Study on Response Process and Time Delay Effect of Groundwater Dynamic in Northeastern Margin of Tibetan Plateau
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Data Source
2.2. Research Methods
2.2.1. Cross-Correlation Function
2.2.2. Wavelet Analysis
2.2.3. Cross-Wavelet Transform
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Identification of the Main Driving Factors on Groundwater
3.2. Response Process of Groundwater to Main Driving Factors
3.2.1. Response Process of Groundwater to Exploitation
3.2.2. Response Process of Groundwater to Rainfall
- (1)
- Response process of groundwater evolution to annual rainfall
- (2)
- Response process of groundwater evolution to monthly rainfall
3.2.3. Response Process of Groundwater to Surface Runoff
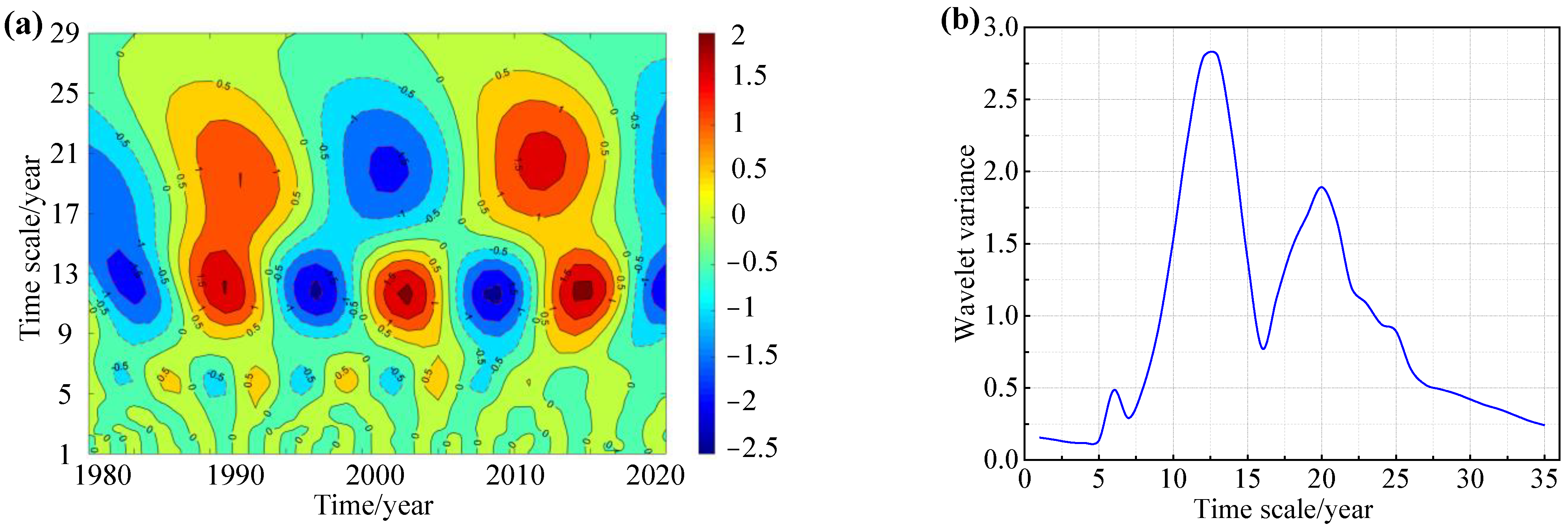
3.3. Periodic Evolution of Groundwater and Main Driving Factors
3.3.1. Variation on Cone of Depression
3.3.2. Periodic Evolution of Key Drivers
3.4. Time Delay Effect of Groundwater and Driving Factors
3.4.1. Continuous Wavelet Analysis of Groundwater and Main Driving Factors
3.4.2. Cross-Correlation Analysis between Groundwater and Driving Factors
3.4.3. Continuous Wavelet Analysis of Groundwater and Driving Factors
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gleeson, T. Global Groundwater Sustainability. Groundwater 2020, 58, 484–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Condon, L.E.; Kollet, S.; Bierkens, M.F.P.; Fogg, G.E.; Abesser, C. Global Groundwater Modeling and Monitoring: Opportunities and Challenges. Water Resour. Res. 2021, 57, e2020WR029500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.; Wu, Q.B.; Lu, N.; Jiang, G.L.; Ball, L. Groundwater in the Tibet Plateau, western China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.W.; Dai, J.C.; Wang, G.X.; Chang, J.; Lu, Y.Q.; Song, C.L.; Hu, Z.Y.; Ahmed, N.; Ye, R.Z. The impact of land surface temperatures on suprapermafrost groundwater on the central Qinghai–Tibet Planteau. Hydrol. Process. 2020, 34, 1475–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.D.; Thompson, L.G.; Mosbugger, V.; Zhang, F.; Ma, Y.M.; Luo, T.X.; Xu, B.Q.; Yang, X.X.; Joswiak, D.R.; Wang, W.C.; et al. Third pole environment (TPE). Environ. Dev. 2012, 3, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.L.; Zhao, J.; Wang, J.X.; Zhao, G.Z.; Zhao, G.Z.; Chen, J.Y.; Li, Z.P. Spatiotemporal Variation and Driving Analysis of Groundwater in the Tibetan Plateau Based on GRACE Downscaling Data. Water 2022, 14, 3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.C.; Xu, Y.W.; You, Q.L.; Flügel, W.A.; Pepin, N.; Yao, T.D. Review of climate and cryospheric change in the Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Res. Lett. 2010, 5, 15101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immerzeel, W.W.; Beek, L.P.H.; Bierkens, M.F.P. Climate change will affect the Asian Water Towers. Science 2010, 328, 1382–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, T.D.; Xue, Y.K.; Chen, D.L.; Chen, F.H.; Thompson, L.; Cui, P.; Koike, T.; Lau, W.K.M.; Lettenmaier, D.; Mosbrugger, V.; et al. Recent Third Pole’s rapid warming accompanies cryospheric melt and water cycle intensification and interactions between monsoon and environment: Multidisciplinary approach with observations, modeling, and analysis. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2019, 100, 423–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.H.; Zhao, H.J.; Wang, H.; Lu, W.T.; Guo, H.C. Integrated planning for regional development planning and water resources management under uncertainty: A case study of Xining, China. J. Hydrol. 2017, 554, 623–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.H.; Zhan, R.Z.; Lu, Y.D.; Zhou, B.; Wu, J. Spatiotemporal Variation and Periodic Evolution Characteristics of Groundwater in the Xining Area of China, Eastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Qiang, M.R.; Huang, X.Z.; Zhao, Y.T.; Leppänen, J.J.; Weckström, J.; Väliranta, M. Lateglacial and Holocene climate change in the NE Tibetan Plateau: Reconciling divergent proxies of Asian summer monsoon variability. Catena 2021, 199, 105089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, T.R.; Taniguchi, M.; Kooi, H.; Gurdak, J.J.; Allen, D.M.; Hiscock, K.M.; Treidel, H.; Aureli, A. Beneath the surface of global change: Impacts of climate change on groundwater. J. Hydrol. 2011, 405, 532–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wood, W.W.; Macumber, P.G. Altithermal climate change and groundwater development. Groundwater 2022, 60, 451–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jykama, M.I.; Sykes, J.F. The impact of climate on spatially varying groundwater recharge in the grandriver watershed. J. Hydrol. 2007, 338, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walvoord, M.A.; Voss, C.I.; Wellman, T.P. Influence of permafrost distribution on groundwater flow in the context of climate-driven permafrost thaw: Example from Yukon Flats Basin, Alaska, United States. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, 7524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, C.; Kumar, S.; Lee, M.K.; Davis, E. Human imprint of water withdrawals in the wet environment: A case study of declining groundwater in Georgia, USA. J. Hydrol.-Reg. Stud. 2021, 35, 100813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Hamm, S.Y.; Jang, S.; Cheong, J.Y.; Kim, G.B. Relationship between groundwater and climate change in South Korea. Geosci. J. 2013, 18, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascott, M.J.; Macdonald, D.M.J.; Sandwidi, W.J.P.; Black, E.; Verhoef, A.; Zongo, G.; Tirogo, J.; Cook, P. Time of emergence of impacts of climate change on groundwater levels in sub-Saharan Africa. J. Hydrol. 2022, 612, 128107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, D.J.; Qian, Y.P.; Han, L.F.; Wang, Z.M.; Li, C.; Zhao, Z.F. Assessing impact of irrigation water on groundwater recharge and quality in arid environment using CFCs, tritium and stable isotopes, in the Zhangye Basin, Northwest China. J. Hydrol. 2011, 405, 194–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Su, X.S. Challenges and impacts of climate change and human activities on groundwater-dependent ecosystems in arid areas—A case study of the Nalenggele alluvial fan in NW China. J. Hydrol. 2019, 573, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.K.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Duan, L.; Wang, Z.F.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Zhang, Q.; Dai, M.L.; Liu, H.Z.; Zheng, X.Y.; Sun, Y.B. Response of the groundwater system in the Guanzhong Basin (central China) to climate change and human activities. Hydrogeol. J. 2018, 26, 1429–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Liu, Q.M.; Peng, W.H.; Liu, X.H. Source apportionment and natural background levels of major ions in shallow groundwater using multivariate statistical method: A case study in Huaibei Plain, China. J. Hydrol. 2022, 301, 113806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.W.; Shao, J.L.; Cui, Y.L.; Zhang, Q.L. Application of a Surrogate Model for a Groundwater Numerical Simulation Model for Determination of the Annual Control Index of the Groundwater Table in China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golian, M.; Abolghasemi, M.; Hosseini, A.; Abbasi, M. Restoring groundwater levels after tunneling: A numerical simulation approach to tunnel sealing decision-making. Hydrogeol. J. 2021, 29, 1611–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.Y.; Yun, S.T.; Yu, S.Y.; Hamm, S.Y. The combined use of dynamic factor analysis and wavelet analysis to evaluate latent factors controlling complex groundwater level fluctuations in a riverside alluvial aquifer. J. Hydrol. 2017, 555, 938–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Wang, G.C. Periodic variations of rainfall, groundwater level and dissolved radon from the perspective of wavelet analysis: A case study in Tengchong, southwest China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, J.J.; Liu, G.L.; Cao, B.B.; Hao, Y.H.; Chen, J.M.; Yeh, T.C.J. Identification of Strong Karst Groundwater Runoff Belt by Cross Wavelet Transform. Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 28, 2903–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chansaengkrachang, K.; Luadsong, A.; Aschariyaphotha, N. A Study of the Time Lags of the Indian Ocean Dipole and Rainfall Over Thailand by Using the Cross Wavelet Analysis. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2015, 40, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, F.; Fard, A.F.; Ghorbani, M.A. Application of cross-wavelet-linear programming-Kalman filter and GIUH methods in rainfall-runoff modeling. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.E.; Shao, Z.G.; Chen, Q.G.; Xu, B.; Zhang, Q.Q. Magnetochronology of Late Miocene Mammal Fauna in Xining Basin, NE Tibetan Plateau, China. Acta Geol. Sin-Engl. 2018, 92, 2067–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.Y.; Zhang, H.F.; Yang, X.N.; Song, Z.Y. Assessing the impacts of ecological-living-productive land changes on eco-environmental quality in Xining city on Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Sci. Cold Arid. Reg. 2019, 11, 0194–0207. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Y.P.; Fang, C.L. Evolution process analysis of urban metabolic patterns and sustainability assessment in western China, a case study of Xining city. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 109, 105784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.B.; Zhang, W.J.; Chen, J.S.; Jiang, S.Y.; Kong, N. Isotope and geochemical study for geothermal assessment of the Xining basin of the northeastern Tibetan Plateau. Geothermics 2012, 42, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javadzadeh, H.; Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Hosseini, S.M.; Simmons, C.T. Interaction of lake-groundwater levels using cross-correlation analysis: A case study of Lake Urmia Basin, Iran. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 729, 138822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.H.; Pu, J.B.; Zhang, T.; Wang, S.N.; Huo, W.J.; Yuan, D.X. Investigation of transport properties and characteristics of a large karst aquifer system in southern China using correlation, spectral, and wavelet analyses. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.H.; Liu, Y.T.; Cao, S.S.; Chen, J.L.; Xia, G.Q.; Wu, X.D. Identification of control regularity of heating stations based on cross-correlation function dynamic time delay method. Energy 2022, 246, 123329.1–123329.15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Yan, G.H.; Bassett, P.; Gopal, A.; Samant, S. Use of local noise power spectrum and wavelet analysis in quantitative image quality assurance for EPIDs. Med. Phys. 2016, 43, 4996–5008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Fei, Z.W.; Xu, X.B. Enhancement method of weak Lidar signal based on adaptive variational modal decomposition and wavelet threshold denoising. Infrared. Phys. Technol. 2022, 120, 103991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.T.M.S.; Hosono, T.; Quilty, J.M.; Das, J.; Basak, A. Multiscale groundwater level forecasting: Coupling new machine learning approaches with wavelet transforms. Adv. Water Resour. 2020, 141, 103595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campozano, L.; Mendoza, D.; Mosquera, G.M.; Palacio-Baus, K.; Célleri, R.; Crespo, P. Wavelet analyses of neural networks based river discharge decomposition. Hydrol. Process. 2020, 34, 2302–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordu, F.; Nachabe, M.H. A physically-constrained wavelet-aided statistical model for multi-decadal groundwater dynamics predictions. Hydrol. Process. 2021, 35, e14308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.C.; Zhang, X.Q.; Wang, W.J.; Lu, C.P.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, W.; Tick, G.R.; Liu, B.; Shu, L.C. Groundwater level modeling framework by combining the wavelet transform with a long short-term memory data-driven model. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 783, 146948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaderpour, E. Least-squares Wavelet and Cross-wavelet Analyses of VLBI Baseline Length and Temperature Time Series: Fortaleza-Hartebeesthoek-Westford-Wettzell. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2020, 133, 014502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.J.; Zhang, G.G.; Liu, F.T.; Zhang, D.S.; Zhang, X.P.; Chen, S.M. Improving the spatial resolution of GRACE-based groundwater storage estimates using a machine learning algorithm and hydrological model. Hydrogeol. J. 2022, 30, 947–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.Y.; Niu, J.; Hu, B.X.; Soltanian, M.R.; Qiu, H.; Yang, L. Prediction of groundwater level in seashore reclaimed land using wavelet and artificial neural network-based hybrid model. J. Hydrol. 2019, 577, 123948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, F.; Wang, T.; Hussain, A. Spatiotemporal Runoff Analysis and Associated Influencing Factors in Chitral Basin, Pakistan. Water 2023, 15, 2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Driving Factor | Groundwater Depth | Order | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural factors | Rainfall | 0.816 | 2 |
| Evaporation | 0.623 | 5 | |
| Temperature | 0.373 | 9 | |
| Surface runoff | 0.736 | 3 | |
| Human factors | Population number | 0.709 | 4 |
| Gross regional domestic product | 0.429 | 8 | |
| Construction land area | 0.539 | 6 | |
| Agricultural acreage | 0.506 | 7 | |
| Exploitation quantity | 0.862 | 1 | |
| Subarea | Groundwater Depth in Washland (m) | Groundwater Depth in Terrace (m) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | This Month | Last Month | This Month | Last Month |
| 1 | 0.357 | 0.384 | −0.394 | 0.435 |
| 2 | 0.338 | 0.354 | 0.345 | 0.385 |
| 3 | −0.541 | 0.392 | 0.347 | 0.443 |
| 4 | −0.573 | 0.488 | −0.464 | 0.424 |
| 5 | 0.562 | 0.552 | 0.478 | −0.528 |
| 6 | −0.751 | −0.646 | 0.573 | −0.587 |
| 7 | −0.722 | −0.678 | −0.719 | −0.795 |
| 8 | −0.867 | −0.717 | −0.745 | −0.809 |
| 9 | −0.878 | −0.824 | −0.817 | −0.884 |
| 10 | −0.528 | −0.404 | 0.408 | −0.740 |
| 11 | 0.419 | 0.496 | 0.367 | 0.464 |
| 12 | 0.369 | 0.379 | 0.342 | 0.399 |
| Sequence | Red Noise Test Period | Period Outside the COI | Main Oscillation Period/a |
|---|---|---|---|
| Precipitation | 1983.2–2020.10 | 1984.5–2018.7 | 9–14 |
| Runoff | 1983.2–2020.10 | 1984.5–1990.10 1992.8–1996.2 1998.3–2001.1 2004.9–2018.7 | 9–14 |
| Groundwater depth | 1983.2–2020.10 | 1984.5–1996.11 1998.3–2003.10 2013.4–2018.7 | 9–14 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, S.; Li, H.; Yang, M.; Gu, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y. Study on Response Process and Time Delay Effect of Groundwater Dynamic in Northeastern Margin of Tibetan Plateau. Water 2023, 15, 2838. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152838
Song S, Li H, Yang M, Gu Z, Wang X, Zhang W, Liu Y. Study on Response Process and Time Delay Effect of Groundwater Dynamic in Northeastern Margin of Tibetan Plateau. Water. 2023; 15(15):2838. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152838
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Shuhong, Huanhuan Li, Mi Yang, Zhao Gu, Xiaohang Wang, Wenting Zhang, and Yongzhi Liu. 2023. "Study on Response Process and Time Delay Effect of Groundwater Dynamic in Northeastern Margin of Tibetan Plateau" Water 15, no. 15: 2838. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152838
APA StyleSong, S., Li, H., Yang, M., Gu, Z., Wang, X., Zhang, W., & Liu, Y. (2023). Study on Response Process and Time Delay Effect of Groundwater Dynamic in Northeastern Margin of Tibetan Plateau. Water, 15(15), 2838. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152838






