Review on the Use of Magnetic Nanoparticles in the Detection of Environmental Pollutants
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Synthesis of Magnetic Nanoparticles
3. Modification and Functionalization of MNPs
3.1. Magnetic Nanomaterials Functionalized with Metal-Organic Frameworks
3.2. Ionic Liquid Functionalized Magnetic Nanomaterials
3.3. Magnetic Nanomaterials Functionalized by Molecularly Imprinted Polymers
4. Application of MNPs in Environment Detection
4.1. Application in Water Environment Detection
4.2. Application in Soil Environmental Detection
5. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gupta, A.K.; Gupta, M. Synthesis and surface engineering of iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 3995–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cheng, J.; Liu, W. Characterization and relaxation properties of a series of Monodispersed magnetic nanoparticles. Sensors 2019, 19, 3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Ji, H.N.; Yu, P.; Niu, J.Q.; Faroop, M.U.; Akram, M.W.; Udego, I.O.; Li, H.; Niu, X. Surface modification of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Wang, C.; Chen, Y.; Tan, L.; Wang, P.; Feng, S. IL-functionalized Mn(II)-doped core-shell Fe3O4@Zr-MOF nanomaterials for the removal of MB from wastewater based on dual adsorption/Fenton catalysis. New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 8534–8544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Z.; Yuan, C.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J. Developed on the Adsorption Properties of 9 Organophosphorus Pesticides in Spinach by Magnetic Nanoparticles Modified Carbon Nanotube Composites. Food Ferment. Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 70–75. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lou, X.Y.; Boada, R.; Verdugo, V.; Simonelli, L.; Pérez, G.; Valiente, M. Decoupling the adsorption mechanisms of arsenate at molecular level on modified cube-shaped sponge loaded superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 121, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhou, L.; Ma, F.; Zhao, H.; Deng, F.; Pi, S.; Tang, A. Magnetic nanocomposite microbial extracellular polymeric substances@Fe3O4 supported nZVI for Sb(V) reduction and adsorption under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. Environ. Res. 2020, 189, 109950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plastiras, O.-E.; Deliyanni, E.; Samanidou, V. Synthesis and Application of the Magnetic Nanocomposite GO-Chm for the Extraction of Benzodiazepines from Surface Water Samples Prior to HPLC-PDA Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Huang, J.; Xu, Z.; Ali, M.; Shan, A.; Fu, R.; Lyu, S. Mechanism of contaminants degradation in aqueous solution by persulfate in different Fe(II)-based synergistic activation environments: Taking chlorinated organic compounds and benzene series as the targets. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 273, 118990–118998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilardi, G.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, J.; Ochando-Pulido, J.M.; Verdone, N.; Martinez-Ferez, A.; Palma, L.D. Large Laboratory-Plant application for the treatment of a Tannery wastewater by Fenton oxidation: Fe(II) and nZVI catalysts comparison and kinetic modelling. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 117, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qasmi, N.; Almughem, F.A.; Jarallah, S.J.; Almaabadi, A. Efficient Green Synthesis of (Fe3O4) and (NiFe2O4) Nanoparticles Using Star Anise (Illicium verum) Extract and Their Biomedical Activity against Some Cancer Cells. Materials 2022, 15, 4832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, M.D.; Tran, H.-V.; Xu, S.; Lee, T.R. Fe3O4 Nanoparticles: Structures, Synthesis, Magnetic Properties, Surface Functionalization, and Emerging Applications. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Peng, X.; Ni, F.; Li, J.; Wang, D.; Luan, Z. Arsenite removal from aqueous solutions by γ-Fe2O3-TiO2 magnetic nanoparticles through simultaneous photocatalytic oxidation and adsorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 246–247, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhbarizadeh, R.; Shayestefar, M.R.; Darezereshki, E. Competitive Removal of Metals from Wastewater by Maghemite Nanoparticles: A Comparison Between Simulated Wastewater and AMD. Mine Water Environ. 2014, 33, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierucka, M.; Biziuk, M. Application of magnetic nanoparticles for magnetic solid-phase extraction in preparing biological, environmental and food samples. Trends Anal. Chem. 2014, 59, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Kim, S.-M.; Yoon, I.-H.; Choi, S.-J.; Kim, I. Selective separation of Cs-contaminated clay from soil using polyethylenimine-coated magnetic nanoparticles. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 706, 136020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Yu, Z.Y.; Yang, T.L.; Xu, G.; Guan, Y.; Guo, C. Modified Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles for COD removal in oil field produced water and regeneration. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 23, 101630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Chaudhary, S.; Dehiya, B.S. Fast removal of heavy metals from water and soil samples using magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 3942–3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, Y.J.; Lee, E.-H.; Lee, S.-W. Adsorptive removal of micron-sized polystyrene particles using magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Huang, K.; Xu, W. Third generation whole-cell sensing systems: Synthetic biology inside, nanomaterial outside. Trends Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Gu, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Q. Preparation and electromagnetic properties of nanosized Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 ferrite. Rare Met. 2022, 41, 3228–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomar, D.; Jeevanandam, P. Synthesis of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles with different morphologies via thermal decomposition approach and studies on their magnetic properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 843, 155815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beygi, H.; Babakhani, A. Microemulsion synthesis and magnetic properties of FexNi(1-x) alloy nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 421, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, S.; Imran, M.; Kanwal, F.; Javaid, A.; Latif, S.; Boczkaj, G. Design and Preparation of Magnetically-Oriented Poly(styr-co-MMA)-3MPS Capped Fe(ZnO) Hybrid Microspheres for Ion Exchange Removal of Toxic Pollutants from Wastewater. Water 2023, 15, 1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, M.S.A.; Al-Harbi, L.M. Self-heating properties of iron oxide nanoparticles prepared at room temperature via ultrasonic-assisted co-precipitation process. Soft Mater. 2022, 10, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Yang, Y.; He, S.; Li, Y.; Gu, N. Biomimetic synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles mediated by magnetosome proteins. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2020, 65, 1476–1485. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, V.; Ganesan, R.; Syedahamed, H.H.A.; Thaiyan, M. Effect of cobalt doping on structural, optical, and magnetic properties of ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by coprecipitation method. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 9715–9725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, S.; Pittman, C.U.; Mohan, D. Magnetic magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticle synthesis and applications for lead (Pb2+) and chromium (Cr6+) removal from water. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2016, 468, 334–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Deng, G.; Wang, D.; Chen, M.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, H.; Yang, S.P. Renal-clearable zwitterionic conjugated hollow ultrasmall Fe3O4 nanoparticles for T-1-weighted MR imaging in vivo. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belaïd, S.; Stanicki, D.; Elst, L.V.; Muller, R.N.; Laurent, S. Influence of experimental parameters on iron oxide nanoparticle properties synthesized by thermal decomposition: Size and nuclear magnetic resonance studies. Nanotechnology 2018, 29, 165603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, M.; Gutiérrez, G.; Noriega, S.; Moyano, A.; Blanco-López, M.C.; Matos, M. Microemulsion Synthesis of Superparamagnetic Nanoparticles for Bioapplications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morán, D.; Gutiérrez, G.; Mendoza, R.; Rayner, M.; Blanco-Lopez, C.; Matos, M. Synthesis of controlled-size starch nanoparticles and superparamagnetic starch nanocomposites by microemulsion method. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 299, 120223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Vincent, A.H.; Chang, H.; Rinehart, J.D. Strengthening nanocomposite magnetism through microemulsion synthesis. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 4133–4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Bian, X.; Yang, C.; Yu, M.; Wang, T. Synthesis of FeCoB amorphous nanoparticles and application in ferrofluids. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 435, 1314–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Pu, X.; Yin, G.; Chen, X.; Yin, J.; Wu, Y. Biomimetic mineralization of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles mediated by bi-functional copolypeptides. Molecules 2019, 24, 1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Zeng, B.; Zhou, R.; Li, X.; Zhang, G. One-pot synthesis of multiple stimuli-responsive magnetic nanomaterials based on the biomineralization of elastin-like polypeptides. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 27946–27954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, K.; Zhao, H.; Zheng, X.; Sun, H.; Hu, L.; Zhu, L.; Shen, Y.; Luo, T.; Dai, H.; Wang, J. NMR studies of the interactions between AMB-1 Mms6 protein and magnetosome Fe3O4 nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correa, T.; Presciliano, R.; Abreu, F. Why Does Not Nanotechnology Go Green? Bioprocess Simulation and Economics for Bacterial-Origin Magnetite Nanoparticles. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 718232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, Z. Adsorption Performance of Reactive Red 2BF onto Magnetic NiFe2O4 Nanoparticles Prepared via the Coprecipitation Process. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2020, 20, 2832–2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zhong, W.; Du, Y. Controllable synthesis and performance of magnetic nanocomposites with core/shell structure. Acta Phys. Sin. 2018, 67, 227501. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Yin, S.; Hu, Y.; Deng, T.; Li, J. Microemulsion-Confined Biomineralization of PEGylated Ultrasmall Fe3O4 Nanocrystals for T2-T1 Switchable MRI of Tumors. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 14223–14230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, D.; Hyeon, T. Chemical design of biocompatible iron oxide nanoparticles for medical applications. Small 2013, 9, 1450–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radoń, A.; Drygała, A.; Hawełek, Ł.; Łukowiec, D. Structure and optical properties of Fe3O4 nanoparticles synthesized by co-precipitation method with different organic modifiers. Mater. Charact. 2017, 131, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Dief, A.M.; Abdelbaky, M.S.M.; Martínez-Blanco, D.; Amghouz, Z.; García-Granda, S. Effect of chromium substitution on the structural and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline zinc ferrite. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2016, 174, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Dief, A.M.; Nassar, I.F.; Elsayed, W.H. Magnetic NiFe2O4 nanoparticles: Efficient, heterogeneous and reusable catalyst for synthesis of acetylferrocene chalcones and their anti-tumour activity. Appl. Organometal. Chem. 2016, 30, 917–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, D.; Ruan, C.; Qiu, J.; Wu, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y. Synthesis of Magnetic Co/C Nanocomposite and Its Adsorption Performance for Congo Red in Aqueous Systems. Univ. Chem. 2020, 35, 212–220. [Google Scholar]
- Lian, L.; Zhang, X.; Hao, J.; Lv, J.; Wang, X.; Zhu, B.; Lou, D. Magnetic solid-phase extraction of fluoroquinolones from water samples using titanium-based metal-organic framework functionalized magnetic microspheres. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1579, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Yue, Y.; Tang, F. Application of Ionic Liquids in Separation and Analysis of Natural Products: A Review. Chem. Ind. For. Prod. 2013, 33, 143–148. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Gao, R.; Lv, D. Preparation of magnetic nano-composite adsorbents and their application in water treatment. Ind. Water Treat. 2021, 41, 1–6. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lu, D.; Qin, M.; Liu, C.; Deng, J.; Shi, G.; Zhou, T. Ionic Liquid-Functionalized Magnetic Metal-Organic Framework Nanocomposites for Efficient Extraction and Sensitive Detection of Fluoroquinolone Antibiotics in Environmental Water. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 5357–5367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, W.; Shi, Y.; Yang, J.; Yang, Q.; Xie, C. HPLC Determination of Bisphenol A in Beverages with Its Separationand Enrichment by Solid Phase Extraction Using Room Temperature-Ionic Liquid Loaded Magnetic Nano-composite of Cyclodextrin Polymer/Fe3O4. Phys. Test. Chem. Anal. 2019, 55, 1091–1094. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fan, W.; Yang, D.; Ding, N.; Chen, P.; Wang, L.; Tao, G.; Zheng, F.; Ji, S. Application of core-satellite polydopamine-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles-hollow porous molecularly imprinted polymer combined with HPLC-MS/MS for the quantification of macrolide antibiotics. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Dong, Y.; Zhao, Y. Synthesis and characterization of photo-responsive magnetic molecularly imprinted microspheres for the detection of sulfonamides in aqueous solution. J. Sep. Sci. 2016, 39, 4866–4875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Li, J.; Luo, L.; Li, P.; Liu, X. Preparation of Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Nanoparticles for Enrichment and Separation of 6-Benzylaminopurine. Food Res. Dev. 2021, 42, 87–93. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kaabipour, M.; Khodadoust, S.; Zeraatpisheh, F. Preparation of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer for dispersive solid-phase extraction of valsartan and its determination by high-performance liquid chromatography: Box-Behnken design. J. Sep. Sci. 2020, 43, 912–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serantes, D.; Chantrell, R.; Gavilán, H.; Morales, M.D.P.; Chubykalo-Fesenko, O.; Baldomir, D.; Satoh, A. Anisotropic magnetic nanoparticles for biomedicine: Bridging frequency separated AC-field controlled domains of actuation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 30445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Hu, L.; Niu, C.; Huang, D.; Zeng, G. A magnetic separation fluorescent aptasensor for highly sensitive detection of bisphenol A. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 266, 805–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Bai, H.; Zhou, Q.; Li, S.; Tong, Y.; Guo, J.; Zhou, B.; Li, Z.; Zhan, Y.; Liu, M.; et al. Preparation of polyamidoamine dendrimer modified magnetic nanoparticles and its application for reliable measurement of Sudan red contaminants in natural waters at parts-per-billion levels. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 708995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Sun, X.; Du, X.; Yue, Y.; Chen, L.; Xu, H.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, H.; Ding, L. Determination of sulfonamides in soil samples based on alumina-coated magnetite nanoparticles as adsorbents. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 665, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Joshi, H.; Kumar, A. Arsenate Removal from the Groundwater Employing Maghemite Nanoparticles. Water 2022, 14, 3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagirani, M.; Uzcan, F.; Soylak, M. A selective and sensitive procedure for magnetic solid-phase microextraction of lead(II) on magnetic cellulose nanoparticles from environmental samples prior to its flame atomic absorption spectrometric detection. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2021, 18, 1005–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Meng, L. Liquid chromatography-UV determination of heavy metal ions in environmental samples using dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction coupled with magnetic nanoparticles. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2018, 17, 1571–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouhestani, H.; Ebrahimi, P. Extraction of carboxin and bensulfuron-methyl using cysteine-functionalized chitosan-coated magnetic nanoparticles and response surface methodology. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 2385–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragab, G.H.; Bahgat, E.A. Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for HPLC determination of valsartan in aqueous environmental samples, biological samples and tablet dosage forms. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 101, 2612–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Xu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wang, D.; Liu, Z.; Si, X. Magnetic solid phase extraction based on Fe3O4@SiO2@CTS nano adsorbent for the sensitive detection of trace polychlorinated biphenyls in environmental water samples. Microchem. J. 2022, 172, 106947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Merino, B.; Bringas, E.; Ortiz, I. Robust system for the regenerative capture of aqueous pollutants with continuously synthesized and functionalized magnetic nanoparticles. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yağci, Ö.; Akkaya, E.; Bakirdere, S. Nano-sized magnetic Ni particles based dispersive solid-phase extraction of trace Cd before the determination by flame atomic absorption spectrometry with slotted quartz tube: A new, accurate, and sensitive quantification method. Env. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leal, M.; Alonso, E.V.; Guerrero, M.M.L.; Cordero, M.T.S.; Pavón, J.M.C.; Torres, A.G.D. Speciation analysis of inorganic arsenic by magnetic solid phase extraction on-line with inductively coupled mass spectrometry determination. Talanta 2018, 184, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Su, S.; Chen, B.; Hu, B. Simultaneous speciation of inorganic selenium and tellurium in environmental water samples by polyaniline functionalized magnetic solid phase extraction coupled with ICP-MS detection. Talanta 2020, 207, 120314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Liu, G.; She, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Jin, F.; Jin, M.; Du, P.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J. Preparation of magnetic metal organic framework composites for the extraction of neonicotinoid insecticides from environmental water samples. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 113144–113151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turiel, E.; Díaz-Álvarez, M.; Martín-Esteban, A. Surface modified-magnetic nanoparticles by molecular imprinting for the dispersive solid-phase extraction of triazines from environmental waters. J. Sep. Sci. 2020, 43, 3304–3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Z.; Xiang, L.; Tang, J. Facile one-pot synthesis of magnetic molecular imprinting polymers as a novel adsorbent for the enrichment of imidacloprid based on a magnetic dispersive micro-solid-phase extraction in water samples. Chem. Pap. 2021, 75, 3787–3795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhou, Q.; Li, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Tong, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhou, X.; Sun, Y.; Sheng, X. Polyamidoamine dendrimer decorated nanoparticles as an adsorbent for magnetic solid-phase extraction of tetrabromobisphenol A and 4-nonylphenol from environmental water samples. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2019, 539, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Guo, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Tang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Sulfur-doped g-C3N4/rGO porous nanosheets for highly efficient photocatalytic degradation of refractory contaminants. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020, 41, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh Rathore, B.; Pal Singh Chauhan, N.; Panneerselvam, P.; Jadoun, S.; Barani, M.; Ameta, S.C.; Ameta, R. Synthesis and Characterization of Ch-PANI-Fe2O3 Nanocomposite and Its Water Remediation Applications. Water 2022, 14, 3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.B.; Irfan, S.; Lam, S.S.; Sun, X.; Chen, S. 3D printed nanofiltration membrane technology for waste water distillation. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 49, 102958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.; Riead, M.M.H.; Bilal, M.; Yang, Y.; Khan, A.; Ali, F.; Karim, S.; Zhou, G.; Wenjie, Y.; Sher, F.; et al. Adsorptive remediation of environmental pollutants using magnetic hybrid materials as platform adsorbents. Chemosphere 2021, 284, 131279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, W.A.W.; Nodeh, H.R.; Aboul-Enein, H.Y.; Sanagi, M.M. Magnetic solid-phase extraction based on modified ferum oxides for enrichment, preconcentration, and isolation of pesticides and selected pollutants. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2015, 45, 270–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; He, M.; Chen, B.; Hu, B. Fe3O4 nanoparticles coated with double imprinted polymers for magnetic solid phase extraction of lead(II). Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.; Coolahan, K.; Mugweru, A. Manganese based magnetic nanoparticles for heavy metal detection and environmental remediation. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 5128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, B.; Baghayeri, M.; Ghanei-Motlagh, M.; Zonoz, F.M.; Amiri, A.; Hajizadeh, F.; Hosseinifar, A.; Esmaeilnezhad, E. Polyamidoamine dendrimer functionalized iron oxide nanoparticles for simultaneous electrochemical detection of Pb2+ and Cd2+ ions in environmental waters. Measurement 2019, 140, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Meng, L.; Song, W. Glutathione-stabilized silver nanoparticles and magnetic nanoparticles combination for determination of lead and cadmium in environmental waters. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2019, 11, 1133–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, J.; Zhou, L.; Song, G.; Lu, F.; You, L.; Li, J. Rapid and ultrasensitive surface enhanced Raman scattering detection of hexavalent chromium using magnetic Fe3O4/ZrO2/Ag composite microsphere substrates. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 610, 125414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faiz, F.; Qiao, J.; Lian, H.; Mao, L.; Cui, X. A combination approach using two functionalized magnetic nanoparticles for speciation analysis of inorganic arsenic. Talanta 2022, 237, 122939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Chen, S.; Ye, F.; Su, L.; Zhang, C.; Shen, S.; Zhao, S. Preparation of magnetic core–shell nanoflower Fe3O4@MnO2 as reusable oxidase mimetics for colorimetric detection of phenol. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christus, A.A.B.; Panneerselvam, P.; Ravikumar, A.; Morad, N.; Sivanesan, S. Colorimetric determination of Hg (II) sensor based on magnetic nanocomposite (Fe3O4@ZIF-67) acting as peroxidase mimics. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2018, 364, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguz, M.; Bhatti, A.A.; Yilmaz, M. Surface coating of magnetite nanoparticles with fluorescence derivative for the detection of mercury in water environments. Mater. Lett. 2020, 267, 127548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Cai, Z.; Sheng, L.; Ma, M.; Wang, X. A magnetic relaxation switching and visual dual-mode sensor for selective detection of Hg2+ based on aptamers modified Au@Fe3O4 nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 388, 121728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wen, Q.; Chen, J.; Sun, W.; Zheng, Y.; Long, C.; Wang, Q. Lanthanide Molecular Species Generated Fe3O4@SiO2-TbDPA Nanosphere for the Efficient Determination of Nitrite. Molecules 2022, 27, 4431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Zheng, X.; Li, H.; Zhao, Z. Human health risk assessment and early warning of heavy metal pollution in soil of a coal chemical Plant in Northwest China. Soil. Sediment. Contam. Int. J. 2020, 5, 481–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Dai, L.; Wang, M.; Su, G.; Wang, T.; Zhao, X.; Liu, X.; Xu, Y.; Meng, J.; Shi, B. Distribution, influence factors, and biotoxicity of environmentally persistent free radical in soil at a typical coking plant. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 835, 155493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, X.; Si, X.; Yang, R.; Zhou, J.; Quan, X. Environmentally persistent free radical generation on contaminated soil and their potential biotoxicity to luminous bacteria. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 687, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, I.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, S.-M.; Park, C.W.; Yoon, I.-H.; Yang, H.-M.; Sihn, Y. Enhanced selective separation of fine particles from Cs-contaminated soil using magnetic nanoparticles. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasa, N.A.; Sel, S.; Özkan, B.Ç.; Bakırdere, S. Determination of palladium in soil samples by slotted quartz tube-flame atomic absorption spectrophotometry after vortex-assisted ligandless preconcentration with magnetic nanoparticle–based dispersive solid-phase microextraction. Env. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patiño-Ropero, M.J.; Díaz-Álvarez, M.; Martín-Esteban, A. Molecularly imprinted core-shell magnetic nanoparticles for selective extraction of triazines in soils. J. Mol. Recognit. 2017, 30, e2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.T.; Yoon, S.A.; Ahn, J.; Choi, Y.; Lee, M.H.; Jung, J.H.; Park, J. Synthesis of fluorescent naphthalimide-functionalized Fe3O4 nanoparticles and their application for the selective detection of Zn2+ present in contaminated soil. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 243, 1034–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Su, P.; Chen, X.; Zhang, R.; Yang, Y. Microwave-assisted synthesis of poly (ionic liquid)-coated magnetic nanoparticles for the extraction of sulfonylurea herbicides from soil for HPLC. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 3246–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.; Song, X.; Huang, X.; Yuan, D. Porous monolith-based magnetism-reinforced in-tube solid phase microextraction of sulfonylurea herbicides in water and soil samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1613, 460672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.; Chen, H.; Huang, X. Magnetism-assisted in-tube solid phase microextraction for the on-line chromium speciation in environmental water and soil samples. Microchem. J. 2021, 164, 105956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, R.; Chen, Z. Metal-organic framework-1210(zirconium/cuprum) modified magnetic nanoparticles for solid phase extraction of benzophenones in soil samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1607, 460403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubetska, T.S.; Kobylinska, N.G.; Menendez, J.R.G. Application of hydrophobic magnetic nanoparticles as cleanup adsorbents for pesticide residue analysis in fruit, vegetable, and various soil samples. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 13550–13561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.M.; Yoon, I.H.; Kim, I. Application of polyethylenimine-coated magnetic nanocomposites for the selective separation of Cs-enriched clay particles from radioactive soil. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 21822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Q.; Ma, A.; Wang, T.; Lin, J.; Wang, H.; Du, B.; Zhuang, X.; Zhuang, G. Detection of bioavailable cadmium, lead, and arsenic in polluted soil by tailored multiple Escherichia coli whole-cell sensor set. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 6865–6871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedotov, P.S.; Kördel, W.; Miró, M.; Peijnenburg, W.J.G.M.; Wennrich, R.; Huang, P. Extraction and fractionation methods for exposure assessment of trace metals, metalloids, and hazardous organic compounds in terrestrial environments. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 42, 1117–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, D.; Zhao, N.; Ma, M.; Fang, L.; Gu, Y.; Yao, J.; Liu, J.; Liu, W. Application of a mobile laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy system to detect heavy metal elements in soil. Appl. Opt. 2017, 56, 5204–5210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
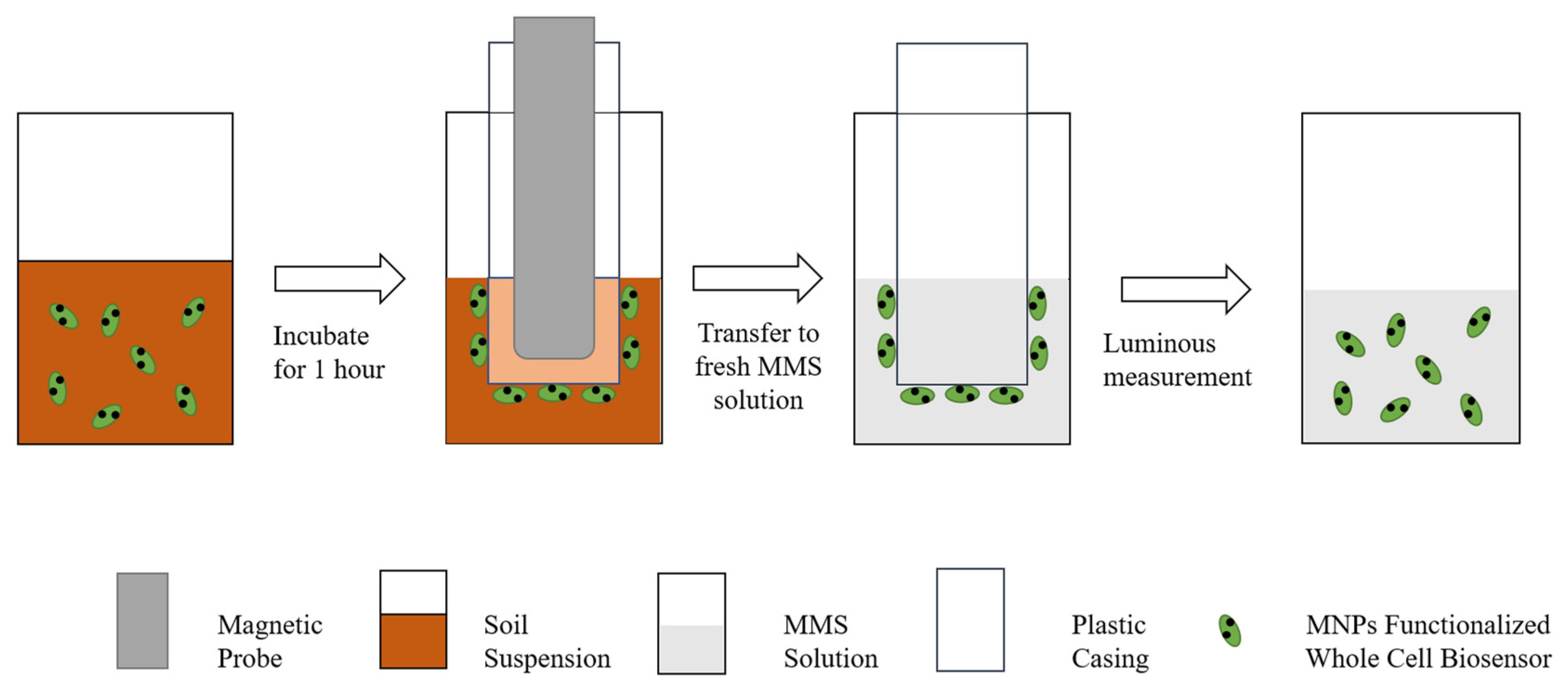
- Jia, J.; Li, H.; Zong, S.; Jiang, B.; Li, G.; Ejenavi, O.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, D. Magnet bioreporter device for ecological toxicity assessment on heavy metal contamination of coal cinder sites. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 222, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Bao, K.; Xiong, Z.; Li, T. Didactic experimental design for characterization of biotoxicity in contaminated soils with MNPs-P. phosphoreum biosensor. Exp. Technol. Manag. 2022, 39, 209–213. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Liu, M.; Song, X.; Wang, D. Application of Luminescent Bacteria Bioassay in the Detection of Pollutants in Soil. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Preparation Method | Advantage | Defect | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Co-precipitation | short process, simple reaction condition, high product purity | Products in the washing, filtering, drying process ear prone to agglomeration | [28,39] |
| High-temperature Pyrolysis | high crystallinity, adjustable particle size, and narrow particle size distribution | The product has hydrophobic group, is not soluble in water, and has poor biocompatibility | [30,40] |
| Microemulsion | size distribution, regular shape, and good dispersion property | The yield is low and the preparation process needs a lot of solvent | [32,41] |
| Biomimetic mineralization | good biocompatibility and bioactivity, good stability under physiological conditions, green and environmental protection | Low yield, harsh preparation conditions, complex technology | [26,37] |
| Type of MNPs | Analyte or Pollutant Type | Real Sample | Analytical Technique | Recovery % | LOD Limit of Detection | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
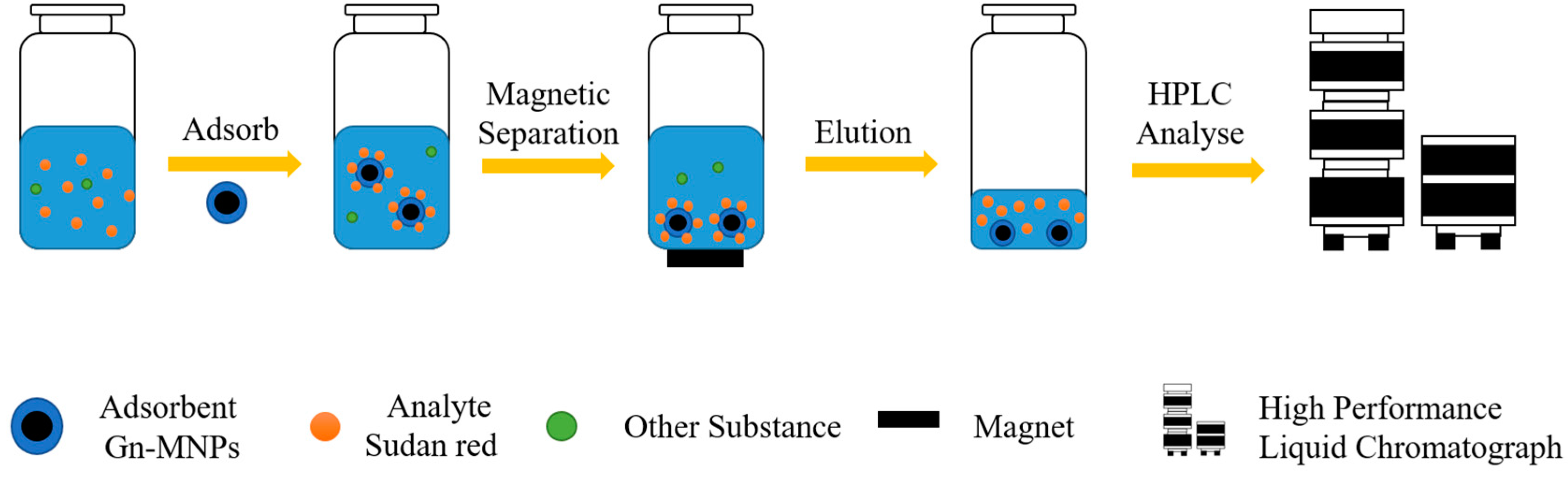
| Gn-MNPs | Sudan red dyes | water | adsorption desorption | 98.12~103.52 | 1.8~5.5 ng/L | [58] |
| (Fe3O4/Al2O3 NPs | sulfonamides | soil | extraction concentration separation | 71~93 | 0.37~6.74 ng/g. | [59] |
| Fe3O4 NPs | N-(Phenylmethyl)-9H-purin-6-amine | food | static adsorption | 82.63~106.27 | 150 ng/mL | [54] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, K.; Song, X.; Liu, M.; Chen, M.; Li, J.; Han, J. Review on the Use of Magnetic Nanoparticles in the Detection of Environmental Pollutants. Water 2023, 15, 3077. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15173077
Zhang K, Song X, Liu M, Chen M, Li J, Han J. Review on the Use of Magnetic Nanoparticles in the Detection of Environmental Pollutants. Water. 2023; 15(17):3077. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15173077
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Kai, Xinlong Song, Meng Liu, Menghua Chen, Jie Li, and Jinglong Han. 2023. "Review on the Use of Magnetic Nanoparticles in the Detection of Environmental Pollutants" Water 15, no. 17: 3077. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15173077





