Degradation of DDT by a Novel Bacterium, Arthrobacter globiformis DC-1: Efficacy, Mechanism and Comparative Advantage
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Culture Media
2.2. Enrichment and Isolation of DDT-Degrading Microorganisms
2.3. Identification of the DC-1 Strain
2.4. Inoculum Preparation
2.5. The Growth and Biodegradation Characteristics of the DC-1 Strain Cultivated in the MSM Supplemented with DDT
2.6. DDT Congeners Degradation Ability of the DC-1 Strain in Pure Culture
2.7. Extraction and Analysis of DDT and DDT Congeners
2.8. Analysis of DDT Metabolites by GC/MS
2.9. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
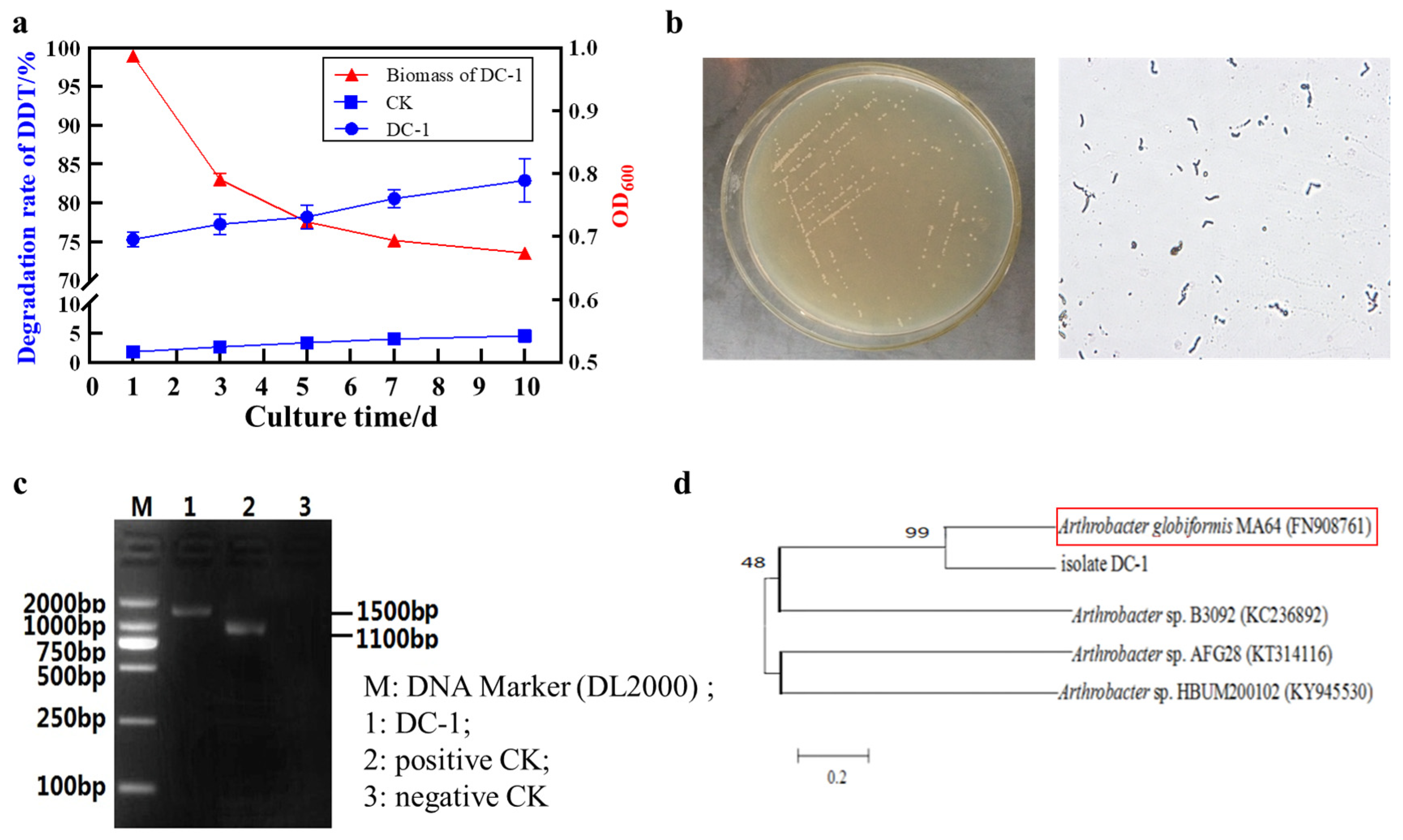
3.1. Identification of the DC-1 Strain
3.2. The Effect of Environmental Conditions on the Growth and Biodegradation of DDT by the DC-1 Strain
3.2.1. The Effect of DDT Concentration
3.2.2. The Effect of Temperature
3.2.3. The Effect of pH
3.2.4. The Effect of Additional Carbon Sources
3.3. DC-1 Strain’s Ability to Degrade DDT Congeners in Pure Culture
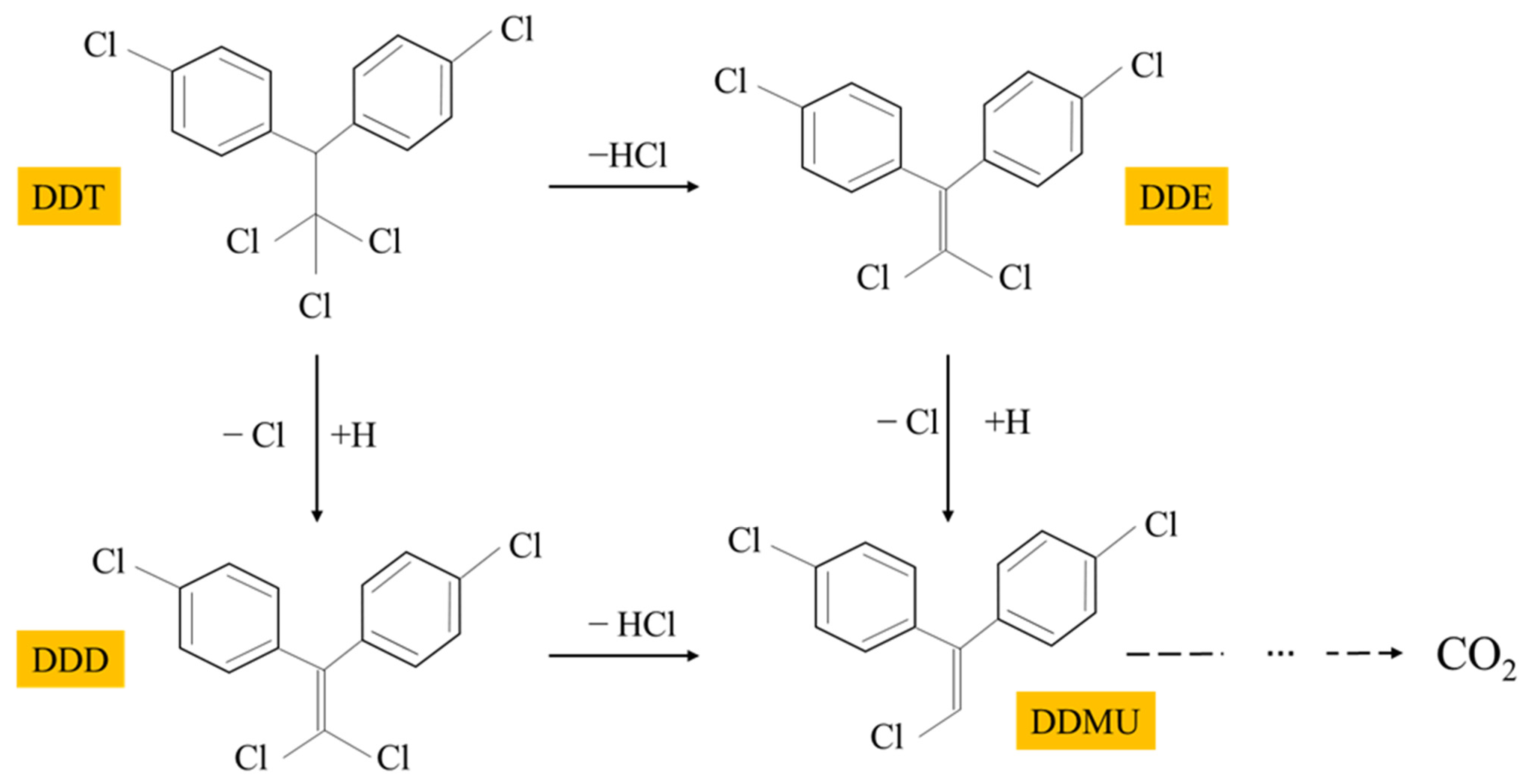
3.4. Identification of DDT Metabolites by GC/MS Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, H.; Bai, J.; Li, W.; Zhao, L.; Li, Y. Removal of persistent DDT residues from soils by earthworms: A mechanistic study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 365, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Zhu, L.S.; Wang, J. Combined treatment of contaminated soil with a bacterial Stenotrophomonas strain DXZ9 and ryegrass (Lolium perenne) enhances DDT and DDE remediation. Environ. Sci. Pollution. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 31895–31905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Wu, C.; Liu, W.; Teng, Y.; Luo, Y.; Christie, P.; Guo, D. Levels and patterns of organochlorine pesticides in agricultural soils in an area of extensive historical cotton cultivation in Henan province, China. Environ. Sci. Pollution. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 6680–6689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, F.; Ceci, A.; Pinzari, F.; Pinzari, F.; Siciliano, A.; Guida, M.; Malusa, E.; Tartanus, M.; Miszczak, A.; Maggi, O.; et al. Bioremediation of DDT-contaminated agricultural soils: The potential of two autochthonous saprotrophic fungal strains. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansouri, A.; Cregut, M.; Abbes, C.; Durand, M.J.; Landoulsi, A.; Thouang, G. The Environmental Issues of DDT Pollution and Bioremediation: A Multidisciplinary Review. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2017, 181, 309–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, H.; Deng, Y.; Ge, Q.; Mei, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Yu, Y. Biodegradability and ecological safety assessment of Stenotrophomonas sp. DDT-1 in the DDT-contaminated soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 158, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van den Berg, H.; Manuweera, G.; Konradsen, F. Global trends in the production and use of DDT for control of malaria and other vector-borne diseases. Malaria. J. 2017, 16, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ivorra, L.; Cardoso, P.G.; Chan, S.K.; Tagulao, K.; Cruzeiro, C. Environmental characterization of 4,4′-dichlorobenzophenone in surface waters from Macao and Hong Kong coastal areas (Pearl River Delta) and its toxicity on two biological models: Artemia salina and Daphnia magna. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 171, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtala, Y.; Nwanguma, B.C.; Ezeanyika, L.U. Staphylococcus sp. Strain MY 83295F: A Potential P,P′-DDT-Degrading Bacterium Isolated from Pesticide Contaminated Soil. Acta. Biol. Marisiensis. 2020, 3, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Yun, X.; Ruan, Z.; Lu, C.; Shi, Y.; Qin, Q.; Men, Z.; Zou, D.; Du, X.; Xing, B.; et al. Review of hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH) and dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT) contamination in Chinese soils. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 749, 141212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutto SU, A.; Xing, X.; Shi, M.; Mao, Y.; Hu, T.; Tian, Q.; Cheng, C.; Liu, W.; Chen, Z.; Qi, S. Occurrence and distribution of OCPs and PAHs in water, soil and sediment of Daye lake. J. Geochem. Explor. 2021, 226, 106769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarova, E.A.; Nazarov, A.V.; Egorova, D.O.; Anan’ina, L.N. Influence of destructive bacteria and red clover (trifolium pratense L.) on the pesticides degradation in the soil. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 44, 339–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGlynn, K.A.; Quraishi, S.M.; Graubard, B.I.; Weber, J.P.; Rubertone, M.V.; Erickson, R.L. Persistent organochlorine pesticides and risk of testicular germ cell tumors. J. Natl. Cancer. Inst. 2008, 100, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Wang, D.; Zhu, F.; Liu, S.; Fang, G.; Gao, J.; Zhou, D. Rapid DDTs degradation by thermally activated persulfate in soil under aerobic and anaerobic conditions: Reductive radicals vs. oxidative radicals. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 402, 123557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Xu, Y.; Ai, G.M.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.P. Novel Chryseobacterium sp. PYR2 degrades various organochlorine pesticides (OCPs)and achieves enhancing removal and complete degradation of DDT in highly contaminated soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 161, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Ding, H.; Xu, X.; Liang, B.; Liu, X.; Zhao, D.; Sun, L. In situ phytoremediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contaminated agricultural greenhouse soil using celery. Environ. Technol. 2020, 42, 3329–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Aborisade, M.A.; Wang, H.; He, P.; Lu, S.; Cui, N.; Wang, S.; Zhang, H.; Ding, H.; Liu, K. Effect of lignin and plant growth-promoting bacteria (Staphylococcus pasteuri) on microbe-plant co-remediation: A PAHs-DDTs co-contaminated agricultural greenhouse study. Chemosphere 2020, 256, 127079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sun, L.; Wang, H.; Wu, H.; Chen, S.; Zheng, X. Surfactant-enhanced bioremediation of DDTs and PAHs in contaminated farmland soil. Environ. Technol. 2018, 39, 1733–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Oba, B.T.; Wang, H.; Shen, C.; Zhao, R.; Zhao, D.; Ding, H. Organo-mineral complexes alter bacterial composition and induce carbon and nitrogen cycling in the rhizosphere. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 836, 155671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Liu, W.; Liu, X.; Franks, A.E.; Teng, Y. Comparative analysis of microbial communities during enrichment and isolation of DDT-degrading bacteria by culture-dependent and-independent methods. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 590–591, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neerja; Grewal, J.; Bhattacharya, A.; Kumar, S.; Singh, D.K.; Khare, S.K. Biodegradation of 1,1,1-trichloro-2,2-bis(4-chlorophenyl) ethane (DDT) by using Serratia marcescens NCIM 2919. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2016, 51, 809–816. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, K.; Mahmood, A.; Kataoka, R.; Takagi, K. Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT) degradation by Streptomyces sp. isolated from DDT contaminated soil. Bioremediat. J. 2021, 21, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purnomo, A.S.; Sariwati, A.; Kamei, I. Synergistic interaction of a consortium of the brown-rot fungus Fomitopsis pinicola and the bacterium Ralstonia pickettii for DDT biodegradation. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Mao, Z.; Lv, M. Screening and degradation characteristics of a DDT-degrading bacteria. China Environ. Sci. 2018, 38, 1935–1942. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Oba, B.T.; Shen, C.; Rong, L.; Zhang, B.; Huang, L.; Feng, L.; Liu, J.; Du, T.; Deng, Y. Effect of the bacterial community assembly process on the microbial remediation of petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated soil. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1196610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Lin, D.L.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yin, Y.M.; Cai, L.; Fang, H.; Yu, Y.L. Biodegradation of DDT by Stenotrophomonas sp. DDT-1: Characterization and genome functional analysis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suman, S.; Tanuja. Isolation and characterization of a bacterial strain Enterobacter cloacae (Accession No. KX438060.1) capable of degrading DDTs under aerobic conditions and its use in bioremediation of contaminated soil. Microbiol. Insights 2021, 14, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, A.A.; Tachibana, S.; Itoh, K. Determination of co-metabolism for 1,1,1-trichloro-2,2-bis(4-chlorophenyl) ethane (DDT) degradation with enzymes from Trametes versicolor U97. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2012, 114, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govarthanan, M.; Ameen, F.; Kamala-Kannan, S.; Selvankumar, T.; Almansob, A.; Alwakeel, S.S.; Kim, W. Rapid biodegradation of chlorpyrifos by plant growth-promoting psychrophilic Shewanella sp. BT05: An eco-friendly approach to clean up pesticide-contaminated environment. Chemosphere 2020, 247, 125948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Oba, B.T.; Wang, H.; Zhang, B.; Shu, C.; Song, Y.; Fu, J.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, N.; et al. Revealing the potential of organo-mineral complexes in agricultural application using bibliometrics. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 401, 136728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Xu, T.H.; Xu, H.Y.; Fang, H.; Yu, Y.L. Characterization and genome functional analysis of the DDT-degrading bacterium Ochrobactrum sp. DDT-2. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 592, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, H.; Zhu, L.; Xu, Q.; Wang, J.; Liu, W.; Jiang, J.; Meng, Y. Isolation and degradation ability of the DDT-degrading bacterial strain KK. Environ. Earth. Sci. 2011, 62, 93–99. [Google Scholar]
- Pant, G.; Mistry, S.K.; Sibi, G. Isolation, identification and characterization of p,p′-ddt degrading bacteria from soil. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 6, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, B.; Liu, W.; Jia, L.; Xu, L.; Xie, J. Isolation and characterization of an Alcaligenes sp. strain DG-5 capable of degrading DDTs under aerobic conditions. J. Environ. Sci. Health. B 2011, 46, 257–263. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, N.; Singh, D.K. Biodegradation of DDT by Achromobacter sp. strain Y12A in broth medium. Inter. J. Microbiol. Res. 2017, 9, 909–912. [Google Scholar]
- Powthong, P.; Jantrapanukorn, B.; Suntornthiticharoen, P. Isolation, identification and analysis of DDT-degrading bacteria for agriculture area improvements. J. Food. Agric. Environ. 2016, 14, 131–136. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Liang, B.; Chen, K.; Li, S.; Jiang, J. Co-metabolism of DDT by the newly isolated bacterium, Pseudoxanthomonas sp. wax. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2010, 41, 431–438. [Google Scholar]
- Bidlan, R.; Manonmani, H.K. Aerobic degradation of dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT) by Serratia marcescens DT-1P. Process. Biochem. 2002, 38, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foght, J.; April, T.; Biggar, K.; Aislabie, J. Bioremediation of DDT-contaminated soils: A review. Bioremediat. J. 2001, 5, 225–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purnomo, A.S.; Maulianawati, D.; Kamei, I. Ralstonia pickettii enhance the DDT Biodegradation by Pleurotus eryngii. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 29, 1424–1433. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Rashed, S.; Marraiki, N.; Syed, A.; Elgorban, A.M.; Prasad, K.S.; Shivamallu, C.; Bahkail, A.H. Bioremediation characteristics, influencing factors of dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT) removal by using non-indigenous Paracoccus sp. Chemosphere 2020, 270, 129474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sariwati, A.; Purnomo, A.S. The effect of Pseudomonas aeruginosa addition on 1,1,1-trichloro-2,2-bis(4-chlorophenyl) ethane (DDT) biodegradation by brown-rot fungus Fomitopsis pinicola. Indones. J. Chem. 2018, 18, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, A.; Mayilraj, S.; Mudiam MK, R.; Patel, D.K.; Manickam, N. Isolation and functional analysis of a glycolipid producing Rhodococcus sp. strain IITR03 with potential for degradation of 1,1,1-trichloro-2,2-bis(4-chlorophenyl) ethane (DDT). Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 167, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Oba, B.T.; Wang, H.; Luo, Q.; Liu, J.; Tang, L.; Yang, M.; Wu, H.; Sun, L. Degradation of DDT by a Novel Bacterium, Arthrobacter globiformis DC-1: Efficacy, Mechanism and Comparative Advantage. Water 2023, 15, 2723. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152723
Wang X, Oba BT, Wang H, Luo Q, Liu J, Tang L, Yang M, Wu H, Sun L. Degradation of DDT by a Novel Bacterium, Arthrobacter globiformis DC-1: Efficacy, Mechanism and Comparative Advantage. Water. 2023; 15(15):2723. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152723
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiaoxu, Belay Tafa Oba, Hui Wang, Qing Luo, Jiaxin Liu, Lanxin Tang, Miao Yang, Hao Wu, and Lina Sun. 2023. "Degradation of DDT by a Novel Bacterium, Arthrobacter globiformis DC-1: Efficacy, Mechanism and Comparative Advantage" Water 15, no. 15: 2723. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152723
APA StyleWang, X., Oba, B. T., Wang, H., Luo, Q., Liu, J., Tang, L., Yang, M., Wu, H., & Sun, L. (2023). Degradation of DDT by a Novel Bacterium, Arthrobacter globiformis DC-1: Efficacy, Mechanism and Comparative Advantage. Water, 15(15), 2723. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152723








