Impacts of Different Gully Consolidation and Highland Protection Models on the Runoff and Sediment Yield in Small Watershed of the Chinese Loess Plateau—A Case Study of Fengbugou in Qingyang City of Gansu
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Experimental Materials
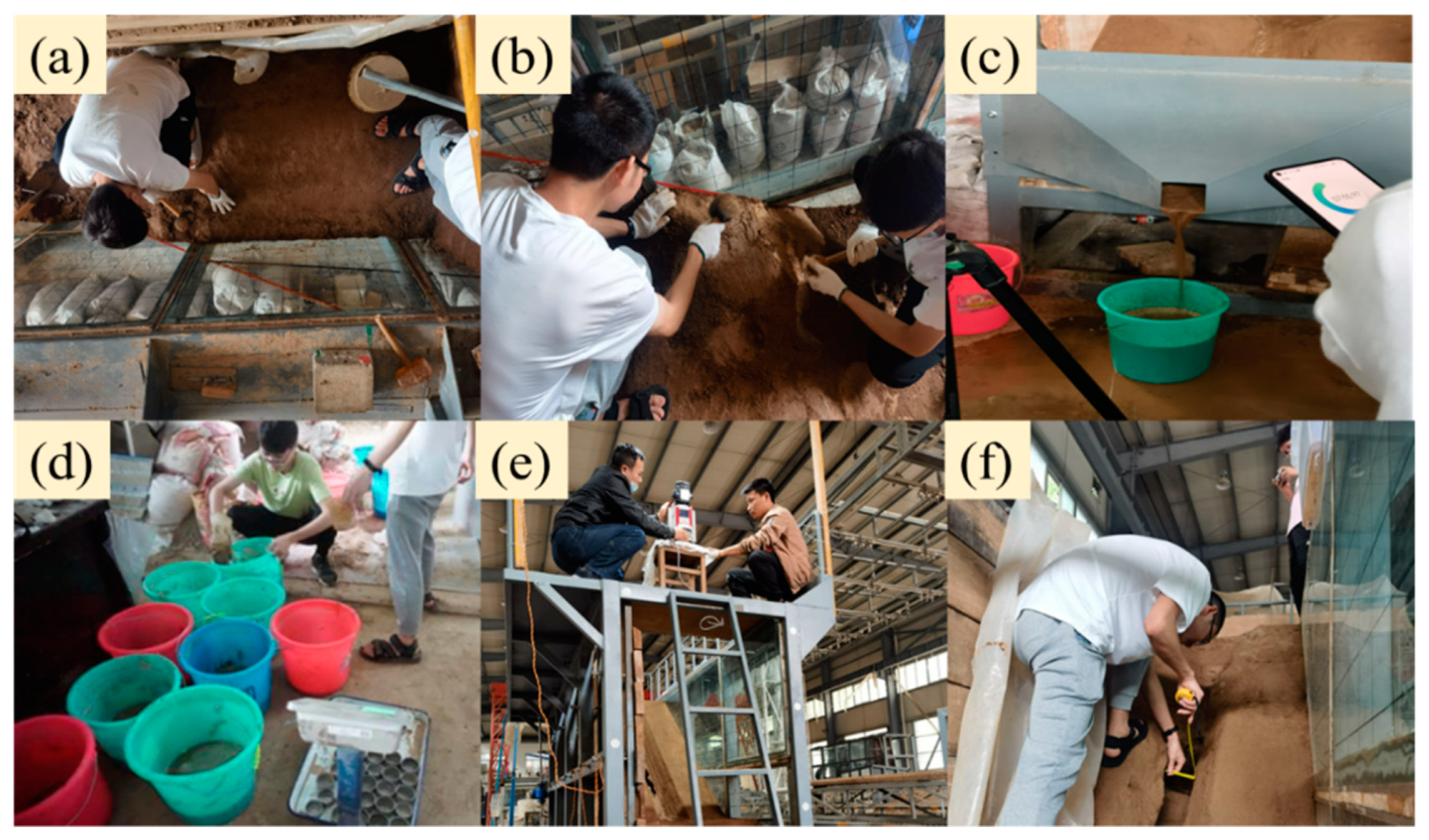
2.3. Experiment Procedures
3. Result
3.1. Morphological Changes
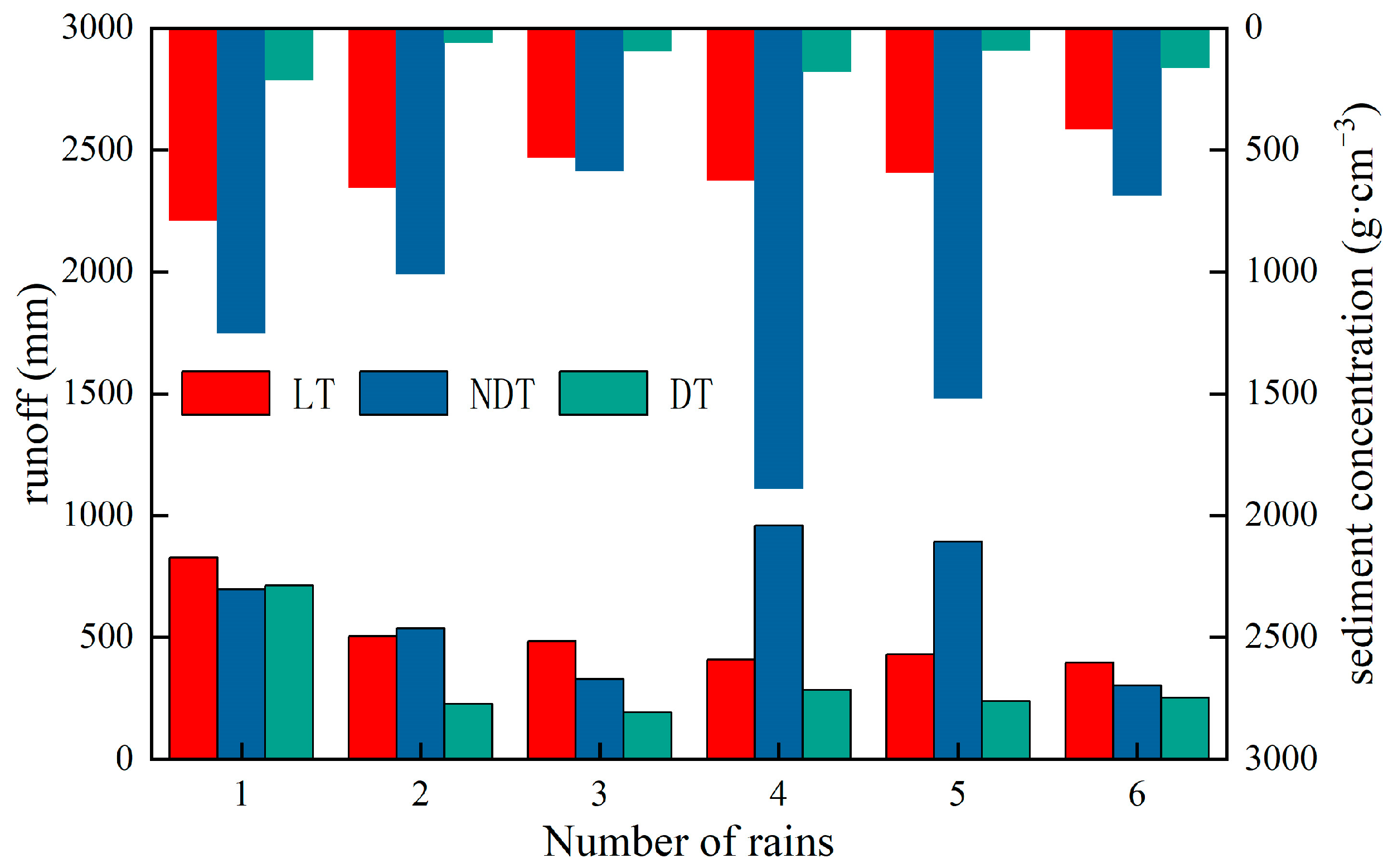
3.2. Runoff
3.3. Sediment
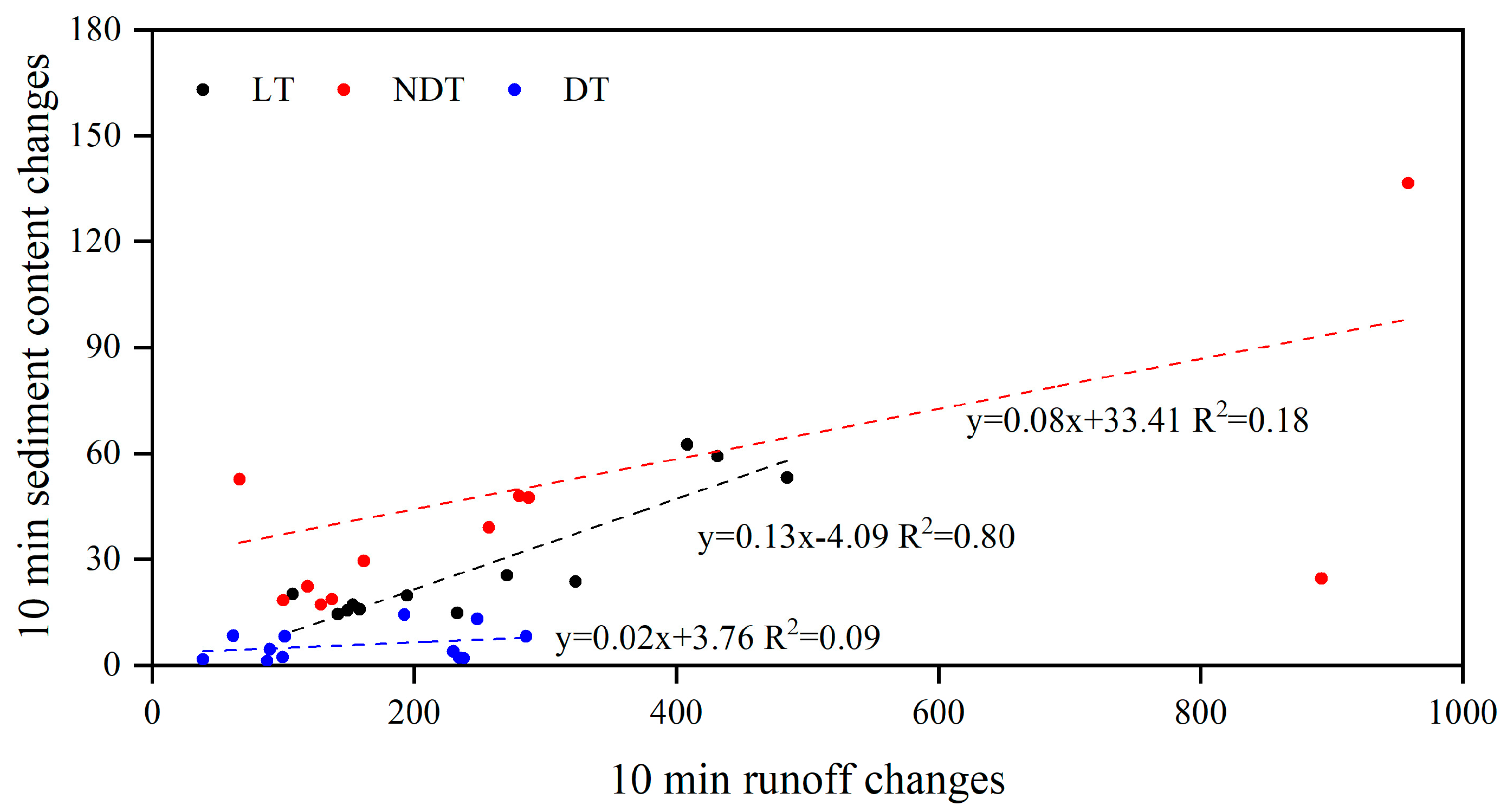
3.4. Relationship between 10 min Runoff and Sediment Content Changes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Under the same conditions, the effect of slope replacement with terraces for GCHP measures is better than that of gully head landfill in reducing soil erosion. The runoff depth of LT is more than that of NDT in the simulated summer rainfall process, and the rainfall in spring and autumn is opposite. In summer rainfall, the runoff depth of LT is 67.83~276.03% more than that of NDT. In spring and autumn rainfall, the runoff depth of NDT is 4.12% to 39.84% more than LT’s.
- (2)
- Under the same conditions, the effect of slope replacement with terraces for GCHP measures is better than that of gully head landfill in reducing secondary geological disasters. LT and NDT are more prone to collapse than DT. NDT has more collapse times in the process of rainfall than LT. However, due to the existence of a terrace in NDT, the falling clods are smaller than LT.
- (3)
- Optimized drainage systems can reduce the occurrence of secondary geological disasters. Under the same conditions, the engineering measures of GCHP with drainage systems have significant sediment reduction effects. DT is more effective than NDT in reducing soil erosion, and this advantage is more significant during rainstorms. The sediment yield of NDT was 2.27–23.93 times higher than that of DT sediment. The total runoff yield of NDT is 0~275.15% more than that of DT.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Đokić, M.; Manić, M.; Đorđević, M.; Gocić, M.; Čupić, A.; Jović, M.; Dragović, R.; Gajić, B.; Smičiklas, I.; Dragović, S. Remote sensing and nuclear techniques for high-resolution mapping and quantification of gully erosion in the highly erodible area of the Malčanska River Basin, Eastern Serbia. Environ. Res. 2023, 235, 116679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Huo, A.; Liu, Q.; Peng, J.; Elbeltagi, A.; Abuarab, M.E.S.; Abu-Hashim, M.S.D. Spatiotemporal Variation in the Coupling Relationship between Human Activities and Soil Erosion—A Case Study in the Weihe River Basin. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.; Gao, Z.; Li, X.; Gao, J.E.; Zhang, G.G.; Ahmad, R.; Liu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Zhou, F. Erosion transportation processes as influenced by Gully Land Consolidation Projects in highly managed small watersheds in the Loess Hilly–Gully Region, China. Water 2021, 13, 1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, A.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, L.; Zhong, F.; Zheng, C.; Gao, N. Risk assessment of heavy metal pollution in farmland soils at the northern foot of the Qinling Mountains, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, F.; Yang, W.; Fu, J.; Li, Z. Effects of vegetation and climate on the changes of soil erosion in the Loess Plateau of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 773, 145514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Asch, T.W.; Yu, B.; Hu, W. The development of a 1-D integrated hydro-mechanical model based on flume tests to unravel different hydrological triggering processes of debris flows. Water 2018, 10, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, C. Gully internal erosion triggered by a prolonged heavy rainfall event in the tableland region of China’s Loess Plateau. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Cheng, H. Monitoring of gully erosion on the Loess Plateau of China using a global positioning system. Catena 2005, 63, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Peng, J.; Zhuang, J.; Feng, L.; Huo, A.; Mu, X.; Wang, W. Gully erosion and expansion mechanisms in loess tablelands and the scientific basis of gully consolidation and tableland protection. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2023, 66, 821–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, A.; Yang, L.; Luo, P.; Cheng, Y.; Peng, J.; Nover, D. Influence of landfill and land use scenario on runoff, evapotranspiration, and sediment yield over the Chinese Loess Plateau. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 107208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Chen, J.; Zhao, G.; Holden, J.; Liu, B.; Chan, F.K.S.; Hu, J.; Wu, P.; Mu, X. Determining the drivers and rates of soil erosion on the Loess Plateau since 1901. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 823, 153674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Huo, A.; Guan, W. Remote Sensing Monitoring Method for Groundwater Level on Aeolian Desertification Area. J. Water Chem. Technol. 2020, 42, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesschen, J.P.; Cammeraat, L.H.; Nieman, T. Erosion and terrace failure due to agricultural land abandonment in a semiarid environment. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. J. Br. Geomorphol. Res. Group 2008, 33, 1574–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Huo, A.; Lyu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhong, F.; Yang, L.; Guan, W. Dynamic changes and driving factors of vegetation coverage in the mainstream of Tarim River, China. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2023, 39, 284–292. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.F.; Huo, A.D.; Zhu, X.H.; Zhao, Y.B.; Jiang, C.; Zheng, X.L. Study on governance mode of gully consolidation and highland protection project in East Gansu. Yellow River 2019, 41, 106–109. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, A.; Peng, J.; Cheng, Y.; Luo, P.; Zhao, Z.; Zheng, C. Hydrological analysis of Loess Plateau highland control schemes in Dongzhi Plateau. Front. Earth Sci. 2020, 8, 528632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.Q.; An, Y.P.; Li, Y.W. Comparative study of impact of different site preparation methods for afforestation efforts. J. Ning Xia Teach. Univ. 2007, 28, 110–113. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Wei, W.; Chen, L. How can terracing impact on soil moisture variation in China? A meta-analysis. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 227, 105849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharabaghi, B.; Singh, M.K.; Inkratas, C.; Fleming, I.R.; McBean, E. Comparison of slope stability in two Brazilian municipal landfills. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 1509–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koerner, R.M.; Soong, T.Y. Stability assessment of ten large landfill failures. In Advances in Transportation and Geoenvironmental Systems Using Geosynthetics, Proceedings of sessions of Geo-Denver 2000, Denver, Colorado, USA, 5–8 August 2000; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2000; pp. 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, S.J.; Chang, J.Y.; Shi, H.; Zheng, Q.T.; Guo, X.Y.; Zhang, X.L. Failure of an unfilled landfill cell due to an adjacent steep slope and a high groundwater level: A case study. Eng. Geol. 2019, 262, 105320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahereh, S.; Mohsen, G.; Ali, T. Design and optimisation of drainage systems for fractured slopes using the XFEM and FEM. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 2020, 103, 102110. [Google Scholar]
- Anache, J.A.; Wendland, E.C.; Oliveira, P.T.; Flanagan, D.C.; Nearing, M.A. Runoff and soil erosion plot-scale studies under natural rainfall: A meta-analysis of the Brazilian experience. Catena 2017, 152, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Wang, W.; Shi, Q.; Chen, T.; Kang, H.; Li, J. An experimental study on the effects of grass root density on gully headcut erosion in the gully region of China’s Loess Plateau. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 2107–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, A.J.; Stone, P.M. Effects of intra-storm variations in rainfall intensity on interrill runoff and erosion. Catena 2006, 67, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Steiner, J.; Zheng, F.; Gowda, P. Impact of rainfall pattern on interrill erosion process. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2017, 42, 1833–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahma, A.E.; Wang, W.; Tang, Z.; Lei, T.; Warrington, D.N.; Zhao, J. Straw mulch can induce greater soil losses from loess slopes than no mulch under extreme rainfall conditions. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 232, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, A.; Zhao, Z.; Luo, P.; Zheng, C.; Peng, J.; Abuarab, M.E.S. Assessment of spatial heterogeneity of soil moisture in the critical zone of gully consolidation and highland protection. Water 2022, 14, 3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haiyan, F.; Liying, S. Modelling soil erosion and its response to the soil conservation measures in the black soil catchment, Northeastern China. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 165, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haiyan, F. Impacts of soil conservation measures on runoff and soil loss in a hilly region, Northern China. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 247, 106740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Huo, A.; Zhao, Z.; Peng, J. Analysis of loess fracture on slope stability based on centrifugal model tests. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2021, 80, 3647–3657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.H.; Yan, F.L.; Li, L.; Li, Z.X.; Cai, C.F. Interrill erosion from disturbed and undisturbed samples in relation to topsoil aggregate stability in red soils from subtropical China. Catena 2010, 81, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Ren, Z.; Li, P.; Li, Z.; Yuan, S.; Zhang, H.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Z. Temporal persistence and stability of soil water storage after rainfall on terrace land. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Q.; Chen, X.; Hong, Y.; Ye, S.; Gao, J. Impacts of terracing on hydrological processes: A case study from the Loess Plateau of China. J. Hydrol. 2020, 588, 125045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo-Comino, J.; Seeger, M.; Iserloh, T.; González, J.M.S.; Ruiz-Sinoga, J.D.; Ries, J.B. Rainfall-simulated quantification of initial soil erosion processes in sloping and poorly maintained terraced vineyards-Key issues for sustainable management systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 1047–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, X.; McNulty, S.G.; Vose, J.M. Potential water yield reduction due to forestation across China. J. Hydrol. 2006, 328, 548–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Pan, D.; Yang, Y. Effects of terracing measures on water retention of pinus Tabulaeformis forest in the dryland loess hilly region of China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2021, 308, 108544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jencso, K.G.; McGlynn, B.L. Hierarchical controls on runoff generation: Topographically driven hydrologic connectivity, geology, and vegetation. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotecchia, F.; Lollino, P.; Petti, R. Efficacy of drainage trenches to stabilise deep slow landslides in clay slopes. Géotech. Lett. 2016, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calsamiglia, A.; Fortesa, J.; García-Comendador, J.; Lucas-Borja, M.E.; Calvo-Cases, A.; Estrany, J. Spatial patterns of sediment connectivity in terraced lands: Anthropogenic controls of catchment sensitivity. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 1198–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siriri, D.; Wilson, J.; Coe, R.; Tenywa, M.M.; Bekunda, M.A.; Ong, C.K.; Black, C.R. Trees improve water storage and reduce soil evaporation in agroforestry systems on bench terraces in SW Uganda. Agrofor. Syst. 2013, 87, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyakov, V.O.; Nichols, M.H.; McClaran, M.P.; Nearing, M.A. Effect of check dams on runoff, sediment yield, and retention on small semiarid watersheds. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2014, 69, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novara, A.; Gristina, L.; Saladino, S.S.; Santoro, A.; Cerdà, A. Soil erosion assessment on tillage and alternative soil managements in a Sicilian vineyard. Soil Tillage Res. 2011, 117, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aidi, H.; Siming, C.; Jianbing, P.; Yuxiang, C. UAV-based gully retrogressive erosion status dynamic variability investigations in Chinese Loess Plateau. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, C.; Merton, L.; Burger, P. Impact of vegetative cover and slope on runoff, erosion, and water quality for field plots on a range of soil and spoil materials on central Queensland coal mines. Soil Res. 2000, 38, 313–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapagain, T.; Raizada, M.N. Agronomic challenges and opportunities for smallholder terrace agriculture in developing countries. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Liu, Q.; Huo, A.; Cheng, Y.; Guan, W.; Mohamed, E.L.; Mokhtar, A.; Elbeltagi, A. A novel integrated approach for monitoring drought stress in an aeolian desertification area using Vegetation Drought Status Index. Water Supply 2023, 23, 738–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.B.; Li, J.J.; He, X.Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, F. The status and sediment reduction effects of level terrace in the Loess Plateau. Yellow River 2015, 37, 89–93. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.; Zhang, G.; Fan, H.; Ji, Q.; Li, A.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, B.; Yu, Y.; Ma, L.; Gao, J. Erosion-Transportation Processes Influenced by Spatial Distribution of Terraces in Watershed in the Loess Hilly–Gully Region (LHGR), China. Water 2022, 14, 1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, G.; Meng, X.; Ye, Z. Impacts of Grass Coverage and Arrangement Patterns on Runoff and Sediment Yield in Slope-Gully System of the Loess Plateau, China. Water 2022, 15, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Cai, Q.; Wang, C.; Liu, J. Effect of vegetation and other measures for soil and water conservation on runoff-sediment relationship in watershed scale. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2007, 38, 47–53. [Google Scholar]
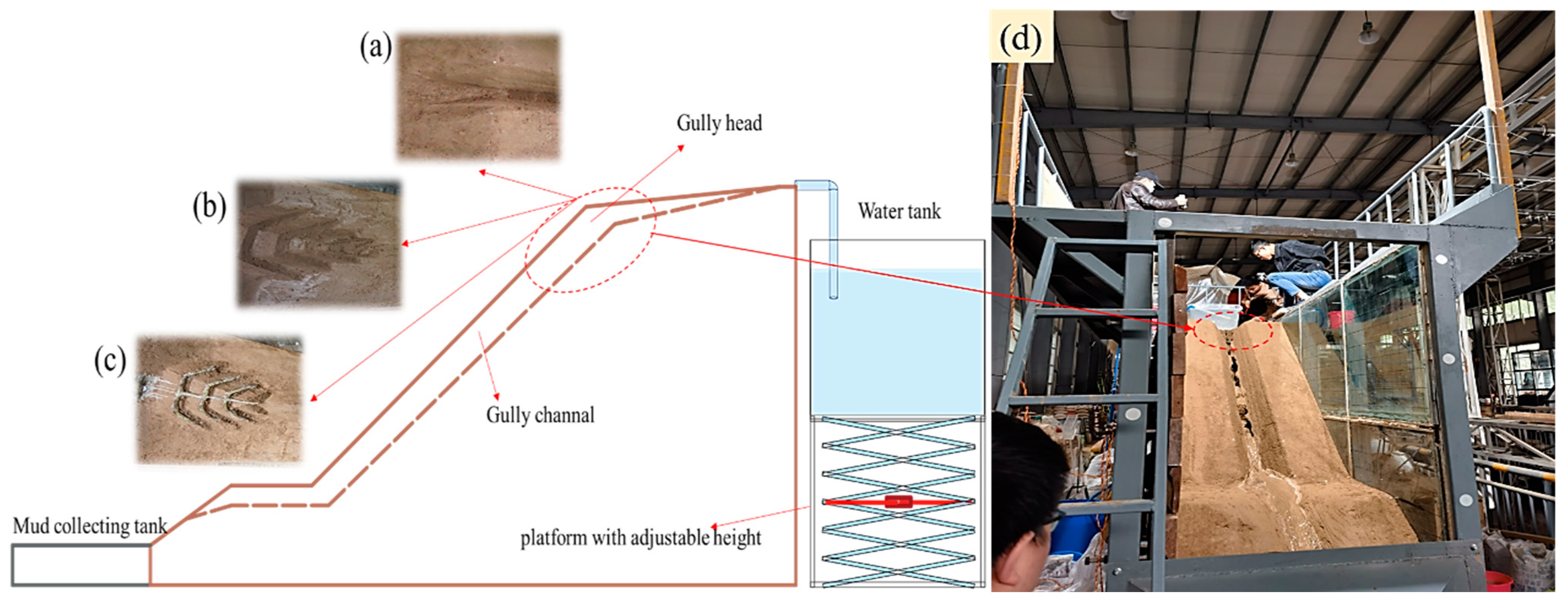



| Simulated Season | Simulated Times | Simulated Flow (m3 h−1) | Time (min) | Prototype Rain Intensity (mm/d) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spring | 2 | 0.43 | 30 | 33.20 |
| 0.32 | 30 | 29.20 | ||
| Summer | 3 | 0.86 | 10 | 63.20 |
| 1.62 | 10 | 118.24 | ||
| 1.24 | 10 | 90.72 | ||
| Fall | 1 | 0.32 | 30 | 29.20 |
| Measures | Rain Time | Soil Erosion Depth (cm) | Proportion of Relative Depth Greater than 0 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum | Maximum | Mean | Median | |||
| LT | 1 | 41.00 | 122.82 | 80.03 | 77.03 | 0.21 |
| 2 | 49.00 | 117.06 | 77.18 | 73.03 | 0.43 | |
| 3 | 47.00 | 121.06 | 79.36 | 76.44 | 0.64 | |
| 4 | 48.00 | 117.06 | 75.14 | 74.67 | 0.29 | |
| 5 | 48.50 | 117.06 | 75.68 | 73.26 | 0.57 | |
| 6 | 47.00 | 125.25 | 73.05 | 68.40 | 0.36 | |
| NDT | 1 | 42.90 | 77.30 | 61.40 | 69.15 | 0.21 |
| 2 | 46.00 | 75.00 | 62.15 | 67.85 | 0.64 | |
| 3 | 45.10 | 75.40 | 61.19 | 68.75 | 0.29 | |
| 4 | 44.50 | 80.00 | 60.92 | 67.40 | 0.29 | |
| 5 | 45.00 | 93.50 | 64.43 | 69.30 | 0.93 | |
| 6 | 45.70 | 101.00 | 65.51 | 68.00 | 0.43 | |
| DT | 4 | 37.50 | 131.50 | 77.80 | 72.30 | 0.00 |
| 5 | 38.00 | 128.50 | 76.06 | 69.55 | 0.17 | |
| 6 | 38.20 | 123.00 | 75.81 | 73.15 | 0.42 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Z.; Huo, A.; Cheng, Y.; Luo, P.; Peng, J.; Elbeltagi, A.; Abuarab, M.E.-S.; Mokhtar, A.; Ahmed, A. Impacts of Different Gully Consolidation and Highland Protection Models on the Runoff and Sediment Yield in Small Watershed of the Chinese Loess Plateau—A Case Study of Fengbugou in Qingyang City of Gansu. Water 2023, 15, 2764. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152764
Zhao Z, Huo A, Cheng Y, Luo P, Peng J, Elbeltagi A, Abuarab ME-S, Mokhtar A, Ahmed A. Impacts of Different Gully Consolidation and Highland Protection Models on the Runoff and Sediment Yield in Small Watershed of the Chinese Loess Plateau—A Case Study of Fengbugou in Qingyang City of Gansu. Water. 2023; 15(15):2764. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152764
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Zhixin, Aidi Huo, Yuxiang Cheng, Pingping Luo, Jianbing Peng, Ahmed Elbeltagi, Mohamed EL-Sayed Abuarab, Ali Mokhtar, and Adnan Ahmed. 2023. "Impacts of Different Gully Consolidation and Highland Protection Models on the Runoff and Sediment Yield in Small Watershed of the Chinese Loess Plateau—A Case Study of Fengbugou in Qingyang City of Gansu" Water 15, no. 15: 2764. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152764
APA StyleZhao, Z., Huo, A., Cheng, Y., Luo, P., Peng, J., Elbeltagi, A., Abuarab, M. E.-S., Mokhtar, A., & Ahmed, A. (2023). Impacts of Different Gully Consolidation and Highland Protection Models on the Runoff and Sediment Yield in Small Watershed of the Chinese Loess Plateau—A Case Study of Fengbugou in Qingyang City of Gansu. Water, 15(15), 2764. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152764










