Examination of an Electrified Bar Rack Fish Guidance Device for Hydropower Turbines
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
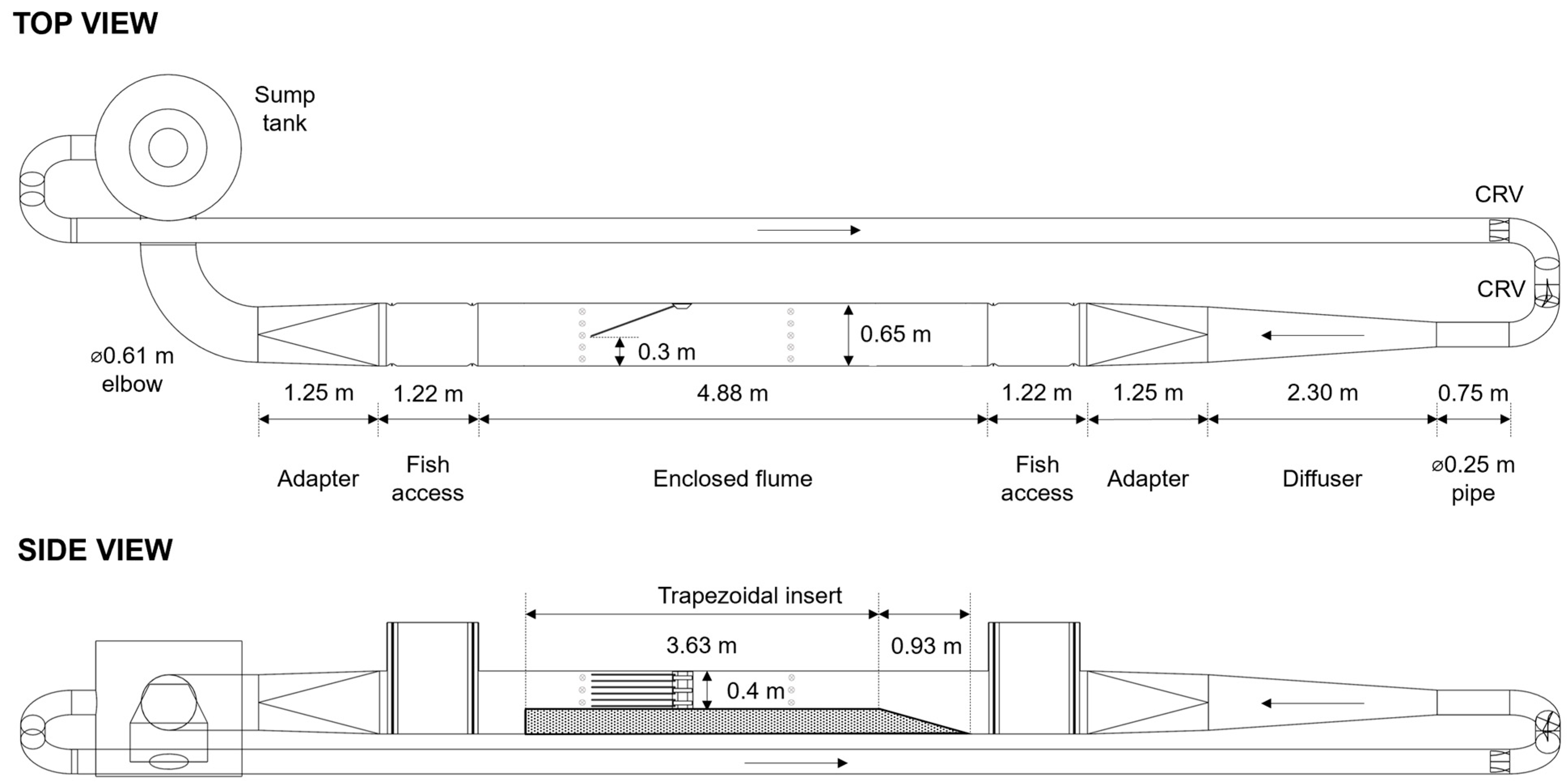
2.1. Test Flume
2.2. Flow Velocity Measurement
2.3. Cantilevered Bar Rack Modules
2.4. Fish
2.5. Water Quality
2.6. Testing Procedure
2.7. Video Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Flow Uniformity
3.2. Fish Approach and Passage
3.3. Regression Analysis
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Čada, G.F. The Development of Advanced Hydroelectric Turbines to Improve Fish Passage Survival. Fisheries 2001, 26, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilt, C.R. Developing fish passage and protection at hydropower dams. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2007, 104, 295–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebel, G. Fischschutz und Fischabstieg an Wasserkraftanlagen: Handbuch Rechen- und Bypasssysteme: Ingenieurbiologische Grundlagen, Modellierung und Prognose, Bemessung und Gestaltung, 1st ed.; Büro für Gewässerökologie und Fischereibiologie: Halle, Germany, 2013. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Schwevers, U.; Adam, B. Fish Protection Technologies and Fish Ways for Downstream Migration; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; Volume 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katopodis, C.; Koon, E.M.; Hanson, L. Sea Lamprey Barriers: New Concepts and Research Needs; Great Lakes Fishery Commission: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1994; p. 63. [Google Scholar]
- Kriewitz-Byun, C.R. Leitrechen an Fischabstiegsanlagen: Hydraulik und Fischbiologische Effizienz. Ph.D. Thesis, ETH Zürich, Zurich, Switzerland, 2015. (In German). [Google Scholar]
- Turnpenny, A.W.H.; O’Keeffe, N. Screening for Intake and Outfalls: A Best Practice Guide; Environment Agency: Bristol, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kempema, E.; Ettema, R. Fish, Ice, and Wedge-Wire Screen Water Intakes. J. Cold Reg. Eng. 2015, 30, 04015004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, D.J.; Cowx, I.G. The selection of suitable pulsed currents for electric fishing in waters. Fish. Res. 1993, 18, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noatch, M.R.; Suski, C.D. Non-physical barriers to deter fish movements. Environ. Rev. 2012, 20, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albayrak, I.; Boes, R.M.; Kriewitz-Byun, C.R.; Peter, A.; Tullis, B.P. Fish guidance structures: Hydraulic performance and fish guidance efficiencies. J. Ecohydraulics 2020, 5, 113–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boes, R.M.; Beck, C.; Meister, J.; Peter, A.; Kastinger, M.; Albayrak, I. Effect of bypass layout on guidance of downstream moving fish at bar rack bypass systems. In Proceedings of the 39th IAHR World Congress, Granada, Spain, 19–24 June 2022; pp. 1312–1321. [Google Scholar]
- Beaumont, W.R.C. Electricity in Fish Research and Management: Theory and Practice; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullen, C.R.; Carlson, T.J. Non-physical fish barrier systems: Their development and potential applications to marine ranching. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2003, 13, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parasiewicz, P.; Wiśniewolski, W.; Mokwa, M.; Zioła, S.; Prus, P.; Godlewska, M. A low-voltage electric fish guidance system—NEPTUN. Fish. Res. 2016, 181, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutzer, R.; Röck, S.; Walde, J.; Zeiringer, B.; Unfer, G.; Führer, S.; Brinkmeier, B.; Haug, J.; Aufleger, M. Ethohydraulic experiments on the fish protection potential of the hybrid system FishProtector at hydropower plants. Ecol. Eng. 2021, 171, 106370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, C.; Albayrak, I.; Meister, J.; Peter, A.; Vetsch, D. Fish Swimming Behavior and Bypass Acceptance at Curved-Bar Rack Bypass Systems. In Proceedings of the 39th IAHR World Congress, Granada, Spain, 19–24 June 2022; pp. 1246–1255. [Google Scholar]
- Haug, J.; Auer, S.; Frees, C.; Brinkmeier, B.; Tutzer, R.; Hayes, D.S.; Aufleger, M. Retrofitting of Existing Bar Racks with Electrodes for Fish Protection—An Experimental Study Assessing the Effectiveness for a Pilot Site. Water 2022, 14, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldenhauer-Roth, A.; Selz, O.M.; Albayrak, I.; Unterberger, F.; Boes, R.M. Development Of Low-Voltage Electrified Fish Guidance Racks For Safe Downstream Fish Migration. In Proceedings of the 39th IAHR World Congress, Granada, Spain, 19–24 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Meister, J.; Moldenhauer-Roth, A.; Beck, C.; Selz, O.M.; Peter, A.; Albayrak, I.; Boes, R.M. Protection and Guidance of Downstream Moving Fish with Electrified Horizontal Bar Rack Bypass Systems. Water 2021, 13, 2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutzer, R.; Brinkmeier, B.; Zeiringer, B.; Führer, S.; Unfer, G.; Aufleger, M. The Fishprotector—An Integral Fish Protection System. In Proceedings of the 38th IAHR World Congress, Panama City, Panama, 1–6 September 2019; pp. 1692–1700. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, J.G.; Armstrong, G.; Katopodis, C.; Larinier, M.; Travade, F. Thinking Like a Fish: A Key Ingredient for Development of Effective Fish Passage Facilities at River Obstructions. River Res. Appl. 2011, 28, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tutzer, R.; Röck, S.; Walde, J.; Haug, J.; Brinkmeier, B.; Aufleger, M.; Unfer, G.; Führer, S.; Zeiringer, B. A Physical and Behavioral Barrier for Enhancing Fish Downstream Migration at Hydropower Dams: The Flexible FishProtector. Water 2022, 14, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haug, J.; Brinkmeier, B.; Tutzer, R.; Aufleger, M. Hybride Barrieren zur Optimierung von Stabrechen zum Fischschutz. Wasserwirtschaft 2021, 111, 48–53. (In German) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolan, C.R.; Miranda, L.E. Immobilization Thresholds of Electrofishing Relative to Fish Size. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2003, 132, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layhee, M.J.; Sepulveda, A.J.; Shaw, A.; Smuckall, M.; Kapperman, K.; Reyes, A. Effects of Electric Barrier on Passage and Physical Condition of Juvenile and Adult Rainbow Trout. J. Fish Wildl. Manag. 2016, 7, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meister, J. Fish Protection and Guidance Atwater Intakes with Horizontal Barrack Bypass Systems. Ph.D. Thesis, ETH Zürich, Zurich, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, P.M.; Martins, E.G.; Algera, D.A.; Rytwinski, T.; Mossop, B.; Leake, A.J.; Power, M.; Cooke, S.J. Turbine entrainment and passage of potadromous fish through hydropower dams: Developing conceptual frameworks and metrics for moving beyond turbine passage mortality. Fish Fish. 2019, 20, 403–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, B.; Lehmann, B. Ethohydraulik: Grundlagen, Methoden und Erkenntnisse; Springer: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; (In German). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. National Aquatic Resource Surveys. National Rivers and Streams Assessment 2018–2019 (Data and Metadata Files). 2021. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/national-aquatic-resource-surveys/data-national-aquatic-resource-surveys (accessed on 14 November 2022).
- Snyder, D.E. Electrofishing and Its Harmful Effects on Fish; USGS, Geological Surveys, Biological Resources Division: Reston, VA, USA, 2003; p. 149. [Google Scholar]
- Henry, T.B.; Grizzle, J.M.; Maceina, M.J. Electroshocking-Induced Mortality of Four Fish Species during Posthatching Development. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2003, 132, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haraldstad, T.; Höglund, E.; Kroglund, F.; Olsen, E.M.; Hawley, K.L.; Haugen, T.O. Anthropogenic and natural size-related selection act in concert during brown trout (Salmo trutta) smolt river descent. Hydrobiologia 2020, 849, 557–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egg, L.; Pander, J.; Müller, M.; Geist, J. Effectiveness of the electric fish fence as a behavioural barrier at a pumping station. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2019, 70, 1459–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Parameters | 20° Module | 40° Module |
|---|---|---|
| Number of bars | 6 | 6 |
| Bar diameter | 8 mm | 10 mm |
| Bar length | 1023 mm | 545 mm |
| Bar spacing | 60 mm | 60 mm |
| Insulated region (projected distance from base wall) | 50–200 mm | 32–129 mm |
| Water | Temperature (°C) | Dissolved Oxygen (mg L−1) | Conductivity (µs cm−1) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Min | Max | Mean | Min | Max | Mean | Min | Max | |
| Holding tanks | 12.2 | 10.0 | 14.4 | 11.0 | 10.3 | 11.7 | 325 | 290 | 360 |
| Flume | 13.0 | 8.2 | 16.3 | 10.7 | 9.2 | 11.9 | 306 | 201 | 320 |
| Water Velocity (m s−1) | Bar Incline Angle | Module Configuration | Voltage (V) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.4 | 20° | All Bars | 0 |
| 0.4 | 20° | All Bars | 0 |
| 0.4 | 20° | All Bars | 75.5 |
| 0.4 | 20° | Top and Bottom | 0 |
| 0.4 | 20° | Top and Bottom | 75.5 |
| 0.4 | 40° | All Bars | 0 |
| 0.4 | 40° | All Bars | 80.0 |
| 0.4 | 40° | Top and Bottom | 0 |
| 0.4 | 40° | Top and Bottom | 76.5 |
| 0.4 | N/A 1 | None 1 | 0 |
| 1.0 | 20° | All Bars | 0 |
| 1.0 | 20° | All Bars | 75.5 |
| 1.0 | 20° | Top and Bottom | 0 |
| 1.0 | 20° | Top and Bottom | 75.5 |
| 1.0 | 40° | All Bars | 0 |
| 1.0 | 40° | All Bars | 80.0 |
| 1.0 | 40° | Top and Bottom | 0 |
| 1.0 | 40° | Top and Bottom | 76.5 |
| 1.0 | N/A 1 | None 1 | 0 |
| Lateral Position X (mm) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.4 m s−1 Condition, Upstream | 0.4 m s−1 Condition, Downstream | |||||||||||
| 108.3 | 216.7 | 325.0 | 433.3 | 541.7 | 108.3 | 216.7 | 325.0 | 433.3 | 541.7 | |||
| Depth Y (mm) | 100 | 0.365 | 0.360 | 0.361 | 0.405 | 0.424 | 100 | 0.376 | 0.374 | 0.377 | 0.381 | 0.376 |
| 200 | 0.362 | 0.381 | 0.376 | 0.3890 | 0.419 | 200 | 0.372 | 0.374 | 0.384 | 0.396 | 0.415 | |
| 300 | 0.392 | 0.394 | 0.400 | 0.413 | 0.427 | 300 | 0.406 | 0.400 | 0.412 | 0.409 | 0.419 | |
| Lateral Position X (mm) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.0 m s−1 Condition, Upstream | 1.0 m s−1 Condition, Downstream | |||||||||||
| 108.3 | 216.7 | 325.0 | 433.3 | 541.7 | 108.3 | 216.7 | 325.0 | 433.3 | 541.7 | |||
| Depth Y (mm) | 100 | 0.990 | 0.941 | 0.936 | 0.982 | 1.033 | 100 | 0.995 | 0.999 | 0.970 | 0.965 | 0.953 |
| 200 | 0.988 | 0.952 | 0.975 | 1.020 | 1.087 | 200 | 1.018 | 1.005 | 0.995 | 0.990 | 1.025 | |
| 300 | 1.009 | 1.032 | 1.039 | 1.0657 | 1.098 | 300 | 1.017 | 1.046 | 1.065 | 1.060 | 1.069 | |
| Water Velocity (m s−1) | Bar Incline Angle | Bars | Voltage (V) | Trials | Number of Fish | Number of Approaches | Approaches per Fish | Number of Passages | Passages per Fish 1 | Passage per Approach Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.4 | N/A | None | 0 | 7 | 70 | 78 | 1.11 | 72 | 1.03 | 92.3% |
| 0.4 | 20 | T&B | 0 | 2 | 20 | 25 | 1.25 | 21 | 1.05 | 84.0% |
| 0.4 | 20 | T&B | 75.5 | 2 | 20 | 67 | 3.35 | 17 | 0.85 | 25.4% |
| 0.4 | 20 | All | 0 | 3 | 30 | 22 | 0.73 | 16 | 0.53 | 72.7% |
| 0.4 | 20 | All | 75.5 | 2 | 20 | 128 | 6.40 | 3 | 0.15 | 2.3% |
| 0.4 | 40 | T&B | 0 | 2 | 20 | 9 | 0.45 | 8 | 0.40 | 88.9% |
| 0.4 | 40 | T&B | 76.5 | 2 | 20 | 100 | 5.00 | 20 | 1.00 | 20.0% |
| 0.4 | 40 | All | 0 | 2 | 20 | 22 | 1.10 | 20 | 1.00 | 90.9% |
| 0.4 | 40 | All | 80.0 | 2 | 20 | 45 | 2.25 | 18 | 0.90 | 40.0% |
| 1.0 | N/A | None | 0 | 8 | 80 | 86 | 1.08 | 79 | 0.99 | 91.9% |
| 1.0 | 20 | T&B | 0 | 2 | 20 | 26 | 1.30 | 25 | 1.25 | 96.2% |
| 1.0 | 20 | T&B | 75.5 | 2 | 20 | 37 | 1.85 | 17 | 0.85 | 45.9% |
| 1.0 | 20 | All | 0 | 2 | 20 | 20 | 1.00 | 19 | 0.95 | 95.0% |
| 1.0 | 20 | All | 75.5 | 2 | 20 | 38 | 1.90 | 13 | 0.65 | 34.2% |
| 1.0 | 40 | T&B | 0 | 2 | 20 | 24 | 1.20 | 24 | 1.20 | 100.0% |
| 1.0 | 40 | T&B | 76.5 | 2 | 20 | 25 | 1.25 | 21 | 1.05 | 84.0% |
| 1.0 | 40 | All | 0 | 2 | 20 | 21 | 1.05 | 21 | 1.05 | 100.0% |
| 1.0 | 40 | All | 80 | 2 | 20 | 28 | 1.40 | 19 | 0.95 | 67.9% |
| Combined | 48 | 480 | 801 | 1.67 | 433 | 0.90 | 54.1% | |||
| Term | Estimate | SE | t Ratio | Prob > |t| | Lower 95% | Upper 95% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 2.556 | 0.268 | 9.540 | <0.001 | 2.027 | 3.086 |
| Entrance location | 0.533 | 0.050 | 10.570 | <0.001 | 0.433 | 0.632 |
| Term | Estimate | SE | t Ratio | Prob > |t| | Lower 95% | Upper 95% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 4.900 | 0.181 | 27.13 | <0.001 | 4.544 | 5.255 |
| Velocity [0.4] | −0.283 | 0.071 | −3.97 | <0.001 | −0.423 | −0.143 |
| Angle [20] | −0.141 | 0.069 | −2.03 | 0.043 | −0.277 | −0.004 |
| Bars [2] | −0.054 | 0.068 | −0.79 | 0.430 | −0.188 | 0.080 |
| Voltage [Off] | −0.161 | 0.067 | −2.38 | 0.018 | −0.293 | −0.028 |
| Approach lane | −0.797 | 0.034 | −23.57 | <0.001 | −0.863 | −0.730 |
| Velocity [0.4] × Angle [20] | −0.175 | 0.069 | −2.55 | 0.012 | −0.311 | −0.040 |
| Velocity [0.4] × (approach lane − 5.004) | 0.088 | 0.035 | 2.55 | 0.011 | 0.020 | 0.156 |
| Bars [2] × (approach lane − 5.004) | 0.089 | 0.033 | 2.73 | 0.007 | 0.025 | 0.154 |
| Voltage [Off] × (approach lane − 5.004) | 0.099 | 0.032 | 3.13 | 0.002 | 0.037 | 0.161 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pflugrath, B.D.; Watson, S.; Haug, J.; Harnish, R.; Colotelo, A.H.A.; Schneider, A. Examination of an Electrified Bar Rack Fish Guidance Device for Hydropower Turbines. Water 2023, 15, 2786. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152786
Pflugrath BD, Watson S, Haug J, Harnish R, Colotelo AHA, Schneider A. Examination of an Electrified Bar Rack Fish Guidance Device for Hydropower Turbines. Water. 2023; 15(15):2786. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152786
Chicago/Turabian StylePflugrath, Brett D., Sterling Watson, Jonas Haug, Ryan Harnish, Alison H. A. Colotelo, and Abe Schneider. 2023. "Examination of an Electrified Bar Rack Fish Guidance Device for Hydropower Turbines" Water 15, no. 15: 2786. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152786
APA StylePflugrath, B. D., Watson, S., Haug, J., Harnish, R., Colotelo, A. H. A., & Schneider, A. (2023). Examination of an Electrified Bar Rack Fish Guidance Device for Hydropower Turbines. Water, 15(15), 2786. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152786








