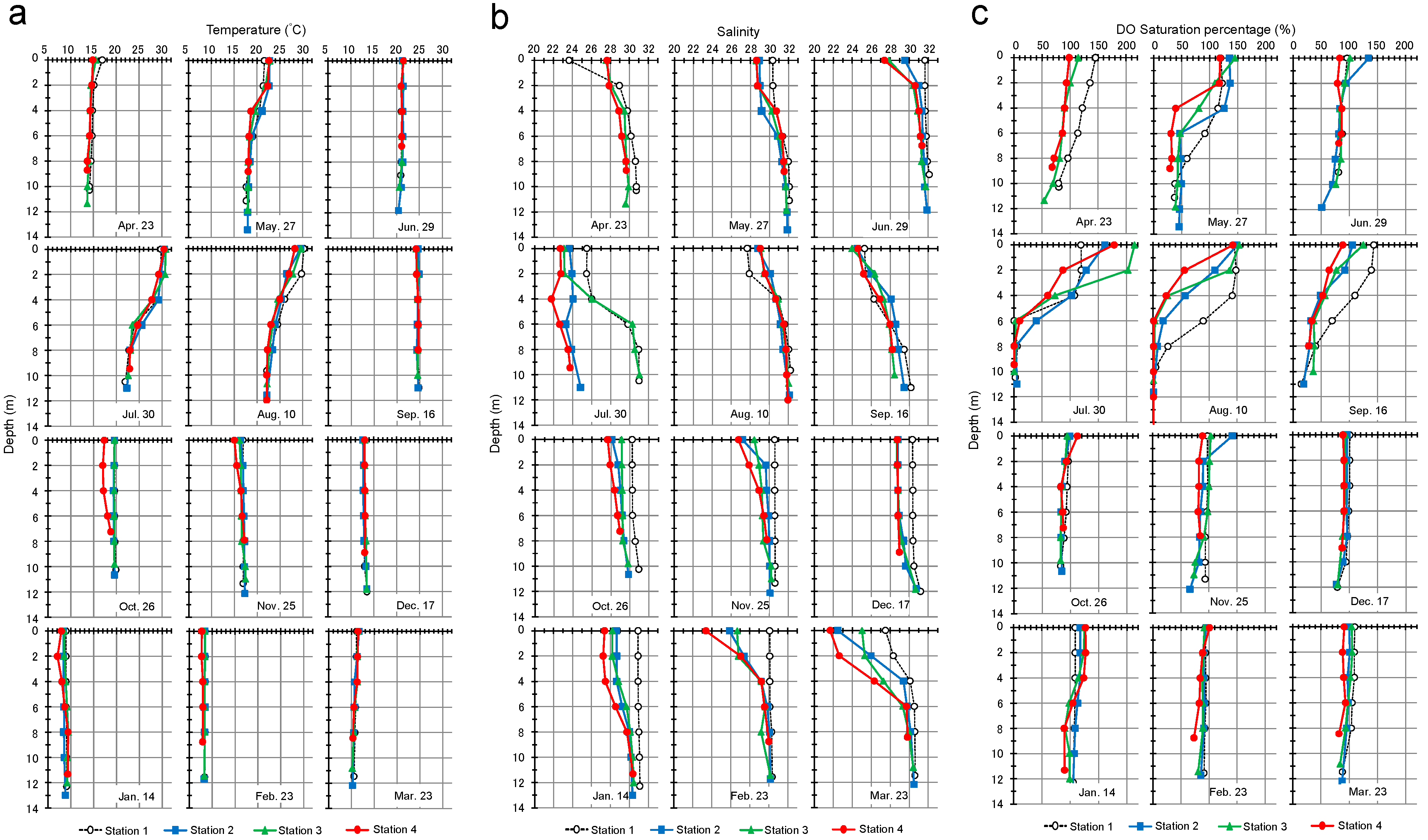
3.1. Temperature, Salinity, and Dissolved Oxygen Profiles of Seawater
3.2. Total Organic Carbon Concentration and Grain Size of the Sediments
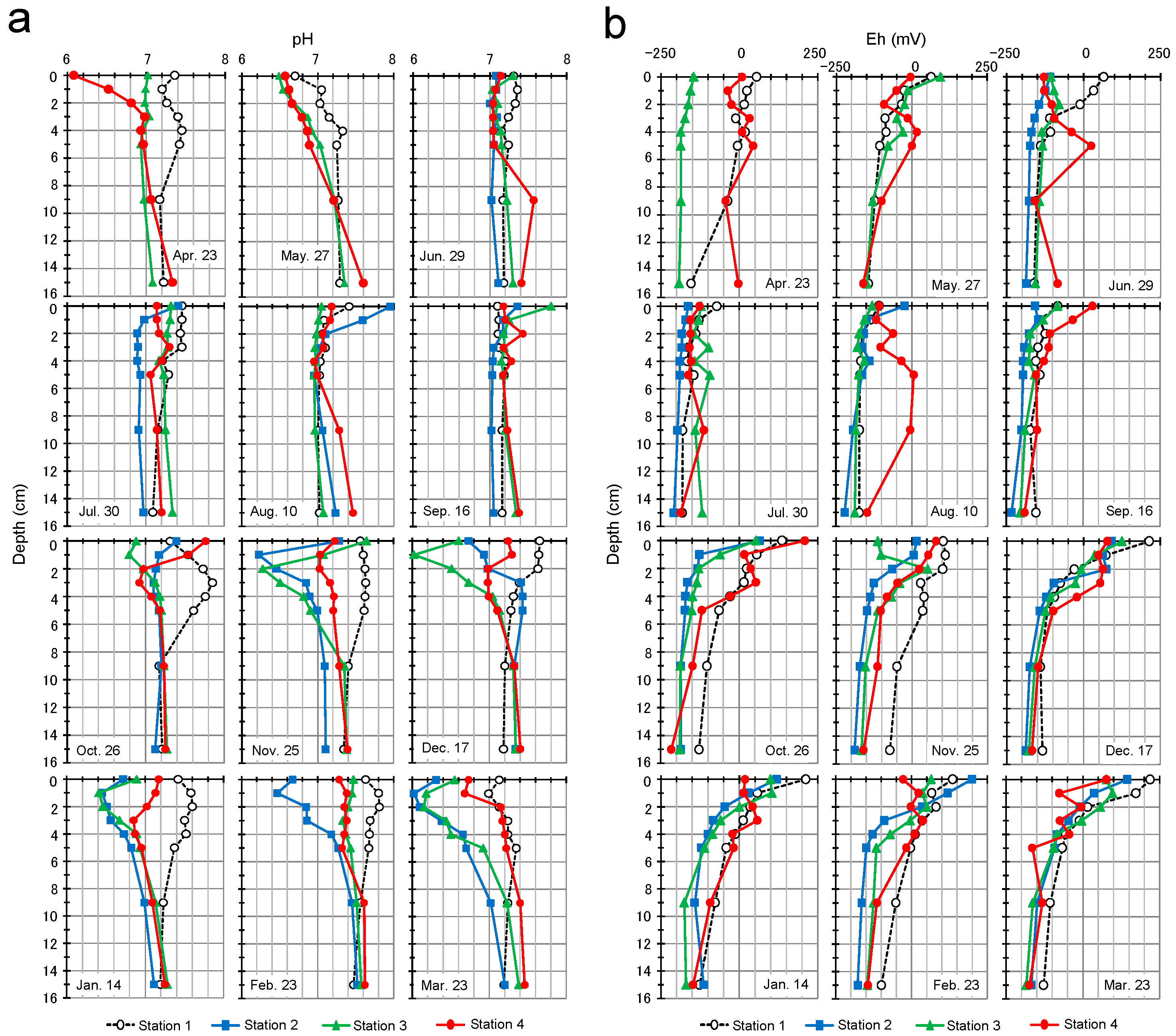
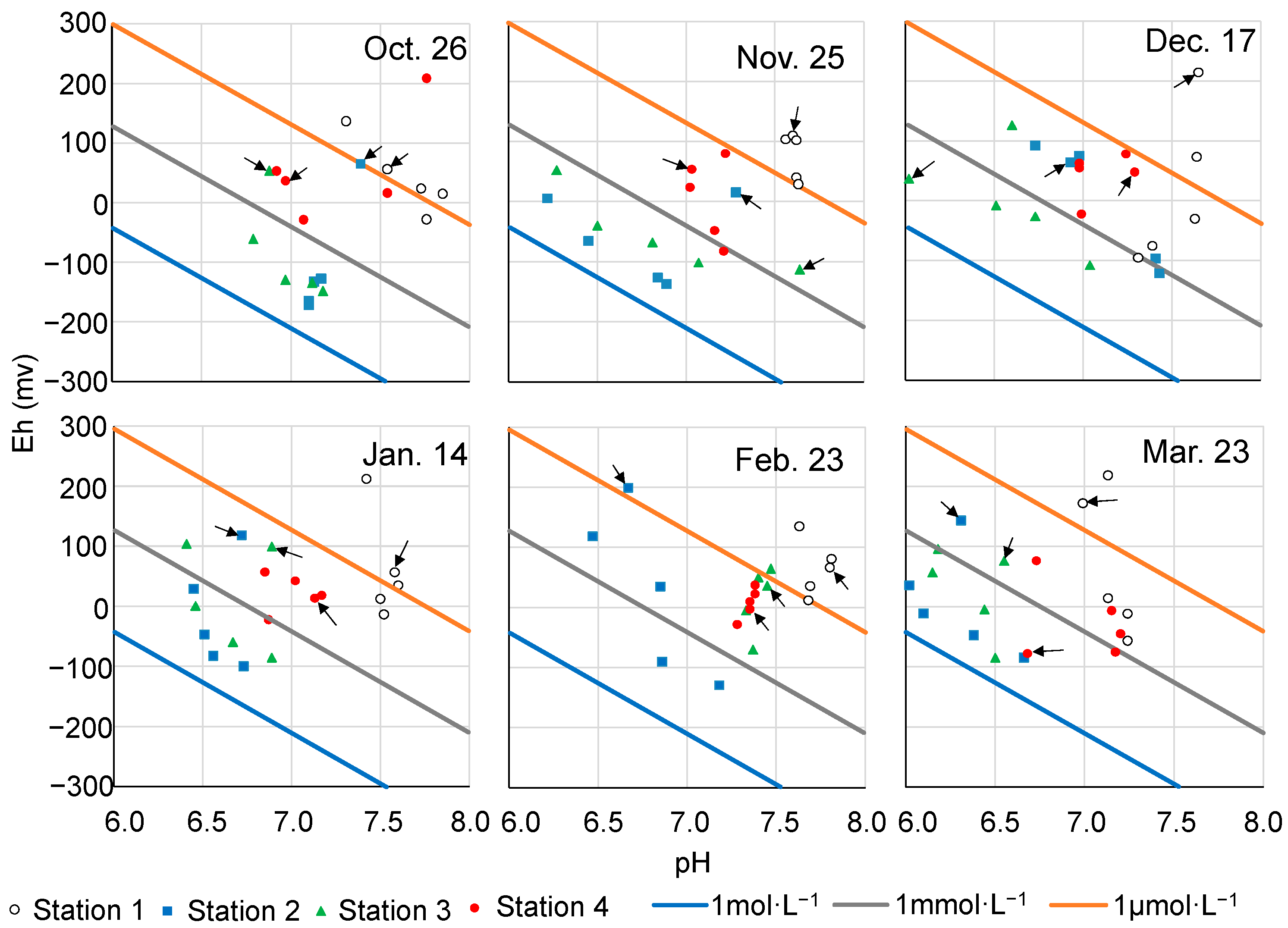
3.3. pH and Redox Potential Profiles of Sediment Porewater
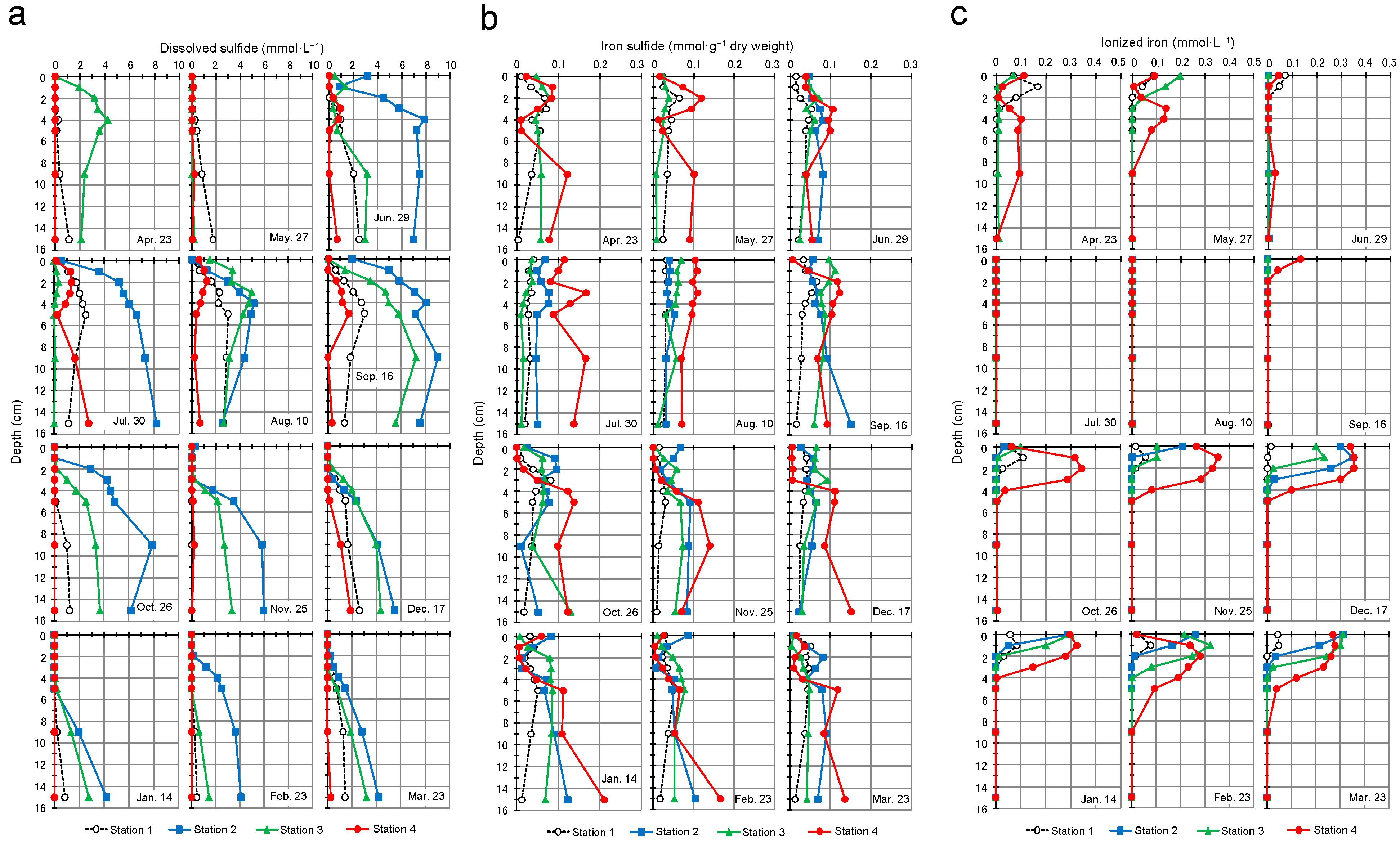
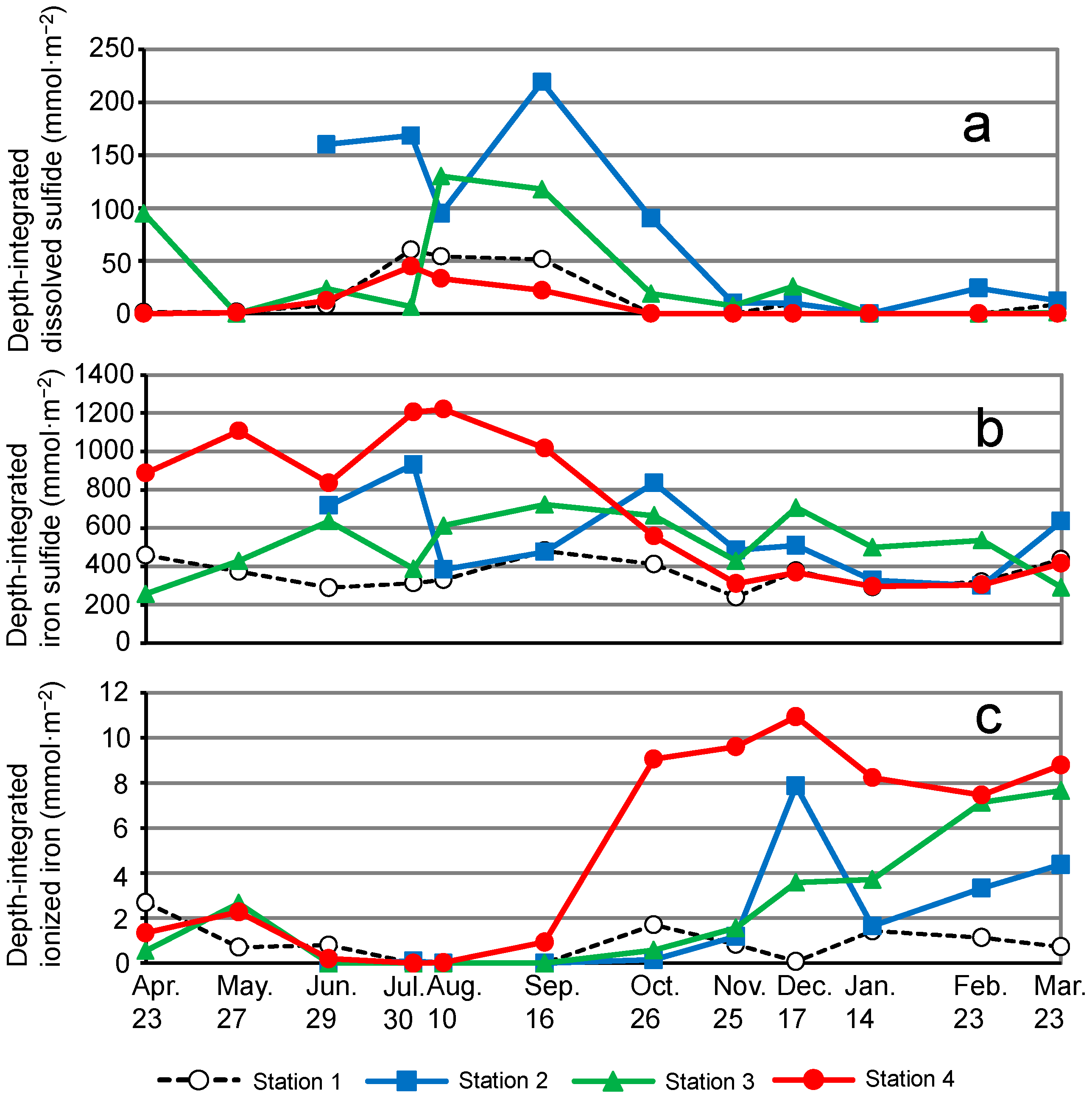
3.4. Dissolved Sulfide, Iron Sulfide, and Ionized Iron Profiles of Sediment Porewater
4. Discussion
4.1. Seasonal Prevalence of Sulfur and Iron Compounds in Sediments of Mikawa Bay
4.2. Intersite Comparison of the Sulfur–Iron Cycle
4.3. Chemical Buffering Capacity toward Sulfide
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kodama, K.; Horiguchi, T. Effects of hypoxia on benthic organisms in Tokyo Bay, Japan: A review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 63, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sone, R.; Waku, M.; Yamada, S.; Suzuki, T.; Takabe, T. Spatio-temporal dynamics and mortality of mega-benthos in relation to the development of hypoxia in an inner bay: A model study in Mikawa Bay, Japan. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Fish. Oceanogr. 2017, 81, 230–244. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, T. Oxygen-deficient waters along the Japanese coast and their effects upon the estuarine ecosystem. J. Environ. Qual. 2001, 30, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamohara, S.; Shiba, S.; Tsurushima, D.; Suzuku, T. Relationship of Manila clam (Ruditapes philippinarum) growth with aged changes of total nitrogen and total phosphorus in Mikawa Bay, Japan. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Fish. Oceanogr. 2021, 85, 69–78. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, T. Large-scale restoration of tidal flats and shallows to suppress the development of oxygen deficient water masses in Mikawa Bay. Bull. Fish. Res. Agen. 2004, 1, 111–121. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, T.; Matsukawa, Y. Hydrography and budget of dissolved total nitrogen and dissolved oxygen in the stratified season in Mikawa Bay, Japan. J. Oceanogr. Soc. Jpn. 1987, 43, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Ishii, K.; Imao, K.; Matsukawa, Y. Box model analysis on phytoplankton production and grazing pressure in a eutrophic estuary. J. Oceanogr. Soc. Jpn. 1987, 43, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waku, M.; Kaneko, K.; Suzuki, T.; Takabe, T. Distribution of dead zones in the coastal waters: A model study in Mikawa Bay, Japan. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Fish. Oceanogr. 2012, 76, 187–196. [Google Scholar]
- Diaz, R.J.; Rosenberg, R. Spreading dead zones and consequences for marine ecosystems. Science 2008, 321, 926–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waku, M.; Hata, K.; Kaneko, K.; Suzuki, T.; Takabe, T. Adverse effects of dead zones in the coastal waters on the bay-wide material cycle and its remedial measures: An analyze with the ecosystem model in Mikawa Bay, Japan. J. Adv. Mar Sci. Tec. Soc. 2013, 19, 15–27. [Google Scholar]
- Brüchert, V.; Jorgensen, B.B.; Neumann, K.; Riechmann, D.; Schlosser, M.; Schulz, H. Regulation of bacterial sulphate reduction and hydrogen sulphide fluxes in the central Namibian coastal upwelling zone. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2003, 67, 4505–4518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavik, G.; Stuhrmann, T.; Brüchert, V.; Van der Plas, A.; Mohrholz, V.; Lam, P.; Mussmann, M.; Fuchs, B.M.; Amann, R.; Lass, U.; et al. Detoxification of sulphidic African shelf waters by blooming chemolithotrophs. Nature 2009, 457, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canfield, D.E. Reactive iron in marine sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1989, 53, 619–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saager, P.M.; De Baar, H.J.W.; Burkill, P.H. Manganese and iron in Indian Ocean waters. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1989, 53, 2259–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Millero, F.J. Oxidation of hydrogen sulfide by hydrous Fe(III) oxides in seawater. Mar. Chem. 1996, 52, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez, F.; Zang, G.J.; Millero, F.J. Effect of metals on the oxidation of H2S in seawater. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1989, 16, 1363–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfield, D.E.; Raiswell, R.; Bottrell, S.H. The reactivity of sedimentary iron minerals toward sulfide. Am. J. Sci. 1992, 292, 659–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmer, M.; Kristensen, E.; Banta, G.; Hansen, K.; Jensen, M.H.; Bussawarit, N. Biogeochemical cycling of sulfur and iron in sediments of a south-east Asian mangrove, Phuket Island, Thailand. Biogeochemistry 1994, 26, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luther, G.W., III; Church, T.M.; Scudlark, J.R.; Cosman, C. Inorganic and organic sulfur cycling in salt-marsh pore waters. Science 1986, 232, 746–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antler, G.; Mills, J.V.; Hutchings, A.M.; Redeker, K.R.; Turchyn, A.V. The sedimentary carbon-sulfur-iron interplay—A lesson from east anglian salt marsh sediments. Front. Earth Sci. 2019, 7, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijsman, J.W.M.; Middelburg, J.J.; Herman, P.M.J.; Böttcher, M.E.; Heip, C.H.R. Sulfur and iron speciation in surface sediments along the northwestern margin of the Black Sea. Mar. Chem. 2001, 74, 261–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeslundi, L.; Thamdrup, B.; Jørgensen, B.B. Sulfur and iron cycling in a coastal sediment: Radiotracer studies and seasonal dynamics. Biogeochemistry 1994, 27, 129–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howarth, R.W. Pyrite: Its rapid formation in a salt marsh and its importance in ecosystem metabolism. Science 1979, 203, 49–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howarth, R.W.; Jørgensen, B.B. Formation of 35S-labelled elemental sulfur and pyrite in coastal marine sediments (Limfjorden and Kysing Fjord, Denmark) during short-term 35SO42− reduction measurements. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1984, 48, 1807–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drobner, E.; Huber, H.; Wächtershäuser, G.; Rose, D.; Stetter, K.O. Pyrite formation linked with hydrogen evolution under anaerobic conditions. Nature 1990, 346, 742–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumm, W.; Morgan, J.J. Aqueous carbonate system open to the atmosphere. In Aquatic Chemistry; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Dong, X.; Wang, M.; Wang, G. Sulfur cycling in freshwater sediments: A cryptic driving force of iron deposition and phosphorus mobilization. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 1294–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Wu, S.; Yu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, G. Seasonal iron-sulfur interactions and the stimulated phosphorus mobilization in freshwater lake sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 768, 144336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Okai, M.; Takeshita, K.; Hashimoto, T. Characteristics of meteorological conditions in the years of intensive red tide occurrence in Mikawa Bay, Japan. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Fish. Oceanogr. 1997, 61, 114–122. [Google Scholar]
- Coastal Oceanography Research Committee, The Oceanographical Society of Japan. Coastal Oceanography of Japanese Islands; Tokai University Press: Tokyo, Japan, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 17892-4:2016; Geotechnical Investigation and Testing–Laboratory Testing of Soil—Part 4: Determination of Particle Size Distribution. Japanese Standards Association: Tokyo, Japan, 2016.
- Sugahara, S.; Suzuki, M.; Kamiya, H.; Yamamuro, M.; Semura, H.; Senga, Y.; Egawa, M.; Seike, Y. Colorimetric determination of sulfide in microsamples. Anal. Sci. 2016, 32, 1129–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, H. Zum Problem der Nachweisgrenze. Z. Anal. Chem. 1965, 209, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 6332:1988; Water Quality–Determination via the Iron-Spectrometric Method Using 1, 10-Phenanthroline. Japanese Standards Association: Tokyo, Japan, 1988.
- Fossing, H. A Model Set-Up for an Oxygen and Nutrient Flux Model for Aarhus Bay (Denmark); NERI Technical Report No. 483; National Environmental Research Institute, Ministry of the Environment: Roskilde, Denmark, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Middelburg, J.J.; Levin, L.A. Coastal hypoxia and sediment biogeochemistry. Biogeosci. Discuss. 2009, 6, 1273–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfield, D.E. Factors influencing organic carbon preservation in marine sediments. Chem. Geol. 1994, 114, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passier, H.F.; Middelburg, J.J.; de Lange, J.J.; Bottcher, M.E. Pyrite contents, microtextures, and sulphur isotopes in relation to formation of the youngest eastern Mediterranean sapropel. Geology 1997, 25, 519–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochida, F.; Nakamura, Y.; Inoue, T.; Higa, H.; Suzuki, T. Reproduction of the suppression effect of iron on sulfide release: Verification of the suppression effect of iron. J. Jpn. Soc. Civ. Eng. Ser. G 2021, 77, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, T.; Hagino, Y. Effects of three iron material treatments on hydrogen sulfide release from anoxic sediments. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 85, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozan, T.F.; Taillefert, M.; Trouwborst, R.E.; Glazer, B.T.; Ma, S.F.; Herszage, J.; Valdes, L.M.; Price, K.S.; Luther, G.W., III. Iron-sulphur-phosphorus cycling in the sediments of a shallow coastal bay: Implications for sediment nutrient release and benthic macroalgal blooms. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2002, 47, 1346–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heijis, S.K.; Jonkers, H.M.; Gemerden, H.V.; Schaub, B.E.M.; Stal, L.J. The buffering capacity towards free sulphide in sediments of a coastal lagoon (Bassin d’Arcachon, France)–the relative importance of chemical and biological processes. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1999, 49, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taillefert, M.; Bono, A.B.; Luther, G.W., III. Reactivity of freshly formed Fe(III) in synthetic solutions and (pore)waters. Voltammetric evidence of an aging process. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 2169–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, E.A.; Edmond, J.M.; Sholkovitz, E.R. The mechanism of iron removal in estuaries. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1977, 41, 1313–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, Y.; Hayashi, A.; Kuwayama, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Tanishiki, K.; Urabe, N. A field experiment of sulfide reduction in silty sediment using steelmaking slag. ISIJ Int. 2014, 100, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sampling Day | Station | TOC (mg·g−1 Dry Weight) | Silt and Clay Content (Particle Diameter < 0.075 mm) (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20 May | 1 | 26.9 | 98.6 |
| 20 June | 2 | 22.1 | 84.9 |
| 22 June | 3 | 21.4 | 92.4 |
| 22 June | 4 | 18.1 | 81.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Waku, M.; Sone, R.; Inoue, T.; Ishida, T.; Suzuki, T. Spatial–Temporal Distribution and Interrelationship of Sulfur and Iron Compounds in Seabed Sediments: A Case Study in the Closed Section of Mikawa Bay, Japan. Water 2023, 15, 3465. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15193465
Waku M, Sone R, Inoue T, Ishida T, Suzuki T. Spatial–Temporal Distribution and Interrelationship of Sulfur and Iron Compounds in Seabed Sediments: A Case Study in the Closed Section of Mikawa Bay, Japan. Water. 2023; 15(19):3465. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15193465
Chicago/Turabian StyleWaku, Mitsuyasu, Ryota Sone, Tetsunori Inoue, Toshiro Ishida, and Teruaki Suzuki. 2023. "Spatial–Temporal Distribution and Interrelationship of Sulfur and Iron Compounds in Seabed Sediments: A Case Study in the Closed Section of Mikawa Bay, Japan" Water 15, no. 19: 3465. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15193465
APA StyleWaku, M., Sone, R., Inoue, T., Ishida, T., & Suzuki, T. (2023). Spatial–Temporal Distribution and Interrelationship of Sulfur and Iron Compounds in Seabed Sediments: A Case Study in the Closed Section of Mikawa Bay, Japan. Water, 15(19), 3465. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15193465







